Abstract
Although hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solution has become a popular electrophilic reagent for industrial uses, the question of which molecule (HOCl or Cl2) undergoes electrophilic addition with olefins remains a controversial issue in some literature and textbooks, and this problem has been largely underexplored in theoretical studies. In this work, we computationally studied the electrophilic addition mechanism of olefins using three experimentally predicted effective electrophilic chlorinating agents, i.e., HOCl, Cl2, and Cl2O molecules. Our results demonstrate that Cl2 and Cl2O are the main electrophilic agents in HOCl solution, whereas the HOCl molecule cannot be the electrophile since the energy barrier when directly adding HOCl molecule to olefins is too high to overcome and the “anti-Markovnikov” regioselectivity for tri-substituted olefin is not consistent with experiments. Notably, the HOCl molecule prefers to form oxonium ion intermediate with a double bond, rather than the generally believed chlorium ion intermediate. This work could benefit mechanistic studies of critical biological and chemical processes with HOCl solution and may be used to update textbooks.
1. Introduction
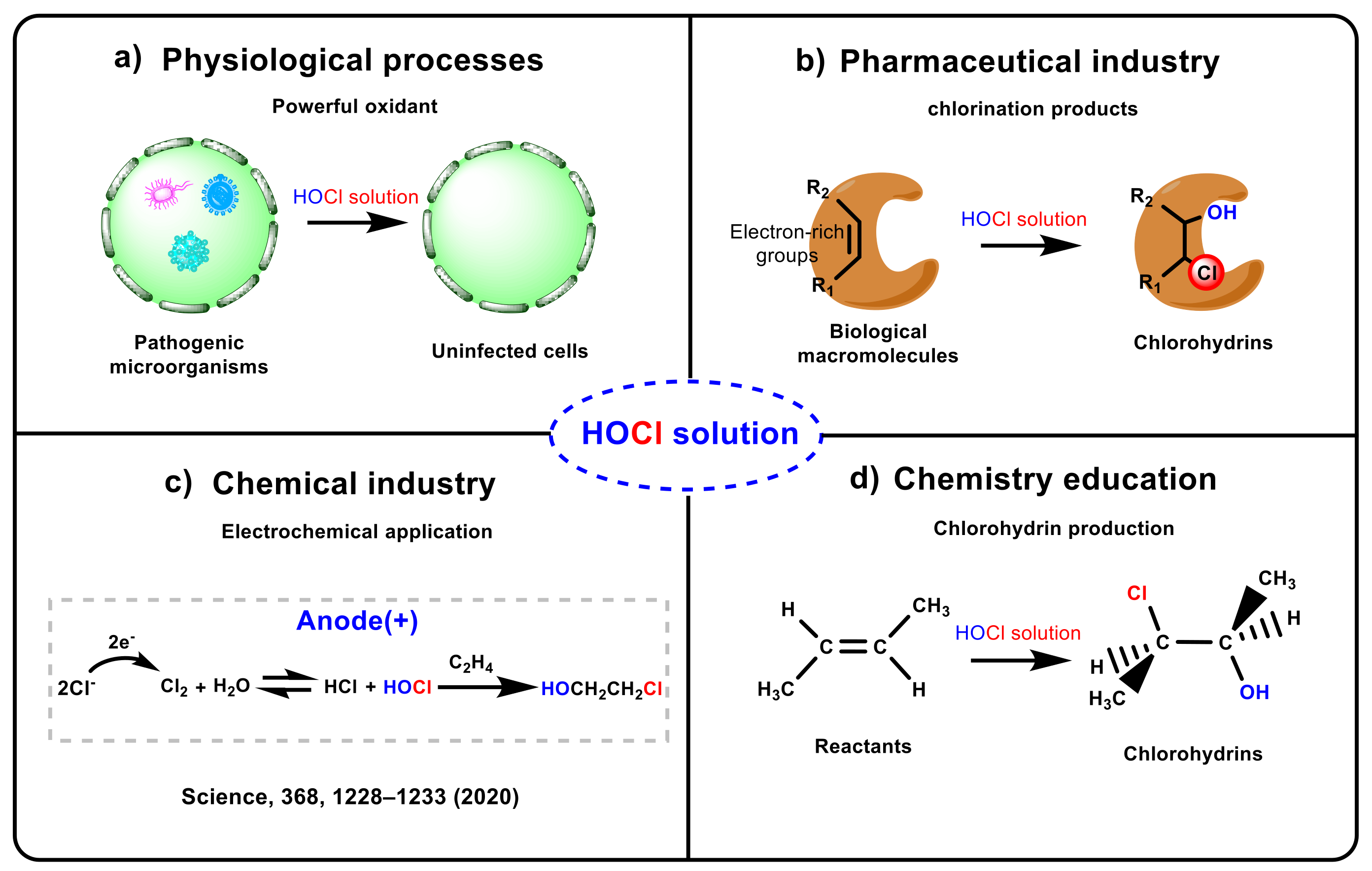
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solution plays a significant role in physiological processes [1,2,3], pharmaceutical industries [4,5,6], chemical industries [7,8,9,10,11,12], and chemistry education [13,14,15,16,17,18,19] (see Scheme 1). HOCl solution is a powerful oxidant that can remove the invading bacteria and pathogens in cells, and it can also undergo electrophilic substitution or addition reactions with biological macromolecules in vivo due to its high electrophilic activity [1,20,21,22,23,24,25], leading to tissue damage and diseases, such as lysosomal lysis, mitochondrial permeability, protease inactivation, and cell necrosis (see Scheme 1a) [26,27,28,29]. Moreover, drugs or biological macromolecules containing electron-rich groups can form chlorohydrins and chloramines mediated by HOCl solution [4,5,6], and previous works reported that many diseases may occur through the toxicity caused by the chlorination products of these compounds (see Scheme 1b) [4,6]. Furthermore, adding HOCl solution to olefins to synthesize chlorohydrins has recently aroused great interest in industrial production [7,8], e.g., Sargent and co-workers applied this strategy to the electrosynthesis of ethylene and propylene oxides (see Scheme 1c) [10]. Finally, HOCl is often selected as a classic case in textbook chapters on electrophilic addition (see Scheme 1d) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
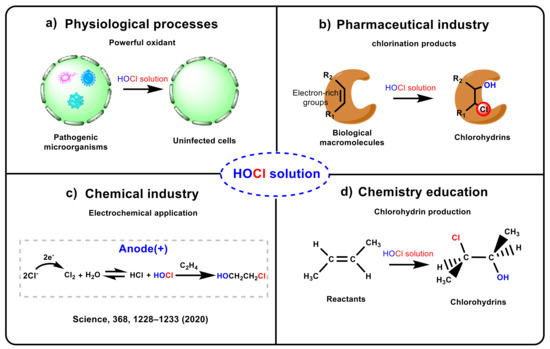
Scheme 1.
The important roles of HOCl solution.
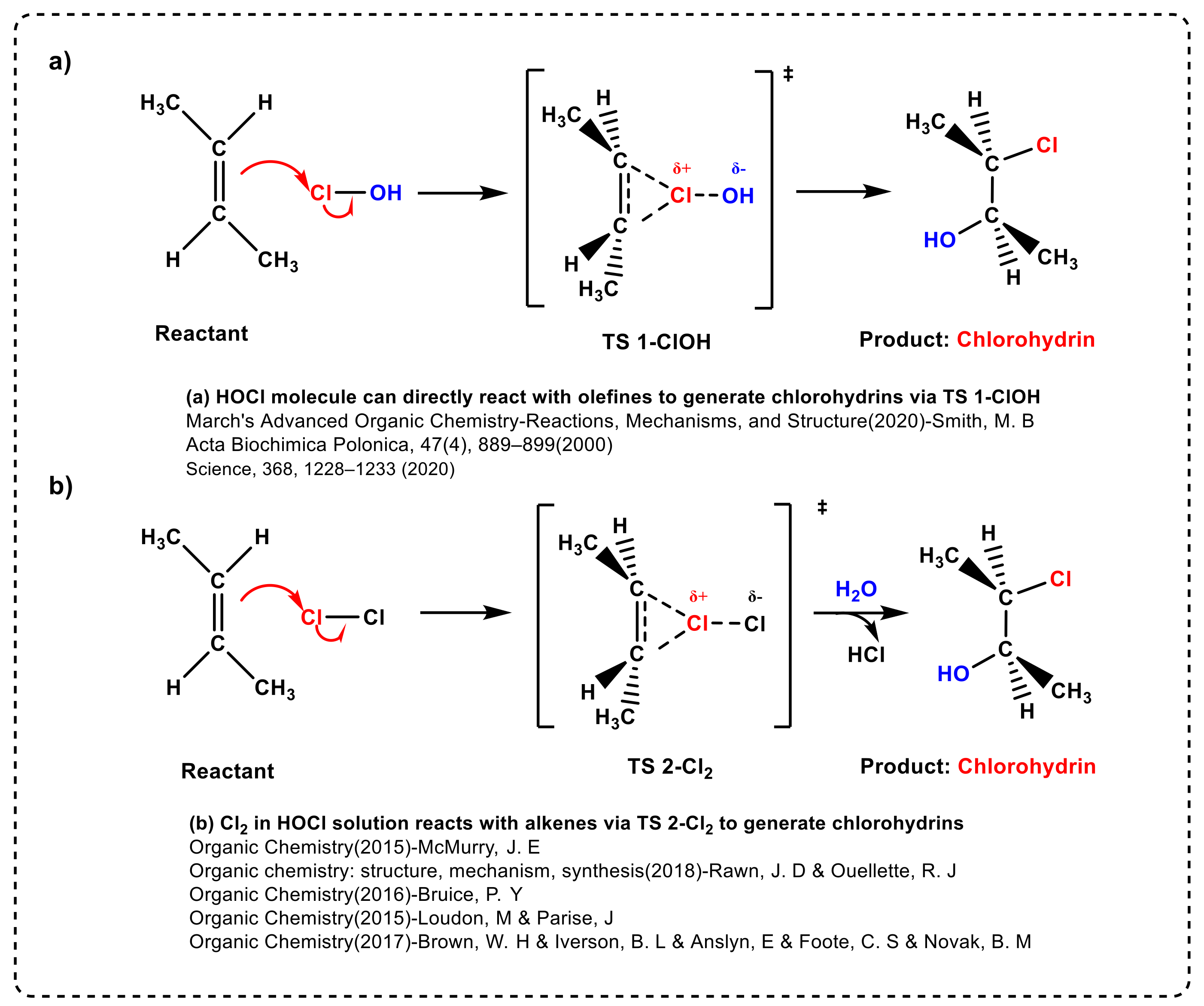
In a typical industrial plant, the reaction chamber is filled with Cl2 gas and water simultaneously, such that HOCl and Cl2 molecules are present in a certain proportion in the mixture [11,12]. Therefore, for an electrophilic addition reaction with olefins mediated by HOCl solution, the mechanism cannot exclude the direct addition of Cl2 to olefins. Except water as the solvent, this reaction can also occur in various organic solvents such as tert-Butanol (t-BuOH) in the Pinnick reaction [30,31]. As shown in Scheme 2, there are two plausible and well-established reaction mechanisms that form chlorohydrin.
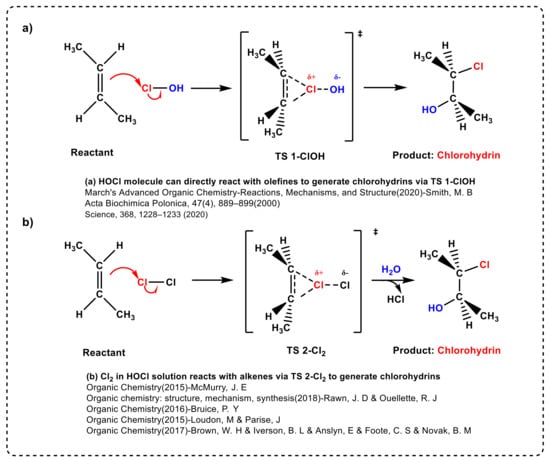
Scheme 2.
Two plausible reaction mechanisms for the formation of chlorohydrin.
To the best of our knowledge, it is widely accepted that the HOCl molecule represents the active electrophile in solutions. A typical example is that proposed by Smith, M. B. et al. on page 996 of Chapter 15 of their eighth edition of March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry (2020), in which the HOCl molecule can be generated in situ through the reaction between Cl2 and H2O [17], where the Cl group in the HOCl molecule is transferred to the olefins (see Scheme 2a). However, McMurry, J. E. et al. proposed the opposite point of view on page 225 of Chapter 8 of his ninth edition of Organic Chemistry (2015), emphasizing that Cl2 can directly react with trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene to form a chlorium ion intermediate, with water as the nucleophilic agent to open the relatively unstable cyclic chloride ring and form a bond with carbon [14]. Furthermore, Rawn, J. D and Ouellette, R. J [16], Bruice, P. Y [15], Loudon, M and Parise, J [18] and Brown, W. H [19] put forward similar pathways in their respective books (see Scheme 2b). Therefore, in response to the above contradiction between the two plausible reaction mechanisms, we aim to study which molecule is the active electrophilic species in HOCl solution for double bond addition reactions.
In addition to the two electrophilic species mentioned above, Sivey, J. D. and Roberts, A. L. first proposed that Cl2O can be another important electrophilic species in HOCl solution. Their prominent work indicated that the reactivities of the HOCl molecule, Cl2, and Cl2O were found to be affected by environmental variables, such as the concentration of various effective chlorinating agents and pH [32,33,34]. Therefore, we also performed theoretical calculations on the reactivity of Cl2O in this context.
2. Materials and Methods
Theoretical calculations were conducted to address the above questions. Two popular density-functional theory (DFT) methods (M06-2X-D3 [35,36], ωB97X-D [37]) were used. The triple-ζ augmented correlation-consistent basis sets, designated aug-cc-pVTZ [38,39,40], were employed for all selected atoms. Structures were optimized by Truhlar’s SMD [41] method (solvation model based on the quantum mechanical charge density), with water as the solvent. Frequency analysis was conducted at the same theoretical level to verify the stationary points as an energy minimum or a transition state and obtain the thermal energy corrections. All of the above calculations were performed using the Gaussian 16 program [42]. Furthermore, to confirm the reliability of our DFT results, the highly accurate DLPNO–CCSD(T) method [43,44], which is a domain-based local pair-natural orbital coupled-cluster method, which can perform CCSD(T) [45,46,47] calculations accurately and quickly, was used with a matched basis set extrapolation scheme for single-point electronic energy calculations using the ORCA program (version 4.0) [48,49]. The optimized structure obtained using the M062X-D3/aug-cc-pVTZ theoretical level was used as the initial structure for the DLPNO–CCSD(T) calculation, and the parameters required in the aug-cc-pVDZ and aug-cc-pVTZ two-point extrapolation are from the ORCA manual. In this article, Gibbs free energies are provided for discussion.
3. Results
3.1. HOCl Molecule Reaction Pathways
3.1.1. The Cl Group in the HOCl Molecule Adding Pathway
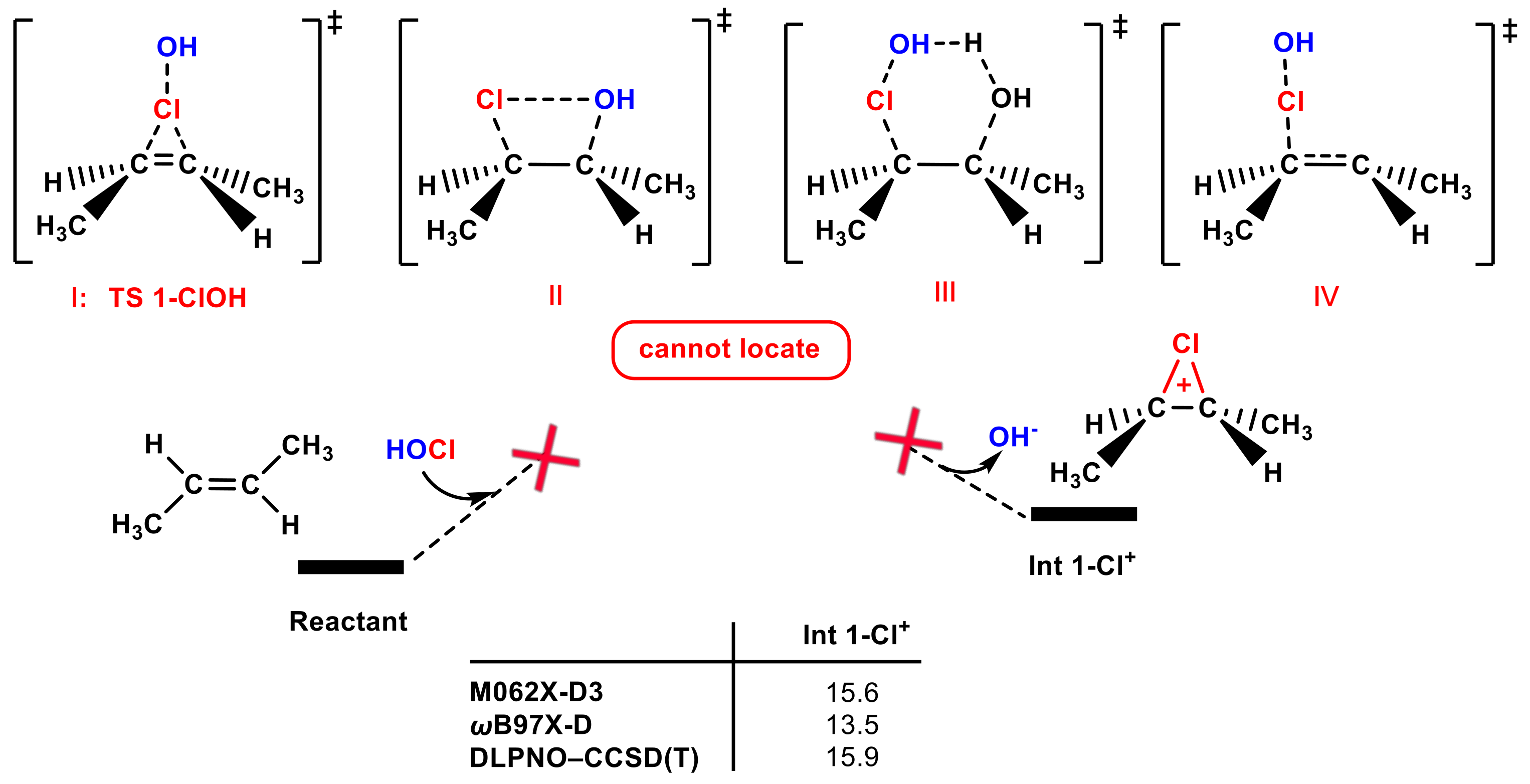
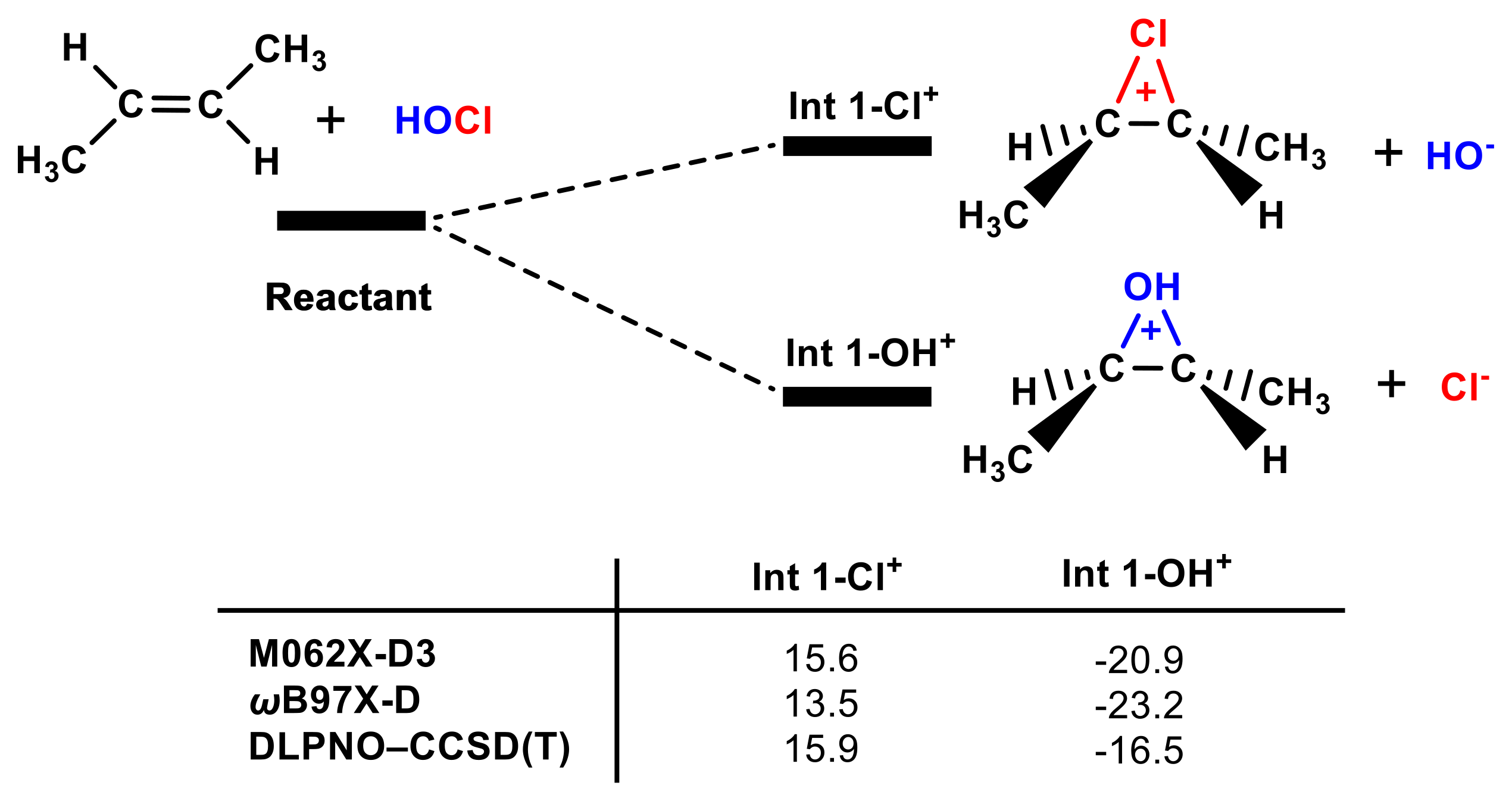
Since many textbooks use trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene as the electrophilic reactant, it was chosen as the olefin to use to perform the calculations. Firstly, a review of the literature was conducted, but no relevant computational work was found on adding HOCl to olefins, so we inferred that there may be some challenges in this fundamental chemical reaction. Then, we carried out calculations to test the performance of the electrophilic addition of the Cl group in the HOCl molecule to trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene. Four possible transition states when adding the Cl group in the HOCl molecule to trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene are shown in Figure 1, involving the most common proposed TS 1-ClOH (I); a concerted four-membered transition state for the one-step transfer of the Cl group to one carbon and the simultaneous transfer of the OH group to another carbon (II); a six-membered transition state with one H2O molecule as the proton shuttle (III); the asynchronicity transition state (IV). However, none of the four transition states can be located. To verify whether these transition states exist, relaxed potential energy surface (PES) scanning was performed (see Figure S1a,b). Instead of reaching a parabolic peak in the scanning process, the energy of the system continues to increase as the C-Cl bond length is gradually shortened from 2.5 Å to 1.6 Å (the C-Cl bond length in the Int 1-Cl+ is 1.9 Å). Moreover, the chlorium ion Int 1-Cl+ is not stable and is ~15 kcal mol−1 higher in energy than the reactants. According to the above computational results, the Cl group in the HOCl molecule adding pathway may not be favorable.
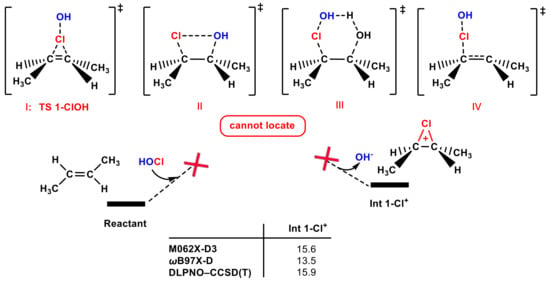
Figure 1.
Four possible transition states of adding the Cl group in the HOCl molecule to trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene, none of which can be located. Different calculation methods were used to calculate the free energies ( to generate Int 1-Cl+ (in kcal mol−1).
3.1.2. The OH Group in the HOCl Molecule Adding Pathway
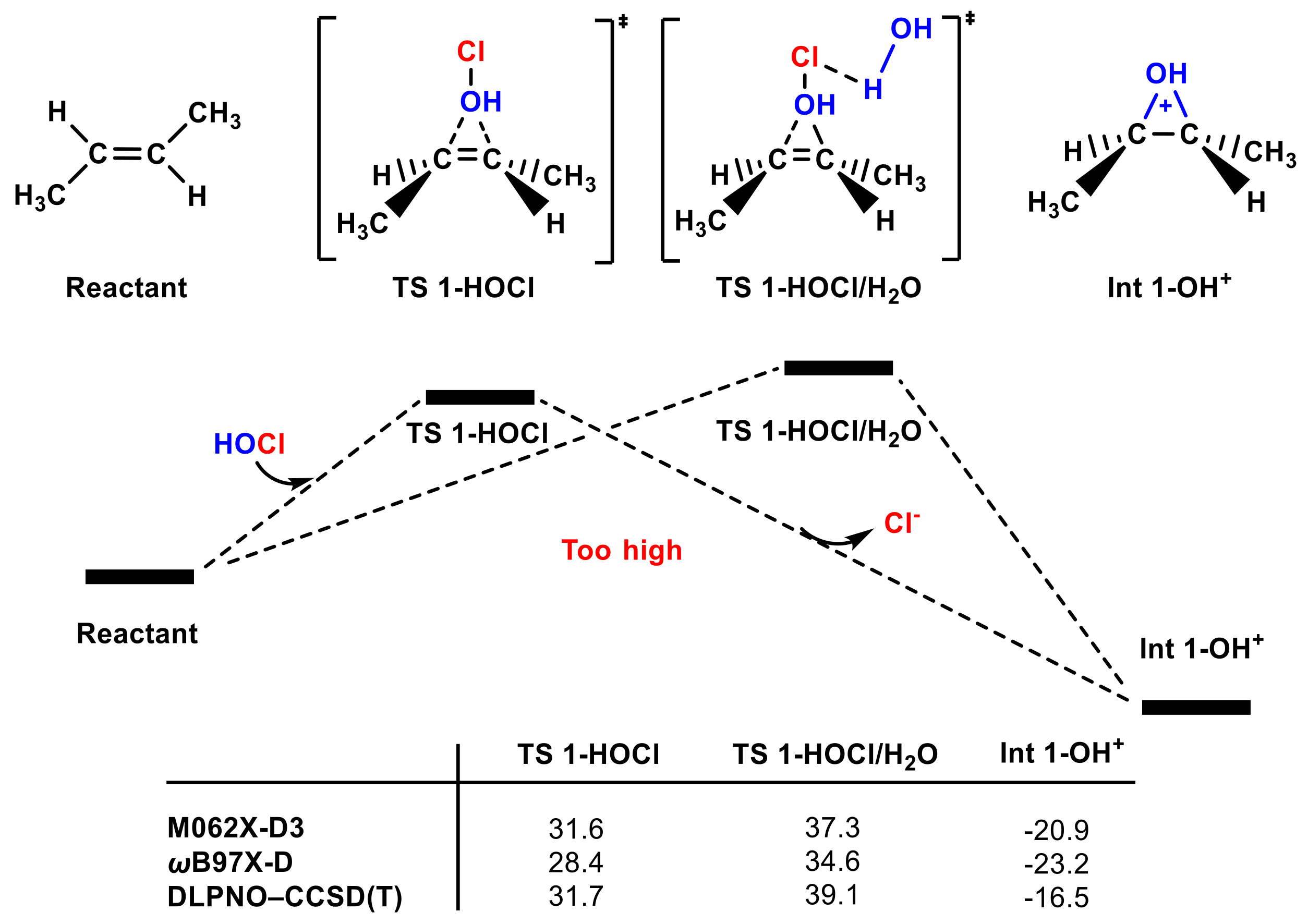
It is surprising that, when we tried to locate four-membered transition state II in Figure 1, the OH group transfer transition state (TS 1-HOCl) was instead located (Figure 2); its energy barrier is ~30 kcal mol−1 relative to reactants by different calculation methods (see Figure 2 and Figure S2); relaxed potential energy surface (PES) scanning also has a peak point similar to the transition state (see Figure S1e). The oxonium ion Int 1-OH+ is >32 kcal mol−1 more stable than Int 1-Cl+ (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). One water molecule was also used to stabilize the negative charge of the Cl group in TS 1-HOCl/H2O, but the energy barrier is ~6 kcal mol−1 higher than that of TS 1-HOCl.
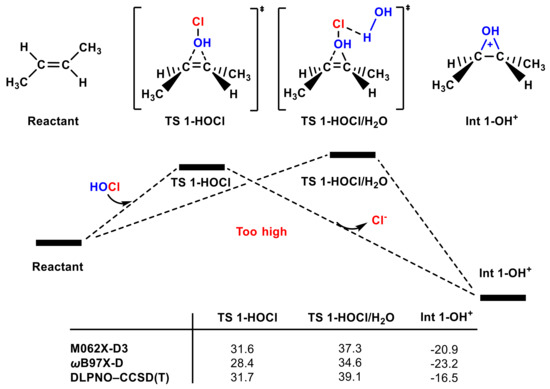
Figure 2.
The partial PES of the OH group in the HOCl molecule attacking trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene. The Gibbs free energies of TS 1-HOCl, TS 1-HOCl/H2O, and Int 1-OH+ according to different methods are included (in kcal mol−1).
Considering that TS 1-HOCl can be located but TS 1-ClOH; Int 1-OH+ is more stable than Int 1-Cl+, we infer that the OH group transfer pathway is more favorable than the Cl group transfer pathway. However, it is known that the ~30 kcal mol−1 energy barrier of the OH group transfer pathway is too high to overcome at the industrial production temperature (35–50 °C) [50], and this electrophilic addition reaction can occur at a very low temperature with a high reaction rate [51,52].
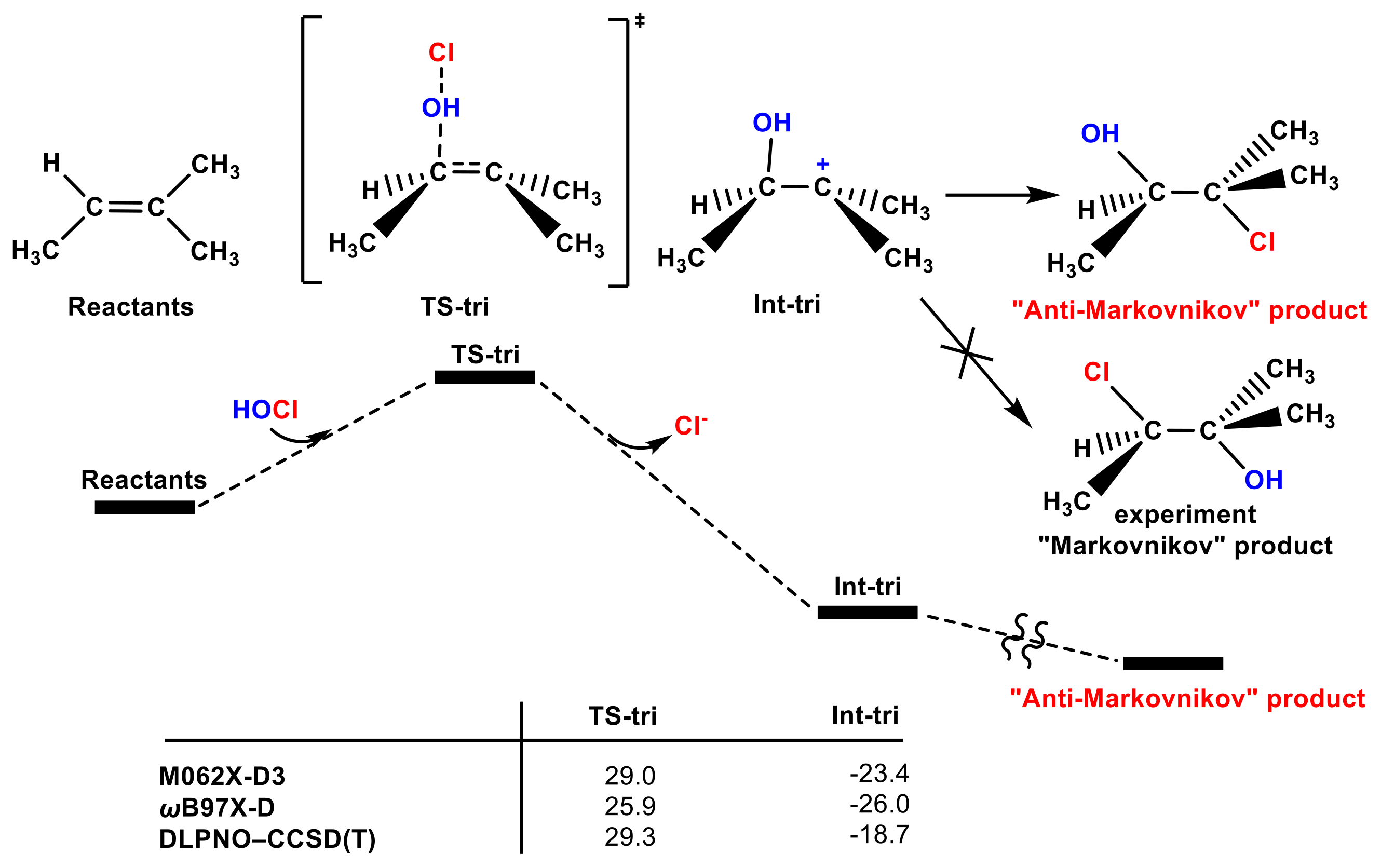
In addition to the high energy barrier, another important issue for the OH group transfer pathway is that, for tri-substituted olefins such as trimethylethylene (see Figure 3 and Figure S3), this pathway leads to an “anti-Markovnikov” product, which is not consistent with the experimental regioselectivity [53]. Therefore, although the transition state could be found, the OH group in the HOCl molecule adding pathway is also not favorable.
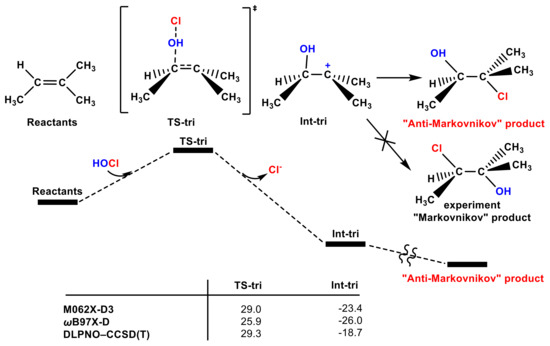
Figure 3.
The partial PES of the OH group in the HOCl molecule attacking trimethylethylene. The Gibbs free energies of the TS-tri and Int-tri according to different methods are included (in kcal mol−1).
The bond-dissociation energy (BDE) of the HO-Cl bond to HO• and Cl• is also high (~60 kcal mol−1), and there are no radical initiators in the reaction conditions. Therefore, the radical addition pathway can also be excluded (see Figure S4 for more details). The above computational results indicate that the HOCl molecule might not be the electrophilic species to use to carry out the addition reaction with trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene.
3.1.3. Oxonium Ion Intermediate vs. Chlorium Ion Intermediate
It is generally believed that, in the HOCl molecule, the Cl group is δ+ and the OH is δ- in terms of electronegativity and that Cl+ prefers to form the chlorium ion intermediate with a double bond [54]. However, our calculations do not support this conclusion, and one should not infer the properties of the ions from the molecule since the covalent bond changes their electronic structure. As shown in Figure 4, Int 1-OH+ is >32 kcal mol−1 more stable than Int 1-Cl+. Electronic configuration analysis was used to explain why Int 1-OH+ is more stable than Int 1-Cl+. The electronic configurations of OH+ and Cl+ are 1s2 2s2 2p4 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4, respectively. There are more electrons in Cl+ than in OH+ that can shield the positive charge. Therefore, the interaction between the OH+ and the double bond is stronger than that of the Cl+.
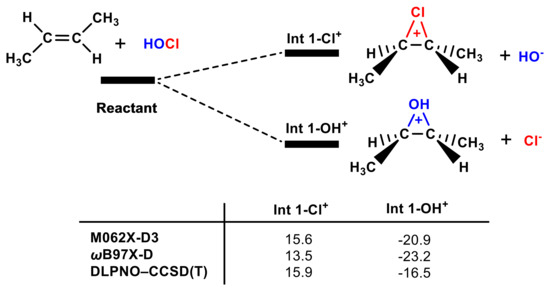
Figure 4.
The Gibbs free energies of Int 1-OH+ and Int 1-Cl+ according to different methods are included (in kcal mol−1).
3.1.4. Other Hypohalous Acids (HOF, HOBr, and HOI)
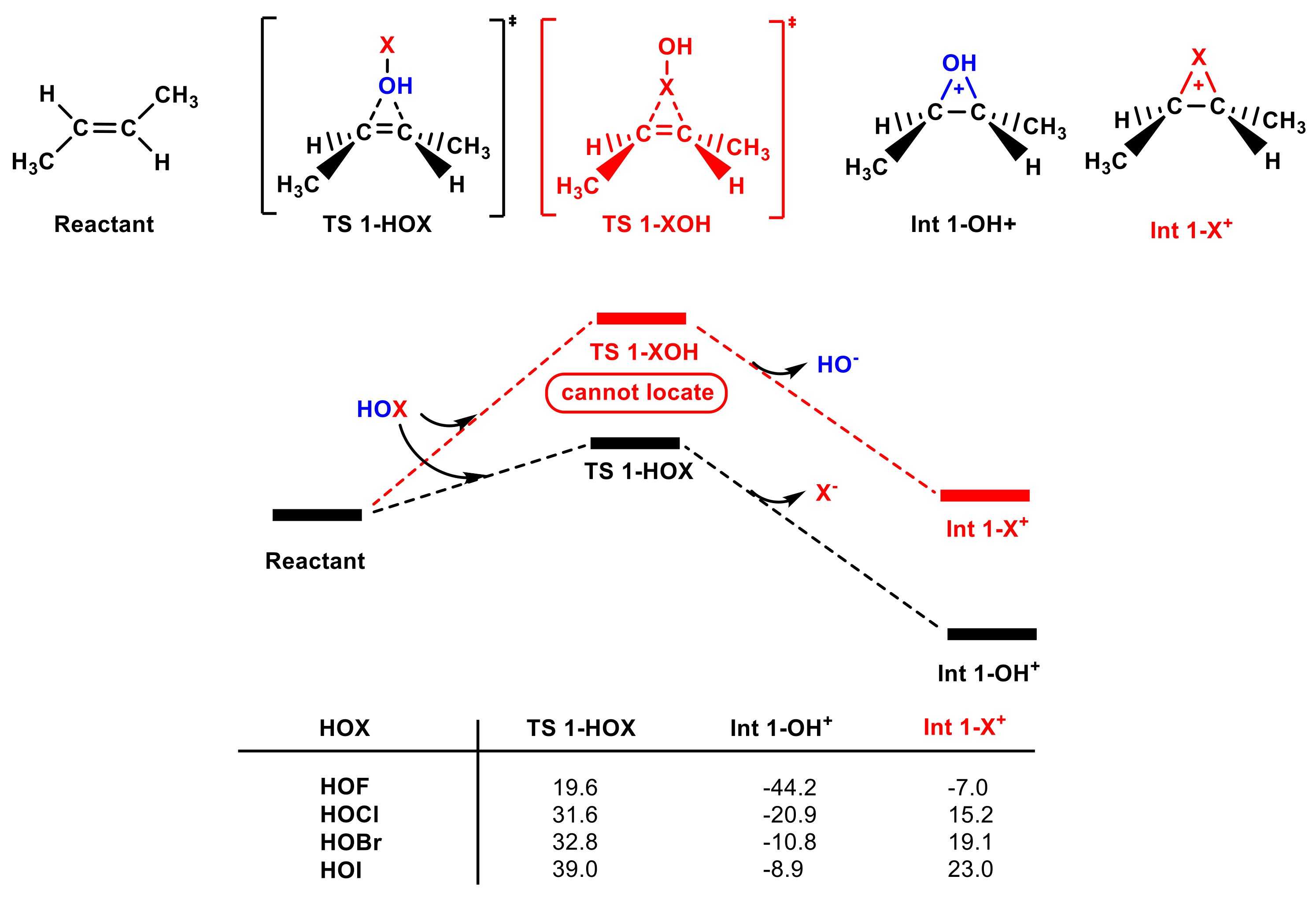
In addition to test the HOCl molecule, we also tested the electrophilic addition of other hypohalous acids (HOF, HOBr, and HOI) to olefins (see Figure S1c,d). Figure 5 shows that the Gibbs free energy of TS 1-HOX, Int 1-OH+, and Int 1-X+ decreases as the electrophilicity of X+ increases. Int 1-F+, Int 1-Br+, and Int 1-I+ are all higher in energy than Int 1-OH+, and TS 1-XOH cannot be located, which is in accordance with the HOCl. The energy barriers of TS 1-HOBr and TS 1-HOI are higher than that of TS 1-HOCl, whereas the energy barrier of HOF is achievable (19.6 kcal mol−1). Accordingly, the HOF molecule can undergo electrophilic addition with olefin [55]. Notably, a large number of studies have shown that the HOBr molecule is not a good brominating agent in water treatment compared to Br2 and Br2O [56], which is also consistent with our computations.
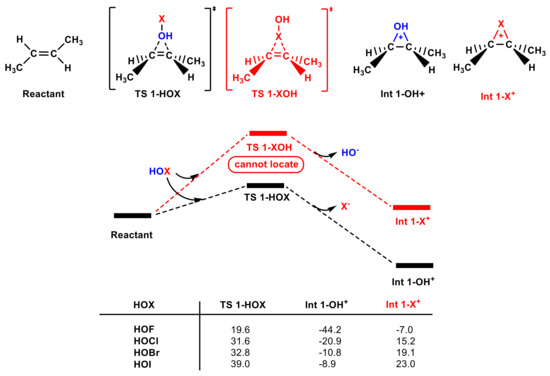
Figure 5.
The partial PES for the reaction of different hypohalous acids with trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene calculated at the M062X-D3/aug-cc-pVTZ theoretical level (see Figure S5 for the M062X-D3/def2-TZVPD theoretical level). The Gibbs free energies of TS 1-HOX, Int 1-OH+, and Int 1-X+ are included (in kcal mol−1).
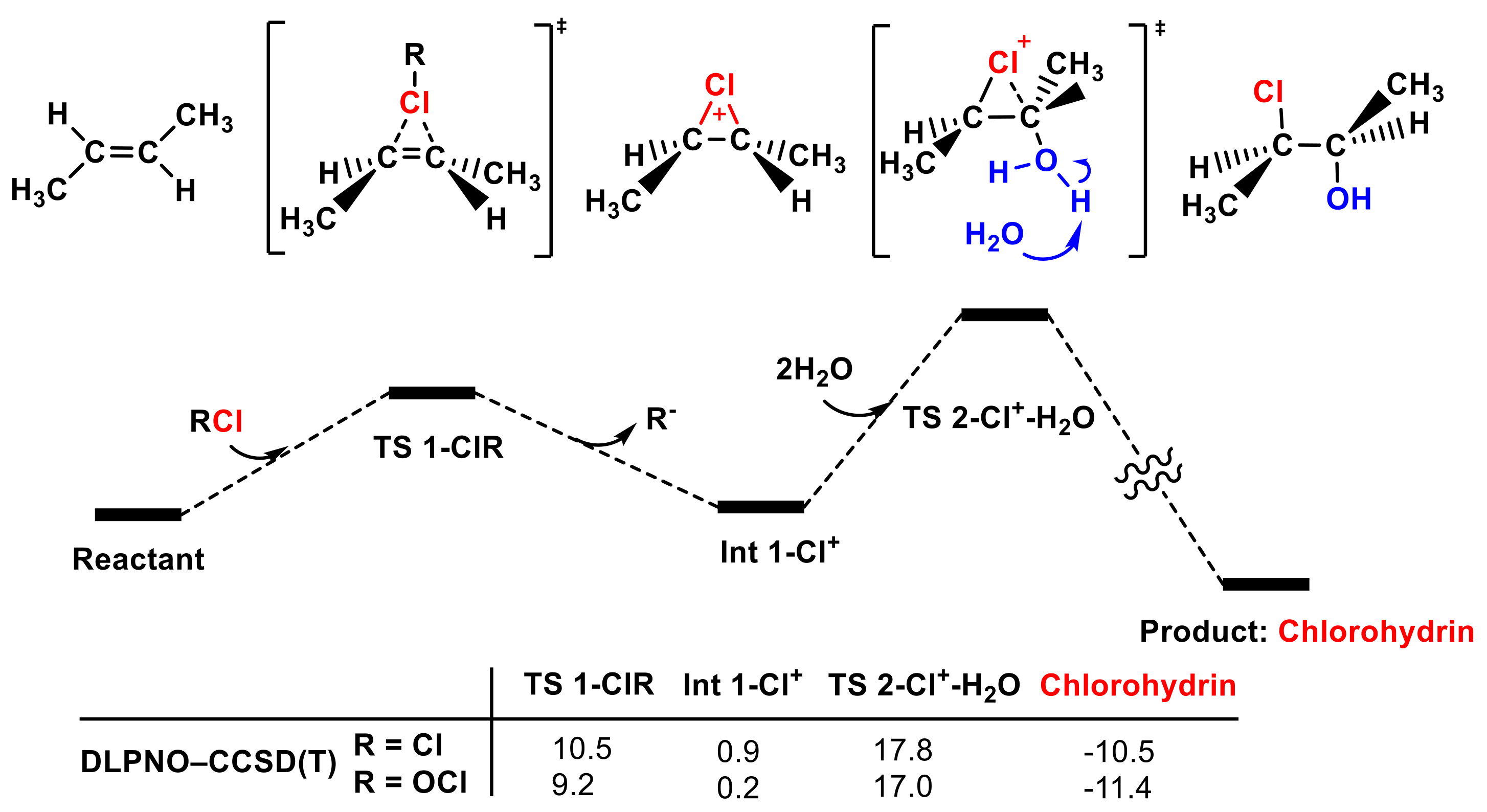
3.2. The Cl2 Reaction Pathway
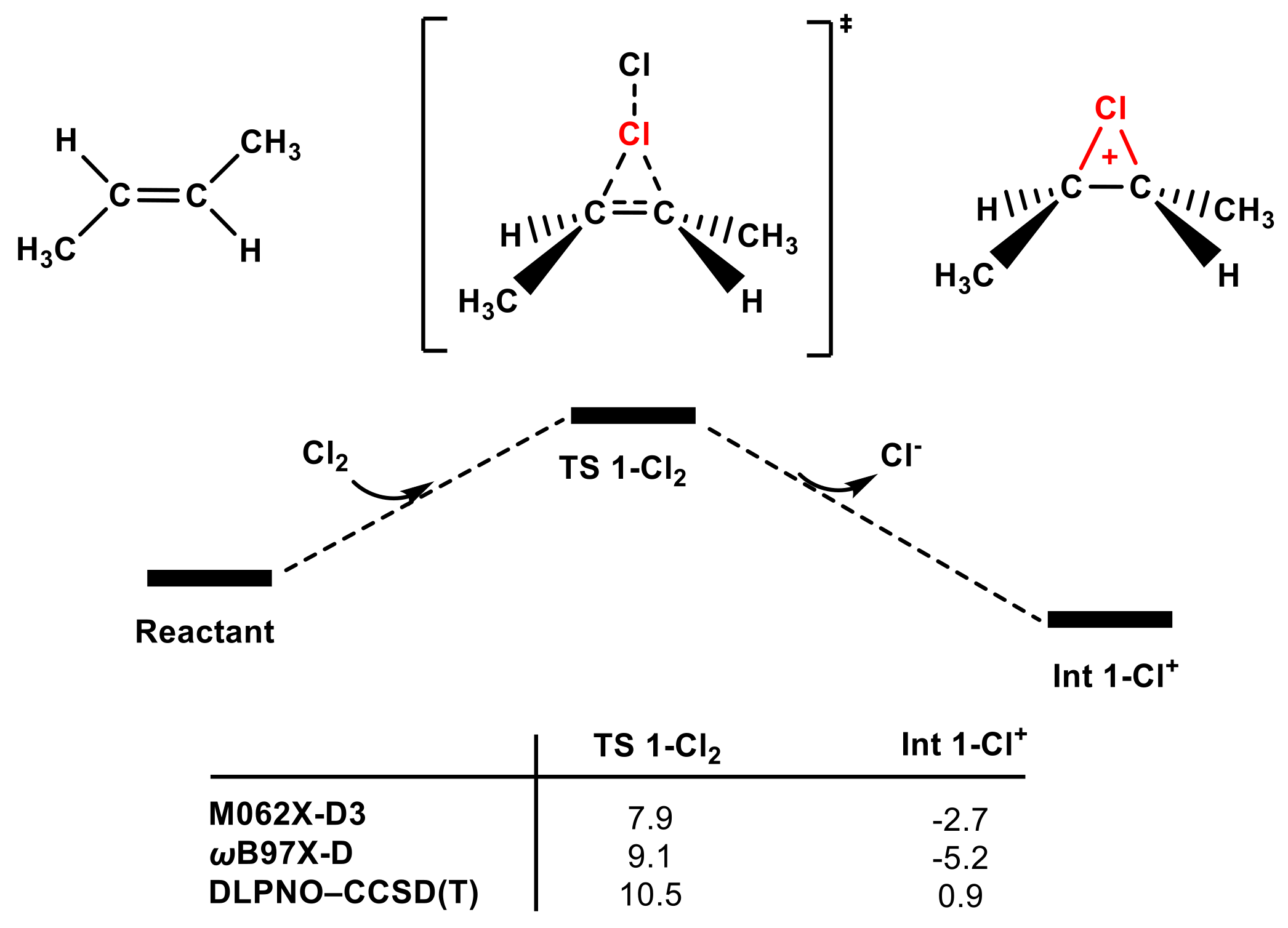
Next, the reactivity of adding Cl2 to olefins was evaluated using the same calculation methods. Our computational results indicate that Cl2 is a non-negligible electrophilic chlorinating agent for trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene. Changes in calculation methods had no discernible influence on the low energy barriers of TS 1-Cl2 (see Figure 6). The energy barrier of TS 1-Cl2 is only 10.5 kcal mol−1 according to the high-level DLPNO–CCSD(T) method, indicating that trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene could be easily chlorinated by Cl2, which is in agreement with McMurry’s proposal (see Figure S6).
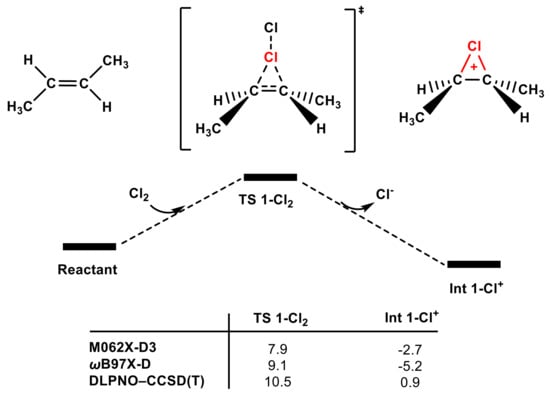
Figure 6.
The partial PES of the reaction of Cl2 attacking trans-1,2-dimethylethylene (see SI for the whole PES). The Gibbs free energies of TS 1-Cl2 and Int 1-Cl+ obtained using different methods are included (in kcal mol−1).
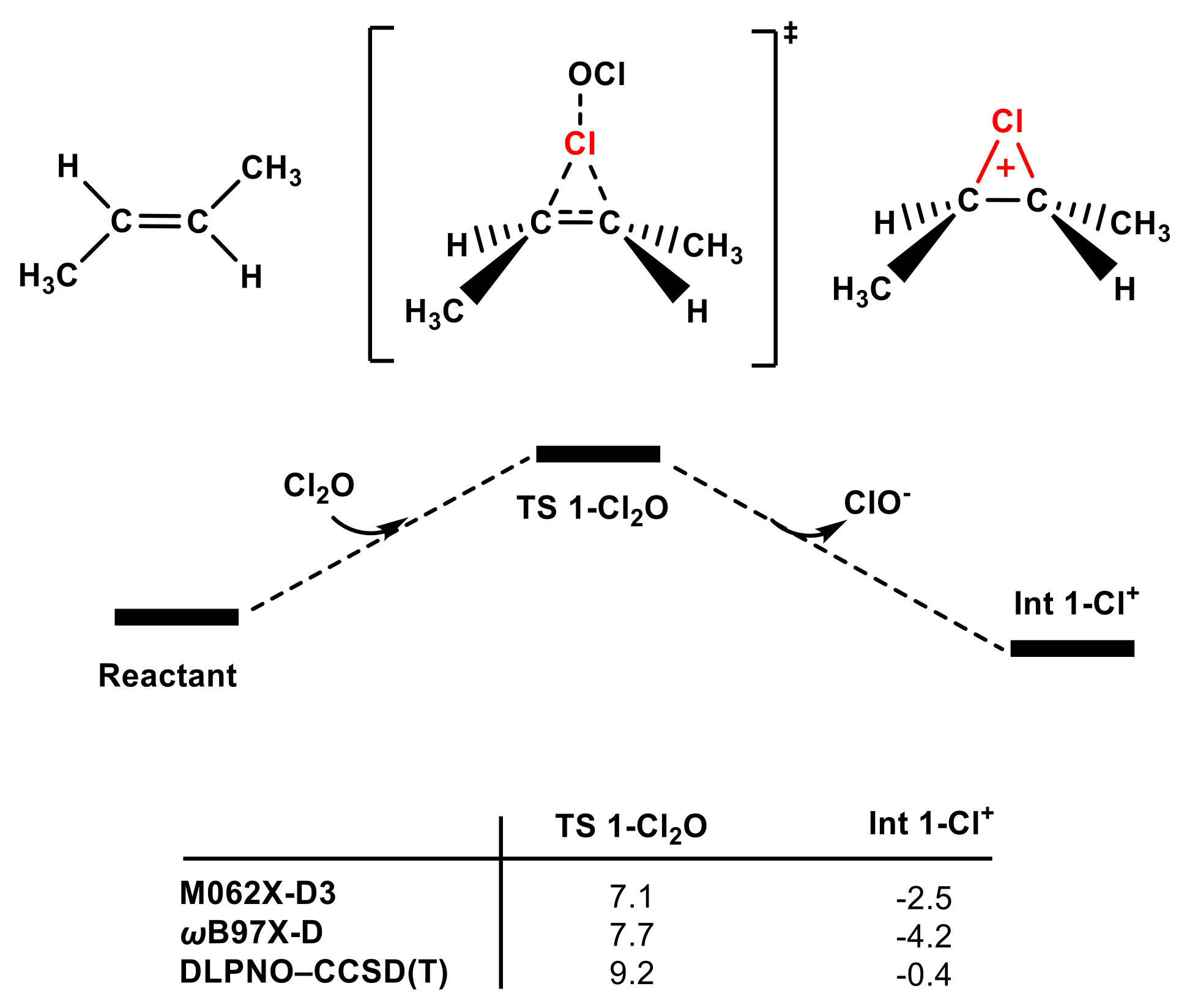
3.3. Another Active Electrophile: The Cl2O Reaction Pathway
Considering the complexity of the chemical composition of HOCl solution, the effects of other active electrophiles should not be overlooked. Previous experimental studies have shown that the main chlorinating agents in HOCl solution are affected by many factors, such as pH, chloride ion [32,33], and chlorite concentration [57]. In recent decades, evidence from multiple reports has quantified the influence of electrophilic species in HOCl solution, including HOCl, Cl2O, Cl2, and H2OCl+ [58]. Collette, T. W. et al. have denied that reactions between H2OCl+ and organic compounds are likely [59]. As mentioned above, Sivey, J. D. and Roberts, A. L. conducted remarkable research on the active components of free available chlorine (FAC). They determined the main electrophilic species and their robust rate constants using kinetic experiments and concluded that Cl2O and Cl2 might be potent electrophilic agents in HOCl solution [32,33,34]. Therefore, the performance of the electrophilic addition of Cl2O to trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene was tested computationally in the present study.
As shown in Figure 7, when the Cl group in Cl2O serves as a chlorinating agent to attack trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene, the energy barrier of TS 1-Cl2O is only 9.2 kcal/mol, which is lower than that of TS 1-Cl2 using the same calculation methods. Therefore, Cl2O and Cl2 are the main contributors of olefins in the electrophilic addition reaction rather than the HOCl molecule (see Figure S7). The ability of Cl2 and Cl2O to function as electrophiles can also be attributed to the superiority of Cl− and ClO− as leaving groups [33].
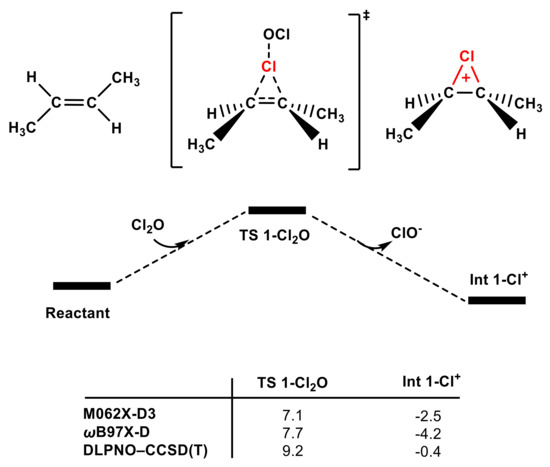
Figure 7.
The partial PES of the reaction of Cl2O attacking trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene (see SI for the whole PES). The Gibbs free energies of TS 1-Cl2O and Int 1-Cl+ were obtained according to different methods (in kcal mol−1).
3.4. The Whole PES for the Formation of Chlorohydrins
After determining that Cl2 and Cl2O are the main electrophilic agents in HOCl solution, we further investigated the following hydrolyzation step to form the final chlorohydrin product (see Figure 8). Int 1-Cl+ is hydrolyzed by water to afford chlorohydrin via TS 2-Cl+-H2O. One water molecule attacks the carbon in the double bond activated with a Cl+ ion, and another water molecule is needed to stabilize the leaving proton. The energy barrier of TS 2-Cl+-H2O is reasonable for these reaction conditions.
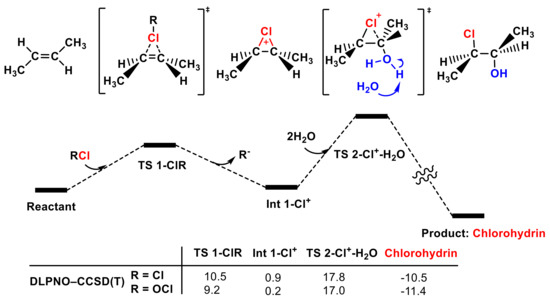
Figure 8.
The whole PES of the reaction of Cl2, Cl2O, and trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene to form chlorohydrins was calculated with the DPLNO-CCSD(T) method (in kcal mol−1).
4. Conclusions
In summary, to solve the controversy regarding the active electrophilic addition species (i.e., whether it is the HOCl molecule or Cl2) in HOCl solution for the double bond addition reaction, various theoretical calculations were carried out. Our results indicate that the HOCl molecule cannot be added to olefin directly due to its high energy barrier (~30 kcal mol−1) and the presence of the wrong regioselectivity. Additionally, electronic configuration analysis was employed to explain the stability of the oxonium ion and chlorium ion intermediates. It is noteworthy that Int 1-OH+ is >32 kcal mol−1 more stable than the generally believed Int 1-Cl+. In comparison, the energy barrier of Cl2 attacking the double bond is just ~10 kcal mol−1, which makes it a non-negligible electrophilic chlorinating agent for olefin. Moreover, Cl2O could become another important chlorinating agent due to its lower energy barrier. Cl2O and Cl2 are more potent electrophilic agents than the HOCl molecule, which agrees with the earlier assessment by Sivey, J. D. and Roberts, A. L. By and large, this theoretical research unambiguously solves the controversy in some studies and textbooks, and should benefit the mechanistic studies of important biological and chemical processes with HOCl solution.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27061843/s1. Figure S1: Schematic diagram of flexible scanning of halogen or oxygen in HOX with C=C double bonds; Figure S2: Select structures located for the transition state (TS 1-HOCl) of the electrophilic addition of trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene and HOCl; Figure S3: Select structures located for the transition state (TS-tri) of the electrophilic addition of trimethylethylene and HOCl; Figure S4: Schematic diagram of the potential energy surface of the reaction of OH or Cl radicals attacking trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene; Figure S5: The potential energy surface for the reaction of different hypohalous acids with trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene; Figure S6: Select structures located for the transition state (TS 1-Cl2) of the electrophilic addition of trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene and Cl2; Figure S7: Select structures located for the transition state (TS 1-Cl2O) of the electrophilic addition of trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene and Cl2O; Figure S8. Free energies for the reaction of different electrophiles (HOCl, Cl2 and Cl2O) with trans-1,2-dimethyl ethylene from the MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ method. Refs. [35,36,37,38,39,40,60,61,62,63] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Computation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, K.-W.C.; writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, Y.-D.W. and T.-Y.S.; funding acquisition, Y.-D.W. and T.-Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 21933004) and the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (grant number 2020B010188001). The calculations were carried out at the SZBL supercomputing center.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
More details about DFT calculation are in Supporting Information. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Wang, L.; Bassiri, M.; Najafi, R.; Najafi, K.; Yang, J.; Khosrovi, B.; Hwong, W.; Barati, E.; Belisle, B.; Celeri, C.; et al. Hypochlorous acid as a potential wound care agent: Part I. Stabilized hypochlorous acid: A component of the inorganic armamentarium of innate immunity. J. Burns Wounds 2007, 6, e5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aratani, Y. Role of Myeloperoxidase in the host defense against fungal infection. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 2006, 47, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Lampert, M.; Test, S. Long-lived oxidants generated by human neutrophils: Characterization and bioactivity. Science 1983, 222, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasenko, O.; Gorudko, I.; Sokolov, A. Hypochlorous acid as a precursor of free radicals in living systems. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 1466–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malle, E.; Marsche, G.; Arnhold, J.; Davies, M.J. Modification of low-density lipoprotein by myeloperoxidase-derived oxidants and reagent hypochlorous acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 392–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Elfarra, A.A. Potential roles of myeloperoxidase and hypochlorous acid in metabolism and toxicity of alkene hydrocarbons and drug molecules containing olefinic moieties. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Dulcère, J.-P. Cohalogenation in organic synthesis. Synthesis 1993, 1993, 1177–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smietana, M.; Gouverneur, V.; Mioskowski, C. An improved synthesis of iodohydrins from alkenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.S.; Rowan, B.G. Hypochlorous acid: A review. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, W.R.; Lum, Y.; Ozden, A.; Wang, Y.; Nam, D.-H.; Chen, B.; Wicks, J.; Zhuang, T.-T.; Li, F.; Sinton, D. Chloride-mediated selective electrosynthesis of ethylene and propylene oxides at high current density. Science 2020, 368, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahleitner, M.; Paulik, C. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pech, G.A.; Witzl, W.J. Process for Producing Chlorohydrins.U.S. Patent. US5523425 A, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Spickett, C.M.; Jerlich, A.; Panasenko, O.M.; Arnhold, J.; Pitt, A.R.; Stelmaszyńska, T.; Schaur, R.J. The reactions of hypochlorous acid, the reactive oxygen species produced by myeloperoxidase, with lipids. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2000, 47, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, J.E. Organic Chemistry, 9th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bruice, P.Y. Organic Chemistry; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rawn, J.D.; Ouellette, R.J. Organic Chemistry: Structure, Mechanism, Synthesis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.B. March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Loudon, M.; Parise, J. Organic Chemistry, 6th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.H.; Iverson, B.L.; Anslyn, E.; Foote, C.S.; Novak, B.M. Organic Chemistry, 8th ed.; Brooks Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn, C.C.; van den Berg, J.J.; Roitman, E.; Kuypers, F.A. Chlorohydrin formation from unsaturated fatty acids reacted with hypochlorous acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 296, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, J.; Osipov, A.N.; Spalteholz, H.; Panasenko, O.M.; Schiller, J. Effects of hypochlorous acid on unsaturated phosphatidylcholines. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.I.; Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Hypochlorous acid-mediated protein oxidation: How important are chloramine transfer reactions and protein tertiary structure? Biochemistry 2007, 46, 9853–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, N.; Knaapen, A.M.; Munnia, A.; Peluso, M.; Haenen, G.R.; Chiu, R.K.; Godschalk, R.W.; van Schooten, F.J. Genotoxic effects of neutrophils and hypochlorous acid. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, A.D.; Houghton, A.M. Tumor-associated neutrophils: New targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.L. Hypochlorous acid-mediated modification of proteins and its consequences. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.W.; Whiteman, M.; Bay, B.H.; Li, Y.; Sheu, F.S.; Qi, R.Z.; Tan, C.H.; Cheung, N.S. Hypochlorous acid induces apoptosis of cultured cortical neurons through activation of calpains and rupture of lysosomes. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Whiteman, M.; Gieseg, S.P. HOCl causes necrotic cell death in human monocyte derived macrophages through calcium dependent calpain activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, T.B.; Jiang, T.; Xiong, X.M.; Luo, X.J.; Ma, Q.L.; Peng, J. Myeloperoxidase-derived hypochlorous acid promotes ox-LDL-induced senescence of endothelial cells through a mechanism involving beta-catenin signaling in hyperlipidemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ling, M.; Lopez, J.A.; Chung, D.W.; Fu, X. Hypochlorous acid generated by neutrophils inactivates ADAMTS13: An oxidative mechanism for regulating ADAMTS13 proteolytic activity during inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, B.S.; Childers, W.E., Jr.; Pinnick, H.W. Oxidation of α, β-un saturated aldehydes. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalcanale, E.; Montanari, F. Selective oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids with sodium chlorite-hydrogen peroxide. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivey, J.D.; McCullough, C.E.; Roberts, A.L. Chlorine monoxide (Cl2O) and molecular chlorine (Cl2) as active chlorinating agents in reaction of dimethenamid with aqueous free chlorine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivey, J.D.; Roberts, A.L. Assessing the reactivity of free chlorine constituents Cl2, Cl2O, and HOCl toward aromatic ethers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.S.; Reber, K.P.; Roberts, A.L. Aqueous chlorination kinetics of cyclic alkenes-is HOCL the only chlorinating agent that matters? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11133–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. Construction of a generalized gradient approximation by restoring the density-gradient expansion and enforcing a tight Lieb–Oxford bound. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 184109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-D.; Head-Gordon, M. Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom–atom dispersion corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.A.; Dunning, T.H., Jr.; Harrison, R.J. Electron affinities of the first-row atoms revisited. Systematic basis sets and wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 96, 6796–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.A.; Kendall, R.A.; Dunning, T.H., Jr. Benchmark calculations with correlated molecular wave functions. II. Configuration interaction calculations on first row diatomic hydrides. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 1930–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, T.H. A road map for the calculation of molecular binding energies. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 9062–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Riplinger, C.; Neese, F. An efficient and near linear scaling pair natural orbital based local coupled cluster method. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 034106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riplinger, C.; Sandhoefer, B.; Hansen, A.; Neese, F. Natural triple excitations in local coupled cluster calculations with pair natural orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 134101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čížek, J. On the correlation problem in atomic and molecular systems. Calculation of wavefunction components in Ursell-type expansion using quantum-field theoretical methods. J. Chem. Phys. 1966, 45, 4256–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, G., III; Bartlett, R.J. A full coupled-cluster singles and doubles model: The inclusion of disconnected triples. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavachari, K.; Trucks, G.W.; Pople, J.A.; Head-Gordon, M. A fifth-order perturbation comparison of electron correlation theories. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1989, 157, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system, version 4.0. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu GY, T.; Richey, W.F.; Betso, J.E.; Hughes, B.; Klapacz, J.; Lindner, J. Chlorohydrins. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, Y.; Luo, G. Chlorohydrination of allyl chloride to dichloropropanol in a microchemical system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 14685–14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G.A.; Roth, B. Synthetic studies toward Verrucarol. 2. Synthesis of the AB ring system. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 4825–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G. The markovnikov rule. J. Chem. Educ. 1961, 38, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B. Organic Chemistry: An Acid-Base Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Migliorese, K.; Appelman, E.; Tsangaris, M. Reaction of unsaturated compounds with hypofluorous acid. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivey, J.D.; Bickley, M.A.; Victor, D.A. Contributions of BrCl, Br2, BrOCl, Br2O, and HOBr to regiospecific bromination rates of anisole and bromoanisoles in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4937–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormányos, B.; Nagypál, I.; Peintler, G.; Horváth, A.K. Effect of chloride ion on the kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between chlorite ion and hypochlorous acid. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 7914–7920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, M.; Simic, N.; Ahlberg, E. Exploring the mechanism of hypochlorous acid decomposition in aqueous solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 19342–19348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.P.; Duirk, S.E.; Tarr, J.C.; Collette, T.W. Monitoring the speciation of aqueous free chlorine from pH 1 to 12 with Raman spectroscopy to determine the identity of the potent low-pH oxidant. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappoport, D.; Furche, F. Property-optimized Gaussian basis sets for molecular response calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 134105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, C.Y.; CYLview, 1.0b. Université de Sherbrooke. 2009. Available online: http://www.cylview.org (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Scott, A.P.; Radom, L. Harmonic vibrational frequencies: An evaluation of Hartree− Fock, Møller− Plesset, quadratic configuration interaction, density functional theory, and semiempirical scale factors. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 16502–16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head-Gordon, M.; Pople, J.A.; Frisch, M.J. MP2 energy evaluation by direct methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 153, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).