Advances in the Biological Application of Force-Induced Remnant Magnetization Spectroscopy
Abstract
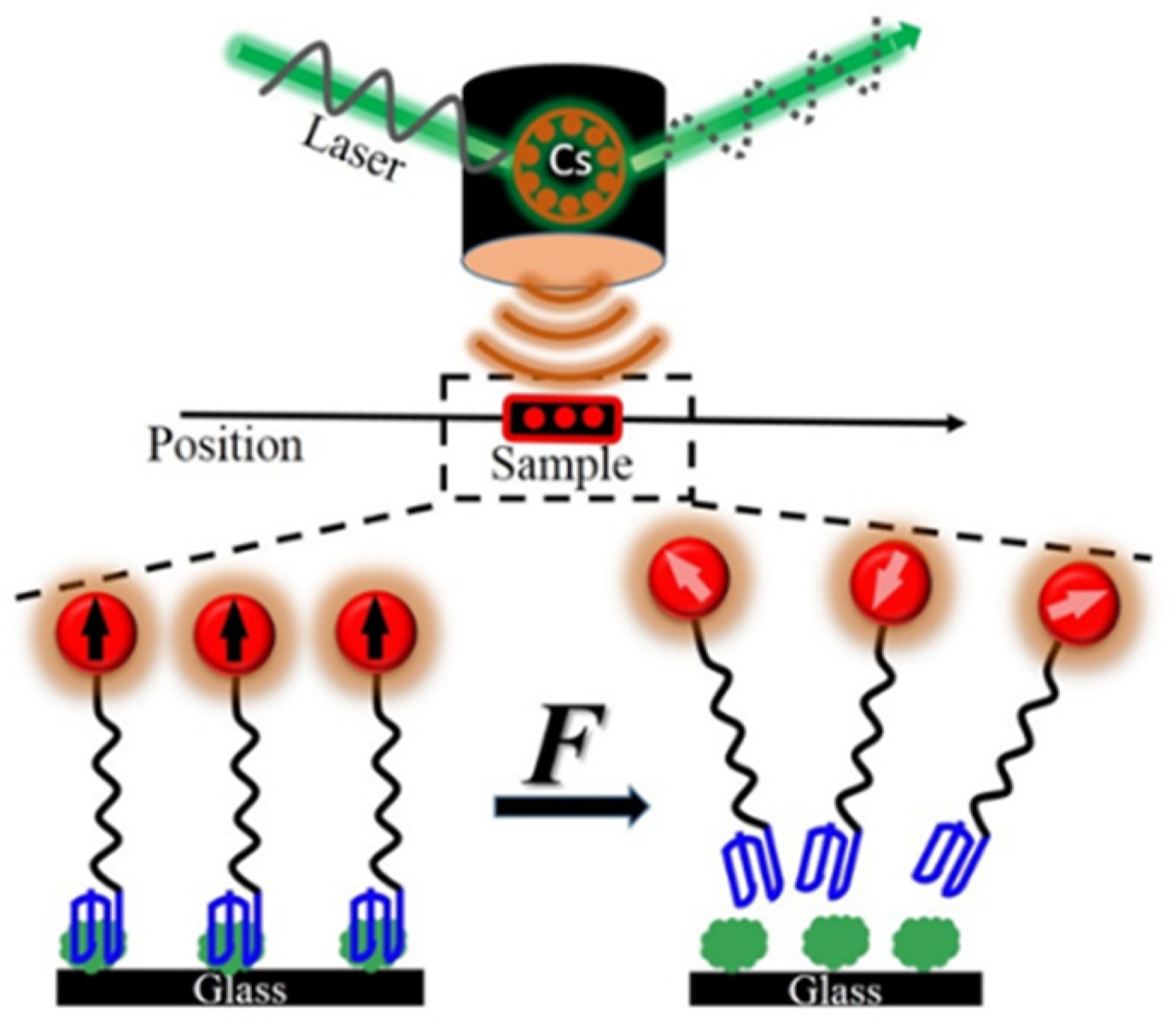
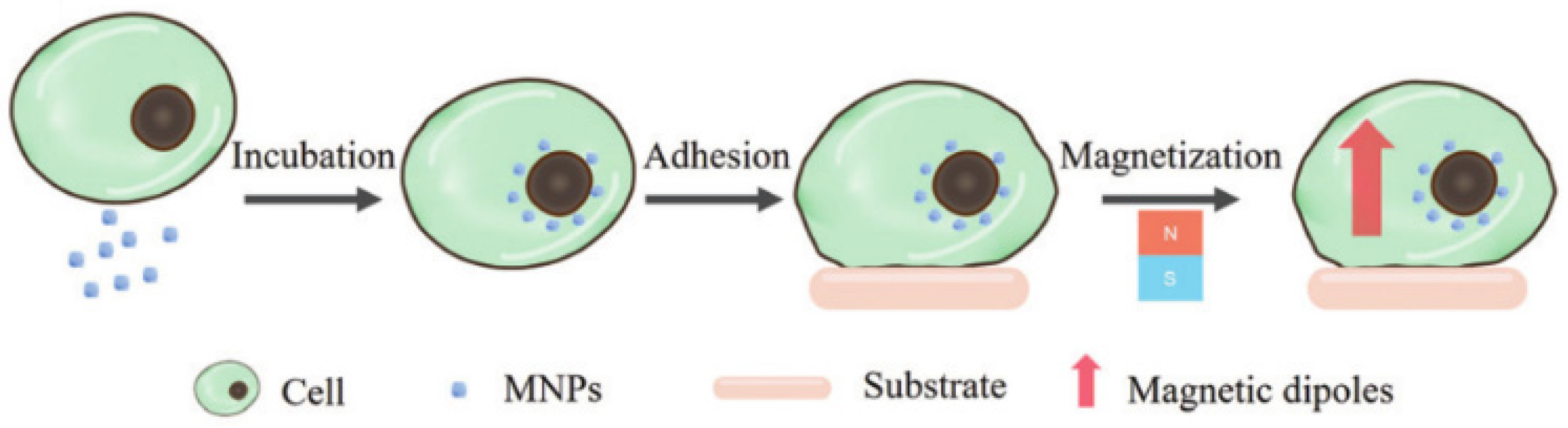
:1. Introduction
2. External Mechanical Force
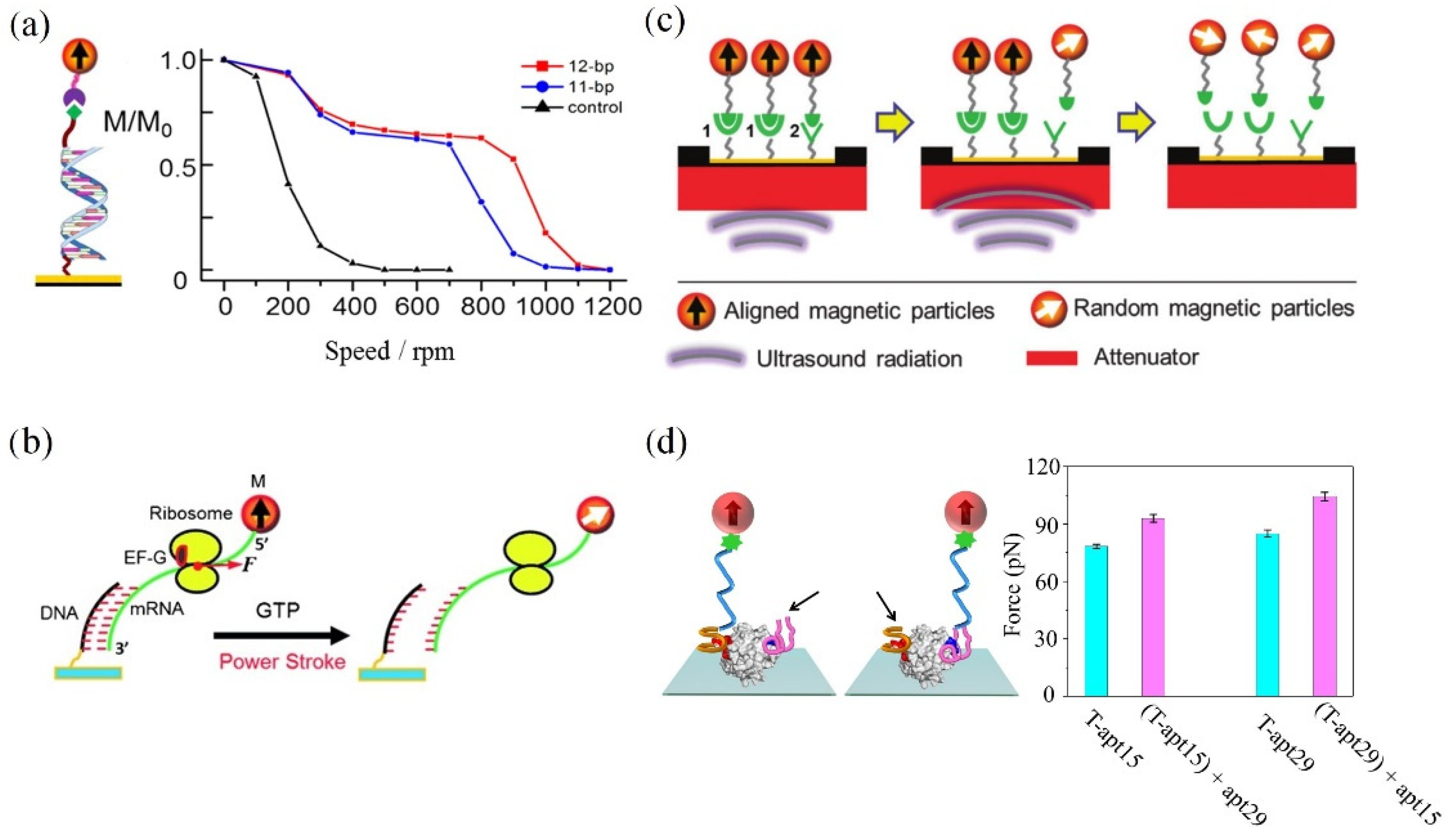
2.1. Shaking Force
2.2. Centrifugation Force
2.3. Ultrasound Radiation Force
2.4. Fluid Shear Force
3. Magnetic Probes
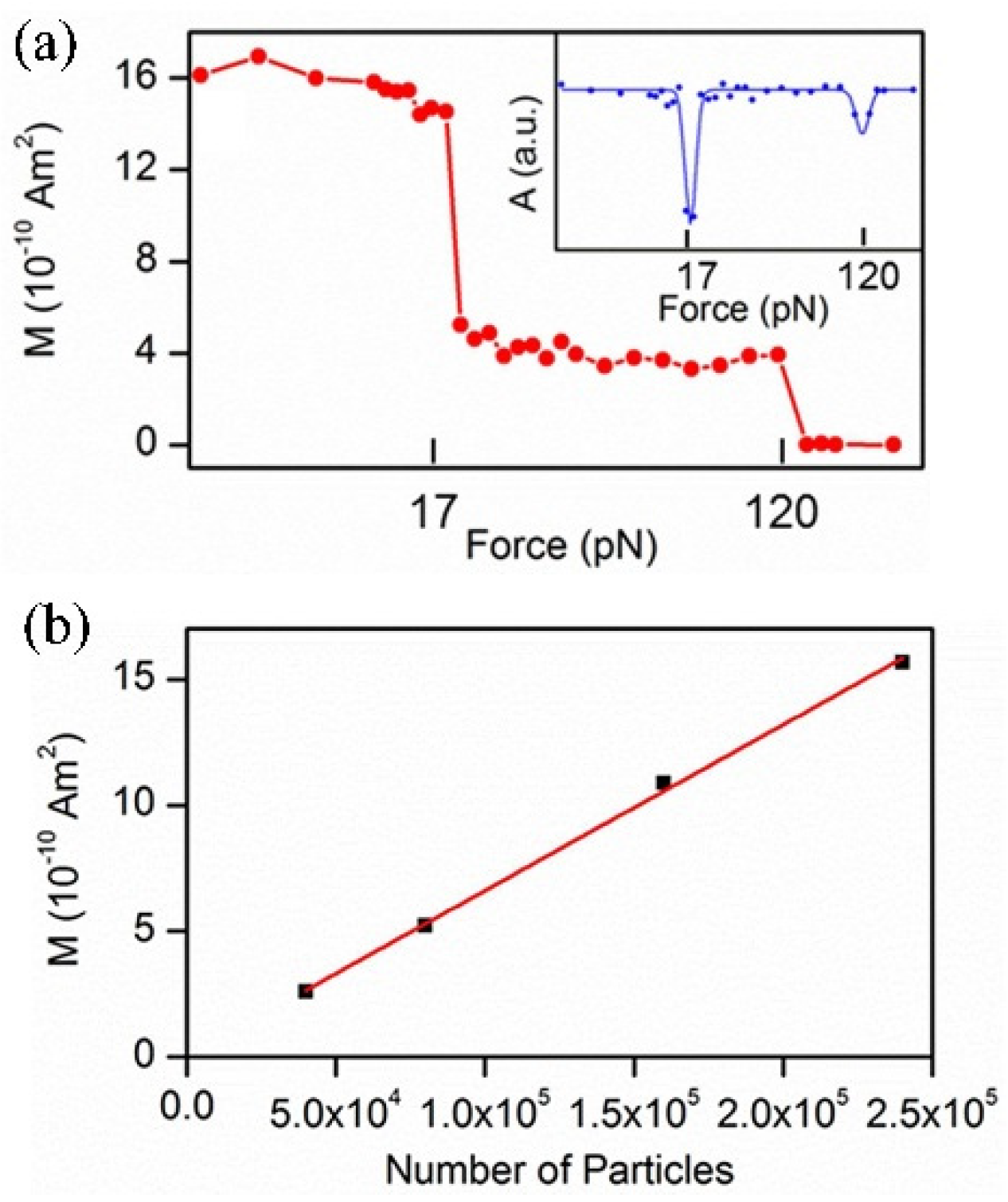
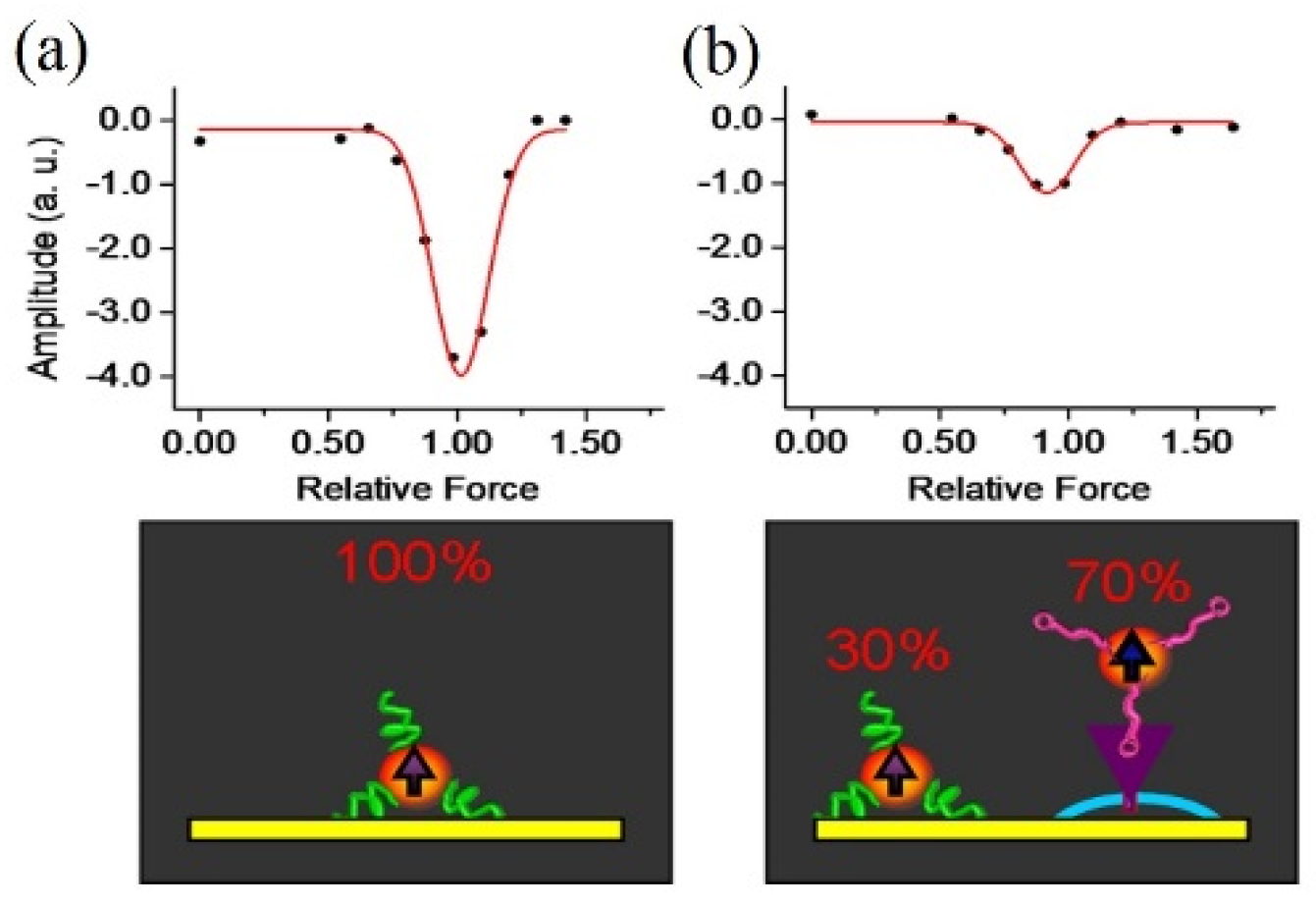
3.1. M280
3.2. Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
4. Prospects and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirtz, D.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Searson, P. The physics of cancer: The role of physical interactions and mechanical forces in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.K.; Martin, J.D.; Stylianopoulos, T. The role of mechanical forces in tumor growth and therapy. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 16, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roca-Cusachs, P.; Conte, V.; Trepat, X. Quantifying forces in cell biology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugita, M.; Onishi, I.; Irisa, M.; Yoshida, N.; Hirata, F. Molecular recognition and self-organization in life phenomena studied by a statistical mechanics of molecular liquids, the RISM/3D-RISM theory. Molecules 2021, 26, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, R.M.; Ferreira, M.A.; Raimundo, G.A.S.; Loriato, V.A.P.; Reis, P.A.B.; Fontes, E.P.B. Virus perception at the cell surface: Revisiting the roles of receptor-like kinases as viral pattern recognition receptors. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.D.; Zhao, P.K.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zou, M.C.; Warszawik, E.; Loznik, M.; Göstl, R.; Herrmann, A. Mechanochemical bond scission for the activation of drugs. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.M.; Wright, N.T. Tumor Metastasis in the Microcirculatio; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, F.; Fan, H.J.; Yang, G.D.; Zhang, F.; He, P.G. Directly investigating the interaction between aptamers and thrombin by atomic force microscopy. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Krieg, M.; Fläschner, G.; Alsteens, D.; Gaub, B.M.; Roos, W.H.; Wuite, G.J.L.; Gaub, H.E.; Gerber, C.; Dufrene, Y.F.; Mueller, D.J. Atomic force microscopy-based mechanobiology. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2018, 1, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Dang, D.; Xi, N.; Wang, Y.C.; Liu, L.Q. A review of nanoscale characterizing individual DNA behaviors using atomic force microscopy. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 920–933. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, D.; Mossa, A.; Jadhav, M.; Cecconi, C. Biomolecular applications of recent developments in optical tweezers. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zaltron, A.; Merano, M.; Mistura, G.; Sada, C.; Seno, F. Optical tweezers in single-molecule experiments. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, G.H.; Winardhi, R.S.; Yao, M.X.; Popa, I.; Fernandez, J.M.; Yan, J. Dynamics of equilibrium folding and unfolding transitions of titin immunoglobulin domain under constant forces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loef, A.; Walker, P.U.; Sedlak, S.M.; Gruber, S.; Obser, T.; Brehm, M.A.; Benoit, M.; Lipfert, J. Multiplexed protein force spectroscopy reveals equilibrium protein folding dynamics and the low-force response of von Willebrand factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18798–18807. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.X.; Le, S.M.; Chen, H.; Muniyappa, K.; Yan, J. Force and ATP hydrolysis dependent regulation of RecA nucleoprotein filament by single-stranded DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 924–932. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, K.C.; Nagy, A. Single-molecule force spectroscopy: Optical tweezers, magnetic tweezers and atomic force microscopy. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.S. Force spectroscopy on single molecules of life. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11271–11278. [Google Scholar]
- Jadvar, H. Molecular imaging of prostate cancer with F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.Z.; Yang, H.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, S.J. Quantitatively resolving multivalent interactions on a macroscopic scale using force spectroscopy. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3705–3708. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, M.; Breeman, W.A.P.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Valkema, R.; Krenning, E.P. Tumor imaging and therapy using radiolabeled somatostatin analogues. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Dupres, V.; Menozzi, F.D.; Locht, C.; Clare, B.H.; Abbott, N.L.; Cuenot, S.; Bompard, C.; Raze, D.; Dufrene, Y.F. Nanoscale mapping and functional analysis of individual adhesins on living bacteria. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kominis, I.K.; Kornack, T.W.; Allred, J.C.; Romalis, M.V. A subfemtotesla multichannel atomic magnetometer. Nature 2003, 422, 596–599. [Google Scholar]
- Budker, D.; Romalis, M.V. Optical magnetometry. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Xu, S.J. Long-range, high-resolution magnetic imaging of nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5679–5682. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Xu, S.J. Force-induced selective dissociation of noncovalent antibody-antigen bonds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9944–9948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Xu, S.J. Force-induced remnant magnetization spectroscopy for specific magnetic imaging of molecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4407–4409. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.T.; Jamison, A.C.; Lee, T.R.; Xu, S.J. Quantitatively resolving ligand-receptor bonds on cell surfaces using force-induced remnant magnetization spectroscopy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, L.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, S.J. Well-defined and sequence-specific noncovalent binding forces of DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 7554–7558. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Tsai, T.W.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, Y.H. Noninvasive measurement of the mechanical force generated by motor protein EF-G during ribosome translocation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 14041–14044. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Gavriliuc, M.; Lin, R.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, Y.H. Modulation and visualization of EF-G power stroke during ribosomal translocation. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.Z.; Xu, S.J. Sequence and chiral selectivity of Drug–DNA interactions revealed by force spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 53, 14135–14138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.B.; Sun, H.X.; Chai, Y.H.; Zhang, S.G.; Guan, A.J.; Li, Q.; Yao, L.; Tang, Y.L. Insulin-like growth factor type I selectively binds to G-quadruplex structures. BBA Gen. Subj. 2018, 1863, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Feng, F.; Li, Q.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L. Nanopurpurin-based photodynamic therapy destructs extracellular matrix against intractable tumor metastasis. Biomaterials 2018, 173, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Silva, L.; Yao, L.; Xu, S.J. Mechanically resolving noncovalent bonds using acoustic radiation force. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10786–10789. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.N.; Tsai, T.W.; Xu, S.J. Probing drug-DNA interactions using super-resolution force spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 193702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.N.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, S.J. Super-resolution force spectroscopy reveals ribosomal motion at sub-nucleotide steps. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5883–5886. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.J.; Lin, R.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, Y.H. High-resolution DNA dual-rulers reveal a new intermediate state in ribosomal frameshifting. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, Y.H. Dual DNA rulers to study the mechanism of ribosome translocation with single-nucleotide resolution. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 149, e59918. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.Y.; Yu, C.C.; Feng, F.; Lu, P.; Chai, Y.H.; Li, Q.L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L. Direct measurement of through-bond effects in molecular multivalent interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar]
- Effenberger, F.B.; Couto, R.A.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Machado, G.; Masunaga, S.H.; Jardim, R.F.; Rossi, L.M. Economically attractive route for the preparation of high quality magnetic nanoparticles by the thermal decomposition of iron (III) acetylacetonate. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 115603. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.H.; Feng, F.; Li, Q.L.; Yu, C.C.; Feng, X.Y.; Lu, P.; Yu, X.L.; Ge, M.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L. One-pot synthesis of high-quality bimagnetic core/shell nanocrystals with diverse exchange coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3366. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.C.; Zhang, D.; Feng, X.Y.; Chai, Y.H.; Lu, P.; Li, Q.L.; Feng, F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L. Nanoprobe-based force spectroscopy as a versatile platform for probing the mechanical adhesion of bacteria. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7648–7655. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Feng, X.Y.; Feng, F.; Pei, H.T.; Liu, R.P.; Li, Q.L.; Yu, C.C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L. Magnetic nanoparticles for the measurement of cell mechanics using force-induced remnant magnetization spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14573–14580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Feng, X.Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.L.; Yao, L. Matrix stiffness induces pericyte-fibroblast transition through YAP activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 698275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Shaking | Centrifugation | Ultrasound Radiation | Fluid Shear | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Force generator | Vortex mixer | Centrifuge | Ultrasonic transducer | Parallel-plate flow chamber |
| Force resolution level (pN) | Low | Medium (~2.0) | Medium (~0.5) | High (~0.5) |
| Typical applications | Antibody–antigen bonds | Antibody–antigen bonds; multivalent interactions; DNA/RNA system; protein–protein bonds on cell surface; cell adhesion | Ribosomal frameshifting and motion; drug–DNA system; | Protein–aptamer complex |
| Features | Non-invasive | High throughput | Clinical | Integration |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, S.; Sun, M.; Zhan, J.; Xu, M.; Yao, L. Advances in the Biological Application of Force-Induced Remnant Magnetization Spectroscopy. Molecules 2022, 27, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072072
Liao S, Sun M, Zhan J, Xu M, Yao L. Advances in the Biological Application of Force-Induced Remnant Magnetization Spectroscopy. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Shuyu, Mengxue Sun, Jinxiu Zhan, Min Xu, and Li Yao. 2022. "Advances in the Biological Application of Force-Induced Remnant Magnetization Spectroscopy" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072072
APA StyleLiao, S., Sun, M., Zhan, J., Xu, M., & Yao, L. (2022). Advances in the Biological Application of Force-Induced Remnant Magnetization Spectroscopy. Molecules, 27(7), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072072








