Effect of Quinoline on the Phospholipid Profile of Curvularia lunata and Its Microbial Detoxification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
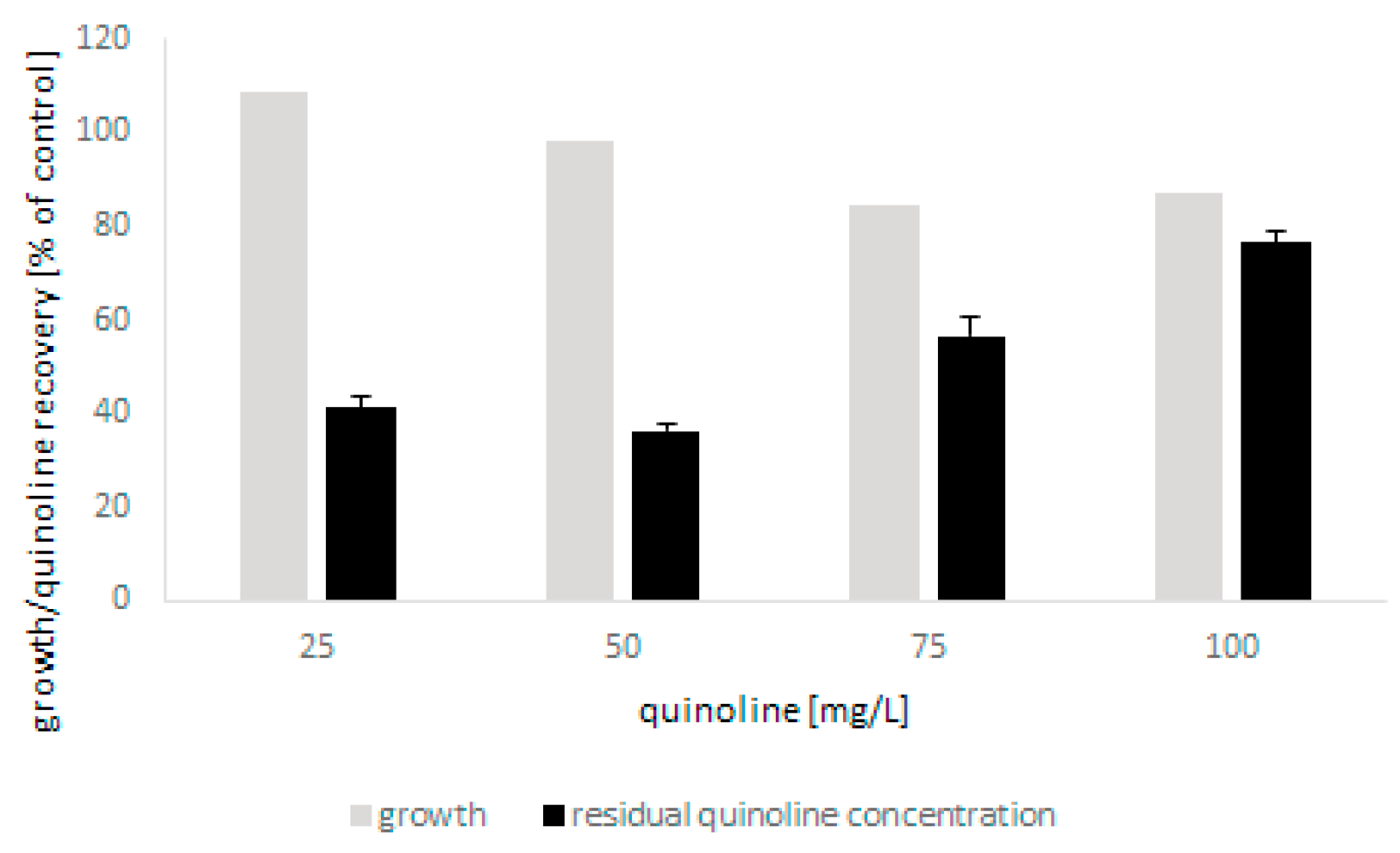
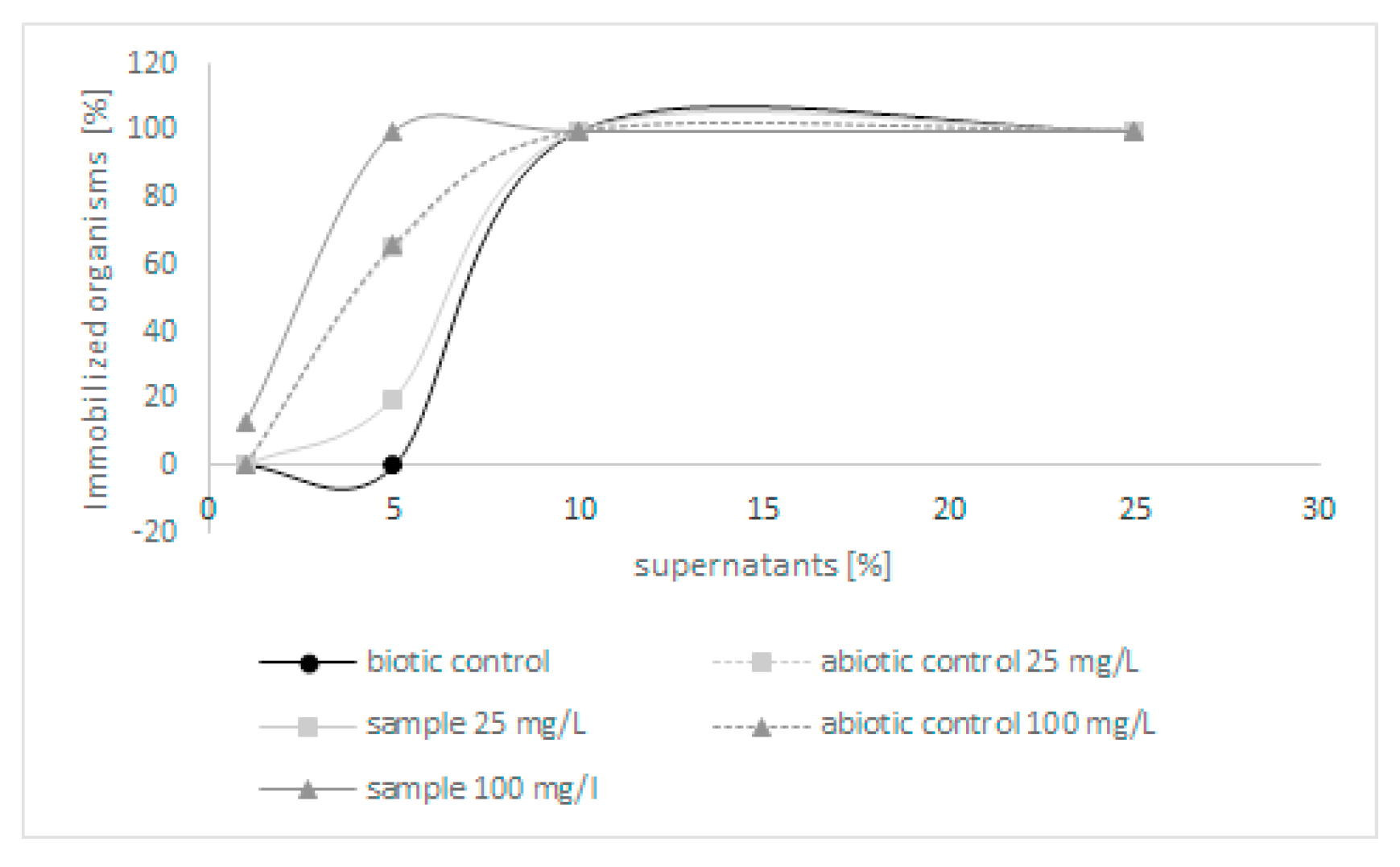
2.1. Biodegradation and Detoxification of Quinoline by C. lunata IM 4417
2.2. Modification of Fatty Acid Profile and Phospholipids of C. lunata IM 4417 during Incubation with Quinoline
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganism
4.2. Preparation of Inoculum
4.3. Dry Weight Assessment
4.4. Lipid Profile Determination
4.5. Elimination of Quinoline
4.6. Quinoline Determination
4.7. Artoxkit M
4.8. Microtox Assay
4.9. Estimation of Fungal Membrane Permeability
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Fetzner, S. Bacterial degradation of pyridine, indole, quinoline, and their derivatives under different redox conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 49, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xu, C.; Han, Y.; Han, H. Enhanced anaerobic biodegradation efficiency and mechanism of quinoline, pyridine, and indole in coal gasification wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. An acid induction strategy to construct an ultralight and durable amino-functionalized graphene oxide aerogel for enhanced quinoline pollutants extraction from coking wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhou, A.; Yue, X.; Luo, Y.; Defemur, Z. Enhanced degradation of quinoline by coupling microbial electrolysis cell with anaerobic digestion simultaneous. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, S.; Zhou, J. Induction conditions and kinetic properties of quinoline biodegradation by a newly isolated bacterial strain. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwoehner, J.; Reineke, A.K.; Hollender, J.; Eisentraeger, A. Ecotoxicity of quinoline and hydroxylated derivatives and their occurrence in groundwater of a tar-contaminated field site. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisentraeger, A.; Brinkmann, C.; Hollert, H.; Sagner, A.; Tiehm, A.; Neuwoehner, J. Heterocyclic compounds: Toxic effects using algae, daphnids, and the Salmonella/microsome test taking methodical quantitative aspects into account. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peddinghaus, S.; Brinkmann, M.; Bluhm, K.; Sagner, A.; Hinger, G.; Braunbeck, T.; Eisenträger, A.; Tiehm, A.; Hollert, H.; Keiter, S.H. Quantitative assessment of the embryotoxic potential of NSO-heterocyclic compounds using zebrafish (Danio rerio). Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraszkiewicz, K.; Długonski, J. Wykorzystanie grzybow mikroskopowych z rodzaju Curvularia w badaniach podstawowych i biotechnologii. Post. Mikrobiol. 2006, 45, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Rossman, A.Y.; Castlebury, L.A.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-appraisal of the genus Curvularia (Pleosporaceae): Human and plant pathogens. Phytotaxa 2015, 212, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kollerov, V.V.; Fokina, V.V.; Sukhodolskaya, G.V.; Shutov, A.A.; Donova, M.V. 11β-Hydroxylation of 6α-fluoro-16α-methyl-deoxycorticosterone 21-acetate by filamentous fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 51, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomcheon, P.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Aree, T.; Sriubolmas, N.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Curvularides A–E: Antifungal hybrid peptide-polyketides from the endophytic fungus Curvularia geniculata. Chemistry 2010, 16, 11178–11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.B.; Lu, Y.H.; Zhang, A.H.; Zhang, G.F.; Mei, Y.N.; Jiang, N.; Lei, X.; Song, Y.C.; Ng, S.W.; Tan, R.X. Curvulamine, a new antibacterial alkaloid incorporating two undescribed units from a Curvularia species. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5366–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, S.; Perumalsamy, M.; Prabhu, H.J.; Thajudin, N. Optimization of process parameters for efficient decolorization of Congo red by novel fungus Curvularia sp. using Box–Behnken design. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Raut, S.; Sharma, M.; Srivastav, C.; Adhikari, B.; Sen, S.K. Enhancing degradation of low density polyethylene films by Curvularia lunata SG1 using particle swarm optimization strategy. Indian J. Microbiol. 2015, 55, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lisowska, K.; Długoński, J. Removal of anthracene and phenanthrene by filamentous fungi capable of cortexolone 11-hydroxylation. J. Basic Microbiol. 1999, 39, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, P.; Szewczyk, R.; Krupiński, M.; Długoński, J. Butyltins degradation by Cunninghamella elegans and Cochliobolus lunatus co-culture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felczak, A.; Bernat, P.; Długoński, J. Biodegradation of octyltin compounds by Cochliobolus lunatus and influence of xenobiotics on fungal fatty acid composition. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianlong, W.; Xiangchun, Q.; Liping, H.; Yi, Q.; Hegemann, W. Microbial degradation of quinoline by immobilized cells of Burkholderia pickettii. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felczak, A.; Zawadzka, K.; Lisowska, K. Efficient biodegradation of quinolone–Factors determining the process. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 96, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Li, B.; Bian, D.; Yang, W.; Huo, H.; Huo, M.; Zhu, S. Enhancing quinolone and phenol removal by adding Comamonas testosteroni bdg06 in treatment of accidental dye wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, Y.K. Quinoline biodegradation characteristics of a new quinoline-degrading strain, Pseudomonas citronellolis PY1. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, K.; Ren, D.; Wang, H. Studies on quinoline biodegradation by a white rot fungus (Pleurotus ostreatus BP) in liquid and solid state substrates. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2007, 16, 632–638. [Google Scholar]
- Felczak, A.; Bernat, P.; Różalska, S.; Lisowska, K. Quinoline biodegradation by filamentous fungus Cunninghamella elegans and adaptive modifications of the fungal membrane composition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8872–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, J.B.; Freeman, J.P.; Williams, A.J.; Cerniglia, C.E. N-oxidation of quinoline and isoquinoline by Cunninghamella elegans. Exp. Mycol. 1994, 18, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Jianlong, W. Biodegradation characteristics of quinoline by Pseudomonas putida. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7683–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, A.S.; Philip, L. Variation in toxicity during the biodegradation of various heterocyclic and homocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in single and multi-substrate systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernat, P.; Gajewska, E.; Szewczyk, R.; Słaba, M.; Długoński, J. Tributyltin (TBT) induces oxidative stress and modifies lipid profile in the filamentous fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4228–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Kaur, A.; Choudhary, R.; Kaushik, R. Phospholipid fatty acid–a bioindicator of environment monitoring and assessment in soil ecosystem. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 1103–1112. Available online: https://www.currentscience.ac.in/Volumes/89/07/1103.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2005).
- Bernat, P.; Długoński, J. Tributyltin chloride interactions with fatty acids composition and degradation ability of the filamentous fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 6, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Mejanelle, L.; Šentjurc, M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitaš, A. Salt-induced changes in lipid composition and membrane fluidity of halophilic yeast-like melanized fungi. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renne, M.F.; de Kroon, A.I. The role of phospholipid molecular species in determining the physical properties of yeast membranes. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1330–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, T.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Y. Phospholipid homeostasis plays an important role in fungal development, fungicide resistance and virulence in Fusarium graminearum. Phytopathol. Res. 2019, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, E.O.; Ribeiro, S.F.F.; Carvalho, A.O.; Santos, I.S.; Da Cunha, M.; Santa-Catarina, C.; Gomes, V.M. Antifungal activity of PvD1 defensin involves plasma membrane permeabilization, inhibition of medium acidification, and induction of ROS in fungi cells. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Jones, A.D.; Lau, M.W.; Yuan, Y.J.; Dale, B.E.; Balan, V. Comparative lipidomic profiling of xylose-metabolizing S. cerevisiae and its parental strain in different media reveals correlations between membrane lipids and fermentation capacity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
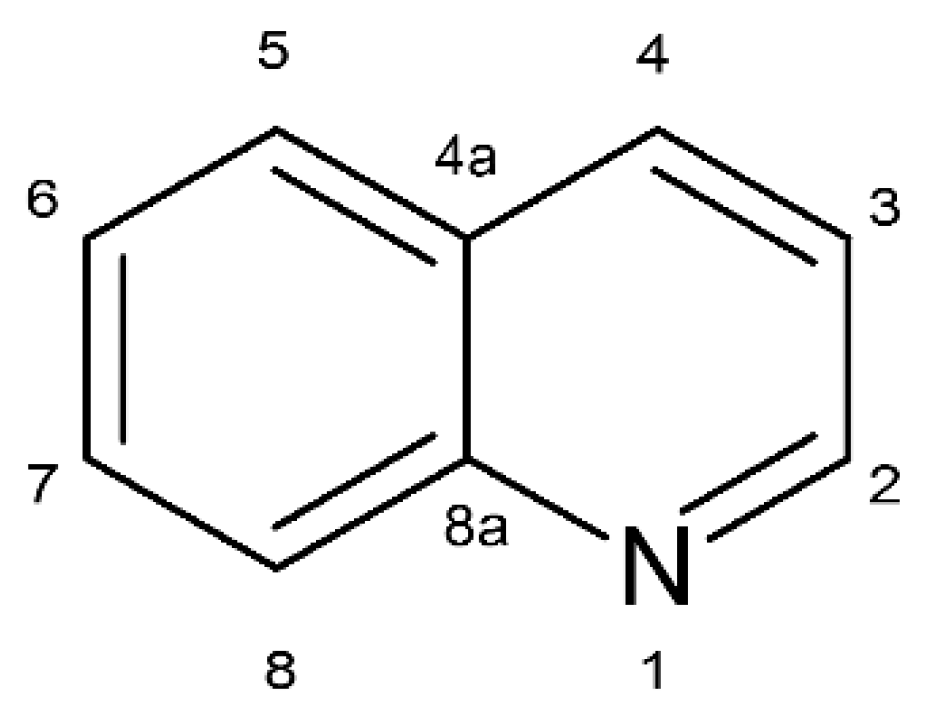



| Compound | Retention Time [min] | Chemical Formula | Metabolite Name | Metabolite Mass (Da) | Mass Spectrum m/z (Relative Intensity of 8 Largest Ions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 4.73 | C15H17NO6 | Glucose-hydroxyquinoline | 307 | 102.96 (28.1), 128.88 (41.7), 130.90 (100), 144.96 (12.5), 172.90 (23.9), 174.84 (63.5), 218.88 (17.7), 306.24 (8.3) |
| M2 | 5.48 | C15H17NO6 | Glucose-hydroxyquinoline | 307 | 102.96 (31.3), 128.91 (31.3), 130.92 (100), 150.96 (18.8), 174.84 (31.3), 174.96 (31.3), 209.16 (25), 306.24 (84.4) |
| M3 | 6.00 | C15H17NO6 | Glucose-hydroxyquinoline | 307 | 102.96 (25), 129.00 (43.8), 129.36 (12.5), 130.92 (100), 147.00 (31.3), 174.96 (100), 218.76 (12.5), 306.24 (43.8) |
| M5 | 6.82 | C15H17NO5 | N-glucose-quinoline | 291 | 128.88 (31.6), 130.92 (100), 174.96 (73.7), 218.90 (36.8), 244.7 (42.1), 245.04 (21), 246.84 (42.1), 290.76 (47.4) |
| Lipid Species | Control | Quinoline Concentration [mg/L] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg/L | 50 mg/L | 75 mg/L | 100 mg/L | ||
| PA | 1.07 ± 0.24 | 0.25 ± 0.05 * | 0.31 ± 0.02 * | 0.34 ± 0.03 * | 0.87 ± 0.17 |
| PC | 27.65 ± 4.48 | 58.32 ± 3.94 * | 64.77 ± 4.22 * | 72.21 ± 2.81 * | 66.21 ± 5.45 * |
| PE | 52.45 ± 9.93 | 38.57 ± 2.77 * | 31.90 ± 4.51 | 23.58 ±1.62 * | 26.65 ± 5.98 * |
| PI | 16.40 ± 4.59 | 2.47 ± 0.81 | 2.55 ± 0.35 | 3.54 ± 1.03 | 5.56 ± 0.38 |
| PS | 2.43 ± 0.62 | 0.39 ± 0.31 * | 0.47 ± 0.07 * | 0.33 ± 0.06 * | 0.72 ± 0.03 |
| PC/PE | 0.53 ± 0.09 | 1.51 ± 0.21 * | 2.03 ± 4.42 * | 3.06 ± 0.34 * | 2.48 ± 0.59 |
| The Gradient of Eluents | The MicroESI Ion Source Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time [min] | Eluent A [%] | Eluent B [%] | ||
| 0.0 | 98 | 2 | Parameter | Value |
| 0.2 | 98 | 2 | Curtain gas | 25 psi |
| 7.0 | 2 | 98 | Ion spray voltage | −4500 V |
| 8.0 | 2 | 98 | Temperature | 400 °C |
| 8.2 | 98 | 2 | Gas 1 | 20 psi |
| 8.6 | 98 | 2 | Gas 2 | 30 psi |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felczak, A.; Zawadzka, K.; Bernat, P.; Nowak-Lange, M.; Lisowska, K. Effect of Quinoline on the Phospholipid Profile of Curvularia lunata and Its Microbial Detoxification. Molecules 2022, 27, 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072081
Felczak A, Zawadzka K, Bernat P, Nowak-Lange M, Lisowska K. Effect of Quinoline on the Phospholipid Profile of Curvularia lunata and Its Microbial Detoxification. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072081
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelczak, Aleksandra, Katarzyna Zawadzka, Przemysław Bernat, Marta Nowak-Lange, and Katarzyna Lisowska. 2022. "Effect of Quinoline on the Phospholipid Profile of Curvularia lunata and Its Microbial Detoxification" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072081
APA StyleFelczak, A., Zawadzka, K., Bernat, P., Nowak-Lange, M., & Lisowska, K. (2022). Effect of Quinoline on the Phospholipid Profile of Curvularia lunata and Its Microbial Detoxification. Molecules, 27(7), 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072081







