Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the CK2 Inhibitor Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in Human Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
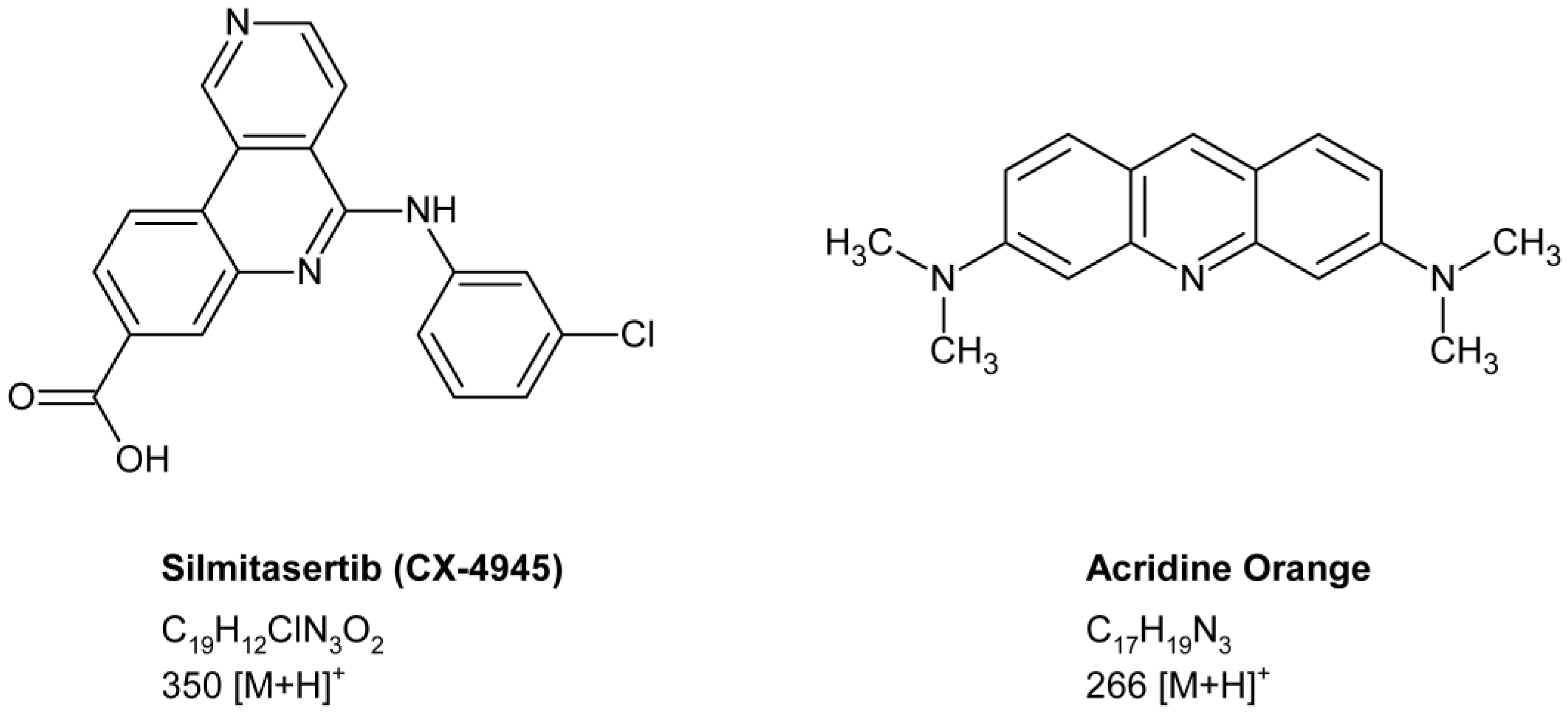
2.1. Method Development
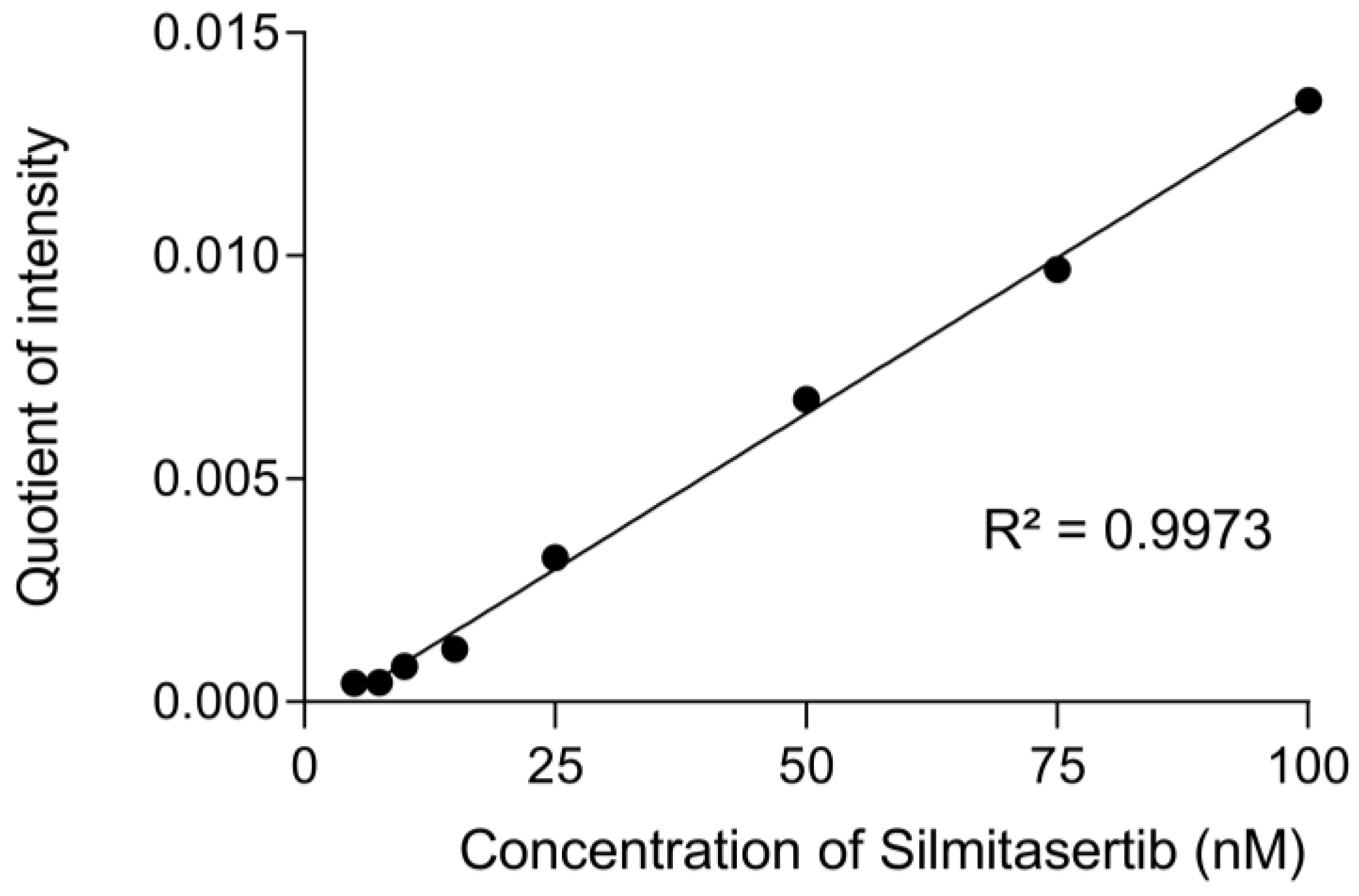
2.2. Calibration Curve
2.3. Selectivity and Carryover
2.4. Sensitivity, Accuracy, and Precision
2.5. Matrix Effect and Recovery
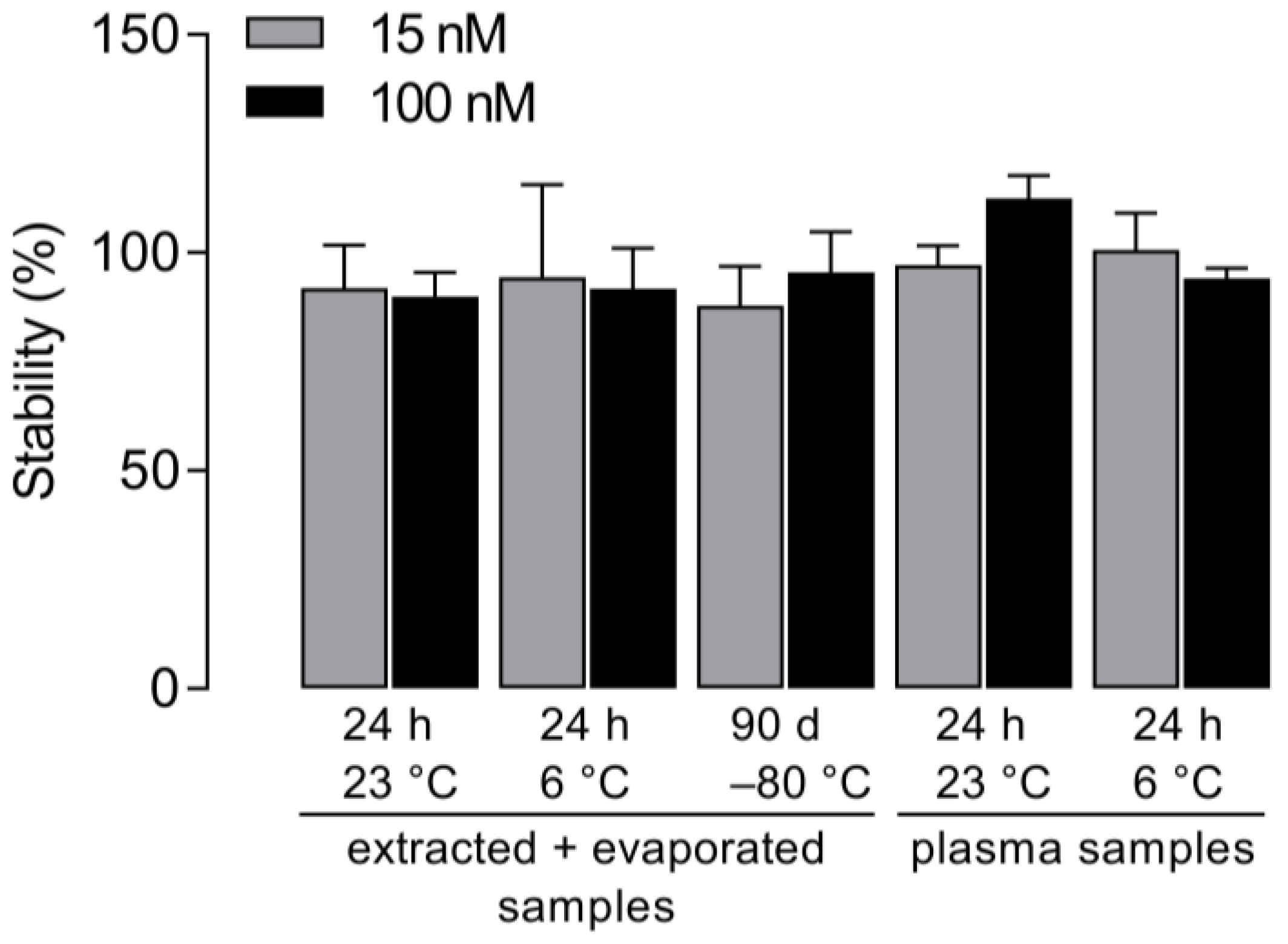
2.6. Stability
2.7. Quantification of Silmitasertib in Artificial Mouse Plasma
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents
3.2. Standard Preparation
3.3. LC–MS/MS Analysis
3.4. Validation
3.5. Preparation of Artificial Mouse Plasma
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.L.; Gray, N.S. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Cross, D.; Jänne, P.A. Kinase drug discovery 20 years after imatinib: Progress and future directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Wang, G.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Ahmed, K. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: CK2: A key player in cancer biology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duncan, J.S.; Litchfield, D.W. Too much of a good thing: The role of protein kinase CK2 in tumorigenesis and prospects for therapeutic inhibition of CK2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purzner, T.; Purzner, J.; Buckstaff, T.; Cozza, G.; Gholamin, S.; Rusert, J.M.; Hartl, T.A.; Sanders, J.; Conley, N.; Ge, X.; et al. Developmental phosphoproteomics identifies the kinase CK2 as a driver of Hedgehog signaling and a therapeutic target in medulloblastoma. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaau5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Tai, C.; Hsu, J.-C.; Li, C.-F.; Fang, C.-L.; Lai, H.-C.; Hseu, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-F.; Uen, Y.-H. Overexpression of nuclear protein kinase CK2 α catalytic subunit (CK2α) as a poor prognosticator in human colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Jiang, S.-S.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Pan, Q.-Z.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhao, J.-J.; Tang, Y.; Xia, J.-C.; Weng, D.-S. Protein kinase CK2α catalytic subunit is overexpressed and serves as an unfavorable prognostic marker in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34800–34817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierre, F.; Chua, P.C.; O’Brien, S.E.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bourbon, P.; Haddach, M.; Michaux, J.; Nagasawa, J.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Stefan, E.; et al. Discovery and SAR of 5-(3-chlorophenylamino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Li, P.; Yuan, W.; Deng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Tao, J.; et al. Targeting protein kinase CK2 suppresses bladder cancer cell survival via the glucose metabolic pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 87361–87372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, G.K.; McFarland, B.C.; Rowse, A.L.; Gibson, S.A.; Benveniste, E.N. Therapeutic CK2 inhibition attenuates diverse prosurvival signaling cascades and decreases cell viability in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6484–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.M.; Jeong, I.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.K.; Kwon, W.S.; Kim, T.S.; Park, K.H.; Jung, M.; Soong, J.; Lin, S.-C.; et al. Casein Kinase 2 Inhibitor, CX-4945, as a Potential Targeted Anticancer Agent in Gastric Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, K.S.; Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, C.M.; Chun, Y.J.; Lee, J.C. AKT/mTOR down-regulation by CX-4945, a CK2 inhibitor, promotes apoptosis in chemorefractory non-small cell lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.W.; So, K.S.; Kim, S.C.; Park, K.-M.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Choi, C.-M.; Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.C. Autophagy Induced by CX-4945, a Casein Kinase 2 Inhibitor, Enhances Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Pancreas 2017, 46, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, F.; Chua, P.C.; O’Brien, S.E.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bourbon, P.; Haddach, M.; Michaux, J.; Nagasawa, J.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Stefan, E.; et al. Pre-clinical characterization of CX-4945, a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of CK2 for the treatment of cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 356, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharia, K.; Miyabe, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Moser, C.D.; Borad, M.J.; Roberts, L.R. Preclinical In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence of an Antitumor Effect of CX-4945, a Casein Kinase II Inhibitor, in Cholangiocarcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Font, L.; Villamañan, L.; Arias-Ramos, N.; Vilardell, J.; Plana, M.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A.; Itarte, E.; Arús, C.; Candiota, A.P. Targeting Protein Kinase CK2: Evaluating CX-4945 Potential for GL261 Glioblastoma Therapy in Immunocompetent Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villamañan, L.; Martínez-Escardó, L.; Arús, C.; Yuste, V.J.; Candiota, A.P. Successful Partnerships: Exploring the Potential of Immunogenic Signals Triggered by TMZ, CX-4945, and Combined Treatment in GL261 Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Song, C.; Dhanyamraju, P.K.; Ehudin, M.; Ding, Y.; Steffens, S.; Bhadauria, P.; Iyer, S.; Aliaga, C.; et al. Mechanistic Basis for In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy of CK2 Inhibitor CX-4945 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Roolf, C.; Hamed, M.; Gladbach, Y.S.; Sender, S.; Konkolefski, C.; Knübel, G.; Sekora, A.; Fuellen, G.; Vollmar, B.; et al. Combined Casein Kinase II inhibition and epigenetic modulation in acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowda, C.; Sachdev, M.; Muthusami, S.; Kapadia, M.; Petrovic-Dovat, L.; Hartman, M.; Ding, Y.; Song, C.; Payne, J.L.; Tan, B.-H.; et al. Casein Kinase II (CK2) as a Therapeutic Target for Hematological Malignancies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amore, C.; Borgo, C.; Sarno, S.; Salvi, M. Role of CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 in anti-cancer combination therapy-potential clinical relevance. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=548516 (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=851021 (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=856821 (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine, clinicaltrials.gov: Bethesda, MD, USA. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?recrs=&cond=&term=CX-4945&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Zhong, B.; Campagne, O.; Salloum, R.; Purzner, T.; Stewart, C.F. LC-MS/MS method for quantitation of the CK2 inhibitor silmitasertib (CX-4945) in human plasma, CSF, and brain tissue, and application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study in children with brain tumors. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1152, 122254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.H.; Song, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J. Pharmacokinetic characterization of CK2 inhibitor CX-4945. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioanalytical Method Validation—Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Silver Spring, MD, USA; Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/ucm070107.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Richter, A.; Sender, S.; Lenz, A.; Schwarz, R.; Hinz, B.; Knuebel, G.; Sekora, A.; Murua Escobar, H.; Junghanss, C.; Roolf, C. Influence of Casein kinase II inhibitor CX-4945 on BCL6-mediated apoptotic signaling in B-ALL in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testing the Safety and Tolerability of CX-4945 in Patients with Recurrent Medulloblastoma Who May or May Not Have Surgery; U.S. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019; Identifier: NCT03904862. 2019. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03904862 (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Annesley, T.M. Ion suppression in mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Used Concentration (nM) | Intra-Day (Day 1) | Intra-Day (Day 2) | Intra-Day (Day 3) | Inter-Day | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (nM) | RE (%) | CV (%) | Measured Concentration (nM) | RE (%) | CV (%) | Measured Concentration (nM) | RE (%) | CV (%) | RE (%) | CV (%) | |
| 5 | 5.20 ± 0.34 | 4.03 ± 6.77 | 6.51 | 5.16 ± 0.42 | 3.28 ± 8.44 | 8.17 | 5.16 ± 0.59 | 3.27 ± 11.82 | 11.45 | 3.53 ± 8.57 | 8.28 |
| 15 | 15.84 ± 0.96 | 5.60 ± 6.37 | 6.03 | 15.46 ± 1.18 | 3.07 ± 7.88 | 7.64 | 15.38 ± 1.37 | 2.54 ± 9.12 | 8.90 | 3.74 ± 7.42 | 7.15 |
| 50 | 51.50 ± 5.39 | 3.01 ± 10.78 | 10.47 | 53.18 ± 3.01 | 6.36 ± 6.01 | 5.65 | 46.31 ± 1.71 | −7.37 ± 3.42 | 3.69 | 0.67 ± 9.14 | 9.08 |
| 100 | 106.47 ± 3.24 | 6.47 ± 3.24 | 3.04 | 101.00 ± 8.22 | 1.00 ± 8.22 | 8.24 | 97.97 ± 7.98 | −2.03 ± 7.98 | 8.14 | 1.81 ± 7.37 | 7.23 |
| Silmitasertib | Acridine Orange | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (nM) | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect (%) | Concentration (nM) | Recovery (%) |
| 15 | 56.89 ± 8.44 | 33.95 ± 7.49 | 50 | 59.02 ± 3.28 |
| 50 | 47.79 ± 7.39 | 26.57 ± 12.44 | ||
| 100 | 57.24 ± 10.24 | 18.36 ± 10.09 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, R.; Richter, A.; Ito, E.R.D.; Murua Escobar, H.; Junghanß, C.; Hinz, B. Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the CK2 Inhibitor Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in Human Plasma. Molecules 2022, 27, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082394
Schwarz R, Richter A, Ito ERD, Murua Escobar H, Junghanß C, Hinz B. Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the CK2 Inhibitor Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in Human Plasma. Molecules. 2022; 27(8):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082394
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Rico, Anna Richter, Elisabeth R. D. Ito, Hugo Murua Escobar, Christian Junghanß, and Burkhard Hinz. 2022. "Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the CK2 Inhibitor Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in Human Plasma" Molecules 27, no. 8: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082394
APA StyleSchwarz, R., Richter, A., Ito, E. R. D., Murua Escobar, H., Junghanß, C., & Hinz, B. (2022). Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the CK2 Inhibitor Silmitasertib (CX-4945) in Human Plasma. Molecules, 27(8), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082394






