Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inhibitors of Microbial Origin
2.1. Peptide Aldehydes
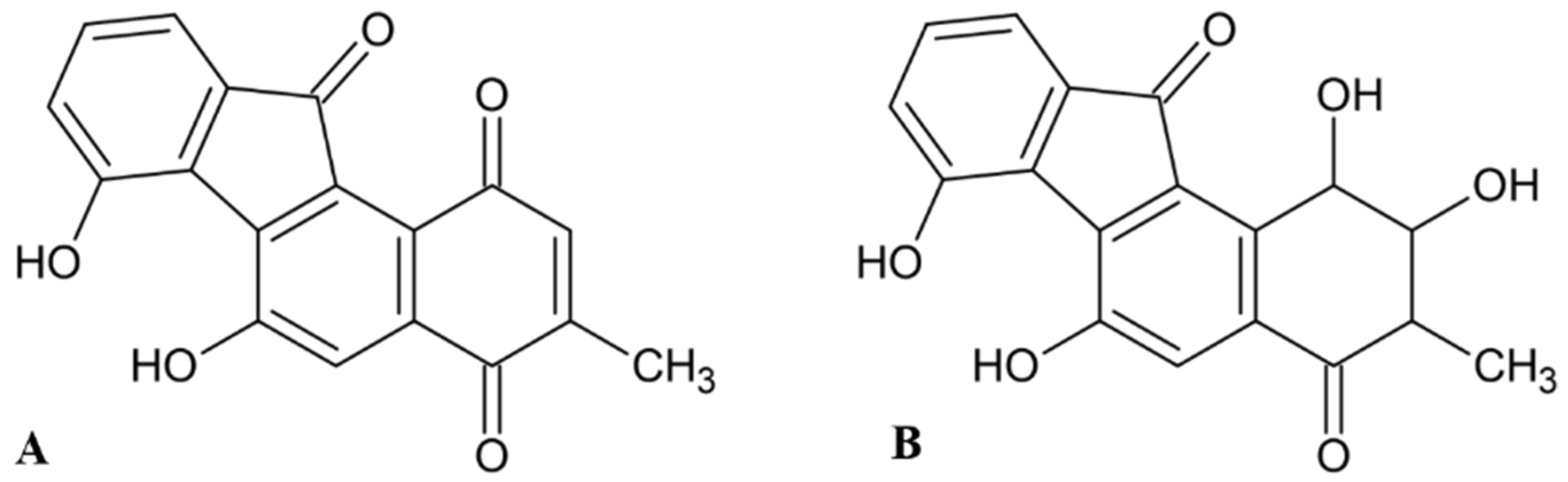
2.2. Fluostatins
2.3. Propioxatins
2.4. Other Protease Inhibitors of Microbial Origin
3. Inhibitors of Plant Origin
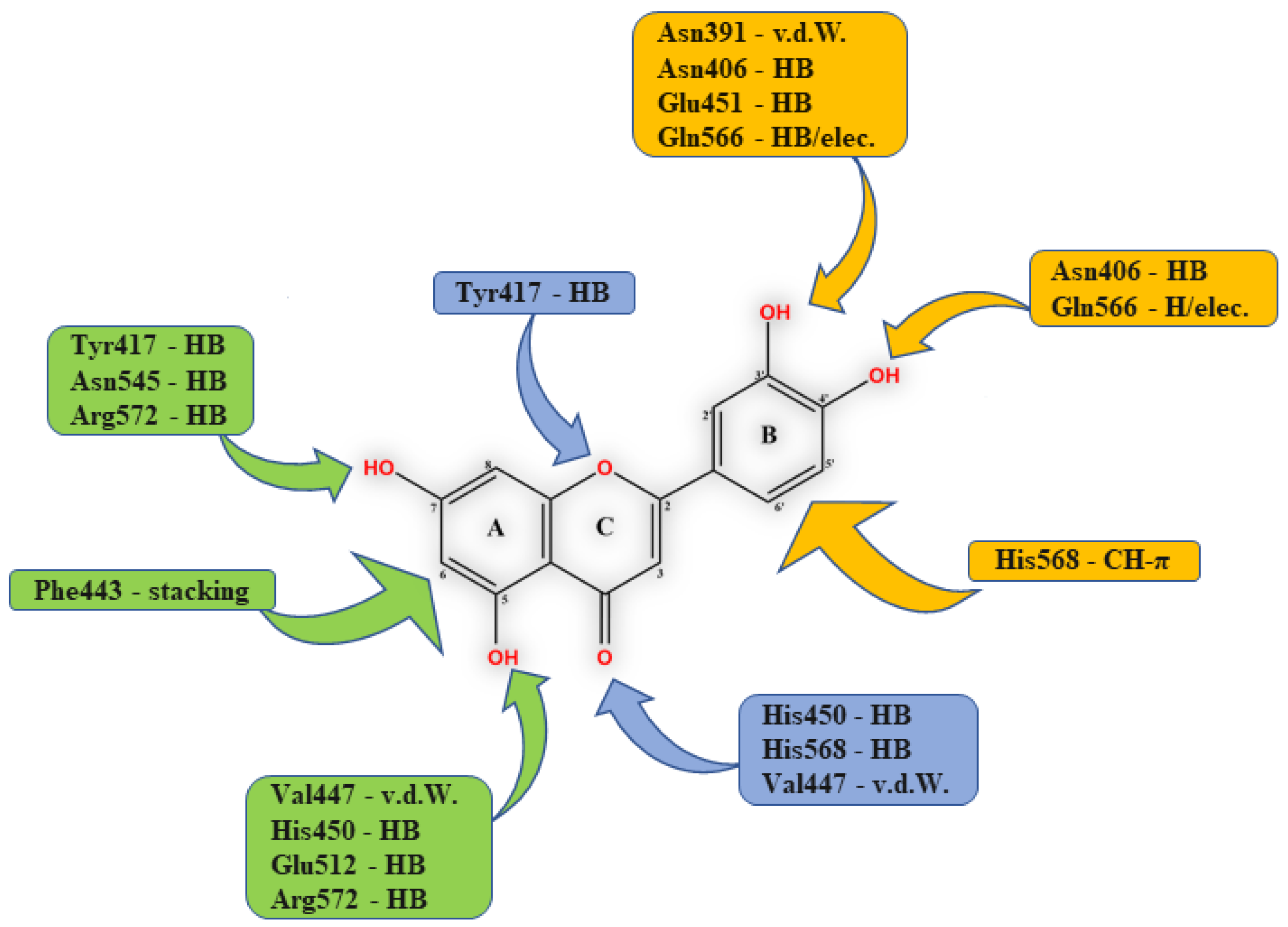
3.1. Flavonoids
3.2. Polyphenolic Compounds in Plant Extracts
4. (Poly)Peptide Inhibitors
4.1. Dipeptides
4.2. Oligopeptides
4.3. Peptidomimetic Inhibitors
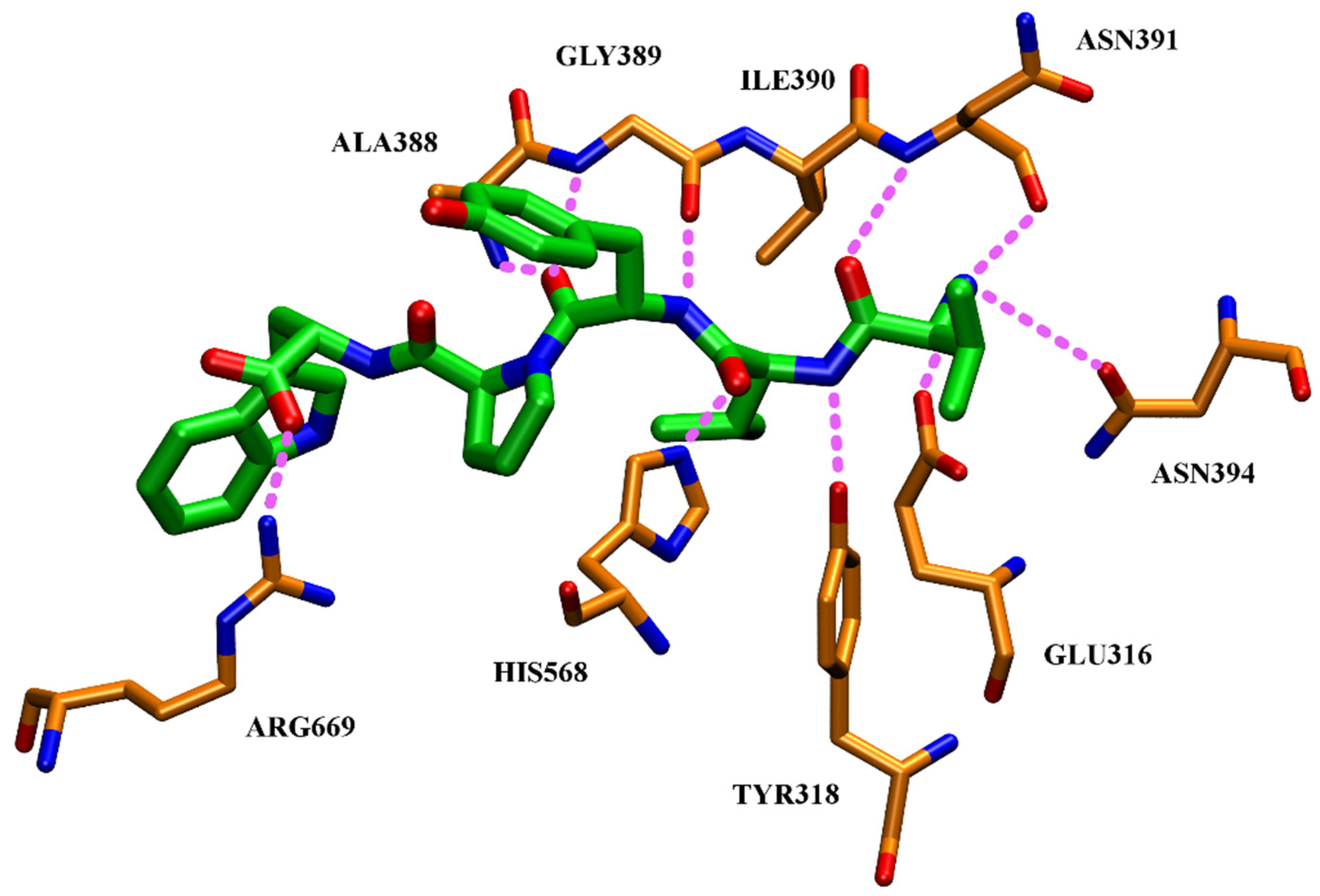
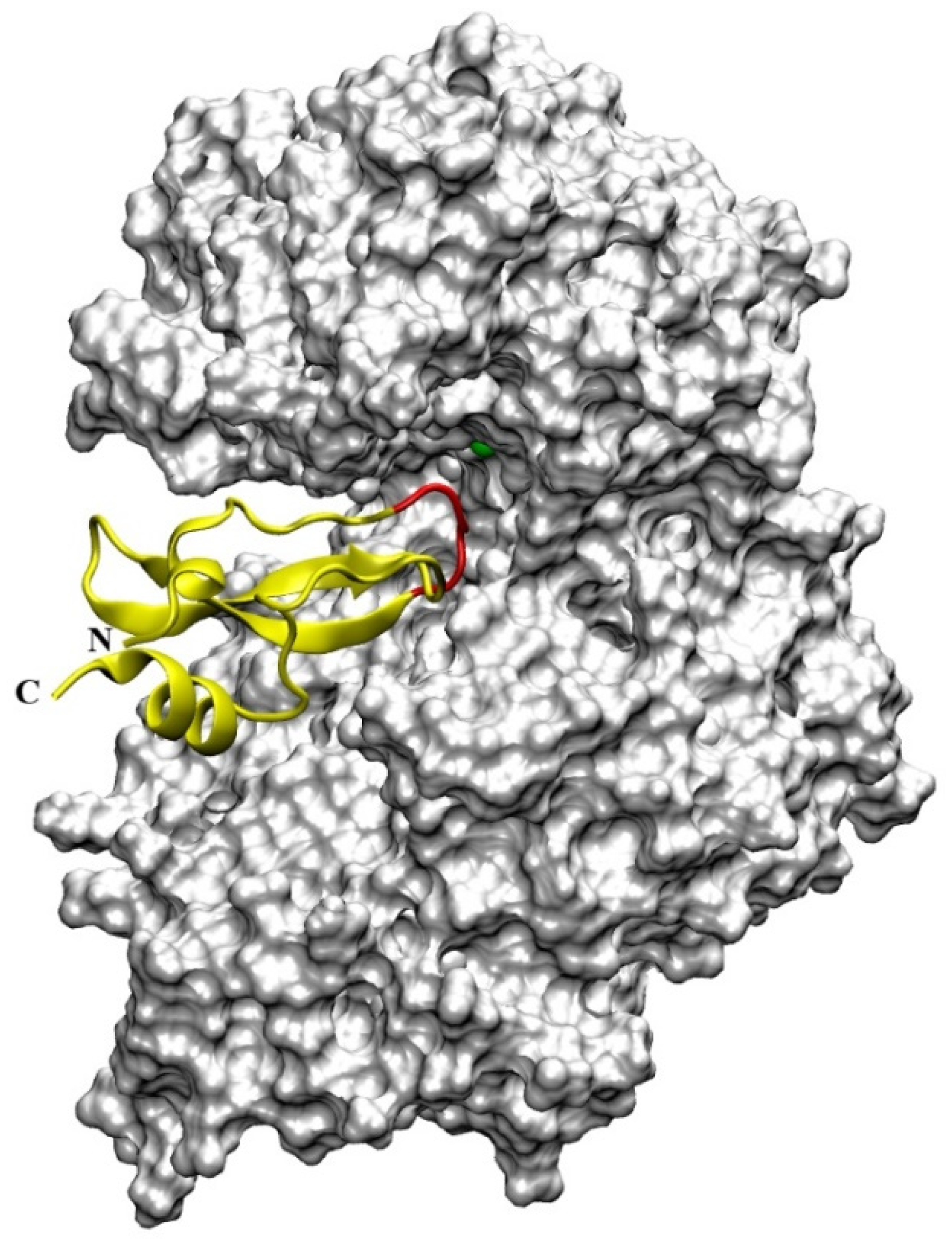
4.4. Aprotinin
5. Synthetic Inhibitors
5.1. Benzimidazole Derivatives
5.2. Analgesic and Antihypertensive Drugs
5.3. Coumarin Derivatives
5.4. Guanidiniocarbonyl-Pyrrole-Aryl Conjugates
5.5. Dipeptidyl Hydroxamic Acids
5.6. Hydroxamate Inhibitor JMV-390
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPTI | bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor |
| CDK1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
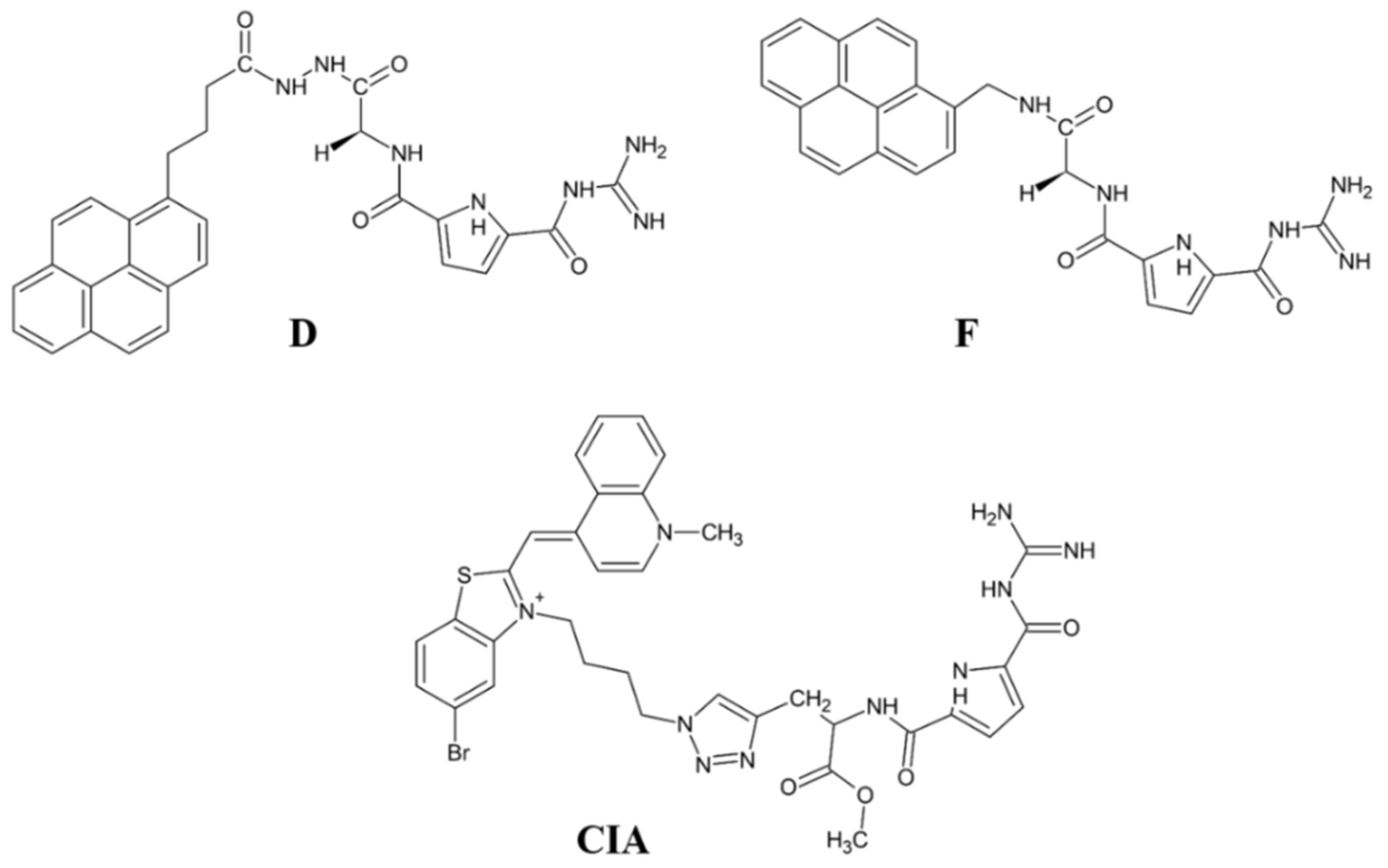
| CIA | cyanine-GCP conjugate |
| DPP I | dipeptidyl peptidase I |
| DPP II | dipeptidyl peptidase II |
| DPP III | dipeptidyl peptidase III |
| DPP IV | dipeptidyl peptidase IV |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| GCP | guanidiniocarbonyl-pyrrole |
| HER | (R)-hydroxyethylene transition state mimetic of tynorphin |
| HB | hydrogen bond |
| HI | hydrophobic interaction |
| JMV-390 | N-[3-[(hydroxyamino) carbonyl]-1-oxo-2(R)-benzylpropyl]-L-leucine |
| MALDI | matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization |
| MD | molecular dynamics |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PCMS | p-chloromercuriphenylsulfonate |
| PCMB | p-chloromercuribenzoic acid |
| pHMB | p-hydroxy-mercuribenzoate |
| QSAR | quantitative structure-activity relationship |
| SHE | (S)-hydroxyethylene transition state mimetic of tynorphin |
| TOF MS | time of flight mass spectrometry |
References
- Ellis, S.; Nuenke, J.M. Dipeptidyl arylamidase III of the pituitary. Purification and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 4623–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.J.; Chen, J.-M. Dipeptidyl-Peptidase III. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Rawlings, N.D., Salvesen, G.S., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; Volumes 1, pp. 1285–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Abramić, M.; Zubanović, M.; Vitale, L. Dipeptidyl peptidase III from human erythrocytes. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1988, 369, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Snyder, S.H. Dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase III of rat brain. Selective affinity for enkephalin and angiotensin. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 12043–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baršun, M.; Jajčanin, N.; Vukelić, B.; Špoljarić, J.; Abramić, M. Human dipeptidyl peptidase III acts as a post-proline-cleaving enzyme on endomorphins. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, I.; Li, Y.H.; Maeda, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamane, T.; Du, P.G.; Nishi, K. Dipeptidyl peptidase III from rat liver cytosol: Purification, molecular cloning and immunohistochemical localization. Biol. Chem. 1999, 380, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimaga, Š.; Babić, D.; Osmak, M.; Ilić-Forko, J.; Vitale, L.J.; Miličić, D.; Abramić, M. Dipeptidyl Peptidase III in Malignant and Non-malignant Gynaecological Tissue. Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, K.; Fukasawa, K.M.; Kanai, M.; Fujii, S.; Hirose, J.; Harada, M. Dipeptidyl peptidase III is a zinc metalloexopeptidase. Molecular cloning and expression. Biochem. J. 1998, 329, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramić, M.; Špoljarić, J.; Šimaga, Š. Prokaryotic homologs help to define consensus sequences in peptidase family M49. Period. biol. 2004, 106, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa, K.; Fukasawa, K.M.; Iwamoto, H.; Hirose, J.; Harada, M. The HELLGH motif of rat liver dipeptidyl peptidase III is involved in zinc coordination and the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 8299–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, P.K.; Jajčanin-Jozić, N.; Deller, S.; Macheroux, P.; Abramić, M.; Gruber, K. The first structure of dipeptidyl-peptidase III provides insight into the catalytic mechanism and mode of substrate binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22316–22324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezerra, G.A.; Dobrovetsky, E.; Viertlmayr, R.; Dong, A.; Binter, A.; Abramić, M.; Macheroux, P.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Gruber, K. Entropy-driven binding of opioid peptides induces a large domain motion in human dipeptidyl peptidase III. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6525–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomić, A.; Abramić, M.; Špoljarić, J.; Agić, D.; Smith, D.M.; Tomić, S. Human dipeptidyl peptidase III: Insights into ligand binding from a combined experimental and computational approach. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomić, A.; González, M.; Tomić, S. The large scale conformational change of the human DPP III-substrate prefers the ‘‘closed’’ form. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomić, A.; Kovačević, B.; Tomić, S. Concerted nitrogen inversion and hydrogen bonding to Glu451 are responsible for protein-controlled suppression of the reverse reaction in human DPP III. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 27245–27256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.H.; Maeda, T.; Yamane, T.; Ohkubo, I. Alteration of rat dipeptidyl peptidase III by site-directed mutagenesis: Cysteine 176 is a regulatory residue for the enzyme activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramić, M.; Šimaga, Š.; Osmak, M.; Čičin-Šain, L.; Vukelić, B.; Vlahoviček, K.; Dolovčak, L. Highly reactive cysteine residues are part of the substrate binding site of mammalian dipeptidyl peptidases III. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramić, M.; Schleuder, D.; Dolovčak, L.J.; Schröder, W.; Strupat, K.; Šagi, D.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Vitale, L.J. Human and rat dipeptidyl peptidase III: Biochemical and mass spectrometric arguments for similarities and differences. Biol. Chem. 2000, 381, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajčanin-Jozić, N.; Deller, S.; Pavkov, T.; Macheroux, P.; Abramić, M. Identification of the reactive cysteine residues in yeast dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biochimie 2010, 92, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, Z.; Špoljarić, J.; Rožman, M.; Abramić, M. Molecular determinants of human dipeptidyl peptidase sensitivity to thiol modifying reagents. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukelić, B.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Špoljarić, J.; Sabljić, I.; Meštrović, N.; Agić, D.; Abramić, M. Reactive cysteine in the active site motif of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron dipeptidyl peptidase III is a regulatory residue for enzyme activity. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamrekelashvili, J.; Kapanadze, T.; Han, M.; Wissing, J.; Ma, C.; Jaensch, L.; Manns, M.P.; Armstrong, T.; Jaffee, E.; White, A.O.; et al. Peptidases released by necrotic cells control CD8(+) T cell cross-priming. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4755–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jha, S.; Taschler, U.; Domenig, O.; Poglitsch, M.; Bourgeois, B.; Pollheimer, M.; Pusch, L.M.; Malovan, G.; Frank, S.; Madl, T.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 modulates the renin-angiotensin system in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13711–13723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Diaz, N.; Wilson, B.A.; Pirro, N.T.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Marshall, A.C.; Chappell, M.C. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase 3 as the Angiotensin-(1-7) degrading peptidase in human HK-2 renal epithelial cells. Peptides 2016, 83, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hast, B.E.; Goldfarb, D.; Mulvaney, K.M.; Hast, M.A.; Siesser, P.F.; Yan, F.; Hayes, D.N.; Major, M.B. Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin ligase KEAP1 reveals associated proteins that inhibit NRF2 ubiquitination. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matić, S.; Kekez, I.; Tomin, M.; Bogar, F.; Šupljika, F.; Kazazić, S.; Hanić, M.; Jha, S.; Brkić, H.; Bourgeois, B.; et al. Binding of dipeptidyl peptidase III to the oxidative stress cell sensor Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 is a two-step process. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 6870–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yan, M.; Xia, Z.; Lai, D. DPP3/CDK1 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer through regulating cell proliferation, cell apoptosis, and cell migration. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimaga, Š.; Babić, D.; Osmak, M.; Šprem, M.; Abramić, M. Tumor cytosol dipeptidyl peptidase III activity is increased with histological aggressiveness of ovarian primary carcinomas. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 91, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Alcivar, A.L.; Ma, J.; Foo, T.K.; Zywea, S.; Mahdi, A.; Huo, Y.; Kensler, T.W.; Gatza, M.L.; Xia, B. NRF2 induction supporting breast cancer cell survival is enabled by oxidative stress-induced DPP3-KEAP1 interaction. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matić, S.; Tomašić Paić, A.; Sobočanec, S.; Pinterić, M.; Pipalović, G.; Martinčić, M.; Matovina, M.; Tomić, S. Interdisciplinary Study of the Effects of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase III Cancer Mutations on the KEAP1-NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniau, B.; Blet, A.; Santos, K.; Ayar, P.V.; Genest, M.; Kästorf, M.; Sadoune, M.; de Sousa Jorge, A.; Samuel, J.L.; Vodovar, N.; et al. Inhibition of circulating dipeptidyl-peptidase 3 restores cardiac function in a sepsis-induced model in rats: A proof of concept study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, D.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Promotion of vascular integrity in sepsis through modulation of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorenstein, C.; Snyder, S.H. Enkephalinases. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 210, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, T.; Li, Y.H.; Yamane, T.; Ogikubo, O.; Fukuoka, M.; Arai, R.; Takahashi, S.; Ohtsuka, T.; Ohkubo, I.; Matsui, N. Inhibition of recombinant dipeptidyl peptidase III by synthetic hemorphin-like peptides. Peptides 2003, 24, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shumiya, S.; Kunimatsu, M.; Nishi, K.; Ohkubo, I.; Kani, K. Peptidases play an important role in cataractogenesis: An immunohistochemical study on lenses derived from Shumiya cataract rats. Histochem. J. 2001, 33, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meliopoulos, V.A.; Andersen, L.E.; Brooks, P.; Yan, X.Z.; Bakre, A.; Coleman, J.K.; Tompkins, S.M.; Tripp, R.A. MicroRNA regulation of human protease genes essential for influenza virus replication. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikiori, T.; Kawahara, F.; Naganawa, H.; Muraoka, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Umezawa, H. Production of acetyl-L-leucyl-L-argininal, inhibitor of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase III by bacteria. J. Antibiot. 1984, 37, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
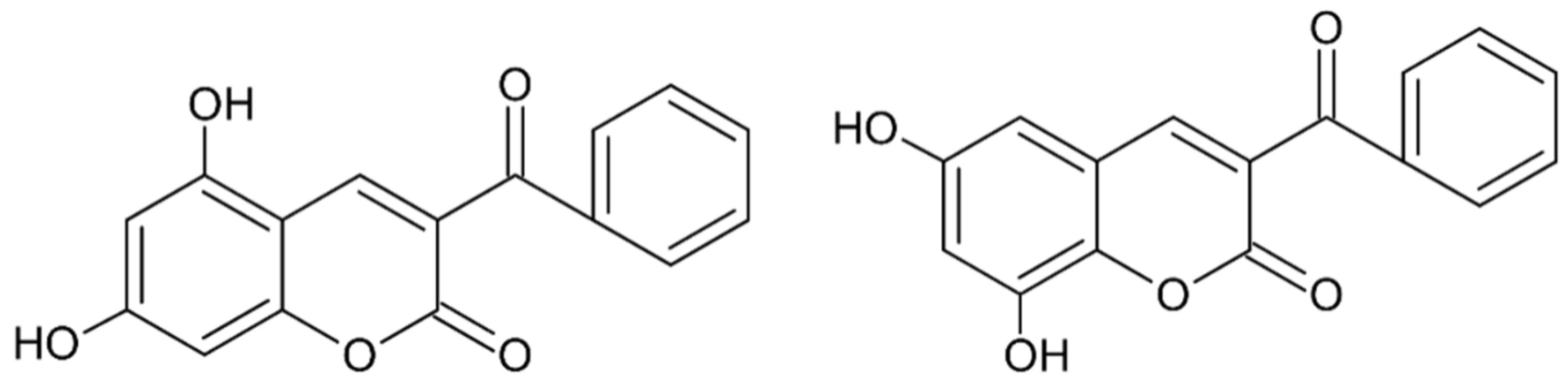
- Akiyama, T.; Harada, S.; Kojima, F.; Takahashi, Y.; Imada, C.; Okami, Y.; Muraoka, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluostatins A and B, new inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase III, produced by Streptomyces sp. TA-3391-I. Taxonomy of producing strain, production, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, T.; Nakamura, K.T.; Takahashi, Y.; Naganawa, H.; Muraoka, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluostatins A and B, new inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase III, produced by Streptomyces sp. TA-3391-II. Structure determination. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaoka, Y.; Tamaoki, H. Purification and characterization of enkephalinase B from rat brain membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 925, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaoka, Y.; Tamaoki, H.; Takahashi, S.; Enokita, R.; Okazaki, T. Propioxatins A and B, new enkephalinase B inhibitors. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inaoka, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Kinoshita, T. Propioxatins A and B, new enkephalinase B inhibitors. II. Structural elucidation. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Carlo, G.; Mascolo, N.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, F. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agić, D.; Brkić, H.; Tomić, S.; Karačić, Z.; Špoljarević, M.; Lisjak, M.; Bešlo, D.; Abramić, M. Validation of flavonoids as potential dipeptidyl peptidase III inhibitors: Experimental and computational approach. Chem. Biol. Drag Des. 2017, 89, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popović, B.M.; Blagojević, B.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Agić, D.; Magazin, N.; Milović, M.; Serra, A.T. Exploring fruits from genus Prunus as a source of potential pharmaceutical agents—In vitro and in silico study. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagojević, B.; Agić, D.; Serra, A.T.; Matić, S.; Matovina, M.; Bijelić, S.; Popović, B.M. An in vitro and in silico evaluation of bioactive potential of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) extracts rich in polyphenols and iridoids. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.; Singh, H.; Singh, J.; Singh, T.P. Functional characterization and specific effects of various peptides on enzymatic activity of a DPP-III homologue from goat brain. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2008, 23, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hashimoto, J.; Shimamura, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hazato, T. Characterization of tynorphin, a potent endogenous inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase III. Peptides 2000, 21, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Shimamura, M.; Ueki, M.; Hazato, T. Inhibitory action of spinorphin, an endogenous regulator of enkephalin-degrading enzymes, on carrageenan-induced polymorphonuclear neutrophil accumulation in mouse air-pouches. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramić, M.; Karačić, Z.; Šemanjski, M.; Vukelić, B.; Jajčanin-Jozić, N. Aspartate 496 from the subsite S2 drives specificity of human dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Reithofer, V.; Reisinger, M.; Wallner, S.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Macheroux, P.; Gruber, K. Substrate complexes of human dipeptidyl peptidase III reveal the mechanism of enzyme inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomić, A.; Tomić, S. Demystifying DPP III Catalyzed Peptide Hydrolysis-Computational Study of the Complete Catalytic Cycle of Human DPP III Catalyzed Tynorphin Hydrolysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivkovic, J.; Jha, S.; Lembacher-Fadum, C.; Puschnig, J.; Kumar, P.; Reithofer, V.; Gruber, K.; Peter Macheroux, P.; Breinbauer, R. Efficient Entropy-Driven Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III by Hydroxyethylene Transition-State Peptidomimetics. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 14108–14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
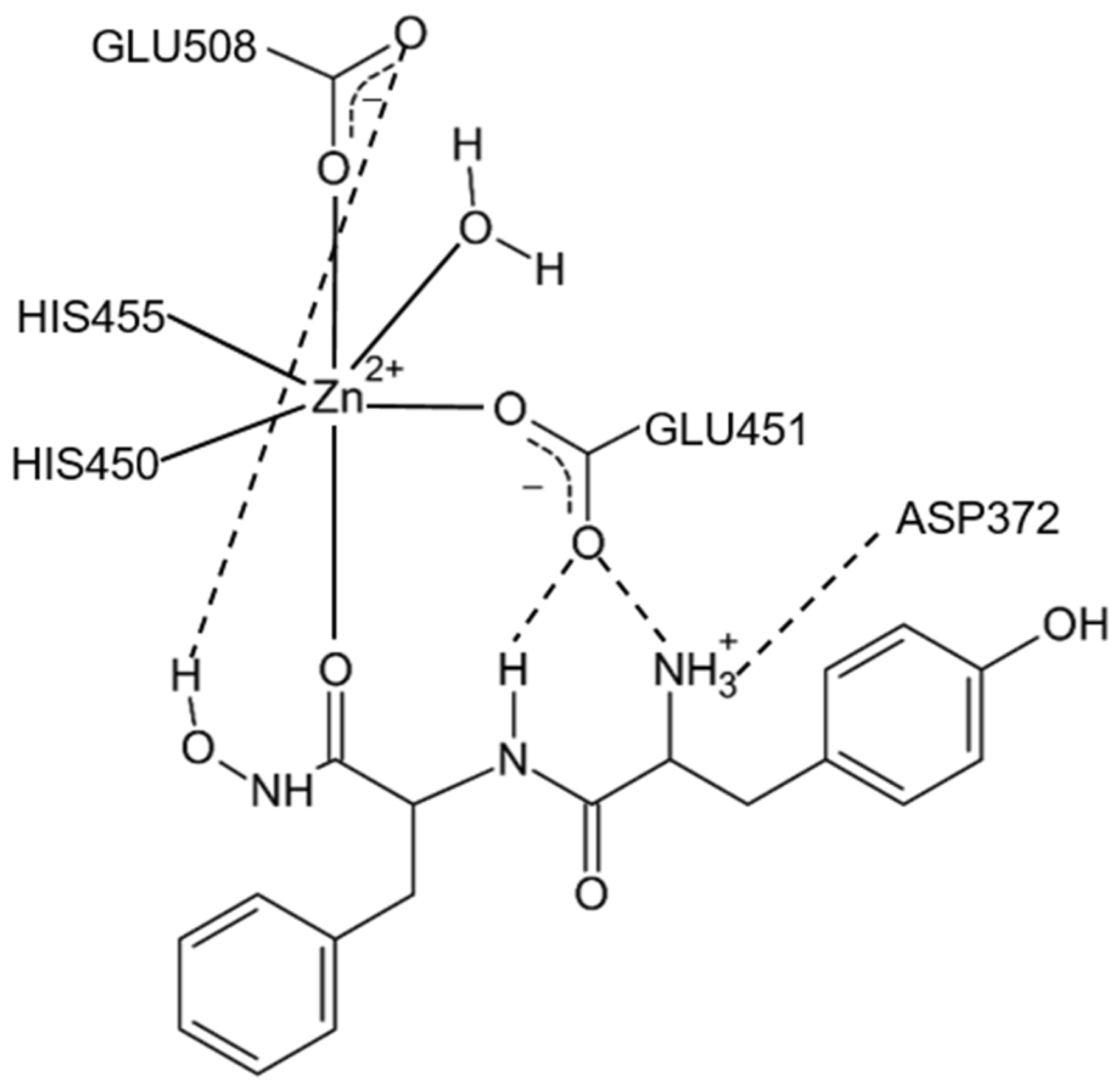
- Agić, D.; Brkić, H.; Kazazić, S.; Tomić, A.; Abramić, M. Aprotinin interacts with substrate-binding site of human dipeptidyl peptidase III. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Hoffmann, T.; Manhart, S.; Heiser, U.; Chambre, S.; Huber, R.; Demuth, H.-U.; Bode, W. Rigidity and flexibility of dipeptidyl peptidase IV: Crystal structures of and docking experiments with DPIV. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 355, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agić, D.; Hranjec, M.; Jajčanin, N.; Starčević, K.; Karminski-Zamola, G.; Abramić, M. Novel amidino-substituted benzimidazoles: Synthesis of compounds and inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase III. Bioorg. Chem. 2007, 35, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastija, V.; Agić, D.; Tomić, S.; Nikolić, S.; Hranjec, M.; Karminski-Zamola, G.; Abramić, M. Synthesis, QSAR, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Amidino-substituted Benzimidazoles as Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhanda, S.; Singh, J.; Singh, H. Goat brain enkephalin degrading enzyme: Interaction with analgesic and antihypertensive drugs. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agić, D.; Karnaš, M.; Šubarić, D.; Lončarić, M.; Tomić, S.; Karačić, Z.; Bešlo, D.; Rastija, V.; Molnar, M.; Popović, B.M.; et al. Coumarin Derivatives Act as Novel Inhibitors of Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase III: Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, J.; Šupljika, F.; Tir, N.; Piotrowski, P.; Carsten Schmuck, C.; Abramić, M.; Piantanida, I.; Sanja Tomić, S. Guanidiniocarbonyl-pyrrole-aryl conjugates as inhibitors of human dipeptidyl peptidase III: Combined experimental and computational study. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83044–83052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćehić, M.; Suć Sajko, J.; Karačić, Z.; Piotrowski, P.; Šmidlehner, T.; Jerić, I.; Schmuck, C.; Piantanida, I.; Tomić, S. The guanidiniocarbonylpyrrole–fluorophore conjugates as theragnostic tools for dipeptidyl peptidase III monitoring and inhibition. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 3790–3800. [Google Scholar]
- Šmidlehner, T.; Karačić, Z.; Tomić, S.; Schmuck, C.; Piantanida, I. Fluorescent cyanine-guanidiniocarbonyl-pyrrole conjugate with pH-dependent DNA/RNA recognition and DPP III fluorescent labelling and inhibition properties. Monatsh. Chem. 2018, 149, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Ž.; Karačić, Z.; Tomić, S.; Amini, H.; Marder, T.B.; Piantanida, I. Triarylborane Dyes as a Novel Non-Covalent and Non-Inhibitive Fluorimetric Markers for DPP III Enzyme. Molecules 2021, 26, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salopek-Sondi, B.; Vukelić, B.; Špoljarić, J.; Šimaga, Š.; Vujaklija, D.; Makarević, J.; Jajčanin, N.; Abramić, M. Functional tyrosine residue in the active center of human dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špoljarić, J.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Makarević, J.; Vukelić, B.; Agić, D.; Šimaga, Š.; Jajčanin-Jozić, N.; Abramić, M. Absolutely conserved tryptophan in M49 family of peptidases contributes to catalysis and binding of competitive inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 37, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvitešić, A.; Sabljić, I.; Makarević, J.; Abramić, M. Novel dipeptidyl hydroxamic acids that inhibit human and bacterial dipeptidyl peptidase III. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31 (Suppl. S2), 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






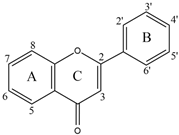 | 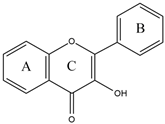 |  | 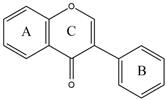 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavone | Flavonol | Flavanone | Isoflavone | |||||
| Group | Name | Substitution | IC50 (μM) | |||||
| 2′ | 3′ | 4′ | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Flavone | Luteolin | H | OH | OH | OH | H | OH | 22.0 |
| Apigenin | H | H | OH | OH | H | OH | 54.0 | |
| 6-Hydroxyflavone | H | H | H | H | OH | H | 82.2 | |
| Chrysin | H | H | H | OH | H | OH | 123.1 | |
| Flavone | H | H | H | H | H | H | 292.5 | |
| Flavonol | Galangin | H | H | H | OH | H | OH | 23.4 |
| Fisetin | H | OH | OH | H | H | OH | 24.9 | |
| Kaempferol | H | H | OH | OH | H | OH | 32.9 | |
| 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone | H | H | H | H | OH | H | 56.4 | |
| Quercetin | H | OH | OH | OH | H | OH | 74.1 | |
| Morin | OH | H | OH | OH | H | OH | 85.0 | |
| 3,7-Dihydroxyflavone | H | H | H | H | H | OH | 98.0 | |
| 3-Hydroxyflavone | H | H | H | H | H | H | 188.2 | |
| Flavanone | Flavanone | H | H | H | H | H | H | 437.2 |
| Isoflavone | Genistein | H | H | OH | OH | H | OH | 36.6 |
| Aprotinin Residue | Human DPP III Residue | HB (%) | HI (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp3 | side | Ser497 | side | 7.5 | - |
| Glu7 | side | Ser500 | side | - | 28.5 |
| Pro8 | side | Thr501 | side | - | 12.2 |
| Pro8 | main | Ser504 (S2) | side | 1.2 | - |
| Tyr10 | side | Ser504 (S2) | side | - | 74.9 |
| Tyr10 | side | Ala567 | side | - | 60.9 |
| Gly12 | main | His568 (S1′, S2′) | side | 2.6 | 6.7 |
| Pro13 | side | Leu413 | side | - | 4.4 |
| Pro13 | side | Glu508 (S2, S1) | side | - | 1.0 |
| Cys14 | side | Ala388 (S1′,S2′, S3′) | side | - | 35.1 |
| Lys15 | main | Ala388 (S1′,S2′, S3′) | main | 88.3 | - |
| Lys15 | main | Ala416 (S3′) | main | 5.2 | - |
| Ala16 | side | Gly385 | main | - | 32.1 |
| Arg17 | side | Ser101 | main | 59.3 | - |
| Arg17 | main | Ser108 | side | 5.7 | - |
| Arg17 | side | Phe109 (S2′) | side | - | 41.5 |
| Arg17 | side | Ser384 | main | 74.6 | - |
| Arg17 | main | Gly385 | main | 75.2 | - |
| Arg17 | side | Ile386 (S3′) | side | - | 90.7 |
| Ile18 | side | Glu316 (S2) | side | - | 88.8 |
| Ile18 | side | Tyr318 (S1, S2′) | side | - | 43.4 |
| Ile18 | side | Gly385 | main | 1.0 | 64.3 |
| Ile18 | side | Pro387 (S1, S1′, S2′) | side | - | 21.5 |
| Ile19 | side | Phe109 (S2′) | side | - | 18.6 |
| Ile19 | main | Tyr318 (S1, S2′) | side | 2.5 | - |
| Arg20 | side | Glu316 (S2) | side | 47.8 | - |
| Compound No. | Structure | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 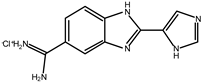 | 53 |
| 2 | 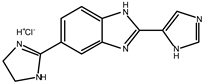 | 18 |
| 3 | 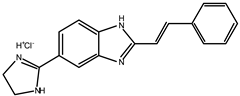 | ~10 |
| 4 | 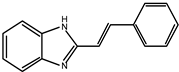 | >100 |
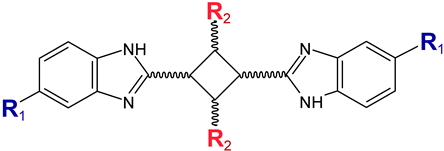 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound No. | R1 | R2 | IC50 (µM) |
| 1′ | 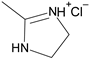 | Phenyl | 2.8 |
| 2′ | 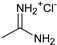 | Phenyl | 5.6 |
| 3′ |  | Phenyl | >10 |
| 4′ | 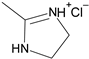 | o-Cl-phenyl | 1.7 |
| 5′ | 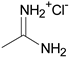 | o-Cl-phenyl | ~7 |
| 6′ |  | o-Cl-phenyl | ~6 |
| 7′ | 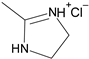 | 2-Furyl | ~8 |
| 8′ | 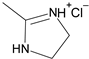 | 2-Thienyl | ~10 |
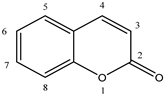 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound No. | Substituents | DPP III inh. (%) |
| 1 | 3-acetyl; 6-bromo | 28.5 |
| 2 | 3-acetyl; 6-hydroxy | 12.8 |
| 3 | 3-acetyl; 7-diethylamino | NA |
| 4 | 3-acetyl; 7-hydroxy | 16.2 |
| 5 | 3-acetyl; 8-ethoxy | NA |
| 6 | 3-acetyl; 8-hydroxy | NA |
| 7 | 3-acetyl | 7.8 |
| 8 | 3-benzoyl; 6-chloro | 4.4 |
| 9 | 3-benzoyl; 6,8-dibromo | NA |
| 10 | 3-benzoyl; 6-hydroxy | 67.5 |
| 11 | 3-benzoyl; 7-benzoyl | 22.8 |
| 12 | 3-benzoyl; 7-hydroxy | 100 (1.10 µM) |
| 13 | 3-benzoyl; 7-methoxy | 16.5 |
| 14 | 3-benzoyl; 8-ethoxy | NA |
| 15 | 3-benzoyl | 9.6 |
| 16 | 3-cyano; 6-bromo | 7.9 |
| 17 | 3-cyano; 6-methoxy | 19.8 |
| 18 | 3-cyano; 6-hydroxy | 44.6 |
| 19 | 3-cyano; 7-benzoyl | 7.1 |
| 20 | 3-cyano; 7-methoxy | NA |
| 21 | 3- cyano; 8-hydroxy | 62.6 |
| 22 | 3-cyano; 8-ethoxy | NA |
| 23 | 3-cyano | NA |
| 24 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 6-bromo | NA |
| 25 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 6-chloro | 20.1 |
| 26 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 6-dihydroxyamino | 59.7 |
| 27 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 6-hydroxy | 66.0 |
| 28 | 3- ethoxycarbonyl; 6,8-dibromo | 29.4 |
| 29 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 7-methoxy | NA |
| 30 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl; 8-ethoxy | NA |
| 31 | 3-ethoxycarbonyl | NA |
| 32 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 6-bromo | 6.5 |
| 33 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 6-dihydroxyamino | 21.2 |
| 34 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 6-hydroxy | 23.5 |
| 35 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 6-methoxy | 9.9 |
| 36 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 7-hydroxy | 100 (2.14 µM) |
| 37 | 3-methoxycarbonyl; 7-methoxy | NA |
| 38 | 3-methoxycarbonyl | 2.3 |
| 39 | coumarin | NA |
| 40 | 7-hydroxycoumarin | 2.1 |
| Inhibitor | Ki (µM) at pH 7.4 | Ki (µM) at pH 8.0 |
|---|---|---|
| H-Phe-Phe-NHOH | 0.028 | 0.11 |
| H-Phe-Leu-NHOH | 0.65 | 1.24 |
| H-Phe-Gly-NHOH | 4.63 | 14.51 |
| H-Tyr-Phe-NHOH | 0.030 | 0.103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abramić, M.; Agić, D. Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin. Molecules 2022, 27, 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093006
Abramić M, Agić D. Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbramić, Marija, and Dejan Agić. 2022. "Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin" Molecules 27, no. 9: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093006
APA StyleAbramić, M., & Agić, D. (2022). Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin. Molecules, 27(9), 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093006






