Ecofriendly Green Synthesis of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Corchorus olitorus Leaves (Molokhaia) Extract and Their Application for the Environmental Remediation of Direct Violet Dye via Advanced Oxidation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Corchorus Olitorus Leaves Extract (Molokhia) Preparation
2.1.2. Conventional CuO NPs (CuO NPs) Preparation
2.1.3. Green CuO NPs (G CuO NPs) Preparation
2.2. Characterization Techniques
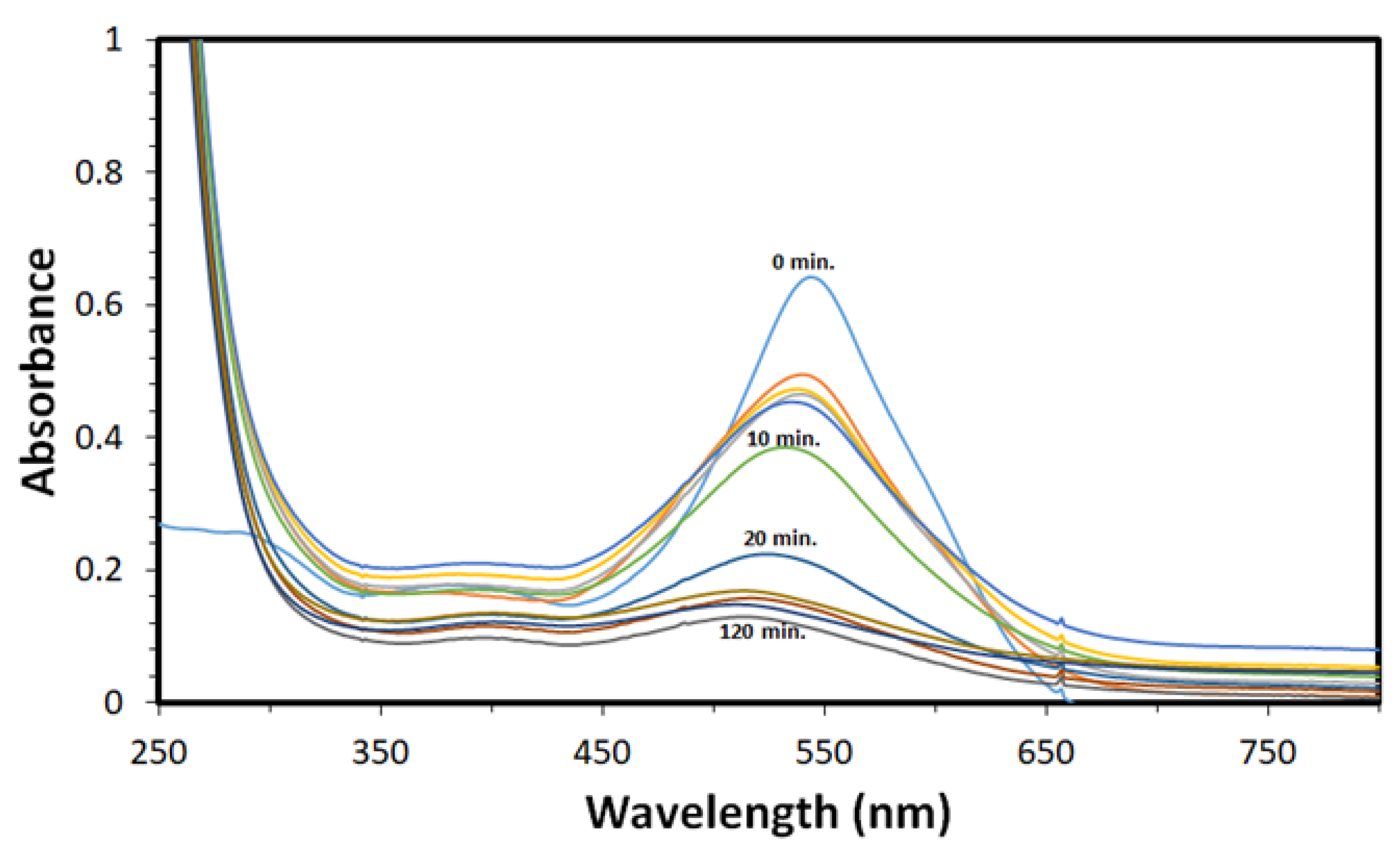
2.3. Removal Study
3. Results & Discussion
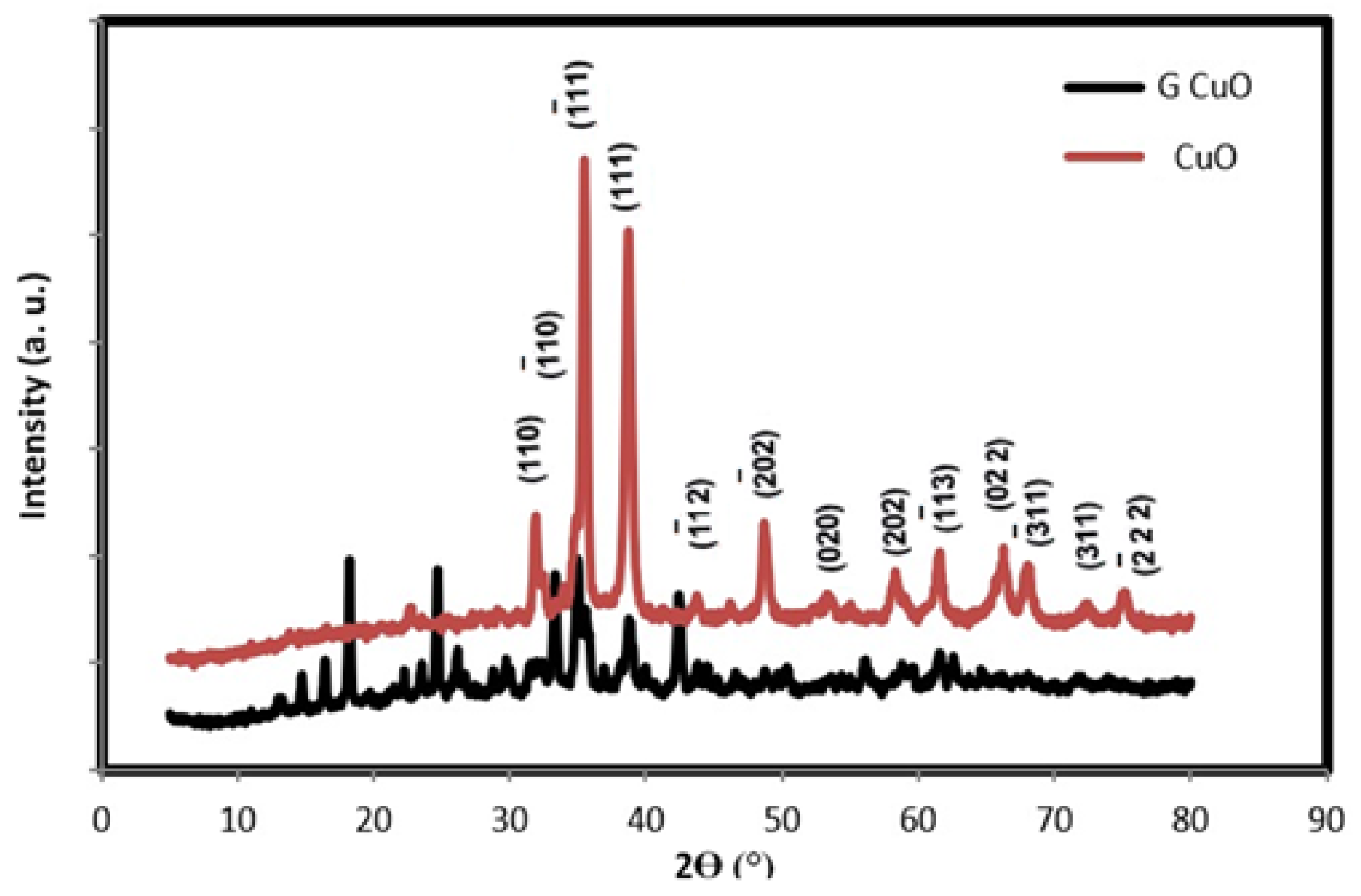
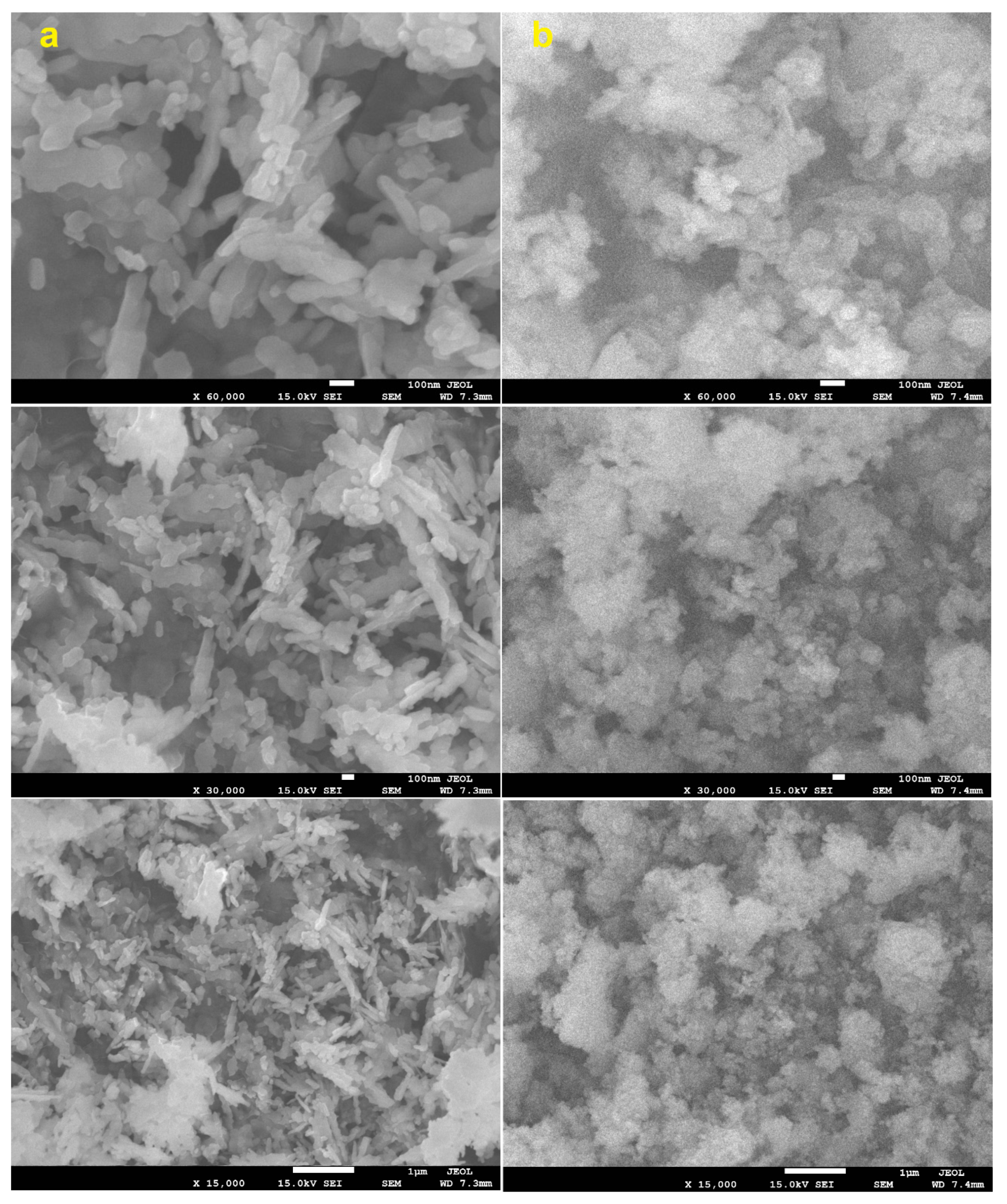
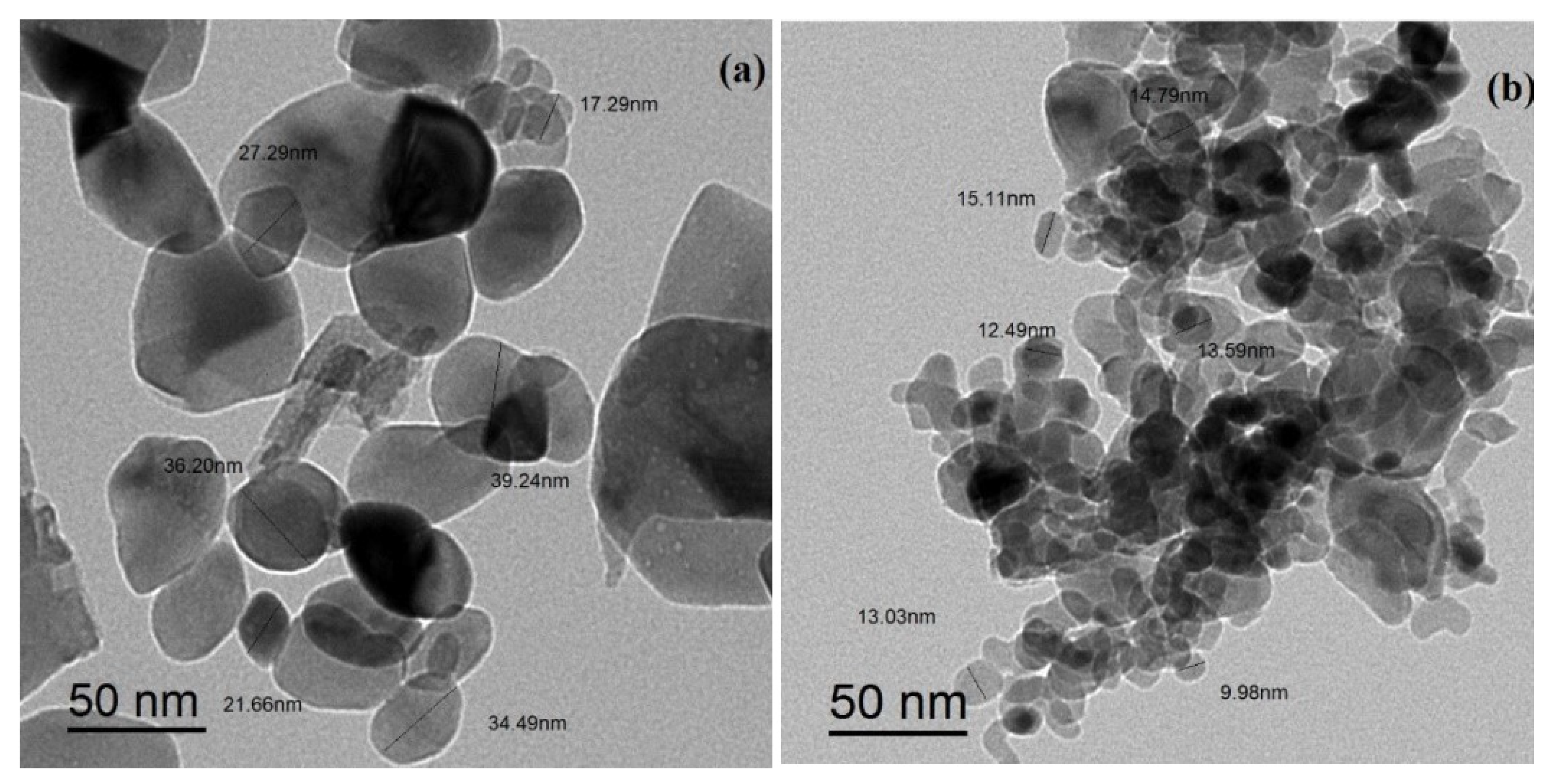
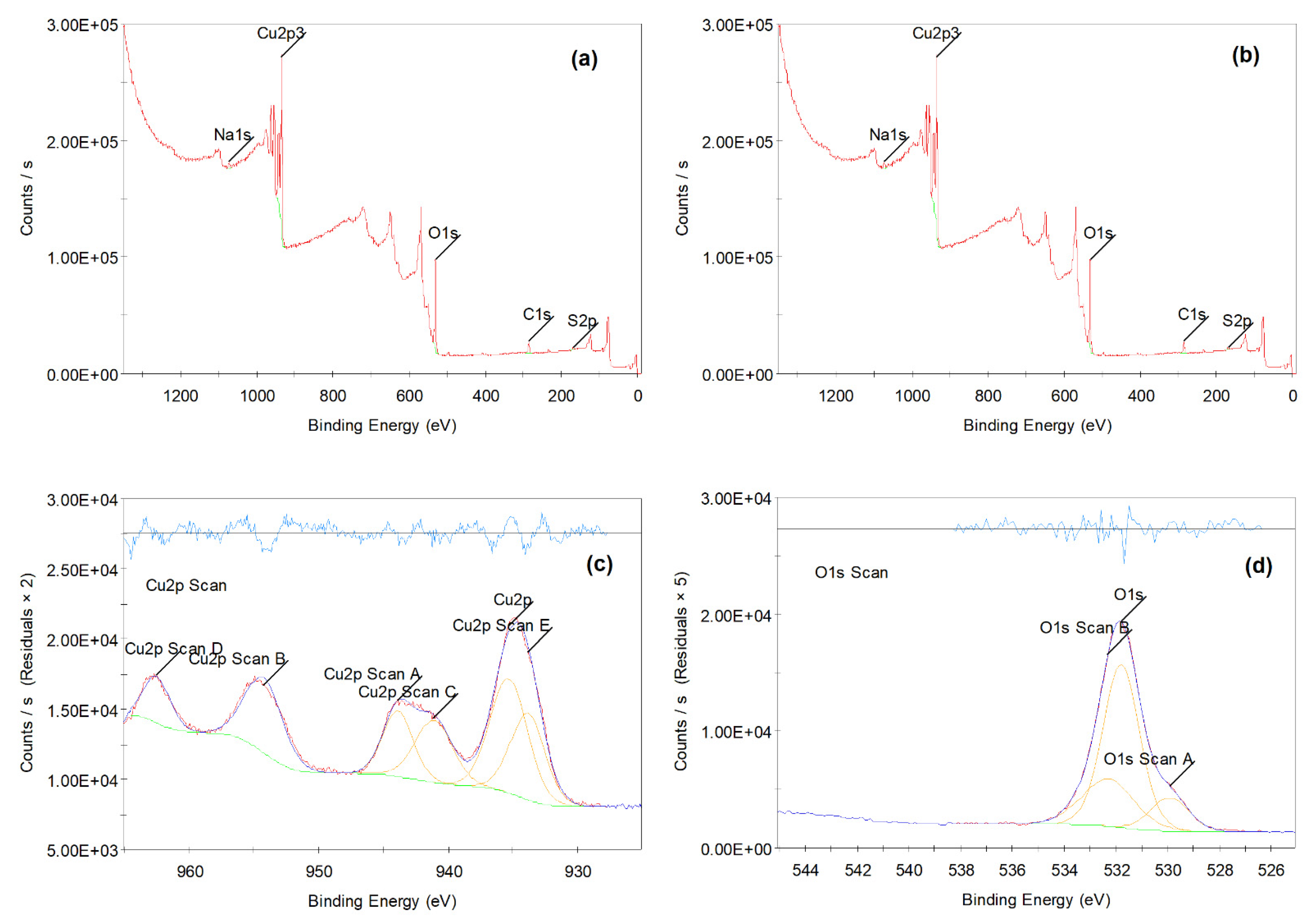
3.1. Characterization of CuO NPs
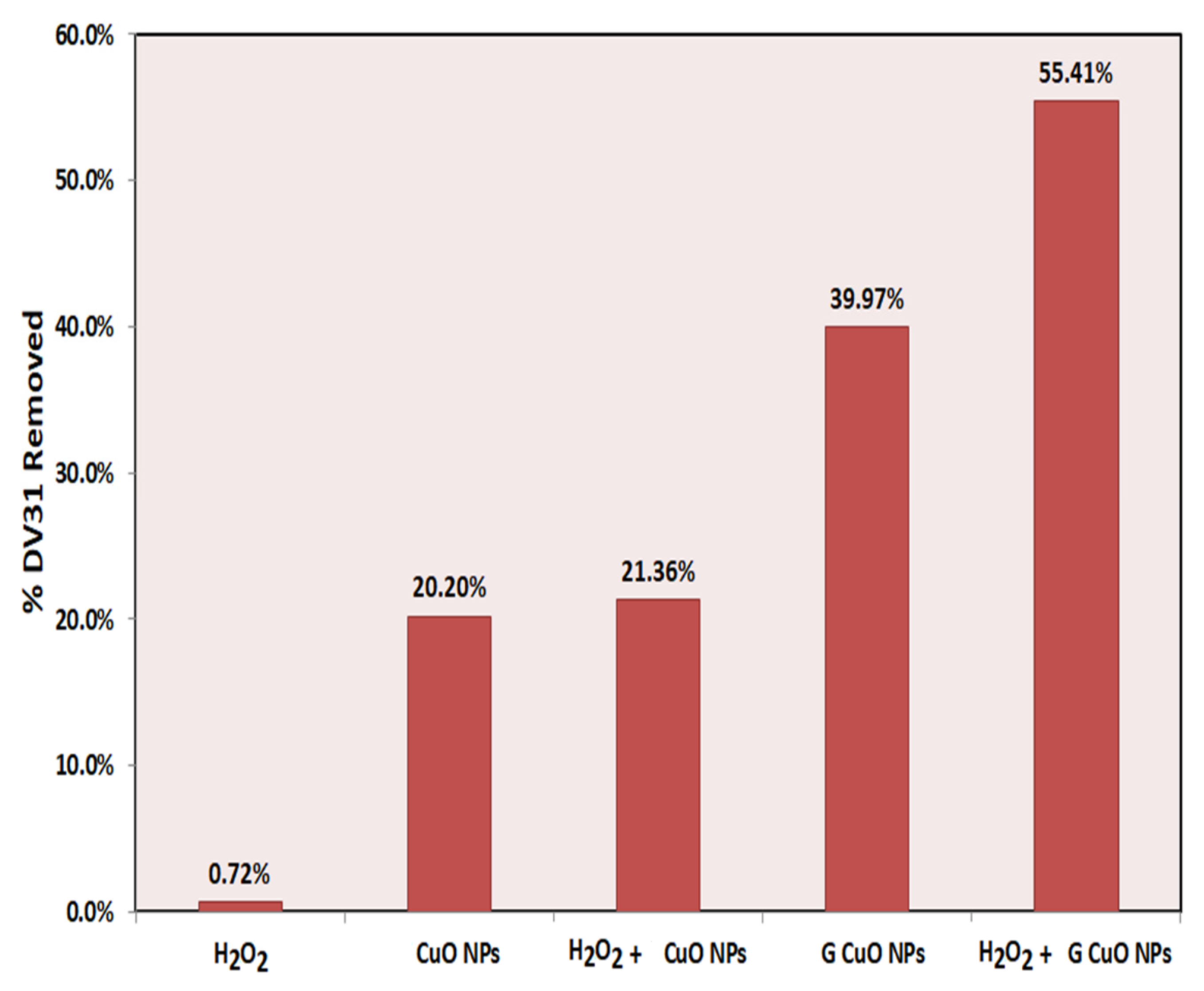
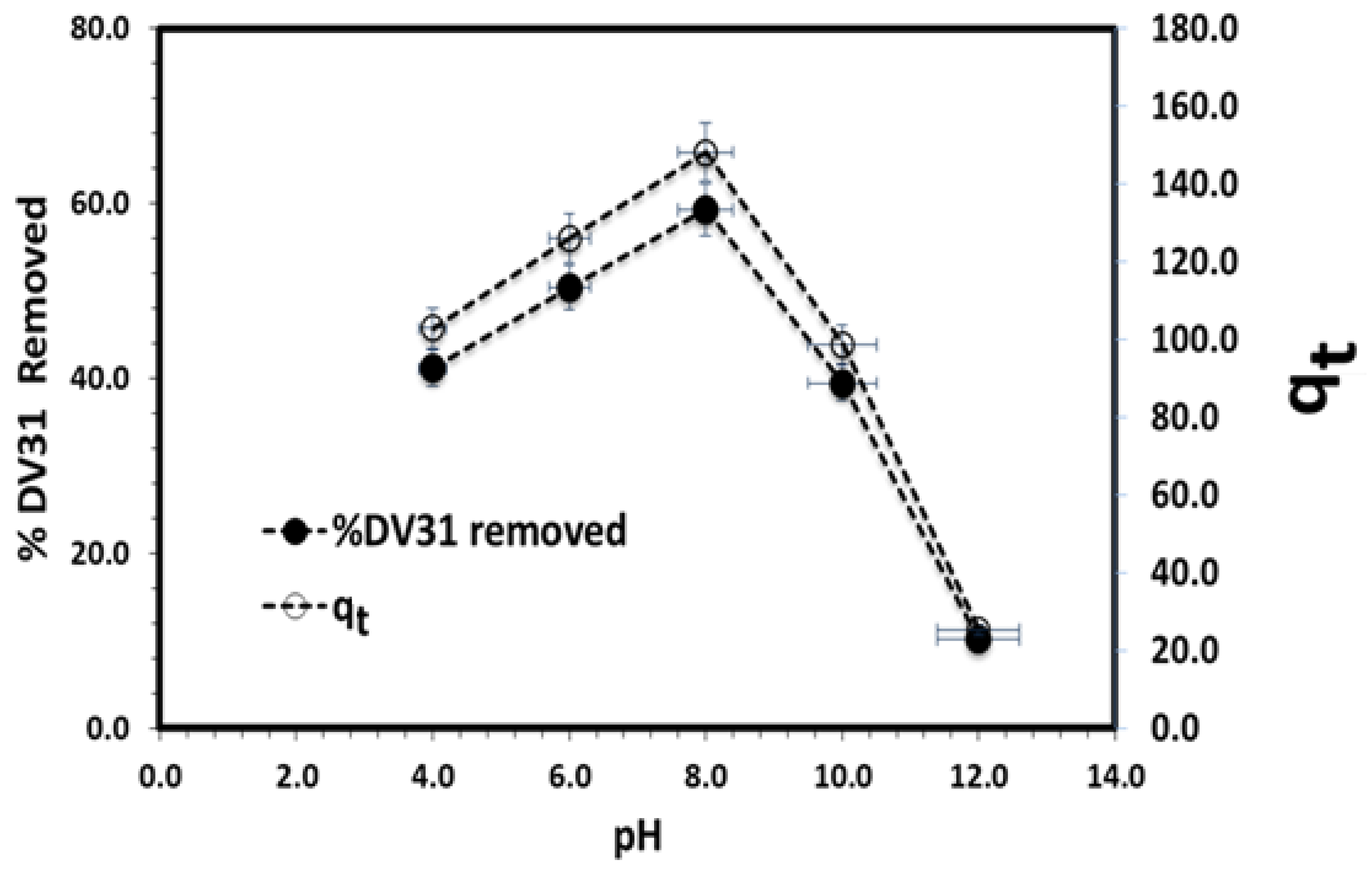
3.2. Removal Study
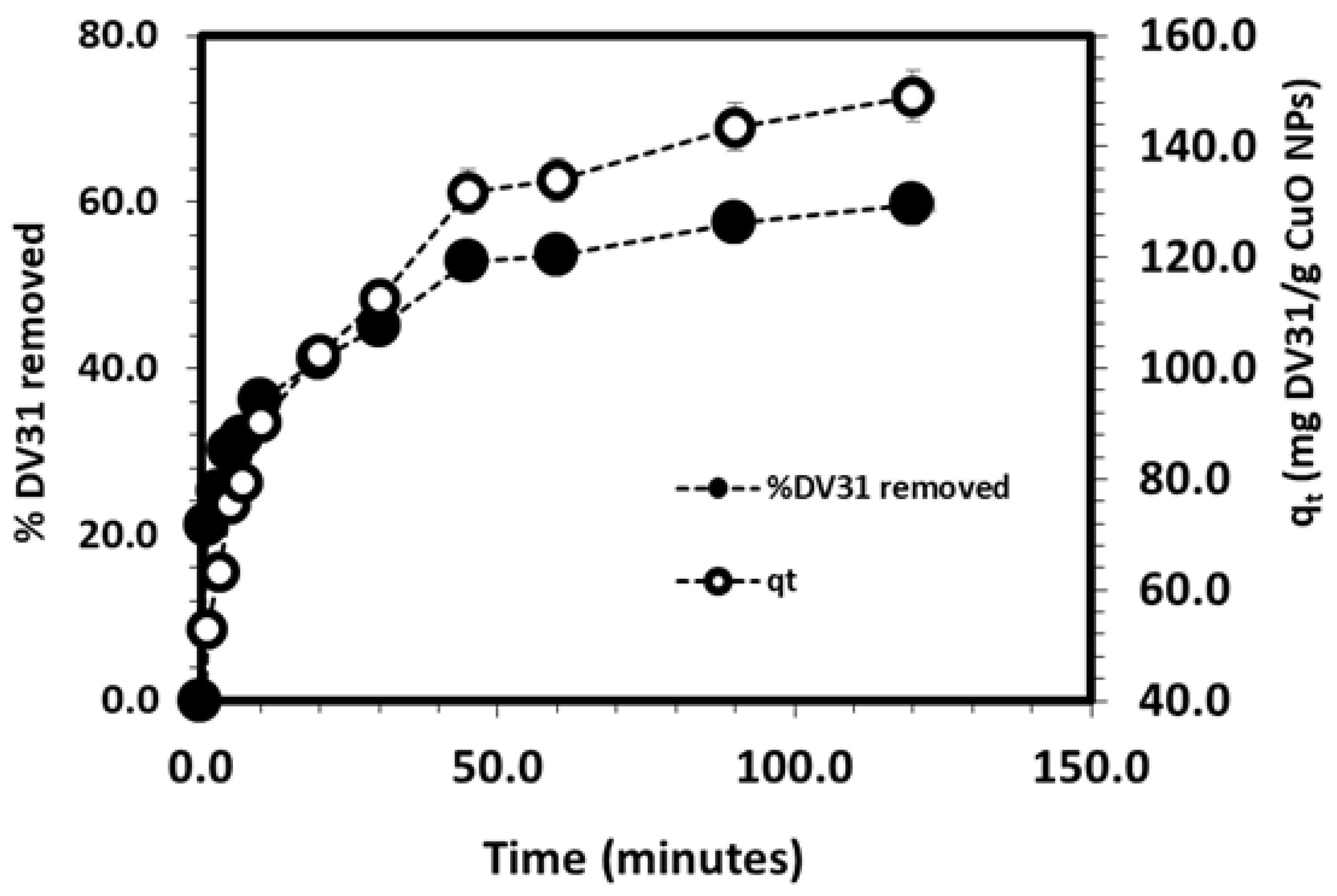
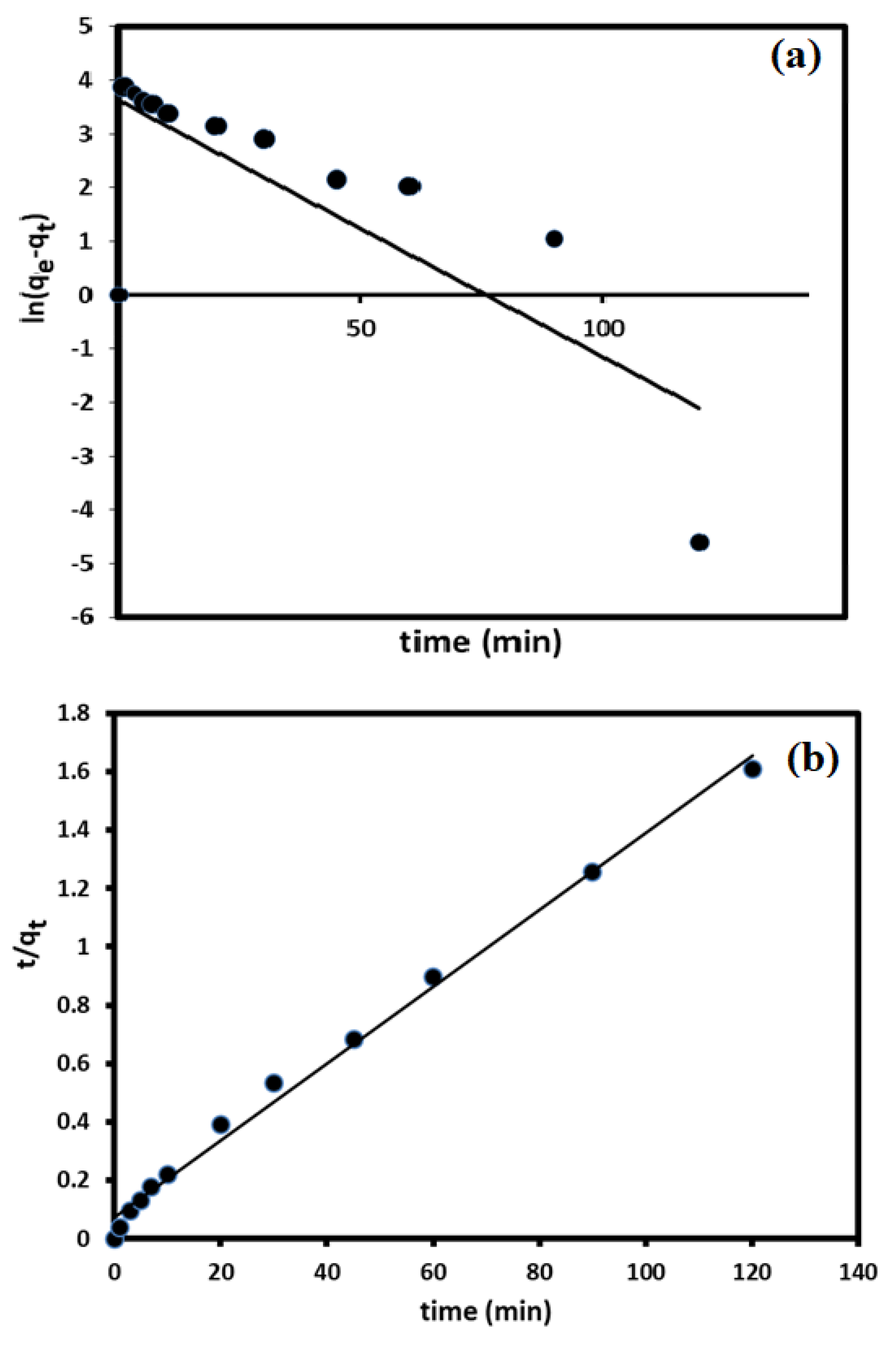
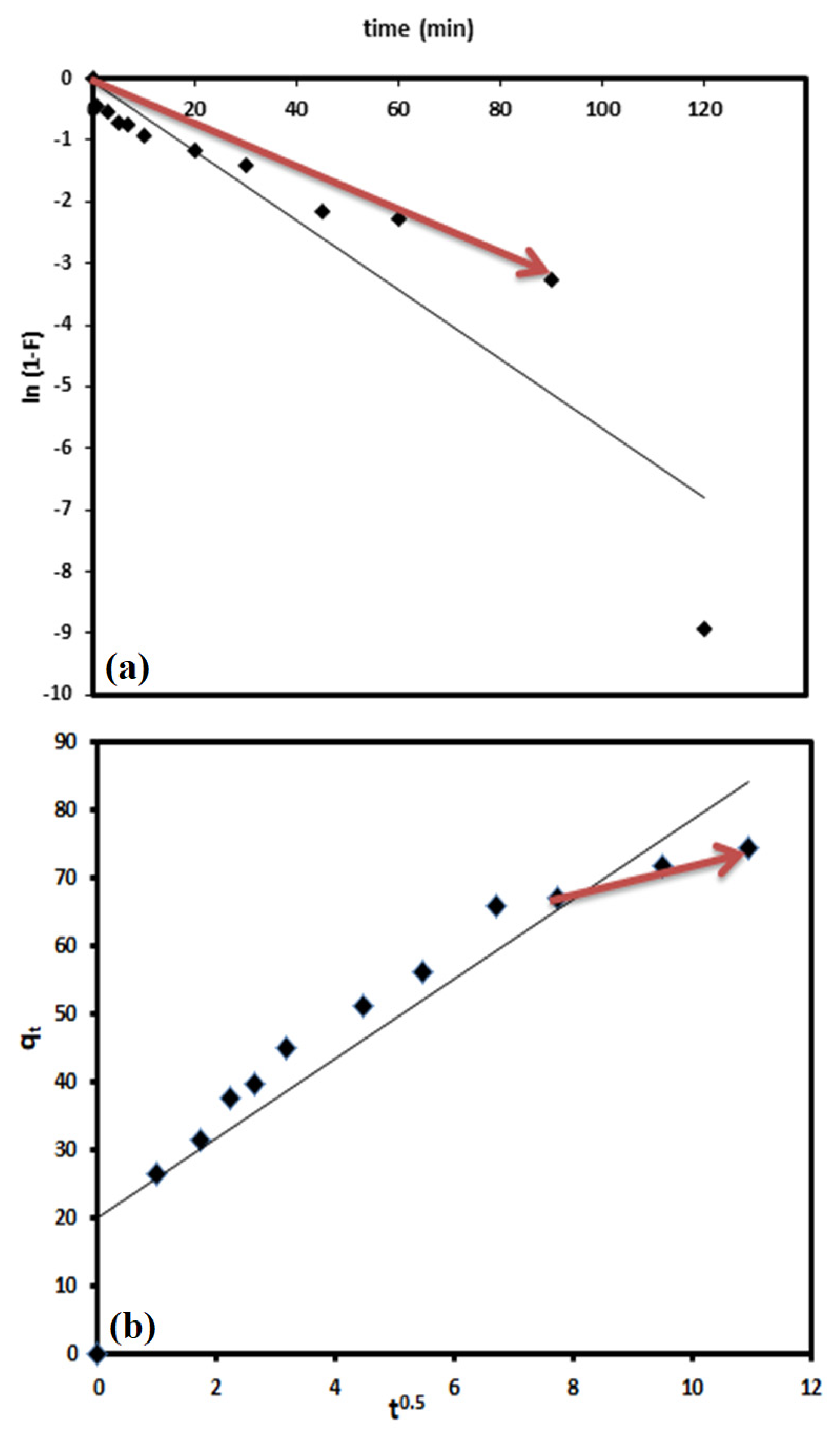
3.3. Kinetic Studies
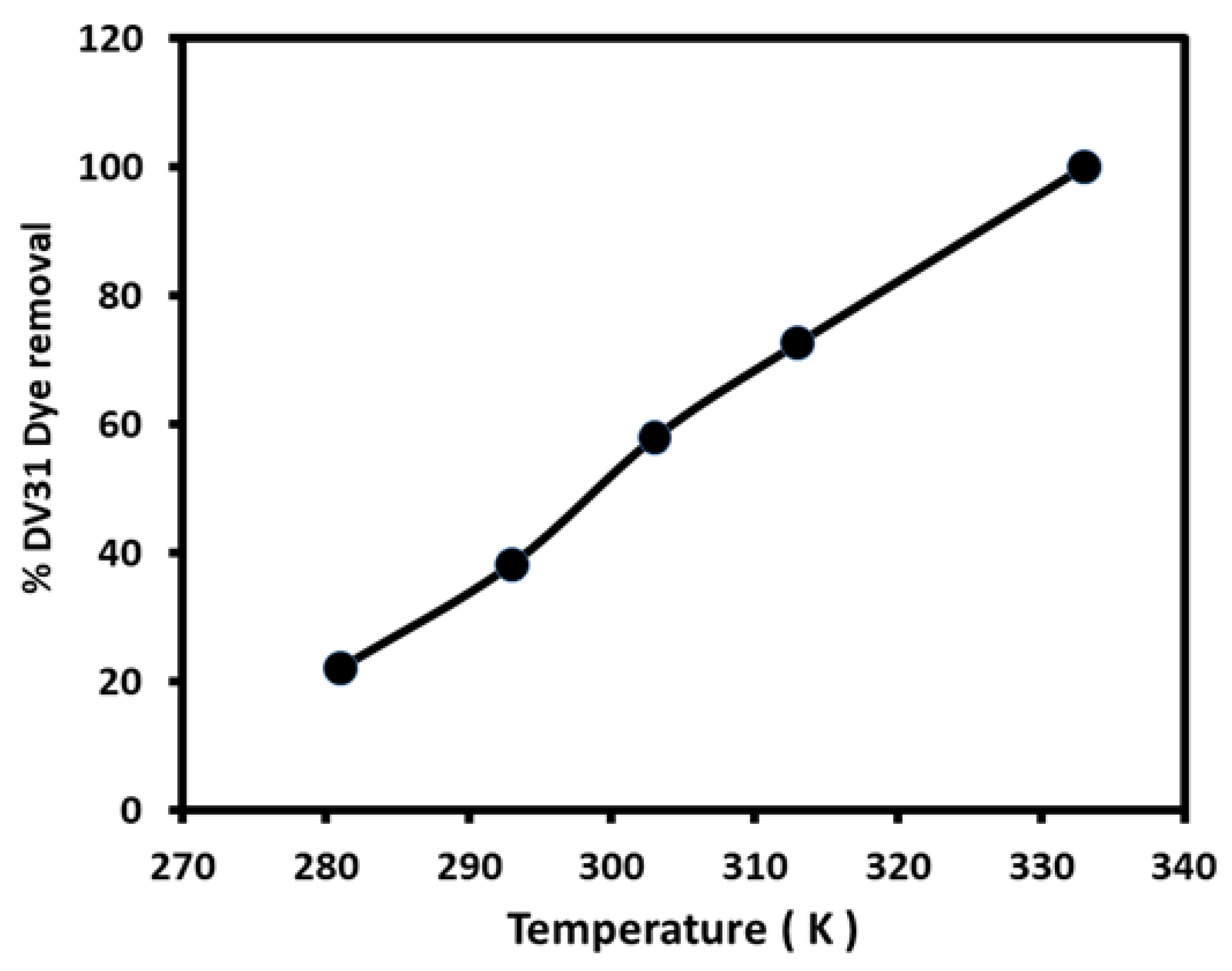
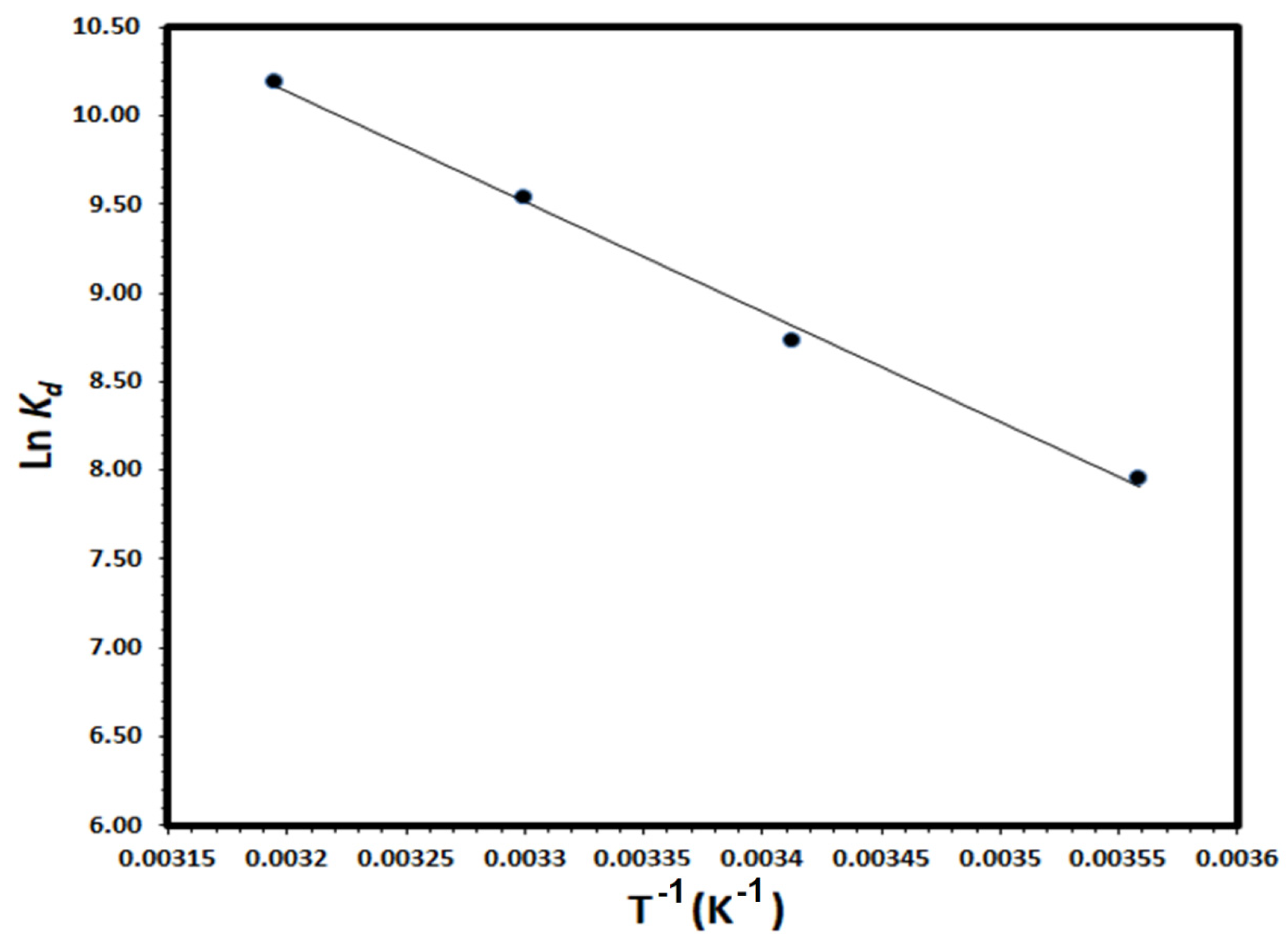
3.4. Thermodynamic Studies
3.5. The Removal Mechanism
3.6. Environmental Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ighalo, J.O.; Sagboye, P.A.; Umenweke, G.; Ajala, O.J.; Omoarukhe, F.O.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Adeniyi, A.G. CuO nanoparticles (CuO NPs) for water treatment: A review of recent advances. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, N.; Manukumar, K.; Viswanatha, R.; Nagaraju, G. Combustion-derived CuO nanoparticles: Application studies on lithium-ion battery and photocatalytic activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, A.P. Nanotechnology for sustainable water treatment—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawana, P.; Fulekar, M.H. Nanotechnology: Remediation technologies to clean up the environmental pollutants. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2012, 2, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Saglam, N.; Korkusuz, F.; Prasad, R. Nanotechnology Applications in Health and Environmental Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Sheikhshoaie, M.; Sheikhshoaie, I.; Ranjbar, M.; Alizadeh, J.; Maxakato, N.W.; Abbaspourrad, A. A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and an-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosma, D.; Urda, A.; Radu, T.; Rosu, M.C.; Mihet, M.; Socaci, C. Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Properties of Copper Oxides/Graphene/TiO2 Nanoparticles Composites. Molecules 2022, 27, 5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, M.M.; Ghayeb, Y.; Menati, M. Facile and green synthesis of CuO nanoneedles with high photo catalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 9454–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Ahmad, S.; Naz, S.S.; Qaisar, S.; Muhammad, S.; Alotaibi, A.; Ullah, R. Synthesis of Copper Oxide-Based Nanoformulations of Etoricoxib and Montelukast and Their Evaluation through Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Pyretic, and Acute Toxicity Activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, M.S.; Kulkarni, S.; Raikar, P.; Barretto, D.A.; Vootla, S.K.; Raikar, U.S. Green biosynthesis of CuO & Ag–CuO nanoparticles from Malus domestica leaf extract and evaluation of antibacterial, antioxidant and DNA cleavage activities. New J. Chem. 2017, 42, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanavel, V.; Palanichamy, V.; Roopan, S.M. Biosynthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles and its anticancer activity on human colon cancer cell lines (HCT-116). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 171, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwanya, A.C.; Ndipingwi, M.M.; Mayedwa, N.; Razanamahandry, L.; Ikpo, C.O.; Waryo, T.; Ntwampe, S.; Malenga, E.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Ezema, F.I.; et al. Maize (Zea mays L.) fresh husk mediated biosynthesis of copper oxides: Potentials for pseudo capacitive energy storage. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 301, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Rostami-Vartooni, A. Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Anthemis nobilis flowers and their catalytic activity for the A3 coupling reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 459, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, B.T.; Diallo, A.; Fuku, X.G.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Biosynthesized CuO nano-platelets: Physical properties & enhanced thermal conductivity nanofluidics. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Bao, Y.; Xu, J. Phase-controlled growth of cubic phase CuO nanoparticles by chemical vapor deposition. Phys. Status Solidi 2017, 214, 1700041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, B.; Jeyakumar, S.J.; Jothibas, M. A sol-gel approach to the synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Lantana camara leaf extract and their photo catalytic activity. Optik 2019, 183, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Qin, H.; Cui, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, X. Energy storage performance of CuO as a cathode material for aqueous zinc ion battery. Mater. Today Energy 2019, 15, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Tezcan, F.; Kardaş, G. Photoelectrochemical characteristics of CuO films with different electrodeposition time. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 23268–23275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Kumar, A.; Tarlochan, F. Highly efficient nonenzymatic glucose sensors based on CuO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, T.; Liguori, A.; Macias-Montero, M.; Padmanaban, D.B.; Carolan, D.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Maguire, P.; Svrcek, V.; Mariotti, D. Ultra-small CuO nanoparticles with tailored energy-band diagram synthesized by a hybrid plasma-liquid process. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 14, 1600224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, H.N.; Pansambal, S.; Ghotekar, S.; Oza, R.; Hai, N.T.T.; Viet, N.M.; Nguyen, V.H. New frontiers in the plant ex-tract mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their potential applications: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Oyedeji, A.O. Biogenic Synthesis of CuO, ZnO, and CuO–ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extracts of Dovyalis caffra and Their Biological Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, K.; Thakur, N.; Chauhan, S.; Chauhan, M.S. Eco-friendly Ocimum tenuiflorum green route synthesis of CuO nanoparticles: Characterizations on photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Banerjee, J.; Chakraborty, P.; Banerjee, A.; Chanda, S.; Ray, K.; Acharya, K.; Sarkar, J. Green synthesis of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles and their applications: A review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, W.H.; Kang, J.-W.; Chapin, D.H. The Chemistry of Water Treatment Processes Involving Ozone, Hydrogen Peroxide and Ultraviolet Radiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2112–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Tang, L.; Tian, R.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Jin, Z.; Xiao, J.; et al. Recent advances in waste wa-ter treatment through transition metal sulfides-based advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Conway, J.R.; Garner, K.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Keller, A.A. Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: Costs, benefits, and applicability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 640–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, I.M.F.; Cardoso, R.M.F.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Advanced Oxidation Processes Coupled with Nanomaterials for Water Treatment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethi, B.; Sonawane, S.H.; Bhanvase, B.A.; Gumfekar, S.P. Nanomaterials-based advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2016, 109, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, R.; Mirzaei, F.; Ghanbari, F.; Feizi, R.; Mehdipour, F. Real textile wastewater treatment by a sulfate radicals-Advanced Oxidation Process: Peroxydisulfate decomposition using copper oxide (CuO) supported onto activated carbon. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.S.; Xing, Q.J.; Dong, W.H.; Luo, X.B.; Dai, W.L.; Xiao, X.; Luo, J.M.; Crittenden, J. Electrochemical oxida-tion and advanced oxidation processes using a 3D hexagonal Co3O4 array anode for 4-nitrophenol decomposition coupled with simultaneous CO2 conversion to liquid fuels via a flower-like CuO cathode. Water Res. 2019, 150, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; You, W.; Zhou, G.; Peng, G. A facile method to fabricate AC/CuO for efficient removal of organic pollutants by adsorption and persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2020, 70, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, N.E.; Fazaeli, R.; Yousefi, M.; Abdolmohammadi, S. Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of CuO, CuO Rod/MWW Com-posite for Advanced Oxidation of Indole and Benzothiophene. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 9529–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthana, M.S.; Mthiyane, M.N.; Ekennia, A.C.; Singh, M.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial effects of silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared using fruit extract of Capsicum Chinense. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhotiya, G.; Bajaj, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Pradhan, D.; Tekade, P.; Rana, A. Enhanced catalytic activity without the use of an external light source using microwave-synthesized CuO nanopetals. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Yang, M.-P.; Meng, W.-J.; Wang, H.; Lu, J.-X. CuO Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2 with High Efficiency for CO2 Electrochemical Reduction to Ethanol. Catalysts 2018, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeid, A.H.S.A. Stress metabolites from Corchorus olitorius L. leaves in response to certain stress agents. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, C.; Deng, L. Performance of CuO/Oxone system: Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation of phenol at ambient condi-tions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.A.W.; Ahmad, A.L.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Sun, S.-P.; Wang, G.-L.; Qiao, L.-P. Degradation of azo dye Amido black 10B in aqueous solution by Fenton oxidation process. Dyes Pigments 2007, 74, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. IV. Update and new approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Park, D.R.; Khan, S.; Akram, M.; Yeom, I.T. The removal of CuO nanoparticles from water by con-ventional treatment C/F/S: The effect of pH and natural organic matter. Molecules 2019, 24, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rahim, W.M.A.; El-Ardy, O.A.M.; Mohammad, F.H. The effect of pH on bioremediation potential for the removal of direct violet textile dye by Aspergillus niger. Desalination 2009, 249, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S.K. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingarl 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinski, W.; Plazinski, W. On the applicability of the pseudo-second order equation to represent the kinetics of adsorption at solid/solution interfaces: A theoretical analysis based on the statistical rate theory. Adsorption 2009, 15, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radini, I.A.; Hasan, N.; Malik, M.A.; Khan, Z. Biosynthesis of iron nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract for photocatalytic methyl orange dye degradation and antibacterial applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagdonavicius, V.; Nikulin, M. Chi-squared goodness-of-fit test for right censored data. Int. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2011, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Karri, R.R.; Sahu, J.; Jayakumar, N. Optimal isotherm parameters for phenol adsorption from aqueous solutions onto coconut shell based activated carbon: Error analysis of linear and non-linear methods. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The Exchange Adsorption of Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Organic Zeolites. II. Kinetics1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owija, N.Y.; Kosa, S.A.; Salam, M.A. Removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solution by zero valent iron nanoparticles: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry, 9th ed.; Chapter 23: Catalysis; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 876–908. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.; Rawindran, H.; Sinnathambi, C.M.; Lim, J.-W. Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes used in remediation of industrial wastewater laden with recalcitrant pollutants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 206, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Y.; Yue, D.; Qian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, Z. CuO nanosheet as a recyclable Fenton-like catalyst prepared from simulated Cu(ii) waste effluents by alkaline H2O2 reaction. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Kinetic Model | |
|---|---|---|
| PFO | PSO | |
| K | 0.0479 | 0.0024 |
| qe,exp (mg/g) | 74.59 | 74.59 |
| qe,calc (mg/g) | 37.79 | 75.90 |
| R2 | 0.603 | 0.994 |
| χ2 | 35.84 | 0.02284 |
| SSE | 1354 | 1.734 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljedaani, R.O.; Kosa, S.A.; Abdel Salam, M. Ecofriendly Green Synthesis of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Corchorus olitorus Leaves (Molokhaia) Extract and Their Application for the Environmental Remediation of Direct Violet Dye via Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules 2023, 28, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010016
Aljedaani RO, Kosa SA, Abdel Salam M. Ecofriendly Green Synthesis of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Corchorus olitorus Leaves (Molokhaia) Extract and Their Application for the Environmental Remediation of Direct Violet Dye via Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljedaani, Reham O., Samia A. Kosa, and Mohamed Abdel Salam. 2023. "Ecofriendly Green Synthesis of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Corchorus olitorus Leaves (Molokhaia) Extract and Their Application for the Environmental Remediation of Direct Violet Dye via Advanced Oxidation Process" Molecules 28, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010016
APA StyleAljedaani, R. O., Kosa, S. A., & Abdel Salam, M. (2023). Ecofriendly Green Synthesis of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Corchorus olitorus Leaves (Molokhaia) Extract and Their Application for the Environmental Remediation of Direct Violet Dye via Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules, 28(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010016








