Clay-Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants in Water and Toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of Molecular Structure and Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Clay Behavior in Aqueous Media
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics on Clay Surface
2.3. Intra-Particle Diffusion Model
2.4. Adsorption Equilibrium
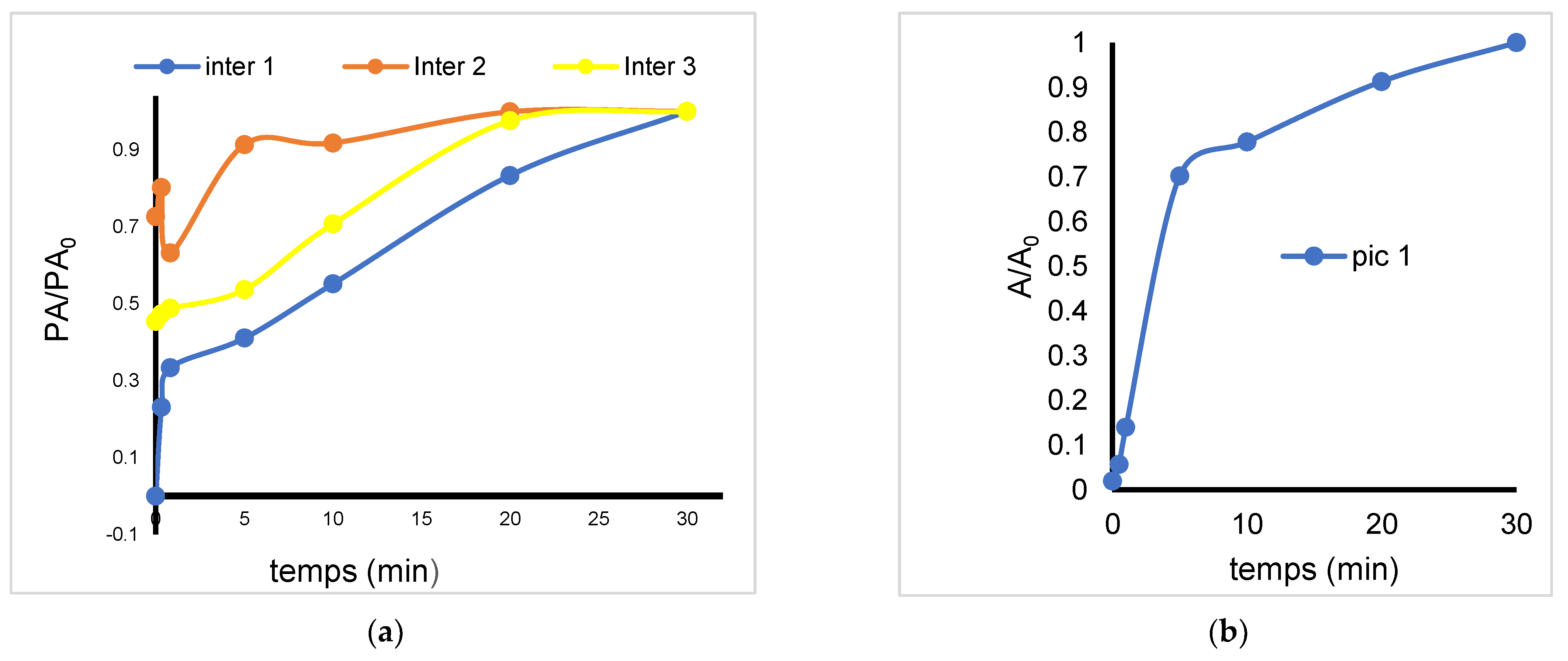
2.5. Non-Catalytic Ozonation
2.6. Effect of Clay Catalyst Addition
2.7. pH Evolution during Ozonation
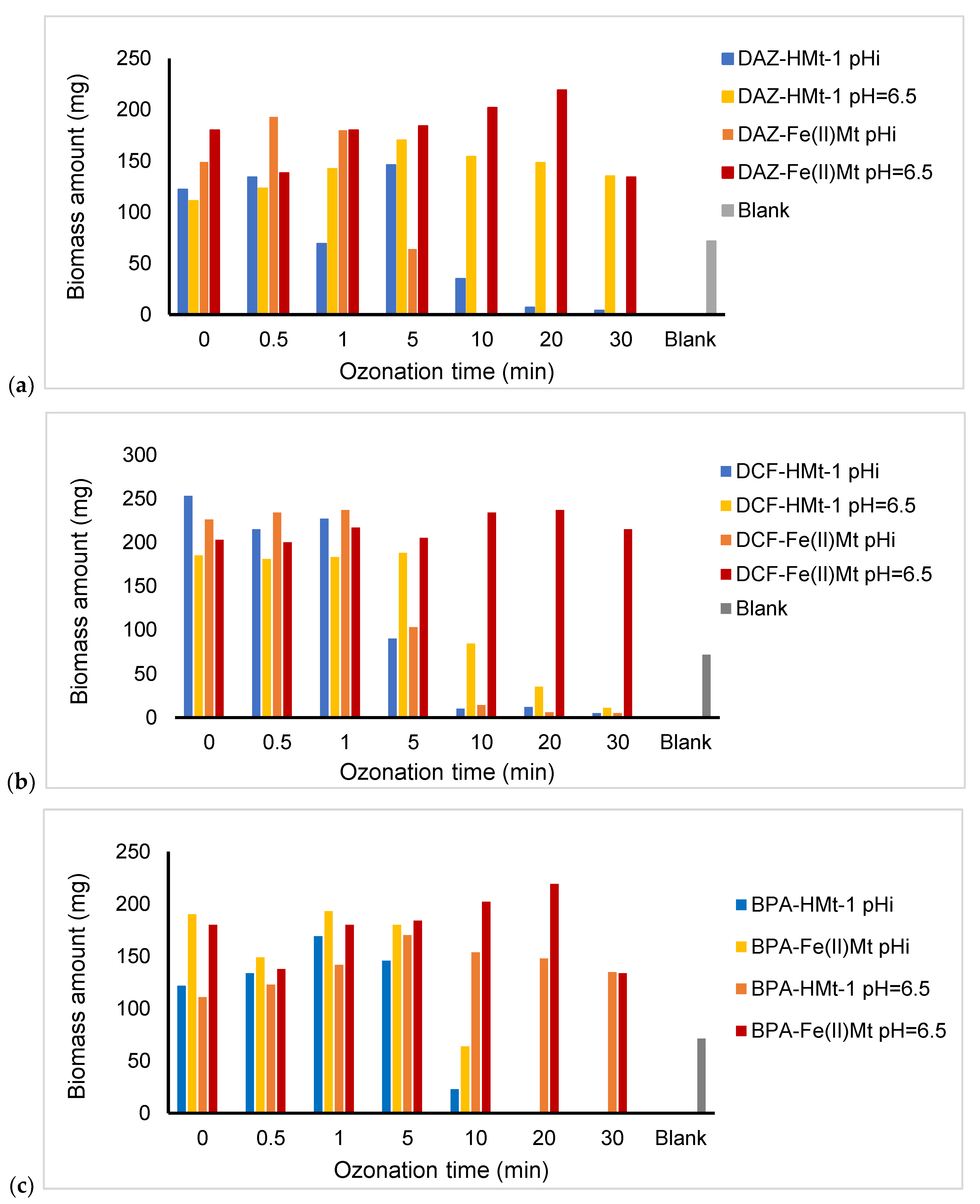
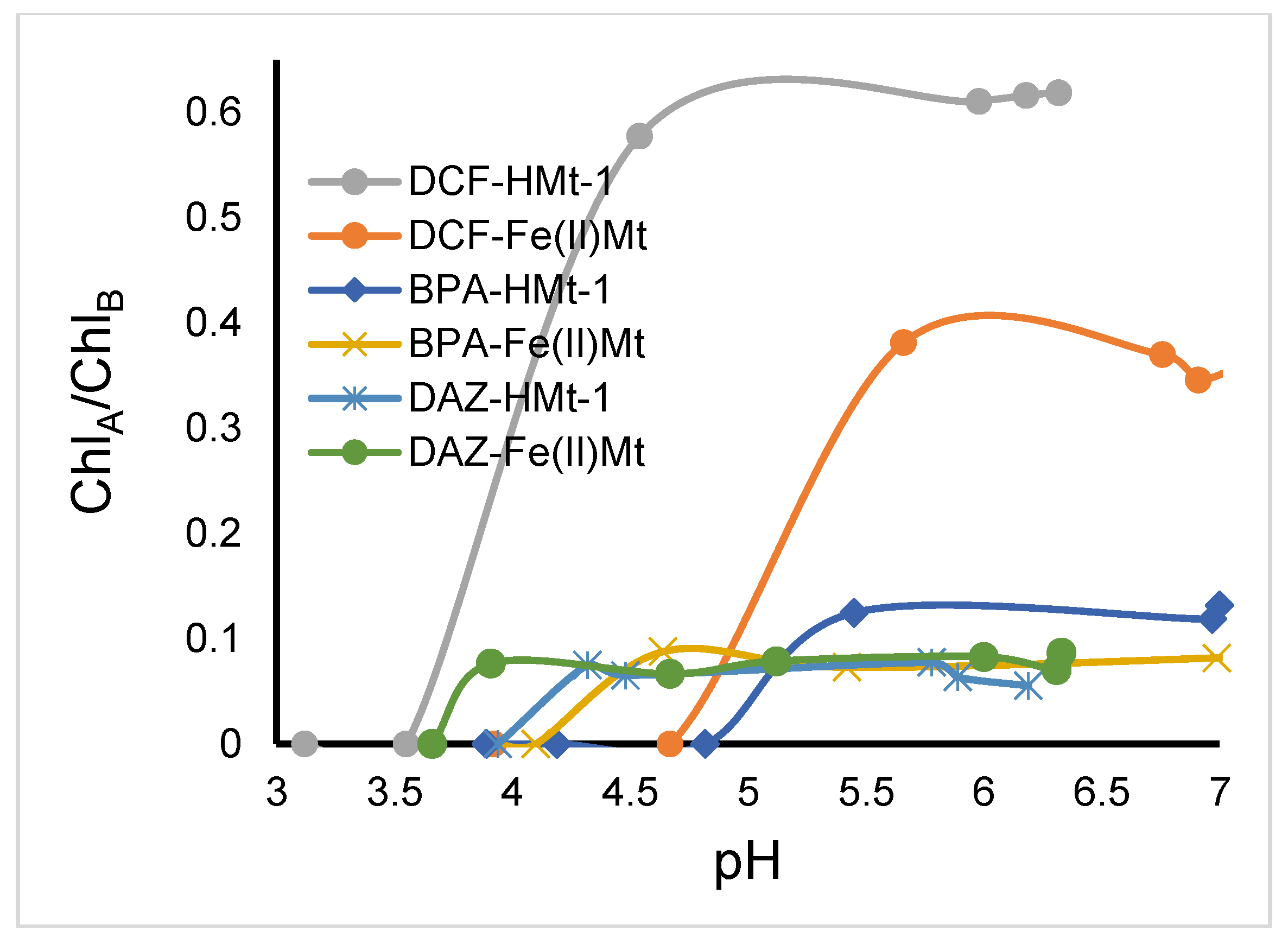
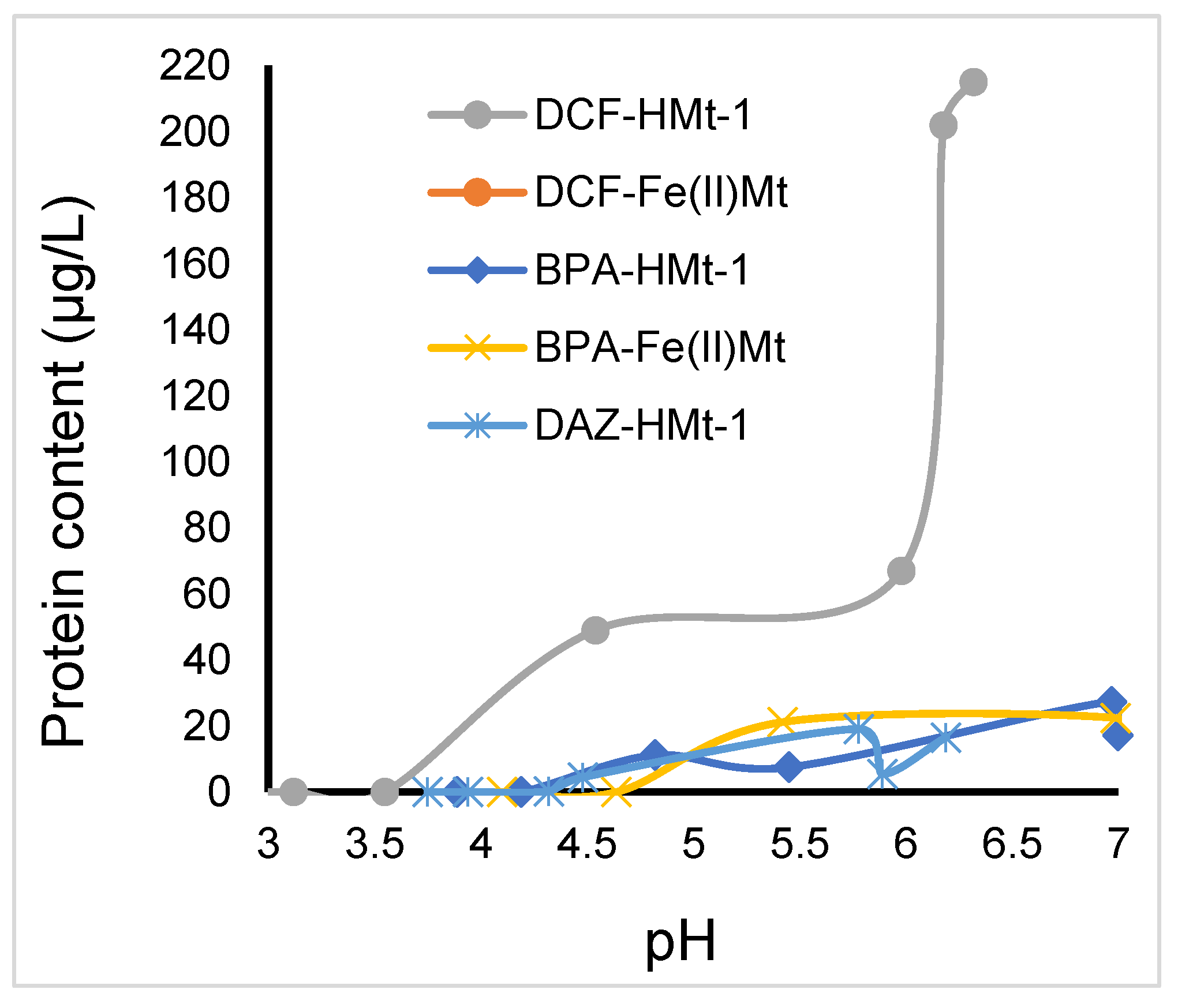
2.8. Toxicity of Ozonized Reaction Mixtures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Clay Materials Preparation
3.2. Clay Behavior Study in Aqueous Media
3.3. Adsorption and Ozonation Tests
3.4. Adsorption and Reaction Mixture Analysis
3.5. Toxicitytests on Lemna minor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Barriuso, E.; Calvet, R.; Schiavon, M.; Soulas, G. Les pesticides et les polluants organiques des sols: Transformations et dissipation. Etude Gest. Sols 1996, 3, 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Advances in catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants-Prospects for thorough mineralization by natural clay catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Watson, A.; Forter, M.; Oliaei, F. Persistent organic pollutants and landfills-a review of past experiences and future challenges. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, R.N.; Rao, S.M. Mechanistic evaluation of mitigation of petroleum hydrocarbon contamination by soil medium. Can. Geotech. J. 1991, 28, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwafune, T. Studies on the behavior and ecotoxicity of pesticides and their transformation products in a river. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liao, X.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Degradation of diazinon in apple juice by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, V.; Ginebreda, A.; Mor, J.; Petrovic, M.; Sabater, S.; Sumpter, J.; Barceló, D. Balancing the health benefits and environmental risks of pharmaceuticals: Diclofenac as an example. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolović, M.; Krstić, D.; Petrović, S.; Leskovac, A.; Joksić, G.; Savić, J.; Franko, M.; Trebše, P.; Vasić, V. Toxic effects of diazinon and its photodegradation products. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 193, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C. Diazinon: Toxicology. J. Pestic. Reform 2000, 20, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lonappan, L.; Brar, S.K.; Das, R.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Diclofenac and its transformation products: Environmental occurrence and toxicity-a review. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Rouissi, T.; Laadila, M.A.; Brar, S.K.; Hernandez Galan, L.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Agro-industrial-produced laccase for degradation of diclofenac and identification of transformation products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5772–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.; Sillanpää, M. Fate of diclofenac in municipal wastewater treatment plant—A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, M.H.; Key, P.B. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in estuarine fish and invertebrates as an indicator of organophosphorus insecticide exposure and effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2001, 20, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.M.; Chu, N.C.; Van Thuan, D.; Ha, M.N.; Hanh, N.T.; Viet, H.D.T.; Minh Thu, N.T.; Van Quan, P.; Thanh Truc, N.T. Novel removal of diazinon pesticide by adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of visible light-driven Fe-TiO2/Bent-Fe photocatalyst. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2678927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, R. Diazinon Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, and Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review; US Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Meite, L.; Szabo, R.; Mazellier, P.; de Laat, J. Kinetics of phototransformation of emerging contaminants in aqueous solution. Rev. Des Sci. L’eau 2010, 23, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, H. Etude de la Dégradabilité et de la Toxicité des Colorants par Ozonation et Photocatalyse. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Monastir, Monastir, Tunisie, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz, A.; Hausler, R.; El-Akhrass, M. Chapter 17—Pesticides and removal approaches. In Sorbents Materials for Controlling Environmental Pollution; Núñez-Delgado, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 435–462. [Google Scholar]
- Mougin, C.; Chaplain, V.; Rama-Mercier, R.; Sohier, L.; Sigoillot, J.-C.; Asther, M. Utilisation de champignons filamenteux pour la dépollution de sols pollués par des polluants organiques. Déchets Sci. Tech. 1996, 4, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Deka, S.; Patra, S. Chapter 5—Algae mediated technologies in biotreatment of phenolic wastewaters. In An Integration of Phycoremediation Processes in Wastewater Treatment; Shah, M., Rodriguez-Couto, S., De La Cruz, C.B.V., Biswas, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 103–120. [Google Scholar]
- Matoh, L.; Žener, B.; Korošec, R.C.; Štangar, U.L. 27—Photocatalytic water treatment. In Nanotechnology in Eco-efficient Construction, 2nd ed.; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Diamanti, M.V., Nazari, A., Granqvist, C.G., Pruna, A., Amirkhanian, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 675–702. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, E.V.; Scialdone, O. Chapter 10—Photo-Electrochemical Technologies for Removing Organic Compounds in Wastewater. In Electrochemical Water and Wastewater Treatment; Martínez-Huitle, C.A., Rodrigo, M.A., Scialdone, O., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 239–266. [Google Scholar]
- Gude, V.G. 8—Microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment and energy generation. In Microbial Electrochemical and Fuel Cells; Scott, K., Yu, E.H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 247–285. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghfar, F.; Ghaedi, M.; Zalipour, Z. Chapter 4—Advanced oxidation. In Interface Science and Technology; Ghaedi, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 32, pp. 225–324. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Sayed, M.; Sohail, M.; Shah, L.A.; Raja, M.A. Chapter 6—Advanced Oxidation and Reduction Processes. In Advances in Water Purification Techniques; Ahuja, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 135–164. [Google Scholar]
- Saharan, V.K.; Pinjari, D.V.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. Chapter 3—Advanced Oxidation Technologies for Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. In Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse; Ranade, V.V., Bhandari, V.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 141–191. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Duan, S.; Li, L.; Qiang, Z. Chapter 19—Sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes for industrial wastewater treatment. In Integrated and Hybrid Process Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Mohammad, A.W., Ang, W.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 431–462. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Shah, M.P. 1—Advanced oxidation processes for complex wastewater treatment. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Effluent Treatment Plants; Shah, M.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Damodhar, G.; Prabir, G. Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Powerful Treatment Option for the Removal of Recalcitrant Organic Compounds. In Advanced Oxidation Processes; Ciro, B.-L., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Bláha, L. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of cyanobacterial toxins from drinking water. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpaud, B.; Al-Shukry, R.; Casteignau, M.; Matejka, G. Adsorption des métaux lourds (Cu, Zn, Cd et Pb) par les sédiments superficiels d’un cours d’eau: Rôle du pH, de la température et de la composition du sédiment. J. Water Sci. 1994, 7, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, C.A.; McSweeney, K.; Lowery, B. Atrazine Adsorption in Sandy Soils of Wisconsin. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Jaldin, H.P.; Blanco-Flores, A.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Martín-Hernández, O. Influence of the chain length of surfactant in the modification of zeolites and clays. Removal of atrazine from water solutions. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zezulka, Š.; Kummerová, M.; Babula, P.; Váňová, L. Lemna minor exposed to fluoranthene: Growth, biochemical, physiological and histochemical changes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Zhang, J.; Wei, R.; Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, B. Effect of organic pollutants stresses on antioxidant defense system of duckweed (Lemna minor). Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 3296–3300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, B.; Song, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Responses and toxin bioaccumulation in duckweed (Lemna minor) under microcystin-LR, linear alkybenzene sulfonate and their joint stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 229, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Depuydt, S.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.; Kim, G.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, J.T.; Han, T.; Park, J. Assessment of Various Toxicity Endpoints in Duckweed (Lemna minor) at the Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Levels as a Measure of Diuron Stress. Biology 2021, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, M.; Neale, P.A.; Nidumolu, B.; Kumar, A. Combined toxicity of therapeutic pharmaceuticals to duckweed, Lemna minor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltauskaite, J.; Sujetoviene, G.; Cypaite, A.; Auzbikaviciute, A. Lemna Minor as a Tool for Wastewater Toxicity Assessment and Pollutants Removal Agent. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference “Environmental Engineering”; Vilnius, Lithuania, 22–23 May 2014.
- Fekete-Kertész, I.; Kunglné-Nagy, Z.; Gruiz, K.; Magyar, Á.; Farkas, É.; Molnár, M. Assessing toxicity of organic aquatic micropollutants based on the total chlorophyll content of Lemna minor as a sensitive endpoint. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2015, 59, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białk-Bielińska, A.; Grabarczyk, Ł.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Puckowski, A.; Stolte, S.; Stepnowski, P. Mixture toxicity of six pharmaceuticals towards Aliivibrio fischeri, Daphnia magna, and Lemna minor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26977–26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, O.; Stanković, S.; Stanojević, O.; Vujčić, Z.; Dojnov, B.; Trifunović-Momčilov, M.; Marković, M. Antioxidative responses of duckweed (Lemna minor L.) to phenol and rhizosphere-associated bacterial strain hafnia paralvei c32-106/3. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Dermastia, M.; Koce, J.D.; Zrimec, A. Oxidative stress in duckweed (Lemna minor L.) caused by short-term cadmium exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Ursu, A.-V.; Nistor, D.; Sajin, T.; Assaad, E.; Roy, R. TPD study of the reversible retention of carbon dioxide over montmorillonite intercalated with polyol dendrimers. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 496, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Levavasseur, G. Analyse comparée des complexes pigment-protéines de chlorophycophytes marines benthiques. Phycologia 1989, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordjiba, O.; Ketif, A. Effect of three pesticides (Hexaconazole, Bromuconazole and Fluazifop-p butyl) on some biochemical metabolites of the hard wheat: Triticum durum. Desf. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 36, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Török, A.; Buta, E.; Indolean, C.; Tonk, S.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, L.; Majdik, C. Biological removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous solution by Lemna minor. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yoo, H.; Ahn, C.; Narantuya, L. Extractions of Chlorophyll from Spinach and Mate Powders and Their Dyeability on Fabrics. J. Korean Soc. Cloth. Text. 2013, 37, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, R.; Arzani, A.; Maibody, S.A.M.M.; Rahimmalek, M.; Razavi, K. Morpho-Physiological and Gene Expression Responses of Wheat by Aegilops cylindrica Amphidiploids to Salt Stress; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.; Buschmann, C. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Measurements and characterization by UV-Vis spectroscopy. In Food Analytical Chemistry: Pigments, Colorants, Flavors, Texture and Bioactive Food Components; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sulpizi, M.; Gaigeot, M.-P.; Sprik, M. The Silica–Water Interface: How the Silanols Determine the Surface Acidity and Modulate the Water Properties. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Arus, V.A.; Platon, N.; Nistor, I.D. Lactic Acid Retention by CO3-Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Improved Milk Clotting-An approach through acidity measurements. Rev. Chim. 2016, 67, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Boudissa, F.; Mirila, D.; Arus, V.A.; Terkmani, T.; Semaan, S.; Proulx, M.; Nistor, I.D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Acid-treated clay catalysts for organic dye ozonation-Thorough mineralization through optimum catalyst basicity and hydrophilic character. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, D.; Moheb, A.; Abbas, R.; Larouk, S.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Total mineralization of sulfamethoxazole and aromatic pollutants through Fe2+-montmorillonite catalyzed ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekkari, M.; Ouargli-Saker, R.; Boudissa, F.; Lachachi, A.K.; El Houda Sekkal, K.N.; Tayeb, R.; Boukoussa, B.; Azzouz, A. Silica-catalyzed ozonation of 17α -ethinyl-estradiol in aqueous media-to better understand the role of silica in soils. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benghaffour, A.; Foka-Wembe, E.-N.; Dami, M.; Dewez, D.; Azzouz, A. Insight into natural medium remediation through ecotoxicity correlation with clay catalyst selectivity in organic molecule ozonation. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 4366–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkenberg, M.; Brandt, F.; Baeyens, B.; Bosbach, D.; Fernandes, M.M. Adsorption of barium and radium on montmorillonite: A comparative experimental and modelling study. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 135, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Montmorillonite Intercalation Compounds with Quaternary Ammonium Surfactant: Adsorption Effect of Zearalenone. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 167402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, S.B. Base Exchange of the Clay Mineral Montmorillonite for Organic Cations and its Dependence upon Adsorption due to van der Waals Forces. J. Phys. Chem. 1941, 45, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Nousir, S.; Platon, N.; Ghomari, K.; Hersant, G.G.; Bergeron, J.-Y.; Shiao, T.C.; Rej, R.; Roy, R. Preparation and characterization of hydrophilic organo-montmorillonites through incorporation of non-ionic polyglycerol dendrimers derived from soybean oil. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3466–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, T.; Leila, M.; Sabrina, B.; Sbartaï, H.; Djebar, M.-R. Effects of the herbicide calliofop 36EC on growth, antioxidant enzyme response and respiratory metabolism in two aquatic plant elodea canadensis and lemna minor. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2012, 6, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar]
- Lemanceau, P.; Alabouvette, C.; Couteaudier, Y. Recherches sur la résistance des sols aux maladies. XIV. Modification du niveau de réceptivité d’un sol résistant et d’un sol sensible aux fusarioses vasculaires en réponse à des apports de fer ou de glucose. Agronomie 1988, 8, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briat, J.-F. Une santé de fer pour les plantes. Biofutur 1998, 1998, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briat, J.-F.; Vert, G. Acquisition et gestion du fer par les plantes. Cah. Agric. 2004, 13, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Arus, V.A.; Nousir, S.; Sennour, R.; Shiao, T.C.; Nistor, I.D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Intrinsic affinity of acid-activated bentonite towards hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 7964–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahr, G.; Madsen, F.T. Determination of the cation exchange capacity and the surface area of bentonite, illite and kaolinite by methylene blue adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 9, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonheydt, R.A.; Johnston, C.T. Chapter 3 Surface and Interface Chemistry of Clay Minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Theng, B.K.G., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. Chapter 1 General Introduction: Clays, Clay Minerals, and Clay Science. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Theng, B.K.G., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]


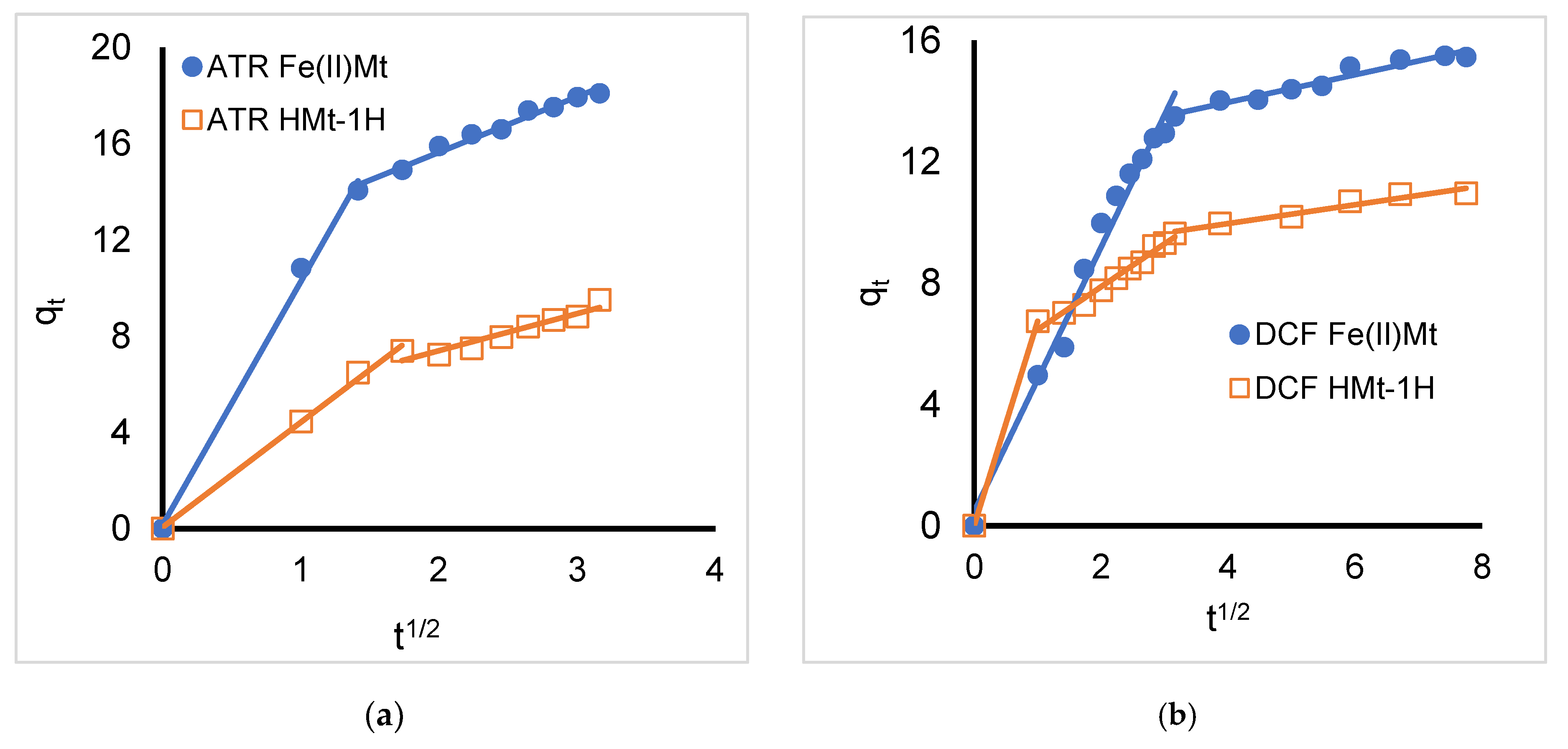
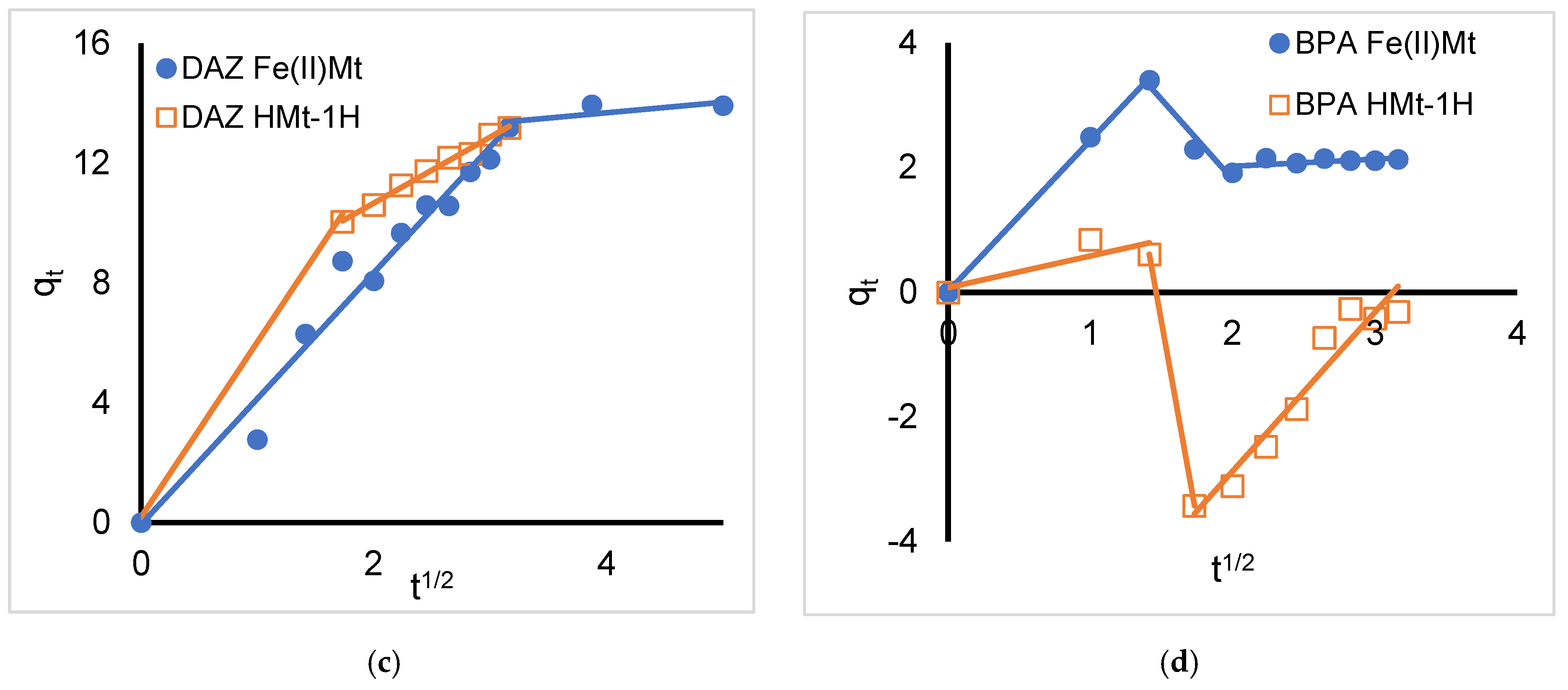
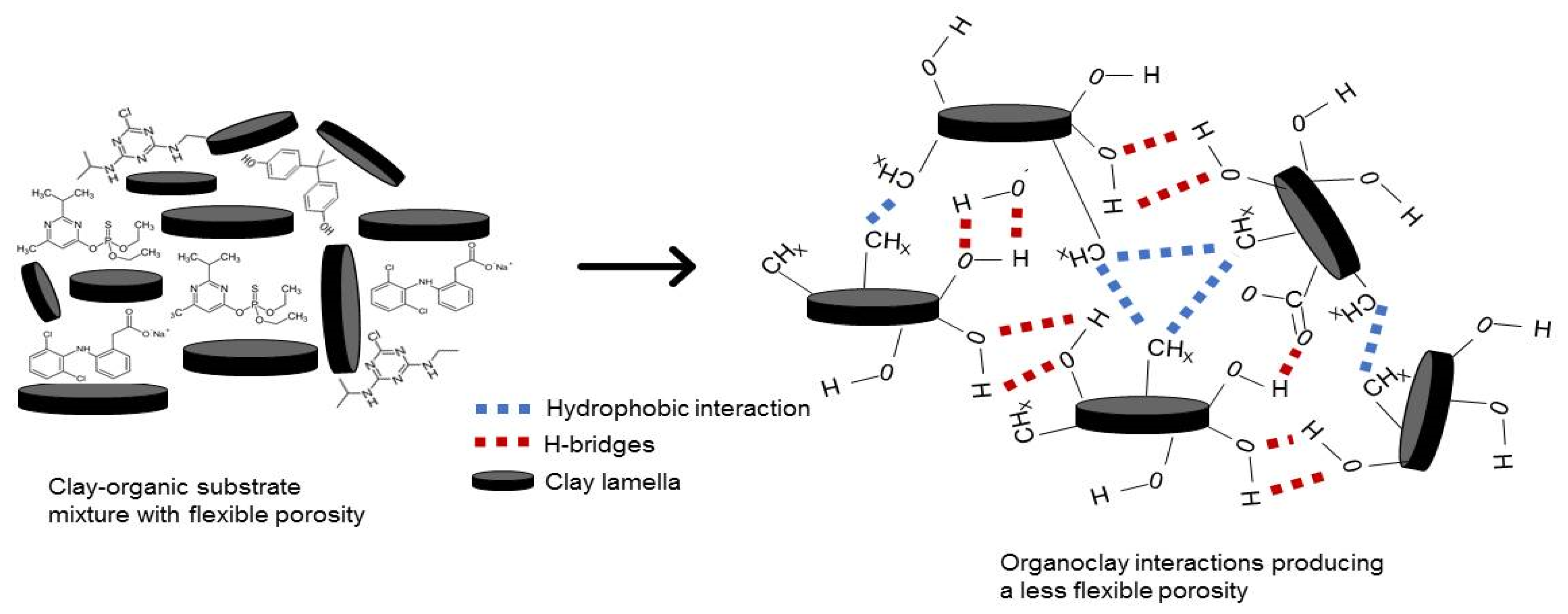
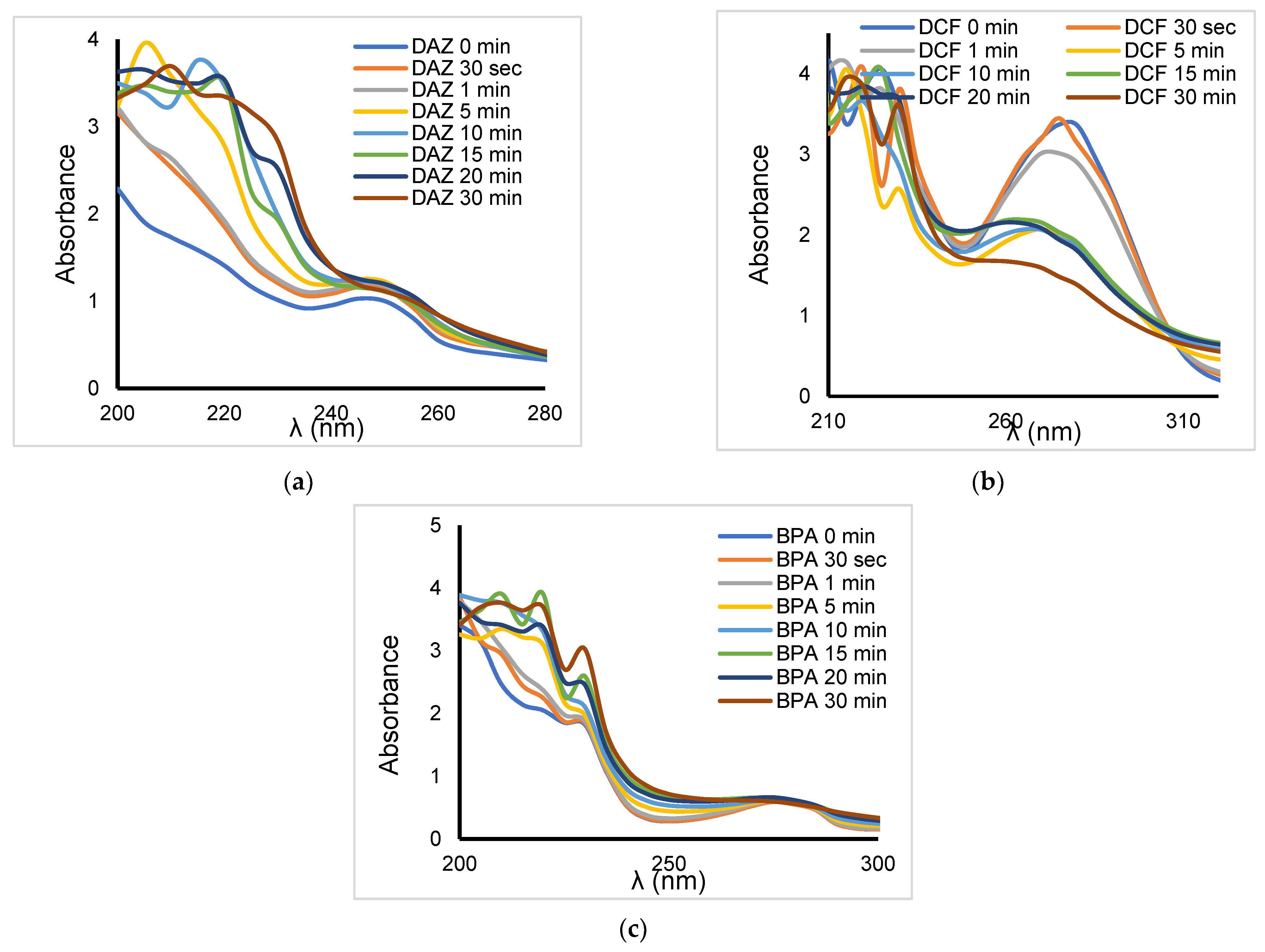





| Organic Compound | Atrazine * | Bisphenol A | Diazinon | Diclofenac Sodium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acronym | ATR | BPA | DAZ | DCF |
| IUPAC denotation | 1-Chloro-3-ethylamino-5-isopropylamino-2,4,6-triazine | 4,4′-(propane-2,2-diyl) diphenol | O,O-Diethyl O-[4-methyl-6-(propan-2-yl) pyrimidin-2-yl] phosphonothioate | Sodium salt of 2-[2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-aminophenyl]-ethanoic acid |
| Formula | C8H14ClN5 | C15H16O2 | C12H21N2O3PS | C14H10Cl2NNaO2 |
| (O + Cl))/C atom ratio | 1/8 = 0.125 | 2/15 = 0.133 | 3/12 = 0.25 | 4/14 = 0.286 |
| Structures |  |  |  |  |
| Application | Herbicide | Plasticizer | Insecticide | Anti-inflammatory drug |
| pKa | 1.60 | 9.6 | 2.6 | 4.2 |
| λmax (nm) | 220 | 275 | 250 | 275 |
| Solubility in water (mg L−1) | 34.7 | 300 | 40 | 50 |
| Molar weight (g mol−1) | 215.68 | 228.29 | 304.35 | 296.15 |
| Solution concentration (mmol L−1) ** | 139.09 | 131.41 | 98.57 | 101.30 |
| Intrinsic pH of the solution | 5.79 | 5.49 | 5.48 | 4.78 |
| Mixture Components | Pseudo-1st Order | Pseudo-2nd Order | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Substrate | Clay Material | k1 (min−1) | R12 | k2 (L (mg−1 min−2) | R22 |
| DAZ | Fe(II)Mt | 0.0790 | 0.9332 | 0.01151 | 0.8919 |
| HMt-1 | 0.0539 | 0.8311 | 0.04167 | 0.9865 | |
| CaMt | 0.0170 | 0.0291 | 0.04239 | 0.7441 | |
| KMt | 0.0016 | 0.0080 | 0.00021 | 0.7656 | |
| DCF | Fe(II)Mt | 0.0852 | 0.9302 | 0.01595 | 0.9463 |
| HMt-1 | 0.0539 | 0.6221 | 0.04167 | 0.9685 | |
| CaMt | 0.0014 | 0.0097 | 0.02154 | 0.9849 | |
| KMt | 0.0067 | 0.2947 | 0 | - | |
| ATR | Fe(II)Mt | 0.1308 | 0.8083 | 0.06413 | 0.9949 |
| HMt-1 | 0.0408 | 0.7920 | 0.02034 | 0.9813 | |
| CaMt | 0.0025 | 0.2248 | 0 | - | |
| KMt | 0.0032 | 0.1925 | 0 | - | |
| BPA | Fe(II)Mt | 0.1587 | 0.4991 | 0.42940 | 0.9996 |
| HMt-1 | −0.0014 | 0.0049 | 0 | - | |
| CaMt | −0.0267 | 0.7055 | - | - | |
| KMt | −0.0203 | 0.1997 | - | - | |
| ATR | DAZ | DCF | BPA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(II)Mt | K1 | 10.108 | 4.2014 | 4.3657 | 2.4242 |
| C1 | 0.1618 | 0.0571 | 0.4583 | 0.0146 | |
| R12 | 0.9955 | 0.9693 | 0.9818 | 0.9994 | |
| K2 | 2.312 | 0.3531 | 0.4543 | 2.5658 | |
| C2 | 11.017 | 12.273 | 12.147 | 6.9438 | |
| R22 | 0.9807 | 0.5877 | 0.9474 | 0.9486 | |
| K3 | - | - | - | 0.1141 | |
| C3 | - | - | - | 1.7951 | |
| R32 | - | - | - | 0.3465 | |
| HMt-1 | K1 | 4.3626 | 5.8454 | 6.7404 | 0.5075 |
| C1 | 0.062 | 0.1894 | 0 | 0.0764 | |
| R12 | 0.9961 | 0.9948 | 1 | 0.7163 | |
| K2 | 1.5403 | 2.2026 | 1.4159 | −12.693 | |
| C2 | 4.3201 | 6.266 | 5.0498 | 18.56 | |
| R22 | 0.912 | 0.9916 | 0.9785 | 1 | |
| K3 | - | - | 0.3102 | 2.5499 | |
| C3 | - | - | 8.7244 | −7.968 | |
| R32 | - | - | 0.9487 | 0.9331 |
| Organic Species | Clay Mineral | Langmuir’s Model | Freundlich’s Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax | KL | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | ||
| ATR | Fe(II)Mt | 30.0 | 0.0799 | 0.9016 | 0.6109 | 3.3146 | 0.8085 |
| HMt-1 | 7.9 | 0.1891 | 0.9748 | 0.6501 | 2.1144 | 0.9375 | |
| BPA * | Fe(II)Mt | 12.4 | 0.0060 | 0.8716 | 1.1158 | 0.0543 | 0.8243 |
| HMt-1 | 0.81 | 0.0246 | 0.0977 | 0.1543 | 1.4260 | 0.0736 | |
| DAZ | Fe(II)Mt | 3.95 | 0.0386 | 0.9992 | 1.6455 | 0.0651 | 0.9756 |
| HMt-1 | 1.24 | 0.0341 | 0.9992 | 1.8359 | 0.0114 | 0.9594 | |
| DCF | Fe(II)Mt | 34.1 | 0.0080 | 0.9962 | 1.096 | 0.2475 | 0.9912 |
| HMt-1 | 28.2 | 0.0237 | 0.9563 | 0.7972 | 0.8327 | 0.9178 | |
| Organic Species | No Clay Mineral | Fe(II)Mt | HMt-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Removal b | Derivative Number | % Adsorption a | % Removal b | Derivative Number | % Adsorption a | % Removal b | Derivative Number | |
| ATR | - | 80.40 | - | - | 42.40 | - | - | |
| DAZ | 99.50 | 3 | 58.70 | 92.10 | 4 | 58.60 | 93.19 | 4 |
| DCF | 97.50 | 1 | 60.00 | 98.60 | 2 | 43.00 | 100.00 | 3 |
| BPA | 90.00 | 4 | 9.50 | 99.20 | 3 | 0.00 | 99.97 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foka Wembe, E.N.; Benghafour, A.; Dewez, D.; Azzouz, A. Clay-Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants in Water and Toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of Molecular Structure and Interactions. Molecules 2023, 28, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010222
Foka Wembe EN, Benghafour A, Dewez D, Azzouz A. Clay-Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants in Water and Toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of Molecular Structure and Interactions. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010222
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoka Wembe, Eric Noel, Amina Benghafour, David Dewez, and Abdelkrim Azzouz. 2023. "Clay-Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants in Water and Toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of Molecular Structure and Interactions" Molecules 28, no. 1: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010222
APA StyleFoka Wembe, E. N., Benghafour, A., Dewez, D., & Azzouz, A. (2023). Clay-Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants in Water and Toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of Molecular Structure and Interactions. Molecules, 28(1), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010222





