Metal-Free Aerobic C–N Bond Formation of Styrene and Arylamines via Photoactivated Electron Donor–Acceptor Complexation
Abstract
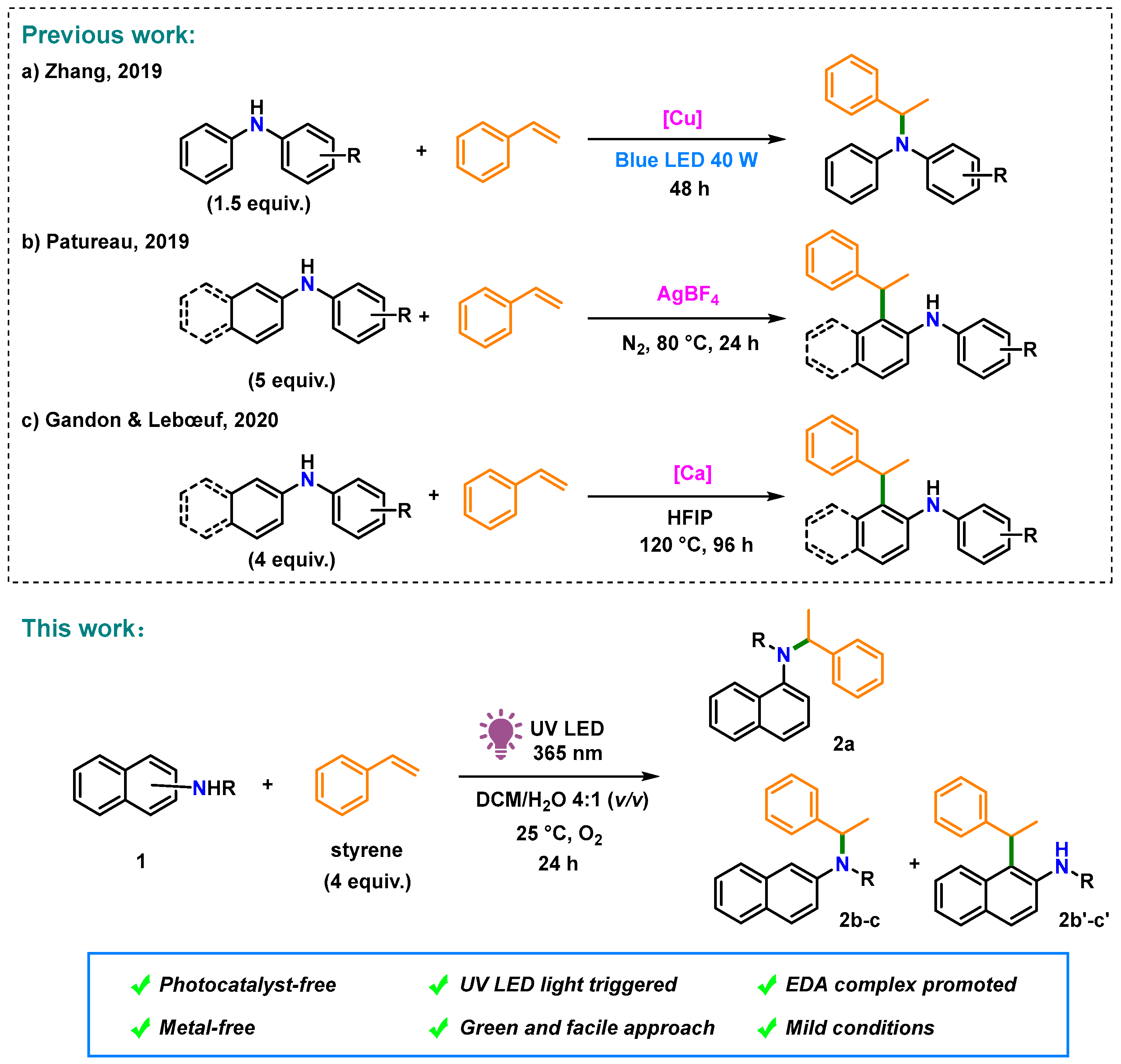
:1. Introduction
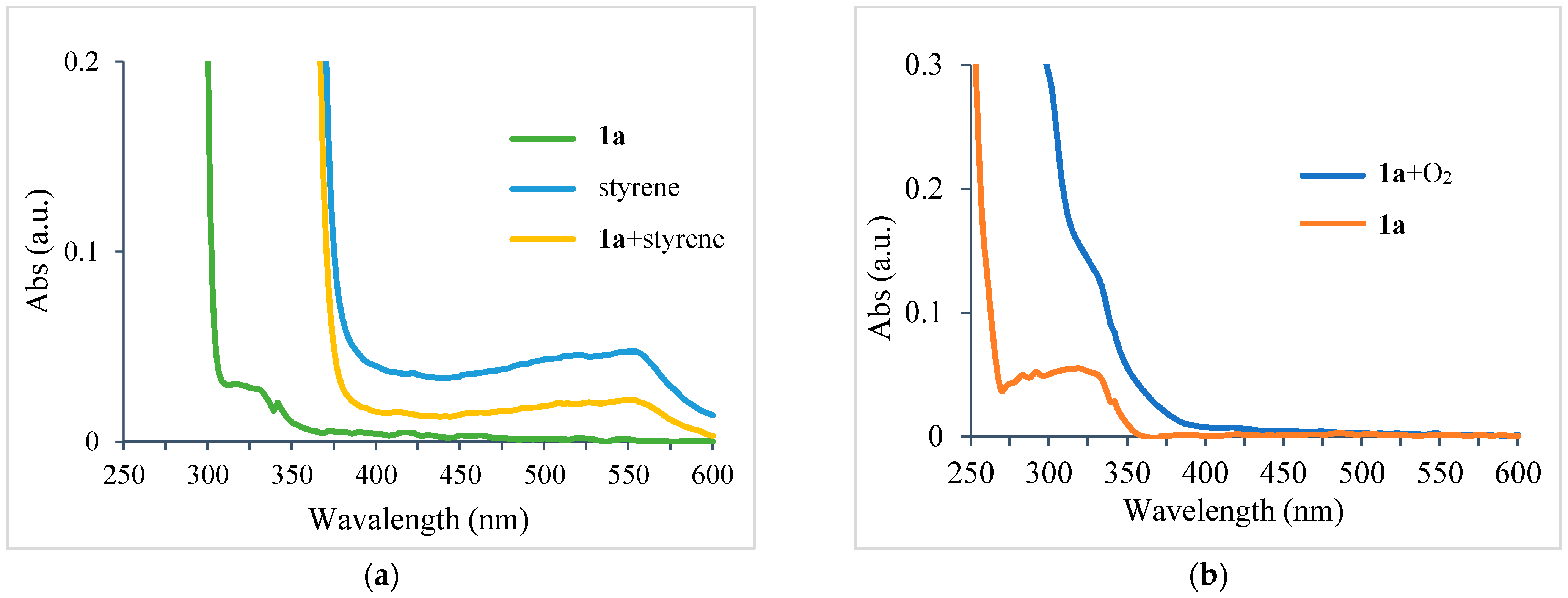
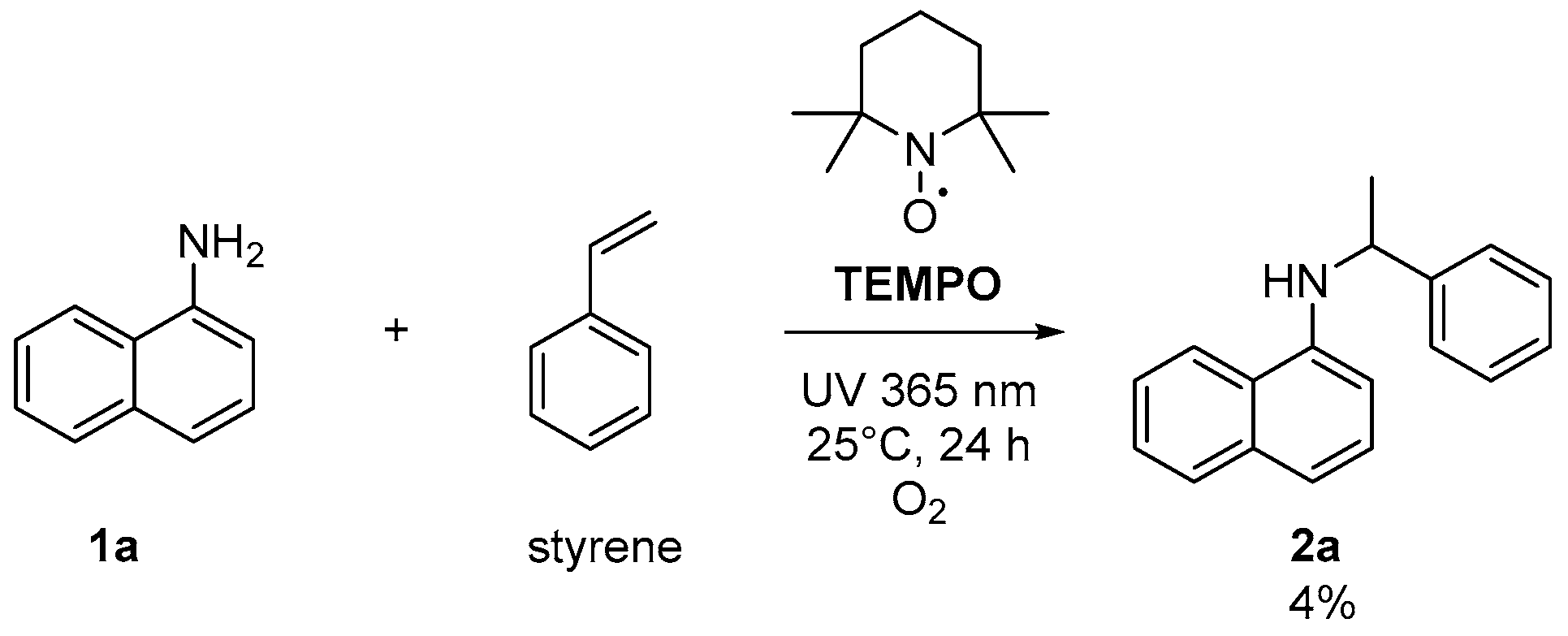
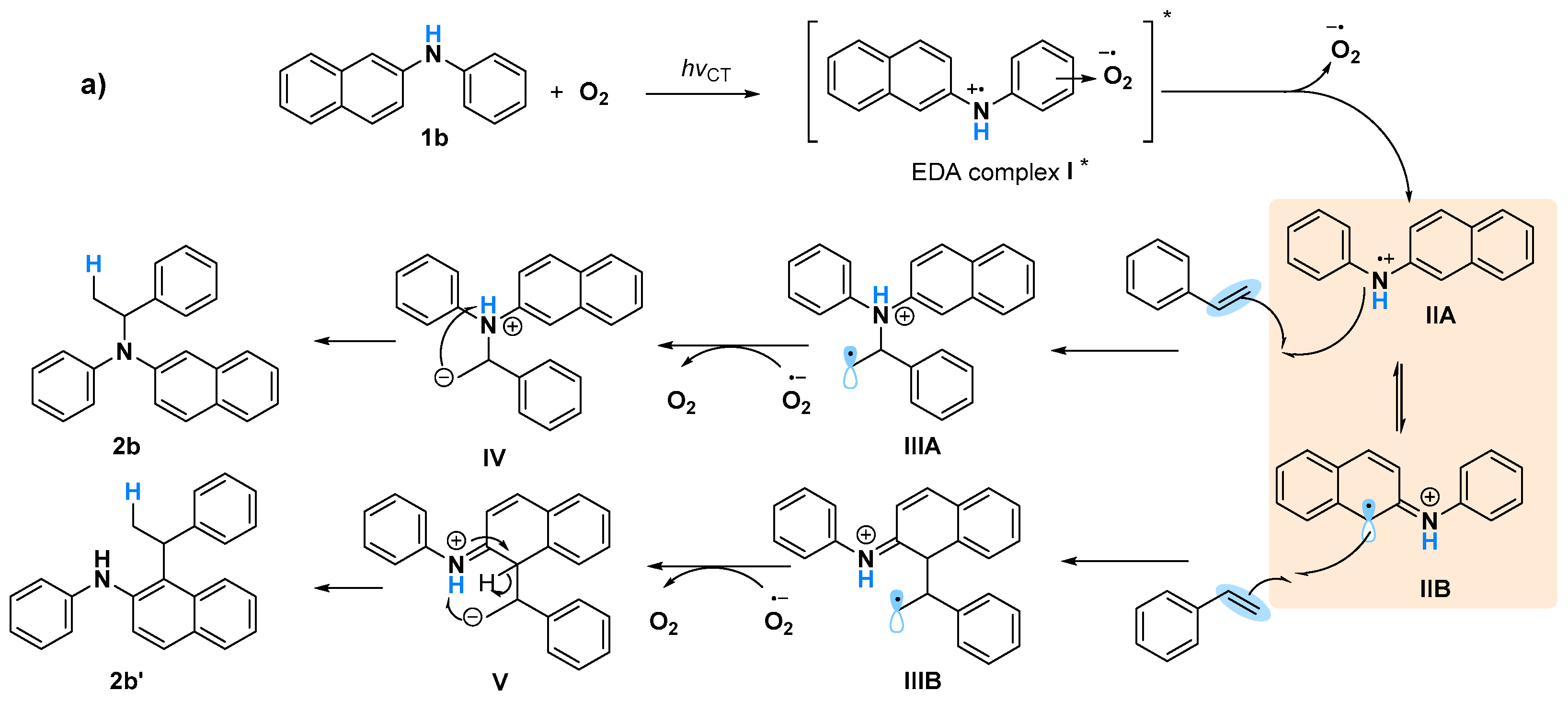
2. Results and Discussions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Spectroscopy and Spectrometry
3.2.2. Synthetic Procedure of N-methylnaphthalen-2-amine (1c)
3.2.3. General Protocol for the Photocatalytic Hydroamination of Styrene
N-(1-Phenylethyl)naphthalen-1-amine (2a)
N-Phenyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)naphthalen-2-amine (2b)
N-Phenyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)naphthalen-2-amine (2b’)
N-Methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)naphthalen-2-amine (2c)
N-Methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)naphthalen-2-amine (2c’)
3.2.4. Procedure for “ON-OFF” Experiment
3.2.5. Procedures for UV–Vis Absorbance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, T.E.; Beller, M. Metal-Initiated Amination of Alkenes and Alkynes. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 675–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, J.F. Evolution of a Fourth Generation Catalyst for the Amination and Thioetherification of Aryl Halides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, J.; Murakami, K.; Itami, K. Catalytic Methods for Aromatic C–H Amination: An Ideal Strategy for Nitrogen-Based Functional Molecules. ACS Catal. 2015, 6, 610–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Reif, P.; Palenicek, P.; Rose, M. Toward Renewable Amines: Recent Advances in the Catalytic Amination of Biomass-Derived Oxygenates. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 10400–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.E.; Hultzsch, K.C.; Yus, M.; Foubelo, F.; Tada, M. Hydroamination: Direct Addition of Amines to Alkenes and Alkynes. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3795–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Cortés, P.A.; Haydl, A.M. The 25th Anniversary of the Buchwald–Hartwig Amination: Development, Applications, and Outlook. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Castillo, P.; Buchwald, S.L. Applications of Palladium-Catalyzed C-N Cross-Coupling Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coman, S.M.; Parvulescu, V.I. Nonprecious Metals Catalyzing Hydroamination and C–N Coupling Reactions. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1327–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Arndt, M.; Goossen, K.; Heydt, H.; Goossen, L.J. Late transition metal-catalyzed hydroamination and hydroamidation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2596–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawatsura, M.; Hartwig, J.F. Palladium-Catalyzed Intermolecular Hydroamination of Vinylarenes Using Arylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9546–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Xue, D.; Li, C.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C. Iron-Catalyzed Anti-Markovnikov Hydroamination and Hydroamidation of Allylic Alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13506–13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorai, S.K.; Gopalsamuthiram, V.G.; Jawalekar, A.M.; Patre, R.E.; Pal, S. Iron catalyzed C N bond formation. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 1769–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, W. Recent advances in radical-based C-N bond formation via photo-/electrochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2591–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratley, C.; Fenner, S.; Murphy, J.A. Nitrogen-Centered Radicals in Functionalization of sp(2) Systems: Generation, Reactivity, and Applications in Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 8181–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganley, J.M.; Murray, P.R.D.; Knowles, R.R. Photocatalytic Generation of Aminium Radical Cations for C horizontal line N Bond Formation. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 11712–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Tan, F.; Lu, L.-Q.; Xiao, W.-J. Visible-Light-Driven Organic Photochemical Reactions in the Absence of External Photocatalysts. Synthesis 2019, 51, 3021–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahjah, R.; Gassama, A.; Dumur, F.; Marinkovic, S.; Richert, S.; Landgraf, S.; Lebrun, A.; Cadiou, C.; Selles, P.; Hoffmann, N. Photochemical electron transfer mediated addition of naphthylamine derivatives to electron-deficient alkenes. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 7104–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, R.S. Molecular Compounds and their Spectra II. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R. Electron donor-acceptor complexes. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runemark, A.; Sunden, H. Aerobic Oxidative EDA Catalysis: Synthesis of Tetrahydroquinolines Using an Organocatalytic EDA Active Acceptor. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runemark, A.; Zacharias, S.C.; Sunden, H. Visible-Light-Driven Stereoselective Annulation of Alkyl Anilines and Dibenzoylethylenes via Electron Donor-Acceptor Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.G.S.; Lima, T.M.; Duarte, M.; Jurberg, I.D.; Paixão, M.W. Organic Synthesis Enabled by Light-Irradiation of EDA Complexes: Theoretical Background and Synthetic Applications. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1389–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Horton, P.; Hursthouse, M.; Kuok, K.; Hii, K. Air- and moisture-stable cationic (diphosphine)palladium(II)complexes as hydroamination catalysts: X-ray crystal structures of two[(diphosphine)Pd(NCMe)(OH2)]2+[OTf]–2 complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 665, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, A.M.; Utsunomiya, M.; Incarvito, C.D.; Hartwig, J.F. A Highly Active Palladium Catalyst for Intermolecular Hydroamination. Factors that Control Reactivity and Additions of Functionalized Anilines to Dienes and Vinylarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Martin, D.; Melaimi, M.; Bertrand, G. Gold-catalyzed hydroarylation of alkenes with dialkylanilines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13594–13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, F.; Lerch, S.; Kaliner, M.; Strassner, T. Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydroarylations and Hydroaminations of Alkenes in Tunable Aryl Alkyl Ionic Liquids. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6215–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beller, M.; Thiel, O.R.; Trauthwein, H. Catalytic Alkylation of Aromatic Amines with Styrene in the Presence of Cationic Rhodium Complexes and Acid. Synlett 1999, 1999, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.L.; Arnold, J.; Bergman, R.G. Proton-Catalyzed Hydroamination and Hydroarylation Reactions of Anilines and Alkenes: A Dramatic Effect of Counteranions on Reaction Efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14542–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seshu Babu, N.; Mohan Reddy, K.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Suryanarayana, I.; Lingaiah, N. Intermolecular hydroamination of vinyl arenes using tungstophosphoric acid as a simple and efficient catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7642–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, G. Visible-Light-Induced Copper-Catalyzed Intermolecular Markovnikov Hydroamination of Alkenes. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, C.K.; Ozkaya, B.; Patureau, F.W. HBF4- and AgBF4-Catalyzed ortho-Alkylation of Diarylamines and Phenols. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6830–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Force, G.; Guillot, R.; Carpentier, J.-F.; Sarazin, Y.; Bour, C.; Gandon, V.; Lebœuf, D. Lewis Acid/Hexafluoroisopropanol: A Promoter System for Selective ortho-C-Alkylation of Anilines with Deactivated Styrene Derivatives and Unactivated Alkenes. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10794–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.T.; Sarralde, J.D.; SanMartin, R.; Bravo, L.; Domínguez, E. Cesium Carbonate-Promoted Hydroamidation of Alkynes: Enamides, Indoles and the Effect of Iron(III) Chloride. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 3054–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.F.; Middleton, B.S.; Ingold, K.U. Oxidation of amines with peroxy radicals. I. N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, S.B.; Huffman, J.C.; Yoder, R.A.; Coalter, J.N.; Johnston, J.N. IAN Amines: Chiral C2-Symmetric Zirconium(IV) Complexes from Readily Modified Axially Chiral C1-Symmetric β-Diketimines. Organometallics 2004, 23, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


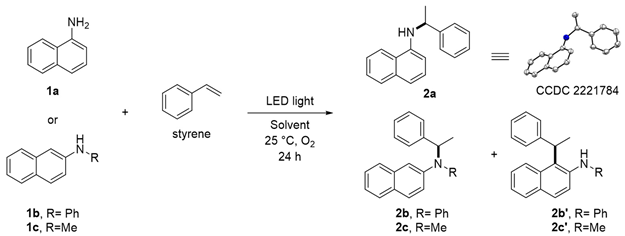 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | Molar Ratio of Substrate (1/styrene) | Wavelength Λ (nm) | Solvent | Additives | Yield a (%) |
| 1 | 1a | 1/1 | 365 | DCM b/H2O = 4/1 | - | 5 |
| 2 | 1a | 1/2 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 24 |
| 3 | 1a | 1/8 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 10 |
| 4 | 1a | 1/4 | 340 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2a: 11 |
| 5 | 1a | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2a: 61 [61 c] |
| 6 | 1a | 1/4 | 448 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | N.R.d |
| 7 | 1a | 1/4 | 365 | MeCN/H2O = 4/1 | 2a: 2 | |
| 8 | 1a | 1/4 | 365 | Acetone/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2a: 13 |
| 9 | 1a | 1/4 | 365 | EtOAc/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2a: 13 |
| 10 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | H2O | - | 2b: 8; 2b’: 26 |
| 11 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | DCM | - | 2b: 15; 2b’: 23 |
| 12 | 1b | 1/1 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2b: 7; 2b’: 7 |
| 13 | 1b | 1/2 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2b:15, 2b’: 15 |
| 14 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2b: 39, 2b’: 51 |
| 15 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | Cs2CO3 (2.0 equiv.) | 2b: 50, 2b’: 46 |
| 16 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | DBU (2.0 equiv.) | 2b: 25, 2b’: 30 |
| 17 | 1b | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | Et3N (2.0 equiv.) | 2b: 25, 2b’: 27 |
| 18 | 1b | 1/4 | 460 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | 9-fluorene (2.0 equiv.) | N.R. |
| 19 | 1b | 1/4 | 460 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | rose bengal (2.0 equiv.) | |
| 20 | 1b | 1/4 | 460 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | 4CzIPN (2.0 equiv.) | |
| 21 | 1b | 1/4 | 460 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | eosin Y (2.0 equiv.) | |
| 22 | 1c | 1/4 | 365 | DCM/H2O = 4/1 | - | 2c: 30, 2c’: 22 |
 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, D.; Sabri, A.; Sasai, H.; Takizawa, S. Metal-Free Aerobic C–N Bond Formation of Styrene and Arylamines via Photoactivated Electron Donor–Acceptor Complexation. Molecules 2023, 28, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010356
Fan D, Sabri A, Sasai H, Takizawa S. Metal-Free Aerobic C–N Bond Formation of Styrene and Arylamines via Photoactivated Electron Donor–Acceptor Complexation. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010356
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Duona, Ahmed Sabri, Hiroaki Sasai, and Shinobu Takizawa. 2023. "Metal-Free Aerobic C–N Bond Formation of Styrene and Arylamines via Photoactivated Electron Donor–Acceptor Complexation" Molecules 28, no. 1: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010356








