Updates on Plant-Based Protein Products as an Alternative to Animal Protein: Technology, Properties, and Their Health Benefits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Types of Plant-Based Protein Products as Alternatives to Animal Proteins
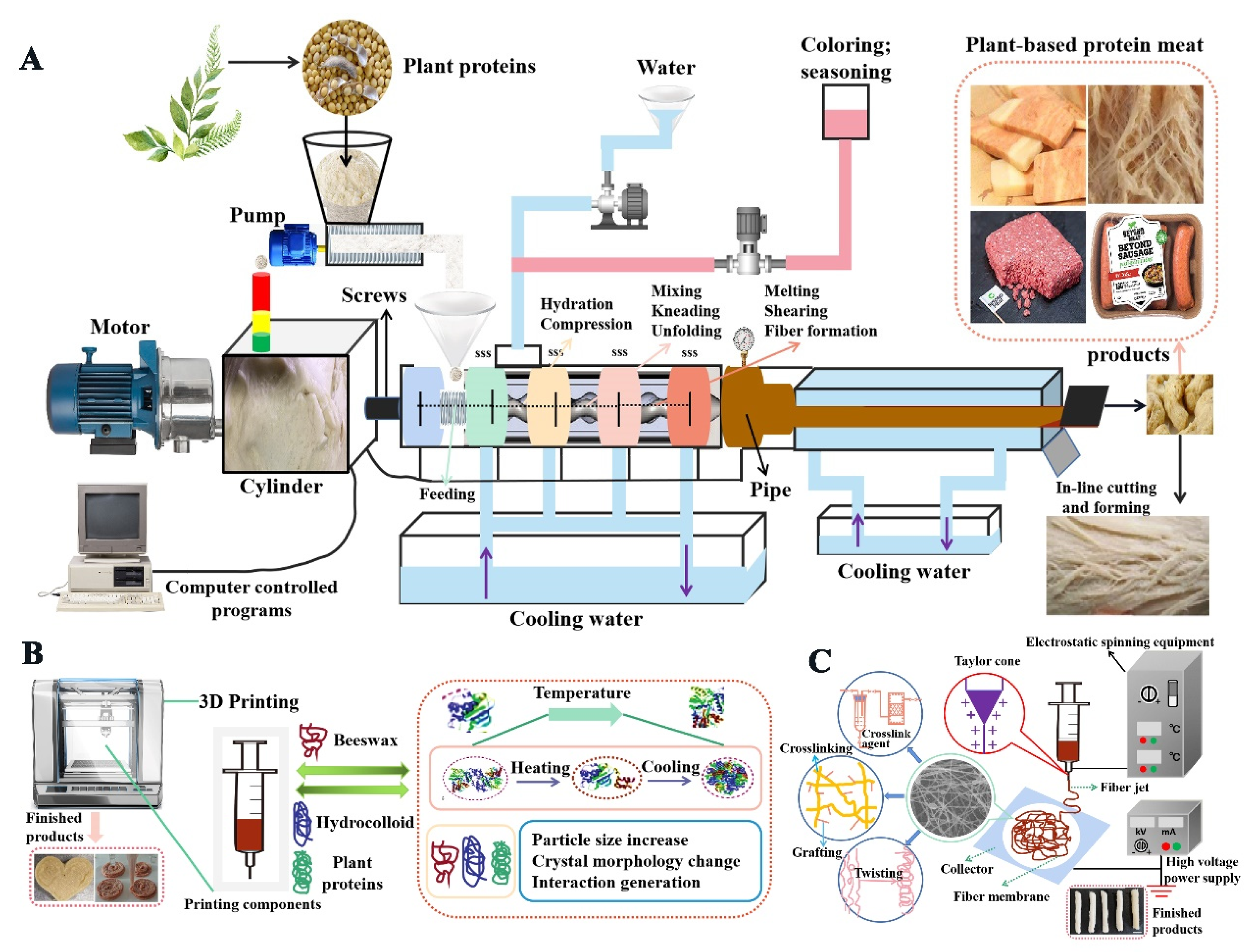
2.1. Plant-Based Protein Meat
2.2. Plant-Based Milk
2.3. Plant-Based Egg Simulation Products
2.4. Plant-Based Protein Emulsion Foods
3. Technologies used for Improving the Functional Properties of Plant-Based Proteins
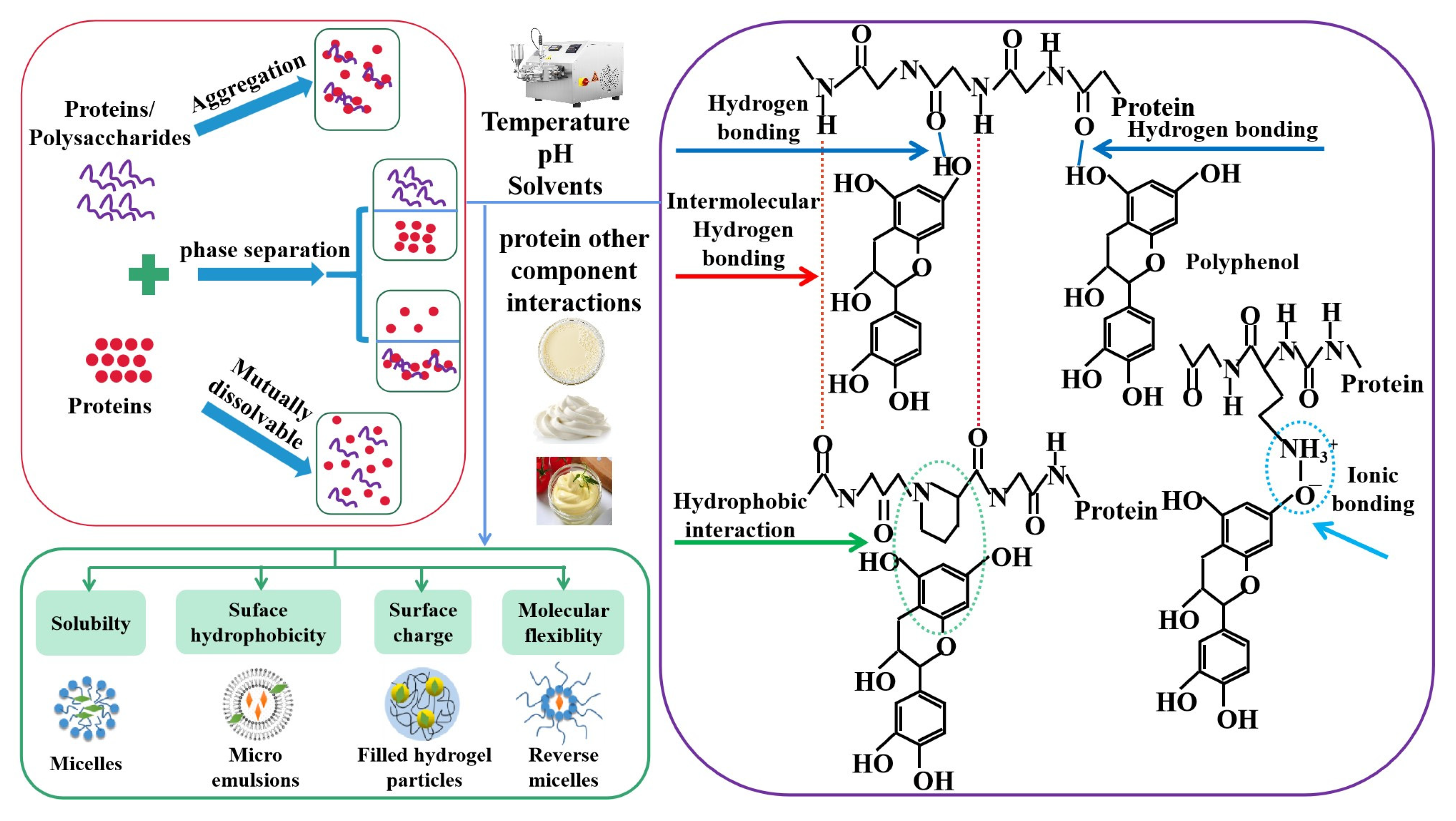
3.1. Protein–Protein, Protein–Polysaccharide, Protein–Other Component Interactions
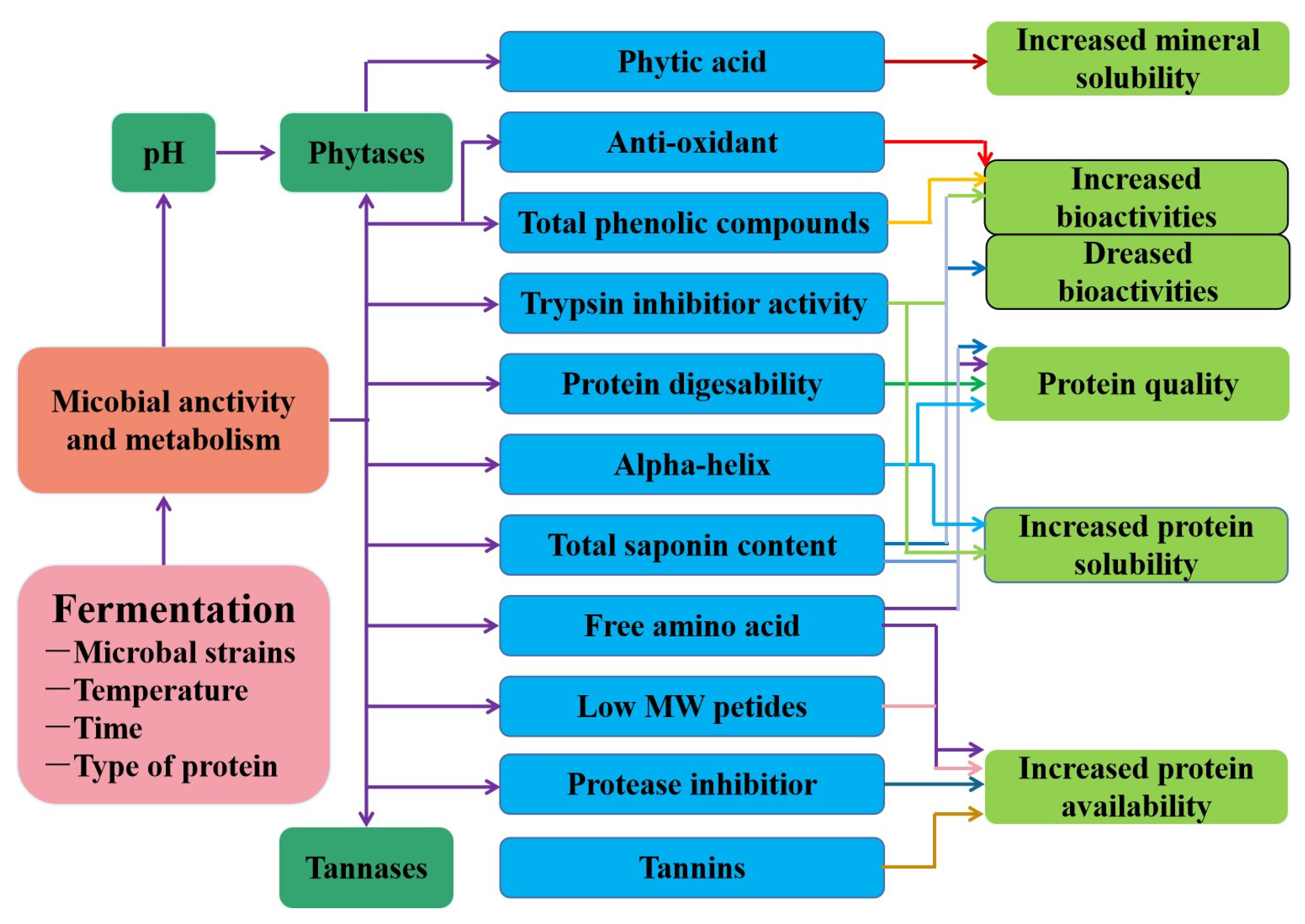
3.2. Fermentation
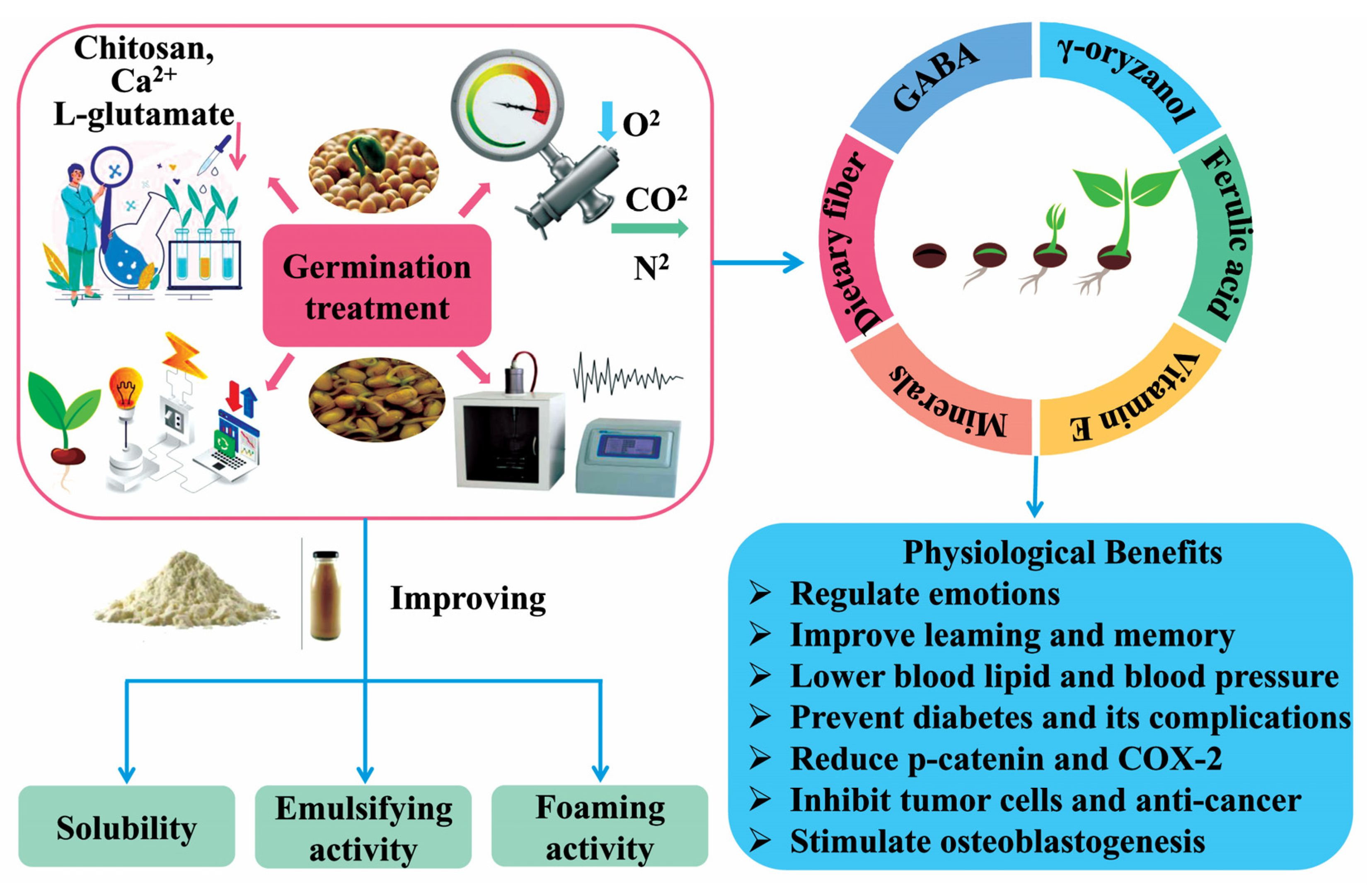
3.3. Germination
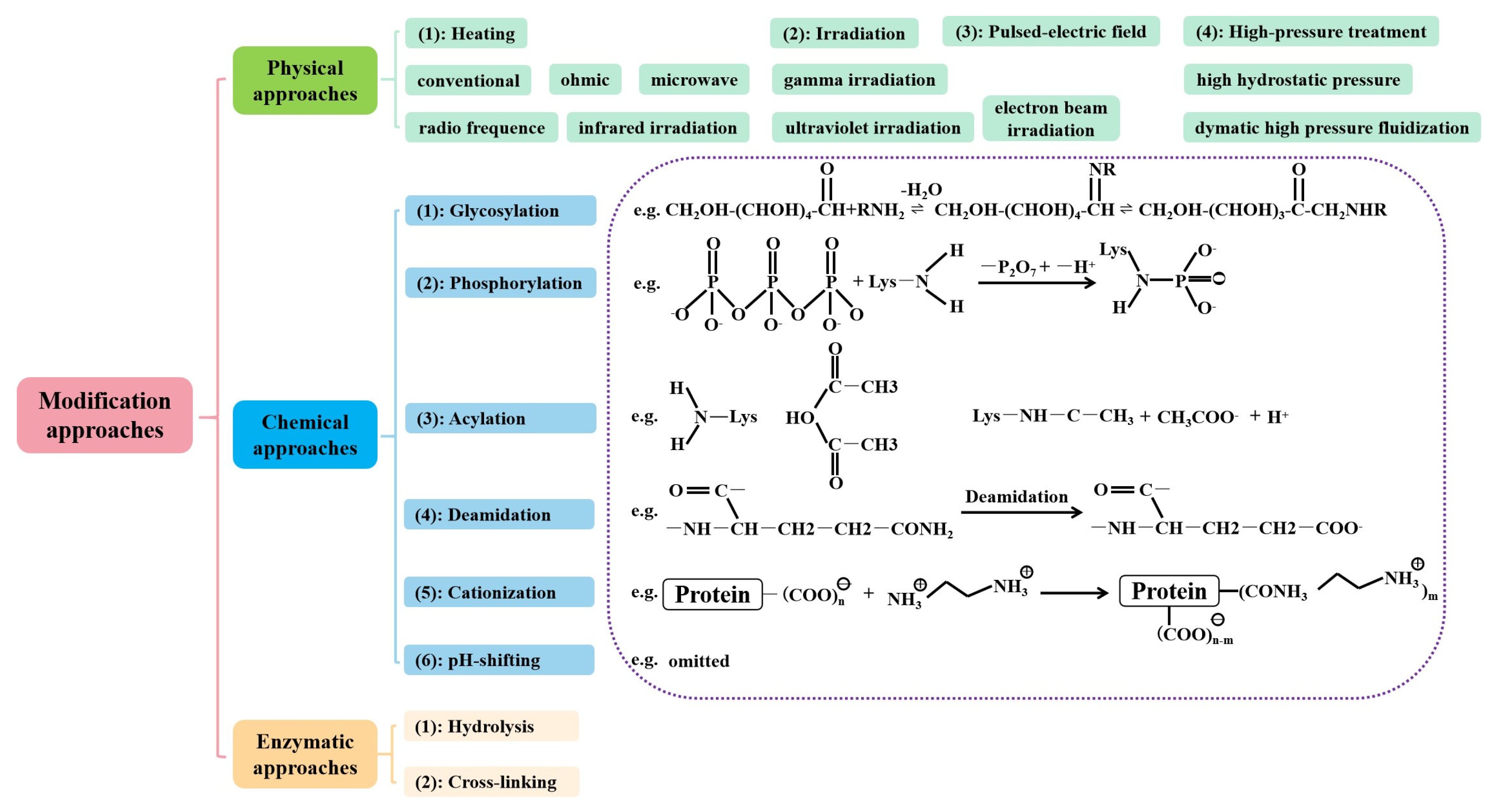
3.4. Physical, Chemical, and Enzyme Modification
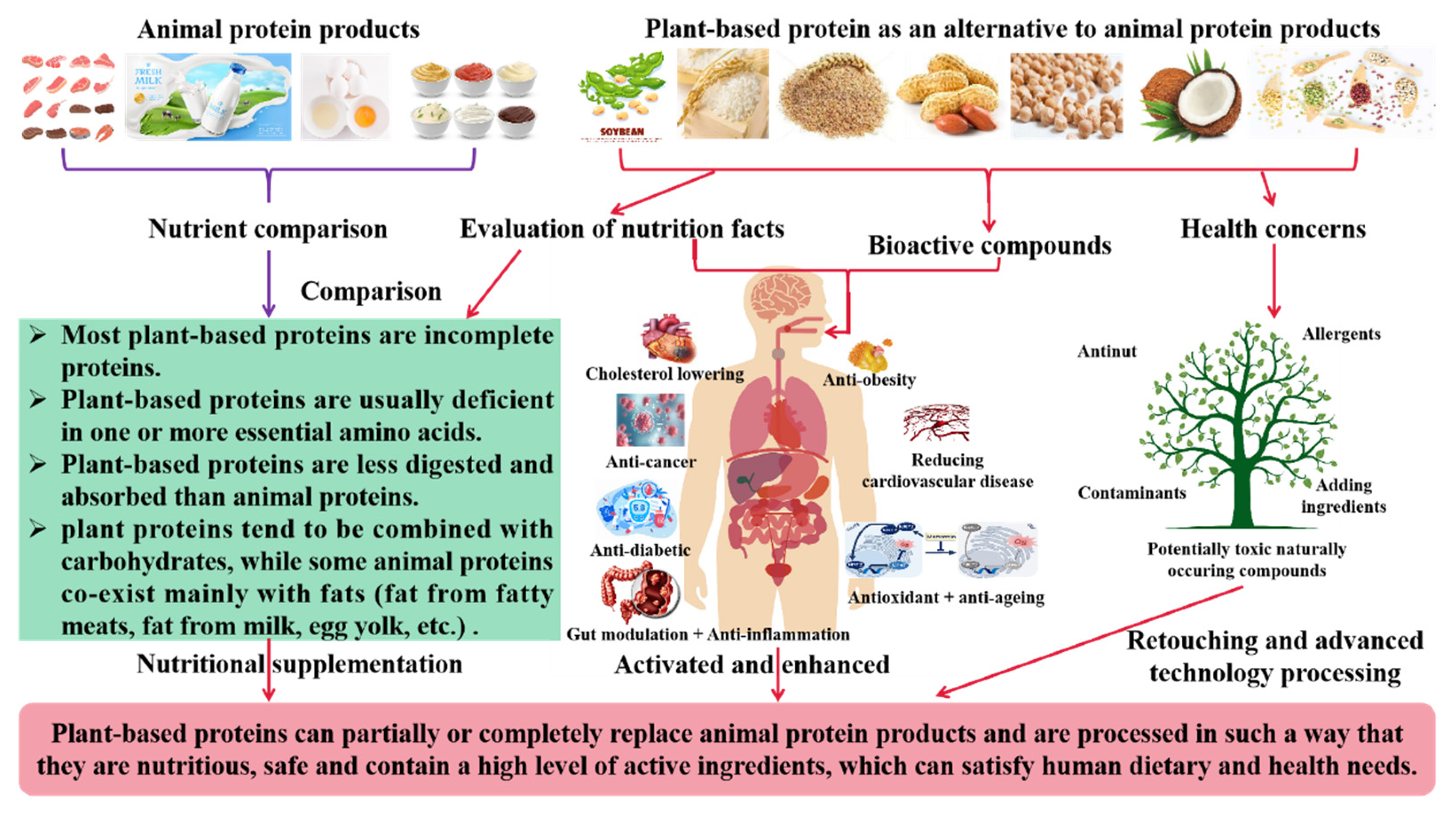
4. Health Benefits of Plant-Based Protein Products
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, W.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, T. Design of novel edible hydrocolloids by structural interplays between wheat gluten proteins and soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappi, J.; Silventoinen-Veijalainen, P.; Vanhatalo, S.; Rosa-Sibakov, N.; Sozer, N. The nutritional quality of animal-alternative processed foods based on plant or microbial proteins and the role of the food matrix. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 129, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Dietary fats and the gut microbiota: Their impacts on lipid-induced metabolic syndrome. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 91, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Heras-Delgado, S.; Shyam, S.; Cunillera, È.; Dragusan, N.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Babio, N. Are plant-based alternatives healthier? A two-dimensional evaluation from nutritional and processing standpoints. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauk, C.; Kaufmann, L.; Theurl, M.C.; Wittmann, F.; Eder, M.; Hortenhuber, S.; Freyer, B.; Krausmann, F. Demand side options to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the land footprint of urban food systems: A scenario analysis for the City of Vienna. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alae-Carew, C.; Green, R.; Stewart, C.; Cook, B.; Dangour, A.D.; Scheelbeek, P.F.D. The role of plant-based alternative foods in sustainable and healthy food systems: Consumption trends in the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.X.; Shen, P. Associations of dietary protein intake with all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.S.; Feng, J.Y.; Ni, Z.J.; Ma, R.H.; Thakur, K.; Wang, S.Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. An update on the nutritional, functional, sensory characteristics of soy products, and applications of new processing strategies. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 112, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, L.; Umberger, W.J. Protein source matters: Understanding consumer segments with distinct preferences for alternative proteins. Future Foods. 2023, 7, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghian, S.; McClements, D.J.; Khalesi, M.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Mirzapour-Kouhdasht, A. Digestibility and bioavailability of plant-based proteins intended for use in meat analogues: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 129, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, D.M.; Mendes, G.D.L.; Lucas, A.J.D.; Christ-Ribeiro, A.; Ribeiro, C.D.F. Exploring alternative protein sources: Evidence from patents and articles focusing on food markets. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogari, G.; Caputo, V.; Petterson, A.J.; Mora, C.; Boukid, F. A Sensory Study on Consumer Valuation for Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: What is liked and disliked the most? Food Res. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Chen, F.; Zhao, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, B. Identifying changes in soybean protein properties during high-moisture extrusion processing using dead-stop operation. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lyu, B.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Ji, L.; Gong, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, H. The development process of plant-based meat alternatives: Raw material formulations and processing strategies. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.T.; Cai, L.L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, C.B. Real meat and plant-based meat analogues have different in vitro protein digestibility properties. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. The development history and recent updates on soy protein-based meat alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 109, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Jr, J.; Stout, A.J.; Rubio, N.R.; Chen, Y.; Kaplan, D.L. 3D porous scaffolds from wheat glutenin for cultured meat applications. Biomaterials 2022, 285, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zou, P.R.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Khan, M.R.; Busquets, R.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Wheat gluten proteins phosphorylated with sodium tripolyphosphate, changes in structure to improve functional properties for expanding applications. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.R.; Hu, F.; Ni, Z.J.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Effects of phosphorylation pretreatment and subsequent transglutaminase cross-linking on physicochemical, structural, and gel properties of wheat gluten. Food Chem. 2022, 392, 133296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.R.; Hu, F.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Rizwan Khan, M.; Busquets, R.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Hydrophilic co-assembly of wheat gluten proteins and wheat bran cellulose improving the bioavailability of curcumin. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.H.; Loveday, S.M.; Hardacre, A.K.; Parker, M.E. Effects of soy protein to wheat gluten ratio on the physicochemical properties of extruded meat analogues. Food Struct-Neth. 2019, 19, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliarti, O.; Kovis, T.J.K.; Yi, N.J. Structuring the meat analogue by using plant-based derived composites. J. Food Eng. 2021, 288, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, M.; Forghani, B.; Vate, K.N.; Abdollahi, M. Combined effects of isolation temperature and pH on functionality and beany flavor of pea protein isolates for meat analogue applications. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Dhumal, S.; Changan, S.; Senapathy, M.; Berwal, M.K.; Sampathrajan, V.; Sayed, A.A.S.; et al. Plant-based proteins and their multifaceted industrial applications. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.Z.; Sui, X.A. High moisture extrusion of soy protein and wheat gluten blend: An underlying mechanism for the formation of fibrous structures. LWT-Food Scie. Technol. 2022, 163, 113561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.A.; Silva, M.M.N.; Ribeiro, B.D. Health issues and technological aspects of plant-based alternative milk. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydar, E.F.; Tutuncu, S.; Ozcelik, B. Plant-based milk substitutes: Bioactive compounds, conventional and novel processes, bioavailability studies, and health effects. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukid, F.; Hassoun, A.; Zouari, A.; Tülbek, M.Ç.; Mefleh, M.; Aït-Kaddour, A.; Castellari, M. Fermentation for Designing Innovative Plant-Based Meat and Dairy Alternatives. Foods 2023, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Production of pulse protein ingredients and their application in plant-based milk alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 110, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapany, A.K.; Murugesan, A.; Annamalai, A.S.; Balasubramanian, A.; Shanmugam, A. An overview on ultrasonically treated plant-based milk and its properties—A Review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocker, R.; Silva, E.K. Innovative technologies for manufacturing plant-based non-dairy alternative milk and their impact on nutritional, sensory and safety aspects. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salve, A.R.; Pegu, K.; Arya, S.S. Comparative assessment of high-intensity ultrasound and hydrodynamic cavitation processing on physico-chemical properties and microbial inactivation of peanut milk. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Lee, P.R.; Yang, H. Chickpea flour and soy protein isolate interacted with κ-carrageenan via electrostatic interactions to form egg omelets analogue. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 130, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoni, A.; Grebitus, C.; Millan, E.; Asioli, D. Exploring consumers’ perceptions of plant-based eggs using concept mapping and semantic network analysis. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 94, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Jafari, S.M.; Babajafari, S.; Niakousari, M.; Mazloomi, S.M. Different food hydrocolloids and biopolymers as egg replacers: A review of their influences on the batter and cake quality. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yi, E.; Jayne, L.; Andrew, C.; Lee, P.R.; Yang, H. Effect of starch addition on the physicochemical properties, molecular interactions, structures, and in vitro digestibility of the plant-based egg analogues. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 403, 134390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Tay, S.H.; Yang, H.S.; Yang, B.; Li, H.L. Replacement of eggs with soybean protein isolates and polysaccharides to prepare yellow cakes suitable for vegetarians. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Recent Developments in Food Foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. A brief review of the science behind the design of healthy and sustainable plant-based foods. Npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.C.; Zhao, X.Z.; Liu, Y.F.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Structural and rheological properties of mung bean protein emulsion as a liquid egg substitute: The effect of pH shifting and calcium. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Vu, G.; McClements, D.J. Formulation and characterization of plant-based egg white analogs using RuBisCO protein. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, M.; Maurya, A.; Das, S.; Prasad, J.; Yadav, A.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, B.K.; Dubey, N.K.; Dwivedy, A.K. Nanoencapsulation strategies for improving nutritional functionality, safety and delivery of plant-based foods: Recent updates and future opportunities. Plant Nano Biol. 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingiardi, N.; Galante, M.; de Sanctis, M.; Spelzini, D. Are quinoa proteins a promising alternative to be applied in plant-based emulsion gel formulation? Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Ma, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, F.; Ren, F.; Wang, P.; der Meeren, V.P. Incorporating surfactants within protein-polysaccharide hybrid particles for high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs): Toward plant-based mayonnaise. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yao, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, B. Comparison of the physical stabilities and oxidation of lipids and proteins in natural and polyphenol-modified soybean protein isolate-stabilized emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Liu, Z.; Mo, H.; Hu, L.; Li, H.; Xu, D.; Chitrakar, B. Preparation of Pickering emulsion gel stabilized by tea residue protein/xanthan gum particles and its application in 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2023, 343, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.; Lopes, J.C.B.; Dias, M.M.; Barreiro, M. Pickering Emulsions Based in Inorganic Solid Particles: From Product Development to Food Applications. Molecules. 2023, 28, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzade, V.; Tehrani, M.M.; Saadatmand-Tarzjan, M. Optimization of low-cholesterol-low-fat mayonnaise formulation: Effect of using soy milk and some stabilizer by a mixture design approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Jiao, B.; Meng, S.; Fu, W.M.; Faisal, S.; Li, X.M.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, Q. Edible mayonnaise-like Pickering emulsion stabilized by pea protein isolate microgels: Effect of food ingredients in commercial mayonnaise recipe. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.J.; Yang, X.Q.; Zeng, L.H.; Qi, J.R. Physical and tribological properties of high internal phase emulsions based on citrus fibers and corn peptides. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Wan, Z.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ruan, Q.J.; Yang, X.Q. Wheat gluten-stabilized high internal phase emulsions as mayonnaise replacers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.M.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.J. Effects of wheat gluten modified by deamidation-heating with three different acids on the microstructure of model oil-in-water emulsion and rheological-physical property of ice cream. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.K.; Salgado, A.M.; Holding, D.R.; Campanella, O.H.; Hamaker, B.R. Dispersion of zein into pea protein with alkaline agents imparts cohesive and viscoelastic properties for plant-based food analogues. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 134, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Wong, S.S.; Pham, S.Q.; Tan, J.J. Effects of globular protein type and concentration on the physical properties and flow behaviors of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by micellar casein-globular protein mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramilli, M.; Longmore, N.; Ghosh, S. Improved stabilization of nanoemulsions by partial replacement of sodium caseinate with pea protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Vasanthan, T.; Ozimek, L. Synergistic enhancement in the co-gelation of salt-soluble pea proteins and whey proteins. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihi, M.L.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Acid gelation of mixed thermal aggregates of pea globulins and beta-lactoglobulin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Dickinson, E. Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid. 2020, 49, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Garg, P.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kulshrestha, S. Microbial Fermentation and Its Role in Quality Improvement of Fermented Foods. Fermentation 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ke, C.X.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Ueberham, E.; Lehmann, J.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Immunoreactivity, sensory and physicochemical properties of fermented soy protein isolate. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.M.; Li, L. The influence of protease hydrolysis of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation induced soybean protein gel: Protein molecule, peptides and amino acids. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Thakur, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, F.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Functionalization of soy residue (okara) by enzymatic hydrolysis and LAB fermentation for B-2 bio-enrichment and improved in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavizadeh, S.; Alencikiene, G.; Vaiciulyte-Funk, L.; Ertbjerg, P.; Salaseviciene, A. Utilization of fermented and enzymatically hydrolyzed soy press cake as ingredient for meat analogues. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Childs, M.; Loos, M.; Taylor, A.; Smart, L.B.; Abbaspourrad, A. The effects of germination on the composition and functional properties of hemp seed protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 134, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilco-Quesada, S.; Tian, Y.; Yang, B.R.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Suomela, J.P. Effects of germination and kilning on the phenolic compounds and nutritional properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) and kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus). J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 94, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, D.D.M.; Martinez, J.E.B.; Velazquez, T.G.G.; Martinez, C.J.; Ruiz, J.C.R. Impact of germination time on protein solubility and anti-inflammatory properties of Pisum sativum L grains. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, X.W.; Gu, R.J.; Duan, X.; Liu, F.G.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, Y.T. Impact of germination on structural, functional properties and in vitro protein digestibility of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) protein. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.C.; Cai, W.X.; Xu, B.J. Improvement in beta-carotene, vitamin B-2, GABA, free amino acids and isoflavones in yellow and black soybeans upon germination. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Saxena, D.C.; Riar, C.S. Changes in the GABA and polyphenols contents of foxtail millet on germination and their relationship with in vitro antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhoza, B.; Qi, B.K.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Koko, M.Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Combined plant protein modification and complex coacervation as a sustainable strategy to produce coacervates encapsulating bioactives. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka, M.; Trusinska, M.; Chraniuk, P.; Drudi, F.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Nguyen, N.P.; Przybyszewska, A.; Pobiega, K.; Tappi, S.; Tylewicz, U. Developments in plant proteins production for meat and fish analogues. Molecules. 2023, 28, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Guo, S.T. Phytic acid and its interactions: Contributions to protein functionality, food processing, and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2081–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Rao, J.J.; Chen, B.C. Gum arabic-mediated synthesis of glyco-pea protein hydrolysate via maillard reaction improves solubility, flavor profile, and functionality of plant protein. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.J.; Nie, P.; Gong, J.T.; Wei, C.K.; Thakur, K.; Hu, F.; Wei, Z.J. Antibacterial and food preservative attributes of maillard reaction products of shrimp shell chitosan. Curr. Top. Nutraceut. Res. 2022, 20, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner-Gühmann, M.; Kratzsch, A.; Sozer, N.; Drusch, S. Oat protein as plant-derived gelling agent: Properties and potential of modification. Future Foods. 2021, 4, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Hong, S.; Singh, G.; Koppel, K.; Li, Y.H. Improving functional properties of pea protein through “green” modifications using enzymes and polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrabadi, M.N.; Doost, A.S.; Mezzenga, R. Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Wu, D.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Meng, D.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Q. Rheological and textural properties of acid-induced soybean protein isolate gel in the presence of soybean protein isolate hydrolysates or their glycosylated products. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accardo, F.; Miguens-Gomez, A.; Lolli, V.; Faccini, A.; Ardevol, A.; Terra, X.; Caligiani, A.; Pinent, M.; Sforza, S. Molecular composition of lipid and protein fraction of almond, beef and lesser mealworm after in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion and correlation with the hormone-stimulating properties of the digesta. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Freire, D.T.; Boom, R.M.; Janssen, A.E.M. The influence of starch and fibre on In Vitro protein digestibility of dry fractionated quinoa seed (Riobamba variety). Food Biophys. 2019, 14, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldello, A.; Giampieri, F.; De Giuseppe, R.; Grosso, G.; Baroni, L.; Battino, M. The rise of processed meat alternatives: A narrative review of the manufacturing, composition, nutritional profile and health effects of newer sources of protein, and their place in healthier diets. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 127, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.J. Plant-based animal product alternatives are healthier and more environmentally sustainable than animal products. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Hou, T.; Guo, D.J.; He, H. Evaluation of hypolipidemic peptide (Val-Phe-Val-Arg-Asn) virtual screened from chickpea peptides by pharmacophore model in high-fat diet-induced obese rat. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, K.; Maani, N.; Milner, J. Meat, money and messaging, How the environmental and health harms of red and processed meat consumption are framed by the meat industry. Food Policy 2022, 109, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Q.; Liao, L.M.; Weinstein, S.J.; Sinha, R.; Graubard, B.I.; Albanes, D. Association Between Plant and Animal Protein Intake and Overall and Cause-Specific Mortality. JAMA Inter. Med. 2020, 180, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. A review on plant-based proteins from soybean: Health benefits and soy product development. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Shoaib, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Javed, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Gupta, R.; Aqil, F. Microbe-based therapies for colorectal cancer: Advantages and limitations. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Beaubier, S.; Ilic, I.; Fine, F.; Kapel, R.; Villeneuve, P. Production and antioxidant capacity of bioactive peptides from plant biomass to counteract lipid oxidation. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 365–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Giovannucci, E.L. Plant-based diet quality and the risk of total and disease-specific mortality, A population-based prospective study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5718–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtain, F.; Grafenauer, S. Plant-Based Meat Substitutes in the Flexitarian Age, An Audit of Products on Supermarket Shelves. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Zou, P.-R.; Hu, F.; Zhu, W.; Wei, Z.-J. Updates on Plant-Based Protein Products as an Alternative to Animal Protein: Technology, Properties, and Their Health Benefits. Molecules 2023, 28, 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104016
Xiao X, Zou P-R, Hu F, Zhu W, Wei Z-J. Updates on Plant-Based Protein Products as an Alternative to Animal Protein: Technology, Properties, and Their Health Benefits. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104016
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xiao, Peng-Ren Zou, Fei Hu, Wen Zhu, and Zhao-Jun Wei. 2023. "Updates on Plant-Based Protein Products as an Alternative to Animal Protein: Technology, Properties, and Their Health Benefits" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104016
APA StyleXiao, X., Zou, P.-R., Hu, F., Zhu, W., & Wei, Z.-J. (2023). Updates on Plant-Based Protein Products as an Alternative to Animal Protein: Technology, Properties, and Their Health Benefits. Molecules, 28(10), 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104016






