Structural Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Loach Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
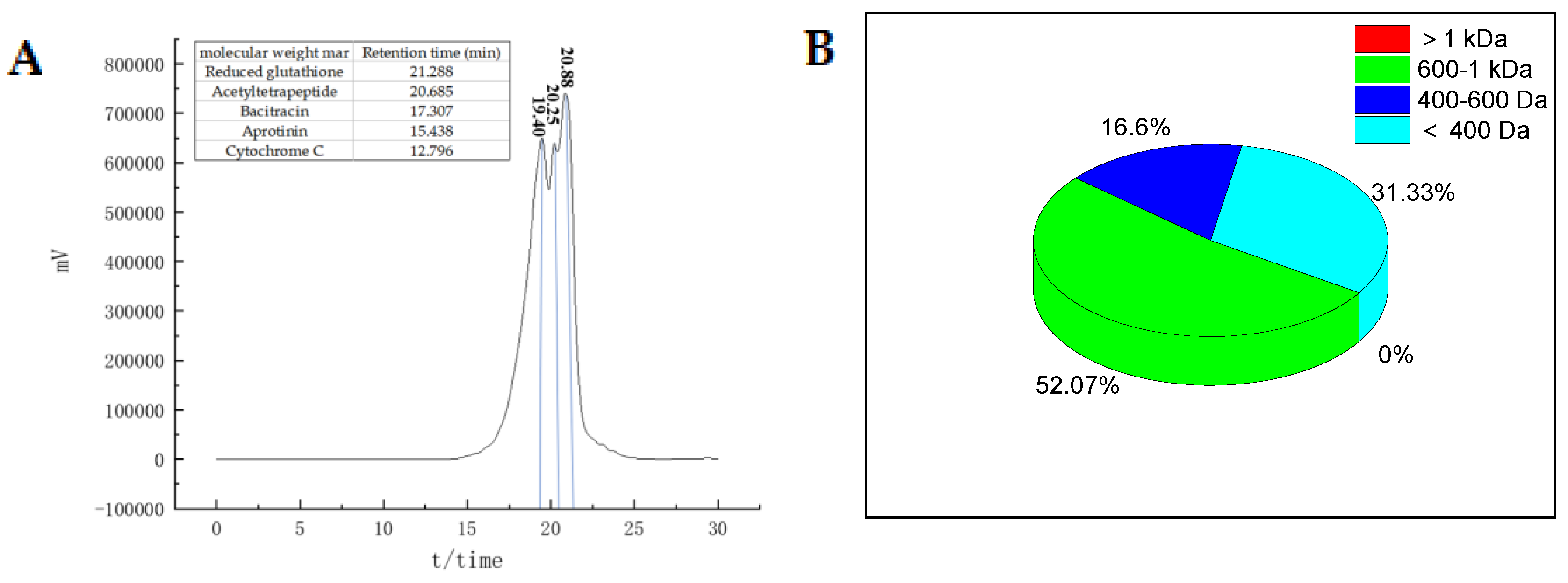
2.1. Separation of LAP Using Gel Filtration Chromatography
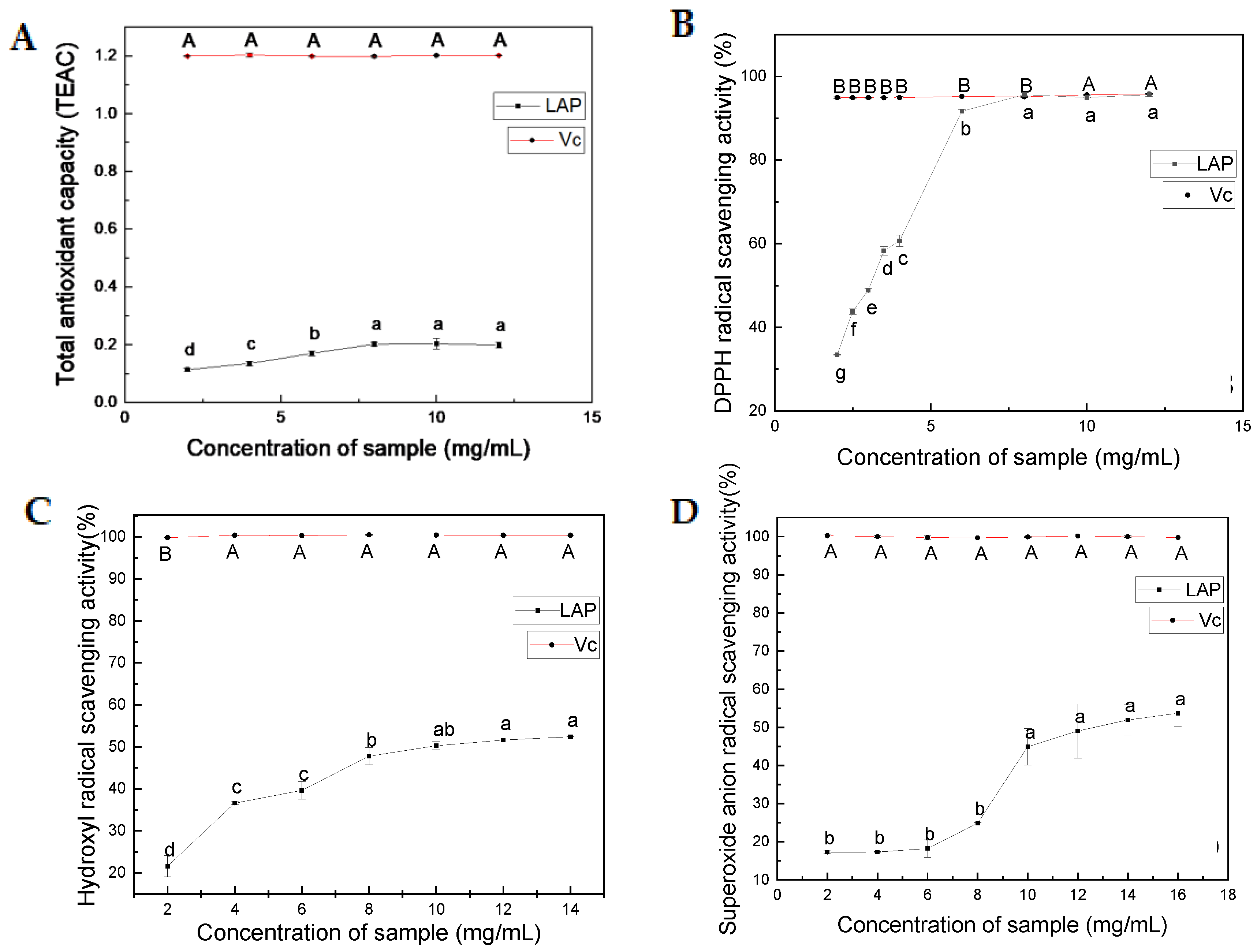
2.2. Antioxidant Activity of LAP
2.2.1. Total Antioxidant Activity
2.2.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2.3. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2.4. Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging Activity
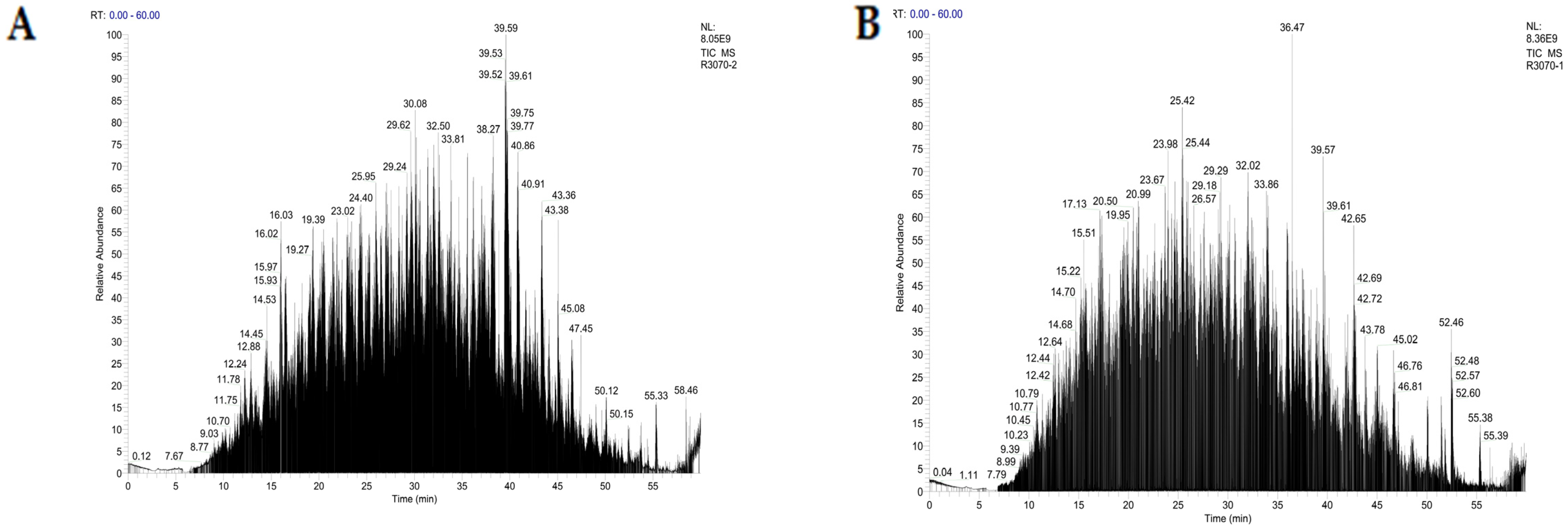
2.3. Amino Acid Sequencing
2.4. Morphological Analysis
2.4.1. FT-IR Analysis
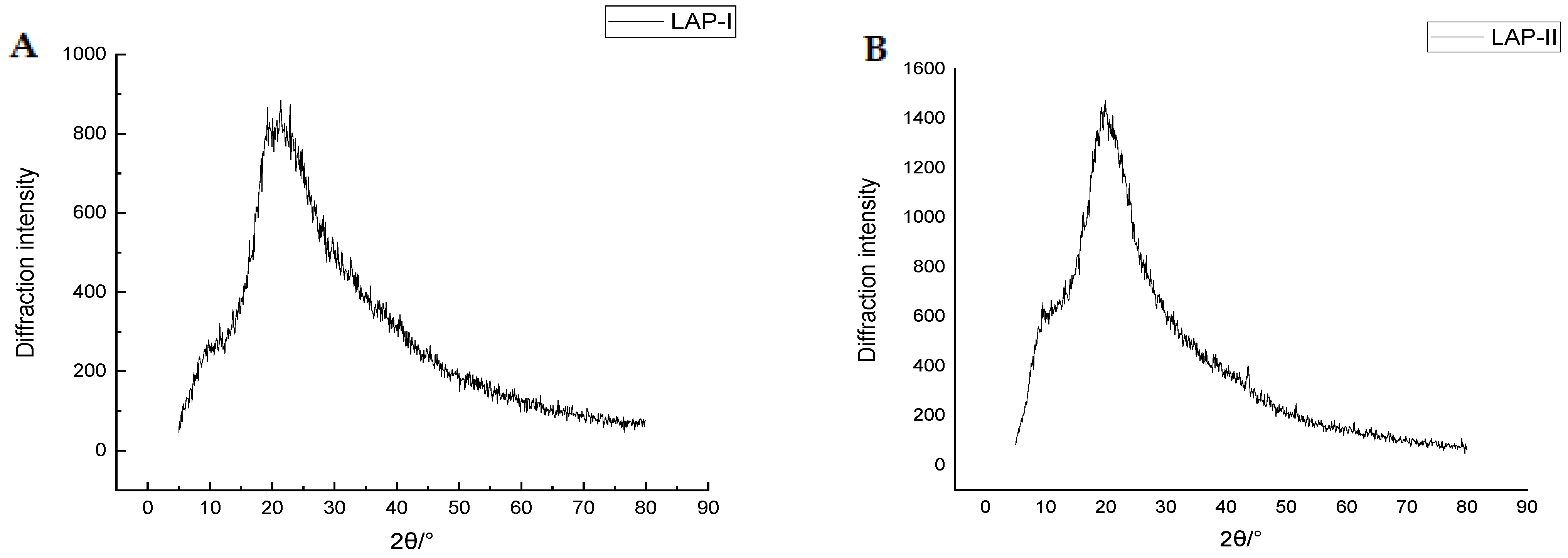
2.4.2. XRD Analysis
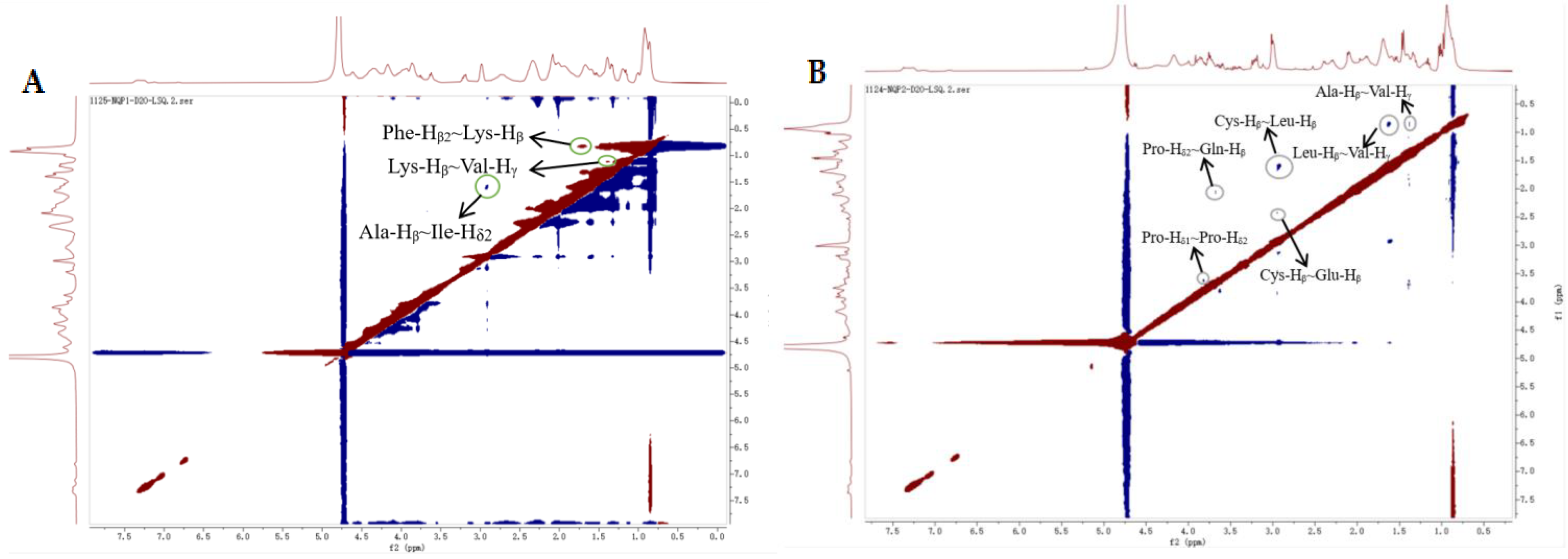
2.4.3. 2D-NMR Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction of Loach Peptides (LAP)
3.3. Molecular Weight Determination
3.4. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
3.4.1. Total Antioxidant Activity Assay
3.4.2. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.4.3. The Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity Determination
3.4.4. The Superoxide Anion Scavenging Activity Determination
3.5. Purification and Fractionation of LAP
3.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.7. FT-IR Analysis
3.8. XRD Analysis
3.9. 2D NMR Analysis
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, K.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X. Purification of a Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide with an Antihypertensive Effect from Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. Purification and identification of antioxidative peptides from loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pei, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble and pepsin-soluble collagen from skin of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 106, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yang, C.H.; Zhang, H.Q.; Pan, X.T.; Xia, X.H. A C-type lectin with antibacterial activity in weather loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yan, J.; Bai, Z.; Li, K.; Huang, K. Hypoglycemic activity and potential mechanism of a polysaccharide from the loach in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Z.; Xu, H.B.; Huang, K.X.; Liou, Q.; Zhou, J. The preparation and characterization of an antimicrobial polypeptide from the loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 26, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, J. Effects of loach skin collagen peptides in reducing osteoporosis in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. In vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo anti-fatigue effect of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) peptides prepared by papain digestion. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; John, A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, B.; Wen, L. Structure identification of walnut peptides and evaluation of cellular antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongling, K.; Ruijuan, M.; Xinyu, L.; Youping, X.; Jianfeng, C. Highly effective peptide-calcium chelate prepared from aquatic products processing wastes: Stickwater and oyster shells. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 168, 113947. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Shi, H.; Song, R. Ultrasonication promotes extraction of antioxidant peptides from oxhide gelatin by modifying collagen molecule structure. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 78, 105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Xue, Q.; Gao, P.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L. Antioxidant peptides from edible aquatic animals: Preparation method, mechanism of action, and structure-activity relationships. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, H. Recent advances of collagen-based biomaterials: Multi-hierarchical structure, modification and biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Anwar, F.; Bakar, F.A.; Philip, R.; Saari, N. Identification and characterization of papain-generated antioxidant peptides from palm kernel cake proteins. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, C.G.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Babini, E.; Rutella, G.S.; Saa, D.L.T.; Gianotti, A. Bioactive peptides from vegetable food matrices: Research trends and novel biotechnologies for synthesis and recovery. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qu, W.; Yang, K.X. Structural Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Corn Peptide-Zn Complex. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 38, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Mao, T.M.; Huang, L.; Yu, Z.C.; Yin, B.; Chen, M.L.; Cheng, Y.H. Purification and identification immunomodulatory peptide from rice protein hydrolysates. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wang, Q.; Teng, J.; Wu, F.; He, Z. Preparation process optimization and evaluation of bioactive peptides from Carya cathayensis Sarg meal. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yin, L.; Abed, S.M. Fractionation and purification of antioxidant peptides from Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) protein hydrolysates prepared using papain and alcalase 2.4 L. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.-k.; Fan, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.-f.; Wang, B.; Bian, X.; Zhang, N. Identification, in silico selection, and mechanism study of novel antioxidant peptides derived from the rice bran protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Manni, L.; Ravallec, R.; Barkia, A.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wagner, A.E.; Motafakkerazad, R.; Yu, N.; Rimbach, G. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of betanin: Electron spin resonance spectroscopy studies and studies in cultured cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 73, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, Z.; Sayyed-Alangi, S.Z.; Najafian, L. Effects of enzyme type and process time on hydrolysis degree, electrophoresis bands and antioxidant properties of hydrolyzed proteins derived from defatted Bunium persicum Bioss. press cake. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeynayake, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Chen, L. Development of antioxidant peptides from brewers’ spent grain proteins. LWT 2022, 158, 113162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yao, X.; Soladoye, O.P.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y. Phosphorylation modification of collagen peptides from fish bone enhances their calcium-chelating and antioxidant activity. LWT 2022, 155, 112978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, X.-R.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Gelatins and antioxidant peptides from Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) skins: Purification, characterization, and cytoprotection on ultraviolet-A injured human skin fibroblasts. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathwar, S.C.; Bijinu, B.; Rai, A.K.; Narayan, B. Simultaneous Recovery of Lipids and Proteins by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Fish Industry Waste Using Different Commercial Proteases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.-C.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Ee, K.-Y.; Chai, T.-T. Advances on the antioxidant peptides from edible plant sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Plant protein-derived antioxidant peptides: Isolation, identification, mechanism of action and application in food systems: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammuang, S.; Sarnthima, R.; Sanachai, K. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) protein hydrolysate and molecular docking study. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Miao, J.; Chen, B.; Guo, J.; Ou, Y.; Liang, X.; Cao, Y. Purification, identification, and antioxidative mechanism of three novel selenium-enriched oyster antioxidant peptides. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shi, C.; Zhou, C.; Sun, X.; Zhou, G. Purification and characterization of novel antioxidant peptides from duck breast protein hydrolysates. LWT 2020, 125, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karas, M. Identification of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory peptides obtained by simulated gastrointestinal digestion of three edible insects species (Gryllodes sigillatus, Tenebrio molitor, Schistocerca gragaria). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, L.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Generation of novel antioxidant peptides from silver carp muscle hydrolysate: Gastrointestinal digestion stability and transepithelial absorption property. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.-P.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.-J. Characterization and film-forming properties of acid soluble collagens from different by-products of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). LWT 2021, 149, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, H. Immunomodulatory effects of different molecular weight sporisorium reilianum polypeptides on LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandekar, J. Amide modes and protein conformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1992, 1120, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjouji, H.; Fakharedine, N.; Baddi, G.A.; Winterton, P.; Bailly, J.; Revel, J.; Hafidi, M. Treatment of olive mill waste-water by aerobic biodegradation: An analytical study using gel permeation chromatography, ultraviolet–visible and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3513–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Guo, Z.; Wei, J.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. Extraction of low molecular weight peptides from bovine bone using ultrasound-assisted double enzyme hydrolysis: Impact on the antioxidant activities of the extracted peptides. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Structural properties, antioxidant and immune activities of low molecular weight peptides from soybean dregs (Okara). Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Hao, X. Preparation of sheep bone collagen peptide–calcium chelate using enzymolysis-fermentation methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11624–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Gu, Z.; Xiong, S. A quantitative comparable study on multi-hierarchy conformation of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggion, C.; Crisma, M.; Toniolo, C.; Formaggio, F. A solvent-dependent peptide spring unraveled by 2D-NMR. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 4429–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodov, I.; Nikiforov, M.Y.; Alper, G.; Blokhin, D.; Efimov, S.; Klochkov, V.; Georgi, N. Spatial structure of felodipine dissolved in DMSO by 1D NOE and 2D NOESY NMR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1035, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, G.; Zeng, W.; Wu, W. Conformations of oxidized glutathione in aqueous urea solution by all-atom molecular dynamic simulations and 2D-NOESY spectrum. J. Solut. Chem. 2013, 42, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, R.; Jia, K.; Lei, Y.; Wu, W. Molecular dynamics simulations and 2D-NOESY spectroscopy studied on conformational features of ACE-inhibitory tripeptide Gly-Glu-Phe in aqueous and DMSO solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Ning, P.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Y.H. Extraction of antioxidant peptides from rice dreg protein hydrolysate via an angling method. Food Chem. 2020, 337, 128069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of quercetin derivatives. Synth. Commun. 2021, 51, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from millet gliadin treated with high hydrostatic pressure. LWT 2022, 164, 113654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Chen, H.; Wan, P.; Luo, L.; Ye, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Pan, J. Isolation and identification of immunomodulatory peptides from the protein hydrolysate of tuna trimmings (Thunnas albacares). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Ding, W.; Wang, X. Insight into the effect of garlic peptides on the physicochemical and anti-staling properties of wheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

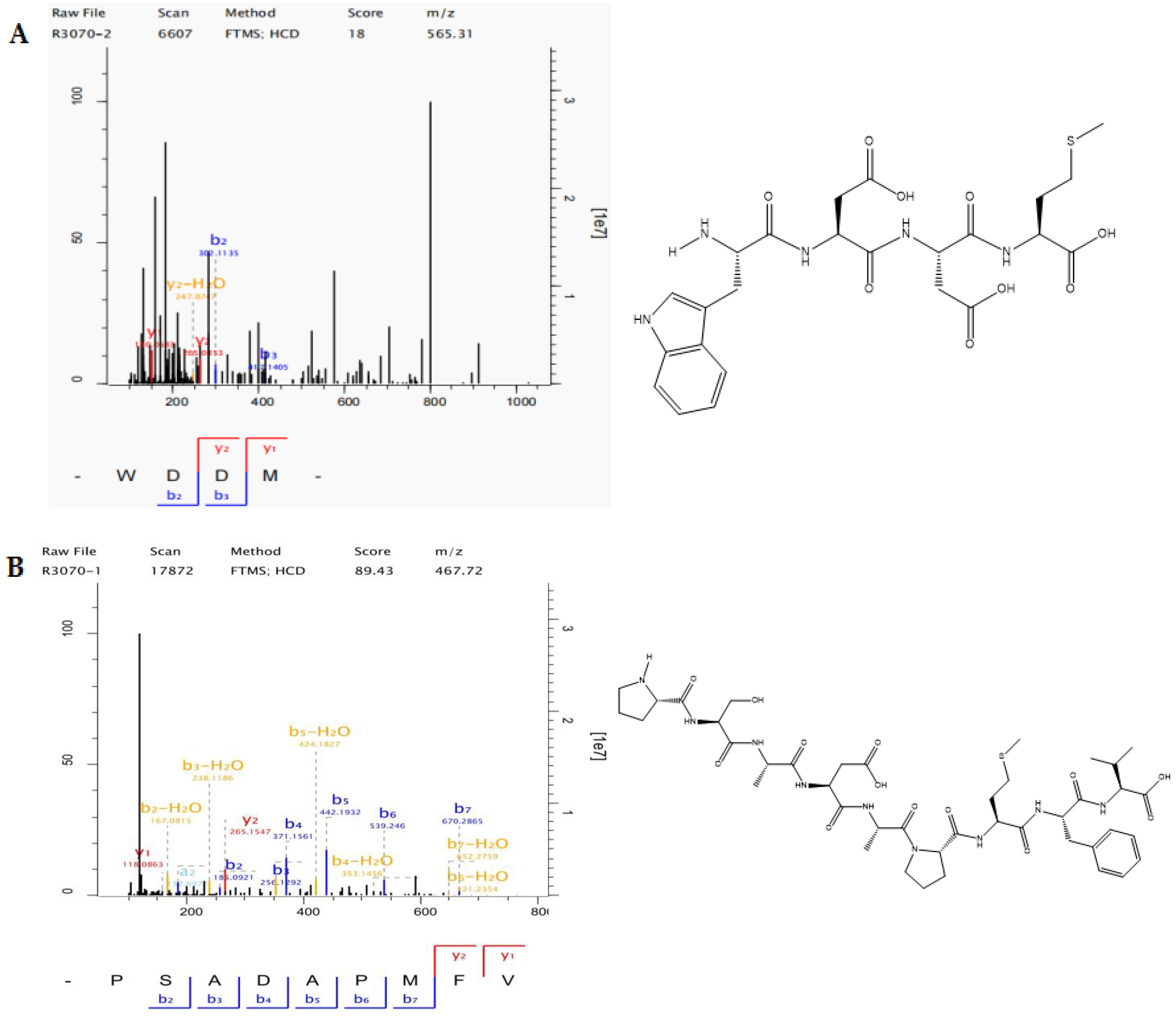


| Components | Amino Acid Sequencing | MW (Da) | Comparison of Scores | Abundance (Strength) | Percentage of Hydrophobic Amino Acids (%) | Charge Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAP-I | NHPGQISQ | 8.79 × 102 | 121.29 | 2.89 × 108 | 25.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | LDAGDGVTH | 8.83 × 102 | 81.32 | 1.51 × 108 | 33.33 | 2 |
| LAP-I | SYELPDGQ | 9.1 × 102 | 60.76 | 8.80 × 107 | 25.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | MYPGIADR | 9.21 × 102 | 93.56 | 4.12 × 108 | 37.50 | 2 |
| LAP-I | YPGIADRM | 9.21 × 102 | 98.42 | 7.26 × 107 | 50.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | MEPVLEQS | 9.31 × 102 | 134.81 | 6.16 × 107 | 50.00 | 1 |
| LAP-I | PSADAPMFV | 9.33 × 102 | 89.43 | 5.01 × 107 | 77.78 | 2 |
| LAP-I | GRDLTDYL | 9.51 × 102 | 116.54 | 1.26 × 109 | 25.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | FIGMESAGIH | 1.06 × 103 | 88.35 | 1.97 × 107 | 50.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | GRDLTDYLM | 1.08 × 103 | 98.46 | 1.77 × 108 | 33.33 | 2 |
| LAP-I | YLRPHIGESL | 1.18 × 103 | 146.81 | 8.03 × 107 | 40.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | HVDPDNFRLL | 1.22 × 103 | 102.51 | 4.72 × 108 | 50.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I | GMHGVNEEVFL | 1.23 × 103 | 86.79 | 2.83 × 107 | 45.45 | 2 |
| LAP-I | EHGDSSVPVWSGV | 1.35 × 103 | 129.42 | 4.86 × 108 | 38.46 | 2 |
| LAP-I | LLPVEVPEHIATM | 1.45 × 103 | 82.43 | 4.68 × 107 | 69.23 | 2 |
| LAP-I | KLHVDPDNFRLL | 1.47 × 103 | 105.20 | 4.02 × 108 | 50.00 | 2; 3 |
| LAP-II | MLTL | 4.76 × 102 | 72.01 | 1.66 × 108 | 75.00 | 1 |
| LAP-II | WDDM | 5.65 × 102 | 61.26 | 1.70 × 108 | 50.00 | 1 |
| LAP-II | NDHFVKL | 8.71 × 102 | 109.63 | 1.15 × 109 | 42.86 | 2 |
| LAP-II | HVDPDNFRL | 1.11 × 103 | 102.51 | 7.65 × 107 | 44.44 | 2 |
| LAP-II | MLFPGDFSPE | 1.14 × 103 | 83.75 | 7.79 × 106 | 60.00 | 1 |
| LAP-II | LFPGDFSPEVH | 1.24 × 103 | 77.28 | 2.71 × 107 | 54.55 | 2 |
| LAP-II | GLTPGEHGFHVH | 1.29 × 103 | 83.21 | 2.78 × 107 | 33.33 | 2 |
| LAP-II | LHVDPDNFRLL | 1.34 × 103 | 78.33 | 8.55 × 107 | 54.55 | 2; 3 |
| LAP-II | LRVAPEEHPTLL | 1.37 × 103 | 165.98 | 9.81 × 107 | 58.33 | 2; 3 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | LTAM | 4.34 × 102 | 63.97 | 2.67 × 107 | 75.00 | 1 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | VAPEEHPT | 8.78 × 102 | 97.60 | 1.77 × 109 | 50.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | TPDVHEAW | 9.53 × 102 | 94.54 | 3.64 × 107 | 50.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | VAPEEHPTL | 9.91 × 102 | 124.89 | 1.51 × 109 | 55.56 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | HVDPDNFR | 9.98 × 102 | 138.83 | 1.08 × 107 | 37.50 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | APSADAPMFV | 1.00 × 103 | 110.90 | 6.09 × 107 | 80.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | ITPPLPEQH | 1.03 × 103 | 137.18 | 3.87 × 108 | 55.56 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | MYPGIADRM | 1.05 × 103 | 95.91 | 9.48 × 108 | 55.56 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | VAPEEHPTLL | 1.10 × 103 | 103.75 | 6.39 × 109 | 60.00 | 2 |
| LAP-I, LAP-II | RVAPEEHPVLL | 1.26 × 103 | 97.64 | 2.10 × 108 | 63.64 | 2; 3 |
| Components | Amino Acid Sequencing | Length | MW (Da) | Toxicity | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAP-II | WDDM | 4 | 565.18 | Non-toxic | 3.57 |
| LAP-I | PSADAPMFV | 9 | 933.43 | Non-toxic | 3.80 |
| LAP-I | Peak | Chemical Displacement | Corresponding Atoms | LAP-II | Peak | Chemical Displacement | Corresponding Atoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.35 | Ala-Hα | 1 | 4.16 | Val-Hα | ||
| 2 | 4.17 | Val-Hα | 2 | 4.01 | Gly-Hα | ||
| 3 | 3.92 | Gly-Hα | 3 | 3.91 | Ser-Hβ | ||
| 4 | 3.75 | Pro-Hδ1 | 4 | 3.77 | Pro-Hδ1 | ||
| 5 | 3.63 | Pro-Hδ2 | 5 | 3.60 | Pro-Hδ2 | ||
| 6 | 3.20 | Phe-Hβ1 | 6 | 3.22 | Phe-Hβ | ||
| 7 | 2.98 | Phe-Hβ2 | 7 | 3.12 | Tyr-Hβ | ||
| 8 | 2.73 | Asp-Hβ | 8 | 3.00 | Cys-Hβ | ||
| 9 | 2.11 | Gln-Hβ | 9 | 2.32 | Glu-Hγ | ||
| 10 | 2.16 | Met-Hβ | 10 | 2.09 | Gln-Hβ | ||
| 11 | 1.75 | Lys-Hβ | 11 | 1.90 | Ile-Hβ | ||
| 12 | 1.39 | Ala-Hβ | 12 | 1.65 | Leu-Hβ | ||
| 13 | 1.18 | Ile-Hδ | 13 | 1.43 | Lys-Hγ | ||
| 14 | 0.93 | Val-Hγ | 14 | 1.34 | Ala-Hβ | ||
| 15 | 1.16 | Ile-Hγ | |||||
| 16 | 0.95 | Val-Hγ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, J.; Li, S.; Yun, L.; Zhang, M. Structural Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Loach Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates. Molecules 2023, 28, 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114391
Mao J, Li S, Yun L, Zhang M. Structural Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Loach Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114391
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Jinrong, Shunqin Li, Liyuan Yun, and Min Zhang. 2023. "Structural Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Loach Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114391
APA StyleMao, J., Li, S., Yun, L., & Zhang, M. (2023). Structural Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Loach Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates. Molecules, 28(11), 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114391