Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Commercial Maize Hybrids Determined by an In Vitro Digestion Model for Poultry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
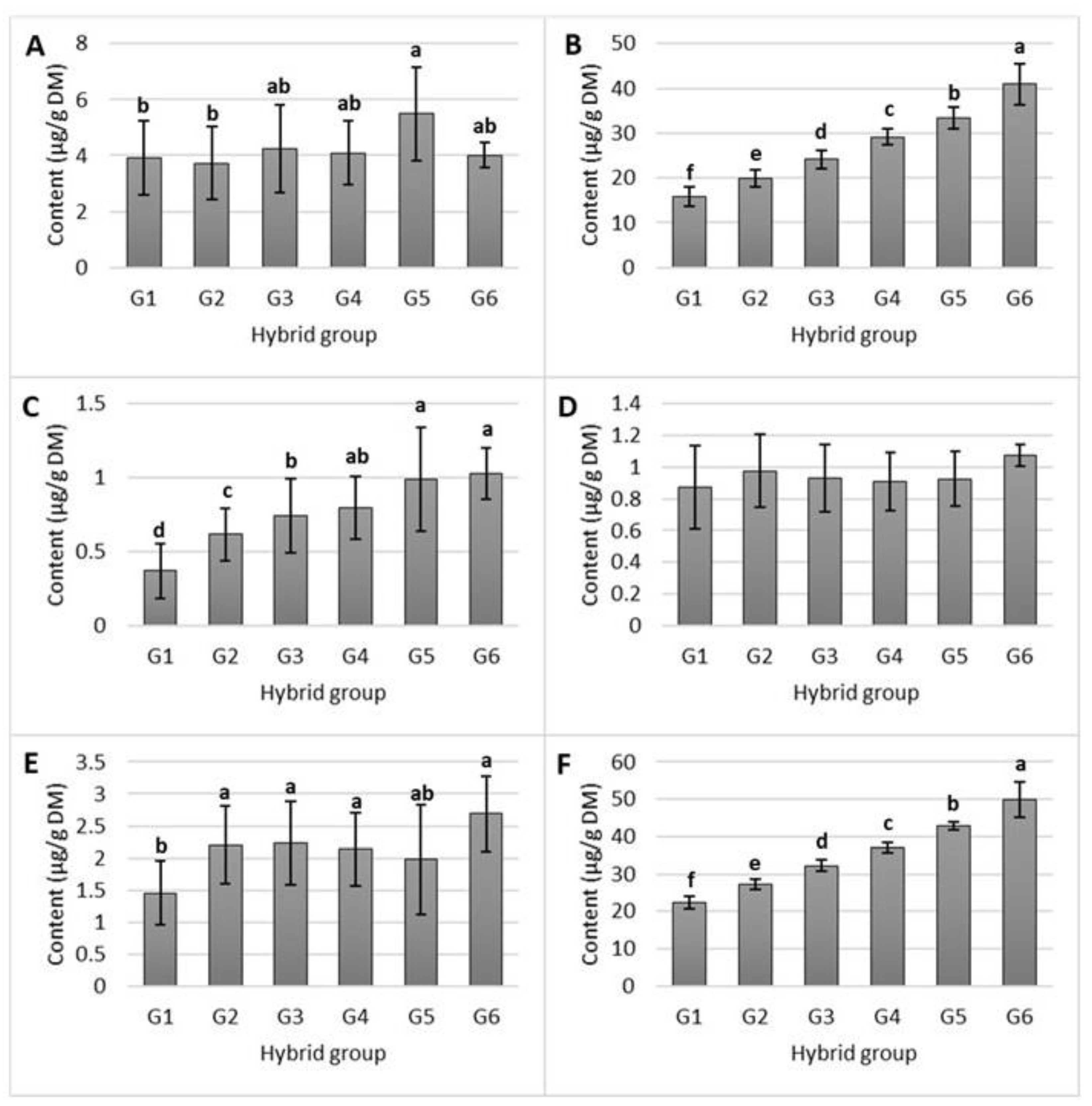
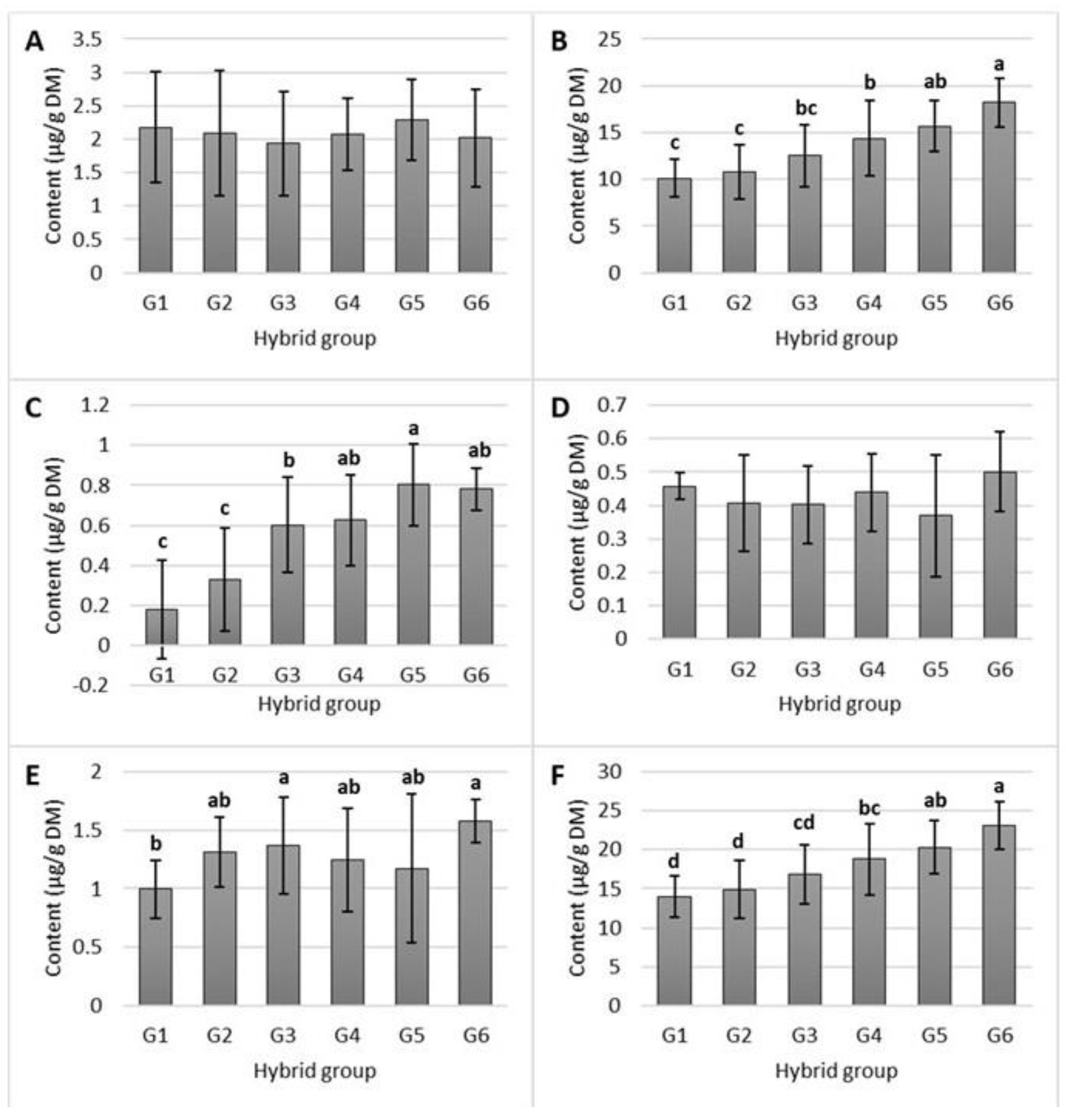
2.1. Tocol Content in Studied Maize Hybrids
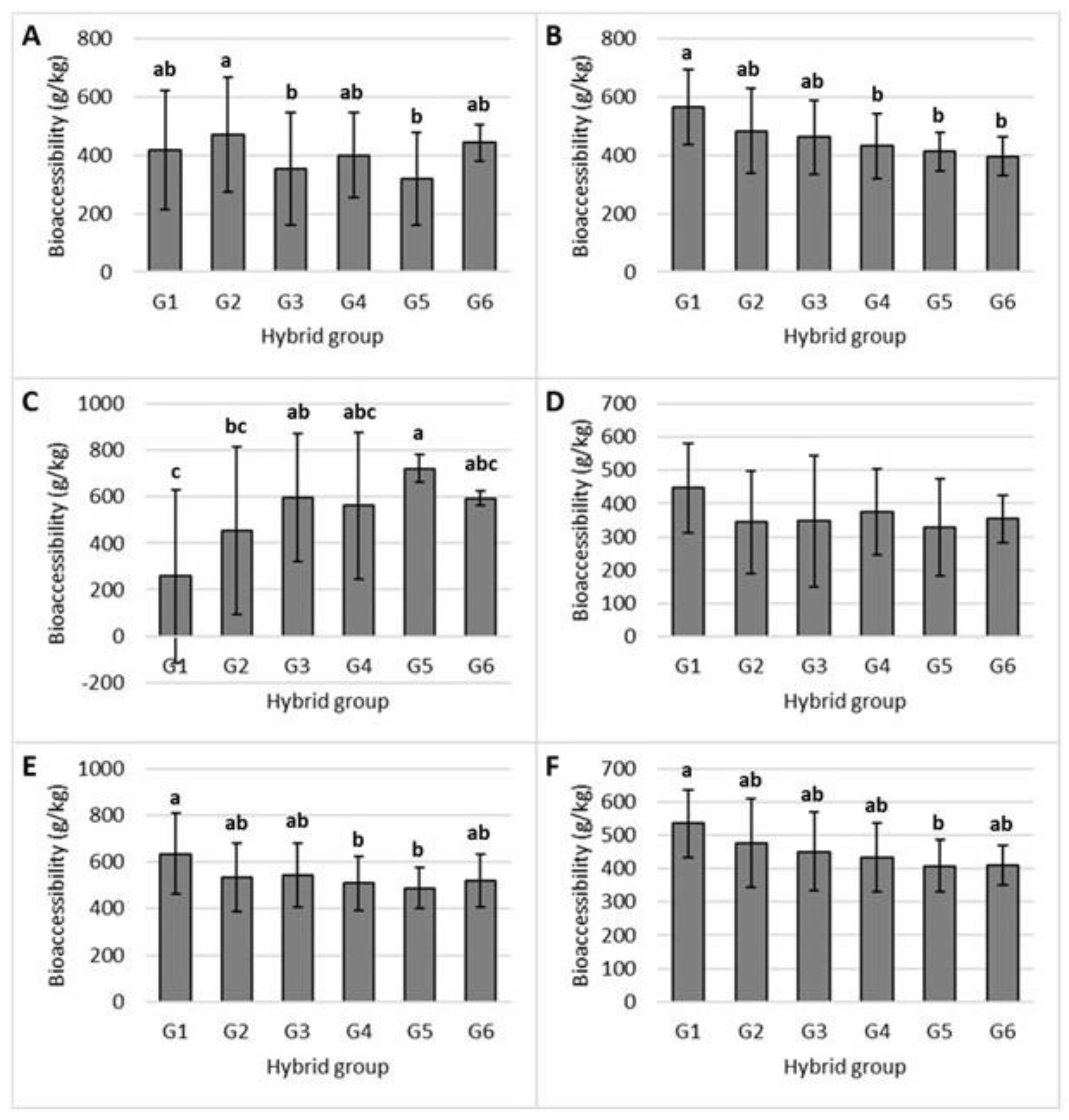
2.2. Bioaccessibility of Tocols in the Studied Maize Hybrids
3. Discussion
3.1. Content of Tocols in Tested Maize Hybrids
3.2. Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Studied Maize Hybrids
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. In Vitro Digestion
4.3. Tocol Extraction from Whole Maize Grain
4.4. Tocol Extraction from the Micellar Fraction
4.5. HPLC Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, A.; Jayadeep, A. Determination of tocopherol and tocotrienol contents in maize by in vitro digestion and chemical methods. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Vitamin E bioaccessibility: Influence of carrier oil type on digestion and release of emulsified α-tocopherol acetate. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, H.Y.; Tan, W.S.D.; Liao, W.; Wong, W.S.F. Vitamin E therapy beyond cancer: Tocopherol versus tocotrienol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, M.E.; Owens, B.F.; Lipka, A.E.; Ortiz, D.; Tiede, T.; Mateos-Hernandez, M.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Rocheford, T. High-density linkage mapping of vitamin E content in maize grain. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Roh, S. The physiological roles of vitamin e and hypovitaminosis e in the transition period of high-yielding dairy cows. Animals 2021, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Decker, E.A.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Enhancing vitamin e bioaccessibility: Factors impacting solubilization and hydrolysis of α-tocopherol acetate encapsulated in emulsion-based delivery systems. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Traber, M.G. Vitamin E: Function and metabolism. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Tocopherols, tocotrienols and tocomonoenols: Many similar molecules but only one vitamin E. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, J. Comparison of nutritional traits variability in selected eighty-seven inbreds from Chinese maize (Zea mays L.) germplasm. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6506–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljak, K.; Carović-Stanko, K.; Kos, I.; Janječić, Z.; Kiš, G.; Duvnjak, M.; Safner, T.; Bedeković, D. Plant carotenoids as pigment sources in laying hen diets: Effect on yolk color, carotenoid content, oxidative stability and sensory properties of eggs. Foods 2021, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Andrys, M.; Korczyński, M.; Opaliński, S.; Łęska, B.; Konkol, D.; Wilk, R.; Rój, E.; Chojnacka, K. Biofortification of hens eggs with polyunsaturated fatty acids by new dietary formulation: Supercritical microalgal extract. Animals 2020, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’sullivan, S.M.; Ball, M.E.E.; McDonald, E.; Hull, G.L.J.; Danaher, M.; Cashman, K.D. Biofortification of Chicken Eggs with Vitamin K—Nutritional and Quality Improvements. Foods 2020, 9, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, M.D.; Gandasasmita, S.; Li, E.; Pelletier, N. Proposing a framework for sustainable feed formulation for laying hens: A systematic review of recent developments and future directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanes, C.G.; Christensen, K.D. Poultry Science, 5th ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2020; ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Suri, D.J.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Effects of Different Processing Methods on the Micronutrient and Phytochemical Contents of Maize: From A to Z. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffman, F.D.; Böhme, T. Relationship between fatty acid profile and vitamin e content in maize hybrids (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4990–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E.; Richelle, M.; Perrot, E.; Desmoulins-Malezet, C.; Pirisi, V.; Borel, P. Bioaccessibility of carotenoids and vitamin E from their main dietary sources. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8749–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E. Vitamin e bioavailability: Mechanisms of intestinal absorption in the spotlight. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.J. Carotenoids and tocols of corn grain determined by HPLC. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1987, 64, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, P.E.; Schneider, J.; Müller, F.; Wiedmaier-Czerny, N.; Vetter, W.; Weiß, T.M.; Würschum, T.; Frank, J. Location and Variety but Not Phosphate Starter Fertilization Influence the Profiles of Fatty Acids, Carotenoids, and Tocochromanols in Kernels of Modern Corn (Zea mays L.) Hybrids Cultivated in Germany. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, S.; Balconi, C.; Valoti, P.; Redaelli, R. Comparison of total polyphenols, profile anthocyanins, color analysis, carotenoids and tocols in pigmented maize. LWT 2021, 144, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, Y.; Larkov, O.; Meir, A.; Minkoff, M.; Lastochkin, E.; Edelstein, M.; Levin, S.; Wong, J.; Rocheford, T.; Lewinsohn, E. Reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic determination of vitamin E components in maize kernels. Phytochem. Anal. 2000, 11, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Im, S.; Wagner, J.G.; Hernandez, M.L.; Peden, D.B. Gamma-tocopherol, a major form of vitamin E in diets: Insights into antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, mechanisms, and roles in disease management. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 178, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E: Metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease prevention and therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, G.F.; McClung, J.P. The Vitamins: Fundamental Aspects in Nutrition and Health, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780128029657. [Google Scholar]
- Rocheford, T.R.; Wong, J.C.; Egesel, C.O.; Lambert, R.J. Enhancement of vitamin e levels in corn. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002, 21, 191S–198S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofius, D.; Sonnewald, U. Vitamin E biosynthesis: Biochemistry meets cell biology. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepenbrock, C.H.; Kandianis, C.B.; Lipka, A.E.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; Vaillancourt, B.; Góngora-Castillo, E.; Wallace, J.G.; Cepela, J.; Mesberg, A.; Bradbury, P.J.; et al. Novel loci underlie natural variation in vitamin E levels in maize grain. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2374–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Preveraud, D.; Desmarchelier, C. Bioavailability of vitamin E in humans: An update. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Jayadeep, A. Infrared heating induced improvement of certain phytobioactives, their bioaccessible contents and bioaccessibility in maize. LWT 2021, 142, 110912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, E.; Carvajal-Lérida, I.; Jarén-Galán, M.; Garrido-Fernández, J.; Pérez-Gálvez, A.; Hornero-Méndez, D. Carotenoids bioavailability from foods: From plant pigments to efficient biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalari, G.; Faulks, R.M.; Rich, G.T.; Lo Turco, V.; Picout, D.R.; Lo Curto, R.B.; Bisignano, G.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Waldron, K.W.; et al. Release of protein, lipid, and vitamin E from almond seeds during digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Böhm, V. Bioaccessibility of carotenoids and vitamin e from pasta: Evaluation of an in vitro digestion model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurak, D.; Grbeša, D.; Duvnjak, M.; Kiš, G.; Dimurec, T.M.; Kljak, K. Carotenoid content and bioaccessibility in commercial maize hybrids. Agriculture 2021, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Enhanced delivery of lipophilic bioactives using emulsions: A review of major factors affecting vitamin, nutraceutical, and lipid bioaccessibility. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marze, S. Bioaccessibility of lipophilic micro-constituents from a lipid emulsion. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3218–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; McClements, D.J. Bioaccessibility of oil-soluble vitamins (A, D, E) in plant-based emulsions: Impact of oil droplet size. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3883–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez-Santiago, R.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Fernández-Jalao, I. Bioaccessibility of provitamin A carotenoids from fruits: Application of a standardised static in vitro digestion method. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.B.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.P.; Jakobsen, J. In vitro bioaccessibility of vitamin K (phylloquinone and menaquinones) in food and supplements assessed by INFOGEST 2.0—vit K. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weurding, R.E.; Veldman, A.; Veen, W.A.; van der Aar, P.J.; Verstegen, M.W. In vitro starch digestion correlates well with rate and extent of starch digestion in broiler chickens. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2336–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Vinarov, Z.; Petkova, Y.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.; Stoyanov, S.; Pelan, E.; Lips, A. Effects of emulsifier charge and concentration on pancreatic lipolysis. 1. in the absence of bile salts. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8127–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, C.; Muriel Mundo, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; McClements, D.J. Chitosan reduces vitamin D bioaccessibility in food emulsions by binding to mixed micelles. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilich, A.C.; Juvik, J.A. Quantification of carotenoid and tocopherol antioxidants in Zea mays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Total Tocol Content (µg/g) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | <25 | 6.67 |
| G2 | 25–30 | 30.48 |
| G3 | 30–35 | 25.71 |
| G4 | 35–40 | 25.71 |
| G5 | 40–45 | 7.62 |
| G6 | >45 | 3.81 |
| Content of Tocols in Maize Hybrids | Content of Digestible Tocols | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αTP | γTP | δTP | αTT | γTT | Total Tocols | |
| αTP | 0.54 *** | NS | NS | 0.23 * | NS | 0.26 ** |
| γTP | NS | 0.54 *** | 0.58 *** | NS | NS | 0.48 *** |
| δTP | NS | NS | 0.75 *** | NS | NS | NS |
| αTT | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | −0.20 * |
| γTT | −0.24 * | −0.20 * | 0.22 * | NS | 0.68 *** | NS |
| Total tocols | NS | 0.52 *** | 0.59 *** | NS | NS | 0.49 *** |
| Content of Tocols in Maize Hybrids | Content of Bioaccessible Tocols | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αTP | γTP | δTP | αTT | γTT | Total Tocols | |
| αTP | 0.52 *** | NS | NS | NS | NS | 0.24 * |
| γTP | NS | 0.54 *** | 0.50 *** | NS | NS | 0.46 *** |
| δTP | NS | NS | 0.71 *** | NS | NS | NS |
| αTT | NS | −0.27 ** | NS | NS | NS | −0.20 * |
| γTT | −0.21 * | NS | 0.20 * | NS | 0.72 *** | NS |
| Total tocols | NS | 0.53 *** | 0.51 *** | NS | NS | 0.48 *** |
| Content of Tocols in Maize Hybrids | Bioaccessibility | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αTP | γTP | δTP | αTT | γTT | Total Tocols | |
| αTP | NS | 0.24 * | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| γTP | NS | −0.32 ** | 0.28 ** | NS | NS | −0.27 ** |
| δTP | NS | −0.35 ** | 0.27 ** | −0.21 * | −0.22 * | −0.30 ** |
| αTT | NS | −0.21 * | NS | −0.47 *** | −0.36 ** | −0.24 * |
| γTT | NS | −0.32 ** | NS | −0.29 ** | −0.42 *** | −0.31 ** |
| Total tocols | NS | −0.31 ** | 0.26 ** | NS | NS | −0.28 ** |
| Company | Hybrid | Company | Hybrid | Company | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bc Institut | Agram | LG | LG 30.3115 | PIO | Os 3150 |
| Bc Institut | Alibi | LG | LG 30.315 | PIO | Os 3450 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 323 | LG | LG 31.322 | PIO | Os 378 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 344 | LG | LG 31.377 | PIO | Os 398 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 415 | LG | LG 31.545 | PIO | Os 4014 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 418 | LG | LG 368/08 | PIO | Os 4015 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 424 | LG | Shannon | PIO | Os 403 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 525 | MAS seeds | MAS 34B | PIO | Os 522 |
| Bc Institut | Bc 572 | MAS seeds | MAS 48L | PIO | Os 3850 |
| Bc Institut | Instruktor | MAS seeds | MAS 56A | PIO | Posavac 36 |
| Bc Institut | Kekec | NS seme | NS 3022 | PIO | Velimir |
| Bc Institut | Majstor | NS seme | NS 4015 | RWA | ES Inventive |
| Bc Institut | Pajdaš | NS seme | NS 4051 | RWA | Ajowan |
| Bc Institut | Tesla | NS seme | NS 6102 | RWA | Inclusiv |
| Bc Institut | Thriler | NS seme | NS Haris | RWA | Persic |
| Dekalb | DKC 4670 | Pioneer | P0023 | RWA | Gladiator |
| Dekalb | DKC 4920 | Pioneer | P0164 | RWA | Glumanda |
| Dekalb | DKC 4943 | Pioneer | P0200 | RWA | Ulyxxe |
| Dekalb | DKC 5031 | Pioneer | P0216 | RWA | Hexagon |
| Dekalb | DKC 5068 | Pioneer | P0217 | RWA | Tweetor |
| Dekalb | DKC 5075 | Pioneer | P0412 | RWA | Urbanix |
| Dekalb | DKC 5093 | Pioneer | P0725 | Syngenta | Sy Andromeda |
| Dekalb | DKC 5182 | Pioneer | P9241 | Syngenta | Sy Atomic |
| Dekalb | DKC 5685 | Pioneer | P9300 | Syngenta | Sy Bilbao |
| Dekalb | DKC 5830 | Pioneer | P9363 | Syngenta | Sy Carioca |
| KWS | Balasco | Pioneer | P9415 | Syngenta | Sy Chorintos |
| KWS | Kapitolis | Pioneer | P9757 | Syngenta | Sy Kreon |
| KWS | Kollegas | Pioneer | P9889 | Syngenta | Sy Lucius |
| KWS | Kolumbaris | Pioneer | P9903 | Syngenta | Sy Photon |
| KWS | Konfites | Pioneer | P9911 | Syngenta | Sy Premeo |
| KWS | Kashmir | Pioneer | P9978 | Syngenta | Sy Sandro |
| KWS | Orlando | PIO | Tomasov | Syngenta | Sy Senko |
| KWS | KxB 8386 | PIO | Jablan | Syngenta | Sy Zoan |
| KWS | KxB 8453 | PIO | Kulak | ||
| KWS | Smaragd | PIO | Os 3114 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunjević, V.; Zurak, D.; Grbeša, D.; Kiš, G.; Međimurec, T.; Pirgozliev, V.; Kljak, K. Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Commercial Maize Hybrids Determined by an In Vitro Digestion Model for Poultry. Molecules 2023, 28, 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135015
Gunjević V, Zurak D, Grbeša D, Kiš G, Međimurec T, Pirgozliev V, Kljak K. Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Commercial Maize Hybrids Determined by an In Vitro Digestion Model for Poultry. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunjević, Veronika, Dora Zurak, Darko Grbeša, Goran Kiš, Tatjana Međimurec, Vasil Pirgozliev, and Kristina Kljak. 2023. "Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Commercial Maize Hybrids Determined by an In Vitro Digestion Model for Poultry" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135015
APA StyleGunjević, V., Zurak, D., Grbeša, D., Kiš, G., Međimurec, T., Pirgozliev, V., & Kljak, K. (2023). Bioaccessibility of Tocols in Commercial Maize Hybrids Determined by an In Vitro Digestion Model for Poultry. Molecules, 28(13), 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135015








