Hybrid Polymer-Silica Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Remediation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Present State of Environmental Pollution
1.2. Treatment Methods
1.3. Silica Nanoparticles: Characteristics and Applications
1.4. Hybrid Polymer—Silica Nanoparticles
2. Synthesis and Functionalization of Mesoporous Silica
2.1. Synthesis of Silica Nanostructured Materials
2.2. Hybridization/Polymerization Techniques
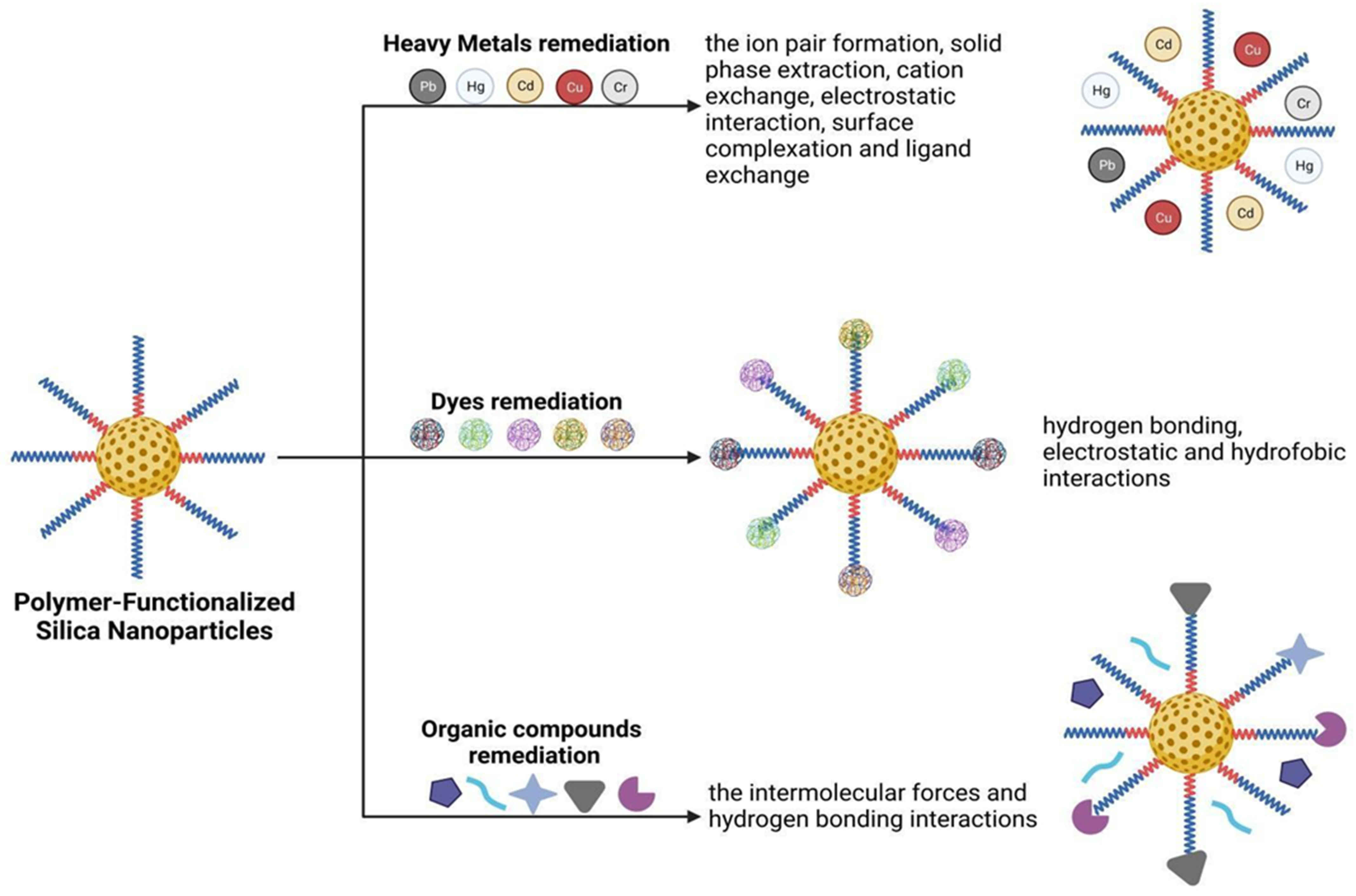
3. Adsorption Applications
3.1. Adsorption of Heavy Metals Pollutants
3.2. Organic Dyes Remediation
3.2.1. Methylene Blue Adsorption
3.2.2. Adsorption of Methyl Orange and Other Dyes
3.3. Remediation of Other Organic Compounds
3.3.1. Drugs
3.3.2. Oil-Derived Organic Compounds and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)
3.3.3. Removal of Gaseous Compounds, CO2 and Other Gases
3.3.4. Other Organic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarocostas, J. The UN reports global asymmetries in population growth. Lancet 2022, 400, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, R. Energy penalty for excess baggage. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, S. Silica-based nanomaterials as designer adsorbents to mitigate emerging organic contaminants from water matrices. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Y.; Ran, J. Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (vocs) and the key factors for vocs adsorption process: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.M.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Fang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Hursthouse, A.S. The application of fluorescence spectroscopy for the investigation of dye degradation by chemical oxidation. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanckaert, B.; Geltmeyer, J.; Rabaey, K.; De Buysser, K.; Bonin, L.; De Clerck, K. A review on ion-exchange nanofiber membranes: Properties, structure and application in electrochemical (waste) water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M. Surfactant assisted nano-composite cation exchanger: Development, characterization and applications for the removal of toxic Pb2+ from aqueous medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, W.; Wu, X.; Cabrera, J.; Chen, D.; Huang, X. Deciphering the spatial fouling characteristics of reverse osmosis membranes for coal chemical wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Haghighi, R. Chemical catalytic reaction and biological oxidation for treatment of non-biodegradable textile effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 95, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ihsanullah, I.; Younas, M.; Shah, M.U.H. Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Hassan, A.A.; Bilal, M.; Hussain, T.; Rizwan, K. Metal-organic frameworks based adsorbents: A review from removal perspective of various environmental contaminants from wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, T.; Kausar, F.; Rizwan, K.; Adeel, M.; Sher, F.; Alwadai, N.; Alshammari, F.H. Two dimensional MXenes as emerging paradigm for adsorptive removal of toxic metallic pollutants from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Adsorption and reusability performance of M-Fe (M=Co, Cu, Zn and Ni) layered double hydroxides for the removal of hazardous Eriochrome Black T dye from different water streams. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heebner, A.; Abbassi, B. Electrolysis catalyzed ozonation for advanced wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juve, J.M.A.; Christensen, F.M.S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, G.; Kumari, A.; Guo, C.; Naushad, M.; Vo, D.V.N.; Iqbal, J.; Stadler, F.J. Construction of dual Z-scheme g-C3N4/Bi4Ti3O12/Bi4O5I2 heterojunction for visible and solar powered coupled photocatalytic antibiotic degradation and hydrogen production: Boosting via I−/I3− and Bi3+/Bi5+ redox mediators. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 284, 119808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Ala’a, H.; Naushad, M.; Stadler, F.J. Highly efficient Sr/Ce/activated carbon bimetallic nanocomposite for photoinduced degradation of rhodamine B. Catal. Today 2019, 335, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Naushad, M.; Dhiman, P.; Vo, D.V.N.; Stadler, F.J. Fe3O4/ZnO/Si3N4 nanocomposite based photocatalyst for the degradation of dyes from aqueous solution. Mater. Lett. 2020, 278, 128359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrar, I.; Yadav, S.; Naji, O.; Alanezi, A.A.; Ghaffour, N.; Déon, S.; Subbiah, S.; Altaee, A. Development in forward Osmosis-Membrane distillation hybrid system for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Mirghorayshi, M.; Zinadini, S.; McKay, T. Electrocoagulation technique for continuous industrial licorice processing wastewater treatment in a single reactor employing Fe-rod electrodes: Process modeling and optimization and operating cost analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Gontijo, D.; Amaral, M.C.S. Membrane distillation and dispersive solvent extraction in a closed-loop process for water, sulfuric acid and copper recycling from gold mining wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 133874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Liu, W.Z.; Wang, A.J.; Gao, X.Y.; Tao, Y.; Ge, X.L.; Lin, Z. Enhanced treatment of oily ink wastewater using a modified degreaser by nano-Fe3O4/Na2S2O8: Efficient coagulation and sedimentation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Duan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, M. Gravity settling and centrifugation increase the acid buffer capacity of activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Fan, T.T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.H.; Lin, J.H.; Long, Y.Z. High performance GO/MXene/PPS composite filtration membrane for dye wastewater treatment under harsh environmental conditions. Compos. Commun. 2022, 29, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Org. Pollut.-Monit. Risk Treat. 2013, 7, 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathiri, M.; Pulingam, T.; Lee, K.T.; Sudesh, K. Activated carbon from biomass waste precursors: Factors affecting production and adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yao, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Tian, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y. Novel insights into the adsorption of organic contaminants by biochar: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagboya, P.; Dikio, E.D. Scavenging of aqueous toxic organic and inorganic cations using novel facile magneto-carbon black-clay composite adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xu, E.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, T.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, G. Phenol adsorption mechanism of organically modified bentonite and its microstructural changes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; De Santo, M.; Lombardo, D.; Leggio, A.; Pasqua, L. Mesoporous silicas in materials engineering: Nanodevices for bionanotechnologies. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 17, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santo, M.; Giovinazzo, A.; Fava, M.; Mazzotta, E.; De Napoli, I.E.; Greco, M.; Comandé, A.; Nigro, A.; Argurio, P.; Perrotta, I.; et al. Engineered mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles as smart chemotherapy nanodevice for bortezomib administration. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Tripathi, D.K.; Yadav, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Živčák, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; El-Sheery, N.I.; Brestic, M. Application of silicon nanoparticles in agriculture. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A Review. Silicon 2020, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachbouri, S.; Mnasri, N.; Elaloui, E.; Moussaoui, Y. Tuning particle morphology of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution. Chem. Soc. 2018, 22, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, D.; Wu, F.; Pleixats, R.; Pan, J. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: Classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15998–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagboya, P.; Dikio, E.D. Silica-based mesoporous materials; emerging designer adsorbents for aqueous pollutants removal and water treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 266, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Ghoshal, A.K. APTES grafted ordered mesoporous silica KIT-6 for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Saxena, M.; Lochab, A. Recent progress in nanomaterials for adsorptive removal of organic contaminants from wastewater. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.H.; Feng, Y.Q. Liquid-phase deposition of silica nanoparticles into a capillary for in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagirani, M.; Soylak, M. A review: Recent advances in solid phase microextraction of toxic pollutants using nanotechnology scenario. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.A.; Mostafa, M.H.; Al-Harbi, L.M. Polymeric Nanocomposites for Environmental and Industrial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, A.; Njuguna, J. (Eds.) Introduction. In Functional and Physical Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, S.A.; Garud, H.B.; Patil, A.H.; Patil, G.D.; Patil, C.R.; Dongale, T.D.; Patil, P.S. Recent advancements in silica nanoparticles based technologies for removal of dyes from water. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 30, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, F.; Wang, X. Polymer-based nanocomposites for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution: A Review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3562–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Li, G.K. Synthesis and application of mesoporous materials: Process status, technical problems, and development prospects: A Mini-review. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 3413–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.A.; Padavettan, V. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles by sol-gel: Size-dependent properties, surface modification, and applications in silica-polymer nanocomposites—A Review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollamby, M.J.; Borisova, D.; Brown, P.; Eastoe, J.; Grillo, I.; Shchukin, D. Growth of mesoporous silica nanoparticles monitored by time- resolved small-angle neutron scattering. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y. Brief history, preparation method, and biological application of mesoporous silica molecular sieves: A Narrative Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Na, J.; Konarova, M.; Wakihara, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Salomon, C.; Gawande, M.B. Functional mesoporous silica nanomaterials for catalysis and environmental applications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 1459–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.T.Y. Microemulsion preparative method (overview). Compr. Nanosci. Technol. 2011, 5, 399–441. [Google Scholar]
- Vansant, E.F.; Van Der Voort, P.; Vrancken, K.C. Characterization and Chemical Modification of the Silica Surface; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bokov, D.; Turki Jalil, A.; Chupradit, S.; Suksatan, W.; Javed Ansari, M.; Shewael, I.H.; Valiev, G.V.; Kianfar, E. Nanomaterial by sol-gel method: Synthesis and application. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.P.; Mou, C.Y. Structural and morphological control of cationic surfactant-templated mesoporous silica. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, X. Synthesis of mesoporous silica with ionic liquid surfactant as template. Mater. Lett. 2021, 291, 129556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, S.M.; Hurley, K.R.; Datt, A.; Swindlehurst, G.; Haynes, C.L. Ultraporous mesostructured silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3193–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoeini, M.; Najafi, A.; Rastegar, H.; Amani, M. Improvement of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles synthesis by hard-templating method via ctab surfactant. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12700–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, A.V.; Lombardo, M.V.; Wolosiuk, A. Rapid pore expansion of mesoporous silica-based materials using microwave irradiation and pore swelling agents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 274, 125185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joni, I.M. Synthesis of Silica Particles by Precipitation Method of Sodium Silicate: Effect of Temperature, ph and Mixing Technique. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; p. 080018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, B. Sonochemical synthesis of silica particles and their size control. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 380, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopic, S.; Wenz, F.; Husovic, T.V.; Friedrich, B. Synthesis of silica particles using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. Metals 2021, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snehal, S.; Lohani, P. Silica nanoparticles: Its green synthesis and importance in agriculture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd, N.K.; Wee, N.N.A.N.; Azmi, A.A. A Green Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles Using Sugarcane Bagasse. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2017; p. 020123. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Kherb, J.; Prakash, J.; Kaushal, R. A novel and facile green synthesis of SiO2 nanoparticles for removal of toxic water pollutants. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, R.J.; Appaturi, J.N.; Pulingam, T.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Al-dhayan, D.M. In-situ incorporation of ruthenium/copper nanoparticles in esoporous silica derived from rice husk ash for catalytic acetylation of glycerol. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagiyalakshmi, M.; Yun, L.J.; Anuradha, R.; Jang, H.T. Utilization of rice husk ash as silica source for the synthesis of mesoporous silicas and their application to CO2 adsorption through tren/tepa grafting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareonpanich, M.; Nanta-Ngern, A.; Limtrakul, J. Short-period synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica sba-15 using ultrasonic technique. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 5153–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.T.; Dinh, Q.K.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, T.D. One-step synthesis of ordered sn-substituted sba-16 mesoporous materials using prepared silica source of rice husk and their selectively catalytic activity. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 91, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.S.; de Jesus, R.A.; Santos, D.O.; Mano, J.F.; Romao, L.P.; Paranhos, C.M. Recent progresses in the adsorption of organic, inorganic, and gas compounds by mcm-41-based mesoporous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 291, 109698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.H.; Stein, A. Comparative studies of grafting and direct syntheses of inorganic− organic hybrid mesoporous materials. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3285–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G.A. Morphogenesis of shapes and surface patterns in mesoporous silica. Nature 1997, 386, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ramli, A.; Yusup, S. Development of polyethylenimine-functionalized mesoporous si-mcm-41 for CO2 adsorption. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Pack, S.P.; Kim, I.; Chung, S. A systematic study of hexavalent chromium adsorption and removal from aqueous environments using chemically functionalized amorphous and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shakeri, M.; Gebbink, R.J.K.; de Jongh, P.E.; de Jong, K.P. Control and assessment of plugging of mesopores in sba-15 materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 170, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, A.; Das, G.; Nardi, M.; Oliverio, M.; Pasqua, L. A mesoporous ErIII-mcm-41 catalyst for the cyanosilylation of aldehydes and ketones under solvent-free conditions. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqua, L.; Procopio, A.; Oliverio, M.; Paonessa, R.; Prete, R.; Nardi, M.; Casula, M.F.; Testa, F.; Nagy, J.B. Hybrid mcm-41 grafted by a general microwave-assisted procedure: A Characterization Study. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadonte, F.; Pasqua, L.; Savino, R.; Terracciano, R. Smart trypsin adsorption into N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl-modified mesoporous silica for ultra fast protein digestion. Chem.—Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8998–9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Anan, A.; Buckley, R.P.; Ouellette, W.; Asefa, T. Toward efficient nanoporous catalysts: Controlling site-isolation and concentration of grafted catalytic sites on nanoporous materials with solvents and colorimetric elucidation of their site-isolation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartmann, N.; Schütze, C.; Ritter, H.; Brühwiler, D. The effect of water on the functionalization of mesoporous silica with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukoussa, B.; Hakiki, A.; Nunes-Beltrao, A.P.; Hamacha, R.; Azzouz, A. Assessment of the intrinsic interactions of nanocomposite polyaniline/sba-15 with carbon dioxide: Correlation between the hydrophilic character and surface basicity. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 26, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswieleh, A. Zwitterionic polymer brushes coated with mesoporous silica nanoparticles as efficient adsorbents for dye removal from aqueous solutions. AACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, F.; He, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Periodic mesoporous organometallic silicas with unary or binary organometals inside the channel walls as active and reusable catalysts in aqueous organic reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1492–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boday, D.; Stover, R.J.; Muriithi, B.; Keller, M.W.; Wertz, J.T.; DeFriend Obrey, K.A.; Loy, D.A. Strong, low-density nanocomposites by chemical vapor deposition and polymerization of cyanoacrylates on aminated silica aerogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Yun, S.; Wie, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Kong, J.; Park, H.S. Cartilage-inspired superelastic ultradurable graphene aerogels prepared by the selective gluing of intersheet joints. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12900–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, G.; Saputra, O.A.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in polymers functionalized nanostructures for analysis of environmental pollutants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 26, e00084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, B.; Pereira, E.D.; Palencia, M.; Sánchez, J. Water-soluble functional polymers in conjunction with membranes to remove pollutant ions from aqueous solutions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 294–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaugeard, V.; Muller, J.; Graillot, A.; Ding, X.; Robin, J.J.; Monge, S. Acidic polymeric sorbents for the removal of metallic pollution in water: A Review. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 152, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Polymer/silica nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3893–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of polymer—Mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Materials 2010, 3, 4066–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, H.Y.; Müller-Plathe, F.; Qian, H.J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Lu, Z.Y. Distribution of the number of polymer chains grafted on nanoparticles fabricated by grafting-to and grafting-from procedures. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3758–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzior, S.A.; Zoppe, J.O.; Berry, R.M.; Cranston, E.D. Recent advances and an industrial perspective of cellulose nanocrystal functionalization through polymer grafting. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, R.; Lavanant, L.; Paripovic, D.; Schuwer, N.; Sugnaux, C.; Tugulu, S.; Klok, H.A. Polymer brushes via surface-initiated controlled radical polymerization: Synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5437–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, T.; Nebhani, L. Light-regulated growth of polymer chains from the surface of raft agent primed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 29, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lu, P.; Wu, Z.; Tang, R.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, H. Highly effective and selective removal of lead ions by polymer- grafted silica-coated acid-resistant magnetic chitosan composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sall, M.; Diaw, A.K.D.; Gningue-Sall, D.; Efremova Aaron, S.; Aaron, J.J. Toxic heavy metals: Impact on the environment and human health, and treatment with conducting organic polymers, A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29927–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandeep, G.; Vijayalatha, K.R.; Anitha, T. Heavy metals and its impact in vegetable crops. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Rafeeq, H.; Hussain, A.; Ambreen, A.; Waqas, M.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M. Functionalized nanoparticles and their environmental remediation potential: A Review. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2022, 12, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kurdi, R.; Chebl, M.; Sillanpää, M.; El-Rassy, H.; Patra, D. Chitosan oligosaccharide/silica nanoparticles hybrid porous gel for mercury adsorption and detection. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnezhad, G.; Moshiri, P.; Dinari, M.; Steiniger, F. In situ synthesis of nanocomposite materials based on modified-mesoporous silica mcm-41 and methyl methacrylate for copper (ii) adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plohl, O.; Ajdnik, U.; Gyergyek, S.; Ban, I.; Vesel, A.; Glaser, T.K.; Zemljič, L.F. Superior stability and high biosorbent efficiency of carboxymethylchitosan covalently linked to silica-coated core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for application in copper removal. J. Environ. 2019, 7, 102913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, M.R.; EL-Masry, E.H.; El-Kenany, W.M. Gamma irradiation-induced preparation of polyacrylonitrile acrylamide nano-silica for removal of some hazardous metals. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betiha, M.; Moustafa, Y.M.; El-Shahat, M.F.; Rafik, E. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-aminopropyl-sba-15 schiff base hybrid for efficient removal of divalent heavy metal cations from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.; Li, X. Preparation of isoelectric point-switchable polymer brush-grafted mesoporous silica using raft polymerization with high performance for ni (ii) adsorption. Powder Technol. 2022, 412, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat Hashami, Z.; Taheri, A.; Alikarami, M. Synthesis of a magnetic SBA-15-NH2@ dual-template imprinted polymer for solid phase extraction and determination of Pb and Cd in vegetables; box behnken design. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1204, 339262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendehdel, M.; Barati, A.; Alikhani, H. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by Poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) modified with porous materials. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Dinari, M.; Mohammadnezhad, G. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of novel nanocomposite of poly (vinyl alcohol) and amino-modified mcm-41: A green adsorbent for cd (ii) removal. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumah, M.; Eid, M.H.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Mohammad, M.A.; Bin-Murdhi, N.S.; Abu-Taweel, G.M.; Altoom, N.; Allam, A.A.; AbuKhadra, M.R. Enhanced remediation of As (V) and Hg (II) ions from aqueous environments using β-cyclodextrin/mcm-48 composite: Batch and column studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ying, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, J. Functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica/poly (m-aminothiophenol) nanocomposite for hg (ii) rapid uptake and high catalytic activity of spent Hg (II) adsorbent. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Emerging natural and tailored materials for uranium-contaminated water treatment and environmental remediation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 180–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Amidoxime-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica for selective sorption of u (vi). RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32710–32717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Arica, M.Y. MCM-41 silica particles grafted with polyacrylonitrile: Modification in to amidoxime and carboxyl groups for enhanced uranium removal from aqueous medium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Egodawatte, S.; Kaplan, D.I.; Larsen, S.C.; Serkiz, S.M.; Seaman, J.C. Functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for u removal from low and high ph groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Egodawatte, S.; Kaplan, D.I.; Larsen, S.C.; Serkiz, S.M.; Seaman, J.C.; Scheckel, K.G.; Lin, J.; Pan, Y. Sequestration of u (vi) from acidic, alkaline, and high ionic-strength aqueous media by functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Capacity and binding mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14330–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhadra, M.; Eid, M.H.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Sharaf, M.; Soliman, A.T. Insight into chitosan/mesoporous silica nanocomposites as eco-friendly adsorbent for enhanced retention of u (vi) and sr (ii) from aqueous solutions and real water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liao, Y.; Xia, L. Poly (amidoamine) dendrimer decorated dendritic fibrous nano-silica for efficient removal of uranium (vi). J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 303, 122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, T.R.; Sahoo, P.K. Highly toxic cr (vi) adsorption by (chitosan-g-pmma)/silica bionanocomposite prepared via emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Astruc, D. Nanocatalysts and other nanomaterials for water remediation from organic pollutants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 408, 213180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, N.; Narasimhulu, K.; PydiSetty, Y. Recent advances in the bio-remediation of persistent organic pollutants and its effect on environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1602–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Pan, B.; Sakkiah, S.; Yavas, G.; Ge, W.; Zou, W.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Persistent organic pollutants in food: Contamination sources, health effects and detection methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okoro, H.K.; Pandey, S.; Ogunkunle, C.O.; Ngila, C.J.; Zvinowanda, C.; Jimoh, I.; Lawal, I.A.; Orosun, M.M.; Adeniyi, A.G. Nanomaterial-based biosorbents: Adsorbent for efficient removal of selected organic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Lee, D.; Cho, H.K.; Choi, S.D. Review of the QuEChERS method for the analysis of organic pollutants: Persistent organic pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and pharmaceuticals. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 22, e00063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Carrascosa, F.M.; Gómez-Peña, C.; Echeverría, R.; Moleón, J.J.J.; Melchor, J.M.; García-Ruiz, A.; Navarro-Espigares, J.L.; Cabeza-Barrera, J.; Martin-Olmedo, P.; Ortigosa-Garcia, J.C.; et al. Historical exposure to persistent organic pollutants and cardiovascular disease: A 15-year longitudinal analysis focused on pharmaceutical consumption in primary care. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Yap, P.S.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Liu, T.; Dulta, K.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Rangabhashiyam, S. Adsorption of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from the aqueous environment by nano-adsorbents: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, a141–a150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, S.S.; Adesibikan, A.A.; Saliu, O.D. Phytogenically bioengineered metal nanoarchitecture for degradation of refractory dye water pollutants: A Pragmatic Minireview. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 37, e6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routoula, E.; Patwardhan, S.V. Degradation of anthraquinone dyes from effluents: A review focusing on enzymatic dye degradation with industrial potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Sood, A.; Mehta, S.K. Comparative study of dye adsorption on silica nanoparticles: Effects of surface functionalization and other operational parameters. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 7433–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Polymer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and methylene blue adsorption. Materials 2018, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Rohani, S.; Lu, J. Fe3O4@SiO2@CS-TETA functionalized graphene oxide for the adsorption of methylene blue (MB) and Cu(II). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Torres, C.; González, F.; Shibue, T.; Nishide, H. Binding of methylene blue to polyelectrolytes containing sulfonate groups. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; You, L.; Xiang, H.; Jiang, Y. Comparison of dye adsorption by mesoporous hybrid gels: Understanding the interactions between dyes and gel surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, C.; Bouhadjar, B.; Adel, M.; Mohammed, H.; Fatima, Z.; Aniss, Z.; Khaldoun, B.; Rachid, M. Preparation of new nanocomposite poly (gdma)/mesoporous silica and its adsorption behavior towards cationic dye. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 153, 104611. [Google Scholar]
- Huq, R.; Mercier, L.; Kooyman, P.J. Incorporation of Cyclodextrin into Mesostructured Silica. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Pan, J. Study on the interaction of methylene blue with cyclodextrin derivatives by absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torad, N.L.; Azriq, R.; Ayad, M.M. Cyclodextrin functionalized mesoporous silica for environmental remediation of methylene blue dye. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Tang, T.; Chen, X. A facile approach to prepare porous cup-stacked carbon nanotube with high performance in adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Al-Ruwayshid, S.H.; Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles grafted with copolymer of acrylic acrylamide for ultra-removal of methylene blue from aquatic solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 130, 109698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, Z.; Hakiki, A.; Boukoussa, B.; Launay, F.; Hamaizi, H.; Bengueddach, A.; Hamacha, R. Preparation of highly hydrophilic pva/sba-15 composite materials and their adsorption behavior toward cationic dye: Effect of pva content. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 7679–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.A.; Nistico, R.; Magnacca, G.; Scalarone, D. Packed hybrid silica nanoparticles as sorbents with thermo-switchable surface chemistry and pore size for fast extraction of environmental pollutants. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouhadjar, B.; Aboubakr, H.; Sarah, M.; Karim, C.; Djamal, E.K.; Larbi, B.; Djahida, G.; Khadidja, M.; Fatima, M.; Rachida, H. Adsorption behaviors of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution on nanocomposite polypyrrole/sba-15. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7372–7386. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Peng, Y.; Luo, J. Chitosan/organic rectorite composite for the magnetic uptake of methylene blue and methyl orange. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Batonneau-Gener, I.; Pouilloux, Y.; Hamad, H. Removal of methylene blue by mesoporous CMK-3: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Ghasemi, N.; Shahivand, M.; Ghasemi, M. Kinetics, equilibrium studies and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption on Ephedra strobilacea saw dust and modified using phosphoric acid and zinc chloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, K.M.; Almethen, A.A.; Beagan, A.M.; Al-Swaidan, H.M.; Ahmad, A.; Bhawani, S.A.; Alswieleh, A.M. Quaternization of poly (2-diethyl aminoethylmethacrylate) ush-grafted magnetic mesoporous nanoparticles using 2-iodoethanol for removing anionic dyes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beagan, A.; Alshammari, R.; Alotaibi, L.; Albarrak, H.; Alotaibi, K.; Alswieleh, A. High-efficient anionic dyes removal from water by cationic polymer brush functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaie, M.; Rashidi, A.; Tayebi, H.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Removal of anionic dye from aqueous media by adsorption onto sba-15/polyamidoamine dendrimer hybrid: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabinejad, A.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Tayebi, H.A. Synthesis of conductive polymer-coated mesoporous mcm-4 for textile dye removal from aqueous media. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2017, 7, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsini, N.N.; Ansari, M.; Kazemipour, M. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer on magnetic core-shell silica nanoparticles for recognition of congo red Eurasian. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanei, M.; Rashidi, A.; Tayebi, H.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Removal of acid blue 25 from aqueous media by magnetic-sba-15/cpaa super adsorbent: Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 3592–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, X. Simultaneous identification of nine carcinogenic dyes from textiles by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry via negative/positive ion witching mode. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 15, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arica, T.A.; Ayas, E.; Arica, M.Y. Magnetic MCM-41 silica particles grafted with poly(glycidylmethacrylate) brush: Modification and application for removal of direct dyes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 243, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerritore, M.; Castaldo, R.; Silvestri, B.; Avolio, R.; Cocca, M.; Errico, M.E.; Avella, M.; Gentile, G.; Ambrogi, V. Hyper-crosslinked polymer nanocomposites containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption towards polar dyes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahalkeh, F.; Mehrabian, R.Z.; Ebadi, M. Removal of brilliant red dye (brilliant red e-4ba) from wastewater using novel chitosan/sba-15 nanofiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, K.; Tayebi, H.A. Synthesis of sba-15/pani mesoporous composite for adsorption of reactive dye from aqueous media: Rbf and mlp networks predicting models. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, C.F.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C. Fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (phacs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Peña, O.I.; López Zavala, M.Á.; Cabral Ruelas, H. Pharmaceuticals market, consumption trends and disease incidence are not driving the pharmaceutical research on water and wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Meric, S.; Nikolaou, A. Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: Current state of knowledge and future research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luján-Facundo, M.J.; Iborra-Clar, M.I.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I. Pharmaceutical compounds removal by adsorption with commercial and reused carbon coming from a drinking water treatment plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wei, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Pan, J.; Zou, T.; Li, C.; Yanb, Y. Highly-controllable imprinted polymer nanoshell at the surface of magnetic halloysite nanotubes for selective recognition and rapid adsorption of tetracycline. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7967–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, Y.; Tao, Q.; Li, A.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y. Synthesizing a surface-imprinted polymer based on the nanoreactor sba-15 for optimizing the adsorption of salicylic acid from aqueous solution by response surface methodology. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Aziz-Zanjani, M.O.; Ahmadifar, M.; Jabbari, A. Design and synthesis of molecularly imprinted polypyrrole based on nanoreactor sba-15 for recognition of ascorbic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Song, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, C. Highly-controllable imprinted polymer nanoshell on the surface of silica nanoparticles for selective adsorption of 17β-estradiol. J. Encapsulation Adsorpt. Sci. 2018, 8, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfhaid, L.H.K. Adsorption of paracetamol in contaminated water through pH-responsive polymer-brush-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, L.Y.; Huang, F.; Ouyang, X.K. Pei-modified core-shell/bead-like amino silica enhanced poly (vinylalcohol)/chitosan for diclofenac sodium efficient adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Khan, Z.M.; Naz, I.; Sultan, M. An overview of heavy metal removal from wastewater using magnetotactic bacteria. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2817–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmobarak, W.F.; Almomani, F. Enhanced oil recovery using hyperbranched polyglycerol polymer-coated silica nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.B.; Siqueira, J.S.; Grayson, S.M. Oil encapsulation advantages of amphiphilic polymer-grafted silica nanoparticle systems. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5893–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, A.; Stensen, J.Å.; Torsæter, O. Experimental investigation of polymer-coated silica nanoparticles for enhanced oil recovery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haruna, M.A.; Gardy, J.; Yao, G.; Hu, Z.; Hondow, N.; Wen, D. Nanoparticle modified polyacrylamide for enhanced oil recovery at harsh conditions. Fuel 2020, 268, 117186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.J. Synthesis of poly (methacrylic acid)-functionalized sba-15 and its adsorption of phenol in aqueous media. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 3570–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, C.; Han, Y.; Duan, Y.; Lai, X.; Fu, R.; Liu, S.; Leong, K.H.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, L. Review on the contamination and remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (pahs) in coastal soil and sediments. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Song, X.; Ding, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Bioremediation of pahs and heavy metals co-contaminated soils: Challenges and enhancement strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkas, M.; Tsiourvas, D. Organic/inorganic hybrid nanospheres based on hyperbranched poly (ethylene imine) encapsulated into silica for the sorption of toxic metal ions and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Cyclodextrin-functionalized mesostructured silica nanoparticles for removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houghton, J.T.; Jenkins, G.J.; Ephraums, J.J. Climate Change, The IPC Assessment; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Muntean, M.; Peters, J.A.H.W. Trends in Global CO2 Emissions: 2016 Report; PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.; Roney, C.; Alsalam, J.; Calvin, K.; Creason, J.; Edmonds, J.; Fawcett, A.A.; Kyle, P.; Narayan, K.; O’Rourke, P.; et al. Deep mitigation of CO2 and non-CO2 greenhouse gases toward 1.5 °C and 2 °C futures. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.R. (Ed.) IPCC Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kenarsari, S.D.; Yang, D.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Russell, A.G.; Weif, Q.; Fan, M. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22739–22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Zhao, A.; Shimizu, G.K.; Sarkar, P.; Gupta, R. Post-combustion CO2 capture using solid sorbents: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 1438–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Murdock, C.R.; Didas, S.A.; Jones, C.W. Direct capture of CO2 from ambient air. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11840–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashaki, M.J.; Khiavi, S.; Sayari, A. Stability of amine-functionalized CO2 adsorbents: A multifaceted puzzle. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3320–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudheir, A.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Chakma, A.; Idem, R. Kinetics of the reactive absorption of carbon dioxide in high CO2 -loaded, concentrated aqueous monoethanolamine solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 5195–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meth, S.; Goeppert, A.; Prakash, G.S.; Olah, G.A. Silica nanoparticles as supports for regenerable CO2 sorbents. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Zhao, X.S.; Chen, Z. Carbon dioxide capture by dendrimer-modified silica nanoparticles. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calleja, G.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S. CO2 adsorption on branched polyethyleneimine-impregnated mesoporous silica sba-15. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5323–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, J.; Tian, S.; Yan, F.; Chen, X. Polyethyleneimine–nano silica composites: A low-cost and promising adsorbent for co 2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomari, K.; Boukoussa, B.; Hamacha, R.; Bengueddach, A.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Preparation of dendrimer polyol/mesoporous silica nanocomposite for reversible CO2 adsorption: Effect of pore size and polyol content. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Chejanovsky, I.; Suckeveriene, R.Y. Grafting of poly(ethylene imine) to silica nanoparticles for odor removal from recycled materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Franz, R. Identification of migratable substances in recycled high density polyethylene collected from household waste. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 1997, 20, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machowski, K.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Dudek, B.; Michalik, M. Elimination of ketone vapors by adsorption on spherical MCM-41 and MCM-48 silicas decorated with thermally activated poly (furfuryl alcohol). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 165, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, K.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with stimuli-responsive polymer brush as an efficient adsorbent for chlorophenoxy herbicides removal from contaminated water. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plohl, O.; Gyergyek, S.; Zemljič, L.F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with n-rich polymer as a potentially environmentally-friendly delivery system for pesticides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 310, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Mao, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, H.; He, S. Thermoresponsive polymer-encapsulated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in insecticide delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Molecularly imprinted core-shell nanoparticles for determination of trace atrazine by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer surface imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4346–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, H.; Rui, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, J. Preparation and properties of aflatoxins imprinted polymer grafted onto the surface of mesoporous silica sba-15 functionalized with double bonds. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 4181–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wang, H.; Fei, G.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y. Magnetically sensitive and high template affinity surface imprinted polymer prepared using porous TiO2-coated magnetite-silica nanoparticles for efficient removal of tetrabromobisphenol a from polluted water. ADV Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Silica | Polymer | Elements Retained by the Silica/Polymer Nanocomposite | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | PAA (Polyacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) | Pb (II)/Cd (II) | [110] |
| MCM-41 | PVA (Poly(vinyl alcohol)) | Cd (II) | [111] |
| Fe3O4_Silica | PmAP (Poly(m-aminophenol)) | Hg (II) | [113] |
| MCM-41 | PMMA (Poly-methyl methacrylate) | Cu (II) | [104] |
| γ-Fe2O3_Silica | CMC (Amino-biopolymer carboxymethyl chitosan) | Cu (II) | [105] |
| Silica | Chitosan + PMMA (Poly(methyl methacrylate) | Cr (VI) | [121] |
| SBA-15 | PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) | Pb (II)/Ni (II)/Cd (II) | [107] |
| Fe3O4_SBA-15 | Imprinted Polymer using Methacrylic Acid | Pb (II)/Cd (II) | [109] |
| Silica | COL (Chitosan oligosaccharide lactate) | Hg (II) | [103] |
| MCM-48 | β-CD (β-cyclodextrin) | As (V)/Hg (II) | [112] |
| Silica | PANAM (Polyacrylonitrile-acrylamide) | Pb (II)/Cs (II)/Cu (II)/Cd (II)/Sr (II) | [106] |
| Silica | Copolymerized 1-vinyl-imidazole + acrylic acid | Ni (II) | [108] |
| Silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (MMS) | Amidoxime (MMS-AO) | U (VI) | [115] |
| MCM-41 | PAN (Polyacrylonitrile) + Amidoxime | U (VI) | [116] |
| MMSNs | PPI (Poly(propyleneimine) dendrimer)) and PANAM (Polyamidoamine dendrimer) | U (VI) | [117] |
| MMSNs | PPI (Poly(propyleneimine) dendrimer)) and PANAM (Polyamidoamine dendrimer) | U (VI) | [118] |
| MCM-48 | Chitosan | U (VI)/Sr (II) | [119] |
| DFNS (Fibrous dendritic silica) | PANAM (Poly(amidoamine)) | U (VI) | [120] |
| Nanocomposite | Adsorbate | Removal Rate | Adsorption Capacity | Recycling | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41-PMMA (Poly-methyl methacrylate) | Cu (II) | ------ | 40.95 mg/g | ------ | [104] |
| γ- Fe2O3_Silica-CMC (Amino-biopolymer carboxymethyl chitosan) | Cu (II) | 35% | ≈ 350 mg/g | 4 cycles | [105] |
| SBA-15–PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) | Pb (II)/Ni (II)/Cu (II) | Pb (II) = 52% Ni (II) = 44% Cu (II) = 35% | Pb (II) = 175 mg/g Ni (II) = 72 mg/g Cu (II) = 128 mg/g | ------ | [107] |
| Silica Copolymerized 1-vinyl-imidazole + acrylic acid | Ni (II) | 99.40% | 62.81 mg/g | 5 cycles | [108] |
| Fe3O4_SBA-15–Imprinted Polymer using Methacrylic Acid | Pb (II)/Cd (II) | Pb (II) = 90.11% Cd (II) = 94.55% | Pb (II) = 18.18 mg/g Cd (II) = 14.28 mg/g | 5 cycles | [109] |
| MCM-41 PAA (Polyacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) | Pb (II)/Cd (II) | Pb (II) = 60–83% Cd (II) = 88–98% | Pb (II) = 14.77 mg/g Cd (II) = 21.15 mg/g | 10 cycles | [110] |
| MCM-41–PVA (Poly(vinyl alcohol)) | Cd (II) | ------ | 46.73 mg/g | ------ | [111] |
| Silica-COL (Chitosan oligosaccharide lactate) | Hg (II) | 77.98% | 116.7 mg/g | ------ | [103] |
| MCM-48–β-CD (β-cyclodextrin) | As (V)/Hg (II) | As (V) = 72.8% Hg (II) = 60.4% | As (V) = 265.6 mg/g Hg (II) = 207.9 mg/g | ------ | [112] |
| Fe3O4_Silica–PmAP (Poly(m-aminothiophenol) | Hg (II) | 97.53% | 243.98 mg/g | 5 cycles | [113] |
| Mesoporous silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (MMS)–Amidoxime (MMS-AO) | U (VI) | > 99% | 277.3 mg/g | 5 cycles | [115] |
| MCM-41–PAN (Polyacrylonitrile + Amidoxime) | U (VI) | 97% | 442.3 mg/g | 10 cycles | [116] |
| MMSNs–PPI (Polypropylene imine dendrimer) and PAMAM (Polyamidoamine dendrimer) | U (VI) | ------ | PPI = 133.3 mg/g PAMAM = 53.8 mg/g | 5 cycles | [118] |
| MCM-48—Chitosan | U (VI)/Sr (II) | U (VI) = 100% at 1.2 g/L of adsorbent Sr (II) = 100% at 1.2 g/L of adsorbent | U (VI) = 260 mg/g Sr (II) = 330 mg/g | 5 cycles | [119] |
| DFNS (Fibrous dendritic silica)–PANAM (Polyamidoamine) | U (VI) | >90% | 215.2 mg/g | 5 cycles | [120] |
| Silica–Chitosan + PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) | Cr (VI) | 98% | 92.5 mg/L | ------ | [121] |
| Material | Polymer | Adsorbate | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Modified-Silica-Magnetic-Nanoparticles | Acrylic Acid (AA) 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid (AMPS) | Methylen Blue | [134] |
| MCM-41 | Polyglycerolmethacrylate poly(GDMA) | Methylen Blue | [139] |
| KIT-6 | β-cyclodextrin | Methylen Blue | [142] |
| Silica Nanoparticles | Acrylic acrylamide (SAA) | Methylen Blue | [144] |
| SBA-15 | Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Methylen Blue | [145] |
| Silica Nanoparticles | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) | Methylen Blue | [146] |
| SBA-15 | Polypyrrole | Methylen Blue Methyl Orange  | [147] |
| Fe3O4@MSN | Poly(2-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) (PDEAEMA) | Methyl Orange E110—Sunset Yellow (SY)  | [151] |
| Magnetic silica nanoparticles | Poly(2-methacryloyloxy)ethyl trimethylammonium chloride—(PMETAC) | Methyl Orange Bromothymol Blue  | [152] |
| SBA-15 | Poly(amidoamine) | Acid Blue 62 | [153] |
| MCM—41 | Polypirrole–PPy Polyaniline–PAni | Acid Blue 62 | [154] |
| Silica magnetic nanoparticles-Aptes modified | Molecular Imprinted Polymer | Congo Red | [155] |
| SBA-15 | Cross-linked poly-(acrylic acid) (CPAA) | Acid Blue 25 | [156] |
| Magnetic MCM-41 | Poly(2-methacryloyloxy)ethyl] trimethylammonium chloride—(PMETAC) | Direct Blue 6 Direct Black 38  | [158] |
| Magnetic Silica Nanoparticles | Zwitterionic polymer derived from: poly(2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate) | Rhodamine B (Rh B) Crystal Violet (CV)  | [85] |
| MSN (Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles) | Hyper-Crosslinked Polymer, based on vinylbenzyl chloride and divinylbenzene | Remazol Brilliant Blue R | [159] |
| SBA-15 | Chitosan | Brilliant Red E-B4A | [160] |
| SBA-15 | Polyaniline | Reactive Orange 16 (RO 16) | [161] |
| Material | Polymer | Adsorbate | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous silica nanoparticles | Poly(2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PTBAEMA) | Paracetamol | [170] |
| SBA-15 | Polypirrole based molecularly imprinted polymers | Acido Ascorbico | [168] |
| Stober Silica Nanoparticles | Molecularly imprinted polymers | 17β-Estradiol | [169] |
| SBA-15 | Molecularly imprinted polymers | Salicylic acid | [167] |
| Core–shell aminografted silica nanoparticle | Polyvinyl alcohol chitosan | Diclofenac sodium | [171] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grisolia, A.; Dell’Olio, G.; Spadafora, A.; De Santo, M.; Morelli, C.; Leggio, A.; Pasqua, L. Hybrid Polymer-Silica Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Remediation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135105
Grisolia A, Dell’Olio G, Spadafora A, De Santo M, Morelli C, Leggio A, Pasqua L. Hybrid Polymer-Silica Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Remediation. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrisolia, Antonio, Gianluca Dell’Olio, Angelica Spadafora, Marzia De Santo, Catia Morelli, Antonella Leggio, and Luigi Pasqua. 2023. "Hybrid Polymer-Silica Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Remediation" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135105
APA StyleGrisolia, A., Dell’Olio, G., Spadafora, A., De Santo, M., Morelli, C., Leggio, A., & Pasqua, L. (2023). Hybrid Polymer-Silica Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Remediation. Molecules, 28(13), 5105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135105








