Combination of RCA and DNAzyme for Dual-Signal Isothermal Amplification of Exosome RNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design and Working Principle of the RCA–DNAzyme Assay
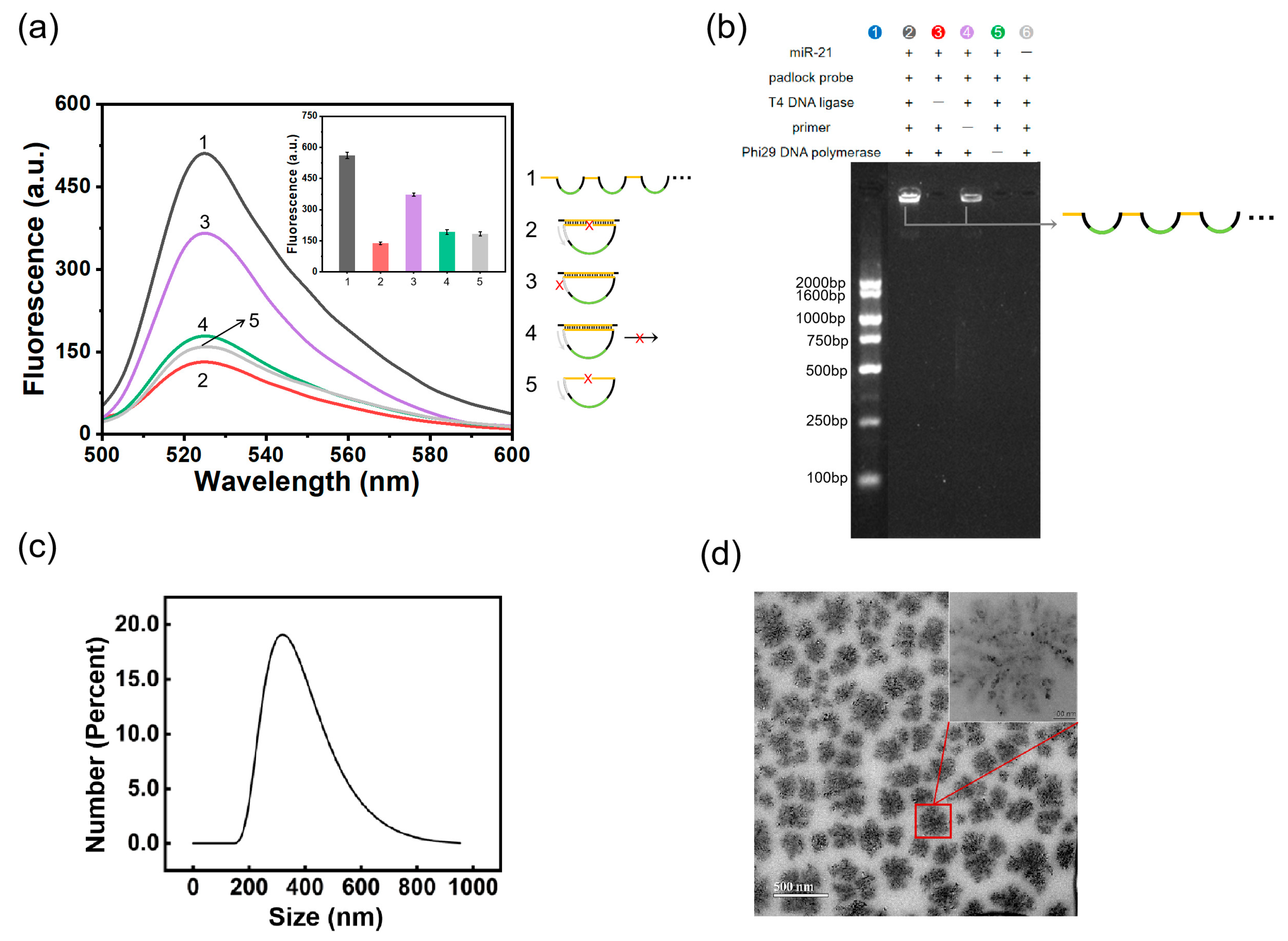
2.2. Feasibility Validation of the RCA–DNAzyme Assay
2.3. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
2.4. Quantification Performance of the RCA–DNAzyme Assay
2.5. Specificity Evaluation of the Assay
2.6. Characterization of Exosomes and Detection of miR-21
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Detection of exRNA Using the RCA–DNAzyme Assay
3.3. Gel Electrophoresis Analysis and Fluorescence Measurements
3.4. Dynamic Light Scattering and Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.5. Cell Culture and Exosomes Extraction
3.6. Characterization of Exosomes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shao, H.; Im, H.; Castro, C.M.; Breakefield, X.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. New Technologies for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1917–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Qin, J. Microfluidic strategies for label-free exosomes isolation and analysis. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, L.; Giurato, G.; Cicchini, C.; Montaldo, C.; Mancone, C.; Tarallo, R.; Battistelli, C.; Alonzi, T.; Weisz, A.; Tripodi, M. The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redzic, J.S.; Balaj, L.; van der Vos, K.E.; Breakefield, X.O. Extracellular RNA mediates and marks cancer progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 28, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhan, S.; Yao, J.; Lowery, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.-C.; Li, P.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 2015, 527, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, B.; Gao, X.; Zou, T.; Luo, Q.; Chen, M.; Fu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Exosomal S100A4 derived from highly metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cells promotes metastasis by activating STAT3. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Pan, Y.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Zhang, H. Complex RNA world in small extracellular vesicles for liquid biopsy in cancer management. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Wei, S.; Su, D.; Zhai, Z.; Hua, X.; Li, H. The emerging role of exosome-derived non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Shu, Y. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3133–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 2001, 294, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dangwal, S.; Bang, C.; Thum, T. Novel techniques and targets in cardiovascular microRNA research. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruby, J.G.; Jan, C.; Player, C.; Axtell, M.J.; Lee, W.; Nusbaum, C.; Ge, H.; Bartel, D.P. Large-scale sequencing reveals 21U-RNAs and additional microRNAs and endogenous siRNAs in C-elegans. Cell 2006, 127, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- t Hoen, P.A.C.; Ariyurek, Y.; Thygesen, H.H.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Vossen, R.H.A.M.; de Menezes, R.X.; Boer, J.M.; van Ommen, G.-J.B.; den Dunnen, J.T. Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandham, S.; Su, X.; Wood, J.; Nocera, A.L.; Alli, S.C.; Milane, L.; Zimmerman, A.; Amiji, M.; Ivanov, A.R. Technologies and Standardization in Research on Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1066–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Miao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Song, J.; Cui, D. Progress in Microfluidics-Based Exosome Separation and Detection Technologies for Diagnostic Applications. Small 2020, 16, e1903916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.H.; Jang, S.; Shin, G.; Jung, G.Y.; Lee, J.W. Sensitive fluorescence detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical samples via one-pot isothermal ligation and transcription. Nat. Biomed. Eng 2020, 4, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.-Q.; Li, Z.-H.; Wen, S.-W.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.-G.; Wang, G.-Y. Identification of Commonly Dysregulated Genes in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Analysis of Microarray Data and qRT-PCR Validation. Lung 2015, 193, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Huang, C.-Y.; Johnson, E.J.; Yang, L.; Zieren, R.C.; Horie, K.; Kim, C.-J.; Warren, S.; Amend, S.R.; Xue, W.; et al. High-Throughput Simultaneous mRNA Profiling Using nCounter Technology Demonstrates That Extracellular Vesicles Contain Different mRNA Transcripts Than Their Parental Prostate Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, F.; Zou, P. Label-free and enzyme-free colorimetric detection of microRNA by catalyzed hairpin assembly coupled with hybridization chain reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Deng, H.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. A Highly Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Biosensor for Direct Detection of MicroRNAs in Serum. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4784–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee-Pour, H.-A.; Behpour, M.; Keshavarz, M. A novel label-free electrochemical miRNA biosensor using methylene blue as redox indicator: Application to breast cancer biomarker miRNA-21. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, R.; Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Quan, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Fan, C.; Xia, F. Lab in a Tube: Ultrasensitive Detection of MicroRNAs at the Single-Cell Level and in Breast Cancer Patients Using Quadratic Isothermal Amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4604–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weizmann, Y.; Beissenhirtz, M.K.; Cheglakov, Z.; Nowarski, R.; Kotler, M.; Willner, I. A Virus Spotlighted by an Autonomous DNA Machine. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2006, 45, 7384–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.Y.; Niu, W.K.; Li, H.; Lei, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.N.; Guo, L.J.; Zou, D.Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.Y.; et al. Rapid detection of Acinetobacter baumannii and molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii in two comprehensive hospitals of Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomar, P.S.; Kumar, S.; Patel, S.; Kumar, J.S. Development and Evaluation of Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of West Nile Virus in Human Clinical Samples. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 619071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Kang, D.-K.; Ankrum, J.A.; Le, X.C.; Zhao, W. Rolling circle amplification: A versatile tool for chemical biology, materials science and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ali, M.M.; Brook, M.A.; Li, Y. Rolling Circle Amplification: Applications in Nanotechnology and Biodetection with Functional Nucleic Acids. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2008, 47, 6330–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.G.; Kool, E.T. The Discovery of Rolling Circle Amplification and Rolling Circle Transcription. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2540–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, J.; Lai, W.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. A rolling circle amplification-based DNA machine for miRNA screening coupling catalytic hairpin assembly with DNAzyme formation. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Qiu, X.; Qing, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; He, Z.; Zhong, D.; et al. Rolling Circular Amplification (RCA)-Assisted CRISPR/Cas9 Cleavage (RACE) for Highly Specific Detection of Multiple Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Elbaz, J.; Teller, C.; Willner, I. Amplified Detection of DNA through an Autocatalytic and Catabolic DNAzyme-Mediated Process. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2011, 50, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, R.-C.; Zhou, Z.-R.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y. Cell Surface Engineering Using DNAzymes: Metal Ion Mediated Control of Cell-Cell Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5737–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda-Plaza, M.; McGhee, C.E.; Lu, Y. Evidence of a General Acid–Base Catalysis Mechanism in the 8–17 DNAzyme. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Khan, M.R.; Zhao, Z.; He, G.; Luo, A.; Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; He, Q. Label-free DNAzyme assays for dually amplified and one-pot detection of lead pollution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Gong, K.; Shang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F. Construction of an Autonomous Nonlinear Hybridization Chain Reaction for Extracellular Vesicles-Associated MicroRNAs Discrimination. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10172–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Kim, D.-M.; Baek, A.; Chung, H.; Jung, W.; Kim, D.-E. Fluorescence-based detection of single-nucleotide changes in RNA using graphene oxide and DNAzyme. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5641–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Elbaz, J.; Orbach, R.; Magen, N.; Willner, I. Amplified Analysis of DNA by the Autonomous Assembly of Polymers Consisting of DNAzyme Wires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17149–17151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yang, P.; Hou, X.; Hou, X.; Chen, J. Accelerating DNA nanomotor by branched DNAzyme for ultrasensitive optical detection of thrombin. Microchem. J. 2018, 139, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; He, M.; Chen, T.; Chu, X. A microRNA-triggered self-powered DNAzyme walker operating in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.Z.; Yin, W.; Shi, Y.K.; Zou, X.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Dai, Z. Dual-Locked DNAzyme Platform for In Vitro and In Vivo Discrimination of Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12221–12230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Lv, W.Y.; Xu, Y.T.; Li, Y.F.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. DNA Logic Nanodevices for the Sequential Imaging of Cancer Markers through Localized Catalytic Hairpin Assembly Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4399–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhu, J.-J.; Zhang, J. Near-Infrared-Light-Mediated DNA-Logic Nanomachine for Bioorthogonal Cascade Imaging of Endogenous Interconnected MicroRNAs and Metal Ions. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 16622–16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Samples | Spiked (pM) | Detected (pM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 9.51 | 95.10 | 4.25 |
| 2 | 100 | 98.17 | 98.17 | 3.55 |
| 3 | 5000 | 5370.32 | 107.41 | 5.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Y.; Lei, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ren, X. Combination of RCA and DNAzyme for Dual-Signal Isothermal Amplification of Exosome RNA. Molecules 2023, 28, 5528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145528
Xia Y, Lei X, Ma X, Wang S, Yang Z, Wu Y, Ren X. Combination of RCA and DNAzyme for Dual-Signal Isothermal Amplification of Exosome RNA. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145528
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Yuqing, Xin Lei, Xiaochen Ma, Shizheng Wang, Zifu Yang, Yifan Wu, and Xiaojun Ren. 2023. "Combination of RCA and DNAzyme for Dual-Signal Isothermal Amplification of Exosome RNA" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145528
APA StyleXia, Y., Lei, X., Ma, X., Wang, S., Yang, Z., Wu, Y., & Ren, X. (2023). Combination of RCA and DNAzyme for Dual-Signal Isothermal Amplification of Exosome RNA. Molecules, 28(14), 5528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145528






