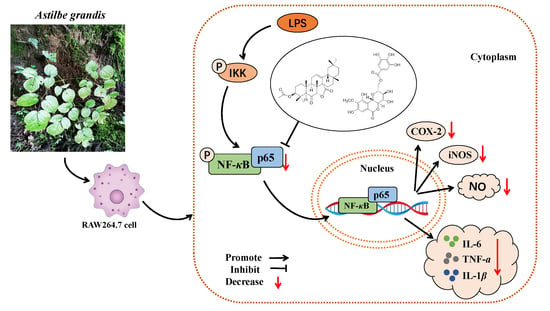
Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from Astilbe grandis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from A. grandis
2.2. Effect of Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on the Cell Viability of RAW264.7 Cells
2.3. Effect of the Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on NO Secretion in the Supernatant of RAW264.7 Cells Induced by LPS
2.4. Effect of the Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on the Content of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in the Supernatant of RAW264.7 Cells Induced by LPS
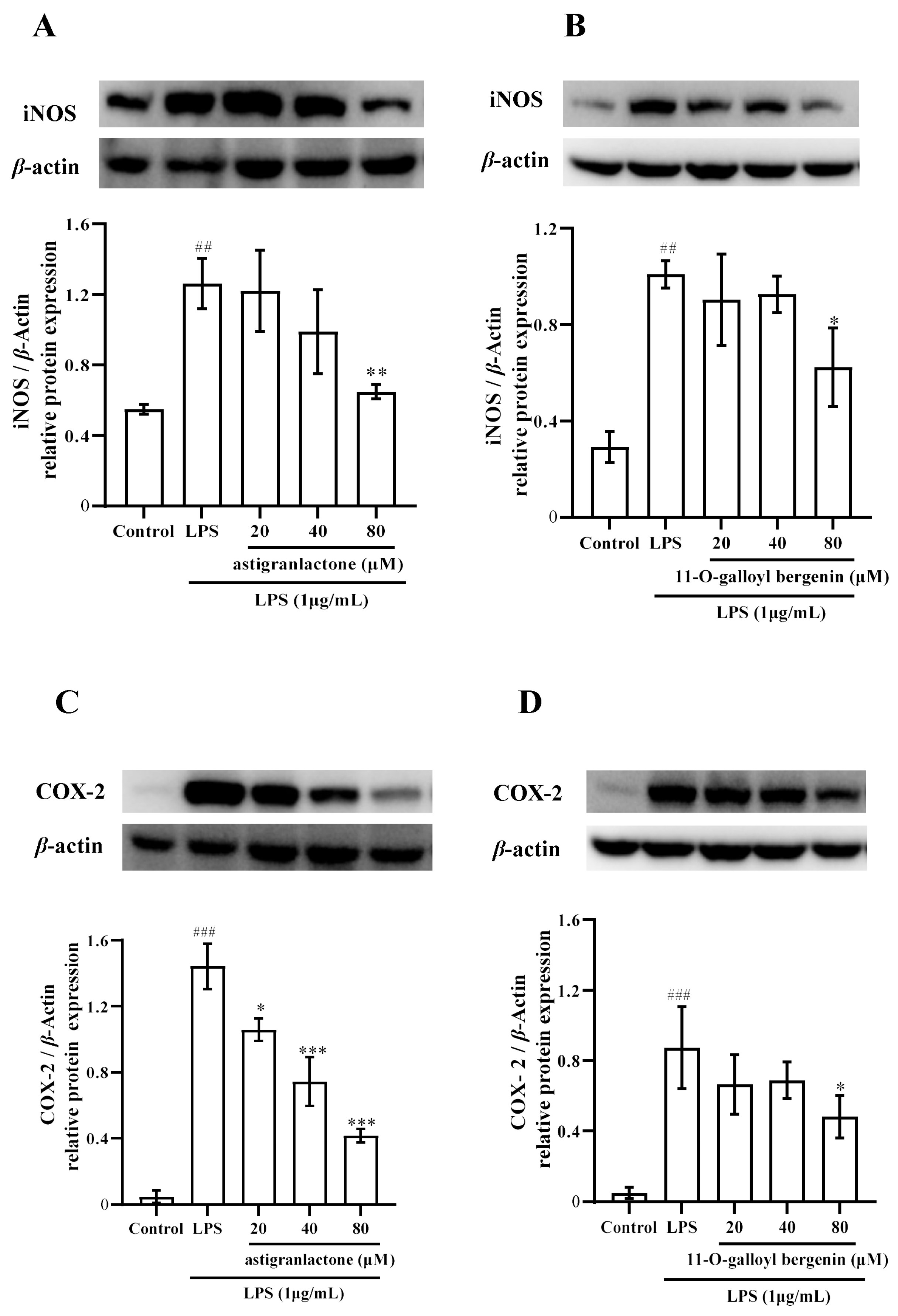
2.5. Effect of the Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on COX-2 and iNOS Expression in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells
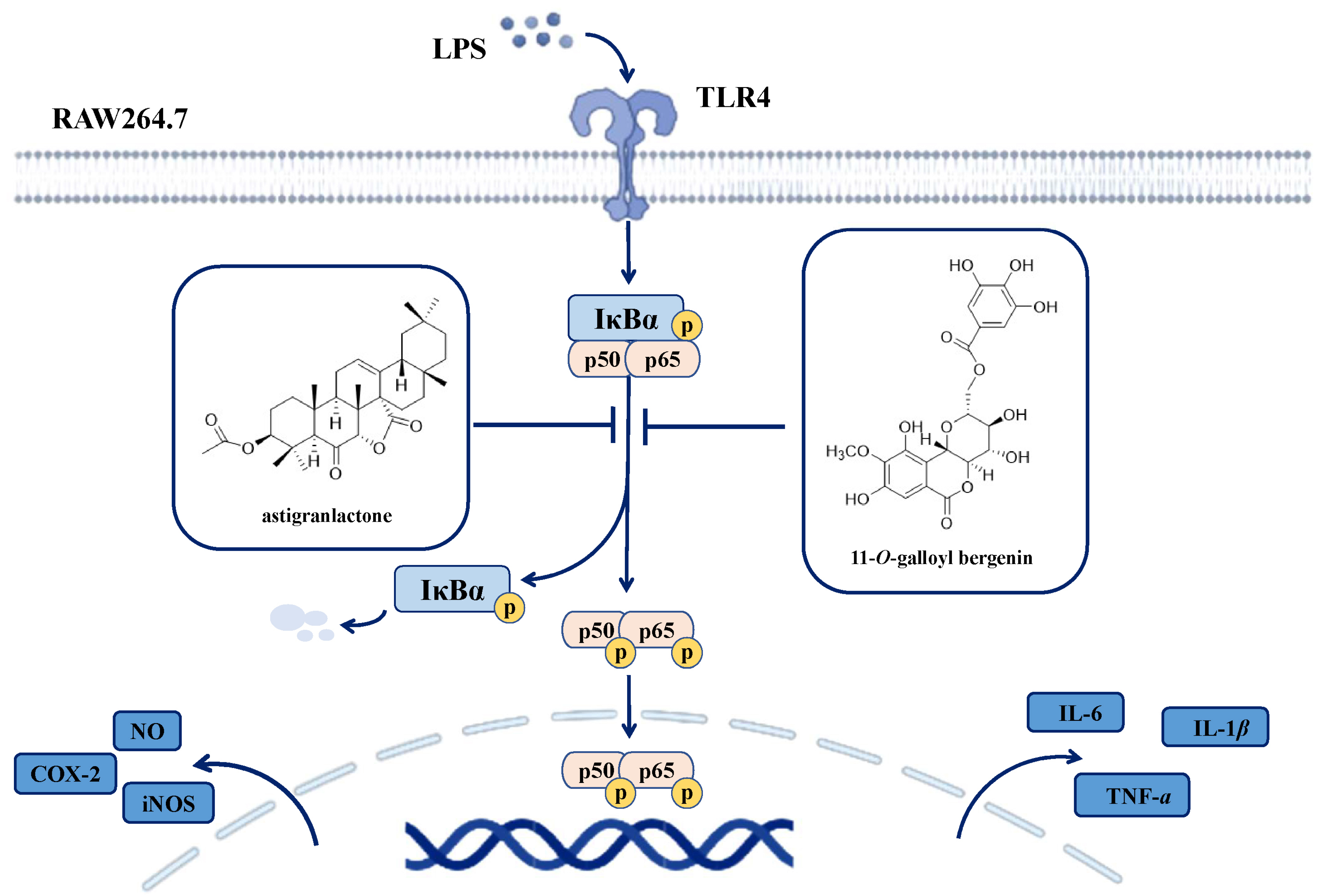
2.6. Effects of Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on the NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells
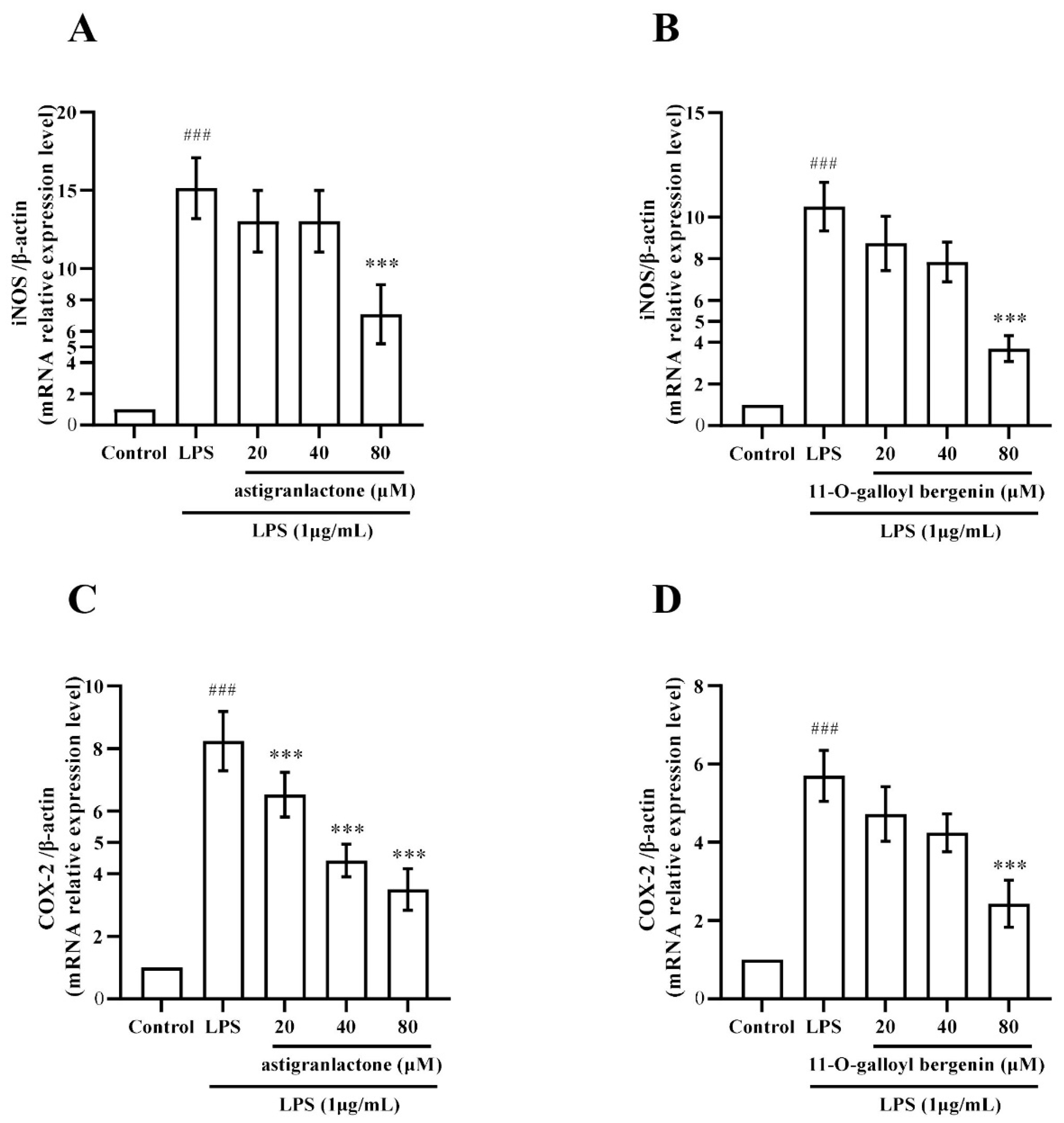
2.7. Effect of Astigranlactone and 11-O-Galloyl Bergenin on iNOS and COX-2 mRNA Expression in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction and Isolation of Triterpenoid and Coumarin from A. grandis
4.3. RAW264.7 Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.5. Assay of Nitric Oxide Concentration, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β
4.6. Western Blotting to Detect the Expression of COX-2, iNOS, and p-p65
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Method
4.7.1. Total Cellular RNA was Extracted
4.7.2. RNA Reverse Transcription into cDNA
4.7.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ferrero-Miliani, L.; Nielsen, O.H.; Andersen, P.S.; Girardin, S. Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 147, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yizhen, L.; Kang, H.; Wukai, M.; Jiang, D. The extraction and isolation of different parts of kidney of Musang Doggo and Cao Doggo and preliminary screening of anti-rheumatism molecular targets in vitro. Imaging Res. Med. Appl. 2017, 1, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, J.G.; Boltjes, A.; Scholman, R.C.; Vervoort, S.J.; Coffer, P.J.; Mokry, M.; Loosdregt, J. Epigenetic changes in inflammatory arthritis monocytes contribute to disease and can be targeted by JAK inhibition. Rheumatology 2023, kead001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hao, C.; Li, W. Traditional Chinese medicine Rhodiola sachalinensis borissova from baekdu mountain (RsBBM) for rheumatoid arthritis: Therapeutic effect and underlying molecular mechanisms. Molecules 2022, 27, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuller, L.H.; Tracy, R.P. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Review article inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Gu, J.; Cao, L.; Li, N.; Ding, G.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Traditional Chinese herbs as chemical resource library for drug discovery of anti-infective and anti-inflammatory. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.N.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, Q.; Mark Evers, B. Alternative medicine products as a novel treatment strategy for inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2008, 36, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huai, Y.; Miao, Z.; Qian, A.; Wang, Y. Systems pharmacology for investigation of the mechanisms of action of traditional Chinese medicine in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Z.H.; Du, J. Study on the acute toxicity and oil safety of Miao medicine Ma sang gou bang. Chin. J. Ethn. Med. 2012, 8, 53–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.F.; Zhu, G.Q.; Lu, C. Observation on the therapeutic effect of Miao Yao Ma Shang Gou Jiu Ji Bang Jiu Ji on 34 cases of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Ethnomedicine Ethnopharmacy 2012, 2, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.X.; Zhao, D.; Cui, J. Research progress on Miao medicine Ma sang gou bang. Chin. J. Ethnomedicine Ethnopharmacy 2016, 25, 42–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Wu, T.T.; Fan, L.L.; Shen, L.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Zou, J. Research on chemical constituents from Astilbe grandis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2021, 43, 105–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Wu, T.T.; Fan, L.L.; Shen, L.Y.; Xu, H.; Zou, J. Research on triterpenes from Astilbe grandis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2020, 42, 1791–1794. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shen, Y. Cytotoxic Pentacyclic Triterpenoids from the Rhizome of Astilbe chinensis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2003, 86, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.Y.; Li, Z.M. The diversity of this bioactivity has resulted in significant attention being paid to this class of triterpenoid. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.L.; Mao, Z.W.; Zuo, A.X.; Rao, G.X. Studies on chemical constituents from the Bergenia pururascens. J. Yunnan Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 37, 34–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Luo, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Basic theories and development of Miao medicine. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2021, 8, S22–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, D.; Cheng, H.; Bussmann, R.W.; He, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, B. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by Miao people in Jijiezi, Yunnan, China. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2019, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Shen, S.S.; Deng, X.; Shiu, H.T.; Siu, W.S.; Leung, P.C.; Cheng, B.C. Dihydrofisetin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects associated with suppressing ERK/p38 MAPK and Heme Oxygenase-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and carrageenan-induced mice paw edema. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, C.M.; Kim, J.J.; Noh, K.H.; Cho, C.M.; Song, Y.S. The protective effect of chlorophyll a against oxidative stress and inflammatory processes in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 16, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, E.H. Hemistepsin A ameliorates acute inflammation in macrophages via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. 2018, 111, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Yoshida, H.; Asakawa, M.; Kawasumi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimura, A. IL-1β and TNFα-initiated IL-6-STAT3 pathway is critical in mediating inflammatory cytokines and RANKL expression in inflammatory arthritis. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Macrophages, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 27, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.H.; Im, H.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Yun, K.J.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, K.T. Anti-inflammatory effect of buddlejasaponin IV through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via the NF-kappaB inactivation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Alam, M.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Madina, M.H.; Fliss, I.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, J.C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by peptide YD1 attenuates inflammatory symptoms through suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB signaling cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.F.; Zhou, H.; Lio, C.K. Akebia saponin D inhibits the inflammatory reaction by inhibiting the IL-6-STAT3-DNMT3b axis and activating the Nrf2 pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.G.; Christman, J.W. The role of nuclear factor kappa B in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases: Implications for therapy. Am. J. Respir. Med. 2003, 2, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Gong, S.Y.; Sohng, J.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Sparassis crispa exerts anti-inflammatory activity via suppression of TLR-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarte, K.; Quimque, M.T.J.; Macaranas, I.T.; Khan, A.; Pastrana, A.M. Villaflores, Attenuation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the NF-κB pathway and the Increased NRF2 Level by a Flavonol-Enriched n -Butanol Fraction from Uvaria alba. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5377–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadleigh, D.J. Transcriptional activation of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene in endotoxin-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6259–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Han, Y.K.; Su, X.D.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.C. Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.M.; Luo, Z.M.; Zhou, D.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Z. Dual role of NF-κB and its target gene iNOS in cerebral ischemic tolerance induced by focal ischemic preconditioning. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010, 90, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Wen, J.K.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, D.Q. Acetylbritannilatone suppresses NO and PGE2 synthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 gene expression. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Hsieh, W.T.; Huang, S.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J.; Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Hsieh, W.T.; Huang, S.S.; et al. Apigenin-7-glycoside prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury via downregulation of oxidative enzyme expression and protein activation through inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1736–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.; Venkataraman, B.; Ojha, S.K.; Almarzooqi, S.; Subramanian, V.S.; Al-Ramadi, B.K. Cis-nerolidol inhibits MAP kinase and NF-kB signaling pathways and prevents epithelial tight junction dysfunction in colon inflammation: In Vivo and in vitro studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, T.; Huang, C.J.; Yen, T.L.; Hsia, C.W.; Sheu, J.R.; Bhavan, P.S.; Hsia, C.H. Activation of Nrf2 by esculetin mitigates inflammatory responses through suppression of NF-kB signaling cascade in RAW 264.7 cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.T.; Wu, Y.C.; Xie, X.X.; Zhou, X.; Wei, M.M.; Soromou, L.W.; Wang, D.C. Phillyrin attenuates LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation via suppression of MAPK and NF-κB activation in acute lung injury mice. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Hyun, C.G. Acenocoumarol exerts anti-inflammatory activity via the suppression of NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S. Dehydromiltirone inhibits osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 and bone marrow macrophages by modulating MAPK and NF-κB activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1015693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | Condition of Culture |
|---|---|
| Control Group | Complete medium was normal normally |
| Model group | Incubation in complete medium containing LPS (1 µg/mL) |
| Medication group | Each group with the added corresponding concentration for compounds for 1 h, and then LPS (1 µg/mL) |
| Content | Temperature | Time | Recurring Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-denaturation | 95 °C | 10 min | 1 |
| Denaturation | 95 °C | 15 s | 40 |
| Annealing extension | 60 °C | 60 s |
| cDNA | 4 μL |
|---|---|
| Forward Primer (10 μM) | 0.4 μL |
| Reverse Primer (10 μM) | 0.4 μL |
| SYBR Green Master Mix | 10 μL |
| 50× ROX Reference Dye 2 | 0.4 μL |
| H2O | 4.8 μL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.-F.; Yue, L.; Wu, T.-T.; Zhao, C.-L.; Ye, J.-H.; He, K.; Zou, J. Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from Astilbe grandis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155731
Luo J-F, Yue L, Wu T-T, Zhao C-L, Ye J-H, He K, Zou J. Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from Astilbe grandis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155731
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jin-Fang, Lan Yue, Tian-Tai Wu, Chen-Liang Zhao, Jiang-Hai Ye, Kang He, and Juan Zou. 2023. "Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from Astilbe grandis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155731
APA StyleLuo, J.-F., Yue, L., Wu, T.-T., Zhao, C.-L., Ye, J.-H., He, K., & Zou, J. (2023). Triterpenoid and Coumarin Isolated from Astilbe grandis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules, 28(15), 5731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155731