Insight into Structure Activity Relationship of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Development of Antidiabetic Agents
Abstract
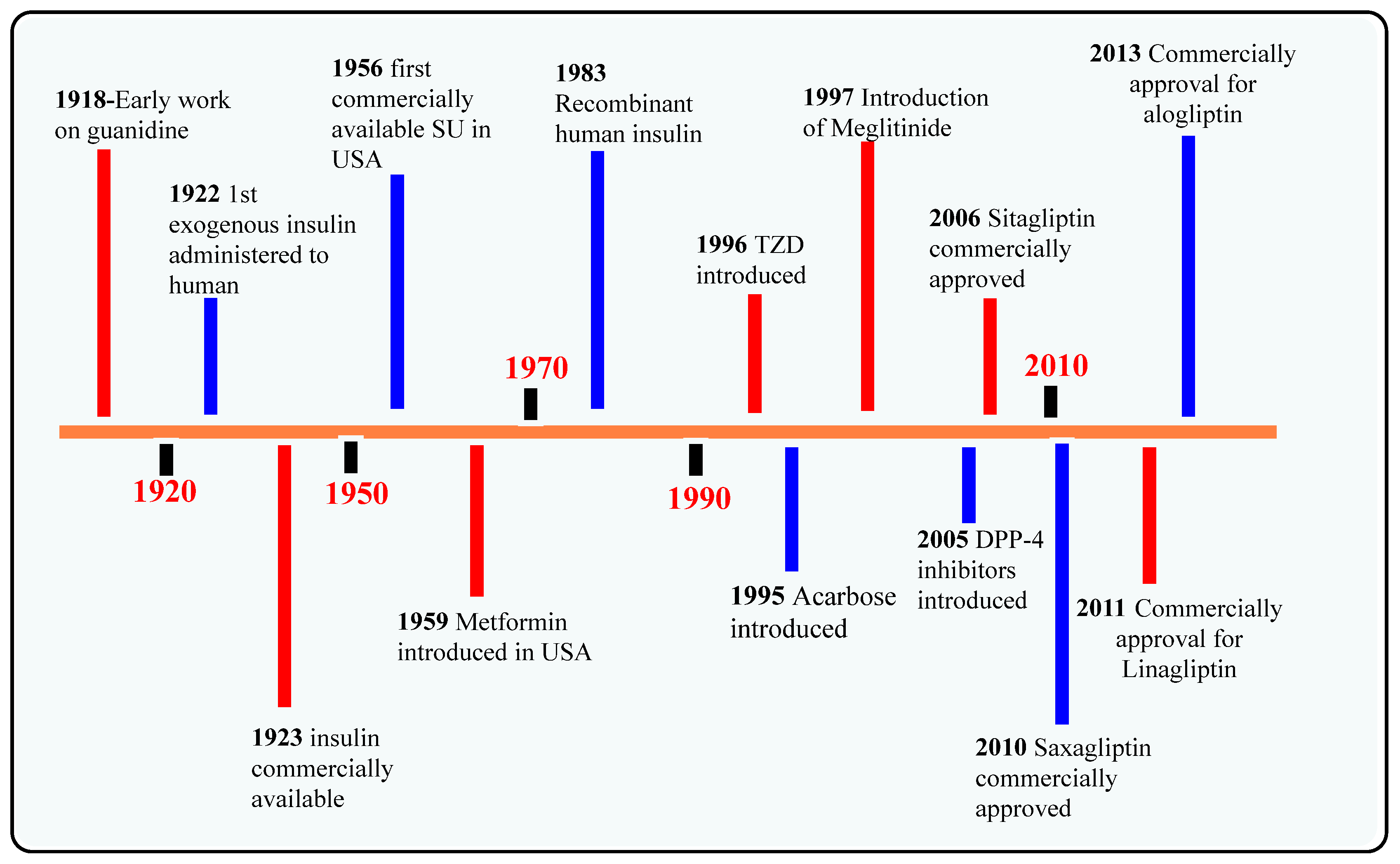
:1. Introduction
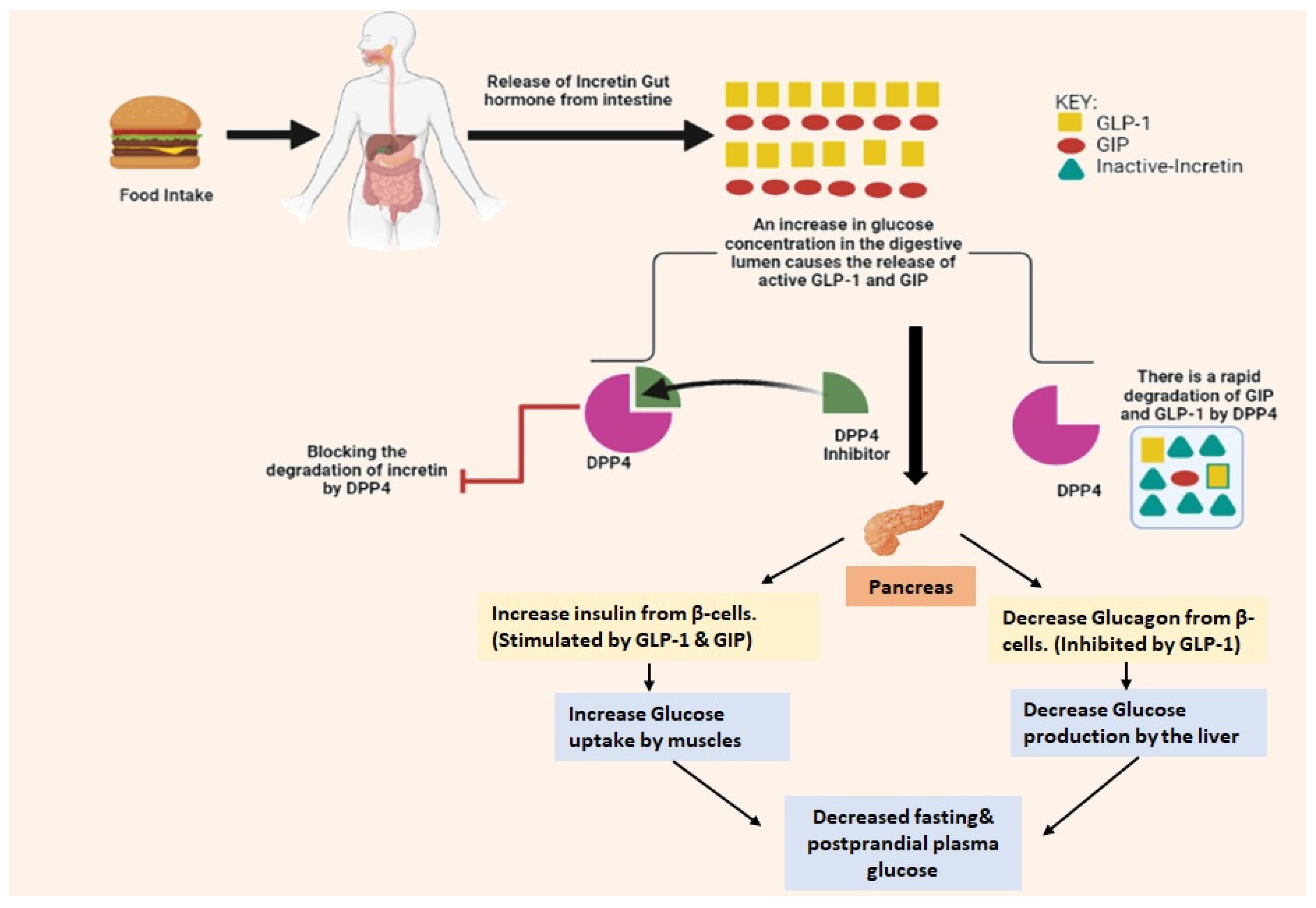
2. Mechanism of DPP-4 Inhibitors
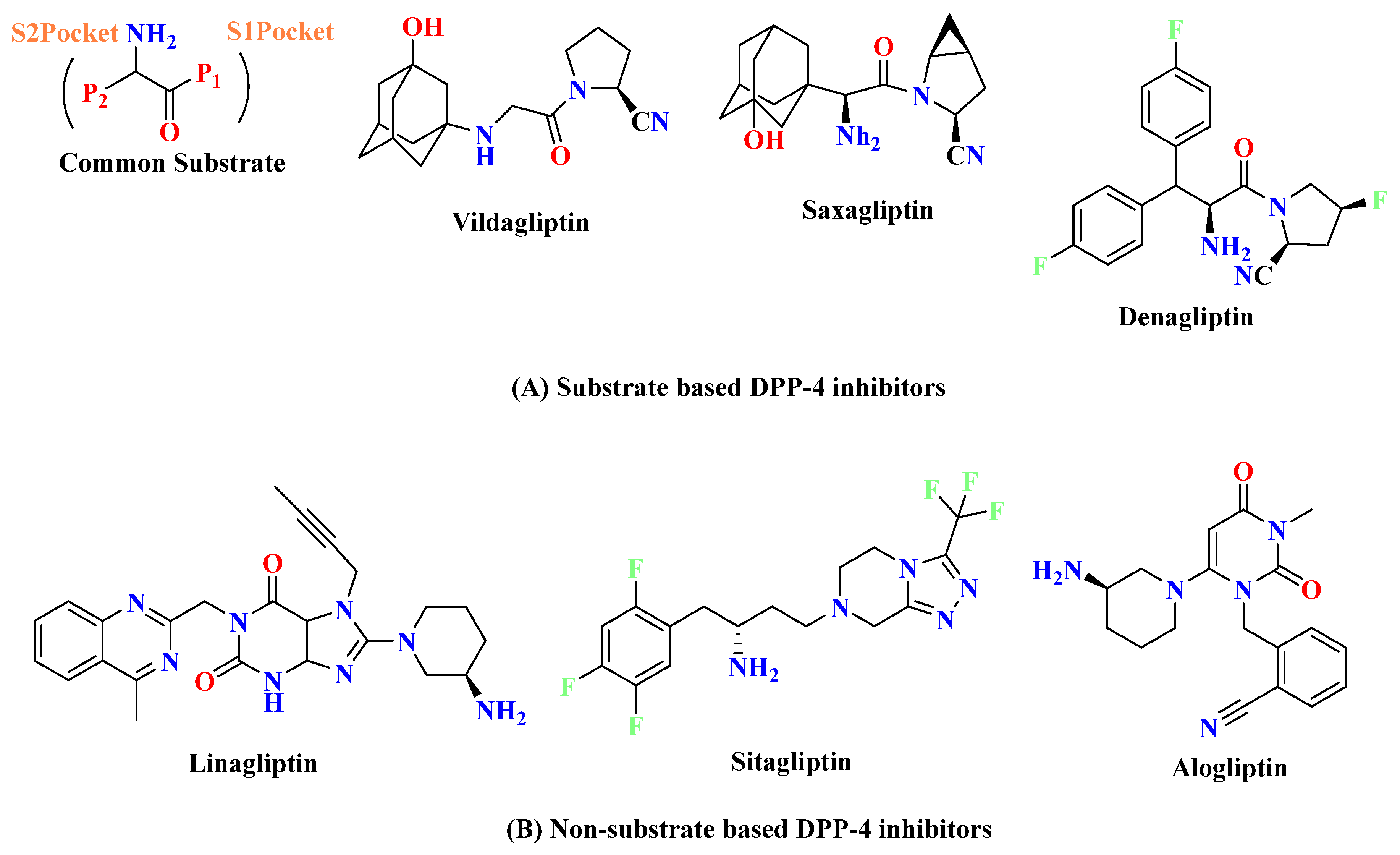
3. Development of DPP-4 Inhibitors
3.1. Substrate-Based DPP-4 Inhibitors
3.2. Non-Substrate Based DPP-4 Inhibitors
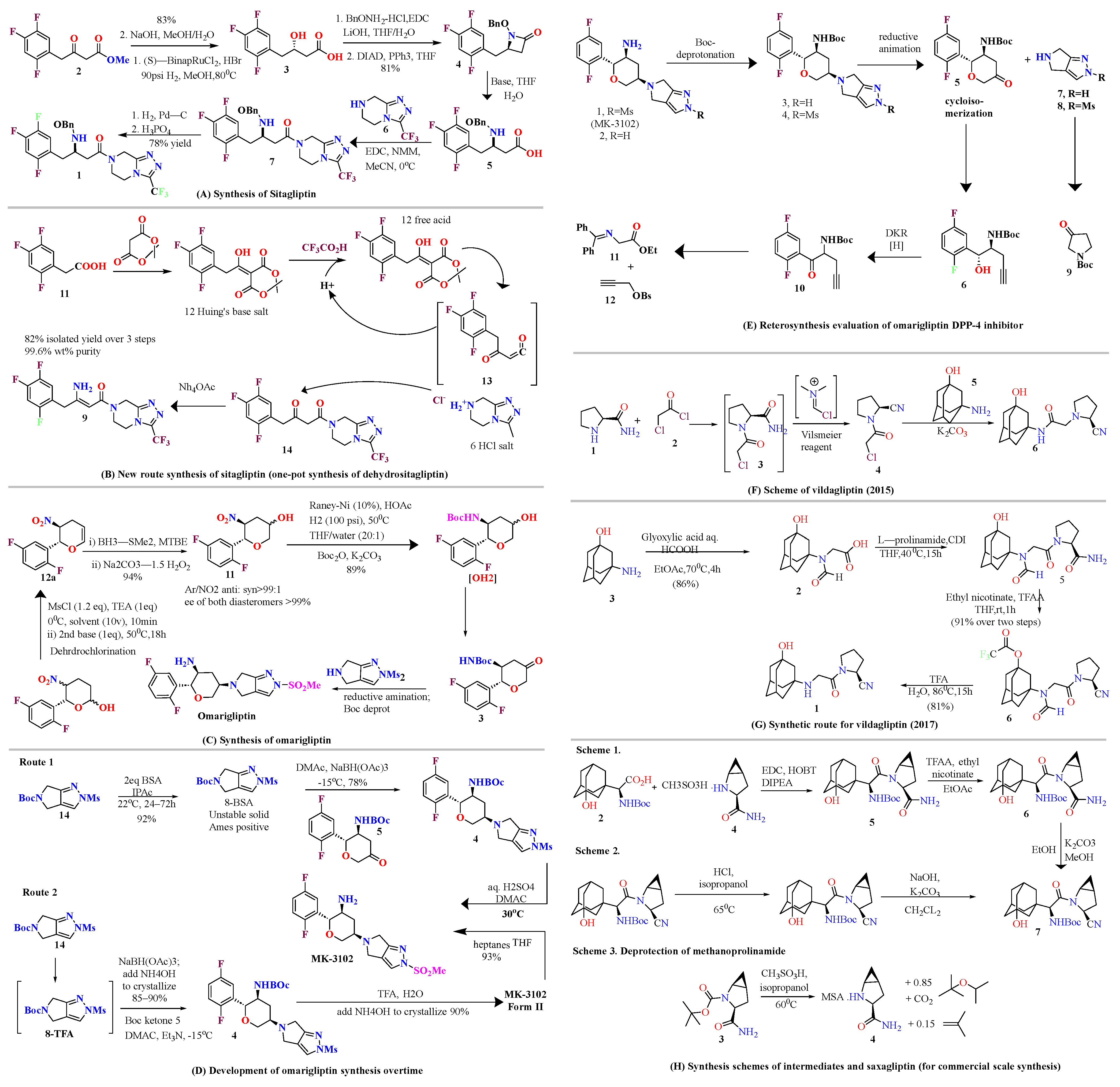
4. Highly Efficient Schemes to Synthesize Compounds
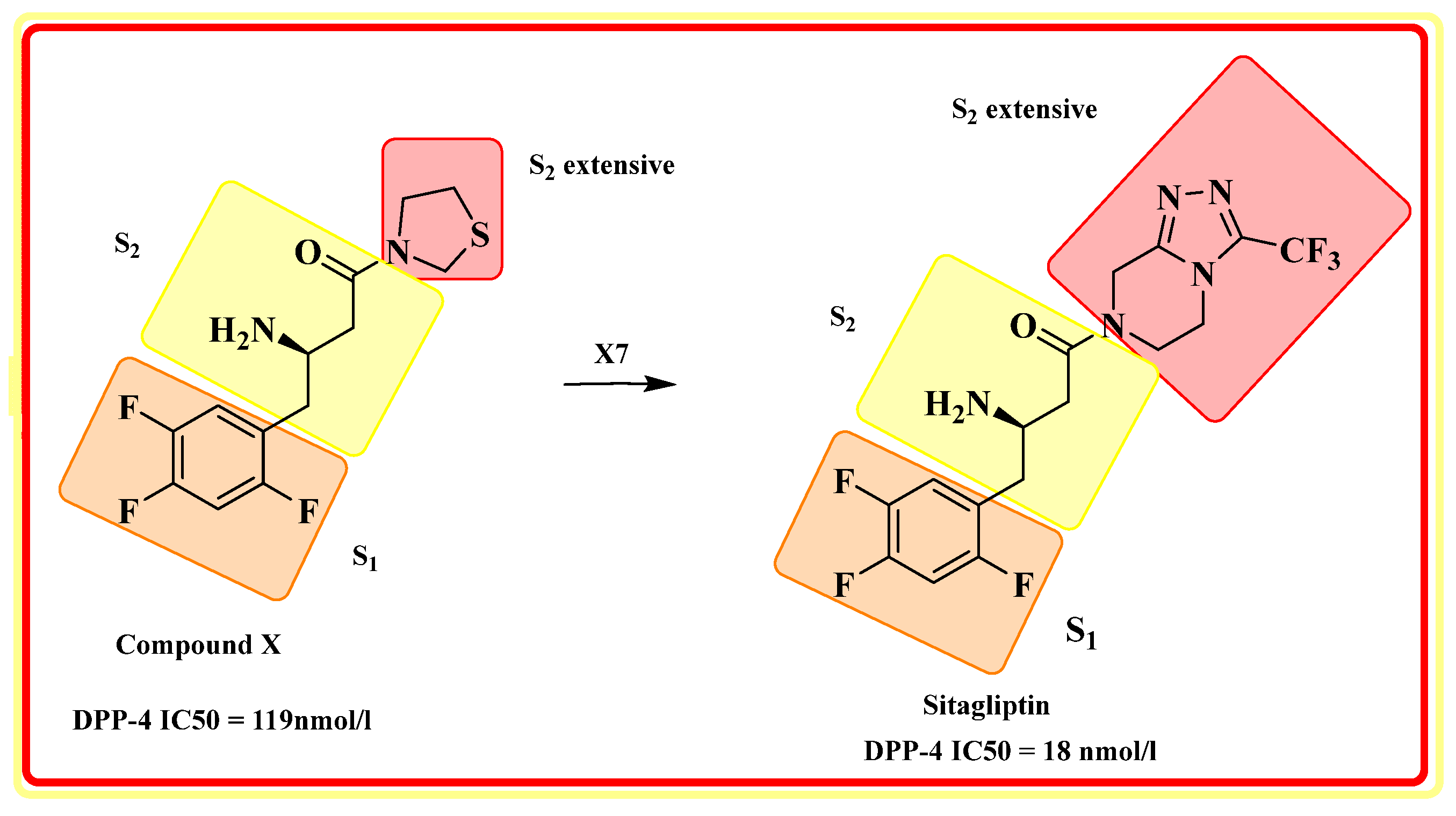
4.1. Sitagliptin
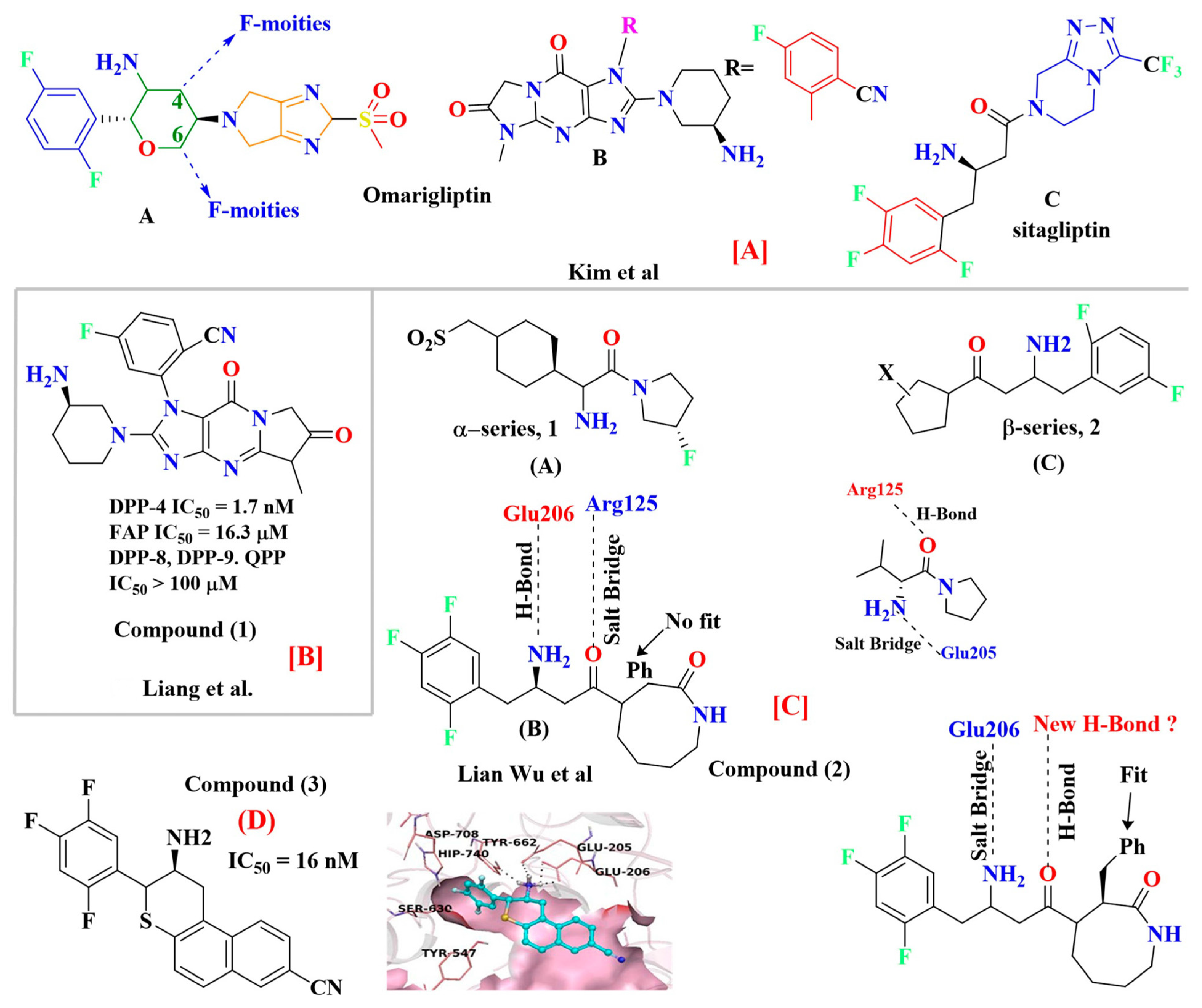
4.2. Omarigliptin
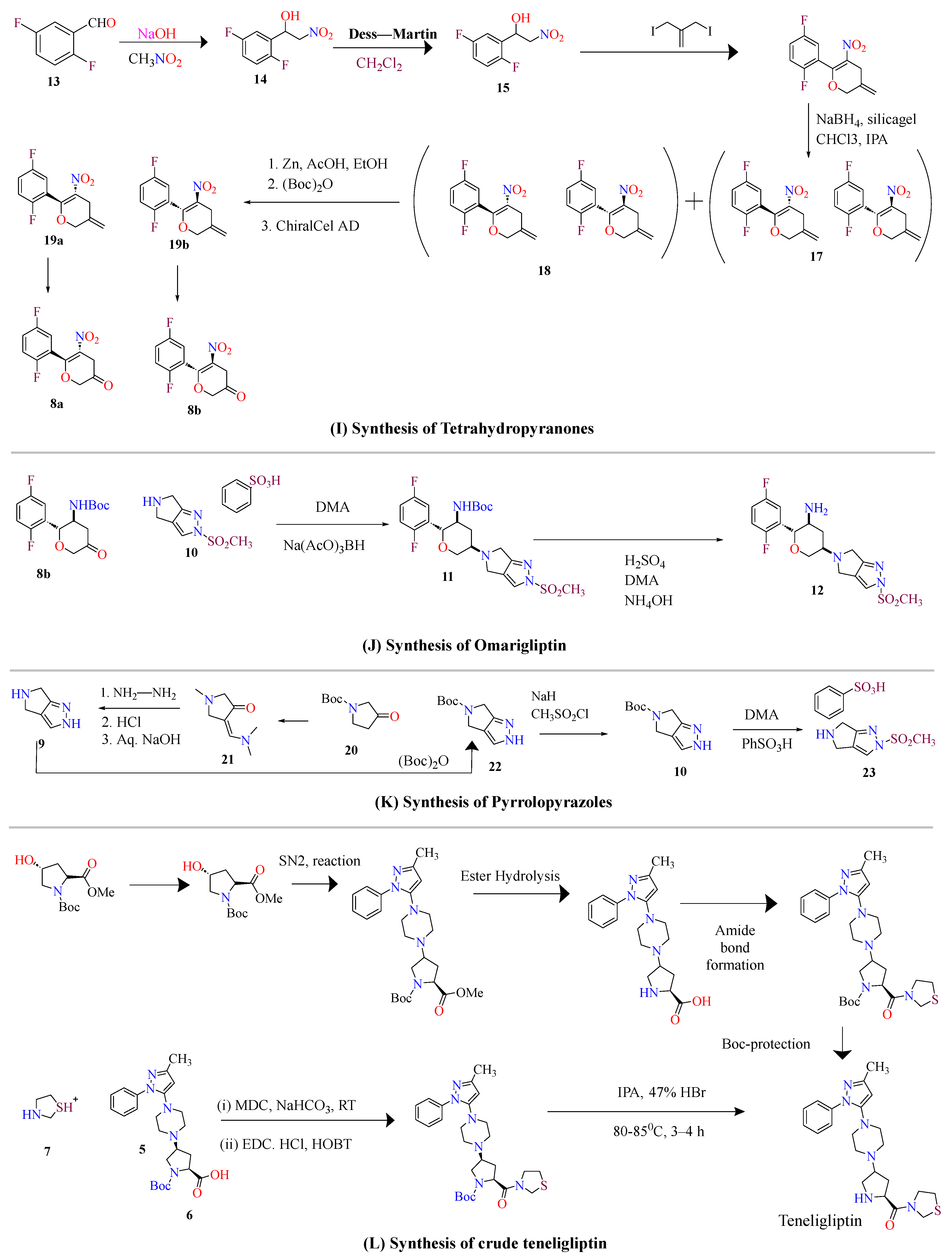
4.3. Vildagliptin
4.4. Saxagliptin
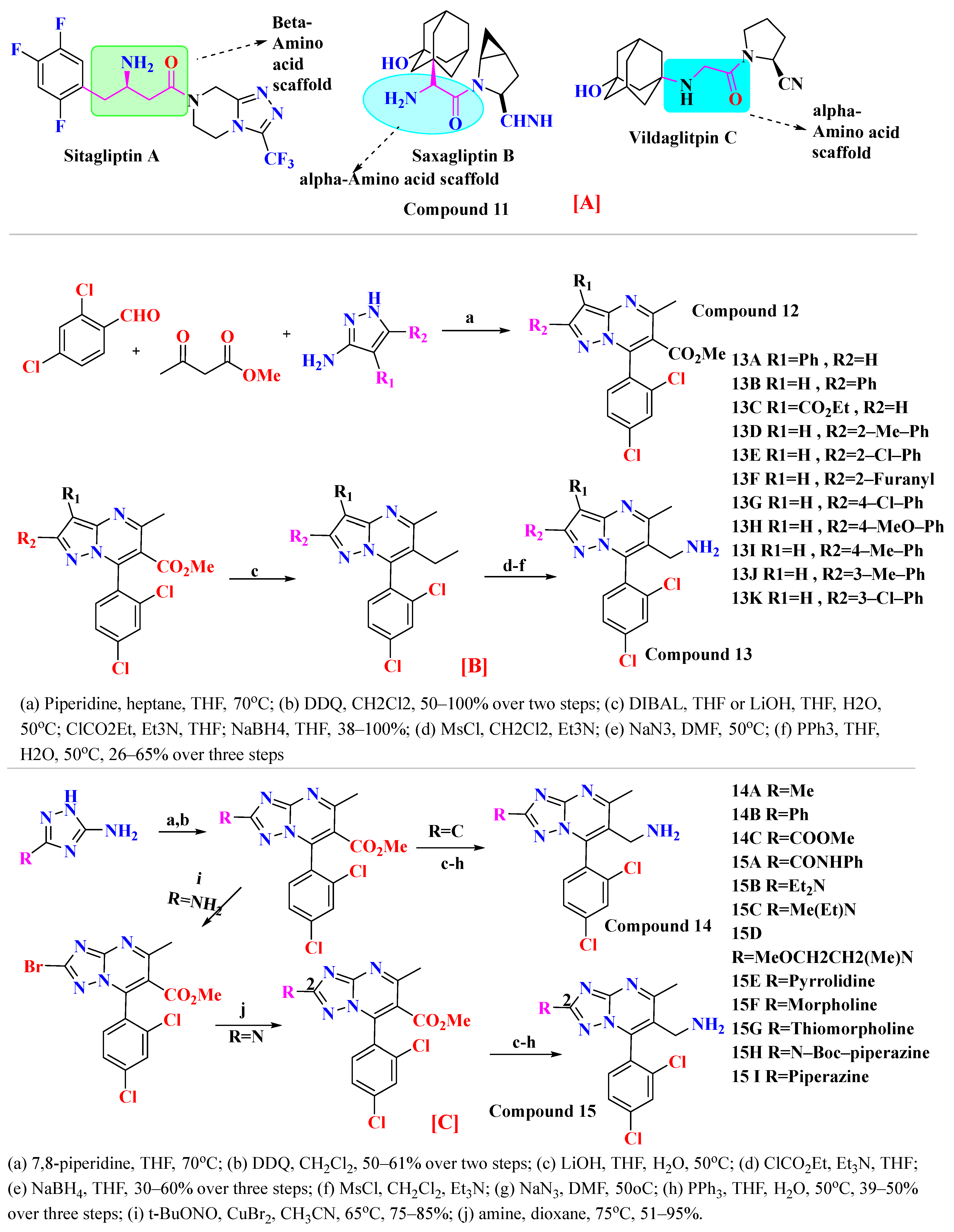
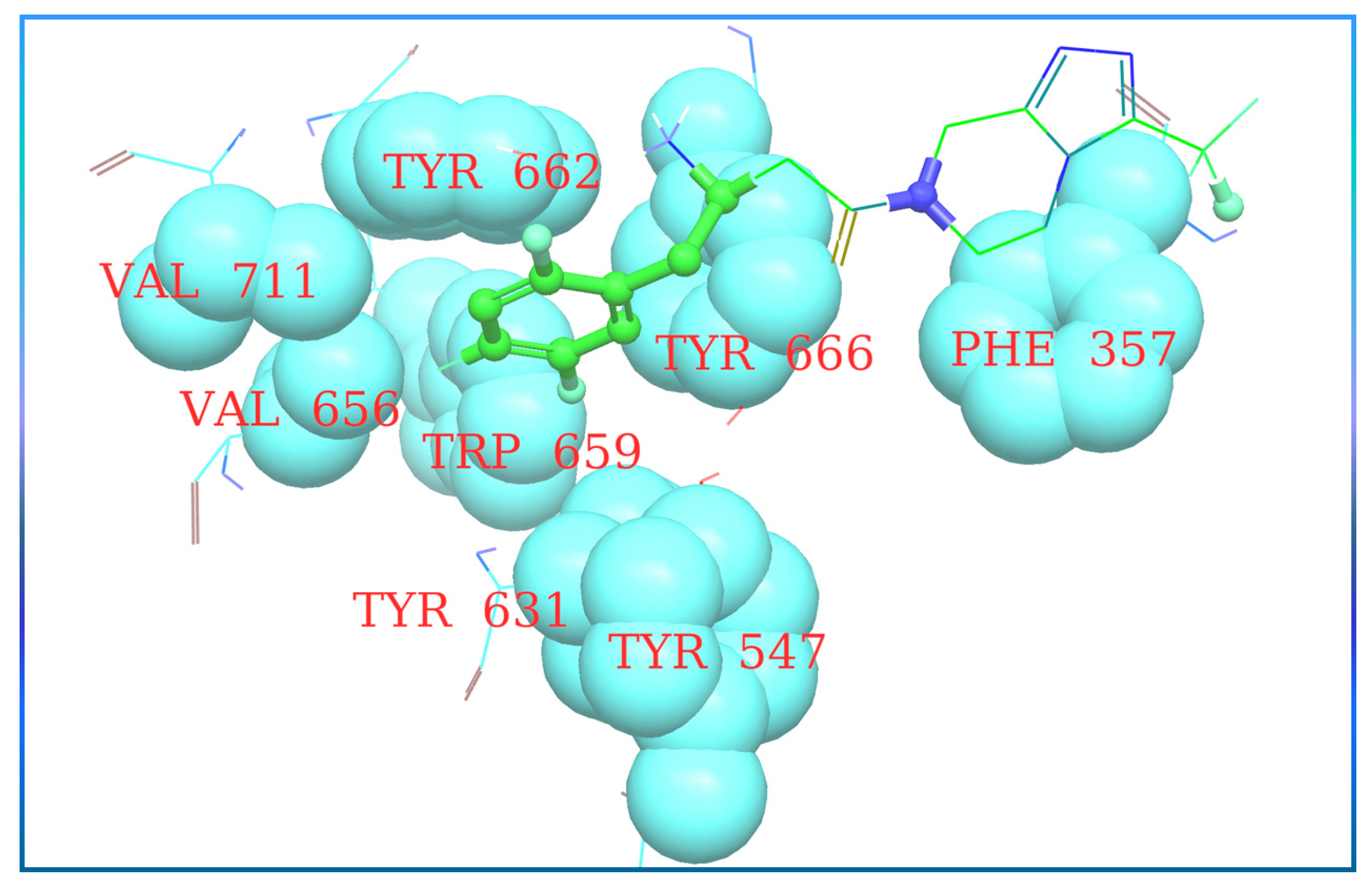
4.5. Teneligliptin
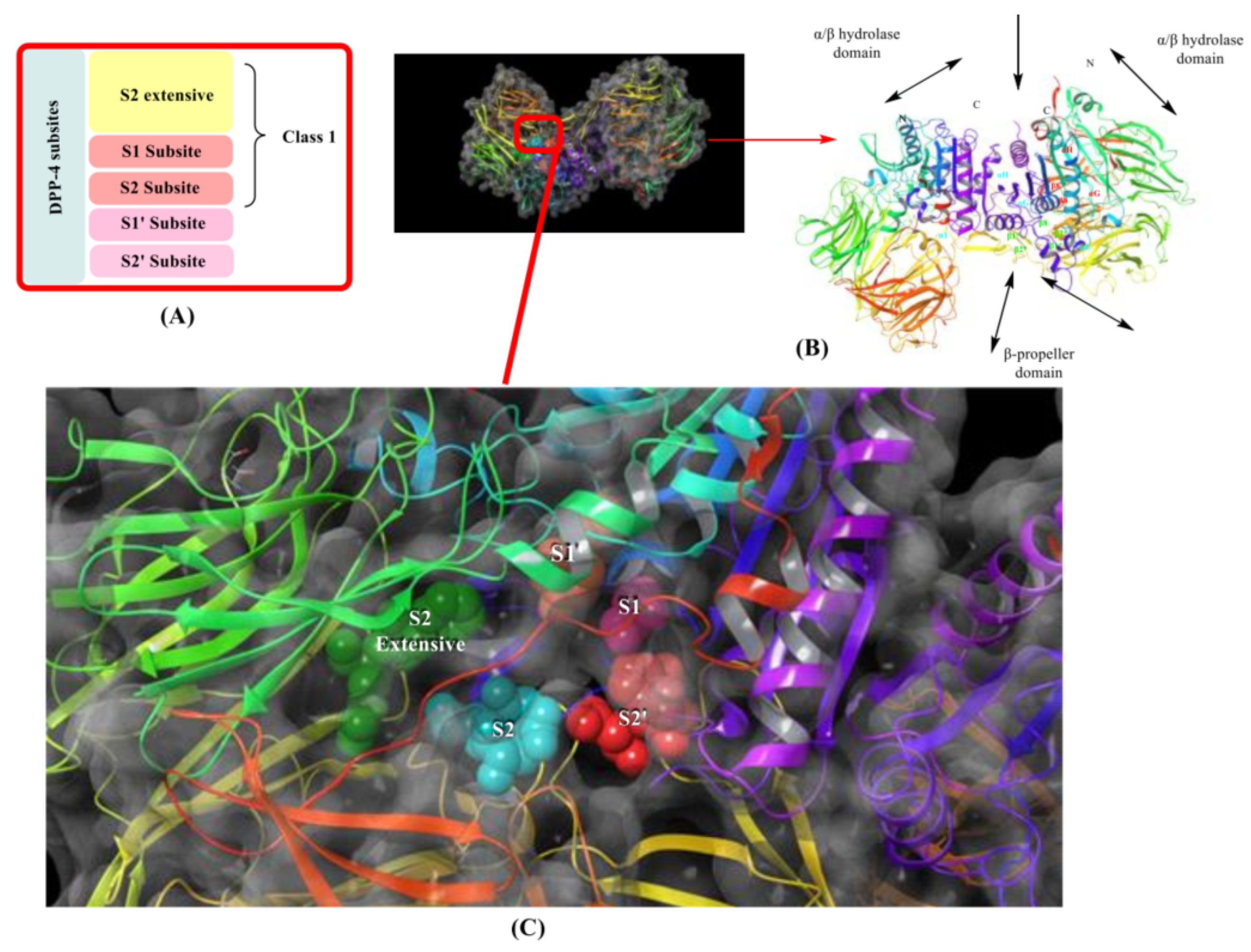
5. SAR Activity of DPP-4 Inhibitors
5.1. Tri-Fluorophenyl-Based Scaffold Compounds
5.2. Adamantane Scaffold
 Y-R′, where X (halogen could act as Lewis acid) & Y can act as electron donor [56]. Wilcken et al. discover, using the natural bond order of CH3Cl (methyl halides), that nucleophiles contact Cl, Br, and F halogens with a “head on” fashion. In contrast, electrophiles approach in a “side chain” fashion. Because of the assembly of several possibilities of ligand-protein interaction, halogen bonding is a significantly suitable tool to improve compound specificities and affinities. Evaluation of halogen bonding strength could be done theoretically using quantum chemical mode calculations (e.g., QM-based evaluation) or experimental studies. Moreover, it is seen that halogen groups form halogen bonds with the carboxyl group (C=O) of amino acid residues, and its electrophilic nature enhances the efficacy of agonists. Adding just a halogen group can affect the effectiveness and potency of the compound, but substituting it on a particular ring could have much more efficacy to yield a much more potent compound [56] (Figure 10A). Introducing halogens in compounds has enhanced the potency of several classes of HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors, hepatitis C virus NS3-Ns4A inhibitors, and α-4, β-2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, DPP-4 inhibitors and have also been exploited in the designing of anticancer drugs (Figure 10B) [40,54,55].
Y-R′, where X (halogen could act as Lewis acid) & Y can act as electron donor [56]. Wilcken et al. discover, using the natural bond order of CH3Cl (methyl halides), that nucleophiles contact Cl, Br, and F halogens with a “head on” fashion. In contrast, electrophiles approach in a “side chain” fashion. Because of the assembly of several possibilities of ligand-protein interaction, halogen bonding is a significantly suitable tool to improve compound specificities and affinities. Evaluation of halogen bonding strength could be done theoretically using quantum chemical mode calculations (e.g., QM-based evaluation) or experimental studies. Moreover, it is seen that halogen groups form halogen bonds with the carboxyl group (C=O) of amino acid residues, and its electrophilic nature enhances the efficacy of agonists. Adding just a halogen group can affect the effectiveness and potency of the compound, but substituting it on a particular ring could have much more efficacy to yield a much more potent compound [56] (Figure 10A). Introducing halogens in compounds has enhanced the potency of several classes of HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors, hepatitis C virus NS3-Ns4A inhibitors, and α-4, β-2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, DPP-4 inhibitors and have also been exploited in the designing of anticancer drugs (Figure 10B) [40,54,55].5.3. Pyrazolopyrimidine Moiety
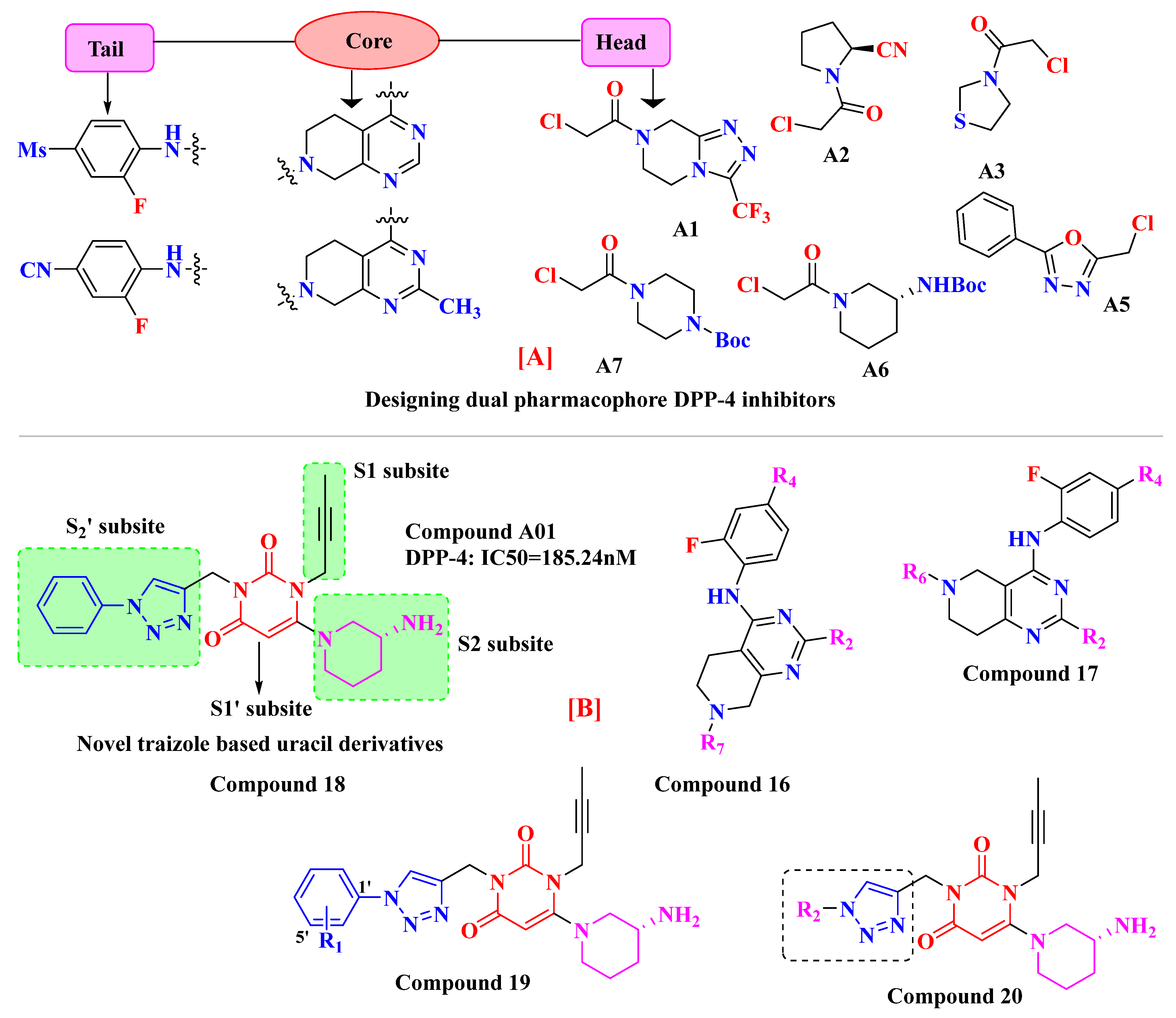
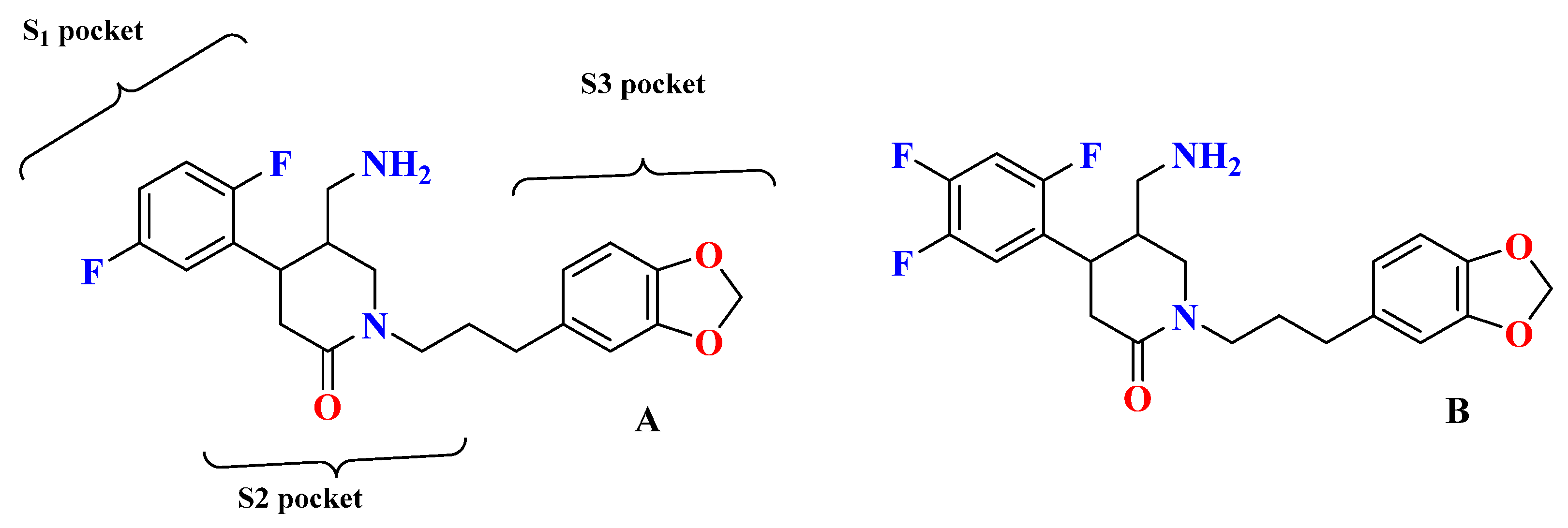
5.4. Tetrahydro-Pyridopyrimidine Moiety
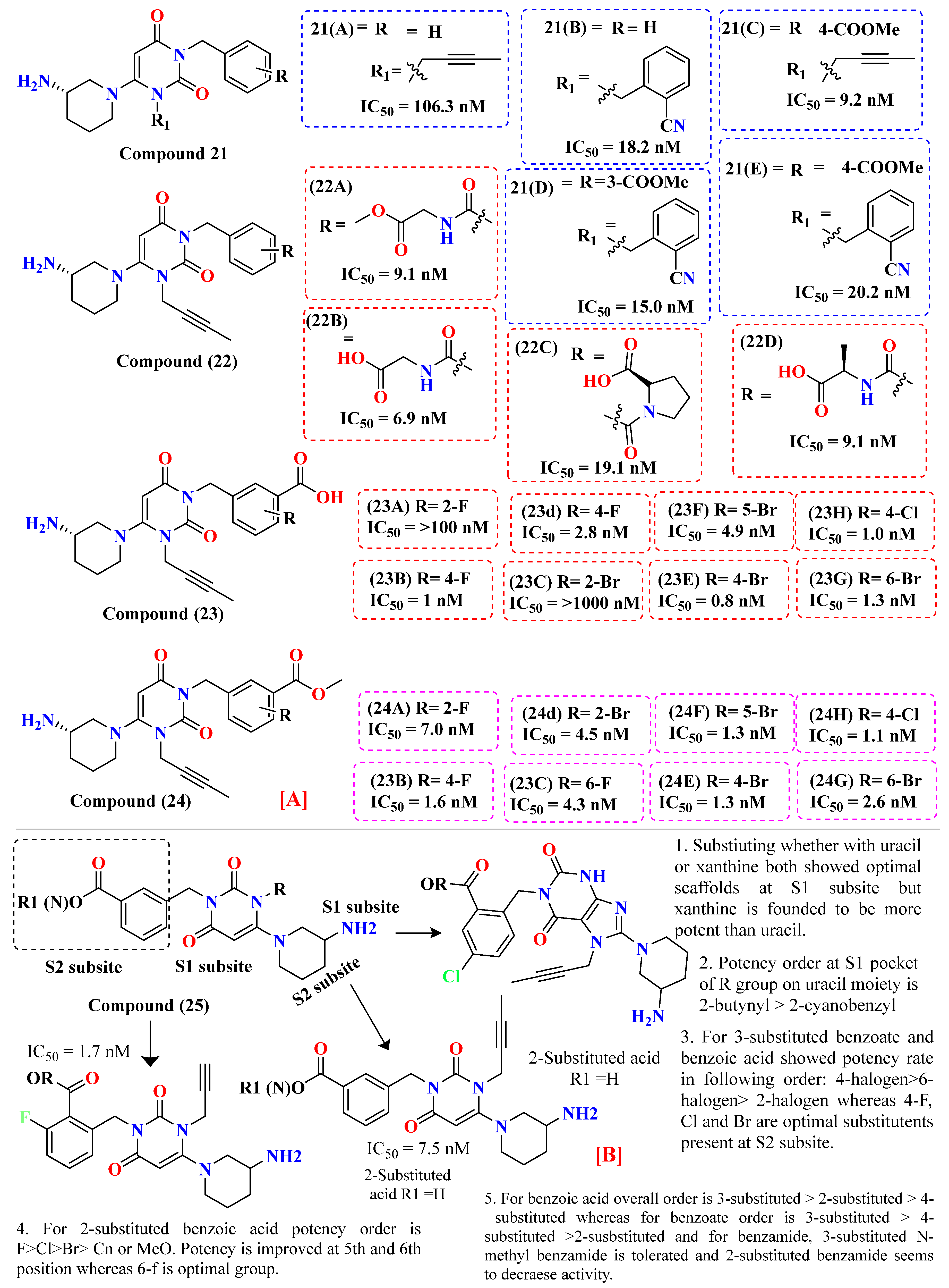
5.5. Triazole-Based Uracil Moiety
5.6. Uracil-Based Benzoic Acid and Ester Derivatives
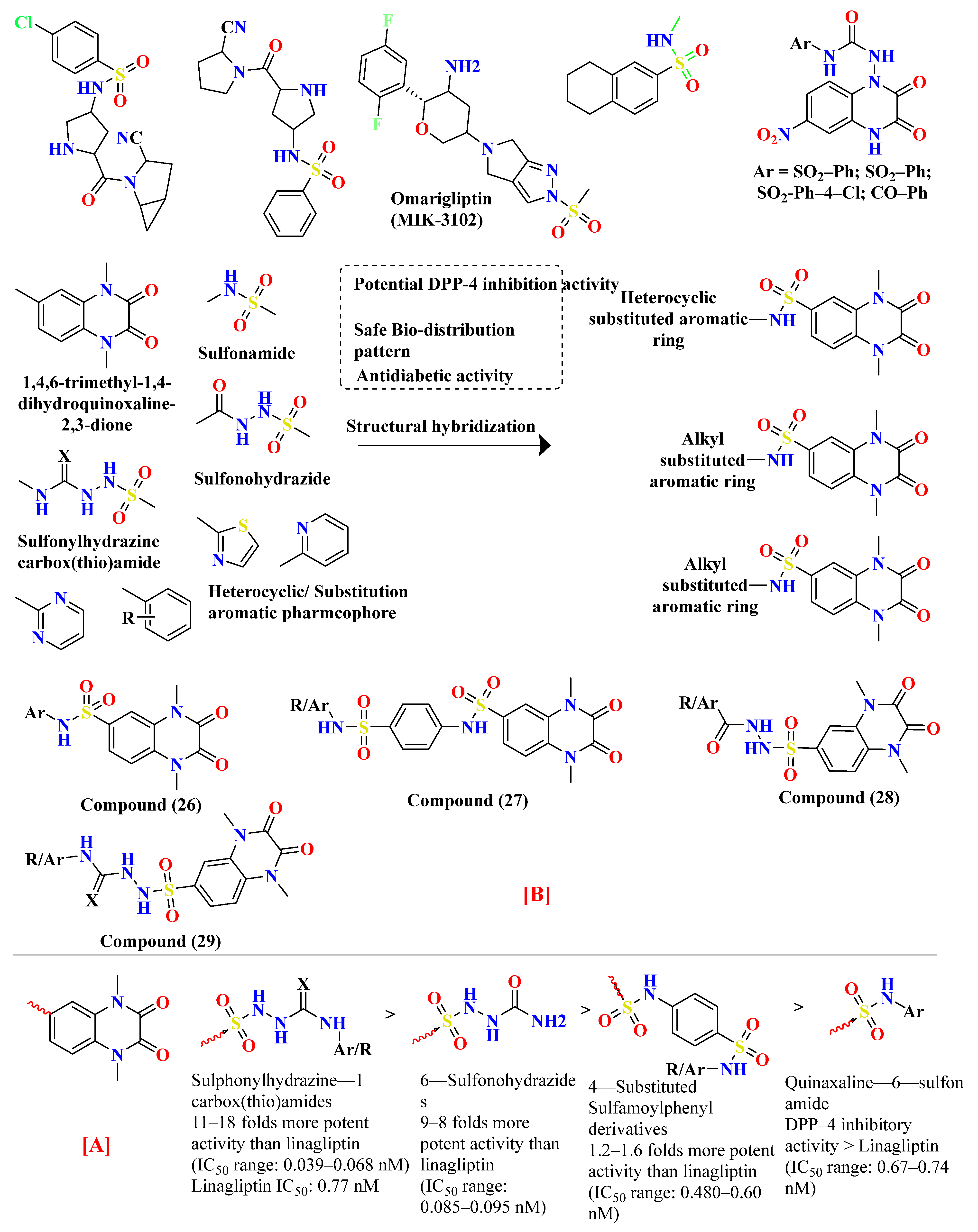
5.7. Quinoxaline Scaffold
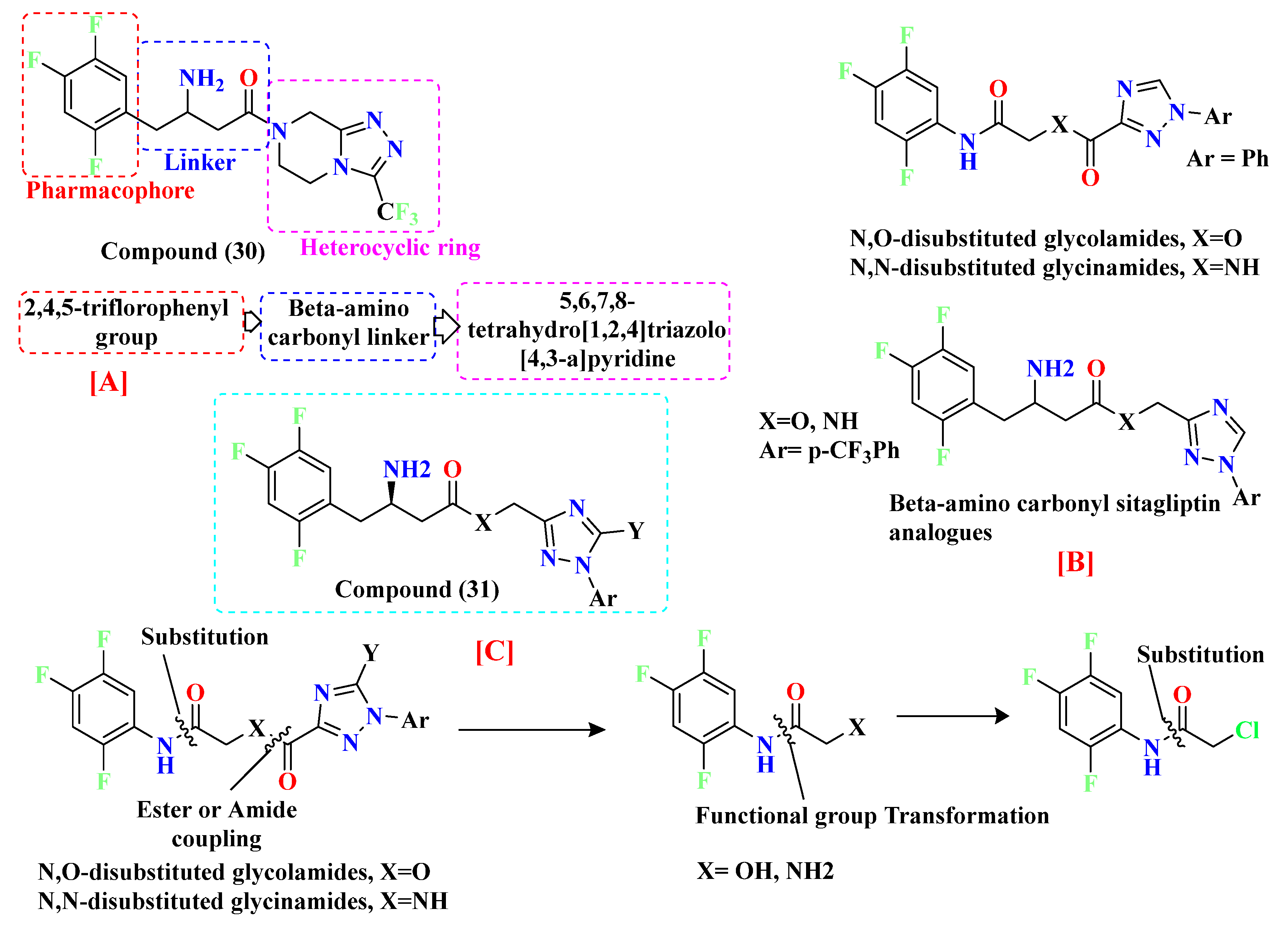
5.8. Glycinamide, Glycolamide and β-Amino Carbonyl 1,2,4-Triazole Scaffold
5.9. Comparing Adamantane and Fluorophenyl-Based Scaffold Molecules
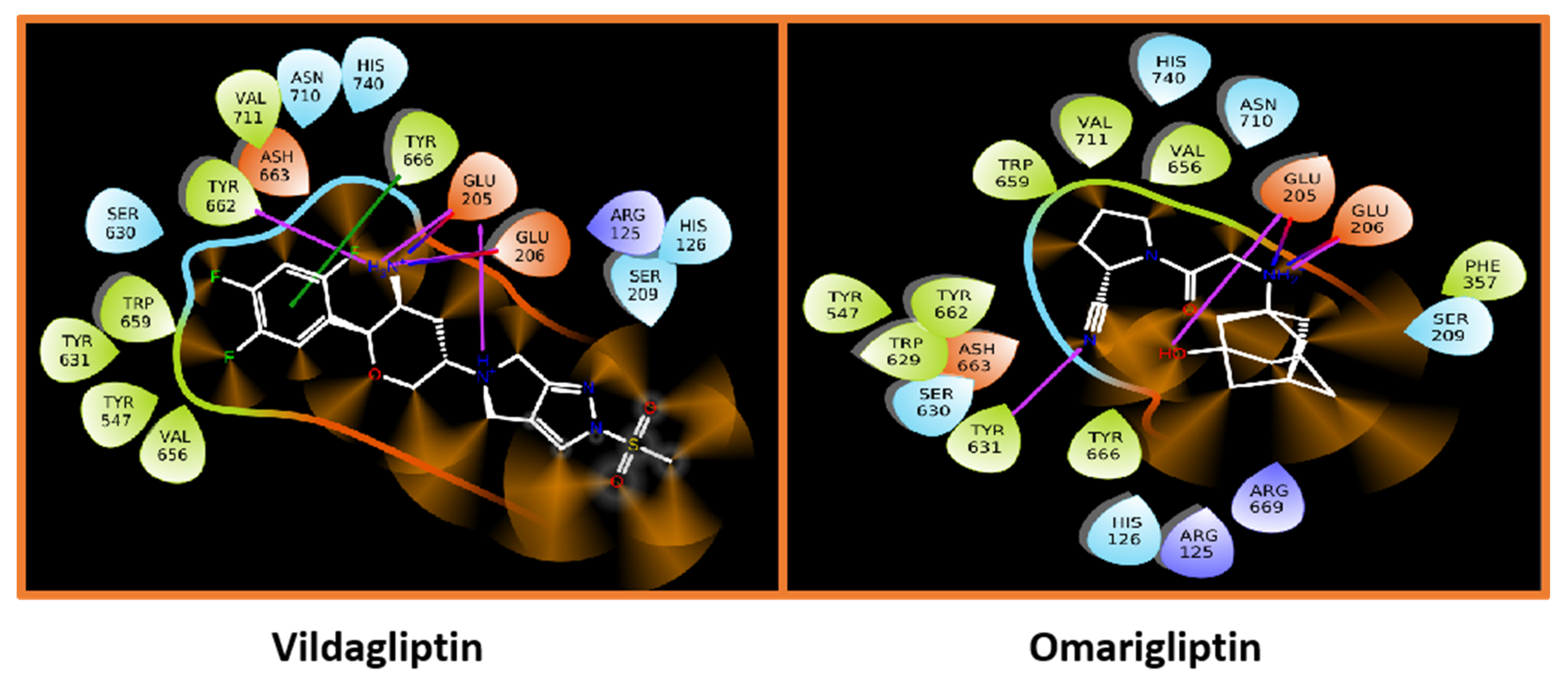
5.9.1. Saxagliptin and Vildagliptin
5.9.2. Sitagliptin and Omariligliptin
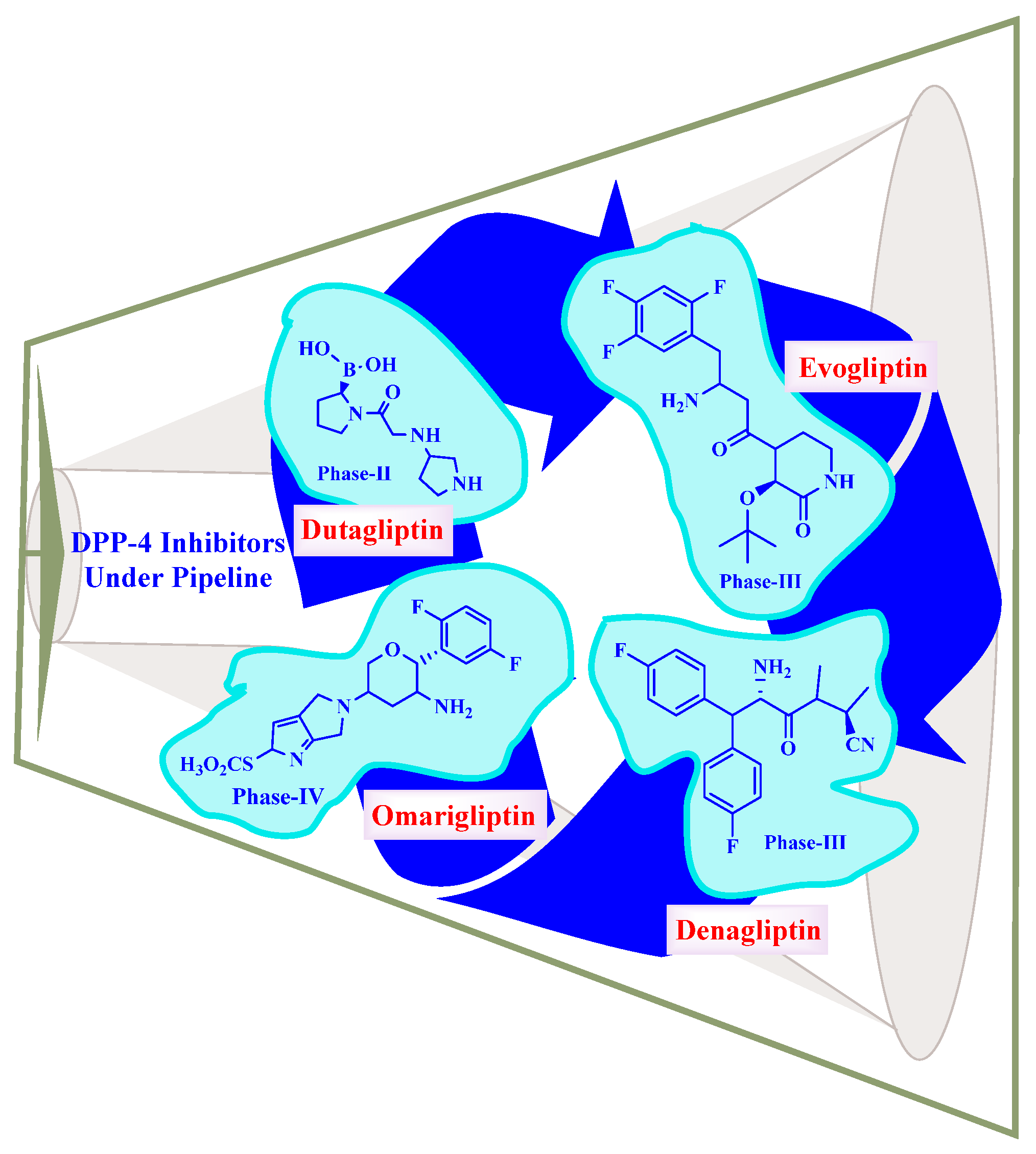
5.10. DPP-4 Inhibitors under Pipeline
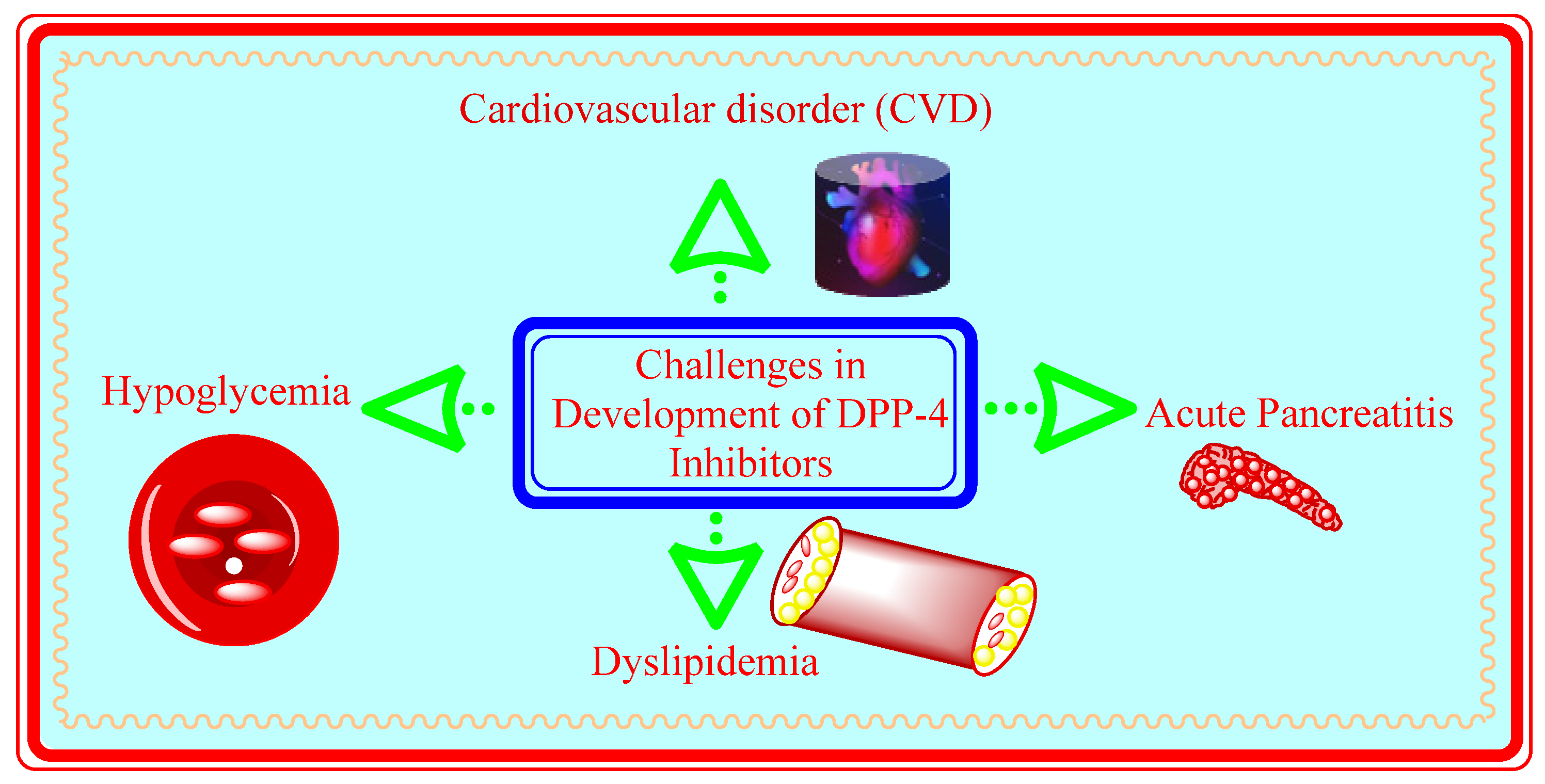
5.11. Challenges in Development of DPP-4 Inhibitors
5.11.1. Acute Pancreatitis
5.11.2. Cardiovascular Risks
5.12. Current Scenario
6. Analysis of Several DPP-4 Inhibitors
7. Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| T2DM | Type-2 diabetes mellitus |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| SAR | Structure activity relationship |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypepide |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| IC50 | inhibitory concentration |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptors |
| MOE | Molecular operating environment |
| Nm | Nanomolar |
| NaH &MsCl | sodium hydride and methanesulfonyl chloride |
| MeCN | methyl cyanide |
| TEA | triethyl amine |
| EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide |
| PrOH | Propyl alcohol |
| FDA | Food and drug administration |
| H-bond & OH | Hydrogen bond and hydroxy |
| COOH | carboxlic acid |
| EDG withEWG | Electron donating group with Electron withdrawing groups |
| µM | Micro molar |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency viruses |
| XP | Extra precision |
References
- Metzler, W.J.; Yanchunas, J.; Weigelt, C.; Kish, K.; Klei, H.E.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Y.; Corbett, M.; Tamura, J.K.; He, B.; et al. Involvement of DPP-IV catalytic residues in enzyme-saxagliptin complex formation. Prot. Sci. 2008, 17, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manaithiya, A.; Alam, O.; Sharma, V.; Javed Naim, M.; Mittal, S.; Khan, I.A. GPR119 agonists: Novel therapeutic agents for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 113, 104998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, J.; Ping, F.; Yang, N.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and gallbladder or biliary disease in type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2022, 377, E068882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomovic, K.; Ilic, B.S.; Smelcerovic, A. Structure-activity relationship analysis of cocrystallized gliptin-like pyrrolidine, trifluorophenyl, and pyrimidine-2,4-dione dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9639–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Ning, B.; Zhao, Q. Pancreatic safety of DPP-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes millitus. Medicine 2022, 101, E29154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jin, F.; Lu, W.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, and pharmacophore modeling studies of pyrazole-3-carbohydrazone derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Jones, A.M. Suspected adverse drug reactions of the type 2 antidiabetic drug class dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors (dpp4i): Can polypharmacology help explain? Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, E01029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shao, Q.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; et al. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of fused β-homophenylalanine derivatives as potent DPP-4 inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, W.K.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, K.W. Cardiovascular outcomes comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylurea as add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. J. Lipid Atheroscl. 2021, 10, E210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaro, B.L.; Coppage, A.L.; Beaudry, J.L.; Varin, E.M.; Kaur, K.; Lai, J.H.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Bachovchin, W.W.; Drucker, D.J. Fibroblast activation protein is dispensable for control of glucose homeostasis and body weight in mice. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Manne, N.; Pal, M. Synthesis of (s)-1-(2-chloroacetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile: A key intermediate for dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2008, 4, E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kridin, K.; Avni, O.; Damiani, G.; Tzur Bitan, D.; Onn, E.; Weinstein, O.; Cohen, A.D. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitor (DPP4I) confers increased odds of bullous pemphigoid even years after drug initiation. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 315, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, W.; Zhao, L.; Mi, Y. Association between use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors with kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, E0267025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösenberg, L.H.; van Zyl, D.G. The mechanism of action of oral antidiabetic drugs: A review of recent literature. J. Endocrinol. Metab. Diab. S. Afr. 2008, 13, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guardado-Mendoza, R.; Prioletta, A.; Jiménez-Ceja, L.M.; Sosale, A.; Folli, F. State of the art paper the role of nateglinide and repaglinide, derivatives of meglitinide, in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aryaeian, N.; Khorshidi Sedehi, S.; Arablou, T. Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review. Med. J. Islamic Repub. Iran 2017, 31, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boath, A.S.; Stewart, D.; McDougall, G.J. Berry components inhibit α-glucosidase in vitro: Synergies between acarbose and polyphenols from black currant and rowanberry. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, J.U.; Siddiqui, N.; Alam, O.; Manaithiya, A.; Chandra, K. Pyrazole scaffold-based derivatives: A glimpse of α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, SAR, and route of synthesis. Arch. Pharm. 2023, 365, E2200421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahova, J.; Martiniakova, M.; Babikova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Mondockova, V.; Omelka, R. Pharmaceutical drugs and natural therapeutic products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, H. Review on the significance of quinazolinone derivatives as potent antihyperglycemic agents. Al-Azhar J. Pharm. 2022, 65, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Pang, X.; Zhao, J.; Deng, P.; Zheng, M.; Zhong, D.; Chen, X. Hydrolytic metabolism of cyanopyrrolidine DPP-4 inhibitors mediated by dipeptidyl peptidases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellegatti, L.; Sedelmeier, J. Synthesis of vildagliptin utilizing continuous flow and batch technologies. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, B.; Ahrén, B. Pleiotropic mechanisms for the glucose-lowering action of DPP-4 inhibitors. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aertgeerts, K. Crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV in complex with a decapeptide reveals details on substrate specificity and tetrahedral intermediate formation. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its inhibitors: Therapeutics for type 2 diabetes and what else? J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdullah, E.S.; Al-Tuwaijri, H.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Haiba, M.E.; Habib, E.E.; El-Emam, A.A. Antimicrobial and hypoglycemic activities of novel N-Mannich bases derived from 5-(1-adamantyl)-4-substituted-1,2,4triazoline-3-thiones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22995–23010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maladkar, M.; Sankar, S.; Kamat, K. Teneligliptin: Heralding change in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Mellitus 2016, 6, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabeno, M.; Akahoshi, F.; Kishida, H.; Miyaguchi, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishii, S.; Kadowaki, T. A comparative study of the binding modes of recently launched dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in the active site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2013, 434, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, R.N.; Haq, W.S.; Katti, S.B. Discovery of 17 gliptins in 17-years of research for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A synthetic overview. Chem. Biol. Interface 2014, 4, 137–162. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, C.F.; Mannucci, E.; Ahrén, B. Glycaemic efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors as add-on therapy to metformin in subjects with type 2 diabetes-A review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waget, A.; Cabou, C.; Masseboeuf, M.; Cattan, P.; Armanet, M.; Karaca, M.; Castel, J.; Garret, C.; Payros, G.; Maida, A.; et al. Physiological and pharmacological mechanisms through which the DPP-4 inhibitor Sitagliptin regulates glycemia in mice. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3018–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vardarli, I.; Nauck, M.A.; Köthe, L.D.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J.; Schweizer, A.; Foley, J. Inhibition of DPP-4 with vildagliptin improved insulin secretion in response to oral as well as “isoglycemic” intravenous glucose without numerically changing the incretin effect in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salehi, M.; Aulinger, B.; Prigeon, R.L.; D’Alessio, D.A. Effect of endogenous GLP-1 on insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Mittal, A.; Mittal, A. A review upon medicinal perspective and designing rationale of DPP-4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 46, E116354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, I.; Donnelly, R. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors: A major new class of oral antidiabetic drug. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, R.N.; Haq, W.; Katti, S.B. Sixteen-years of clinically relevant dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors for treatment of type-2 diabetes: A perspective. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 4013–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, B.; Schmitz, O. GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Hormone Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, S.; Farooqi, A. Alogliptin-a new DPP-4 inhibitor for type 2 diabetes. Prescriber 2014, 25, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Meng, X.; Cai, Z.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, W. Synthesis of phenylpyridine derivatives and their biological evaluation toward dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Chem. Heterocyc. Comp. 2017, 53, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.B.; Hsiao, Y.; Xu, F.; Rivera, N.; Clausen, A.; Kubryk, M.; Krska, S.; Rosner, T.; Simmons, B.; Balsells, J.; et al. Highly efficient asymmetric synthesis of sitagliptin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8798–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Dormer, P.G.; Kassim, A.; McLaughlin, M.; Reamer, R.A.; Sherer, E.C.; Song, Z.J.; Tan, L.; et al. Asymmetric formal synthesis of the long-acting DPP-4 inhibitor omarigliptin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9023–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Scott, J.P.; Anderson, C.; Bishop, B.; Bremeyer, N.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Dunn, R.; Kassim, A.; Lieberman, D.; et al. Evolution of a manufacturing route to omarigliptin, a long-acting DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Devineni, S.R.; Aggile, K.; Gajjala, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Dubey, S.K. Facile new industrial process for synthesis of teneligliptin through new intermediates and its optimization with control of impurities. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 44, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biftu, T.; Sinha-Roy, R.; Chen, P.; Qian, X.; Feng, D.; Kuethe, J.T.; Scapin, G.; Gao, Y.D.; Yan, Y.; Krueger, D.; et al. Omarigliptin (MK-3102): A novel long-acting DPP-4 inhibitor for once-weekly treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, M.; Baratella, M.; Menegotto, I.G.; Castaldi, G.; Giovenzana, G.B. A concise and efficient synthesis of vildagliptin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 3426–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ye, F.; Wang, J.; He, P.; Lei, M.; Huang, L.; Huang, A.; Tang, P.; Lin, H.; Liao, Y.; et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a series of novel super long-acting DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7108–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Wang, L.; Beconi, M.; Eiermann, G.J.; Fisher, M.H.; He, H.; Hickey, G.J.; Kowalchick, J.E.; Leiting, B.; Lyons, K.; et al. (2R)-4-Oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1, 2, 4]triazolo[4,3-a] pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: A potent, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.L.; Hao, J.; Domalski, M.; Burnett, D.A.; Pissarnitski, D.; Zhao, Z.; Stamford, A.; Scapin, G.; Gao, Y.D.; Soriano, A.; et al. Discovery of novel tricyclic heterocycles as potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, G.B.; Qian, X.; Biftu, T.; Singh, S.; Gao, Y.D.; Scapin, G.; Patel, S.; Leiting, B.; Patel, R.; Wu, J.; et al. Discovery of new binding elements in DPP-4 inhibition and their applications in novel DPP-4 inhibitor design. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Fang, X.; Su, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z. Design, synthesis and sar studies of novel and potent dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 39, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Joubert, J.; Blacque, O.; Al-Shaalan, N.H.; El-Emam, A.A. Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and DFT studies of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-chlorobenzyl)sulfanyl]-4-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazole, a potential 11β-HSD1 inhibitor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, E56331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spasov, A.A.; Vasil’ev, P.M.; Babkov, D.A.; Prokhorova, T.Y.; Sturova, E.A.; Klimochkin, Y.N.; Leonova, M.V.; Baimuratov, M.R. New dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors among adamantane derivatives. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmozhiraja, S.; Matsuo, N.; Ishitsubo, E.; Okazaki, S.; Shimano, H.; Tokiwa, H. Comparative binding analysis of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) with anti-diabetic drugs -An Ab initio fragment molecular orbital study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, E0166275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villhauer, E.B.; Brinkman, J.A.; Naderi, G.B.; Burkey, B.F.; Dunning, B.E.; Prasad, K.; Mangold, B.L.; Russell, M.E.; Hughes, T.E. 1-[[(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)amino]acetyl]-2-cyano-(s)-pyrrolidine: A potent, selective, and orally bioavailable dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor with antihyperglycemic properties. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2774–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, B.; Soybir, H.; Görgülü, S.; Cantürk, Z.; Altıntop, M.D. Pyrazole incorporated new thiosemicarbazones: Design, synthesis and investigation of DPP-4 inhibitory effects. Molecules 2020, 25, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimha, S.; Battula, K.S.; Ravinder, M.; Reddy, Y.N.; Nagavelli, V.R. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 1,2,3-triazole-based xanthine derivatives as DPP-4 inhibitor. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 132, E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigance, R.P.; Meng, W.; Fura, A.; Harrity, T.; Wang, A.; Zahler, R.; Kirby, M.S.; Hamann, L.G. Synthesis and SAR of azolopyrimidines as potent and selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors for type 2 diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4395–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.A.E.; Khodir, A.E.; Saber, S.; Mourad, M.A.E. Novel potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitors: Design, synthesis and molecular docking study of dihydropyrimidine phthalimide hybrids. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, H.; Jin, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Design and synthesis of tetrahydropyridopyrimidine derivatives as dual GPR119 and DPP-4 modulators. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, E103390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Han, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q. Discovery of triazole-based uracil derivatives bearing amide moieties as novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 75, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Deng, X.; Jiang, N.; Meng, L.; Xing, J.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y. Identification and structure–activity relationship exploration of uracil-based benzoic acid and ester derivatives as novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 225, E113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, Y.M.; Anwar, M.M.; Abd El-Karim, S.S.; Elseginy, S.A.; Essa, B.M.; Sakr, T.M. New quinoxaline compounds as DPP-4 inhibitors and hypoglycemics: Design, synthesis, computational and bio-distribution studies. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36989–37010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, M.T.; Tseng, C.C.; Li, S.M.; Tsai, S.E.; Chuang, T.J.; Lu, C.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Tsai, H.; Wong, F. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of glycolamide, glycinamide, and β-amino carbonyl 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as DPP-4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, E105049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwehm, C.; Li, J.; Song, H.; Hu, X.; Kellam, B.; Stocks, M.J. Synthesis of new DPP-4 inhibitors based on a novel tricyclic scaffold. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, C.; Ge, H.; Song, M.; Chen, J.-H.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Discovery of imigliptin, a novel selective DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; He, Z.X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.X.; Duan, W.; Zhou, F.S. Clinical pharmacology of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors indiacted for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 999–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, G.; Lewinski, D.V.; Eaton, D.M.; Sourji, H.; Houser, S.R.; Wallner, M. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Current and Future Therapies. Beyond Glycemic Control. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saini, K.; Sharma, S.; Khan, K. DPP-4 inhibitors for treating T2DM-hype or hope? an analysis based on the current literature. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 625. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, A.; Sportiello, L.; Maiorino, M.I.; Rossi, F.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes therapy-focus on alogliptin. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 989–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.S.; Yasuda, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Okada, S.; Motoyama, T.; Takahashi, R.; Oka, M. Anagliptin, a potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor: Its single-crystal structure and enzyme interactions. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, M.; Singh, D.; Kumar, M.; Kaur, P. Synthesis, evaluation and molecular docking of prolyl-fluoropyrrolidine derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 82, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Skene, R.J.; Shi, L.; Caster, C.L.; Kassel, D.B.; Xu, R.; Gwaltney, S.L. Structure-based design and synthesis of benzimidazole derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.D.; Ghate, M.D. Recent approaches to medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 574–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, M.; Singh, J.; Kalász, H.; Tekes, K.; Adeghate, E. Medicinal chemistry and applications of Incretins and DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Open Med. Chem. J. 2011, 5, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, Y.M.; El-Karim, S.S.; Nasr, T.; Elseginy, S.A.; Anwar, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Ali, H.F. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of Spiro cyclohexane-1,2- quinazoline derivatives as potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.J.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.-Q.; Guo, C.-L.; Guo, S.J.; Shi, D.Y. Recent progress of the development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Han, L.; Cao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of imidazo[1, 2-a]pyridine derivatives as novel DPP-4 inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.J.; Jiang, B.; Guo, S.J.; Li, X.Q.; Chen, X.C.; Luo, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D.Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of n0ovel pyrimidinedione derivatives as DPP-4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrilakis, K. The role of DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment algorithm of type 2 diabetes mellitus: When to select, what to expect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savage, S.A.; Jones, G.S.; Kolotuchin, S.; Ramrattan, S.A.; Vu, T.; Waltermire, R.E. Preparation of Saxagliptin, a Novel DPP-IV Inhibitor. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2009, 13, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S.No | Class of Drug | DPP-4 Inhibitor Drugs | Interaction Subsite of DPP-4 | Brief Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | First | Sitagliptin and teneligliptin |  |
|
| 2. | Second | Vildagliptin and saxagliptin |  |
|
| 3. | Third | Alogliptin and linagliptin | 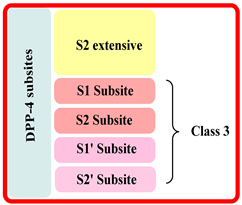 |
|
| S. N. | Compounds | DPP-4 IC50 (nM) | Types of Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 10A | 14.71 ± 0.82 | 2 H-bond interacting with Arg125 and Tyr547 |
| 2. | 10B | 2.19 ± 0.14 | 3 H-bond interacting with Arg125 1 H-bond interacting with Tyr547 1 π-bond interacting with Tyr547 |
| 3. | 10C | 1.42 ± 0.11 | 3 H-bond interacting with Arg125 1 H-bond interacting with Tyr547 |
| 4. | 10D | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 2 H-bond interacting with Lys554 and Glu206 |
| 5. | 10E | 0.66 ± 0.04 | 2 H-bond interacting with Tyr547 and Glu206 2 H-bond interacting with Arg125 |
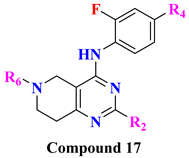 | 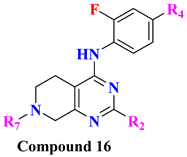 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp. | R2 | R4 | R6 | DPP-4 Inhibition (%Inhibition-10 µM) | Comp. | R2 | R4 | R7 | DPP-4 Inhibition (%Inhibition-10 µM) |
| 17A | Me | CN | A5 | 54.3 | 18A | H | Ms | A2 | 75.8 |
| 17B | Me | Ms | A2 | 83.2 | 18B | H | Ms | A7 | 77.9 |
| 17C | Me | Ms | A3 | 52.4 | 18C | Me | CN | A2 | 74.5 |
| 17D | Me | Ms | A6 | 65.1 | 18C | Me | Ms | A2 | 72.5 |
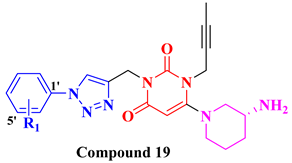 |  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | R1 | DPP-4 Inhibition (nM) | Compounds | R1 | DPP-4 Inhibition (nM) |
| 19A | H | 185.24 | 20A | 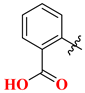 | 65.63 |
| 19B | 2′-F | 64.05 | 20B | 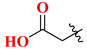 | 84.72 |
| 19C | 4′-F | 135.45 | 20C |  | 12.45 |
| 19D | 2’,4′-diF | 243.67 | 20D | 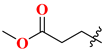 | 64.31 |
| 19E | 3′-Cl | 168.63 | 20E | 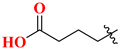 | 26.81 |
| 19F | 3′-MeO | 88.53 | 20F | 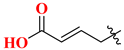 | 9.56 |
 |  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
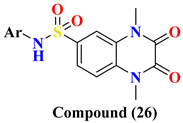
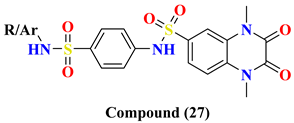
| Compound Number | Ar = | IC50 nM | |
| 26A | -2-Thizolyl | ND | |
| 26B | -C6H5-4-COCH3 | 1.28 ± 0.099 | |
| 26C | -C6H5-4-COOH | 0.74 ± 0.103 | |
| 26D | -C6H5-4-F | 0.70 ± 0.112 | |
| 26E | -C6H5-4-Br | 0.71 ± 0.075 | |
| 26F | -C6H5-2-SH | 0.67 ± 0.055 | |
| 27A | H | 0.60 ± 0.086 | |
| 27B | -2-Thizolyl | 0.93 ± 0.128 | |
| 27C | -2-Pyridinyl | 0.48 ± 0.052 | |
| 27D | -2-Pyrimidinyl | 0.48 ± 0.050 | |
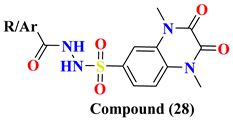 |  | ||
| 28A | -CH3 | 0.085 ± 0.004 | |
| 28B | -CH2Cl | 0.095 ± 0.006 | |
| 28C | -C6H5 | 0.095 ± 0.012 | |
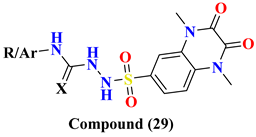
| 29A | X; O, -CH(CH3)2 | 0.039 ± 0.042 | |
| 29B | X; O, -CH2-C6H5 | 0.048 ± 0.067 | |
| 29C | X; O, -CO-C6H5 | 0.144 ± 0.107 | |
| 29D | X; O, -C6H5-4-Cl | ND | |
| 29E | X; S, -C2H5 | 0.068 ± 0.044 | |
| 29F | X; S, -C6H11 | 0.055 ± 0.110 | |
| 29G | X; S, -C6H5 | 0.049 ± 0.031 | |
| 29H | X; S, -C6H5-4-OCH3 | ND | |
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
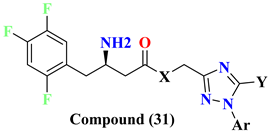
| Compounds | X | Y | Ar | DPP-4 IC50 (nM) |
| 31A | O | H |  | 775 nM |
| 31B | NH | 34.4 nM | ||
| 31C | O |  |  | 80.3 nM |
| 31D | NH | 131 nM | ||
| 31E | O | 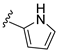 | 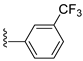 | 49.9 nM |
| 31F | NH | 99.8 nM | ||
| 31G | O | 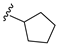 |  | 81.6 nM |
| 31H | NH | 119 nM | ||
| 31I | O | 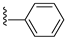 | 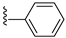 | 91.3 nM |
| 31J | NH | 50.4 nM | ||
| 31K | O | 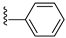 | 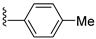 | 497 nM |
| 31L | NH | 138 nM | ||
| IC50 (nM) of Several Marketed Drugs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorophenyl-based scaffold drugs | Adamantane-based scaffold drugs | ||
| Sitagliptin | Omarigliptin | Vildagliptin | Saxagliptin |
| 18 nM | 1.6 nM | 2.3 nM | 26 nM |
| Other marketed DPP-4 marketed inhibitors | |||
| Alogliptin | 6.5 nM | Teneligliptin | 1 nM |
| S.N. | Structure of Compound | Scaffold | IC50 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 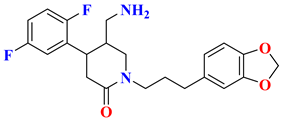 | Fluorophenyl-piperidine based | 8.5 nM | [29] |
| 2 | 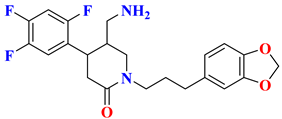 | Fluorophenyl-piperidine based | 19 nM | [29] |
| 3 | 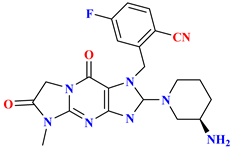 | Tricyclic scaffold | 1.7 nM | [49] |
| 4 | 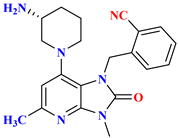 | Based on the Alogliptin scaffold (Scaffold hopping) | 9 nM | [67] |
| 5 | 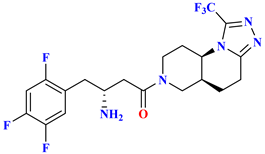 | Based on Sitagliptin scaffold (Scaffold hopping) | 28 nM | [59] |
| 6 | 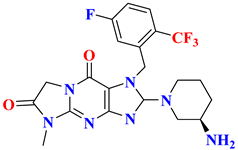 | Tricyclic scaffold | 11.2 nM | [49] |
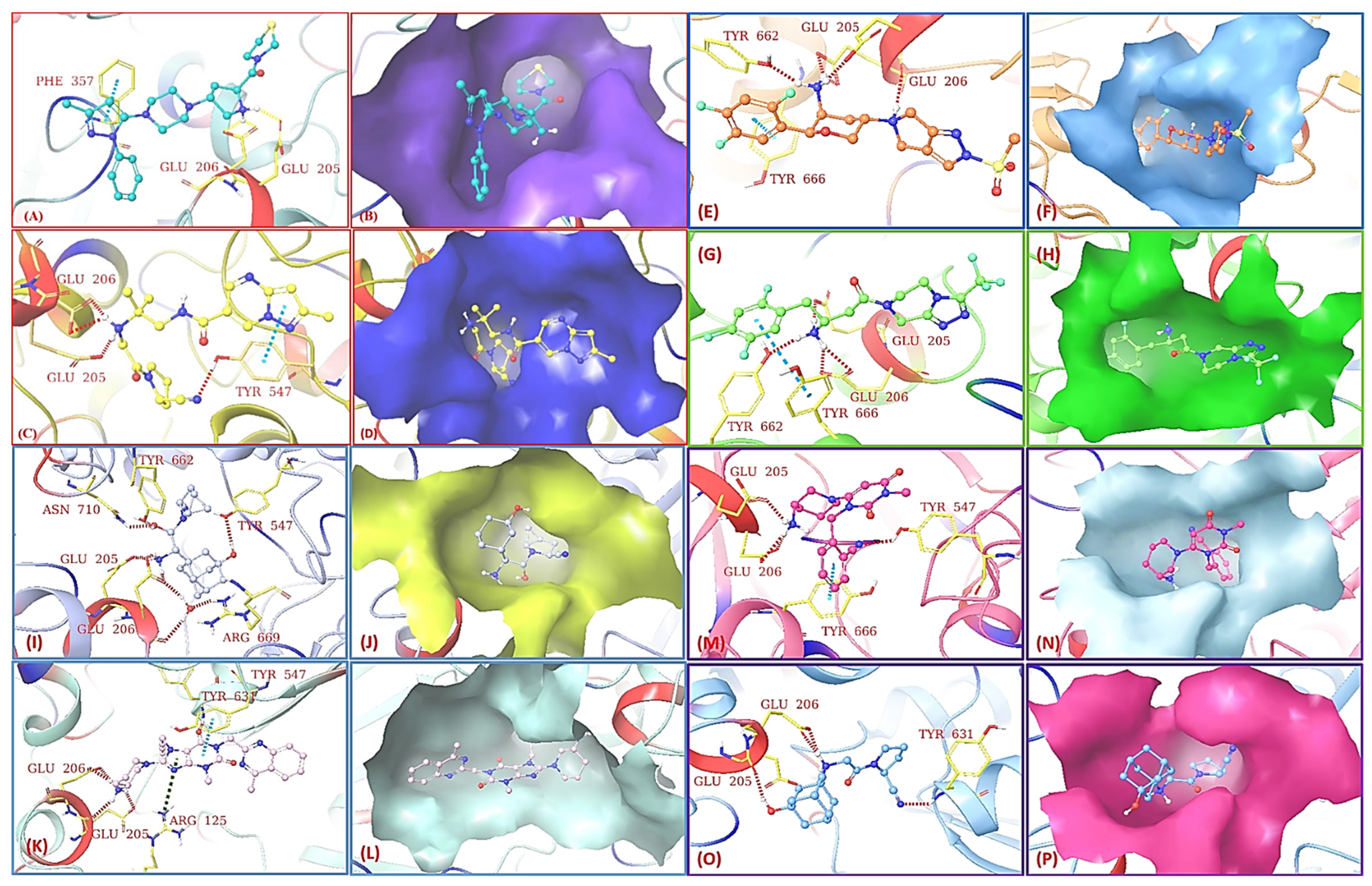
| S.N. | Compounds | Structure | Residue | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Omarigliptin | 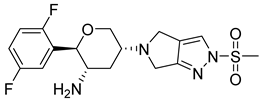 | GLU205 | H-bond [NH..C=O] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [C=O..NH and OH..NH] | |||
| TYR666 | π-bond [C..C] | |||
| 2. | Sitagliptin |  | GLU205 | H-bond [O..NH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [OH..NH and NH..C=O] | |||
| TYR662 | H-bond [O..NH] | |||
| 3. | Teneligliptin |  | GLU205 | H-bond [OH..NH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [OH..NH] | |||
| PHE357 | π-bond [C..C] | |||
| 4. | Anagliptin | 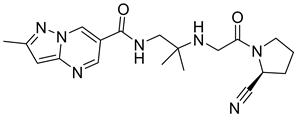 | GLU205 | H-bond [OH..NH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [NH..C=O and NH..OH] | |||
| TYR547 | H-bond and π-bond | |||
| 5. | Linagliptin | 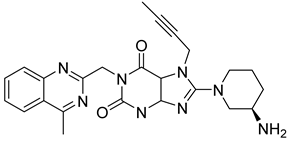 | GLU205 | H-bond [OH..NH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [OH..NH and C=O..NH] | |||
| ARG125 | π-cation bond [NH..CH] | |||
| TYR547 | π-bond [C..C] | |||
| TYR631 | H-bond [C=O..NH] | |||
| 6. | Saxagliptin | 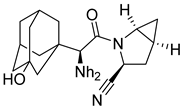 | GLU205 | H-bond [OH..NH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [NH..C=O] | |||
| TYR662 | H-bond [NH..C=O] | |||
| TYR547 | H-bond [OH..OH] | |||
| ARG669 | H-bond [NH..OH] | |||
| ASN710 | H-bond [NH..OH] | |||
| 7. | Alogliptin | 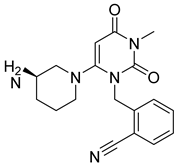 | GLU205 | H-bond [NH..C=O] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [NH..OH] | |||
| TYR666 | π-bond [C..C] | |||
| TYR547 | H-bond [N..OH] | |||
| 8. | Vildagliptin | 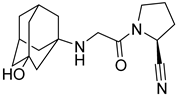 | GLU205 | H-bond [C=O..OH] |
| GLU206 | H-bond [C=O..NH] and [OH..NH] | |||
| TYR631 | H-bond [N..NH] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathur, V.; Alam, O.; Siddiqui, N.; Jha, M.; Manaithiya, A.; Bawa, S.; Sharma, N.; Alshehri, S.; Alam, P.; Shakeel, F. Insight into Structure Activity Relationship of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Development of Antidiabetic Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155860
Mathur V, Alam O, Siddiqui N, Jha M, Manaithiya A, Bawa S, Sharma N, Alshehri S, Alam P, Shakeel F. Insight into Structure Activity Relationship of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Development of Antidiabetic Agents. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155860
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathur, Vishal, Ozair Alam, Nadeem Siddiqui, Mukund Jha, Ajay Manaithiya, Sandhya Bawa, Naveen Sharma, Sultan Alshehri, Prawez Alam, and Faiyaz Shakeel. 2023. "Insight into Structure Activity Relationship of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Development of Antidiabetic Agents" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155860
APA StyleMathur, V., Alam, O., Siddiqui, N., Jha, M., Manaithiya, A., Bawa, S., Sharma, N., Alshehri, S., Alam, P., & Shakeel, F. (2023). Insight into Structure Activity Relationship of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Development of Antidiabetic Agents. Molecules, 28(15), 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155860









