Sponge-liked Silica Nanoporous Particles for Sustaining Release and Long-Term Antibacterial Activity of Natural Essential Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
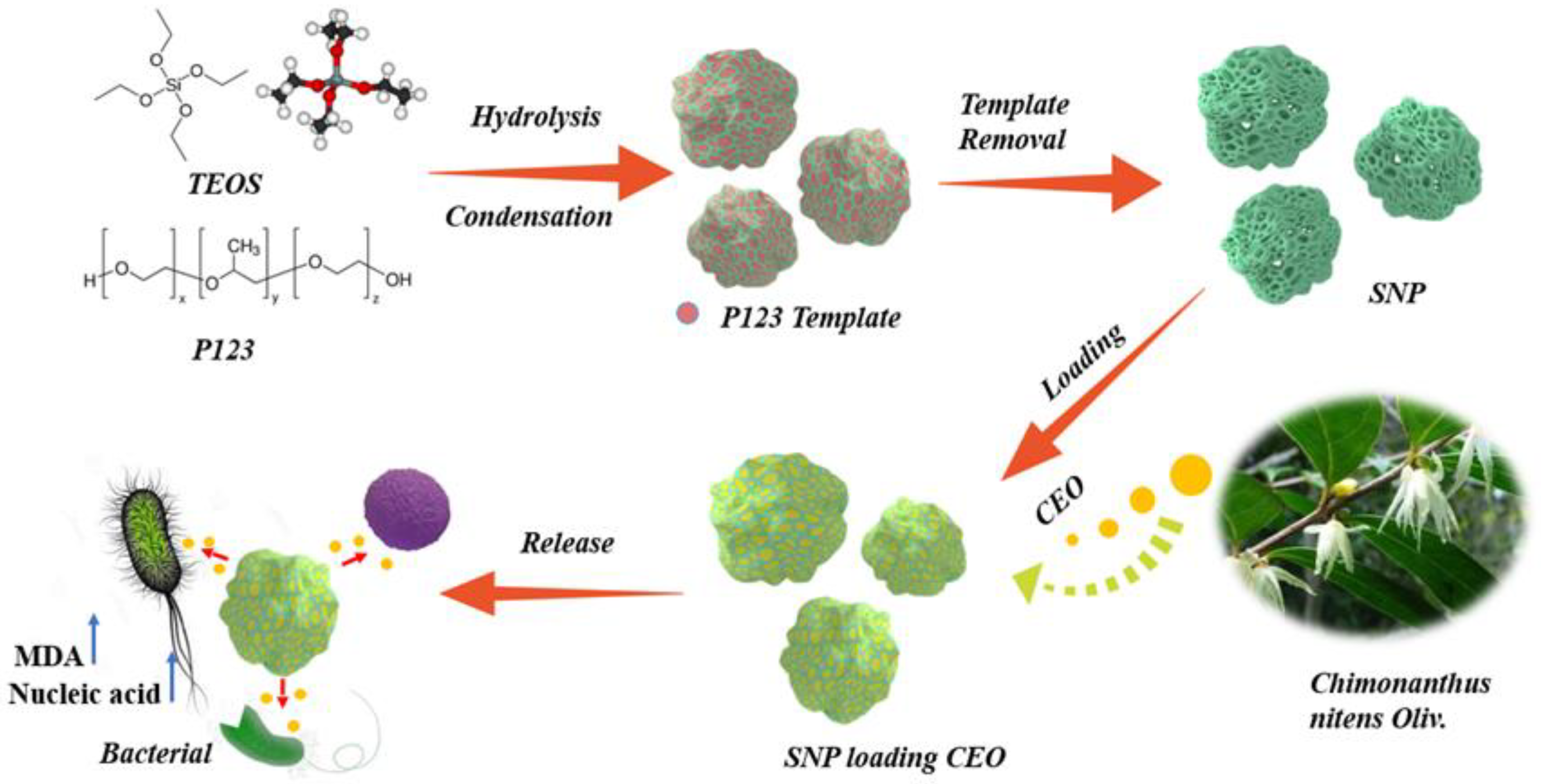
2.1. Characterization of SNP Loading Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. Essential Oil (CEO-SNP) and CEO-SNP
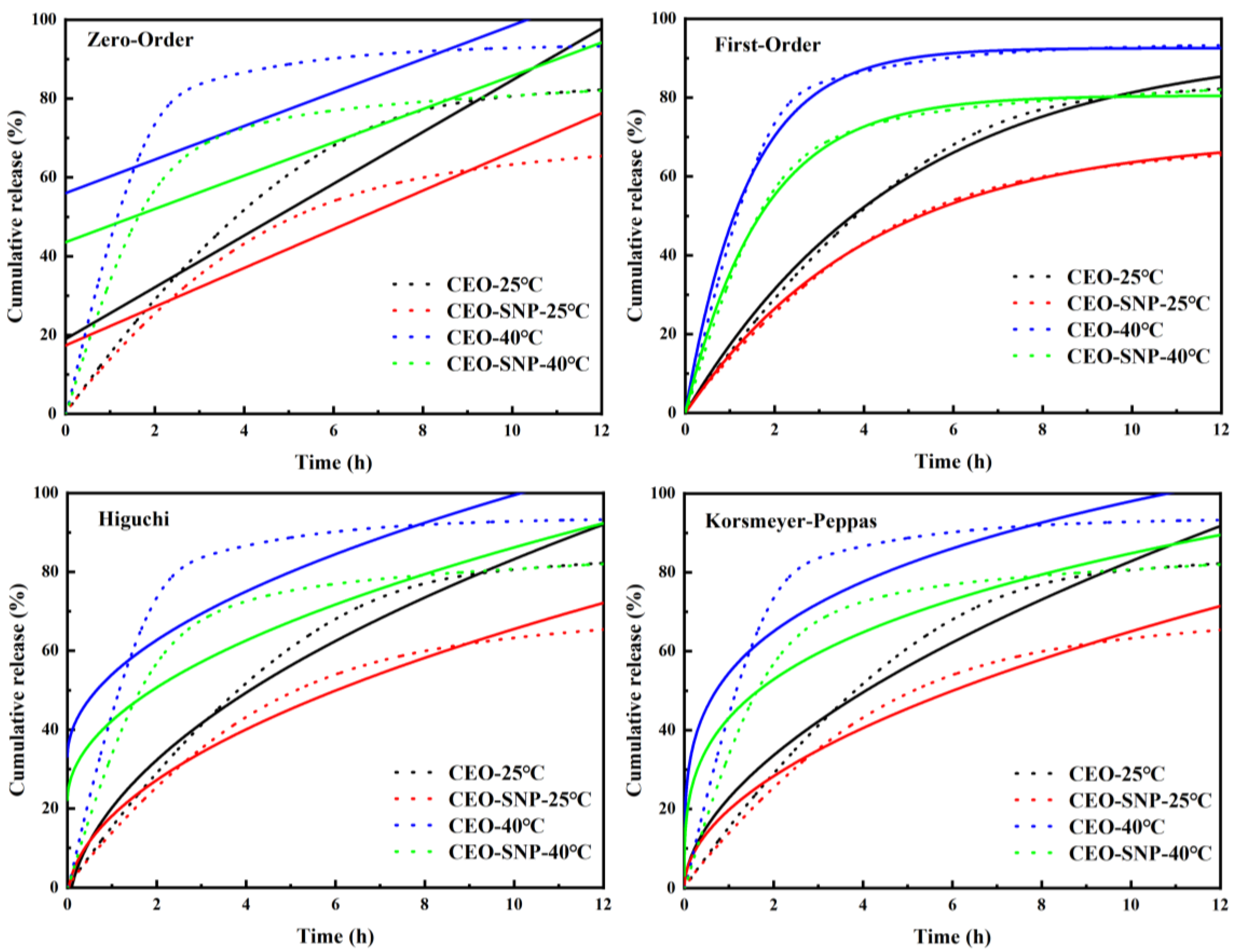
2.2. Sustained Release Evaluation of CEO-SNP
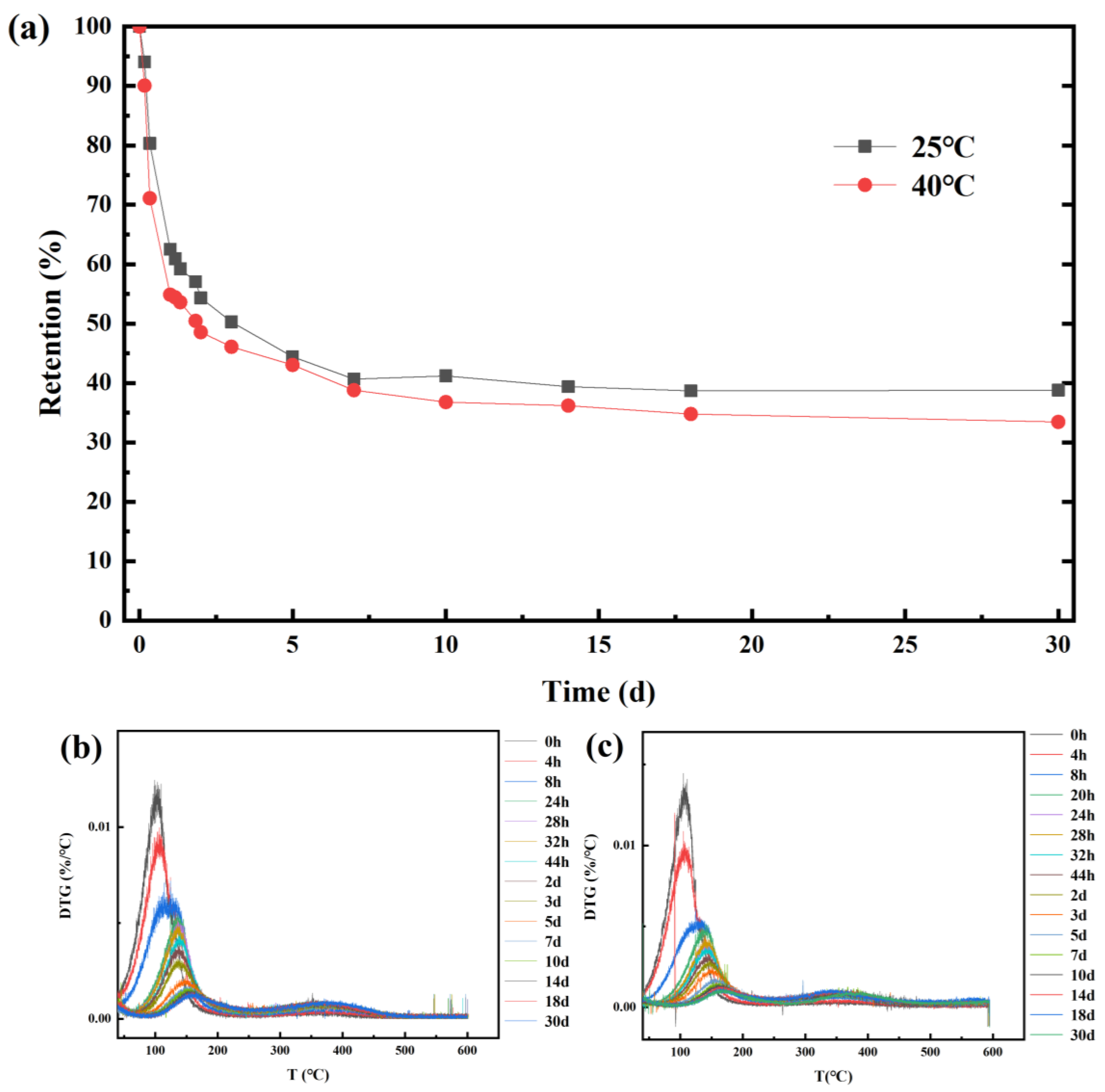
2.3. Stability Evaluation of CEO-SNP
2.4. Antibacterial Performance Analysis
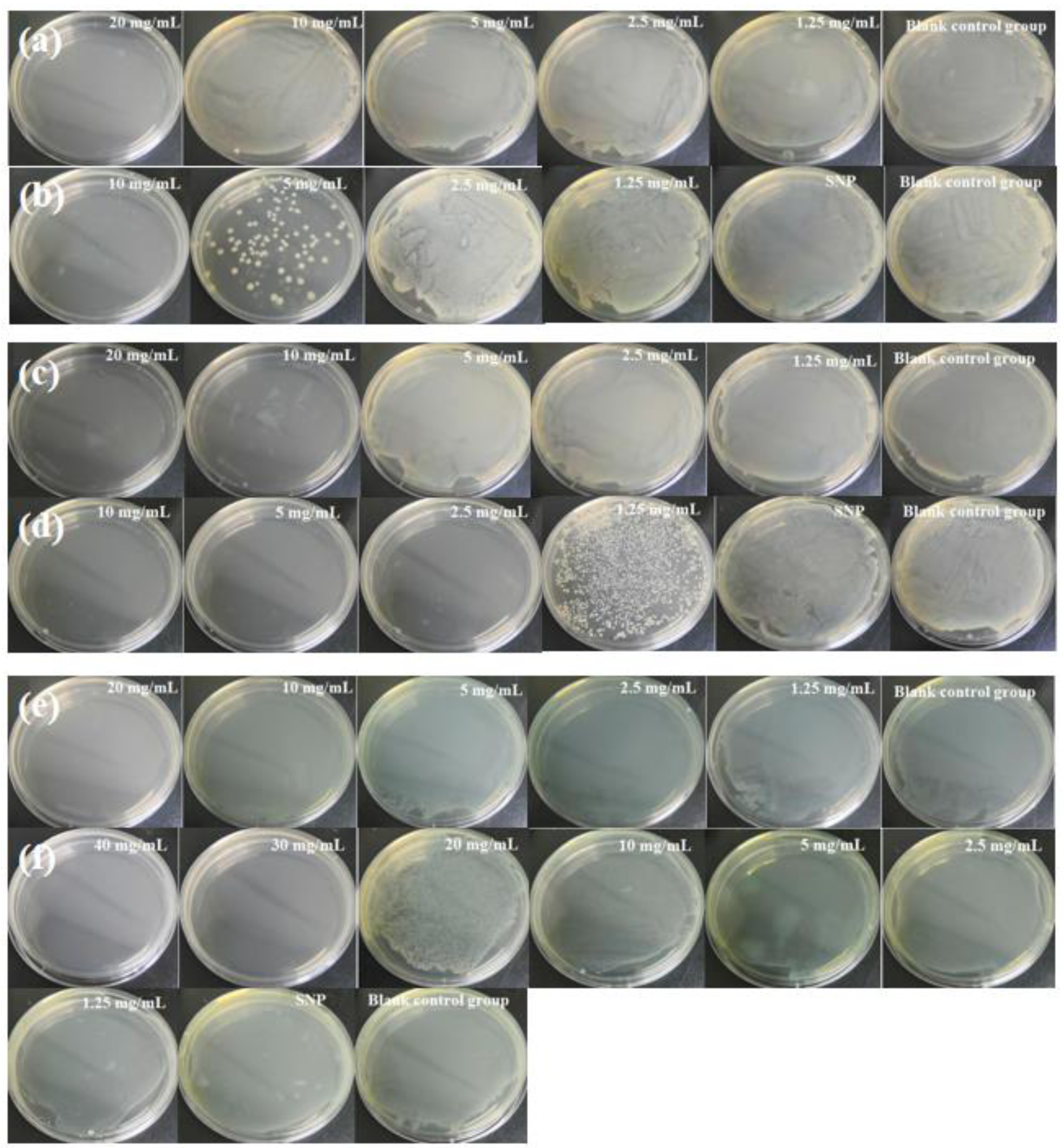
2.4.1. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
2.4.2. Long-Term Antibacterial Effect Test
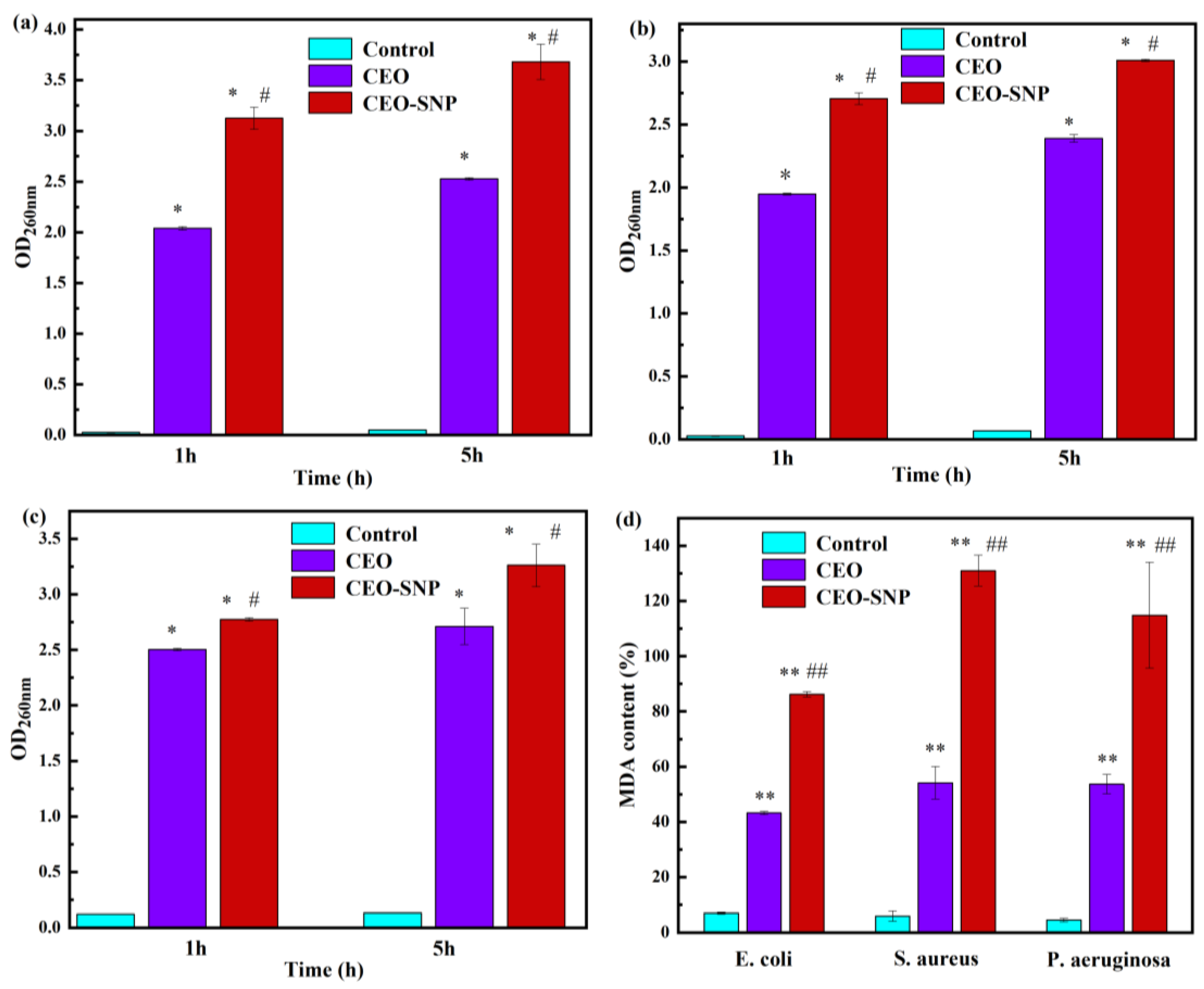
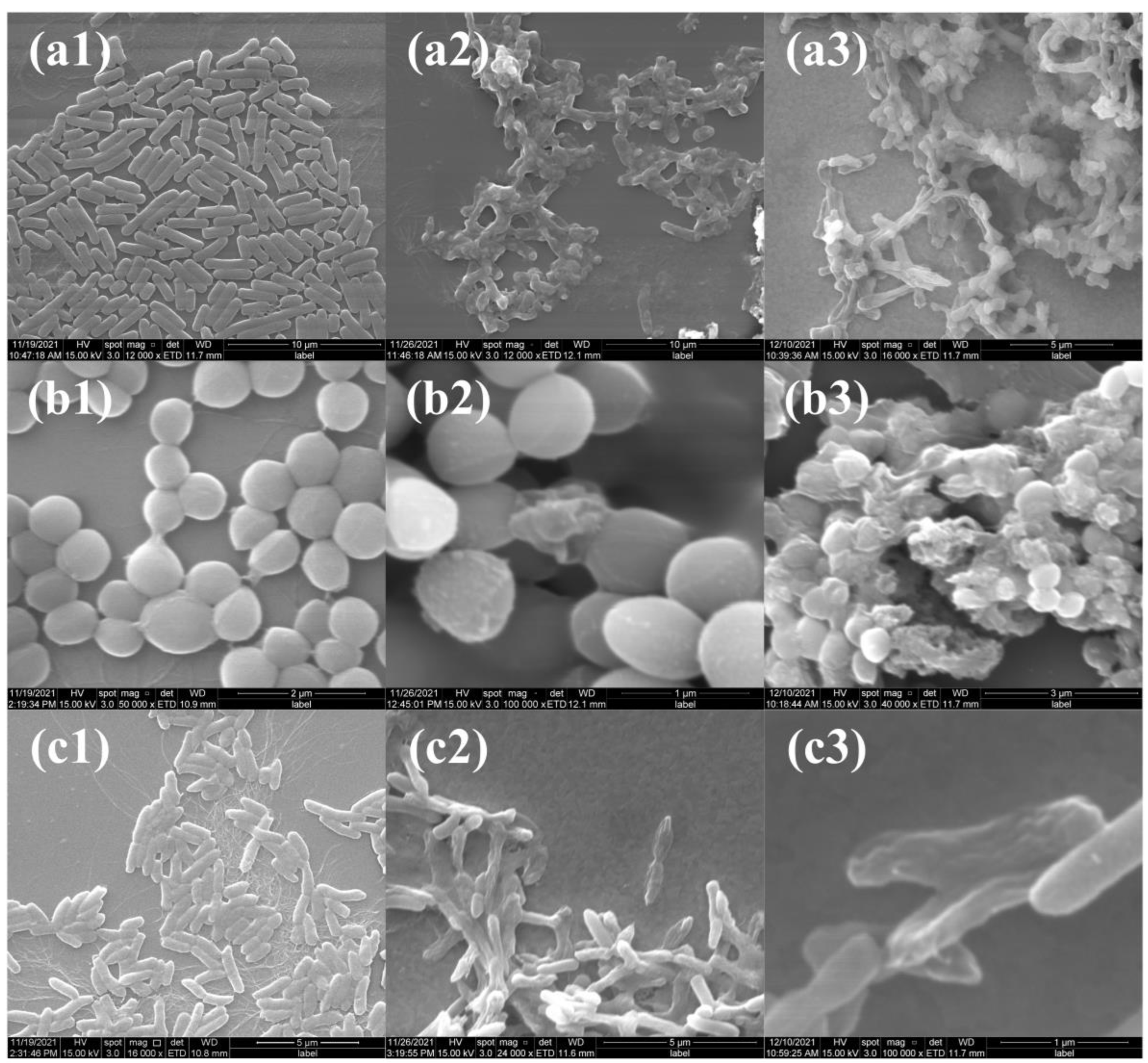
2.4.3. Antibacterial Mechanism Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of SNP
3.3. Preparation of CEO-SNP
3.4. Characterization of SNP and CEO-SNP
3.5. The Sustained-Release Characterization and Loading Capacity Evaluation of CEO-SNP
3.6. Stability Test
3.7. Anti-Bacterial Activity and Anti-Bacterial Mechanism Evaluation of CEO-SNP on E. coli, S. aureus and P. aeruginosa
3.7.1. Culture of Bacterial Strains
3.7.2. Assay of MBC of CEO
3.7.3. Long-Term Antibacterial Activity Evaluation of CEO-SNP
3.7.4. Nucleic Acid Detection of the Bacteria
3.7.5. MDA Content Detection of the Bacteria
3.7.6. Morphology Evaluation of the Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, P.; Liu, J.; Gu, C.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. In Vivo Study of the Efficacy of the Essential Oil of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Pericarp in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Experimental Colitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, S.; Wani, S.; Rasool, W.; Shafi, K.; Bhat, M.A.; Prabhakar, A.; Shalla, A.H.; Rather, M.A. A comprehensive review of the antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral potential of essential oils and their chemical constituents against drug-resistant microbial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 134, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of essential oils: A short review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, E.; Cantamessa, S.; Pavan, M.; Novello, G.; Massa, N.; Rocchetti, A.; Berta, G.; Gamalero, E. Sensitivity of Candida Albicans to Essential Oils: Are They an Alternative to Antifungal Agents? J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranraj, P.; Devi, V.D. Essential oils and its antibacterial properties—A Review. Life Sci. Arch. (LSA) 2017, 3, 994–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Shen, L.; Li, H.; Qin, W. Antioxidant activity and chemical compositions of essential oil and ethanol extract of Chuanminshen violaceum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivieso-Ugarte, M.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Gil, Á. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties of essential oils: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, S.-Z.; Li, M.-J.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, P.; Cheng, D. Study on quality standards for Chimonanthus nitens. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 15038984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-P.; Tan, T.; Li, Z.-F.; OuYang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, B.; Feng, Y.-L. Structural Characterization and Discrimination of Chimonanthus Nitens Oliv. Leaf from Different Geographical Origins Based on Multiple Chromatographic Analysis Combined with Chemometric Methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 154, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Yao, Y.; Wu, W.; Fu, W.; Wu, R.; Li, W. Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. essential oil mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 156, 112445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aysegul, M.; Dilara, D.; Nur, D.D.; Funda, K.; Esra, C. Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antimycotoxigenic, and Antioxidant Activities of Essential Oils: An Updated Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, R.H.; Asensio, C.M.; Grosso, N.R. Thermal stability and antioxidant activity of essential oils from aromatic plants farmed in Argentina. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Zaghdoudi, K.; Pereira, J.A.; Peres, A.M. Kinetic-thermodynamic study of the oxidative stability of Arbequina olive oils flavored with lemon verbena essential oil. LWT 2021, 140, 110711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Zandi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Two-Step Method for Encapsulation of Oregano Essential Oil in Chitosan Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization and in vitro Release Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetika, W.; Sunil, K.; Lovely, C.; Sheefali, M.; Rekha, R. Essential oil–cyclodextrin complexes: An updated review. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2017, 89, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, L.; Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Palmieri, G.F. An Overview of Micro- and Nanoemulsions as Vehicles for Essential Oils: Formulation, Preparation and Stability. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cinzia, C.; Maria, M.O.; Teresa, M.; Angela, B.; Filippo, D.; Barbosa, S.E.M.; Rosario, P.; Claudia, C. Essential Oils: Pharmaceutical Applications and Encapsulation Strategies into Lipid-Based Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Caldera, F.; Trotta, F.; Nerín, C.; Domingues, F.C. Encapsulation of coriander essential oil in cyclodextrin nanosponges: A new strategy to promote its use in controlled-release active packaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 56, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionato, I.; Domingues, F.C.; Nerín, C.; Silva, F. Encapsulation of cinnamon oil in cyclodextrin nanosponges and their potential use for antimicrobial food packaging. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacine, N.B.; Ryma, N.B.; Amel, H.-Z.-Z. Nanodispersions stabilized by β-cyclodextrin nanosponges: Application for simultaneous enhancement of bioactivity and stability of sage essential oil. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Y. Encapsulation and controlled release of fragrances from functionalized porous metal–organic frameworks. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Guo, T.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, L. Solidification of volatile D-Limonene by cyclodextrin metal-organic framework for pulmonary delivery via dry powder inhalers: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartik, T.; Sankha, B. The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: Preparation, characterization, and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleňák, V.; Halamová, D.; Almáši, M.; Žid, L.; Zeleňáková, A.; Kapusta, O. Ordered cubic nanoporous silica support MCM-48 for delivery of poorly soluble drug indomethacin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 443, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hua, M.; Liu, H.; Li, J. How to design nanoporous silica nanoparticles in regulating drug delivery: Surface modification and porous control. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Therapeutic Biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y. Basic evaluation of typical nanoporous silica nanoparticles in being drug carrier: Structure, wettability and hemolysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, D.; Ashley, C.E.; Min, X.; Carnes, E.C.; Zink, J.I.; Brinker, C.J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Nanocarriers: Biofunctionality and Biocompatibility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, P.; Ma, B.; Hung, C.T.; Li, W.; Zhao, D. Spherical Mesoporous Materials from Single to Multilevel Architectures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2928–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, H. Recent advances in porous nanostructures for cancer theranostics. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Han, Y.H.; Na, J.; Lee, C.H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.B.; Kimura, T.; Ok, Y.S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Nanoarchitectured Structure and Surface Biofunctionality of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1907035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Han, Y.H.; Xia, H.Y.; Wang, S.B.; Chen, A.Z. Nanoarchitectured prototypes of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for innovative biomedical applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Liu, C.-G.; Yang, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Ultrasmall platinum nanoparticles enable deep tumor penetration and synergistic therapeutic abilities through free radical species-assisted catalysis to combat cancer multidrug resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.B.; Chen, A.Z. Nanoarchitecting Hierarchical Mesoporous Siliceous Frameworks: A New Way Forward. iScience 2020, 23, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatova, A.; Bernardos, A.; Smid, J.; Frankova, A.; Lhotka, M.; Kourimská, L.; Pulkrabek, J.; Kloucek, P. Long-Term Antifungal Activity of Volatile Essential Oil Components Released from Mesoporous Silica Materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhou, H.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Synergistic Antimicrobial Activities of Tea Tree Oil Loaded on Mesoporous Silica Encapsulated by Polyethyleneimine. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximing, Z.; Fan, G.; Haoyan, L.; Guofeng, S.; Hongjun, Z.; Xinhua, Z. One-pot self-assembly strategy to prepare mesoporous silica-based nanocomposites with enhanced and long-term antibacterial performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Gao, F.; Zhijun, L.; Zhong, X.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H. Rosin modified aminated mesoporous silica adsorbed tea tree oil sustained-release system for improve synergistic antibacterial and long-term antibacterial effects. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 275707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhou, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, G.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zhou, X. Long-Lasting Anti-Bacterial Activity and Bacteriostatic Mechanism of Tea Tree Oil Adsorbed on The Amino-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica-coated by PAA. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas Adsorption Characterization of Ordered Organic-Inorganic Nanocomposite Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenares-Zerpa, J.; Chimentão, R.J.; Gispert-Guirado, F.; Peixoto, A.F.; Llorca, J. Preparation of SBA-15 and Zr-SBA-15 materials by Direct-Synthesis and pH-Adjustment Methods. Mater. Lett. 2021, 301, 130326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cheng, M.; Han, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Characterization and release kinetics study of potato starch nanocomposite films containing mesoporous nano-silica incorporated with Thyme essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shen, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Xu, H.; Zhou, X. Long effective tea tree oil/mesoporous silica sustained release system decorated by polyethyleneimine with high antibacterial performance. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yue, P. Fabrication and Antibacterial Evaluation of Peppermint Oil-Loaded Composite Microcapsules by Chitosan-Decorated Silica Nanoparticles Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Templating. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Quan, P.; Fang, L.; Cun, D.; Yang, M. Sustained Release Donepezil Loaded PLGA Microspheres for Injection: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo Study. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahab, S.I.; Zaman, F.Q.; Mariod, A.A.; Yaacob, M.; Abdelmageed, A.; Khamis, S. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of the essential oils of Etlingera elatior and Cinnamomum pubescens Kochummen. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Paralikar, P.; Jogee, P.; Agarkar, G.; Ingle, A.P.; Derita, M.; Zacchino, S. Synergistic antimicrobial potential of essential oils in combination with nanoparticles: Emerging trends and future perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their Antibacterial Properties and Potential Applications in Foods-A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Martino, L.D.; Coppola, R.; Feo, V.D. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morten, H.; Tina, M.; Louise, M.R. Essential Oils in Food Preservation: Mode of Action, Synergies, and Interactions with Food Matrix Components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sattary, M.; Amini, J.; Hallaj, R. Antifungal activity of the lemongrass and clove oil encapsulated in mesoporous silica nanoparticles against wheat’s take-all disease. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 170, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, M.B.; Preston, G.M.; Hoorn, R.A.L.V.D.; Townley, H.E.; Thompson, I.P. Species-specific antimicrobial activity of essential oils and enhancement by encapsulation in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.M.; Cox, S.D.; Markham, J.L. The outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCTC 6749 contributes to its tolerance to the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 30, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longbottom, C.J.; Carson, C.F.; Hammer, K.A.; Mee, B.J.; Riley, T.V. Tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil is associated with the outer membrane and energy-dependent cellular processes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Quek, S. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2016, 59, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. The inhibitory effect of plant essential oils on foodborne pathogenic bacteria in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cui, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Antifungal activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil loaded into mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugénia, P.; Luís, V.-S.; Carlos, C.; Lígia, S. Antifungal activity of the clove essential oil from Syzygium aromaticum on Candida, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Gao, F.; Wei, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X. Functionalization of mesoporous silica as an effective composite carrier for essential oils with improved sustained release behavior and long-term antibacterial performance. Nanotechnology 2021, 33, 035706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kailasam, K.; Xie, X.; Zhu, J. High-Surface-Area SBA-15 with Enhanced Mesopore Connectivity by the Addition of Poly(vinyl alcohol). Chem. Mater. A Publ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 23, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, H.; Bao, W. Synthesis and characteristics of SBA-15 with thick pore wall and high hydrothermal stability. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Teng, J.; Hu, L.; Lan, X.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, M. Pepper Fragrant Essential Oil (PFEO) and Functionalized MCM-41 Nanoparticles: Formation, Characterization, and Bactericidal Activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5168–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, D.S.E.; Carneiro, D.B.J.; Vasconcelos, D.O.C.E.; Lúcia, D.C.M. Influence of Origanum Vulgare L. Essential Oil on Enterotoxin Production, Membrane Permeability and Surface Characteristics of Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 137, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
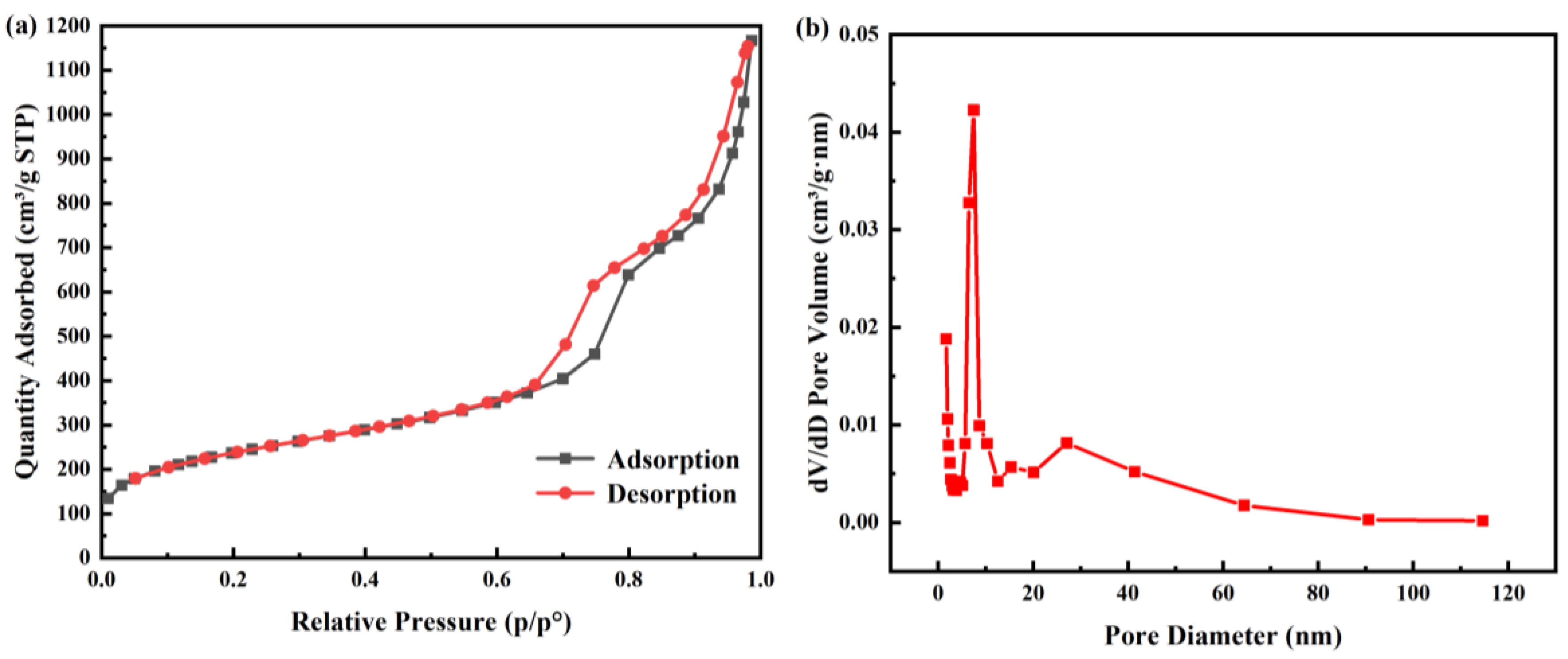




| Analyzed Materials | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter Dv (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 815.7278 | 1.804470 | 8.7026 |
| T (°C) | Samples | Zero-Order Equation | First-Order Equation | Higuchi Equation | Korsmeyer–Peppas Equation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y = k t + b | Y = k (1 − e b t) | Y = k t 1/2 + b | Y = k t b | ||||||||||
| k | b | R2 | k | b | R2 | k | b | R2 | k | b | R2 | ||
| 25 | CEO | 1.0900 × 10−3 | 0.1899 | 0.8856 | 0.9327 | −0.0034 | 0.9950 | 0.0376 | −0.0889 | 0.9684 | 0.0230 | 0.5602 | 0.9600 |
| CEO-SNP | 8.1820 × 10−4 | 0.1739 | 0.8749 | 0.7017 | −0.0040 | 0.9990 | 0.0283 | −0.0375 | 0.9678 | 0.0239 | 0.5163 | 0.9637 | |
| 40 | CEO | 7.0912 × 10−4 | 0.5602 | 0.5215 | 0.9257 | −0.0119 | 0.9930 | 0.0272 | 0.3298 | 0.7076 | 0.1921 | 0.2548 | 0.8086 |
| CEO-SNP | 7.0348 × 10−4 | 0.435 | 0.6166 | 0.8055 | −0.0097 | 0.9966 | 0.0262 | 0.2198 | 0.7931 | 0.1295 | 0.2939 | 0.8647 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, H.; Chen, S.; Su, X.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, M.; Shen, B.; Yue, P. Sponge-liked Silica Nanoporous Particles for Sustaining Release and Long-Term Antibacterial Activity of Natural Essential Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020594
Lai H, Chen S, Su X, Huang X, Zheng Q, Yang M, Shen B, Yue P. Sponge-liked Silica Nanoporous Particles for Sustaining Release and Long-Term Antibacterial Activity of Natural Essential Oil. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020594
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Huazhang, Shuiyan Chen, Xiaoyu Su, Xiaoying Huang, Qin Zheng, Ming Yang, Baode Shen, and Pengfei Yue. 2023. "Sponge-liked Silica Nanoporous Particles for Sustaining Release and Long-Term Antibacterial Activity of Natural Essential Oil" Molecules 28, no. 2: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020594
APA StyleLai, H., Chen, S., Su, X., Huang, X., Zheng, Q., Yang, M., Shen, B., & Yue, P. (2023). Sponge-liked Silica Nanoporous Particles for Sustaining Release and Long-Term Antibacterial Activity of Natural Essential Oil. Molecules, 28(2), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020594





