Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
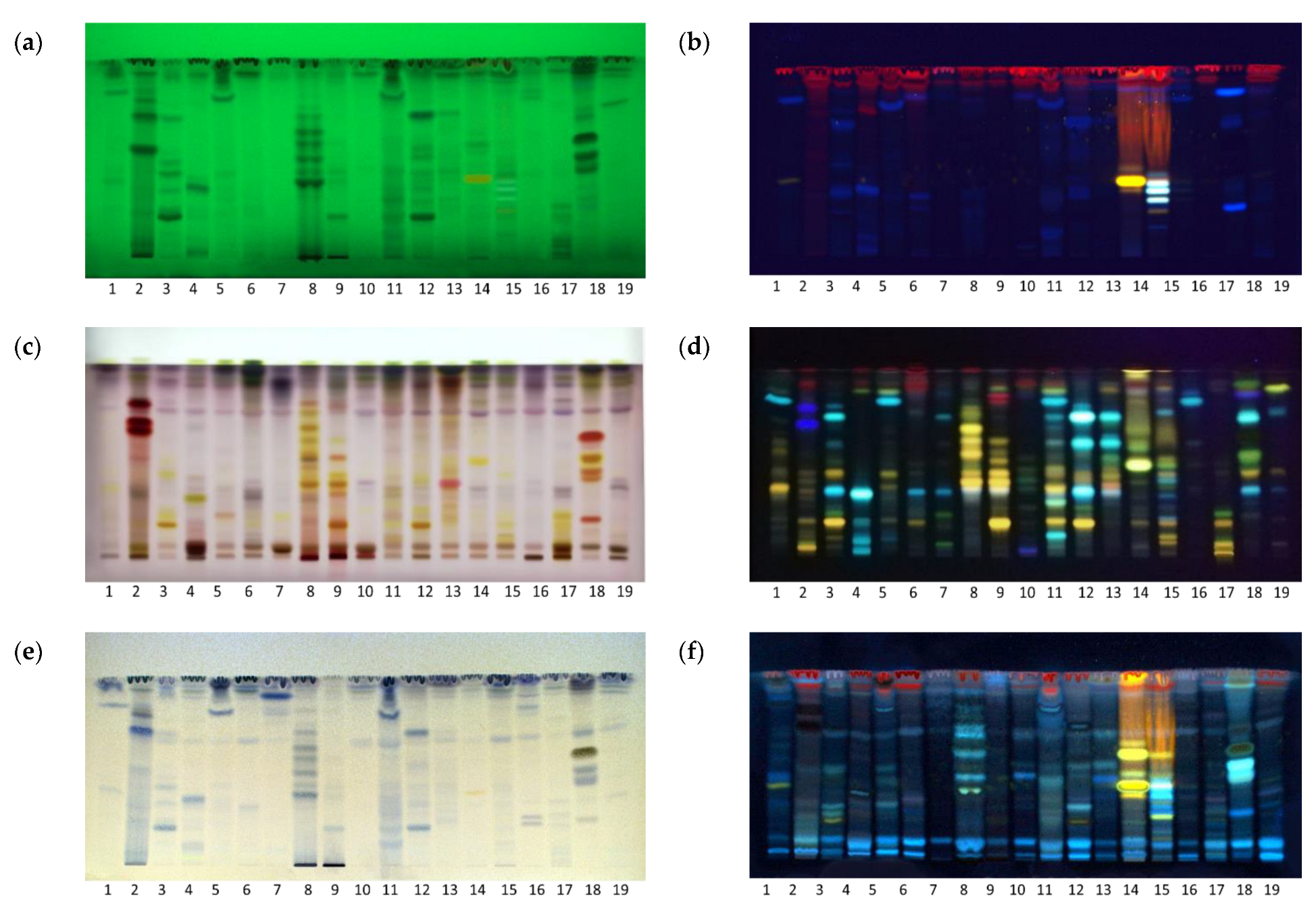
2.1. HPTLC Fingerprints and Chemical Profiling
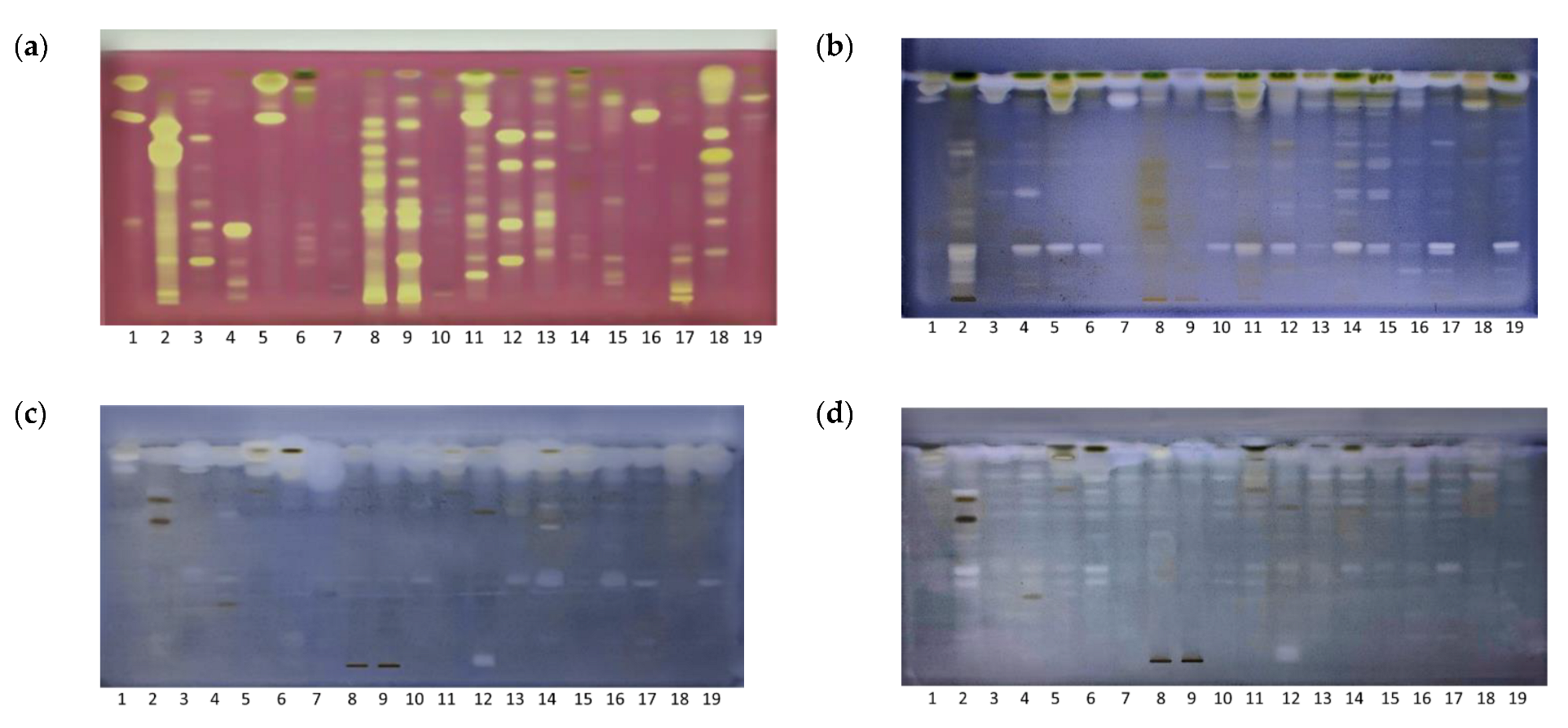
2.2. HPTLC Bioassay Profiling
2.3. Quantification of Phenolics and Biological Activity of Medicinal Plants
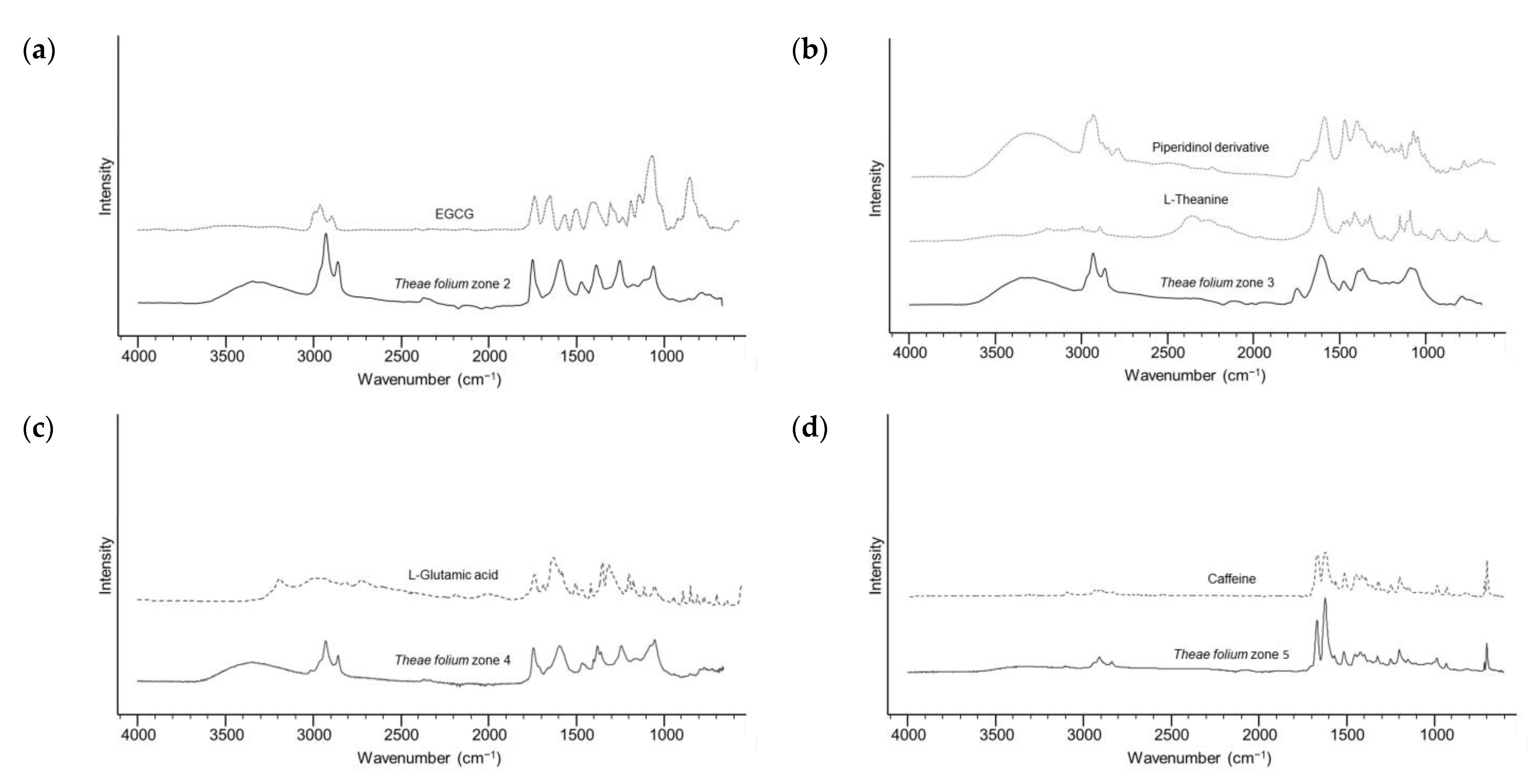
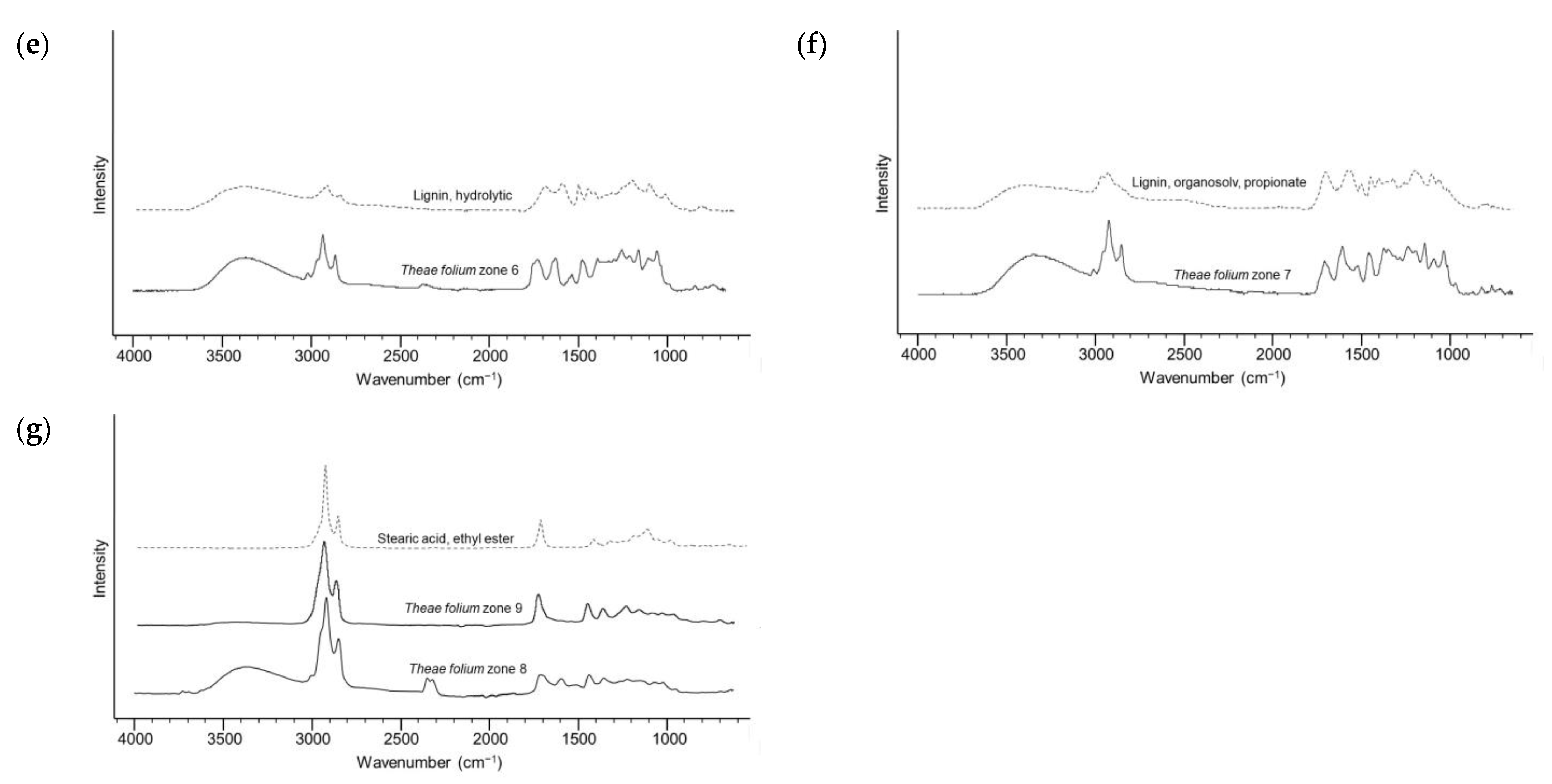
2.4. Target Analysis of Most Promising Extracts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Plant Material and Extraction of Secondary Metabolites
3.3. Planar Chromatography
3.4. Chemical Derivatization
3.5. COX-1 Inhibitory Assay
3.6. Antibacterial Assays
3.7. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
3.8. Spectrophotometric Assays
3.9. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salmerón-Manzano, E.; Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide research trends on medicinal plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofowora, A.; Ogunbodede, E.; Onayade, A. The role and place of medicinal plants in the strategies for disease prevention. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. The value of plants used in traditional medicine for drug discovery. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S1), 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marston, A. Thin-layer chromatography with biological detection in phytochemistry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Wong, S.; Dolzhenko, A.V.; Gegechkori, V.; Ku, H.; Tucci, J.; Morton, D.W. Evaluation of bioactive compounds from Ficus carica L. leaf extracts via high-performance thin-layer chromatography combined with effect-directed analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1706, 464241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choma, I.M.; Jesionek, W. TLC-direct bioautography as a high throughput method for detection of antimicrobials in plants. Chromatography 2015, 2, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Marti, G.; Thomas, A.; Bertrand, S. Current approaches and challenges for the metabolite profiling of complex natural extracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1382, 136–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, A.; Hidalgo, O.; D’Ambrosio, U.; Parada, M.; Garnatje, T.; Vallès, J. The role of botanical families in medicinal ethnobotany: A phylogenetic perspective. Plants 2021, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner Fialová, S.; Rendeková, K.; Mučaji, P.; Nagy, M.; Slobodníková, L. Antibacterial activity of medicinal plants and their constituents in the context of skin and wound infections, considering European legislation and folk medicine-A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köberl, M.; Schmidt, R.; Ramadan, E.; Bauer, R.; Berg, G. The microbiome of medicinal plants: Diversity and importance for plant growth, quality and health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, M.R.F.; Stahl, E. Thin-Layer Chromatography: A Laboratory Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, D.G.; Maihs, A.E. Selective spray reagents for the identification and estimation of flavonoid compounds associated with condensed tannins. J. Chromatogr. A 1960, 4, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jork, H.; Funk, W.; Fisher, W.; Wimmer, H. Thin-Layer Chromatography: Reagents and Detection Methods. Volume 1b; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 117, p. 1186. [Google Scholar]
- Degot, P. Extraction and Formulation of Plant Substances. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Corradini, E.; Foglia, P.; Giansanti, P.; Gubbiotti, R.; Samperi, R.; Laganà, A. Flavonoids: Chemical properties and analytical methodologies of identification and quantitation in foods and plants. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 469–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Gegechkori, V.; Petrovich, D.S.; Ilinichna, K.T.; Morton, D.W. HPTLC and FTIR fingerprinting of olive leaves extracts and ATR-FTIR characterisation of major flavonoids and polyphenolics. Molecules 2021, 26, 6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazier, R.H., Jr.; Harlow, R.L. Oxidative coupling of ketone enolates by ferric chloride. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 5408–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, Ł.; Kryszeń, J.; Stochmal, A.; Oleszek, W.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M. Approach to develop a standardized TLC-DPPH• test for assessing free radical scavenging properties of selected phenolic compounds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßmann, J. Terpenoids as Plant Antioxidants. In Vitamins and Hormones; Litwack, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 72, pp. 505–535. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesooriya, S.S.; Pandithavidana, D.R. Investigation and comparison of antioxidant potential of catechins present in green tea: DFT study. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2022, 16, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Kenaan, A.; Geng, F.; Li, H.B.; Gunaratne, A.; Li, H.; Gan, R.Y. L-Theanine: A unique functional amino acid in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) with multiple health benefits and food applications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasstani, O.A.; Moin, S.; Tham, C.L.; Liew, C.Y.; Ismail, N.; Rajajendram, R.; Harith, H.H.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Mohamad, A.S.; Sulaiman, M.R.; et al. Flavonoid combinations cause synergistic inhibition of proinflammatory mediator secretion from lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and therapies of antibiotic-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elez Garofulić, I.; Malin, V.; Repajić, M.; Zorić, Z.; Pedisić, S.; Sterniša, M.; Smole Možina, S.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Phenolic profile, antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity of nettle leaves extracts obtained by advanced extraction techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sahadevan, R.; Roy, R.; Biswas, M.; Ghosh, P.; Kar, P.; Sonawane, A.; Sadhukhan, S. Structure-based design and synthesis of a novel long-chain 4’’-alkyl ether derivative of EGCG as potent EGFR inhibitor: In vitro and in silico studies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 17821–17836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Zhang, Y.; Nair, M.G. Inhibition of proliferation of human cancer cells and cyclooxygenase enzymes by anthocyanidins and catechins. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 46, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T. Chemopreventive Activities of Phytochemicals; MDPI-Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; An, J.; Liu, X. Anti-inflammatory function of plant-derived bioactive peptides: A review. Foods 2022, 11, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.G.; Skwarecki, A.S.; Milewska, M.J. Amino Acid Based Antimicrobial Agents—Synthesis and Properties. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3513–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Kurihara, S.; Titchenal, C.A.; Ohtani, M. Suppression of exercise-induced neutrophilia and lymphopenia in athletes by cystine/theanine intake: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Qian, M.C.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Insight into aroma dynamic changes during the whole manufacturing process of chestnut-like aroma green tea by combining GC-E-Nose, GC-IMS, and GC × GC-TOFMS. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redzicka, A.; Wiatrak, B.; Jęśkowiak-Kossakowska, I.; Kochel, A.; Płaczek, R.; Czyżnikowska, Ż. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking study of 4,6-dimethyl-5-aryl/alkyl-2-[2-hydroxy-3-(4-substituted-1-piperazinyl)propyl]pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,3(2H,5H)-diones as anti-Inflammatory agents with dual inhibition of COX and LOX. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Z.-B.; Meng, Y.-M.; Hong, X.-Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.-J.; Cheng, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.-Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mejia, E.G.; Ramirez-Mares, M.V.; Puangpraphant, S. Bioactive components of tea: Cancer, inflammation and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, K.; Yokoyama, H.; Noda, H.; Yuguchi, Y. Antioxidant capacity of lignin from green tea waste. J. Food Biochem. 2010, 34, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Wei, L.; Li, W.; Gong, D.; Qin, H.; Feng, X.; Li, G.; Ling, Z.; Wang, P.; Yin, B. Isolating high antimicrobial ability lignin from bamboo kraft lignin by organosolv fractionation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 683796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaw, L.J.; Jäger, A.K.; van Staden, J. Antibacterial effects of fatty acids and related compounds from plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2002, 68, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Eduardo-Figueira, M.; Barateiro, A.; Fernandes, A.; Brites, D.; Bronze, R.; Duarte, C.M.; Serra, A.T.; Pinto, R.; Freitas, M.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of rosmarinic acid and an extract of Rosmarinus officinalis in rat models of local and systemic inflammation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 116, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althobaiti, F. Antibacterial activity and genotoxicity effect of ethanolic leaves extract of Rosmarinus officinalis. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Chandra, S.; Dey, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effects of green tea and black tea: A comparative in vitro study. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Arora, D.; Jeet Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Antibacterial activity of tea and coffee: Their extracts and preparations. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.S.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Nunes, F.M.; Silva, A.M. Elderberry ( Sambucus nigra L.) extracts promote anti-inflammatory and cellular antioxidant activity. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkova-Tomova, I.; Kazakova, Z.; Buhalova, D.; Gentscheva, G.; Nikolova, K.; Minkova, S. Antioxidant properties and antibacterial activity of water extracts from Sambucus nigra L. under different conditions. Folia Med. 2023, 65, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarizadeh, A.; Mikaili, P.; Moloudizargari, M.; Aghajanshakeri, S.; Javaherypour, S. Therapeutic uses and pharmacological properties of Plantago major L. and its active constituents. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Monawer, A.T.; Mammani, I.M.A. Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extracts of Plantago major leaves against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from burn infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2023, 17, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindisi, M.; Bouzidi, C.; Frattaruolo, L.; Loizzo, M.R.; Cappello, M.S.; Dugay, A.; Deguin, B.; Lauria, G.; Cappello, A.R. New insights into the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Italian Salvia officinalis leaf and flower extracts in lipopolysaccharide and tumor-mediated inflammation models. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, F.S.F.; Garcia, L.M.; Moraes, T.D.S.; Casemiro, L.A.; Alcântara, C.B.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Miranda, M.L.D.; Martins, C.H.G. Antibacterial activity of Salvia officinalis L. against periodontopathogens: An in vitro study. Anaerobe 2020, 63, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, H.P.; Paudel, K.R.; Khanal, S.; Baral, A.; Panth, N.; Adhikari-Devkota, A.; Jha, N.K.; Das, N.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; et al. Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.): Nutritional composition, bioactive compounds, and food functional properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, F.; Furner-Pardoe, J.; Connelly, E. An assessment of the evidence for antibacterial activity of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) extracts. Access Microbiol. 2022, 4, 000336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Ferreira, M.S.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M.; Cruz, M.T.; Almeida, I.F. Anti-inflammatory activity of Calendula officinalis L. flower extract. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Ruíz-Posadas, L.; Rodríguez-López, V.A.; Cadena-Iñíguez, J.; Delgadillo-Martínez, J.; San Miguel-Chávez, R.; Salazar-Aguilar, S.; Valdez-Carrasco, J. Antibacterial activity of the Calendula officinalis L. essential oil on Escherichia coli. Agro Product. 2023, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Zarei, H.; Taghiabadi, E. Antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and acute toxicity effects of juglans regia L. leaves in mice. Iran Red Crescent Med. J. 2011, 13, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Turki, O.H.; Jafar, Z.J. Antibacterial activity of Juglans regia L. dry husk extract against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus: An in vitro study. Dent. Hypotheses 2023, 14, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, N. Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) beyond depression: A therapeutic perspective for pain conditions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 200, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, M.M.; Elshikh, H.H.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Elaasser, M.M.; Yosri, M. In vitro antibacterial and phytochemical screening of Hypericum perforatum extract as potential antimicrobial agents against multi-drug-resistant (MDR) strains of clinical origin. Biomed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 6934398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benso, B.; Franchin, M.; Massarioli, A.P.; Paschoal, J.A.; Alencar, S.M.; Franco, G.C.; Rosalen, P.L. Anti-inflammatory, anti-osteoclastogenic and antioxidant effects of Malva sylvestris extract and fractions: In vitro and in vivo studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Ghane, M.; Pishkar, L. Phytochemical composition, antibacterial, and antibiofilm activity of Malva sylvestris against human pathogenic bacteria. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2022, 17, e114164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, E.; Awoleye, O.; Davis, A.; Mishra, S. Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of thyme oil and Its main constituents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babotă, M.; Frumuzachi, O.; Nicolescu, A.; Stojković, D.; Soković, M.; Rocchetti, G.; Zhang, L.; Lucini, L.; Crișan, G.; Mocan, A. Phenolic profile, in vitro antimicrobial and in vivo diuretic effects of endemic wild thyme Thymus comosus Heuff ex. Griseb. (Lamiaceae) from Romania. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1115117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tămaş, M.; Vostinaru, O.; Soran, L.; Lung, I.; Opris, O.; Toiu, A.; Gavan, A.; Dinte, E.; Mogosan, C. Antihyperuricemic, anti-inflammatory and antihypertensive effect of a dry extract from Solidago virgaurea L. (Asteraceae). Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, B.; Kowalski, R.; Kędzia, B. Antibacterial and antimutagenic activity of extracts aboveground parts of three Solidago species: Solidago virgaurea L., Solidago canadensis L. and Solidago gigantea Ait. J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 6770–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, A.; Naseef, P.P.; Kuruniyan, M.S.; Jain, G.K.; Zakir, F.; Aggarwal, G. A comprehensive study of therapeutic applications of chamomile. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, L.P.; Marjanovic-Balaban, Z.R.; Kalaba, V.D.; Stanojevic, J.S.; Cvetkovic, D.J. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of chamomile flowers essential oil (Matricaria chamomilla L.). J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2016, 19, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczak, P.Ł.; Kędzia, B.; Ożarowski, M.; Kujawski, R.; Bogacz, A.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Białas, W.; Gryszczyńska, A.; Buchwald, W.; Szulc, M.; et al. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of extracts from herb of Chelidonium majus L. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 40, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyżek, P.; Junka, A.; Słupski, W.; Dołowacka-Jóźwiak, A.; Płachno, B.J.; Sobiecka, A.; Matkowski, A.; Chodaczek, G.; Płusa, T.; Gościniak, G. Antibiofilm and antimicrobial-enhancing activity of Chelidonium majus and Corydalis cheilanthifolia extracts against multidrug-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raafat, K.M.; El-Zahaby, S.A. Niosomes of active Fumaria officinalis phytochemicals: Antidiabetic, antineuropathic, anti-inflammatory, and possible mechanisms of action. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamtache-Abderrahim, S.; Lequart-Pillon, M.; Gontier, E.; Gaillard, I.; Pilard, S.; Mathiron, D.; Djoudad-Kadji, H.; Maiza-Benabdesselam, F. Isoquinoline alkaloid fractions of Fumaria officinalis: Characterization and evaluation of their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, C. Comfrey: A clinical overview. Phytother Res. 2012, 26, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlani, M.; Scheibel, D.M.; Barbakadze, V.; Gogilashvili, L.; Amiranashvili, L.; Geronikaki, A.; Catania, V.; Schillaci, D.; Gallo, G.; Gitsov, I. Enzymatic synthesis and antimicrobial activity of oligomer analogues of medicinal biopolymers from comfrey and other species of the boraginaceae family. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapatskyy, M.; Gumienna, A.; Sowa, P.; Kapusta, I.; Puchalski, C. Bioactive phenolic compounds from Primula veris L.: Influence of the extraction conditions and purification. Molecules 2021, 26, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, S.; Kopeinig, B.; Bauer, R.; Pahl, A.; Haunschild, J. In vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial activity of cowslip flowers (Primula veris L.). Planta Med. 2012, 78, PD101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Recio, M.d.C.; Giner, R.M.; Máñez, S.; Tournier, H.; Schinella, G.; Ríos, J.-L. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Helichrysum italicum. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dănăilă-Guidea, S.M.; Eremia, M.C.; Dinu, L.D.; Miu, D.-M. Helichrysum arenarium: From cultivation to application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.-J.; Kang, H.-J.; Jung, H.-J.; Kang, Y.-S.; Lim, C.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Park, E.-H. Anti-inflammatory activity of Taraxacum officinale. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, K.; Espinoza, L.; Madrid, A.; Pizarro, L.; Chamy, R. Isolation and identification of compounds from bioactive extracts of Taraxacum officinale Weber ex FH Wigg. (Dandelion) as a potential source of antibacterial agents. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 2706417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannhardt, G.; Kiefer, W.; Krämer, G.; Maehrlein, S.; Nowe, U.; Fiebich, B. The pyrrole moiety as a template for COX-1/COX-2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 35, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | TPC | TFC | RSA | COX-1 | S. aureus | E. coli | DPPH• | FeCl3 | AlCl3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAE (mg/g) | RUE (mg/g) | TE (mg/g) | SAE (mg/g) | StrpE (mg/g) | StrpE (mg/g) | GAE (mg/g) | GAE (mg/g) | RUE (mg/g) | |
| 1 | 57.7 | 24.8 | 98.7 | 21,363.0 | 470.4 | 2146.2 | 161.4 | 196.6 | 132.6 |
| 2 | 237.9 | 98.3 | 571.1 | 74,121.4 | 1594.8 | 5620.6 | 935.7 | 695.2 | 219.3 |
| 3 | 37.3 | 32.4 | 50.5 | 37,332.0 | 1405.0 | 1736.5 | 170.4 | 243.2 | 208.5 |
| 4 | 41.6 | 87.0 | 63.5 | 40,756.1 | 1543.6 | 2680.2 | 202.6 | 237.6 | 180.2 |
| 5 | 38.1 | 104.5 | 65.3 | 51,571.7 | 885.2 | 3751.8 | 169.0 | 461.5 | 239.2 |
| 6 | 19.9 | 92.3 | 18.7 | 28,924.8 | 3555.5 | 5443.9 | 203.9 | 365.0 | 162.8 |
| 7 | 17.0 | 40.9 | 10.9 | 47,790.6 | 1822.0 | 1587.6 | 7.0 | 442.9 | 18.8 |
| 8 | 132.8 | 161.5 | 214.3 | 11,470.7 | 539.3 | 2177.9 | 815.8 | 730.3 | 596.2 |
| 9 | 134.0 | 130.0 | 248.3 | 13,807.7 | 815.2 | 1308.1 | 706.2 | 167.8 | 39.3 |
| 10 | 17.8 | 32.5 | 13.7 | 30,069.2 | 1417.2 | 1601.1 | 16.0 | 165.1 | 271.2 |
| 11 | 81.6 | 40.1 | 127.6 | 58,022.4 | 998.6 | 3872.7 | 688.5 | 535.5 | 472.2 |
| 12 | 72.3 | 35.2 | 135.1 | 50,226.1 | 2191.9 | 3787.5 | 529.3 | 416.9 | 328.8 |
| 13 | 53.7 | 17.9 | 59.9 | 22,730.5 | 2001.3 | 1434.3 | 417.0 | 255.7 | 278.3 |
| 14 | 30.4 | 26.3 | 22.5 | 50,989.9 | 2850.3 | 2617.3 | 91.1 | 148.4 | 177.2 |
| 15 | 35.5 | 10.1 | 33.1 | 8055.9 | 1417.1 | 1459.6 | 127.1 | 371.5 | 512.5 |
| 16 | 24.3 | 30.8 | 35.6 | 27,849.1 | 1986.7 | 2703.3 | 90.0 | 346.2 | 74.1 |
| 17 | 47.1 | 52.0 | 42.2 | 29,343.9 | 1895.7 | 1920.4 | 188.5 | 170.2 | 160.4 |
| 18 | 140.8 | 109.3 | 155.9 | 16,577.4 | 667.3 | 606.0 | 678.2 | 719.7 | 162.9 |
| 19 | 16.7 | 31.1 | 18.5 | 22,584.6 | 1222.7 | 858.6 | 22.2 | 253.0 | 269.3 |
| Sample, Plant Species and Family | Anti-Inflammatory Potential | Antimicrobial Potential | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rosemary leaf, Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) | [40] | [41] |
| 2. | Green tea leaf, Camellia sinensis L. (Theaceae) | [42] | [43] |
| 3. | Elder flower, Sambucus nigra L. (Caprifoliaceae) | [44] | [45] |
| 4. | Plantain leaf, Plantago major L. (Plantaginaceae) | [46] | [47] |
| 5. | Sage leaf, Salvia officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) | [48] | [49] |
| 6. | Nettle leaf, Urtica dioica L. (Urticaceae) | [50] | [51] |
| 7. | Calendula flower, Calendula officinalis L. (Asteraceae) | [52] | [53] |
| 8. | Walnut leaf, Juglans regia L. (Juglandaceae) | [54] | [55] |
| 9. | St. John’s wort herb, Hypericum perforatum L. (Hypericaceae) | [56] | [57] |
| 10. | Mallow flower, Malva silvestris L. (Malvaceae) | [58] | [59] |
| 11. | Wild thyme herb, Thymus serpyllum L. (Lamiaceae) | [60] | [61] |
| 12. | European Goldenrod herb, Solidago virgaurea L. (Asteraceae) | [62] | [63] |
| 13. | Chamomile flower, Matricaria chamomilla L. (Asteraceae) | [64] | [65] |
| 14. | Greater celandine herb, Chelidonim majus L. (Papaveraceae) | [66] | [67] |
| 15. | Fumitory herb, Fumaria officinalis L. (Fumariaceae) | [68] | [69] |
| 16. | Comfrey root, Symphytum officinale L. (Boraginaceae) | [70] | [71] |
| 17. | Cowslip flower, Primula veris L. (Primulaceae) | [72] | [73] |
| 18. | Immortelle flower, Helichrysum arenarium L. (Asteraceae) | [74] | [75] |
| 19. | Dandelion leaf, Taraxacum officinale L. (Asteraceae) | [76] | [77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jović, M.D.; Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Ristivojević, P.M.; Trifković, J.Đ.; Morton, D.W. Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography. Molecules 2023, 28, 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217346
Jović MD, Agatonovic-Kustrin S, Ristivojević PM, Trifković JĐ, Morton DW. Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217346
Chicago/Turabian StyleJović, Marko D., Snezana Agatonovic-Kustrin, Petar M. Ristivojević, Jelena Đ. Trifković, and David W. Morton. 2023. "Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217346
APA StyleJović, M. D., Agatonovic-Kustrin, S., Ristivojević, P. M., Trifković, J. Đ., & Morton, D. W. (2023). Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography. Molecules, 28(21), 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217346







