High-Value Oil–Water Separation Materials Prepared from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
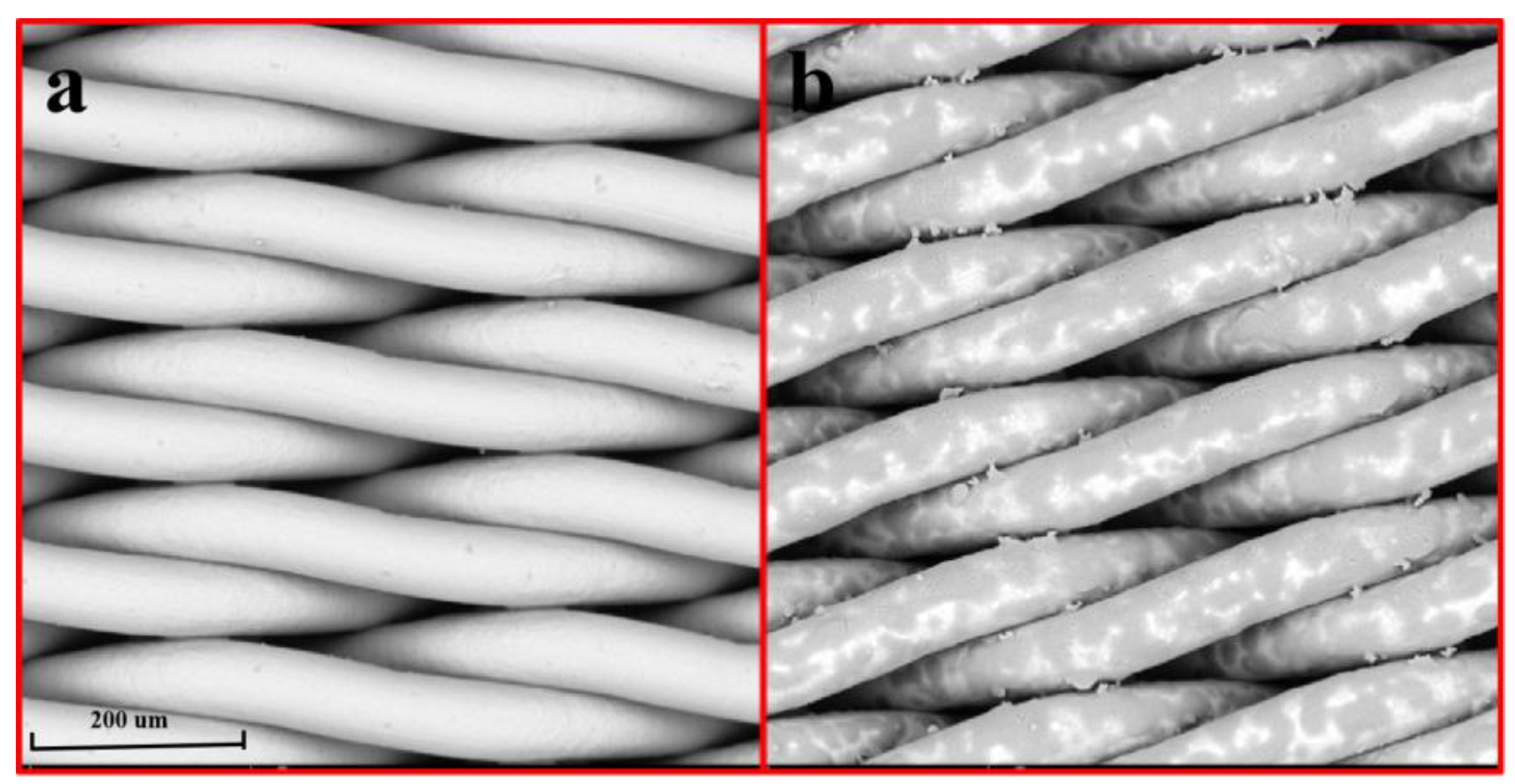
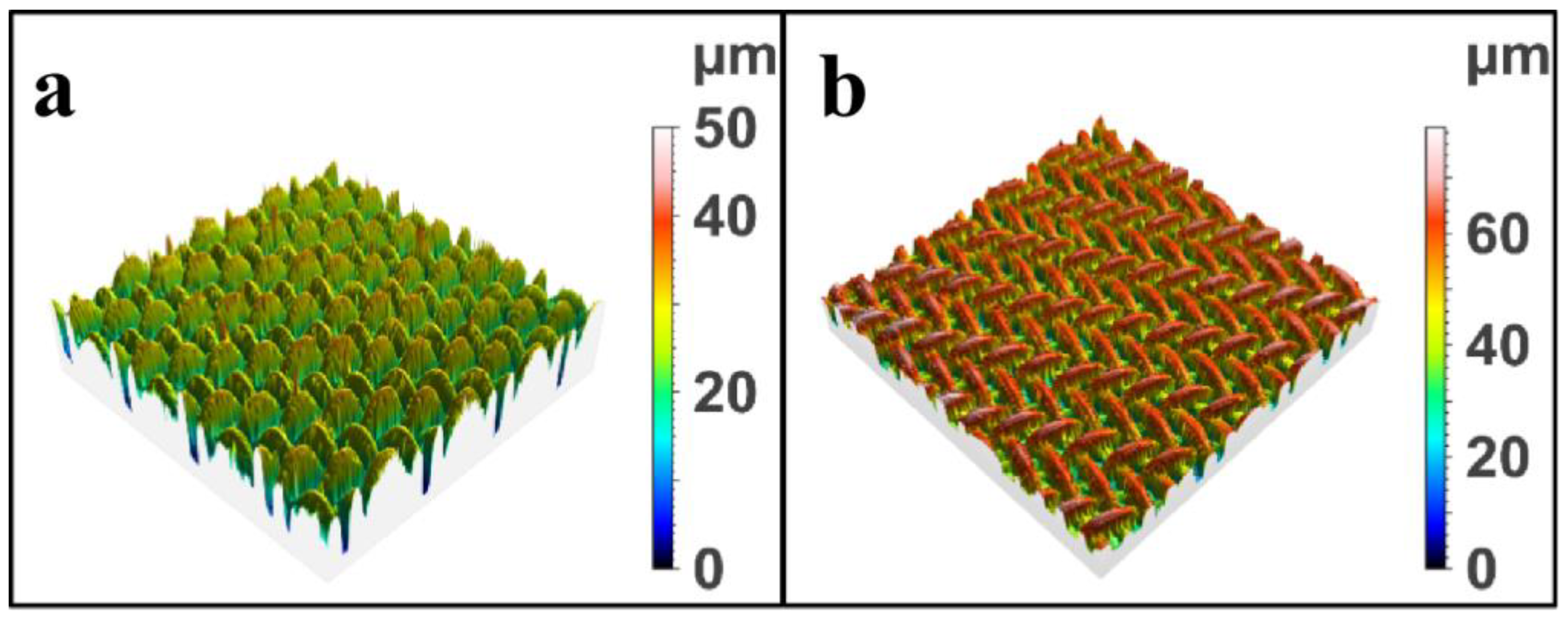
2.1. Surface Morphology Analysis of Modified SSM
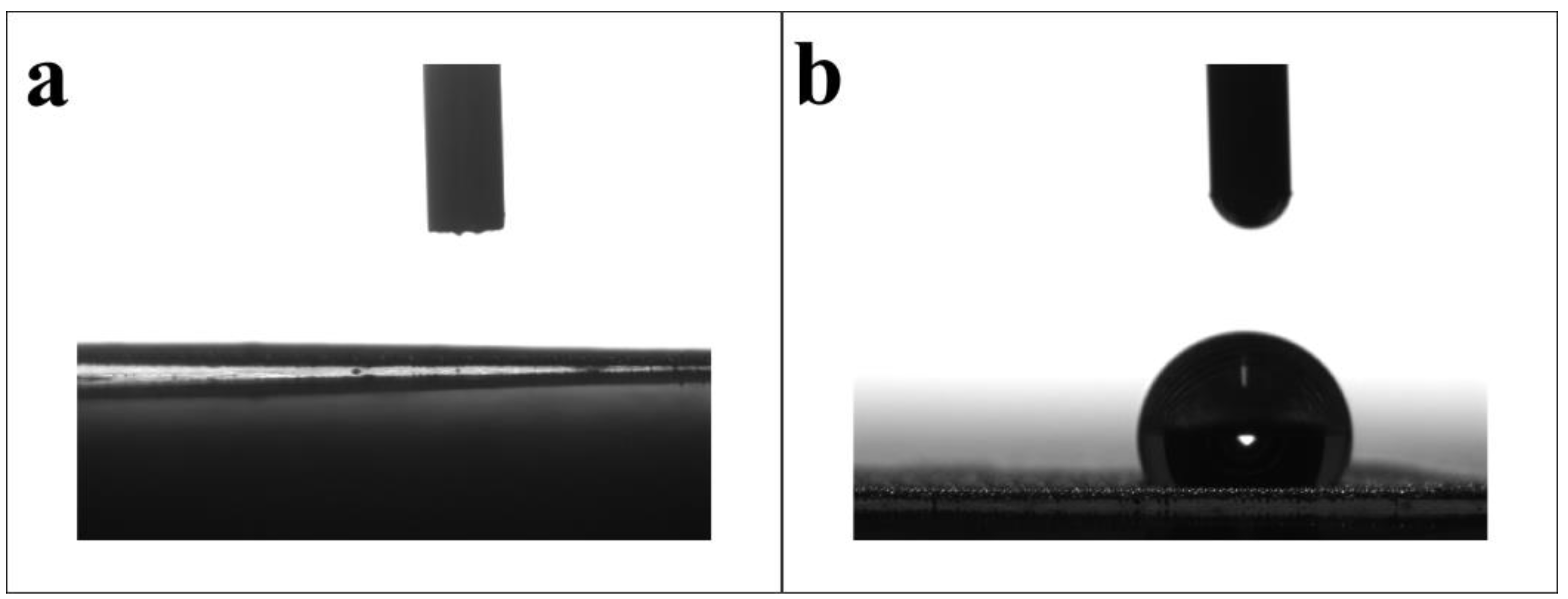
2.2. Surface Wettability Analysis of Modified SSM
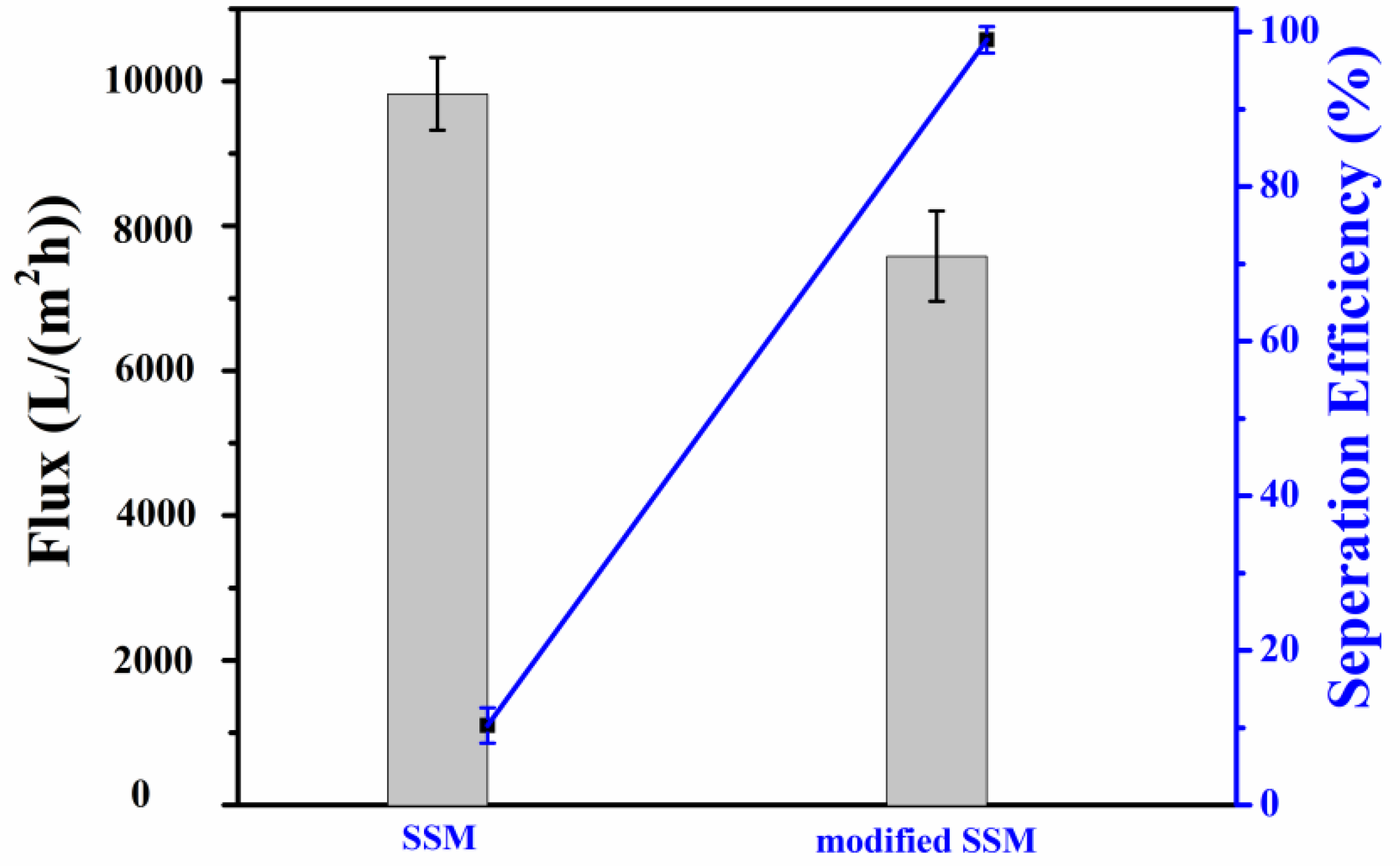
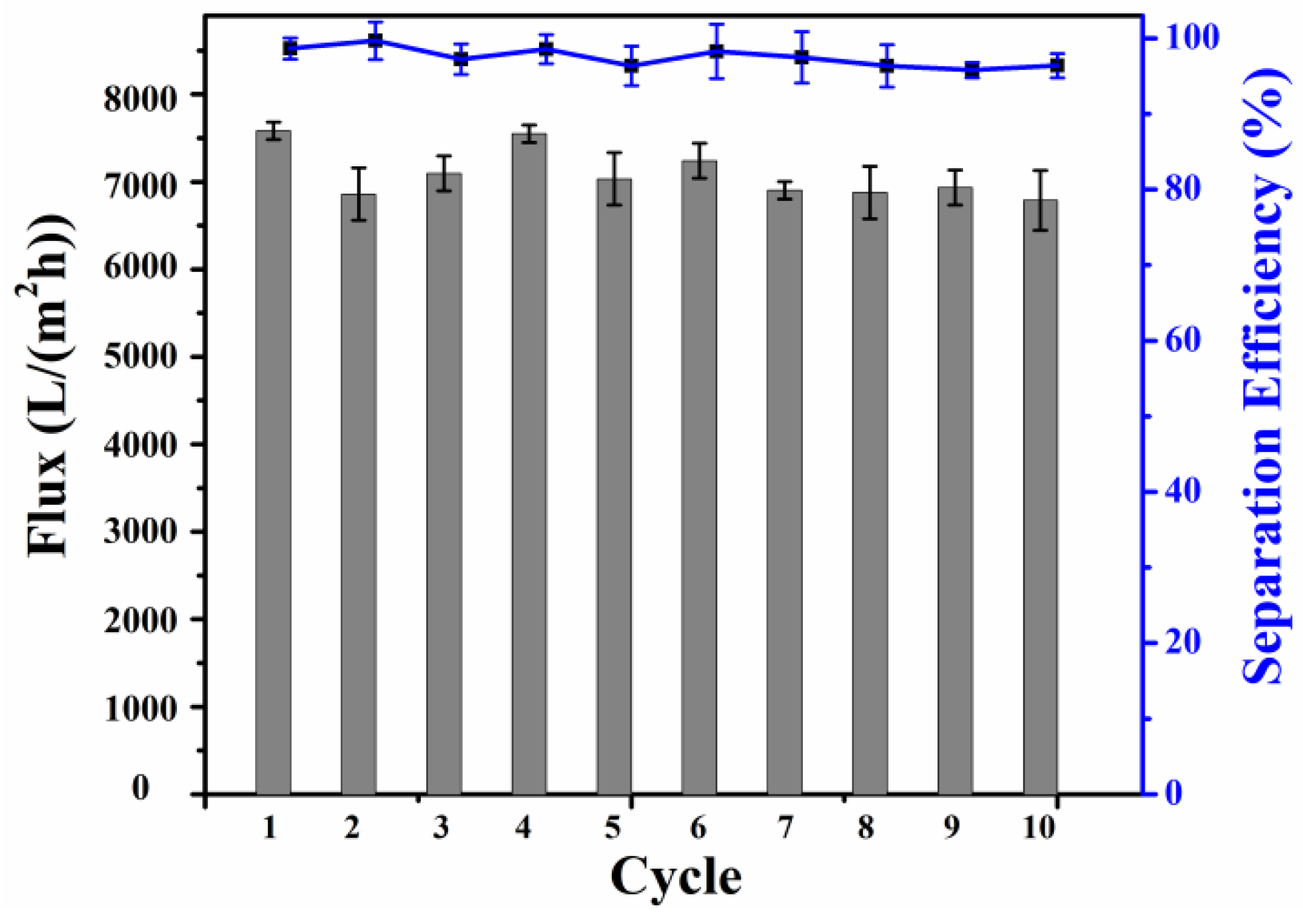
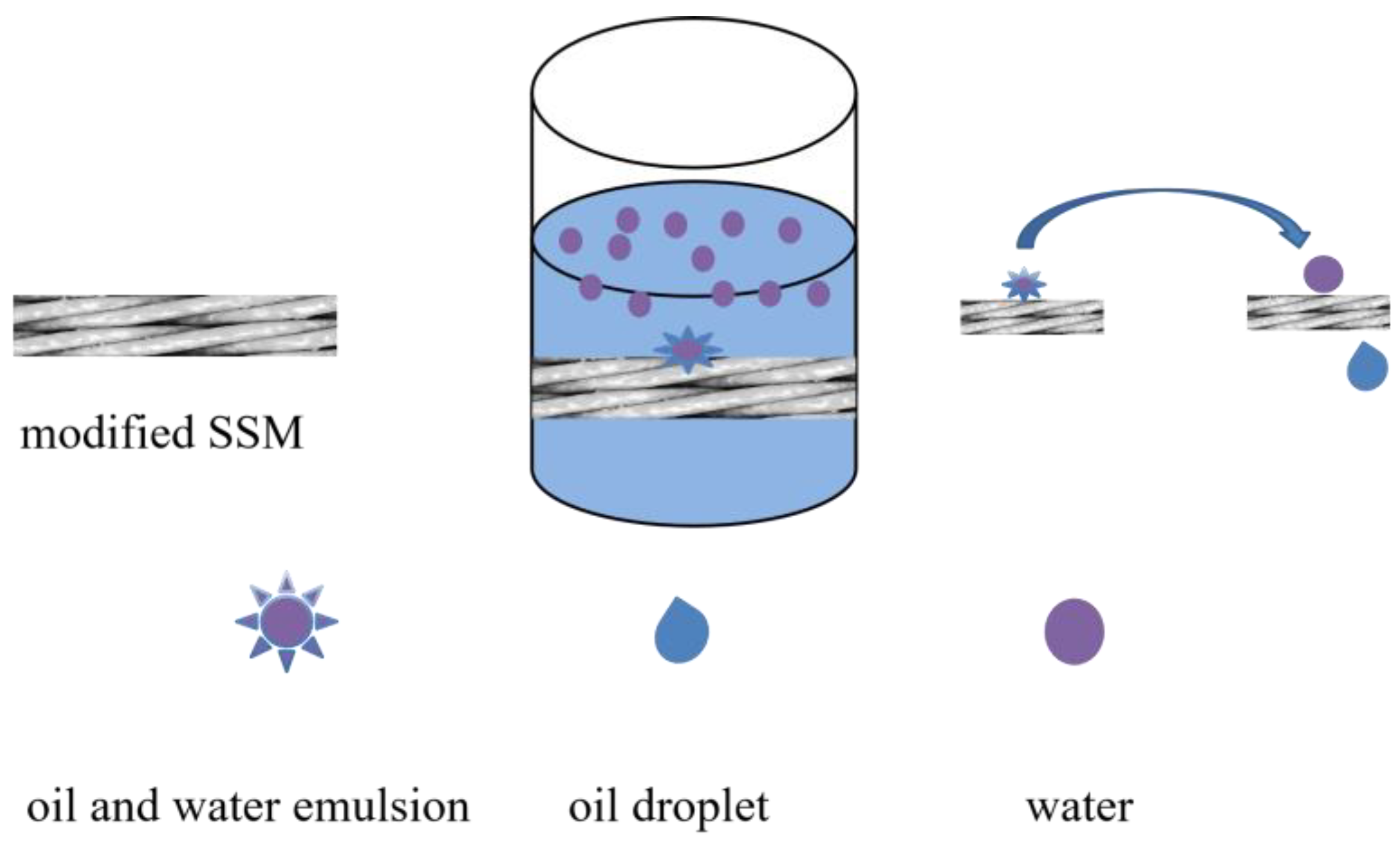
2.3. Analysis of Oil–Water Separation Efficiency of Modified SSM
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. PET Degradation
4.3. SSM Modification
4.4. Preparation of Emulsion
4.5. Oil/Water Separation
4.6. Characterization of Modified SSM
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kratish, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Marks, T.J. Polyethylene terephthalate deconstruction catalyzed by a carbon-supported single-site nolybdenum-dioxo complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19857–19861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilara, H.M.; Dilek, S.F. Fate and effects of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics during anaerobic digestion of alkaline-thermal pretreated sludge. Waste Manag. 2022, 153, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, H. New effective catalysts for glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate waste: Tropine and tropine-zinc acetate complex. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scé, F.; Cano, I.; Martin, C.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, Ó.; de Pedro, I. Comparing conventional and microwave-assisted heating in PET degradation mediated by imidazolium-based halometallate complexes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3476–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaq, G.; ElMetwally, A.E. (Mg-Zn)-Al layered double hydroxide as a regenerable catalyst for the catalytic glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Laminated PET-based membranes with sweat transportation and dual thermal insulation properties. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 450, 138177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.E.; Eskander, S.B. Chemical recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) waste using ethanolamine. Sorting of the end products. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2010, 95, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zeng, M.; Yappert, R.D.; Sun, J.; Lee, Y.H.; LaPointe, A.M.; Peters, B.; Abu-Omar, M.M.; Scott, S.L. Polyethylene upcycling to long-chain alkylaromatics by tandem hydrogenolysis/aromatization. Science 2020, 370, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lindqvist, K.; Motte, H. An efficient recycling process of glycolysis of PET in the presence of a sustainable nanocatalyst. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, E.; Odelius, K.; Hakkarainen, M. Ultrafast microwave assisted recycling of PET to a family of functional precursors and materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 151, 110441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, X.; Tsui, T.H.; Barcelo, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yong, Z.D. Microplastics as an underestimated emerging contaminant in solid organic waste and their biological products: Occurrence, fate and ecological risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 445, 130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulos, I.; Faraca, G.; Tonini, D. Recycling of post-consumer plastic packaging waste in the EU: Recovery rates, material flows, and barriers. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, N.D.; Shukla, S.R. Microwave assisted ecofriendly recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottle waste. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 4151–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Sridhar, V.; Park, H. Taguchi method for optimization of reaction conditions in microwave glycolysis of waste PET. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 22, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Chatterjee, K.; Madras, G. Enzymatic degradation of polymers: A brief review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, P.; Daioglou, V.; Londo, M.; Vuuren, D.P.; Junginger, M. Plastic futures and their CO2 emissions. Nature 2022, 612, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Sun, J.; Cui, L.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Z. Stabilization of heavy metals in piggery wastewater sludge through coagulation-hydrothermal reaction-pyrolysis process and sludge biochar for tylosin removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.M.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S.; et al. An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Breite, D.; Song, C.; Gräsing, D.; Ploss, T.; Hille, P.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; Matysik, J.; Schulze, A.; Zimmermann, W. Biocatalytic degradation efficiency of postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate packaging determined by their polymer microstructures. Adv.Sci. 2019, 6, 1900491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.A.; Hossain, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sahajwalla, V. Recycling of polymer laminated aluminum packaging (PLAP) materials into carbonaceous metallic microparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fonseca, R.; Duque-Ingunza, I.; Rivas, B.D.; Flores-Giraldo, L.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Kinetics of catalytic glycolysis of PET wastes with sodium carbonate. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.L.; Zapata, T.T.; Sanchez, N.M. Directing depolymerization of PET with subcritical and supercritical ethanol to different monomers through changes in operation conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 9846–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, D.R.; Kuang, W.; Malhotra, D.; Petrossian, G.; Zhong, L.; Simmons, K.L.; Zhang, J.; Cosimbescu, L. Waste PET chemical processing to terephthalic amides and their effect on asphalt performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Kirlikovali, K.O.; Gong, X.; Atilgan, A.; Ma, K.; Schweitzer, N.M.; Glanneschi, N.C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Catalytic degradation of polyethylene terephthalate using a phase-transitional zirconium-based metal-organic framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202117528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X. Flexible, Durable, and Unconditioned Superoleophobic/Superhydrophilic Surfaces for Controllable Transport and Oil-Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, T.; Lai, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, X. Vapor-liquid interfacial reaction to fabricate superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic thiol-ene/silica hybrid decorated fabric for oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Tian, D.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Kim, J.H.; Jiang, L.; Dou, S.X. Fish Gill Inspired Crossflow for Efficient and Continuous Collection of Spilled Oil. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisala, H.; Geyer, F.; Haapanen, J.; Juuti, P.; Makela, J.M.; Vollmer, D.; Butt, H.J. Ultrafast Processing of Hierarchical Nanotexture for a Transparent Superamphiphobic Coating with Extremely Low Roll-Off Angle and High Impalement Pressure. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Hong, F.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.; Ding, B. Superwetting hierarchical porous silica microemulsion separation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12445. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 11146-2009; Determination of Water Content in Crude Oil Carl Fischer Coulomb Drops. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, H. High-Value Oil–Water Separation Materials Prepared from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Molecules 2023, 28, 7503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227503
Zhou C, Zhang J, Fu Y, Wu M, Zhang H, Shi Q, Dai Y, Zhao H. High-Value Oil–Water Separation Materials Prepared from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Molecules. 2023; 28(22):7503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227503
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Changjian, Jiahao Zhang, Yuqing Fu, Maowan Wu, Heng Zhang, Qingle Shi, Yong Dai, and He Zhao. 2023. "High-Value Oil–Water Separation Materials Prepared from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate" Molecules 28, no. 22: 7503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227503
APA StyleZhou, C., Zhang, J., Fu, Y., Wu, M., Zhang, H., Shi, Q., Dai, Y., & Zhao, H. (2023). High-Value Oil–Water Separation Materials Prepared from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Molecules, 28(22), 7503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227503





