Dimethyl Bisphenolate Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
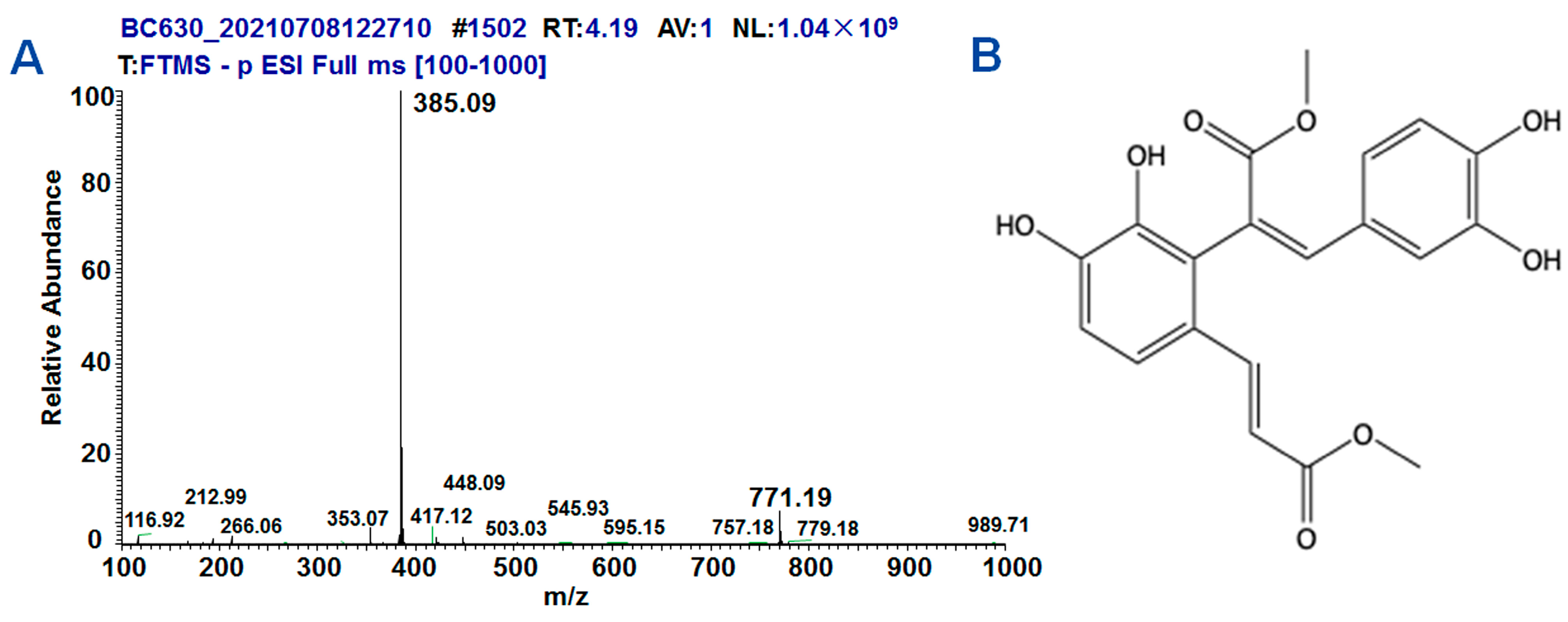
2.1. Synthesis and Structure of DMB
2.2. Biochemical and Histological Changes in CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Oxidative Stress
2.3. DMB Ameliorated Biochemical and Histological Changes in CCl4-Induced Liver Injury
2.4. DMB Increased Oxidative Stress-Related Nrf2/GCLC in CCl4-Induced Liver Injury of Rats
2.5. DMB Ameliorated Oxidative Stress Induced by CCl4 to HepG2 and MHCC-97H Cells
2.6. DMB Reversed Cell Apoptosis Induced by CCl4
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. DMB Synthesis
4.2. DMB Structure Analysis
4.3. Rat Model
4.4. Biochemical Indicator Analysis
4.5. Pathological Changes in Liver Tissues
4.6. Detection of MDA and GSH Content
4.7. Prediction of DMB-Related Proteins
4.8. Cell Culture
4.9. MTT Assay
4.10. ROS Content Analysis
4.11. Cell Apoptosis
4.12. Western Blot
4.13. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.14. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Launches “One Life, One Liver” Campaign on World Hepatitis Day. World Health Organization. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-07-2023-who-launches--one-life--one-liver--campaign-on-world-hepatitis-day (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Jia, J.D.; Tian, Q.J.; Aggarwal, R.; Muljono, D.H.; et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 167–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I.; Fernández, M.C.; Pelaez, G.; Pachkoria, K.; García-Ruiz, E.; García-Muñoz, B.; González-Grande, R.; Pizarro, A.; Durán, J.A.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury: An analysis of 461 incidences submitted to the Spanish registry over a 10-year period. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarey, D.; Verma, S. Drug-induced liver injury. Clin. Med. 2016, 16 (Suppl. S6), s104–s109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H. Reactive oxygen and mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardallo, R.G.; Panisello-Roselló, A.; Sanchez-Nuno, S.; Alva, N.; Roselló-Catafau, J.; Carbonell, T. Nrf2 and oxidative stress in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 5463–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Khan, J.A.; Arshad, M.I. Crosstalk of liver immune cells and cell death mechanisms in different murine models of liver injury and its clinical relevance. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. HBPD INT 2017, 16, s1499–s3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobe, M.C.; Mthiyane, D.M.N.; Dludla, P.V.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Mwanza, M. Pathological Role of Oxidative Stress in Aflatoxin-Induced Toxicity in Different Experimental Models and Protective Effect of Phytochemicals: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Shimizu, S.; Tatara, Y.; Mimura, J.; Itoh, K. Regulation of Nrf2 by Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Physiology and Pathology. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Sun, T.T.; Xv, G.P.; Wang, S.S.; Gu, J.G.; Liu, C.Y. Berberine ameliorates CCl4-induced liver injury in rats through regulation of the Nrf2-Keap1-ARE and p53 signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rahaman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, F.; Mithi, F.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; Alghamdi, S.Q.; Al-ruwaili, A.S.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Role of Phenolic Compounds in Human Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Pro-spects. Molecules 2021, 27, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Qu, G.; Jiang, W.; Fu, F. ND-309, a novel compound, ameliorates cerebral infarction in rats by antioxidant action. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 442, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Modafferi, S.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Ontario, M.L.; Interdonato, L.; Salinaro, A.T.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cui, S.; Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, W. Cyanidin Alleviated CCl(4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Regulating the Nrf2 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xie, G.; Liang, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, A.; Huang, F.; Hu, P.; Liu, P.; Jia, W.; Wang, X. Herbal medicine Yinchenhaotang protects against α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, P.; Mohammed, S.A.D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. TAK-242 Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis by Regulating the Liver-Gut Axis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4949148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, C.; Cui, G.; Shao, H.; Du, Z. Activation of pyroptosis and ferroptosis is involved in the hepatotoxicity induced by polystyrene microplastics in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.A.; Mohamed, N.M.; Abdelrahaman, S. Histological and Biochemical Changes in Adult Male Rat Liver after Spinal Cord Injury with Evaluation of the Role of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2020, 44, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, J.; Je, N.K.; Chung, H.Y.; Yokozawa, T.; Yoon, S.; Moon, J.O. Oligonol Ameliorates CCl₄-Induced Liver Injury in Rats via the NF-Kappa B and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3935841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jian, T.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Ren, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; et al. Ellagic acid a-meliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells via miR-223/ke-ap1-Nrf2 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrini, C.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, F.; Shao, J.; Zheng, S. Nrf2 Knockdown Disrupts the Protective Effect of Curcumin on Alcohol-Induced Hepatocyte Necroptosis. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 4043–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, H.; Tao, S.; Lau, A.; Fang, D.; Zhang, D.D. Does Nrf2 contribute to p53-mediated control of cell survival and death? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.; Wang, S.; Liang, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Fan, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; He, R.; Wang, W. Quaternary ammonium iminofullerenes improve root growth of oxidative-stress maize through ASA-GSH cycle modulating redox homeostasis of roots and ROS-mediated root-hair elongation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Surhio, M.M.; Ye, H.; Gao, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Ye, M. Protective effects of a Lachnum polysaccharide against liver and kidney injury induced by lead exposure in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Ba, C.; Shi, W. Protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharides on liver injury in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3496–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Jahan, A.; Samrana, S.; Ali, A.; Ali, S.; Kabir, N.; Ali, A.; Ullah, R.; Mothana, R.A.; Murtaza, B.N.; et al. Hepatoprotective Potential of Pomegranate in Curbing the Incidence of Acute Liver Injury by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 694607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, G. Protective effect of Anneslea fragrans ethanolic extract against CCl(4)-induced liver injury by inhibiting inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Public Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2023, 175, 113752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebaid, H.; Bashandy, S.A.; Alhazza, I.M.; Rady, A.; El-Shehry, S. Folic acid and melatonin ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury, oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, V.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Glutathione and mitochondria. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.C. Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Shin, B.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, M.G.; Wi, J.E.; Kim, Y.W.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C.; Shin, S.M.; Ki, S.H. Isorhamnetin protects against oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 and inducing the expression of its target genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 274, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.H.; Cho, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Xu, J.; Seo, K.; Ki, S.H. 5-Caffeoylquinic acid ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated cell death via Nrf2 activation in hepatocytes. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, G.; Sayed, E.A.; Waly, H.; Hassan, K.A.; Mahmoud, M.H.; Selamoglu, Z. The Therapeutic Mechanisms of Propolis Against CCl(4) -Mediated Liver Injury by Mediating Apoptosis of Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells and Improving the Hepatic Architecture through PI3K/AKT/mTOR, TGF-β/Smad2, Bcl2/BAX/P53 and iNOS Signaling Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 53, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papackova, Z.; Heczkova, M.; Dankova, H.; Sticova, E.; Lodererova, A.; Bartonova, L.; Poruba, M.; Cahova, M. Silymarin prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Capasso, R.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Milk thistle in liver diseases: Past, present, future. Phytother. Res. PTR 2010, 24, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.M.; Sawy, D.M.; Kandeil, M.A.; Farghaly, H.S. Chlorogenic acid, quercetin, coenzyme Q10 and silymarin modulate Keap1-Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling in thioacetamide-induced acute liver toxicity. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Hu, J.X.; Li, Y.J.; Xie, N.; Song, D.D.; Zhao, W.; Yan, Y.F.; Li, B.S.; Wang, P.Y.; Xie, S.Y. MiR-320a effectively suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating STAT3 signals. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.F.; Lv, Q.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, R.R.; Sun, G.B.; Pan, L.; Hu, J.X.; Xie, N.; Zhang, C.; et al. miR-4293 upregulates lncRNA WFDC21P by suppressing mRNA-decapping enzyme 2 to promote lung carcinoma proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, W.; Huang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, G.; Xie, S. Delivery of miR-320a-3p by gold nanoparticles combined with photothermal therapy for directly targeting Sp1 in lung cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6528–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Song, D.D.; Liang, D.M.; Li, Y.J.; Yan, Y.F.; Sun, H.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Hu, J.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liang, Y.; et al. Oncogenic TRIB2 interacts with and regulates PKM2 to promote aerobic glycolysis and lung cancer cell procession. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.; Xie, N.; Li, Y.; Qu, G.; et al. Dimethyl Bisphenolate Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes. Molecules 2023, 28, 7989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247989
Wang R, Shen H, Zhang J, Li X, Guo Y, Zhao Z, Wang P, Xie N, Li Y, Qu G, et al. Dimethyl Bisphenolate Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):7989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247989
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rong, Huanhuan Shen, Jiaxiang Zhang, Xiyan Li, Yang Guo, Zhenjun Zhao, Pingyu Wang, Ning Xie, Youjie Li, Guiwu Qu, and et al. 2023. "Dimethyl Bisphenolate Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes" Molecules 28, no. 24: 7989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247989
APA StyleWang, R., Shen, H., Zhang, J., Li, X., Guo, Y., Zhao, Z., Wang, P., Xie, N., Li, Y., Qu, G., & Xie, S. (2023). Dimethyl Bisphenolate Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes. Molecules, 28(24), 7989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247989





