A Review of Dual-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of DE-CDs
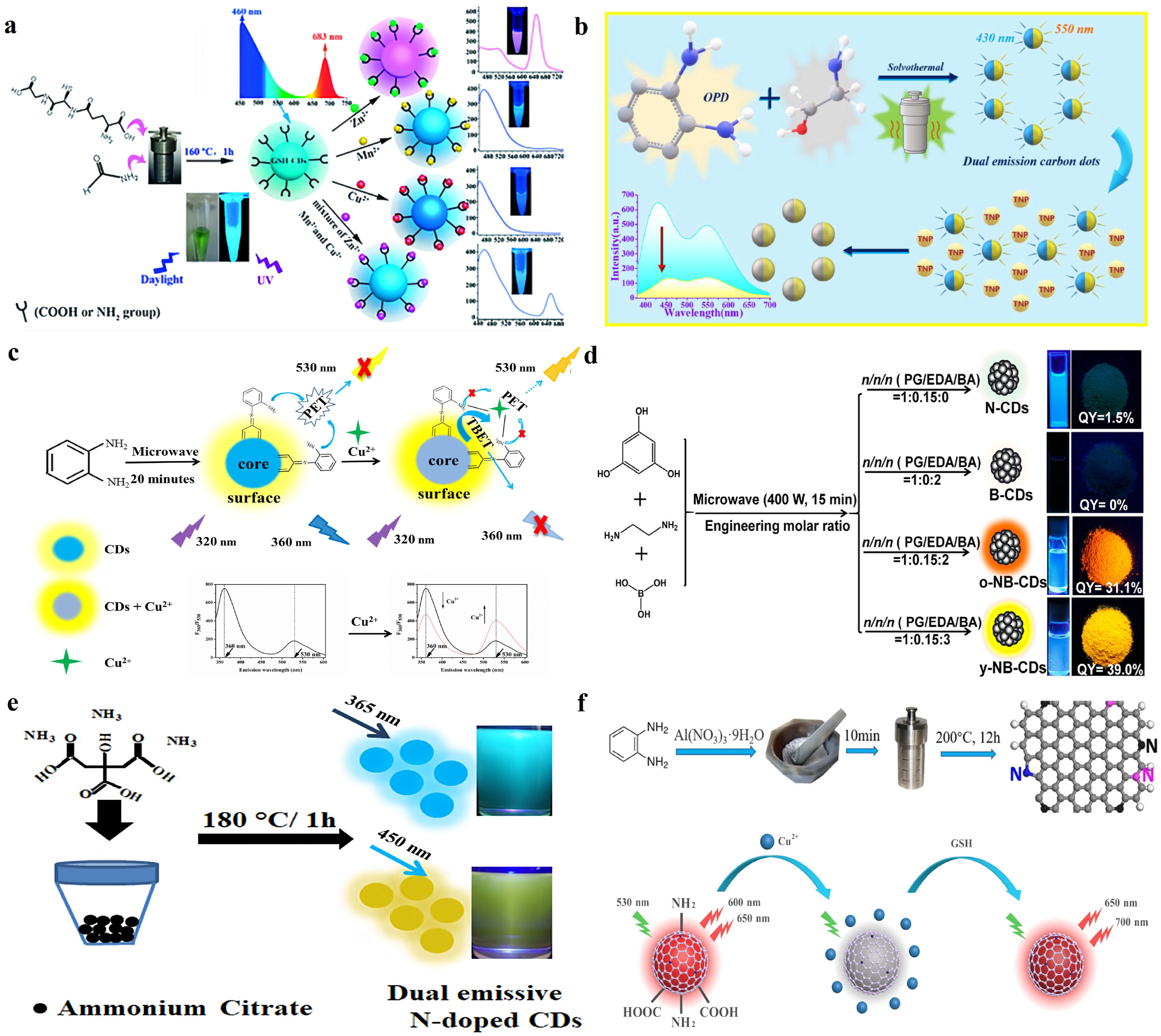
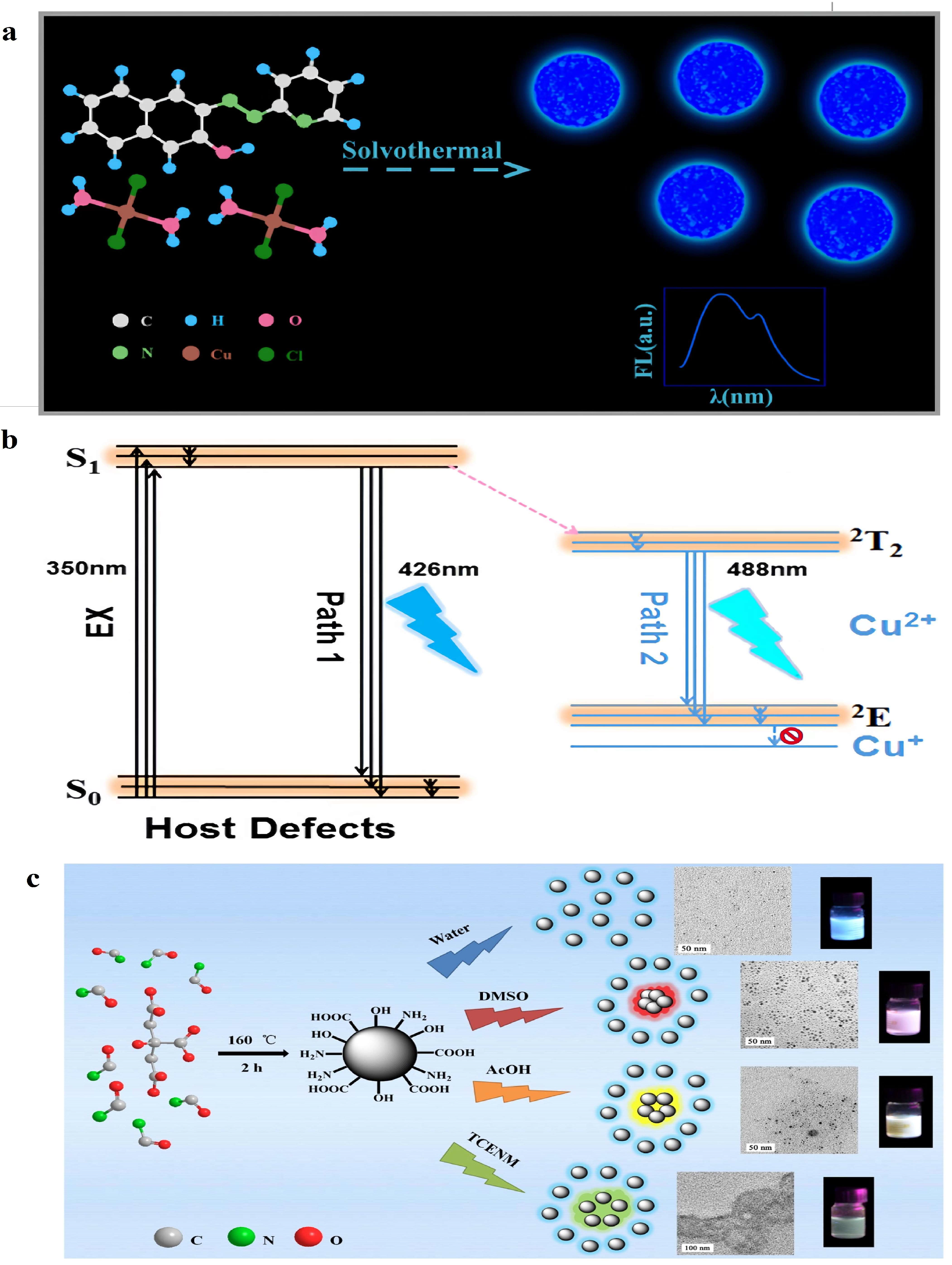
2.1. Preparation Methods for DE-CDs
2.2. Commonly Used Precursors for DE-CDs Preparation
| Ref. | Synthetic Method | Precursors | Reaction Conditions | Size (nm) | Peaks (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [64] | hydrothermal | o-PD, citric acid | 200 °C, 5 h | 1.59 | 370/446 |
| [68] | hydrothermal | glycine, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid | 200 °C, 24 h | - | 454/515 |
| [69] | hydrothermal | L-tryptophan, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | 160 °C, 6 h | 9.4 | 360/450 |
| [71] | hydrothermal | m-PD, H2SO4 | 200 °C, 10 h | 4.3 | 360/520 |
| [72] | hydrothermal | o-PD, phosphoric acid | 200 °C, 24 h | 5 | 440/624 |
| [73] | hydrothermal | o-PD, oxalic acid | 180 °C, 8 h | 3.29 | 453/560 |
| [74] | hydrothermal | o-PD, gallic acid | 180 °C, 4 h | 3.21 | 470/570 |
| [75] | hydrothermal | o-PD, 2-hydroxy-3 methoxybenzaldehyde | 180 °C, 8 h | 2.40 | 430/570 |
| [76] | hydrothermal | o-PD, o-aminophenol, ethanol | 220 °C, 24 h | - | 598 /650 |
| [77] | hydrothermal | o-PD, phosphoric acid | 200 °C, 24 h | 4 | 439/630 |
| [78] | hydrothermal | glutathione, Sodium alginate, formamide | 160 °C, 2 h | 3.60 | 480/650 |
| [79] | hydrothermal | sodium citrate, Triethylenetetramine, Rose bengal | 180 °C, 5 h | 2.8 | 440/525 |
| [80] | solvothermal | formamide, citric acid | - | 3.51 | 457/643 |
| [81] | solvothermal | p-PD, folic acid | 200 °C, 2 h | 5.65 | rufous/red |
| [82] | solvothermal | biomass-cabbage | 85 °C, 24 h; 75 °C, 4 h | 3.4 | 500/678 |
| [83] | solvothermal | biomass-kiwi fruit | 100 °C, 20 h; 75 °C, 4 h | 8.5 | 471/671 |
| [84] | solvothermal | biomass-red tea | 180 °C, 1 h | 2.9 | 478/671 |
| [63] | solvothermal | o-PD, sorbitol | 200 °C, 12 h | 4.36 | 597/645 |
| [66] | solvothermal | o-PD, L-arginine, H2SO4 | 200 °C, 12 h | 3.26 | 468/628 |
| [67] | solvothermal | L-arginine, DL-malic acid | 195 °C, 2 h | 5.6 | 445/514 |
| [57] | solvothermal | o-PD, ethanolamine | 220 °C, 10 h | 2.5 | 430/550 |
| [65] | solvothermal | o-PD, L-cystine, ethanol | 220 °C, 12 h | 2.97 | 595/648 |
| [56] | solvothermal | formamide, glutathione | 160 °C, 1 h | 2.8 | 460/683 |
| [38] | microwave | o-PD | 700 W, 20 min | 7.65 | 360/530 |
| [58] | microwave | phloroglucinol dihydrate, ethylenediamine, boric acid | 400 W, 15 min | 3.80 | 484/585 |
| [58] | microwave | phloroglucinol dihydrate, ethylenediamine, boric acid | 400 W, 15 min | 2.85 | 484/565 |
| [59] | solvent-free | ammonium citrate | 180 °C, 1 h | 6.8 | 462/560 |
| [60] | solvent-free | o-PD, Al(NO3)3·9H2O | 200 °C, 12 h | 10 | 600/650 |

3. Photoluminescence Mechanism of DE-CDs
3.1. PL Mechanism of CDs
3.2. PL Mechanism of DE-CDs
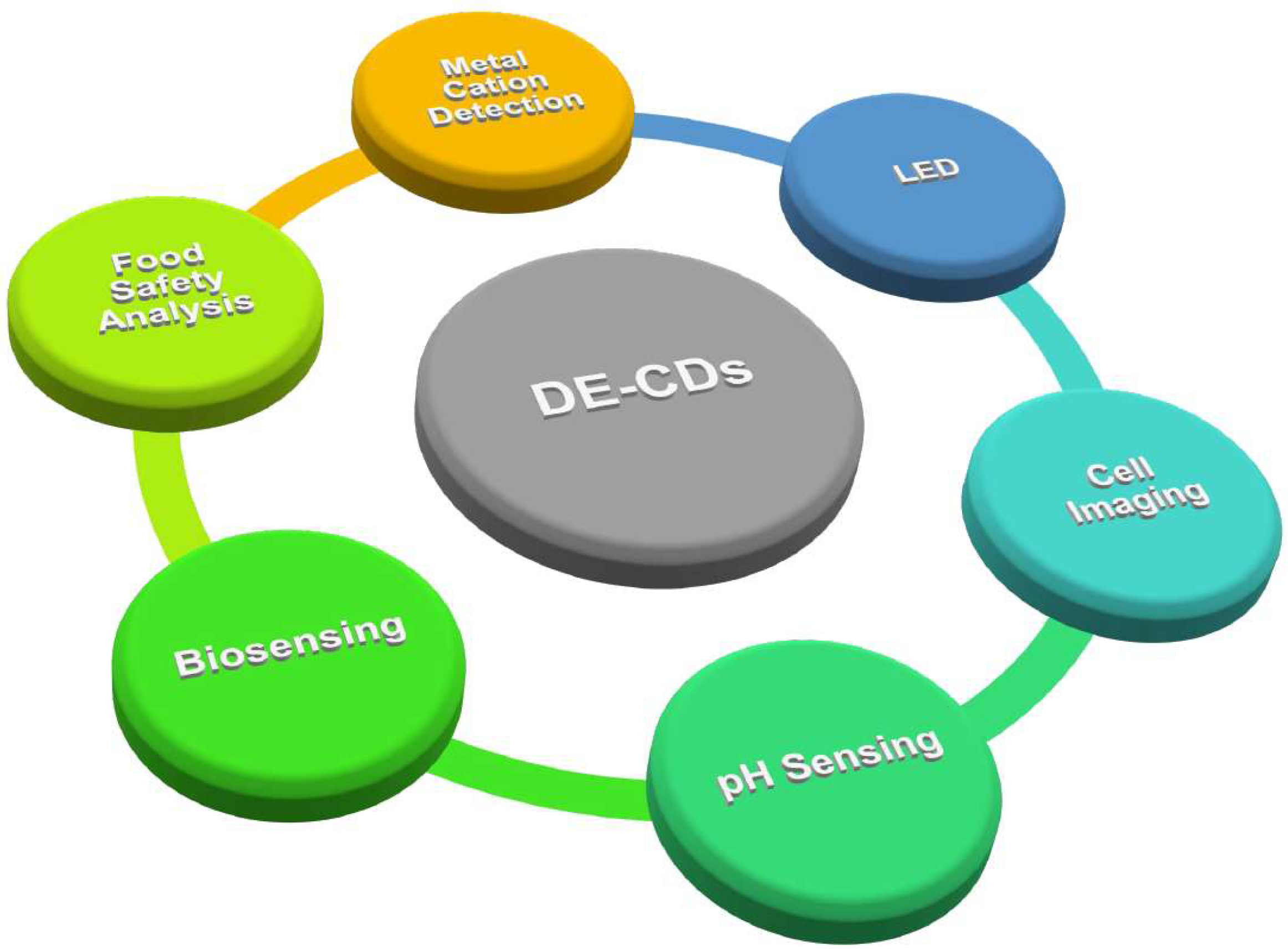
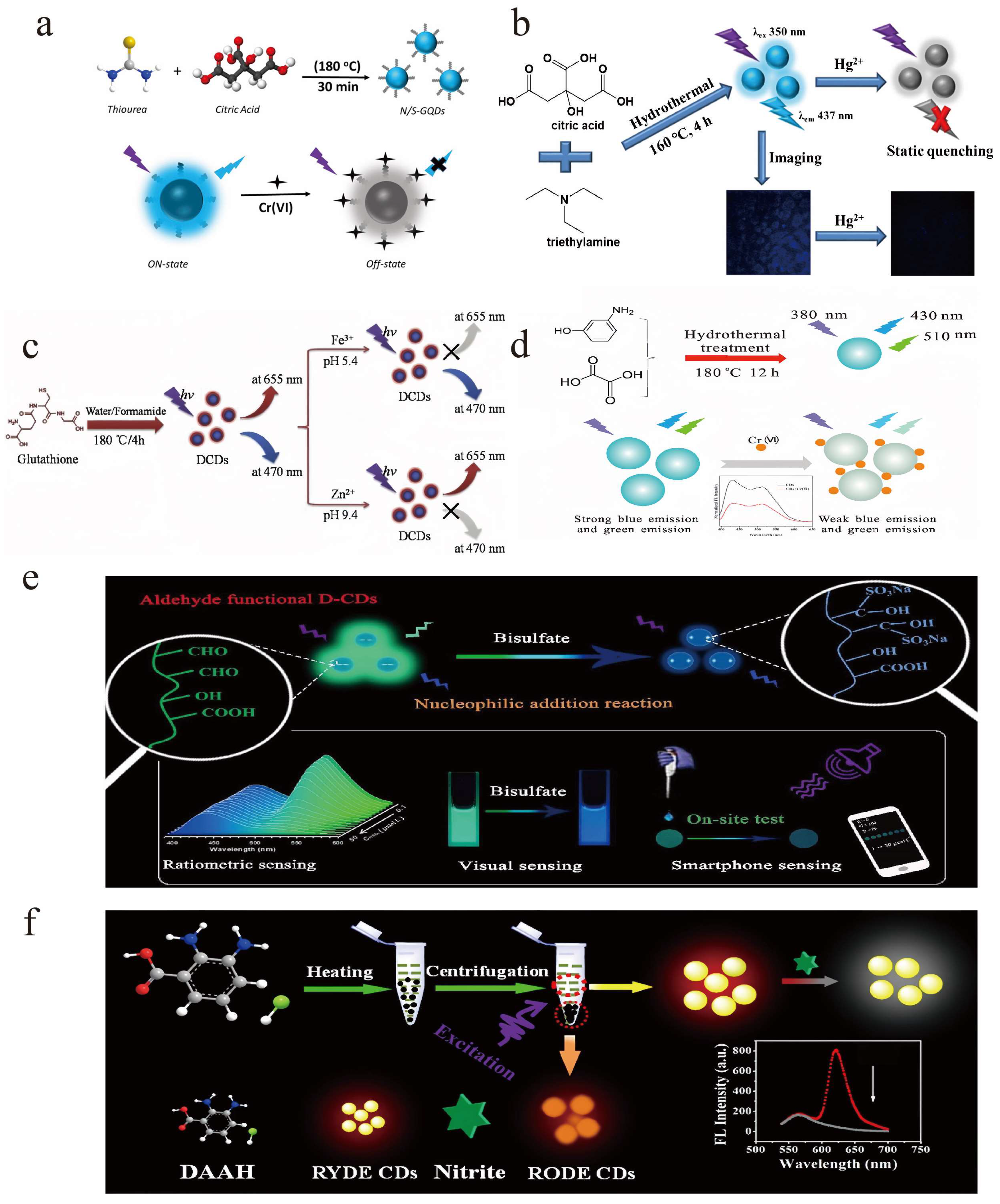
4. Application of DE-CDs
4.1. Metal Cation Detection
4.2. Food Safety Analysis
4.3. Biosensing and Cell Imaging
4.3.1. Biosensing
4.3.2. pH Sensor
4.3.3. Cell Imaging
4.4. Optoelectronic Devices
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDs | carbon dots |
| DE-CDs | dual-emission carbon dots |
| o-PD | o-phenylenediamine |
| PL | photoluminescence |
| QY | quantum yield |
| TNP | 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol |
| PET | photoinduced electron transfer |
| TPPs | tea polyphenols |
| QDs | quantum dots |
| GSH | glutathione |
| LCF | light conversion film |
| IFE | inner filtering effect |
References
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.J. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, H. Defects coordination triggers red-shifted photoluminescence in carbon dots and their application in ratiometric Cr (VI) sensing. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Li, C.; Ma, H. A Green, Economic “Switch-On” Sensor for Cefixime Analysis Based on Black Soya Bean Carbon Quantum Dots. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, J. A review of carbon dots in biological applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerhong, M.; Yang, X.; Xue-Bo, Y. Review on carbon dots and their applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtesabi, H.; Hallaji, Z.; Najafi Nobar, S.; Bagheri, Z. Carbon dots with pH-responsive fluorescence: A review on synthesis and cell biological applications. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Tian, R.; Ma, H. Ratiometric detection of propafenone hydrochloride with one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Jia, C.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon dots for intracellular sensing. Small Struct. 2022, 3, 2200033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-P.; Ren, X.-F.; Bai, P.-R.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.-Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, R.-P. Near-infrared emission carbon dots for bio-imaging applications. New Carbon Mater. 2021, 36, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, T.N.J.I.; Atchudan, R.; Sethuraman, M.G.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Microwave assisted green synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots: Cytotoxicity and bio-imaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, R.; Liang, L.; Teng, P.; Zheng, H. Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon 2013, 59, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, G.; De Luca, G.; Nocito, G.; Rizzo, M.G.; Lombardo, S.P.; Chisari, G.; Forte, S.; Sciuto, E.L.; Conoci, S. Carbon dots: An innovative tool for drug delivery in brain tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Tan, Z.a. Fluorescent carbon dots: Fantastic electroluminescent materials for light-emitting diodes. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wei, Z.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Chi, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Ran, X.; Guo, L. Broadened optical absorption, enhanced photoelectric conversion and ultrafast carrier dynamics of N, P co-doped carbon dots. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 5794–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zhou, Y.; Leblanc, R.M.; Peng, Z. Recent developments of carbon dots in biosensing: A review. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2724–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hu, M.; Zhan, P.; Peng, X. Energy transfer cassettes based on organic fluorophores: Construction and applications in ratiometric sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Recent advances in ratiometric luminescence sensors. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yu, H.; Zeng, X.; Yang, S.; Gong, S.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, K.; Shao, G. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe based on thienocoumarin and its application for the selective detection of hypochlorite in real water samples and in vivo. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 6232–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, J.; Yung, B.C.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X. Ratiometric optical nanoprobes enable accurate molecular detection and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2873–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-B.; Liu, M.-L.; Gao, Y.-T.; Chang, S.; Qian, R.-C.; Li, D.-W. Design and applications of carbon dots-based ratiometric fluorescent probes: A review. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1064–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Liu, F.; Zu, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. Ratiometric fluorescence probes based on carbon dots. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ning, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. Dual-colored carbon dot ratiometric fluorescent test paper based on a specific spectral energy transfer for semiquantitative assay of copper ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18897–18903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.C.; Páscoa, R.N.; Saraiva, M.L.M.; Santos, J.L.; Ribeiro, D.S. Photoluminescent and visual determination of ibandronic acid using a carbon dots/AgInS2 quantum dots ratiometric sensing platform. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 267, 120592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Jiang, C.; Huang, L.; Wen, H.; Hu, J. Ratiometric fluorometric and visual determination of cyanide based on the use of carbon dots and gold nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, S.G.; Han, L.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. A ratiometric fluorescent and colorimetric dual-signal sensing platform based on N-doped carbon dots for selective and sensitive detection of copper (II) and pyrophosphate ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chen, B.; Li, F.; Weng, S.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, W.; Lin, X.; Yang, C. Positive carbon dots with dual roles of nanoquencher and reference signal for the ratiometric fluorescence sensing of DNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ni, J.; Luo, F.; Weng, W.; Wei, Q.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G. Cationic carbon dots for modification-free detection of hyaluronidase via an electrostatic-controlled ratiometric fluorescence assay. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8384–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, H.; Yu, H.; Sun, M.; Huang, D.; Wang, S. Visualizing gaseous nitrogen dioxide by ratiometric fluorescence of carbon nanodots–quantum dots hybrid. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Wang, B.; Bu, X.; Fu, Y. Ratiometric fluorescence and visual imaging detection of dopamine based on carbon dots/copper nanoclusters dual-emitting nanohybrids. Talanta 2018, 178, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Hou, H.; Yang, X. Carbon dots-based dual-emission proportional fluorescence sensor for ultra-sensitive visual detection of mercury ions in natural water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 675, 132080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B. Microwave-assisted synthesis of cyclen functional carbon dots to construct a ratiometric fluorescent probe for tetracycline detection. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 9636–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jin, H.; Sun, Y.; Gui, R. Colorimetric and fluorometric dual-channel ratiometric determination of fungicide cymoxanil based on analyte-induced aggregation of silver nanoparticles and dually emitting carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lao, S.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of iron ions and zinc ions based on dual-emission carbon dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Luo, X.; He, X.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. Dual-emission carbon dots based ratiometric fluorescent sensor with opposite response for detecting copper (II). Dye. Pigment. 2021, 196, 109803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Tan, K. Dual-Emission Carbon Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Permanganate. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 21194–21200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Millan, T.; Ramos-Soriano, J.; Ghirardello, M.; Liu, X.; Santi, C.M.; Eloi, J.-C.; Pridmore, N.; Harniman, R.L.; Morgan, D.J.; Hughes, S. Multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots à la carte for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 44711–44721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, G.; Madonia, A.; Panniello, A.; Fanizza, E.; Curri, M.L.; Striccoli, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Dual Color-Emitting CDs: Numerical and Experimental Optimization towards White LEDs. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, N.; Choudhury, K.; Sarkar, P.; Barnwal, N.; Sahu, K. Ratiometric Multimode Detection of pH and Fe3+ by Dual-Emissive Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Dots for Living Cell Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 17315–17324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The light of carbon dots: From mechanism to applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Jiang, Z.; Shangguan, J.; Qing, T.; Zhang, P.; Feng, B. Applications of carbon dots in environmental pollution control: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Aryee, A.A.; Qu, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z. Mechanisms for carbon dots-based chemosensing, biosensing, and bioimaging: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1209, 338885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots: Synthesis, formation mechanism, fluorescence origin and sensing applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.X.; Yuan, Y.H. Carbon dots: Materials, synthesis, properties and approaches to long-wavelength and multicolor emission. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3794–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ji, H.; Ju, E.; Guan, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Synthesis of Fluorinated and Nonfluorinated Graphene Quantum Dots through a New Top-Down Strategy for Long-Time Cellular Imaging. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3791–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Booker, C.; Li, R.; Zhou, X.; Sham, T.-K.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z.J.J.o.t.A.C.S. An electrochemical avenue to blue luminescent nanocrystals from multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 744–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Xia, L.J.N. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Tu, H.; Zhang, H.; Silvester, D.S.; Banks, C.E.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X.J.M.T. The development of carbon dots: From the perspective of materials chemistry. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-C.; Wang, M.; Yong, A.M.; Wong, S.Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Tan, H.; Chang, A.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Intrinsically fluorescent carbon dots with tunable emission derived from hydrothermal treatment of glucose in the presence of monopotassium phosphate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11615–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties. Chem. Commun. 2009, 34, 5118–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.M.; Lim, G.; Leo, C. Comparison between hydrothermal and microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon dots from biowaste and chemical for heavy metal detection: A review. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ren, G.; Tang, M.; Zhu, B.; Chai, F.; Li, G.; Xu, D.J.E.J.o.I.C. Effective Determination of Zn2+, Mn2+, and Cu2+ Simultaneously By Using Dual-Emissive Carbon Dots as Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 3418–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, E.; Zhao, R.; Yang, S.J.J.o.M.S. Facile synthesis of dual emission carbon dots for the ratiometric fluorescent detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol and cell imaging. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1263, 133167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. N,B-codoping induces high-efficiency solid-state fluorescence and dual emission of yellow/orange carbon dots. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2224–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Zhou, P.; Qin, L.; Alam, A.; Ge, Z.; Wang, Y. Solvent-free synthesis of nitrogen doped carbon dots with dual emission and their biological and sensing applications. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 18, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, P.; Duan, C. Solid-phase synthesis of red dual-emissive nitrogen-doped carbon dots for the detection of Cu2+ and glutathione. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, T.V.; Manioudakis, J.; Noun, F.; Macairan, J.-R.; Victoria, F.; Naccache, R. Microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon dots and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 7175–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, R.; Singh, D.; Savu, R.; Moshkalev, S. Progress in microwave-assisted synthesis of quantum dots (graphene/carbon/semiconducting) for bioapplications: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 282–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, H.-G.; Cheng, R.; Guo, J.; Liang, Z.-B.; Li, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Red dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric sensing of veterinary drugs. J. Lumin. 2021, 236, 118092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Nan, D.; Yang, H.; Sun, Q.; Pan, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, X. Carbon quantum dots based ratiometric fluorescence probe for sensitive and selective detection of Cu2+ and glutathione. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, R.; Zhong, J.; Fei, L.; Cai, W.; Guan, Q.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; et al. Red/orange dual-emissive carbon dots for pH sensing and cell imaging. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Dong, C. Synthesis of intrinsic dual-emission type N, S-doped carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of Cr (VI) and application in cellular imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7253–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Angelina, E.; Gu, F.; Zheng, K.; Cui, L. Arginine–malate-based dual-emission carbon dots for uric acid determination in human serum with a miniaturized device. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, A.; Zeng, Y.; Cai, H.; Ye, S.; Li, H.; Yan, W.; Zhou, F.; Song, J.; Qu, J. Noval dual-emission fluorescence carbon dots as a ratiometric probe for Cu2+ and ClO− detection. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jana, J.; Chung, J.S.; Hur, S.H. Fabrication of dual emission carbon dots and its use in highly sensitive thioamide detection. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 175, 108126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, E.; Mao, Q.-X.; Wang, J.-H.; Chen, X.-W. Carbon dots with tunable dual emissions: From the mechanism to the specific imaging of endoplasmic reticulum polarity. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6852–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, W.; Hu, C.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y.J.J.o.M.C.C. Towards efficient dual-emissive carbon dots through sulfur and nitrogen co-doped. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8014–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Duan, W.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Qi, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Xiao, L. Ratiometric detection of intracellular lysine and pH with one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13626–13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y.; Qin, J.; Chen, M.; Feng, F. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of l-glutamic acid based on dual-emission carbon dots. Talanta 2022, 245, 123416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Liu, S. Dual-emission carbon dots for ratiometric detection of Fe3+ ions and acid phosphatase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, H.; Yu, M.; Wei, L.; Li, Z. Synthesis of dual-emission fluorescent carbon quantum dots and their ratiometric fluorescence detection for arginine in 100% water solution. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13234–13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, J.; Gong, X. Dual-emission carbon dots for sensitive fluorescence detection of metal ions and ethanol in water. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 3562–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.-X.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Ji, X.-M.; Li, S.-J.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, S. A visual and reversible nanoprobe for rapid and on-site determination of hexavalent chromium and lysine based on dual-emission carbon quantum dots coupled with smartphone. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Feng, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, X. Nitrogen/sulfur-doped dual-emission carbon dots with tunable fluorescence for ratiometric sensing of ferric ions and cell membrane imaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 151447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of dual-emission fluorescent carbon dots for hypochlorous acid detection. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 180, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Hu, H.; Lei, B.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y. Synthesis of dual-emissive carbon dots with a unique solvatochromism phenomenon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Ren, L. Study on the Origin of Fluorescence by Using Dual-Emission Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 18543–18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Tang, C.; Li, T.; Tong, X.; Tong, C.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wu, L.; Shi, S. Dual-emissive carbon dots for dual-channel ratiometric fluorometric determination of pH and mercury ion and intracellular imaging. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, C.; Shi, S.; Long, R.; Guo, Y. Simultaneous sensing γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase by robust dual-emission carbon dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1178, 338829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, F.; Shuang, S. Novel single excitation dual-emission carbon dots for colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent dual mode detection of Cu2+ and Al3+ ions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38568–38575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lian, S.; Tsang, C.H.A.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.T.J.A.C.I.E. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Lee, G.; Do, S.; Joo, T.; Rhee, S.W.J.S. Size-controlled soft-template synthesis of carbon nanodots toward versatile photoactive materials. Small 2014, 10, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Rhee, S.-W. Facile synthesis of graphitic carbon quantum dots with size tunability and uniformity using reverse micelles. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5256–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.-p.; Cheng, Z.; Du, L.-l.; Chen, Q.; Tan, K.-j.J.L. Synthesis of the Cu-doped dual-emission fluorescent carbon dots and its analytical application. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9982–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Kwak, B.E. Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 20227–20237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuneh, T.T.; Fereja, T.H.; Li, H.; Jin, Y. Solid-Phase Pyrolysis Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Nitrogen/Sulfur Codoped Graphene Quantum Dots for Selective and Sensitive Diversity Detection of Cr (VI). Langmuir 2023, 39, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Jin, J.-C.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Jiang, Z.-W.; Li, X.; Jiang, F.-L.; Liu, Y. Single-step synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots for rapid detection of Hg2+ with excellent sensitivity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 551, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, X. Ratiometric fluorescent detection of chromium (VI) in real samples based on dual emissive carbon dots. Talanta 2018, 185, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.C.; Xu, Z.Y.; Sun, Z.; Xie, J.H.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. One-step synthesis of aldehyde-functionalized dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of bisulfite in food samples. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Na, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Modification-free fabricating ratiometric nanoprobe based on dual-emissive carbon dots for nitrite determination in food samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Hu, L.; Wang, W.-J.; Kong, F.-Y.; Wei, M.-J.; Fang, H.-L.; Li, Q.-L.; Wang, W. One-pot green preparation of deep-ultraviolet and dual-emission carbon nanodots for dual-channel ratiometric determination of polyphenol in tea sample. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, W.; Luo, X.; He, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. Cu2+-triggered carbon dots with synchronous response of dual emission for ultrasensitive ratiometric fluorescence determination of thiophanate-methyl residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12576–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamd-Ghadareh, S.; Salimi, A.; Fathi, F.; Soleimani, F. Dual-emission carbon dots as biocompatible nanocarrier for in vitro/in vivo cell microenvironment ratiometric pH sensing in broad range. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Cao, M.; Xia, J.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, H. An ultrafast responsive and sensitive ratiometric fluorescent pH nanoprobe based on label-free dual-emission carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, L.; Jia, J.; Eltayeb, O.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Dual photoluminescence emission carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescent GSH sensing and cancer cell recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18250–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lu, X.; Guo, J.; Cheng, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Facile synthesis of red dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescence sensing and cellular imaging. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5494–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. One-step synthesis of red/green dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric sensitive ONOO− probing and cell imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13589–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.-Q.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zeng, J.-Y.; Wu, Y.-N.; Lai, J.-P.; Sun, H. A novel fluorescence ratio probe based on dual-emission carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of chlortetracycline and cell imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3043–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Su, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Xu, M.; Fei, L.; Xu, Q. Highly fluorescent dual-emission red carbon dots and their applications in optoelectronic devices and water detection. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Strategy to synthesize dual-emission carbon dots and their application for pH variation and hydrogen sulfide sensing and bioimaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 293, 122483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Synthesis Approaches | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrothermal/Solvothermal | Simple, easy, and low-cost synthesis | Long reaction times and high-temperature treatment |
| Microwave | Short reaction times and high yields | Lack of heating uniformity and unsuitable for scale-up industrial production |
| Solvent-free | Simple, solvent-free, large-scale preparation | High-temperature treatment |
| Ref. | Size (nm) | Peaks (nm) | Applications | Linear Range | Detection Limits | Signal Readout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 3.61 | 470/655 | Fe3+/Zn2+ | 2.5~30 µM/2.5~50 µM | 0.8/1.2 μM | F470/F655 |
| [38] | 7.65 | 360/530 | Cu2+ | 0.8~55 μM | 44.63 nM | F360/F530 |
| [56] | 2.8 | 460/683 | Zn2+/Mn2+/Cu2+ | 0.005~8/0.0001~10/0.0001~50 µM | 9.64/3.24/1.7 nM | F683/F652 |
| [72] | 5 | 440/624 | Lysine/pH | 0.5~260 mΜ/1.5~5.0 | 94 nM/- | F440/F624 |
| [73] | 3.29 | 453/560 | L-Glu | 0~200 μM; 200~400 μM | 0.085 μM | F560/F453 |
| [65] | 2.97 | 595/648 | Ag+/pH/cell imaging | 0~100 μM/1.0~13.0/- | 0.4 μΜ/-/- | ΔF |
| [89] | 2.22 | 431–500/650 | wLED | - | - | - |
| [92] | 3.2 | 430/510 | Cr6+ | 2~300 μM | 0.4 μM | F510/F430 |
| [88] | 3.72 | 426/488 | Fe3+/vitamin A acetate/pH | 0~4000 μM/-/6.09~11.70 | - | (F0-F)/F0 |
| [93] | 2 | 435/520 | HSO3− | 0.1~30 μM | 42 nM | F435/F520 |
| [94] | 4.6 | 566/621 | nitrite | 0.1~100 μM | 31.61 nM | F621/F566 |
| [95] | 3 | 297/395 | TPPs | 5.0~100 µg/mL | 3.5 ± 0.04 ng/mL | F297/F395 |
| [96] | 5.87 | 416/481 | TM | 0.10~20.00 μM | 2.90 × 10−6 μM | F416/F481 |
| [97] | 2.88 | 393/580 | pH | 2.2~8.0; 2.2~4.0 | - | F393/F580 |
| [98] | 3.5 | 336/540 | pH/cell imaging | 2.5~12.0/- | - | F336/F540 |
| [99] | 2.37 | 430/642 | GSH/cell imaging | 1~10 μM; 25 ~150 μM/- | 0.26 μM/- | F430/F642 |
| [100] | 5.71 | 630/680 | methyl blue/cell imaging | 0.5~300 μM/- | 0.43 μM/- | F630/F680 |
| [101] | 5.2 | 525/603 | ONOO−/cell imaging | 0.03~60 μM/- | 11.6 nM/- | F525/F603 |
| [102] | 1.8 | 345/450 | CTC/cell imaging | 0.25~25.0 μM/- | 16.45 nM/- | F430/F345 |
| [103] | 2.89 | 600/650 | water in ethanol/wLEDs | 0%~70%/- | - | ΔF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Sun, L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H. A Review of Dual-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248134
Ma J, Sun L, Gao F, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ma H. A Review of Dual-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248134
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jing, Lingbo Sun, Feng Gao, Shiyu Zhang, Yuhan Zhang, Yixuan Wang, Yuecheng Zhang, and Hongyan Ma. 2023. "A Review of Dual-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Applications" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248134
APA StyleMa, J., Sun, L., Gao, F., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Ma, H. (2023). A Review of Dual-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Molecules, 28(24), 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248134






