Chemical Modification of Auranofin Yields a New Family of Anticancer Drug Candidates: The Gold(I) Phosphite Analogues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
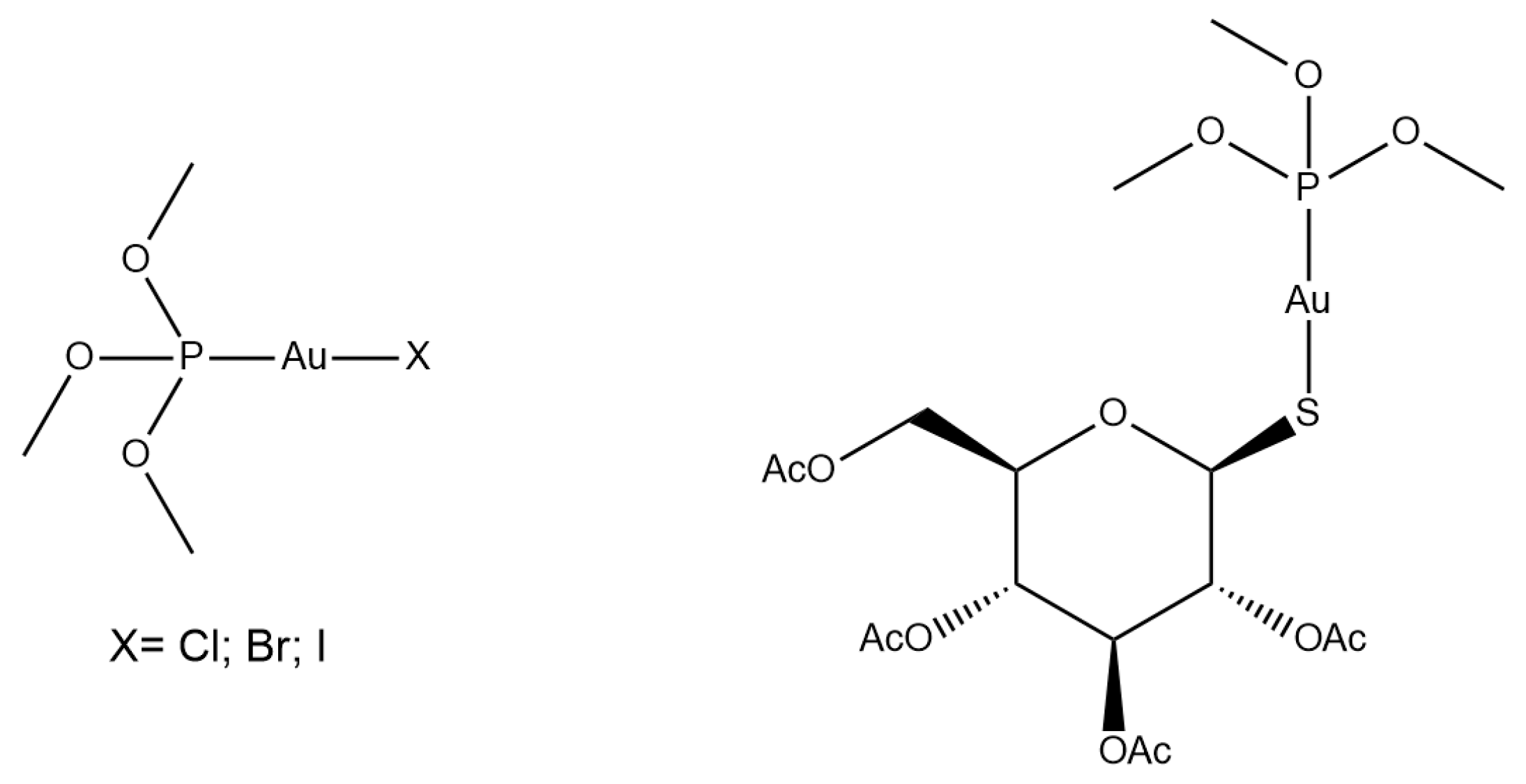
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Protein Interactions
2.3. Biological Evaluations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. NMR Experiments
3.3. Solubility and LogP Determination Protocols
3.4. ESI-MS Experiments
3.5. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assessment
3.7. Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibition
3.8. Assessment of Caspase-3 Activity by Flow Cytometry
3.9. Gold Uptake Assessment
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The gold complex auranofin: New perspectives for cancer therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=auranofin&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Landini, I.; Massai, L.; Cirri, D.; Gamberi, T.; Paoli, P.; Messori, L.; Mini, E.; Nobili, S. Structure-activity relationships in a series of auranofin analogues showing remarkable antiproliferative properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 208, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirri, D.; Massai, L.; Giacomelli, C.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Guerri, A.; Gabbiani, C.; Messori, L.; Pratesi, A. Synthesis, chemical characterization, and biological evaluation of a novel auranofin derivative as an anticancer agent. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 13527–13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.T.; Isab, A.A.; Griswold, D.E.; DiMartino, M.J.; Matz, E.D.; Figueroa, A.L.; Wawro, J.E.; DeBrosse, C.; Reiff, W.M.; Elder, R.C.; et al. Seleno-Auranofin (Et3PAuSe-tagl): Synthesis, Spectroscopic (EXAFS, 197Au Mössbauer, 31P, 1H, 13C, and 77Se NMR, ESI-MS) Characterization, Biological Activity, and Rapid Serum Albumin-Induced Triethylphosphine Oxide Generation. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 7663–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiekink, E.R.T. Gold derivatives for the treatment of cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Chen, J.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M.; Krause Bauer, J.A.; Hill, D.T. Formation of a Cationic Gold(I) Complex and Disulfide by Oxidation of the Antiarthritic Gold Drug Auranofin. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 2203–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirri, D.; Landini, I.; Massai, L.; Mini, E.; Maestrelli, F.; Messori, L. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes of Auranofin and Its Iodido Analog: A Chemical and Biological Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, C.E.; Cronje, S.; Schmidbaur, H.; Raubenheimer, H.G. The preparation, properties and X-ray structures of gold(I) trithiophosphite complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 4788–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Gabbiani, C.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Pratesi, A.; Guerri, A.; Biver, T.; Binacchi, F.; Stefanini, M.; et al. Auranofin, Et3PAuCl, and Et3PAuI are highly cytotoxic on colorectal cancer cells: A chemical and biological study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, S.; Rizzi, G.; Biancalana, L.; Pratesi, A.; Zacchini, S.; Pampaloni, G.; Chiellini, F.; Marchetti, F. Anticancer Diiron Vinyliminium Complexes: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhabak, K.P.; Bhuyan, B.J.; Mugesh, G. Bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry: Aspects of gold(i)-protein complexes. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccoccia, F.; Angelucci, F.; Boumis, G.; Brunori, M.; Miele, A.E.; Williams, D.L.; Bellelli, A. On the mechanism and rate of gold incorporation into thiol-dependent flavoreductases. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 108, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoppi, C.; Messori, L.; Pratesi, A. ESI MS studies highlight the selective interaction of Auranofin with protein free thiols. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 5906–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massai, L.; Zoppi, C.; Cirri, D.; Pratesi, A.; Messori, L. Reactions of Medicinal Gold(III) Compounds With Proteins and Peptides Explored by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry and Complementary Biophysical Methods. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 581648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groessl, M.; Terenghi, M.; Casini, A.; Elviri, L.; Lobinski, R.; Dyson, P.J. Reactivity of anticancer metallodrugs with serum proteins: New insights from size exclusion chromatography-ICP-MS and ESI-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messori, L.; Marzo, T.; Michelucci, E.; Russo Krauss, I.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Quiroga, A.G.; Merlino, A. Interactions between Anticancer trans-Platinum Compounds and Proteins: Crystal Structures and ESI-MS Spectra of Two Protein Adducts of trans-(Dimethylamino)(methylamino)dichloridoplatinum(II). Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7806–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Vančo, J.; Trávníček, Z.; Hošek, J.; Klusáková, J.; Dvořák, Z. Platinum(II) Iodido Complexes of 7-Azaindoles with Significant Antiproliferative Effects: An Old Story Revisited with Unexpected Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalini, S.; Dorstyn, L.; Dawar, S.; Kumar, S. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis and Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulmer, G.R.; Miller, A.J.M.; Sherden, N.H.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Nudelman, A.; Stoltz, B.M.; Bercaw, J.E.; Goldberg, K.I. NMR Chemical Shifts of Trace Impurities: Common Laboratory Solvents, Organics, and Gases in Deuterated Solvents Relevant to the Organometallic Chemist. Organometallics 2010, 29, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, D.; Pillozzi, S.; Gabbiani, C.; Tricomi, J.; Bartoli, G.; Stefanini, M.; Michelucci, E.; Arcangeli, A.; Messori, L.; Marzo, T. PtI2(DACH), the iodido analogue of oxaliplatin as a candidate for colorectal cancer treatment: Chemical and biological features. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 3311–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becatti, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Barygina, V.; Cecchi, C.; Lotti, T.; Prignano, F.; Silvestro, A.; Nassi, P.; Taddei, N. SIRT1 regulates MAPK pathways in vitiligo skin: Insight into the molecular pathways of cell survival. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| X = Cl | X = Br | X = I | X = SAtg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au(PEt3)X | 0.68 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.34 |
| AuP(OCH3)3X | 1.24 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 2.76 |
| Compound | A2780 | A2780R | SKOV-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AuP(OCH3)3Cl | 2.32 ± 0.25 | 9.49 ± 1.56 | 2.39 ± 0.44 |
| AuP(OCH3)3Br | 2.63 ± 0.39 | 8.23 ± 1.50 | 4.57 ± 0.10 |
| AuP(OCH3)3I | 2.93 ± 0.46 | 7.81 ± 1.28 | 0.99 ± 0.19 |
| AuP(OCH3)3SAtg | 1.26 ± 0.22 | 2.98 ± 0.23 | 2.44 ± 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cirri, D.; Geri, A.; Massai, L.; Mannelli, M.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Becatti, M.; Gabbiani, C.; Pratesi, A.; Messori, L. Chemical Modification of Auranofin Yields a New Family of Anticancer Drug Candidates: The Gold(I) Phosphite Analogues. Molecules 2023, 28, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031050
Cirri D, Geri A, Massai L, Mannelli M, Gamberi T, Magherini F, Becatti M, Gabbiani C, Pratesi A, Messori L. Chemical Modification of Auranofin Yields a New Family of Anticancer Drug Candidates: The Gold(I) Phosphite Analogues. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031050
Chicago/Turabian StyleCirri, Damiano, Andrea Geri, Lara Massai, Michele Mannelli, Tania Gamberi, Francesca Magherini, Matteo Becatti, Chiara Gabbiani, Alessandro Pratesi, and Luigi Messori. 2023. "Chemical Modification of Auranofin Yields a New Family of Anticancer Drug Candidates: The Gold(I) Phosphite Analogues" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031050
APA StyleCirri, D., Geri, A., Massai, L., Mannelli, M., Gamberi, T., Magherini, F., Becatti, M., Gabbiani, C., Pratesi, A., & Messori, L. (2023). Chemical Modification of Auranofin Yields a New Family of Anticancer Drug Candidates: The Gold(I) Phosphite Analogues. Molecules, 28(3), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031050












