Peptidic Inhibitors and a Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Inhibition and Labelling of Factor XIIIa Transglutaminase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Design
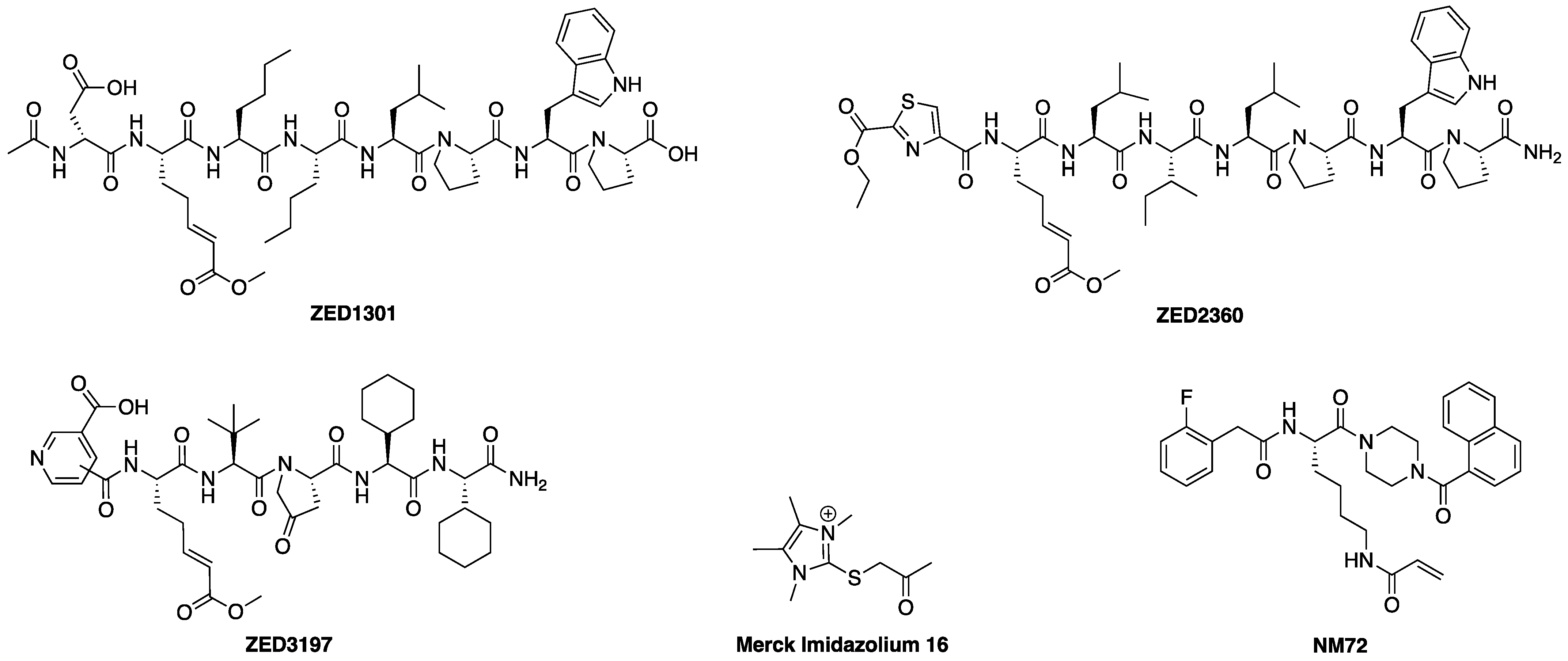
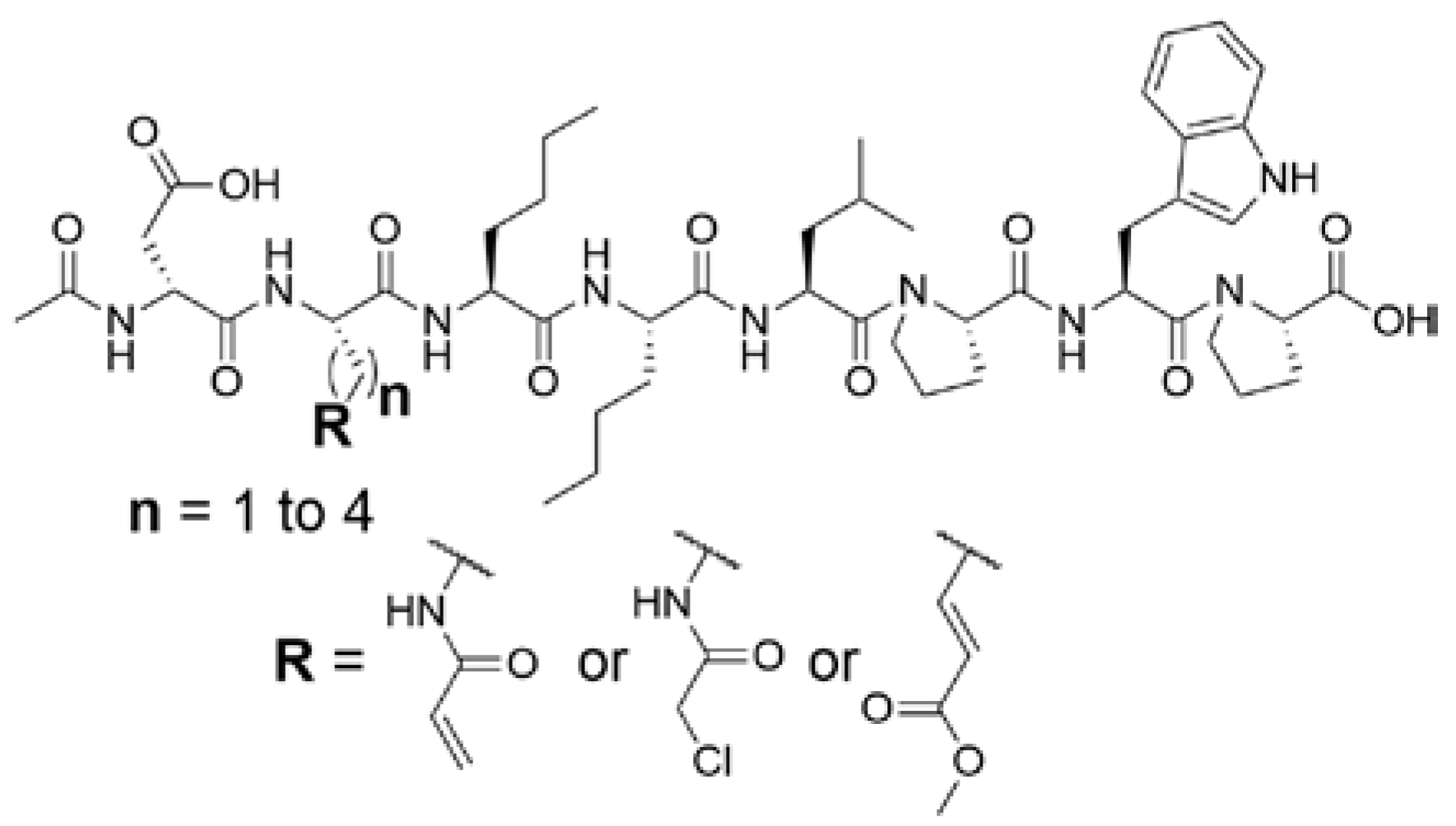
2.1.1. Design of Peptidic Inhibitors of FXIIIa
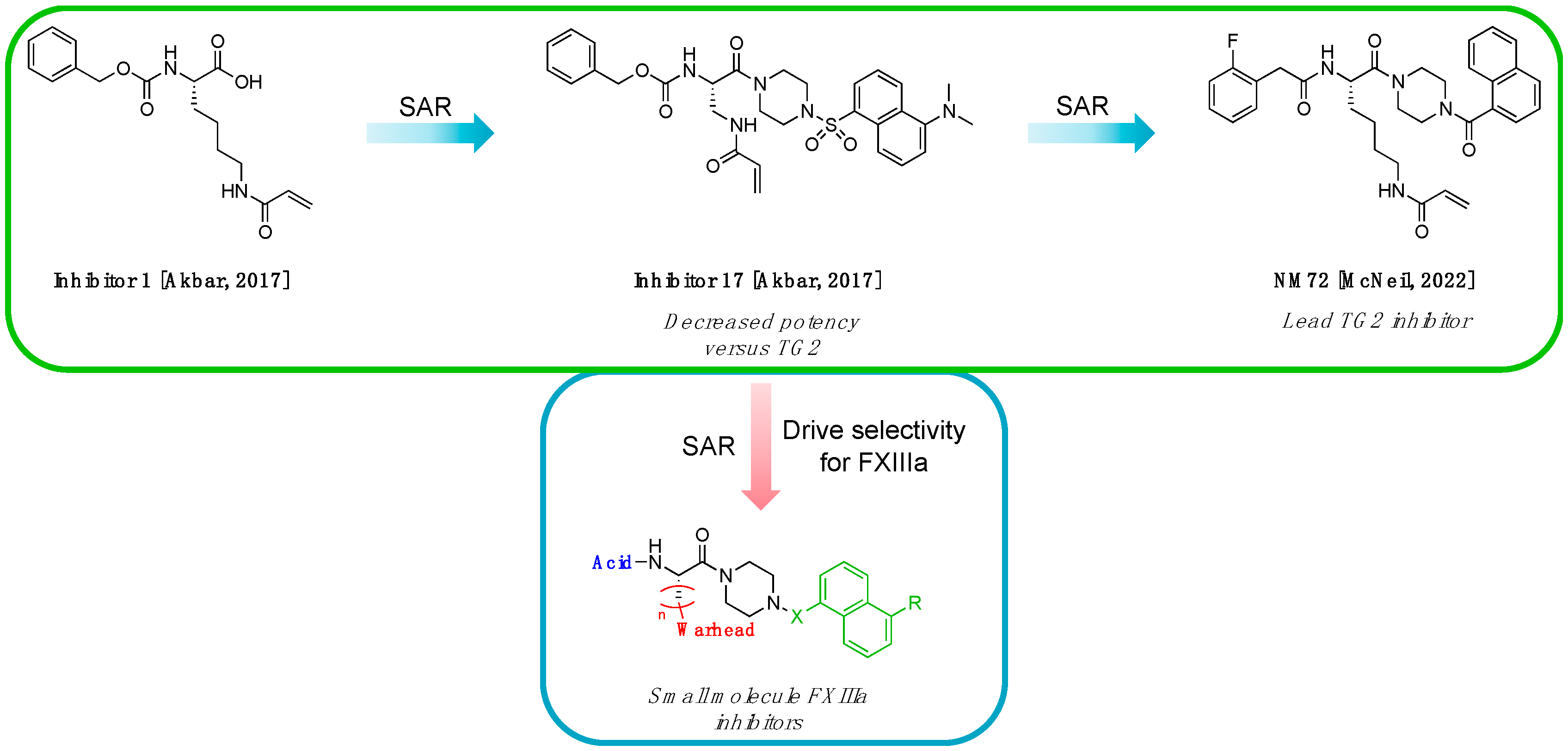
2.1.2. Design of Small Molecule Inhibitors of FXIIIa
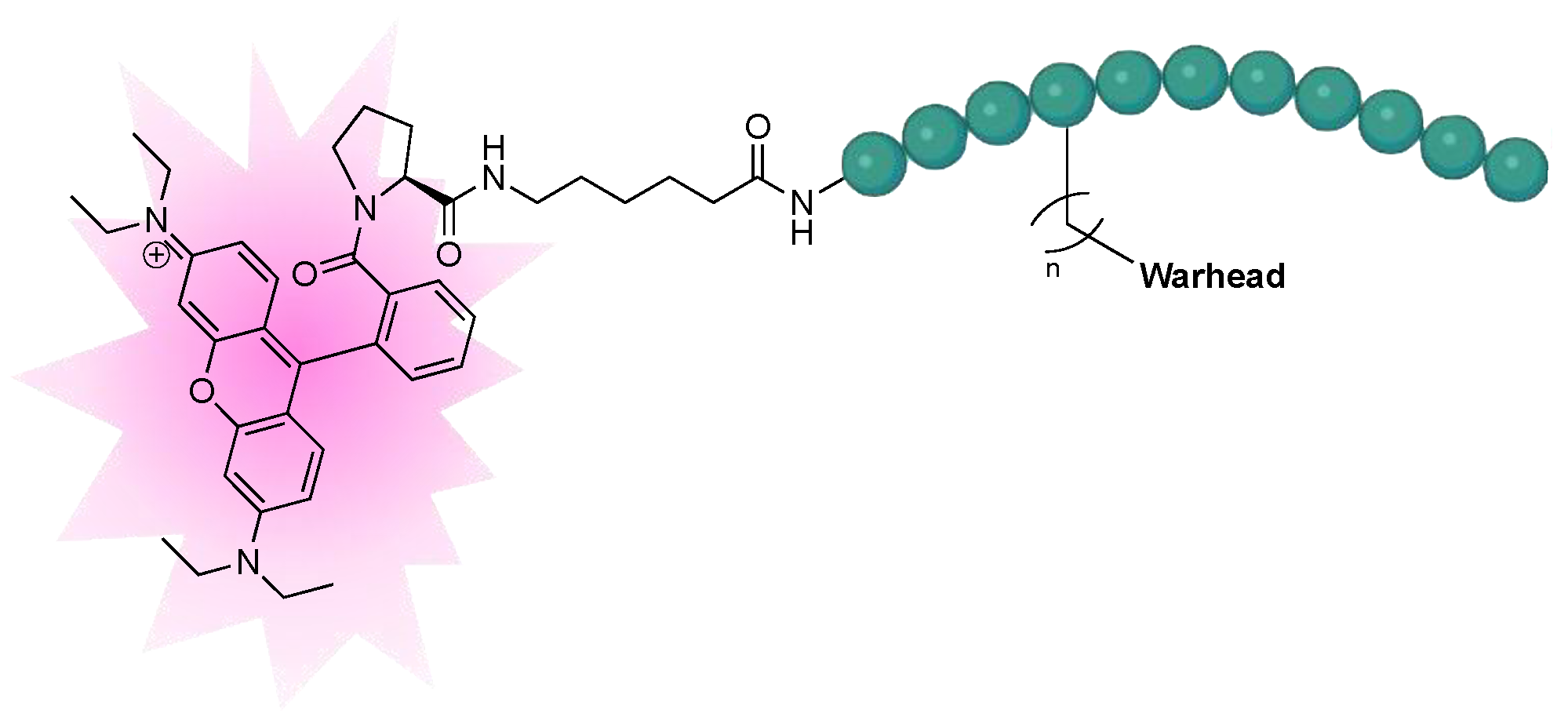
2.1.3. Design of Fluorescent Probe of FXIIIa
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Kinetic Evaluation
2.3.1. Kinetic Evaluation of Peptidic Inhibitors of FXIIIa
2.3.2. Kinetic Evaluation of Small Molecule Inhibitors of FXIIIa
2.3.3. Kinetic Evaluation of Fluorescent Rhodamine B FXIIIa Probe
2.4. Irreversible Labelling of Purified FXIIIa by SDS-PAGE
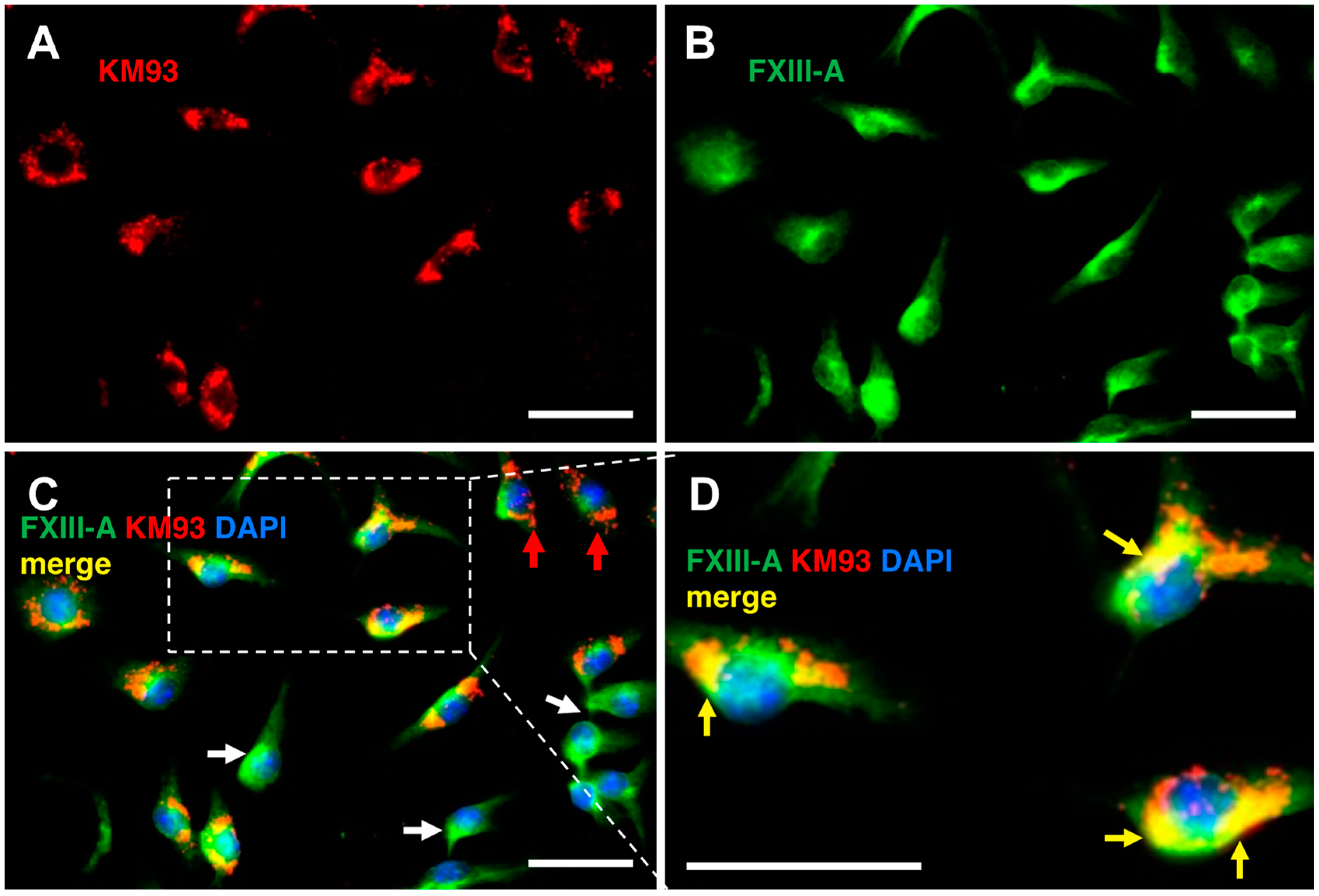
2.5. Labelling of FXIIIa in Bone Marrow Macrophages
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Kinetic Evaluation of FXIIIa Inhibition
4.2. Kinetic Evaluation of TG2 Inhibition
4.3. Determination of Type of Inhibition
4.4. Analysis of In Vitro Kinetic Data
4.5. Fluorescent Labelling of FXIIIa by SDS-PAGE
4.6. Synthesis of Peptidic Inhibitors, Small Molecule Inhibitors, and Fluorescent Probe
4.7. Cellular Labelling and Microscopy of FXIIIa
4.7.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.7.2. Animals
4.7.3. Bone Marrow Macrophage Isolation Culture
4.7.4. Protein Extraction and SDS-PAGE
4.7.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorand, L.; Graham, R.M. Transglutaminases: Crosslinking Enzymes with Pleiotropic Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.; Eckert, R. Transglutaminases: Family of Enzymes with Diverse Functions; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2005; Volume 38. ISBN 380557 9012.
- Beninati, S.; Bergamini, C.M.; Piacentini, M. An Overview of the First 50 Years of Transglutaminase Research. Amino Acids 2009, 36, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoca, M.P.; Tonoli, E.; Atobatele, A.G.; Verderio, E.A.M. Biocatalysis by Transglutaminases: A Review of Biotechnological Applications. Micromachines 2018, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica, R.A.; Gagnon, P.; Keillor, J.W.; Pelletier, J.N. Tissue Transglutaminase Acylation: Proposed Role of Conserved Active Site Tyr and Trp Residues Revealed by Molecular Modeling of Peptide Substrate Binding. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keillor, J.W.; Clouthier, C.M.; Apperley, K.Y.P.; Akbar, A.; Mulani, A. Acyl Transfer Mechanisms of Tissue Transglutaminase. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 57, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundemir, S.; Colak, G.; Tucholski, J.; Johnson, G.V.W. Transglutaminase 2: A Molecular Swiss Army Knife. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katt, W.P.; Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. The Diamond Anniversary of Tissue Transglutaminase: A Protein of Many Talents. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szondy, Z.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Király, R.; Sarang, Z.; Tsay, G.J. Transglutaminase 2 in Human Diseases. BioMedicine 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, D.C.; Kontos, J.L.; Greenberg, C.S. Roles of Transglutaminases in Cardiac and Vascular Diseases. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 2530–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, W.; Ehnis, T.; Bauer, M.; Donner, P.; Volta, U.; Riecken, E.O.; Schuppan, D. Identification of Tissue Transglutaminase as the Autoantigen of Celiac Disease. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Xu, A.M.; Liu, W. Transglutaminase 2 in Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2756–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.T.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, W.C.; Tsai, C.S.; Chao, Y.L.; Liu, S.H.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.J. Transglutaminase 2 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, C.; Szmacinski, H.; Fisher, M.L.; Nance, B.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Akbar, A.; Keillor, J.W.; Lok Wong, T.; Godoy-Ruiz, R.; Toth, E.A.; et al. Transamidase Site-Targeted Agents Alter the Conformation of the Transglutaminase Cancer Stem Cell Survival Protein to Reduce GTP Binding Activity and Cancer Stem Cell Survival. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabolacci, C.; de Martino, A.; Mischiati, C.; Feriotto, G.; Beninati, S. The Role of Tissue Transglutaminase in Cancer Cell Initiation, Survival and Progression. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayinde, O.; Wang, Z.; Pinton, G.; Moro, L.; Griffin, M. Transglutaminase 2 Maintains a Colorectal Cancer Stem Phenotype by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4556–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.L.; Keillor, J.W.; Xu, W.; Eckert, R.L.; Kerr, C. Transglutaminase Is Required for Epidermal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stem Cell Survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Sang, Y. Fibrinogen and Factor XIII in Venous Thrombosis and Thrombus Stability. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.; Weitz, J.I.; Veltkamp, R. Anticoagulant-Associated Intracranial Hemorrhage in the Era of Reversal Agents. Stroke 2017, 48, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Es, N.; Coppens, M.; Schulman, S.; Middeldorp, S.; Büller, H.R. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Compared with Vitamin K Antagonists for Acute Venous Thromboembolism: Evidence from Phase 3 Trials. Blood 2014, 124, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokusai-VTE Investigators; Büller, H.; Décousus, H.; Grosso, M.; Mercuri, M.; Middeldorp, S.; Prins, M.; Raskob, G.; Schellong, S.; Schwocho, L.; et al. Edoxaban versus Warfarin for the Treatment of Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, R.; Büchold, C.; Jähnig, R.; Pelzer, C.; Sommer, M.; Heil, A.; Florian, P.; Nowak, G.; Gerlach, U.; Hils, M. Novel Inhibitor ZED3197 as Potential Drug Candidate in Anticoagulation Targeting Coagulation FXIIIa (F13a). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordell, P.A.; Kile, B.T.; Standeven, K.F.; Josefsson, E.C.; Pease, R.J.; Grant, P.J. Association of Coagulation Factor XIII-A with Golgi Proteins within Monocyte-Macrophages: Implications for Subcellular Trafficking and Secretion. Blood 2010, 115, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckert, F.; Jung, E.; Shmerling, D.H. A Hitherto Undescribed Congenital Haemorrhagic Diathesis Probably Due to Fibrin Stabilizing Factor Deficiency. Thromb. Diath. Haemorrh. 1960, 5, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, P.; Metzner, H.J.; Zettlmeißl, G.; Li, M.; Smith, A.G.; Lathe, R.; Dickneite, G. Targeted Inactivation of the Mouse Locus Encoding Coagulation Factor XIII-A: Hemostatic Abnormalities in Mutant Mice and Characterization of the Coagulation Deficit. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 88, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardik, R.; Solomon, A.; Loscalzo, J.; Eskaraev, R.; Bialik, A.; Goldberg, I.; Schiby, G.; Inbal, A. Novel Proangiogenic Effect of Factor XIII Associated with Suppression of Thrombospondin 1 Expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszbek, L.; Bereczky, Z.; Bagoly, Z.; Komáromi, I.; Katona, É. Factor XIII: A Coagulation Factor with Multiple Plasmatic and Cellular Functions. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 931–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobbervig, C.; Williams, E. FXIII Polymorphisms, Fibrin Clot Structure and Thrombotic Risk. Biophys. Chem. 2004, 112, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. Factor XIII: Structure and Function. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Biswas, A.; Akhter, M.S.; Krettler, C.; Reinhart, C.; Dodt, J.; Reuter, A.; Philippou, H.; Ivaskevicius, V.; Oldenburg, J. Revisiting the Mechanism of Coagulation Factor XIII Activation and Regulation from a Structure/Functional Perspective. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handrkova, H.; Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. The Activation Peptide of Coagulation Factor XIII Is Vital for Its Expression and Stability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornyak, T.J.; Shafer, J.A. Role of Calcium Ion in the Generation of Factor XIII Activity. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 6175–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieler, M.; Weber, J.; Hils, M.; Kolb, P.; Heine, A.; Büchold, C.; Pasternack, R.; Klebe, G. Structure of Active Coagulation Factor-Xiii Triggered by Calcium Binding: Basis for the Design of next-Generation Anticoagulants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 11930–11934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, G.K.; Andersen, M.D. Reversible Activation of Cellular Factor XIII by Calcium. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Kar, S. Factor XIIIa Inhibitors as Potential Novel Drugs for Venous Thromboembolism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, R.L.; Kaartinen, M.T.; Nurminskaya, M.; Belkin, A.M.; Colak, G.; Johnson, G.V.W.; Mehta, K. Transglutaminase Regulation of Cell Function. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 383–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, Z.A.; Hettasch, J.M.; Lai, T.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Greenberg, C.S. Tissue Transglutaminase Is Expressed, Active, and Directly Involved in Rat Dermal Wound Healing and Angiogenesis. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Perez, M.; Caja, S.; Melino, G.; Johnson, T.S.; Lindfors, K.; Griffin, M. A Novel Extracellular Role for Tissue Transglutaminase in Matrix-Bound VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, K.F.; Doshi, K.P.; Gaul, S.L.; Claremon, D.A.; Remy, D.C.; Baldwin, J.J.; Pitzenberger, S.M.; Stern, A.M. Transglutaminase Inhibition by 2-[(2-Oxopropyl)Thio]Imidazolium Derivatives: Mechanism of Factor Xllla Inactivation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 10109–10119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, Y.; Hosono, M.; Wada, F.; Yoshimura, T.; Maki, M.; Hitomi, K. Screening for the Preferred Substrate Sequence of Transglutaminase Using a Phage-Displayed Peptide Library: Identification of Peptide Substrates for TGase 2 and Factor XIIIa. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17699–17706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieler, M.; Büchold, C.; Schmitt, M.; Heine, A.; Hils, M.; Pasternack, R.; Klebe, G. Structure-Based Design of FXIIIa-Blockers: Addressing a Transient Hydrophobic Pocket in the Active Site of FXIIIa. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, N.M.R.; Gates, E.W.J.; Firoozi, N.; Cundy, N.J.; Leccese, J.; Eisinga, S.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Adhikary, G.; Eckert, R.L.; Keillor, J.W. Structure-Activity Relationships of N-Terminal Variants of Peptidomimetic Tissue Transglutaminase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 232, 114172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, C.H.; Ho, N.H.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Jaffer, F.A.; Reed, G.L.; Weissleder, R. Novel Factor XIII Probes for Blood Coagulation Imaging. ChemBioChem 2003, 4, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, F.A.; Tung, C.H.; Wykrzykowska, J.J.; Ho, N.H.; Houng, A.K.; Reed, G.L.; Weissleder, R. Molecular Imaging of Factor XIIIa Activity in Thrombosis Using a Novel, Near-Infrared Fluorescent Contrast Agent That Covalently Links to Thrombi. Circulation 2004, 110, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswamy, A.M.M.; Navals, P.; Gates, E.W.J.; Shad, S.; Watt, S.K.I.; Keillor, J.W. Structure–Activity Relationships of Hydrophobic Alkyl Acrylamides as Tissue Transglutaminase Inhibitors. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; McNeil, N.M.R.; Albert, M.R.; Ta, V.; Adhikary, G.; Bourgeois, K.; Eckert, R.L.; Keillor, J.W. Structure-Activity Relationships of Potent, Targeted Covalent Inhibitors That Abolish Both the Transamidation and GTP Binding Activities of Human Tissue Transglutaminase. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7910–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keillor, J.W.; Akbar, A.; Eckert, R.L.; Fisher, M.; Johnson, G.V.W. TG2 Inhibitor Piperazine Compounds and Uses Thereof. WO2017179018A1, 19 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, N.; Moreau, S.; Mulani, A.; Moreau, P.; Keillor, J.W. Fluorescent Probes of Tissue Transglutaminase Reveal Its Association with Arterial Stiffening. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardin, C.; Pelletier, J.N.; Lubell, W.D.; Keillor, J.W. Cinnamoyl Inhibitors of Tissue Transglutaminase. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5766–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, A.; Gravel, C.; Labelle, J.; Keillor, J.W. Kinetic Studies of Guinea Pig Liver Transglutaminase Reveal a General-Base-Catalyzed Deacylation Mechanism. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8335–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hils, M.; Pasternack, R.; Büchold, C.; Weber, J.; Heine, A.; Klebe, G.; Stieler, M. Crystal Structure of Blood Coagulation Factor XIIIa. WO2014090835A1, 19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas, D.M.; Strop, P.; Brunger, A.T.; Khosla, C. Transglutaminase 2 Undergoes a Large Conformational Change upon Activation. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchold, C.; Gerlach, U.; Hils, M.; Pasternack, R.; Weber, J. Pyridinone Derivatives as Tissue Transglutaminase Inhibitors. WO2014012858A1, 23 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack, R.; Hils, M.; Büchold, C. Inhibitors of Blood Coagulation Factor XIII. WO2019201432A1, 24 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pardin, C.; Gillet, S.M.F.G.; Keillor, J.W. Synthesis and Evaluation of Peptidic Irreversible Inhibitors of Tissue Transglutaminase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8379–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, K.; Hunfeld, A.; Specker, E.; Reiff, C.; Seitz, R.; Pasternack, R.; Dodt, J. A Highly Sensitive Fluorometric Assay for Determination of Human Coagulation Factor XIII in Plasma. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 367, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Király, R.; Thangaraju, K.; Nagy, Z.; Collighan, R.; Nemes, Z.; Griffin, M.; Fésüs, L. Isopeptidase Activity of Human Transglutaminase 2: Disconnection from Transamidation and Characterization by Kinetic Parameters. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitz, R.; Wilson, I.B. Esters of Methanesulfonic Acid as Irreversible Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.R.; Hofsteenge, J. Specificity of Activated Human Protein C. Biochem. J. 1985, 230, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilich, P. Direct Observation of Acrylamide Fluorescence. Croat. Chem. Acta 1994, 67, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, M.; Büchold, C.; Pasternack, R.; Binder, N.B.; Moore, G.W. Clinical Validation of an Automated Fluorogenic Factor XIII Activity Assay Based on Isopeptidase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Putnam, F.W. Primary Structure of Blood Coagulation Factor XIIIa (Fibrinoligase, Transglutaminase) from Human Placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8019–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádány, R.; Bárdos, H. Review Factor XIII Subunit A as an Intracellular Transglutaminase. CMLS Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I.; Smith, O.; Clouthier, C.M.; Keillor, J.W. Expression, Purification and Kinetic Characterisation of Human Tissue Transglutaminase. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 87, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Johnson, D.D.; Reddy, R.E. Collagen Cross-Links: A Convenient Synthesis of Tert-Butyl-(2S)-2-[(Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)Amino]-4-(2-Oxiranyl)Butanoate. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1999, 10, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotos, G.; Padrón, J.M.; Martín, T.; Gibbons, W.A.; Martín, V.S. A General Approach to the Asymmetric Synthesis of Unsaturated Lipidic α-Amino Acids. the First Synthesis of α-Aminoarachidonic Acid. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3741–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.K.; Ramasamy, K.; Emery, T. Synthesis of N.alpha.,N.delta.-protected N.delta.-hydroxy-L-ornithine from L-glutamic acid. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 3527–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, D.R.; Sharma, A.K.; Hergenrother, P.J. Using Peptidic Inhibitors to Systematically Probe the S1′ Site of Caspase-3 and Caspase-7. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3529–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulmer, G.R.; Miller, A.J.M.; Sherden, N.H.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Nudelman, A.; Stoltz, B.M.; Bercaw, J.E.; Goldberg, K.I. NMR Chemical Shifts of Trace Impurities: Common Laboratory Solvents, Organics, and Gases in Deuterated Solvents Relevant to the Organometallic Chemist. Organometallics 2010, 29, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Guengerich, F.P. Mechanism of Aqueous Decomposition of Trichloroethylene Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11656–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Matsuhara, K.; Itoh, J.; Akiyama, Y.; Dan, S.; Yamori, T.; Ito, A.; Yoshida, M.; Katoh, T. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel FK228 Analogues as Potential Isoform Selective HDAC Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissler, S.; Kley, M.; Bächle, D.; Loidl, G.; Meier, T.; Samson, D. Substitution Determination of Fmoc-Substituted Resins at Different Wavelengths. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neises, B.; Steglich, W. Simple Method for the Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1978, 17, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Atkinson, R.N.; Bruce King, S. Preparation and Evaluation of New L-Canavanine Derivatives as Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6557–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, S.; Xi, Z.; Yi, L. Design and Synthesis of NBD-S-Dye Dyads for Fluorescently Discriminative Detection of Biothiols and Cys/Hcy. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 6651–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachal, P.; Fletcher, J.M.; Fong, T.M.; Huang, C.C.R.R.; Lao, J.; Xiao, J.C.; Shen, C.P.; Strack, A.M.; Shearman, L.; Stribling, S.; et al. 1-Sulfonyl-4-Acylpiperazines as Selective Cannabinoid-1 Receptor (CB1R) Inverse Agonists for the Treatment of Obesity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2550–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousbie, M.; Vivancos, M.; Brouillette, R.L.; Besserer-Offroy, É.; Longpré, J.M.; Leduc, R.; Sarret, P.; Marsault, É. Structural Optimization and Characterization of Potent Analgesic Macrocyclic Analogues of Neurotensin (8–13). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7103–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


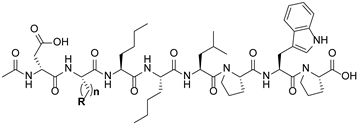 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inh. | R | n | E+ C Position | CO C Position |
| 11 | 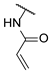 | 1 | f | d |
| 12 | 2 | g | e | |
| 13 | 3 | h | f | |
| 14 | 4 | i | g | |
| 20 | 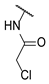 | 1 | e | d |
| 21 | 2 | f | e | |
| 22 | 3 | g | f | |
| 23 | 4 | h | g | |
| 45 | 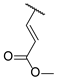 | 1 | c | e |
| 46 | 2 | d | f | |
| 47 | 3 | e | g | |
| FXIIIa | TG2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inh. | Inh. Mode | kinact (min−1) | Ki or KI (μM) | kinact/KI (M−1 min−1) | Inh. Mode | kinact/KI (M−1 min−1) | Selectivity |
| 11 | None * | NA | NA | NA | None ** | NA | NA |
| 12 | Rev | NA | 193 ± 20 | NA | None ** | NA | FXIIIa |
| 13 | Rev | NA | 135 ± 16 | NA | None ** | NA | FXIIIa |
| 14 | Rev | NA | 125 ± 20 | NA | None ** | NA | FXIIIa |
| 20 | None * | NA | NA | NA | Irrev | 1962 ± 82 | TG2 |
| 21 | Irrev | - | - | 7422 ± 525 | None ** | NA | FXIIIa |
| 22 | Irrev | 0.0988 ± 0.0185 | 7.1 ± 3.1 | 13,922 ± 6664 | Irrev | 2922 ± 260 | 2.6 FXIIIa |
| 23 | Irrev | - | - | 4907 ± 325 | Irrev | 3565 ± 229 | 1.4 FXIIIa |
| 45 | Rev | NA | 53 ± 12 | NA | None ** | NA | FXIIIa |
| 46 | Irrev | 0.1765 ± 0.0160 | 0.4732 ± 0.0847 | 372,992 ± 74,839 | Irrev | 56,520 ± 2044 | 6.6 FXIIIa |
| 47 | Rev | NA | 0.0941 ± 0.0105 | NA | Irrev | 31,780 ± 2218 | Irrev TG2 |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inh. | R1 | R2 | R3 | FXIIIa Ki (µM) | TG2 KI (µM) |
| 71 | 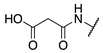 | 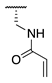 |  | Interference * | >360 |
| 79 | 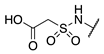 |  | 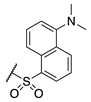 | Interference * | >360 |
| 75 | 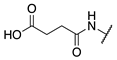 |  | 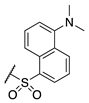 | Interference * | >360 |
| 74 | 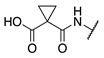 | 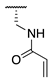 |  | Interference * | >360 |
| 73 |  | 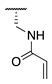 |  | Interference * | >360 |
| 76 | 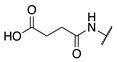 | 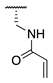 | 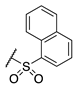 | Interference * | >360 |
| 72 | 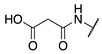 | 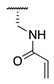 |  | 249.1 ± 69.3 | >360 |
| 77 | 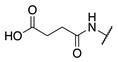 | 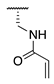 | 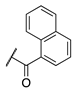 | 69.0 ± 4.1 | >360 |
| 84 | 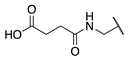 | 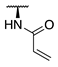 | 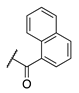 | 107.6 ± 19.1 | >360 |
| 87 |  | 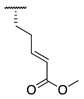 | 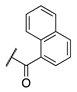 | 131.1 ± 7.9 | 14.3 ± 7.0 |
| 88 | 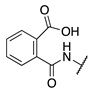 | 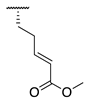 | 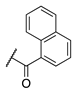 | 265.0 ± 46.8 | 21.2 ± 9.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gates, E.W.J.; Mansour, K.; Ebrahimi Samani, S.; Shad, S.; Kaartinen, M.T.; Keillor, J.W. Peptidic Inhibitors and a Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Inhibition and Labelling of Factor XIIIa Transglutaminase. Molecules 2023, 28, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041634
Gates EWJ, Mansour K, Ebrahimi Samani S, Shad S, Kaartinen MT, Keillor JW. Peptidic Inhibitors and a Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Inhibition and Labelling of Factor XIIIa Transglutaminase. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041634
Chicago/Turabian StyleGates, Eric W. J., Kian Mansour, Sahar Ebrahimi Samani, Sammir Shad, Mari T. Kaartinen, and Jeffrey W. Keillor. 2023. "Peptidic Inhibitors and a Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Inhibition and Labelling of Factor XIIIa Transglutaminase" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041634
APA StyleGates, E. W. J., Mansour, K., Ebrahimi Samani, S., Shad, S., Kaartinen, M. T., & Keillor, J. W. (2023). Peptidic Inhibitors and a Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Inhibition and Labelling of Factor XIIIa Transglutaminase. Molecules, 28(4), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041634







