Decomposition of Phosphorus Pollution and Microorganism Analysis Using Novel CW-MFCs under Different Influence Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of the System Phosphorus Removal Effect
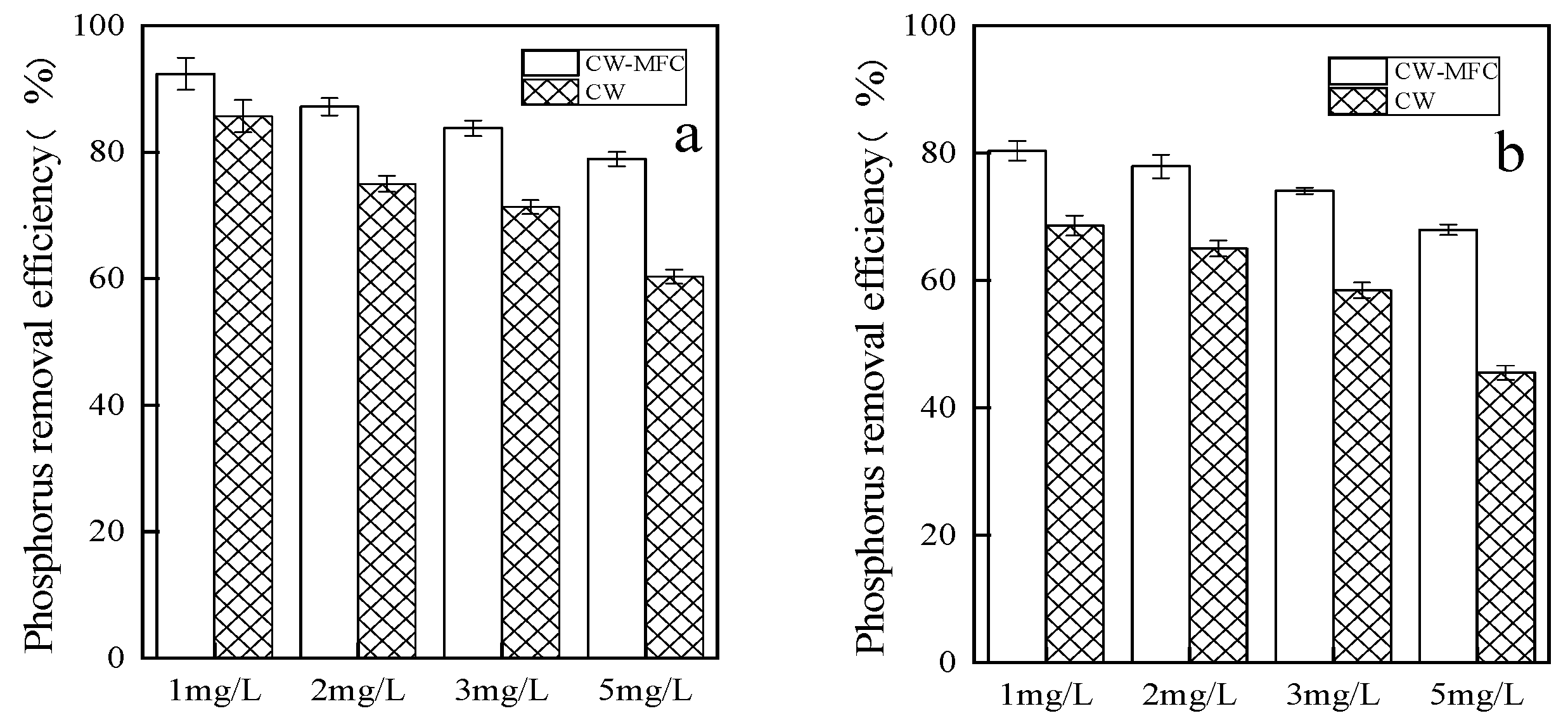
2.1.1. Total Phosphorus Removal Efficiency at Different Pollutant Concentrations
2.1.2. Comparison between the Phosphorus Removal Effects of the CW-MFC and CW Systems
2.2. Power Generation Performance of the CW-MFC System
2.3. Microbial Community Structure in Wetlands
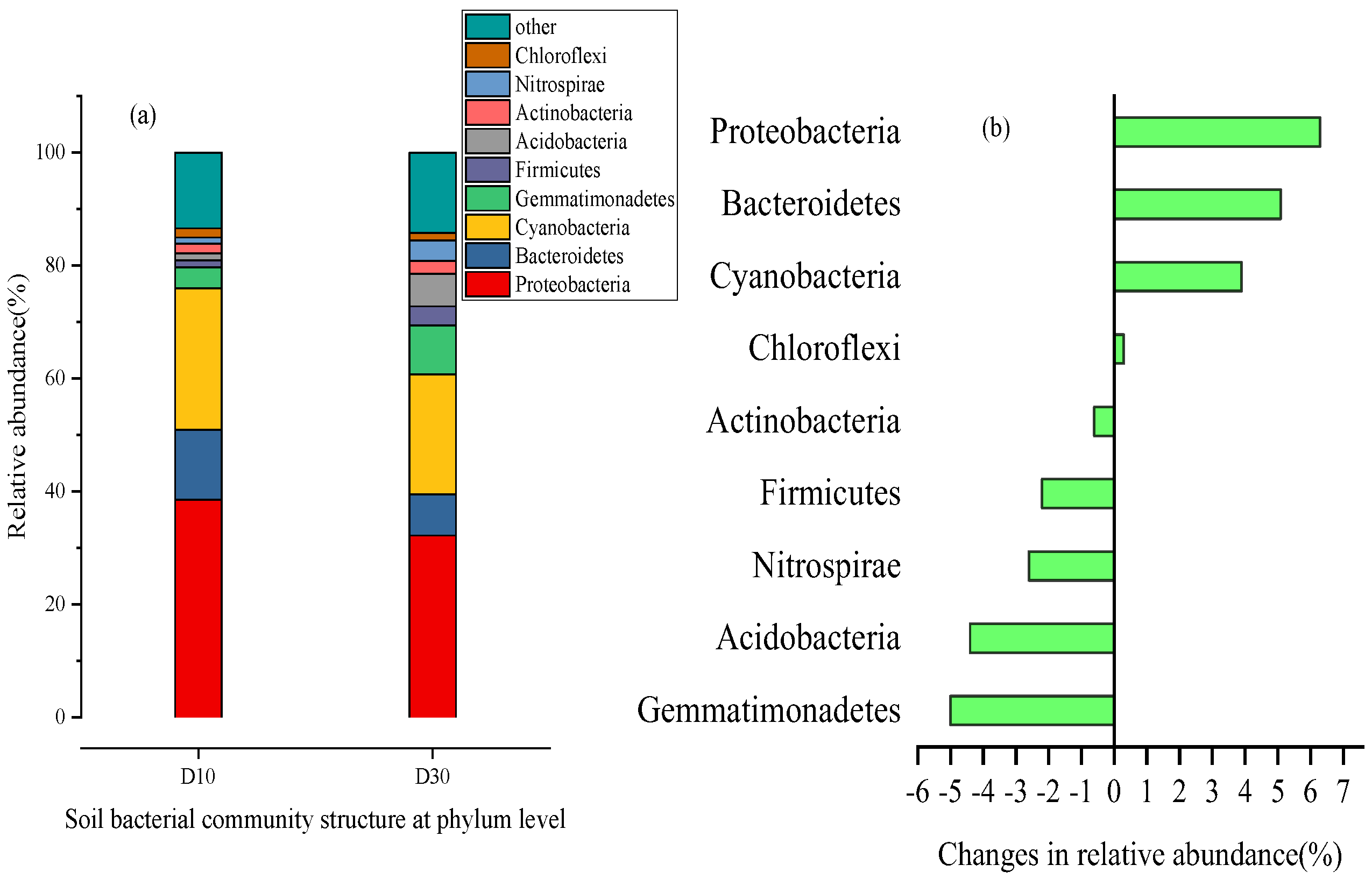
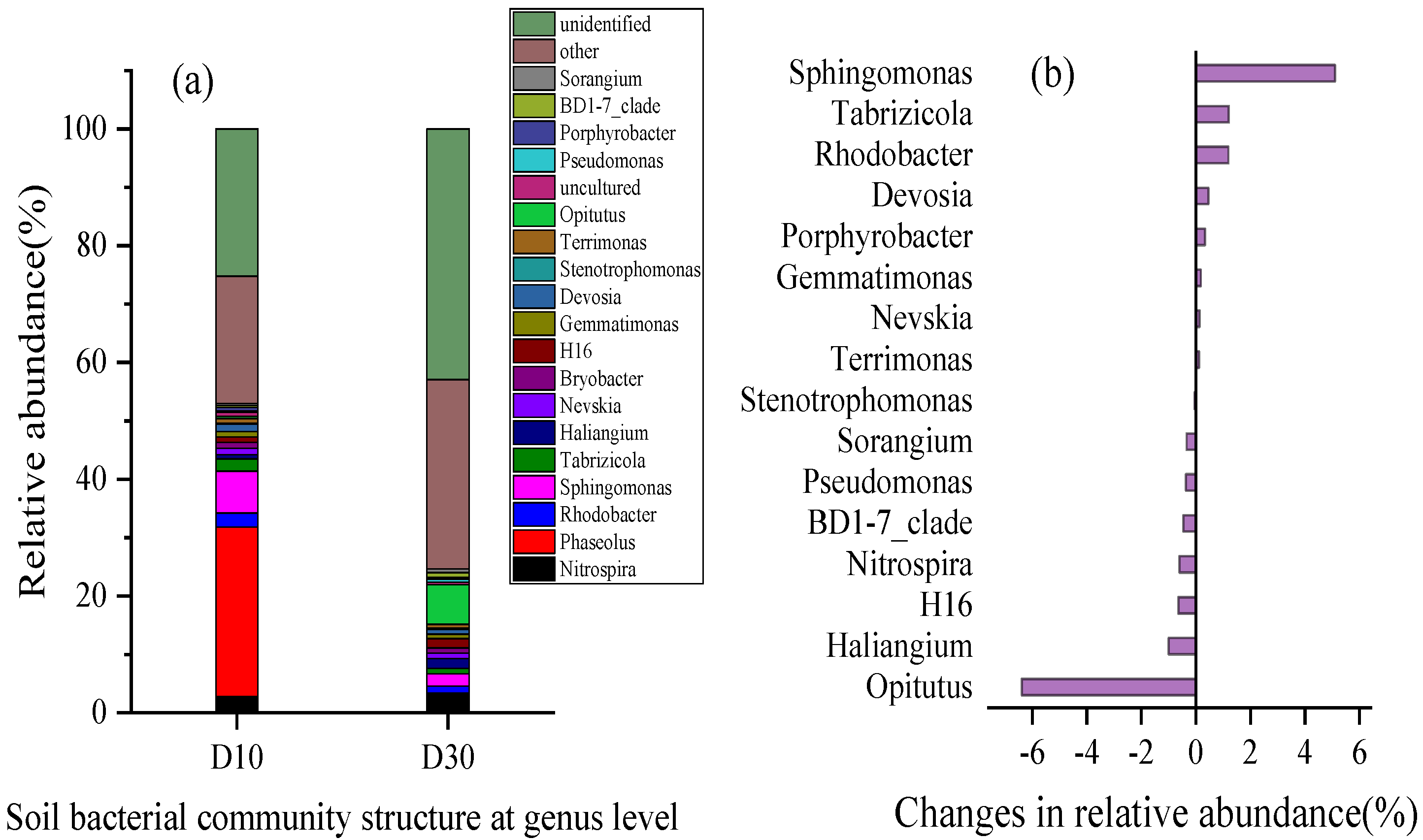
2.3.1. Community Structure Characteristics of Soil Microorganisms in Wetland Sediments
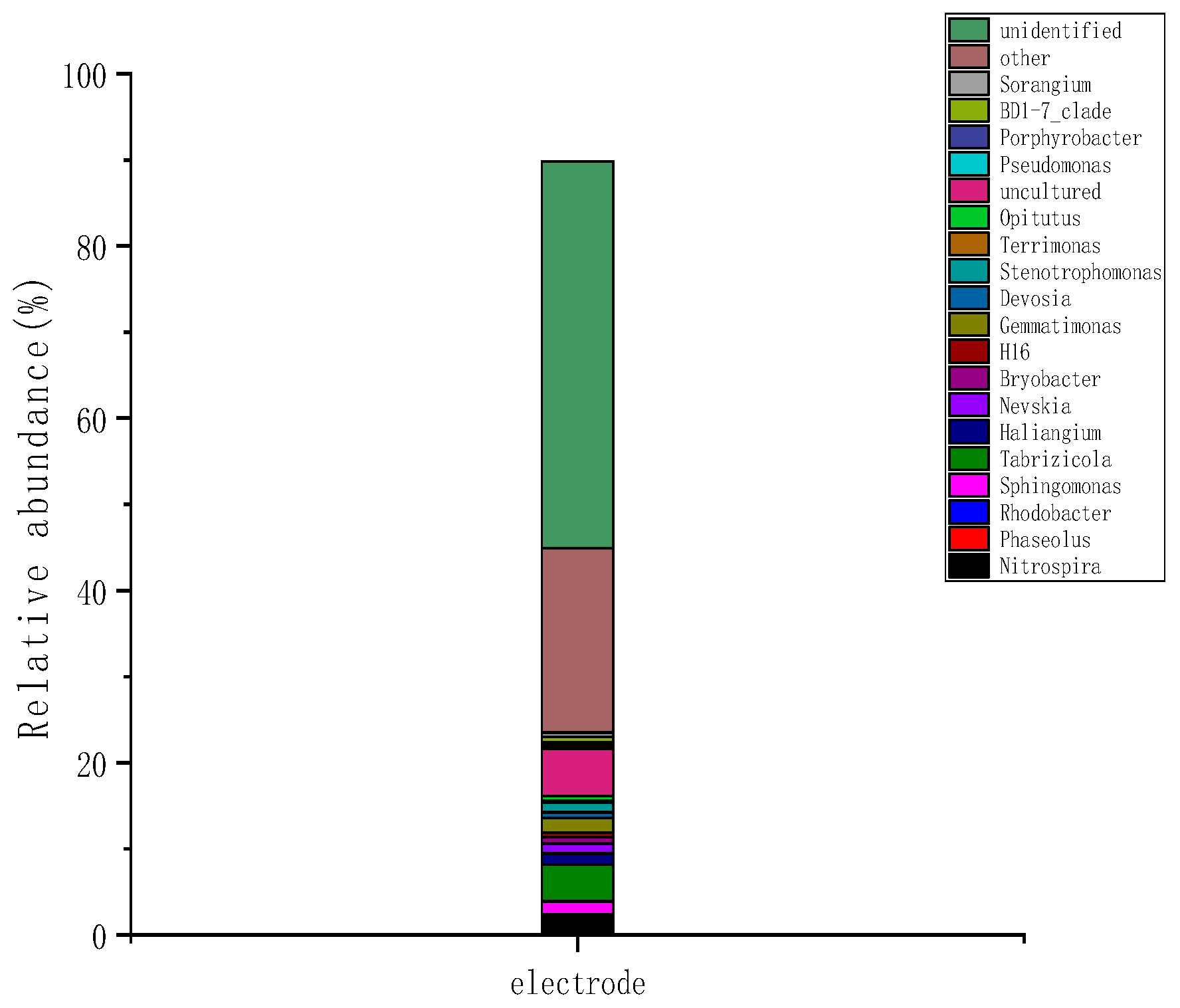
2.3.2. Microbial Community Structure at the Wetland Electrode
2.4. Analysis of the Phosphorus Removal Mechanism Used by the Two Matrices
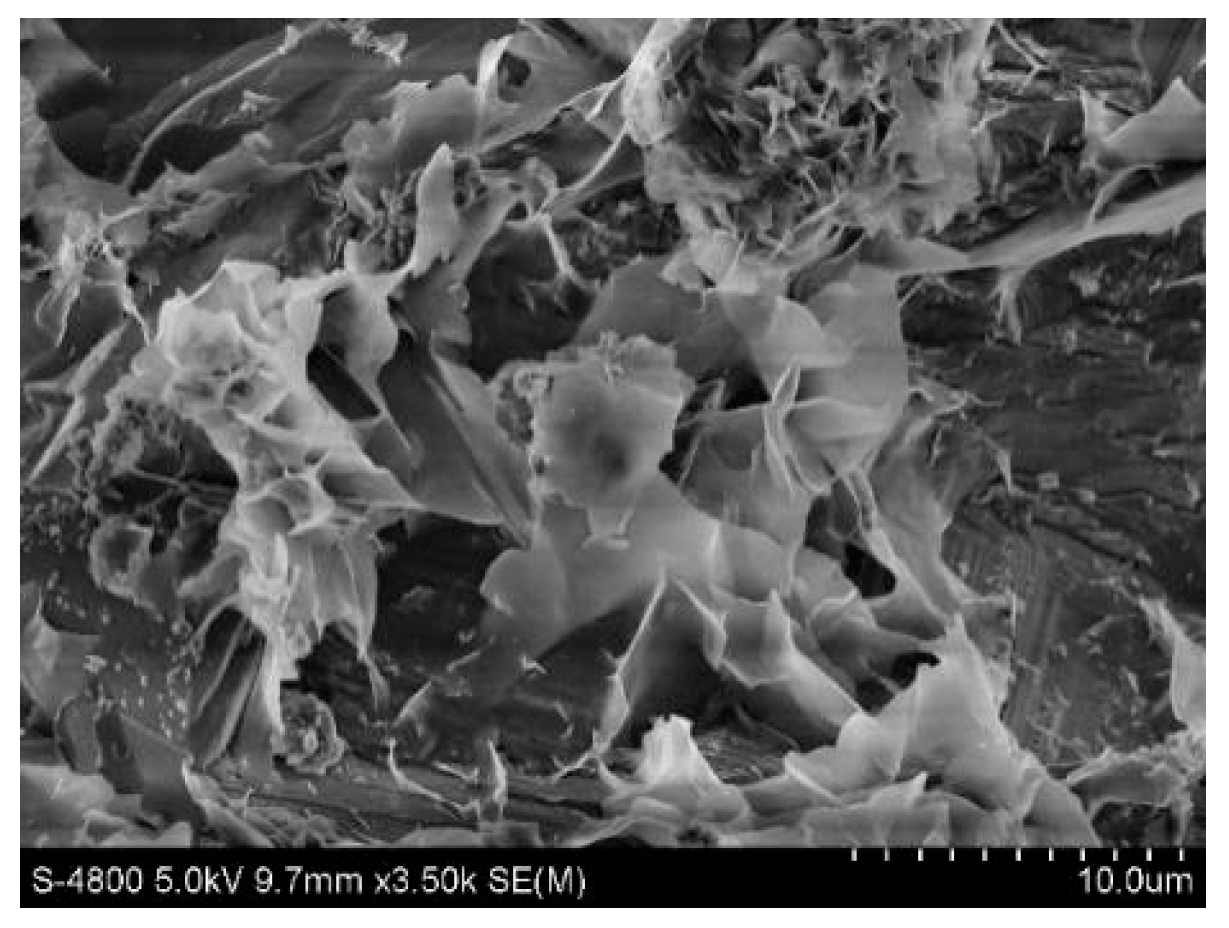
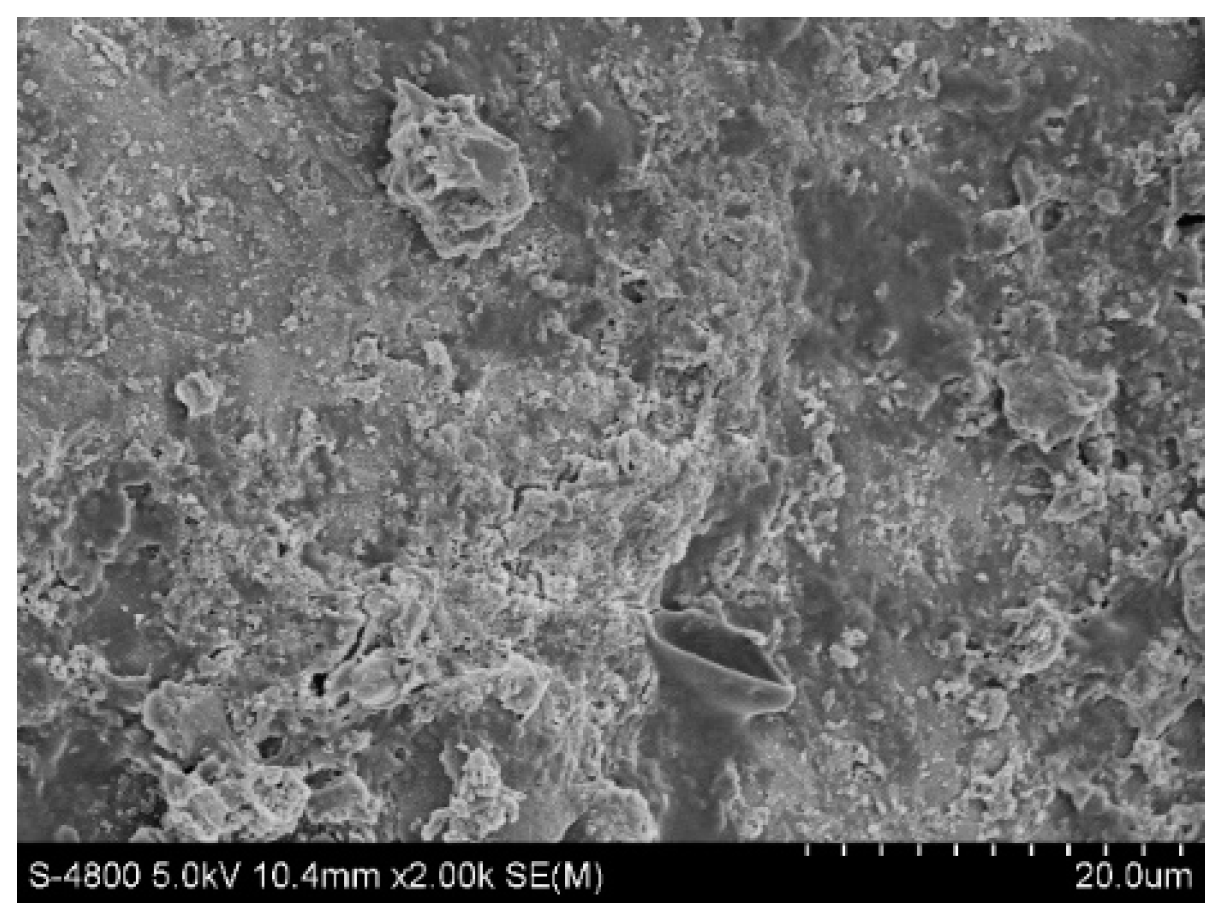
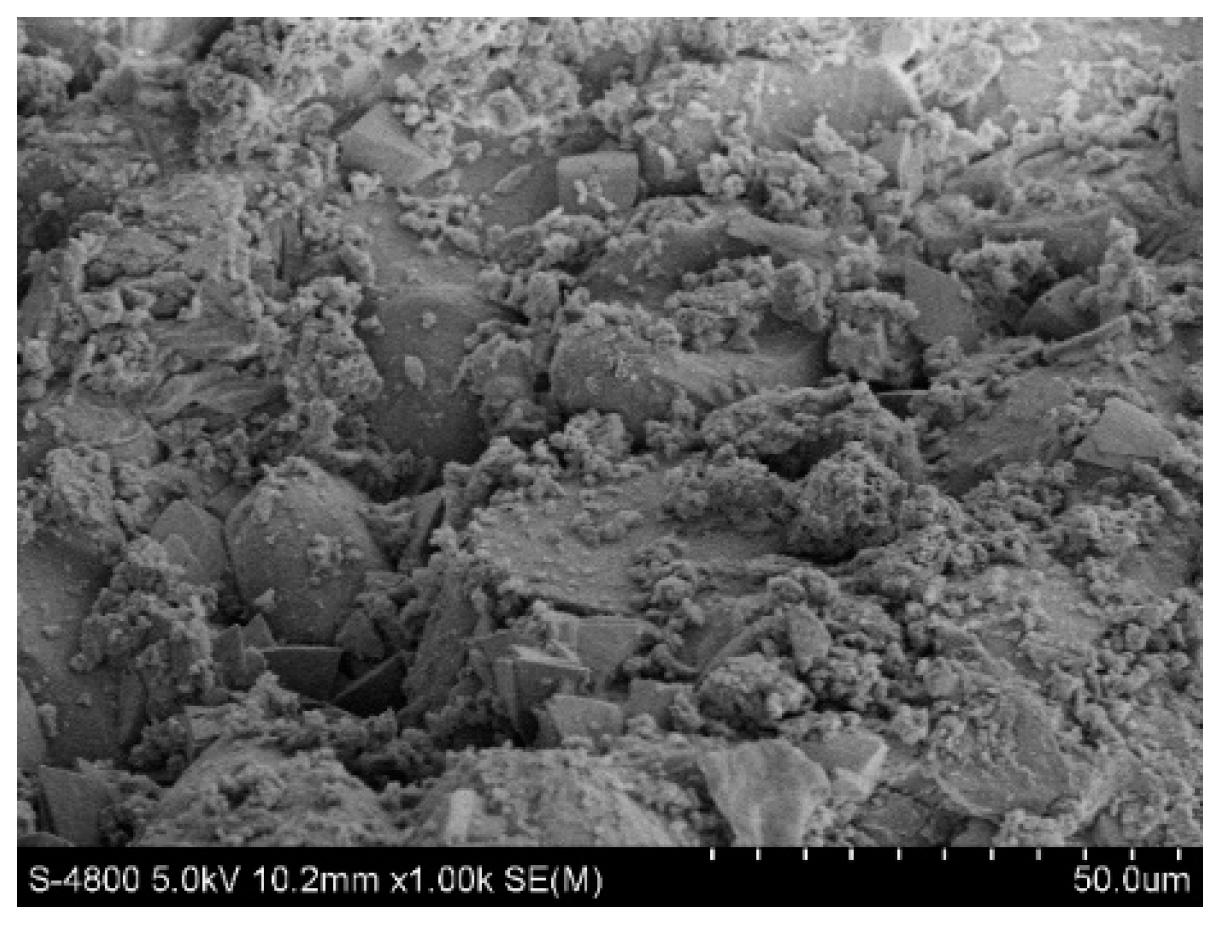
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
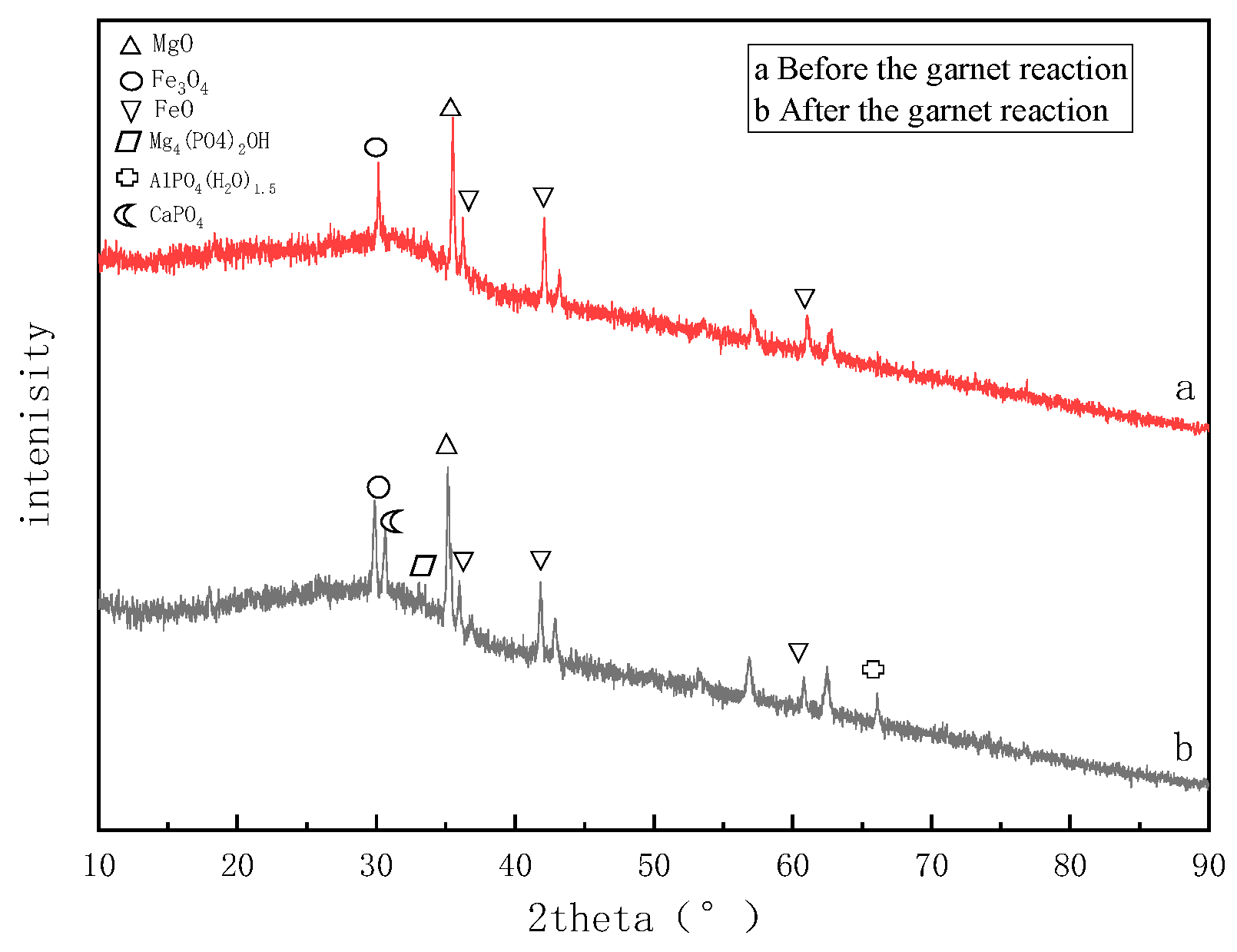
2.4.2. XRD Detection and Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
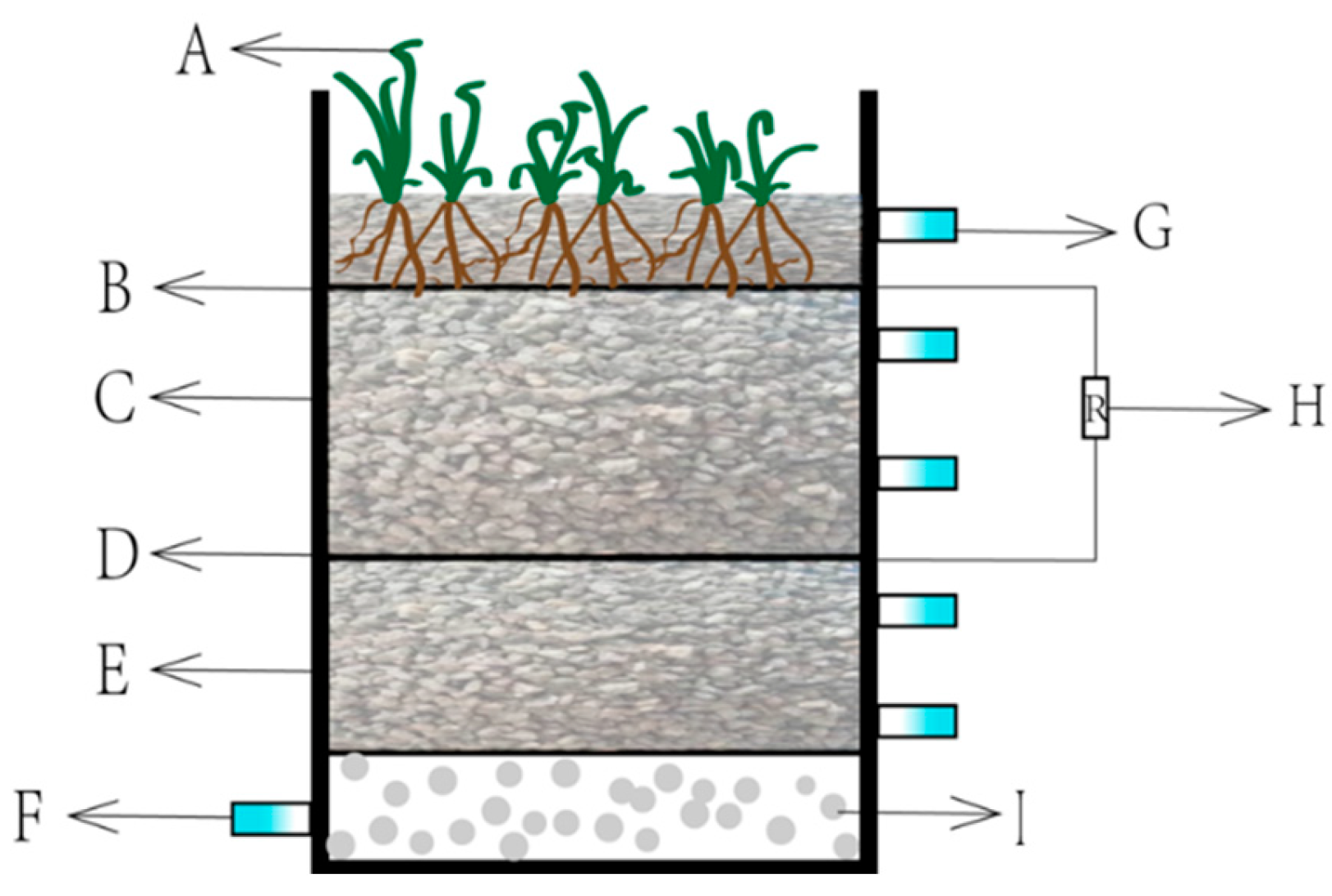
3.1. Experimental Device
3.2. Selection of Experimental Materials
3.2.1. Matrix Selection
3.2.2. Plant Selection
3.2.3. Selection of Activated Sludge
3.2.4. Electrode Selection
3.2.5. Chemicals
3.2.6. Experimental Equipment
3.2.7. Water Used in the Experiment
- -
- COD concentration in influent, mg/L;
- -
- COD concentration in effluent, mg/L.
3.3. Experimental Procedure
3.4. Measurement and Calculation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhou, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.E.; Sun, H.F.; Zhang, J.N.; Zhang, X.X.; Xin, L.X. Nutrient removal, methane and nitrous oxide emissions in a hybrid constructed wetland treating anaerobic digestate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.Y.; Zhu, H.; Yan, B.X.; Shutes, B.; Yu, X.F.; Cheng, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.Y. Constructed wetlands integrated with microbial fuel cells for COD and nitrogen removal affected by plant and circuit operation mode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3008–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, Ü.; Tournebize, J.; Espenberg, M.; Chaumont, C.; Torga, R.; Garnier, J.; Muhel, M.; Maddison, M.; Lebrun, J.D.; Uher, E.; et al. High denitrification potential but low nitrous oxide emission in a constructed wetland treating nitrate-polluted agricultural run-off. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.Y.; Yang, Z.N.; Niu, Y.X.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Han, J.L.; Wang, H. Removal of microplastics and attached heavy metals from secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plant using interpenetrating bipolar plate electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.X.; Yang, Z.N.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.R.; Xu, R.Y. Decomposition of perfluorooctanoic acid from wastewater using coating electrode: Efficiency, the anode characteristics and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.X.; Yin, Y.; Xu, R.Y.; Yang, Z.N.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Han, J.L.; Wang, H. Electrocatalytic oxidation of low concentration cefotaxime sodium wastewater using Ti/SnO2–RuO2 electrode: Feasibility analysis and degradation mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Song, H.L.; Singh, R.P.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Yang, X.L. Simultaneous reduction of antibiotics leakage and methane emission from constructed wetland by integrating microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Han, J.L.; Xu, R.Y.; Han, D.Y. Reshaped structure of microbial community within a subsurface flow constructed wetland response to the increased water temperature: Improving low-temperature performance by coupling of water-source heat pump. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Bapodra, S.L.; Madamwar, D.; Desai, C. Electroactive bacterial community augmentation enhances the performance of a pilot scale constructed wetland microbial fuel cell for treatment of textile dye wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazarian, E.; Gheshlaghi, R.; Mahdavi, M.A. Impact of light/dark cycle on electrical and electrochemical characteristics of algal cathode sediment microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2020, 475, 228686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Srivastava, P.; Patil, S.A.; Yadav, K.A. A comprehensive review on emerging constructed wetland coupled microbial fuel cell technology: Potential applications and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.L.; Li, H.; Song, H.L.; Wang, R.C.; Dai, Z.Q. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in bioelectrochemical system with power supplied by constructed wetland-coupled microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cao, F.Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, L.L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.D.; Wang, Z.D. Electricity production and evolution of microbial community in the constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Yu, W.Z. Applying multiple bio-cathodes in constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell for promoting energy production and bioelectrical derived nitrification-denitrification process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oon, Y.L.; Ong, S.A.; Ho, L.N.; Wong, Y.S.; Dahalan, F.A.; Oon, Y.S.; Lehl, H.K.; Thung, W.E.; Nordin, N. Up-flow constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell for azo dye, saline and nitrate remediation and bioelectricity generation: From waste to energy approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.Y.; Cao, X.; Song, X.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Si, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, W.T.; Tesfahunegn, A.A. Bioenergy generation and simultaneous nitrate and phosphorus removal in a pyrite-based constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Fu, Z.S.; Qiao, H.X.; Liu, F.X. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Dai, W.Q.; Zheng, P.R.; Zheng, X.Y.; He, S.B.; Zhao, M. Iron scraps enhance simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Nguyen, T.H.H.; Soda, S.; Vu, N.D.; Bui, T.K.A.; Vo, T.D.H.; Bui, X.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. White hard clam (Meretrix lyrata) shells media to improve phosphorus removal in lab-scale horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands: Performance, removal pathways, and lifespan. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.K.C.; Wu, Y.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, M.H. Nitrogen and phosphate mass balance in a sub-surface flow constructed wetland for treating municipal wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Connor, G.A.O.; Gale, P.M. Phosphorus sorption capacities of wetland soils and stream sediments impacted by dairy effluent. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



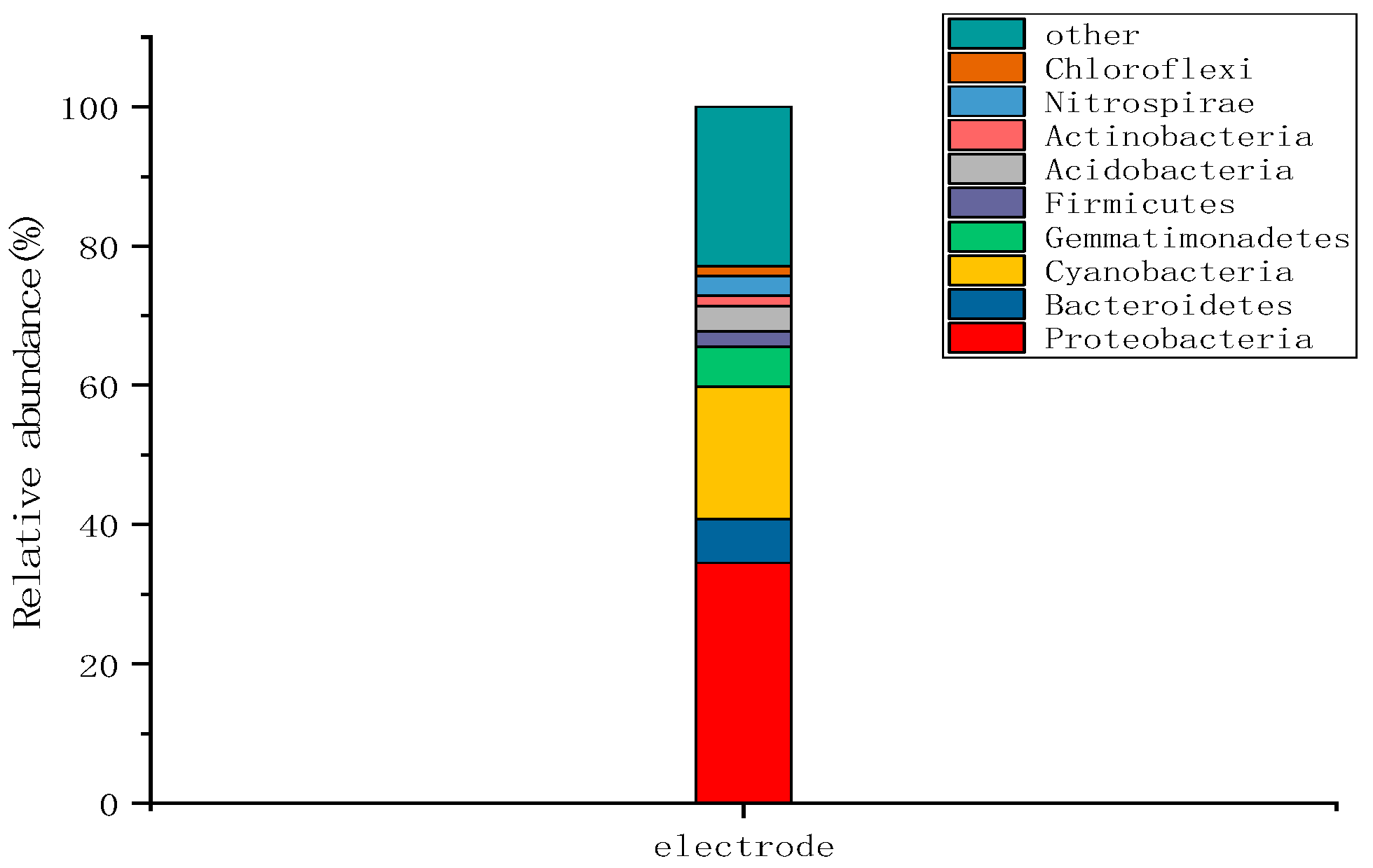





| Equipment Name | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic analytical balance | FA2204B | Shanghai Jingke Tianmei Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Smart digester | CM-05 | Beijing Shuanghui Jingcheng Electronic Products Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) |
| Electric heating constant Temperature blast drying oven | DHG-9101 | Jintan Medical Instrument Factory (Changzhou, China) |
| Magnetic stirrer | BBC-7X | Hangzhou Changsheng Group (Hangzhou, China) |
| UV-visible Spectrophotometer | T6 | Beijing Puxi General Instrument Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) |
| Peristaltic pump | YZ15 | Baoding Refu Fluid Technology Co., Ltd. (Baoding, China) |
| Infrared spectrometer | IRAffinity-1s | Japan Shimadzu Corporation (Kyoto, Japan) |
| pH meter | PHS-3C | Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Ultra-pure water machine | GWA-UN | Beijing Universal. (Beijing, China) |
| Water bath constant temperature oscillator | THZ-82 | Jiangsu Ronghua Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd. (Taizhou, China) |
| Multi-channel data acquisition system | PISO813 | Shenzhen Changxin Automation Equipment Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China) |
| Number | Total Phosphorus Concentration mg/L | COD mg/L | Ammonia Nitrogen Concentration mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 230 | 5 |
| 2 | 2 | 460 | 10 |
| 3 | 3 | 690 | 15 |
| 4 | 5 | 1000 | 25 |
| Experiment Number | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Groups | Output Current (A) | Current Density (mA/cm2) | Time (min) | pH | COD Value (mg/L) | COD Removal Rate % |
| 1 | 1.199 | 5.995 | 15 | 2.97 | 37.6667 | 1.74 |
| 2 | 1.199 | 5.995 | 30 | 5.03 | 33.0000 | 13.91 |
| 3 | 1.199 | 5.995 | 45 | 6.95 | 34.6667 | 9.57 |
| 4 | 1.199 | 5.995 | 60 | 8.92 | 21.6667 | 19.75 |
| 5 | 1.599 | 7.995 | 15 | 5.00 | 36.3333 | 9.21 |
| 6 | 1.599 | 7.995 | 30 | 3.02 | 18.0000 | 28.95 |
| 7 | 1.599 | 7.995 | 45 | 8.99 | 42.0000 | 65.79 |
| 8 | 1.599 | 7.995 | 60 | 7.00 | 12.3333 | 54.32 |
| 9 | 1.906 | 9.530 | 15 | 7.00 | 23.6667 | 6.58 |
| K1 | 0.450 | 0.478 | 0.668 | 4.576 | ||
| K2 | 1.583 | 1.194 | 1.194 | |||
| K3 | 1.217 | 1.556 | 1.556 | |||
| K4 | 1.326 | 1.347 | 1.515 | |||
| 0.113 | 0.120 | 0.167 | 0.396 | |||
| 0.385 | 0.299 | 0.299 | ||||
| 0.304 | 0.389 | 0.389 | ||||
| 0.332 | 0.337 | 0.379 | ||||
| R | 0.272 | 0.269 | 0.222 | |||
| Drug | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| (NH4)6Mo7O24 | 0.0011 |
| H3BO3 | 0.0015 |
| FeSO4 | 0.004 |
| CuSO4 | 0.0015 |
| MnCl2 | 0.005 |
| ZnSO4 | 0.022 |
| CoCl2 | 0.0016 |
| CaCl2 | 0.0052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leng, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, H. Decomposition of Phosphorus Pollution and Microorganism Analysis Using Novel CW-MFCs under Different Influence Factors. Molecules 2023, 28, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052124
Leng C, Yuan Y, Zhang Z, Shi Q, Li F, Wang H. Decomposition of Phosphorus Pollution and Microorganism Analysis Using Novel CW-MFCs under Different Influence Factors. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeng, Chunpeng, Yonggang Yuan, Zhiyu Zhang, Qiushi Shi, Fuping Li, and Hao Wang. 2023. "Decomposition of Phosphorus Pollution and Microorganism Analysis Using Novel CW-MFCs under Different Influence Factors" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052124
APA StyleLeng, C., Yuan, Y., Zhang, Z., Shi, Q., Li, F., & Wang, H. (2023). Decomposition of Phosphorus Pollution and Microorganism Analysis Using Novel CW-MFCs under Different Influence Factors. Molecules, 28(5), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052124





