One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b—5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[18F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole—A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregates
Abstract
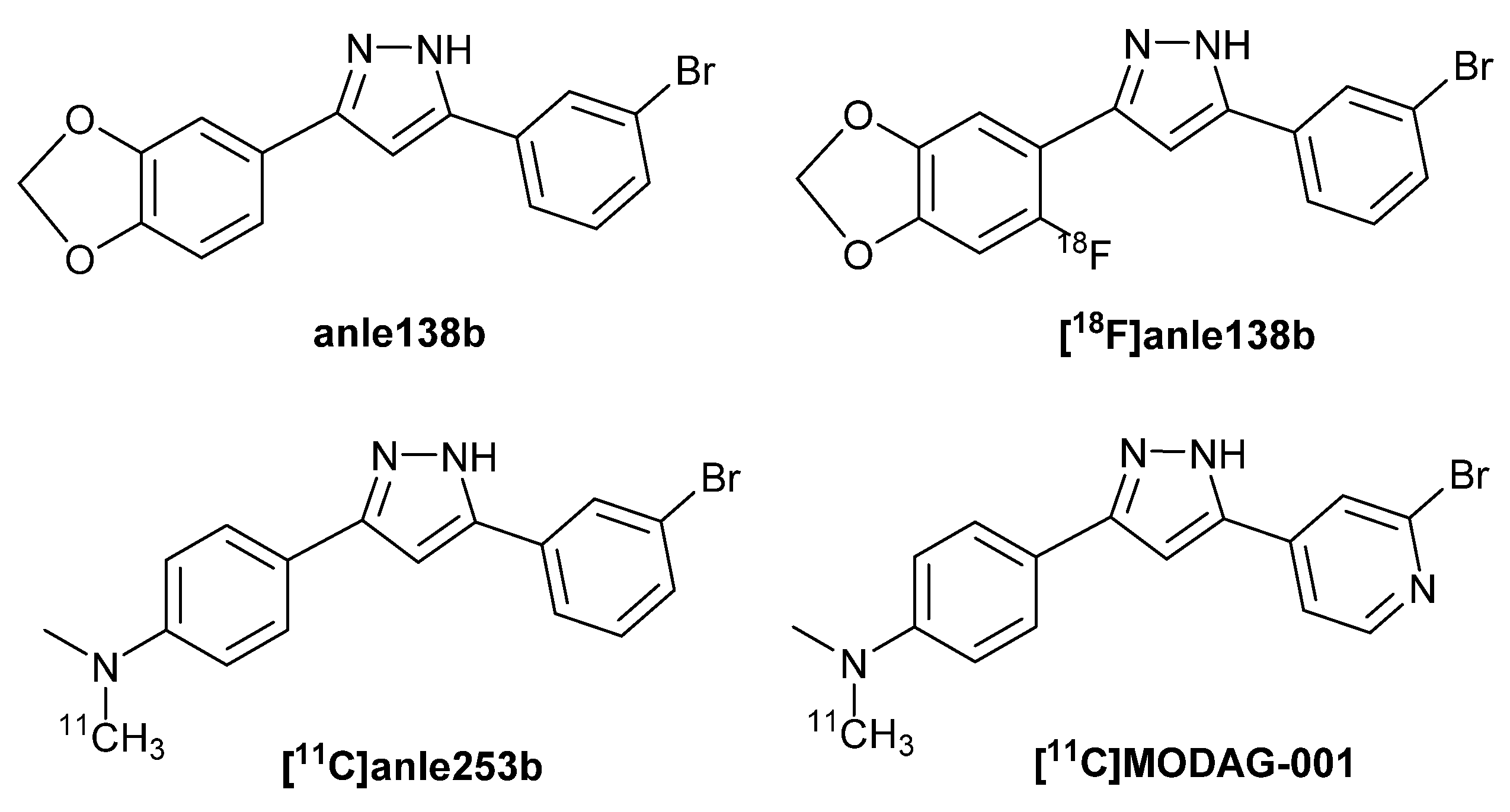
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
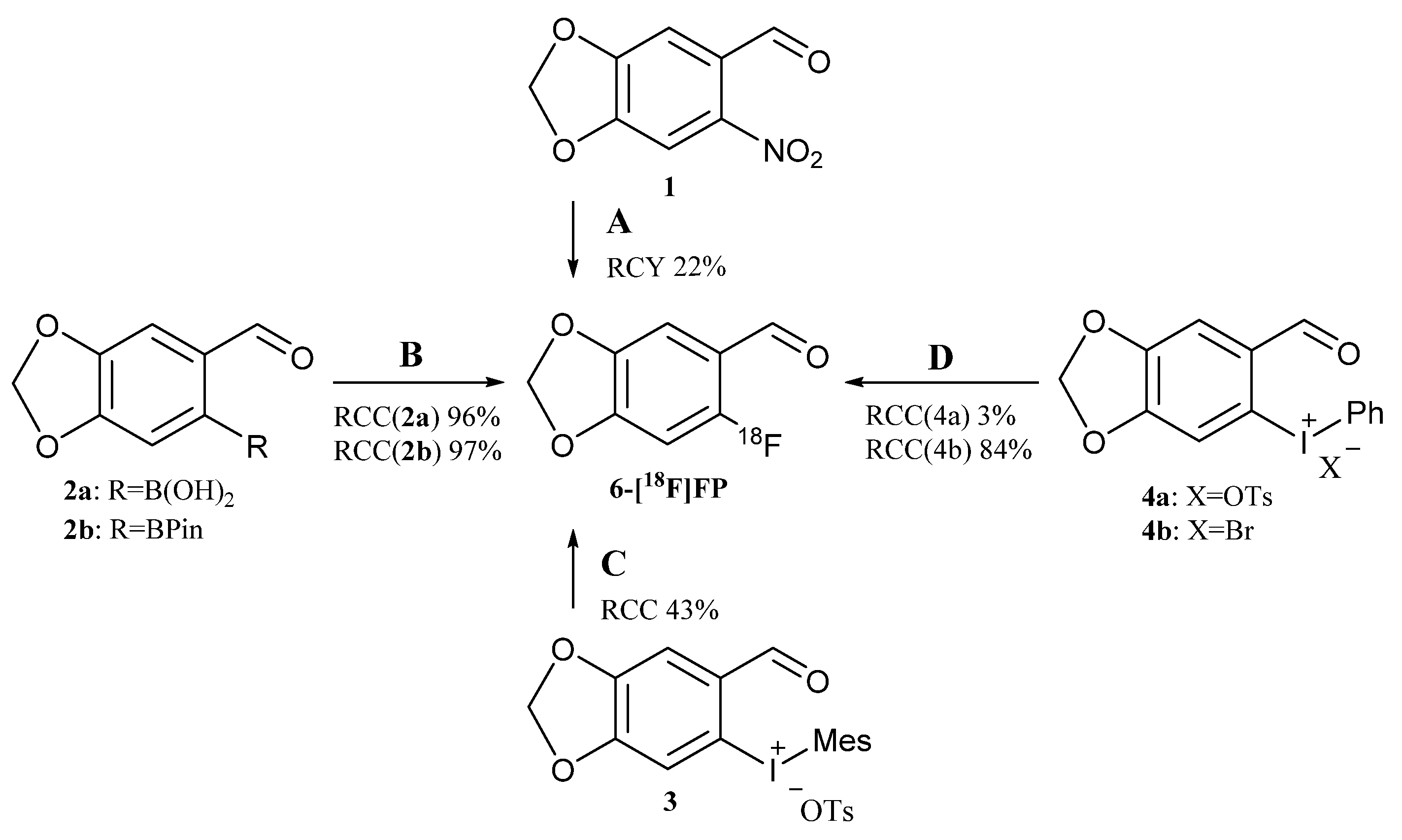
2.1. Radiolabeling Approach for [18F]Anle138b
2.2. Synthesis of 6-[18F]FP via Copper-Mediated 18F-Fluorodeboronation (Method B)
2.3. Synthesis of 6-[18F]FP via Diaryliodonium Salts Precursors (Methods C and D)
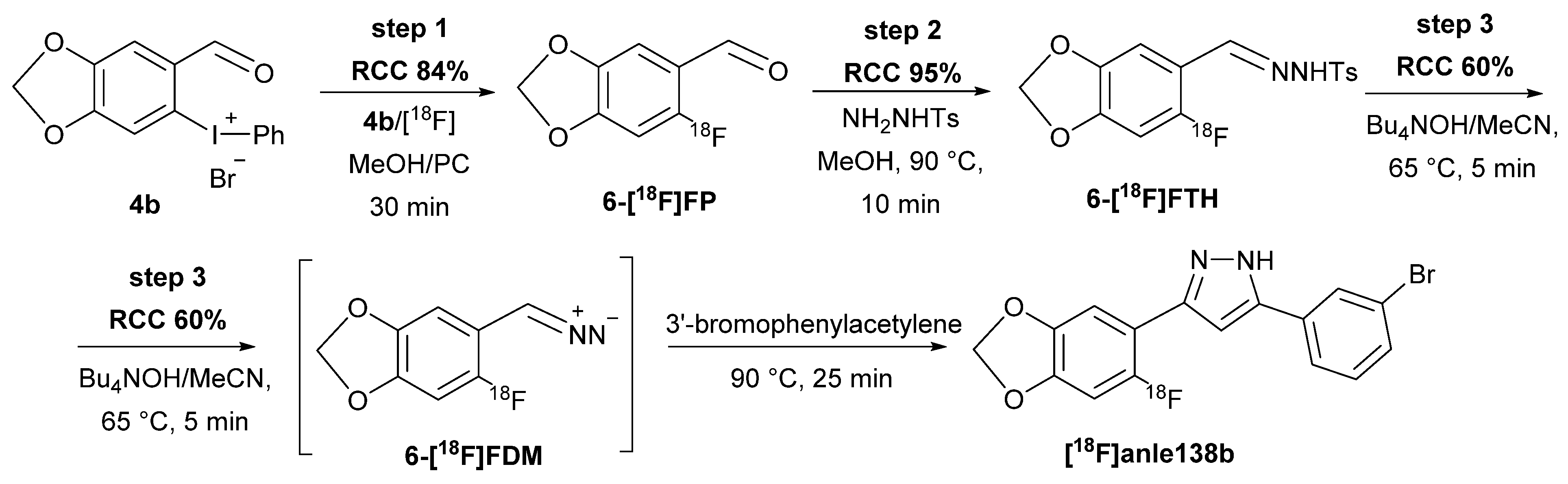
2.4. Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b
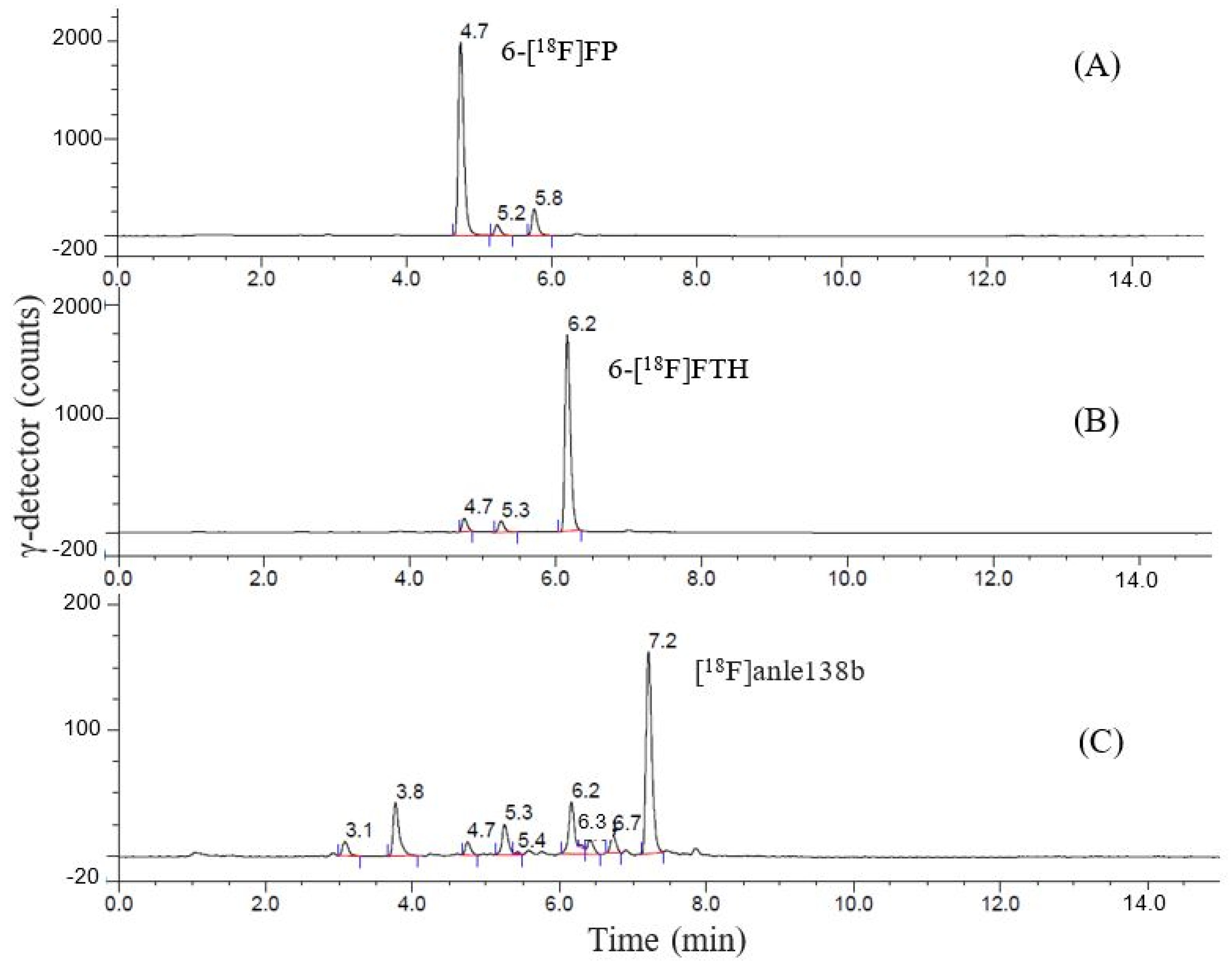
2.5. Purification and Quality Control of [18F]Anle138b
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Chemistry
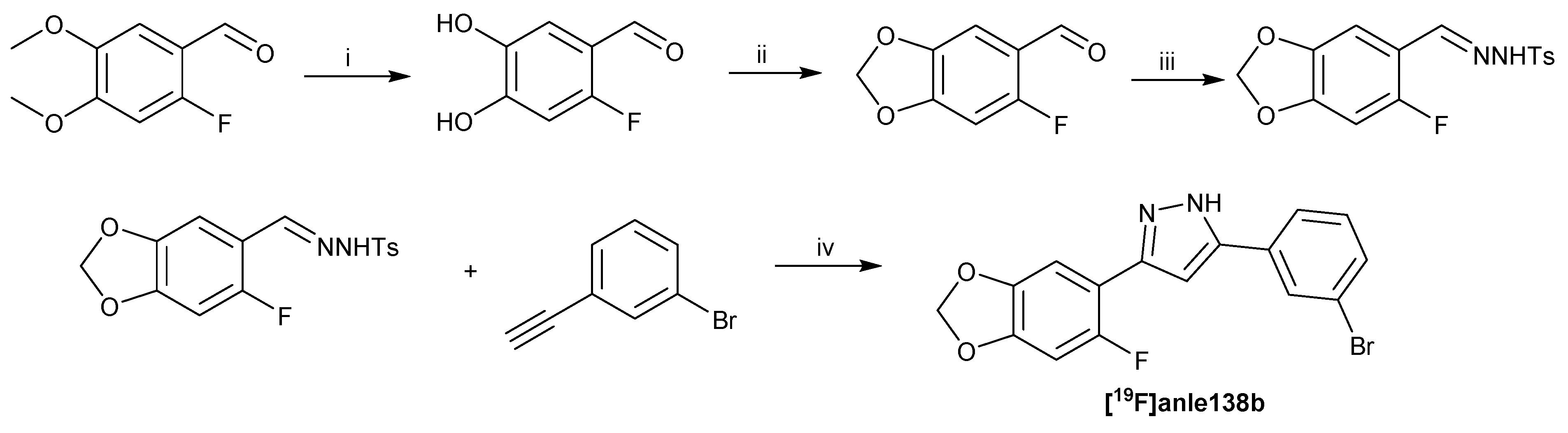
3.1.1. The 4 Steps Synthesis of 3-(6-Fluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-(3-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrazole ([19F]Anle138b) (Scheme 3)
2-Fluoro-4,5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde [49]
6-Fluorobenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-carbaldehyde [50]
N′-((6-Fluorobenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-yl)methylene)-4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide
(6-Fluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-(3-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrazole ([19F]Anle138b)
3.1.2. (6-Formylbenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-yl)(phenyl)iodonium Bromide (4b) (Figure 2) [44]
3.1.3. (6-Formylbenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-yl)(phenyl)iodonium Tosylate (4a) (Figure 2)
3.1.4. (6-Formylbenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-yl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)iodonium Bromide
3.1.5. (6-Formylbenzo-1,3-dioxole-5-yl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)iodonium Tosylate (3) (Figure 2)
3.2. Radiochemistry
3.2.1. General
3.2.2. Production of [18F]Fluoride
3.2.3. Synthesis of 6-[18F]Fluoropiperonal (6-[18F]FP)
3.2.4. Synthesis of [18F]Anle138b from 4b (Scheme 2)
3.2.5. HPLC Purification
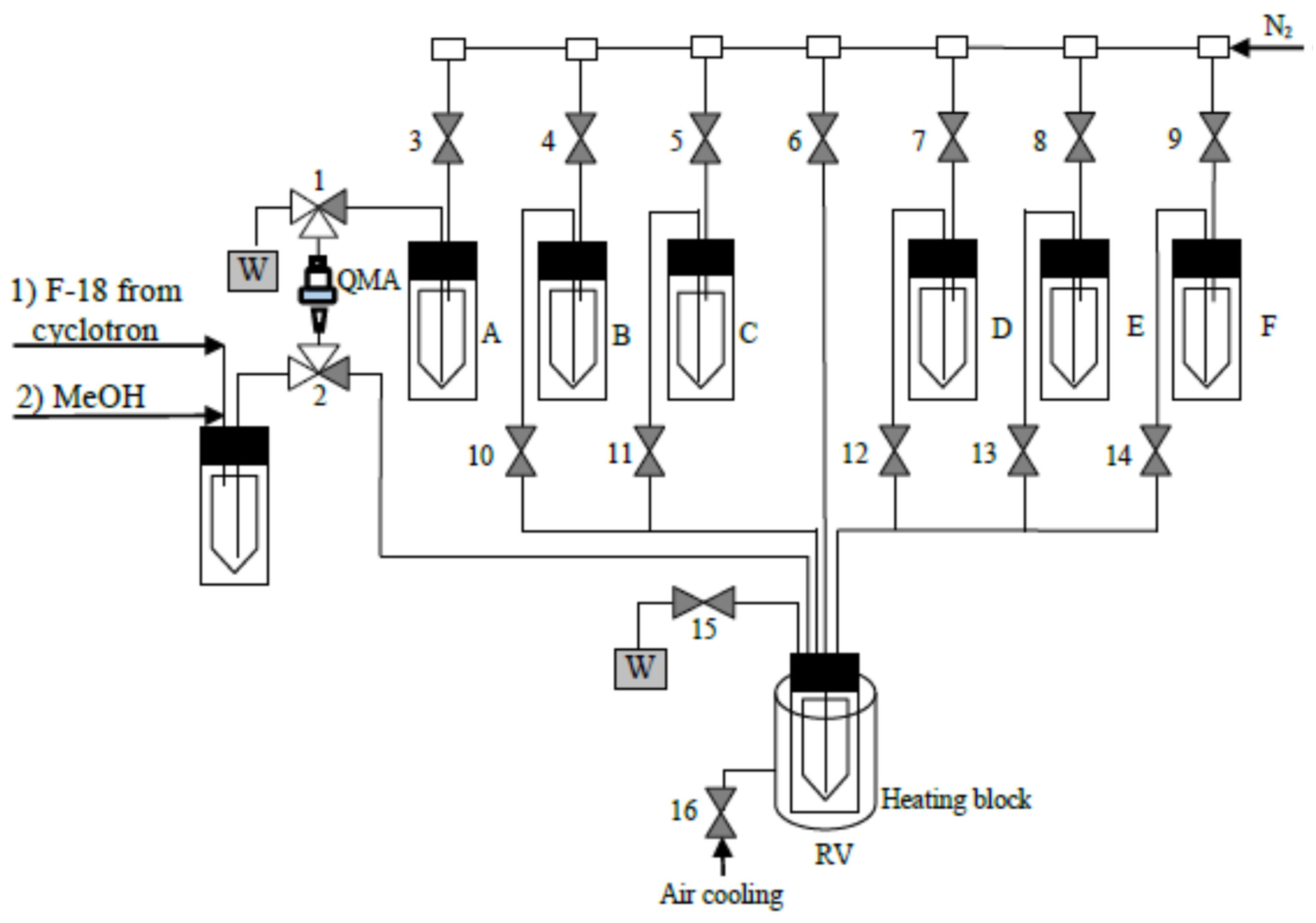
3.3. Semi-Automated Synthesis of [18F]Anle138b (Figure 5)
- Loading of [18F]fluoride (9.0–11.0 GBq) onto a QMA anion exchange cartridge.
- Washing of the cartridge with MeOH (2 mL) and drying with N2 gas for 2 min.
- Elution of [18F]fluoride from the QMA cartridge with a solution of 4b (20 µmol) in 44% MeOH/PC (0.9 mL) into reaction vessel (RV).
- Heating reaction mixture in the RV at 85 °C for 10 min with stirring by N2 with valve 16 open; then, valve 16 is closed and the reaction mixture is heated at 120 °C for 20 min.
- Cooling down RV to 40 °C; valve 16 is open.
- Addition of NH2NHTs (40 µmol) in MeOH (1 mL).
- Heating reaction mixture at 90 °C for 10 min with stirring by N2 gas..
- Cooling down RV to 65 °C.
- Addition of Bu4NOH (26 µmol) in MeCN (0.4 mL).
- Heating reaction mixture at 65 °C for 5 min; valve 16 is closed.
- Addition of the solution of 3′-bromophenylacetylene (0.4 mmol) in MeCN (0.4 mL) (valve 16 is open).
- Valve 16 is closed, heating reaction mixture in RV at 90 °C for 25 min.
- Cooling down RV to 40 °C; valve 16 is open.
- Loading reaction mixture (100 µL) into HPLC loop (HPLC system B).
- Isolation of the product using EtOH-H2O gradient system with flow rate of 4 mL/min.
- Manual collection of the product fraction into a vented collection vial.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Uzuegbunam, B.C.; Librizzi, D.; Hooshyar Yousefi, B. PET radiopharmaceuticals for Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease diagnosis, the current and future landscape. Molecules 2020, 25, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, E.S.; Firnau, G.; Nahmias, C. Dopamine visualized in the basal ganglia of living man. Nature 1983, 305, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, F.F.; Calabria, E.; Gangemi, V.; Cascini, G.L. Current status and future challenges of brain imaging with [18F]-DOPA PET for movement disorders. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 19, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioka, C.; Fotopoulos, A.; Kyritsis, A.P. Recent advances in PET imaging for evaluation of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2010, 37, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrone, A.; Halldin, C. New developments of dopaminergic imaging in Parkinson’s disease. Q.J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2012, 56, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schou, M.C.; Steiger, C.; Varrone, A.; Guilloteau, D.; Halldin, C. Synthesis, radiolabeling and preliminary in vivo evaluation of [18F]FE-PE2I, a new probe for the dopamine transporter. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 19, 4843–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, P.; Svenningsson, P.; Cselényi, Z.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L.; Varrone, A. Nigrostriatal dopamine transporter availability in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, A.; Stewart, T.; Zhang, J. Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker for Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, M. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers—Neurotoxic Molecules in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Lewy Body Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskey, M.J.; Perez, R.G.; Manfredsson, F.P. The contribution of alpha synuclein to neuronal survival and function—Implications for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Filamentous Inclusions of Lewy Bodies from Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korat, Š.; Bidesi, N.S.R.; Bonanno, F.; Di Nanni, A.; Hoàng, A.N.N.; Herfert, K.; Maurer, A.; Battisti, U.M.; Bowden, G.D.; Thonon, D.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein PET tracer development-an overview about current efforts. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.; Rouvière, L.; Giorla, E.; Farrugia, C.; El Waly, B.; Poindron, P.; Callizot, N. Alpha-Synuclein: The Spark That Flames Dopaminergic Neurons, In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, S.; Theis, H.; Banwinkler, M.; van Eimeren, T. Molecular Imaging in Parkinsonian Disorders-What’s New and Hot? Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzghool, O.M.; van Dongen, G.; van de Giessen, E.; Schoonmade, L.; Beaino, W. α-Synuclein Radiotracer Development and In Vivo Imaging: Recent Advancements and New Perspectives. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capotosti, F.; Vokali, E.; Molette, J.; Ravache, M.; Delgado, C.; Kocher, J.; Pittet, L.; Vallet, C.; Serra, A.; Piorkowska, K.; et al. Discovery of [18F]ACI-12589, a Novel and Promising PET-Tracer for Alpha-Synuclein. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, e064680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Levin, J.; Shi, S.; Schmidt, F.; Prix, C.; Pan-Montojo, F.; Bertsch, U.; Mitteregger-Kretzschmar, G.; et al. Anle138b: A novel oligomer modulator for disease-modifying therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as prion and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 795–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.; Schmidt, F.; Boehm, C.; Prix, C.; Bötzel, K.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Griesinger, C.; Giese, A. The Oligomer Modulator anle138b Inhibits Disease Progression in a Parkinson Mouse Model Even with Treatment Started after Disease Onset. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 779–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeg, A.A.; Reiner, A.M.; Schmidt, F.; Schueder, F.; Ryazanov, S.; Ruf, V.C.; Giller, K.; Becker, S.; Leonov, A.; Griesinger, C.; et al. Anle138b and related compounds are aggregation specific fluorescence markers and reveal high affinity binding to α-synuclein aggregates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1850, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Garvin, A.; Weckbecker, D.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Griesinger, C.; Giese, A.; Wenning, G.K.; Stefanova, N. Anle138b modulates α-synuclein oligomerization and prevents motor decline and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.; Sing, N.; Melbourne, S.; Morgan, A.; Mariner, C.; Spillantini, M.G.; Wegrzynowicz, M.; Dalley, J.W.; Langer, S.; Ryazanov, S.; et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the oligomer modulator anle138b with exposure levels sufficient for therapeutic efficacy in a murine Parkinson model: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1a trial. EBioMedicine. 2022, 80, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.; Leonov, A.; Ryazanov, S.; Herfert, K.; Kuebler, L.; Buss, S.; Schmidt, F.; Weckbecker, D.; Linder, R.; Bender, D.; et al. 11C Radiolabeling of anle253b: A Putative PET Tracer for Parkinson’s Disease That Binds to α-Synuclein Fibrils in vitro and Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier. ChemMedChem. 2020, 15, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebler, L.; Buss, S.; Leonov, A.; Ryazanov, S.; Schmidt, F.; Maurer, A.; Weckbecker, D.; Landau, A.M.; Lillethorup, T.P.; Bleher, D.; et al. 11CMODAG-001-towards a PET tracer targeting α-synuclein aggregates. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2021, 48, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.R.; Madsen, C.A.; Shalgunov, V.; Nasser, A.; Battisti, U.M.; Beaman, E.E.; Juhl, M.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Herth, M.M.; Hansen, H.D.; et al. Evaluation of the α-synuclein PET radiotracer (d3)-[11C]MODAG-001 in pigs. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2022, 114–115, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, H.H.; Ermert, J. 18F-labelling innovations and their potential for clinical application. Clin. Transl. Imaging. 2018, 6, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, R.N.; Orlovskaya, V.V. Phase Transfer Catalysts and Role of Reaction Environment in Nucleophilc Radiofluorinations in Automated Synthesizers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrad, F.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Urusova, E.A.; Neumaier, B. First radiosynthesis of F-18-labeled anle138b a potential tracer for imaging of neurodegenerative diseases associated with protein deposition in brain. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, S241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrad, F. Efficient Preparation of PET Tracers for Visualization of Age-Related Disorders Using Emerging Methods of Radiofluorination. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Koln, Koln, Germany, 2017. Available online: https://kups.ub.uni-koeln.de/7640/ (accessed on 12 January 2033).
- Preshlock, S.; Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. 18F-Labeling of Arenes and Heteroarenes for Applications in Positron Emission Tomography. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 719–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarganes-Tzitzikas, T.; Clemente, G.S.; Elsinga, P.H.; Dömling, A. MCR Scaffolds Get Hotter with 18F-Labeling. Molecules. 2019, 24, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, V.W. Hypervalent Aryliodine Compounds as Precursors for Radiofluorination. J. Label. Compds. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 196–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.S.; Kaur, T.; Preshlock, S.; Tanzeyl, S.S.; Winton, W.P.; Sharninghausen, L.S.; Wiesner, N.; Brooks, A.F.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Copper-mediated late-stage radiofuorination: Five years of impact on preclinical and clinical PET imaging. Clin. Transl. Imaging. 2020, 8, 167–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredwell, M.; Preshlock, S.M.; Taylor, N.J.; Gruber, S.; Huiban, M.; Passchier, J.; Mercier, J.; Genicot, C.; Gouverneur, V. A general copper-mediated nucleophilic 18F-luorination of arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7751–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossine, A.V.; Brooks, A.F.; Makaravage, K.J.; Miller, J.M.; Ichiishi, N.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Synthesis of [18F] Arenes via the Copper-Mediated [18F] Fluorination of Boronic Acids. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5780–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaravage, K.J.; Brooks, A.F.; Mossine, A.V.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Copper-Mediated Radiofluorination of Arylstannanes with [18F] KF. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5440–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischler, J.; Kolks, N.; Modemann, D.; Neumaier, B.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Alcohol-Enhanced Cu-Mediated Radiofluorination. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuganov, D.; Zykov, M.; Timofeev, V.; Timofeeva, K.; Antuganova, Y.; Fedorova, O.; Orlovskaya, V.; Krasikova, R. Copper-mediated radiofluorination of aryl pinacolboronate esters: A straightforward protocol using pyridinium sulfonates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossine, A.V.; Brooks, A.F.; Ichiishi, N.; Makaravage, K.J.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Development of Customized [18F] Fluoride Elution Techniques for the Enhancement of Copper-Mediated Late-Stage Radiofuorination. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Zischler, J.; Schäfer, D.; Urusova, E.A.; Guliyev, M.; Bannykh, O.; Endepols, H.; Neumaier, B. Discovery of 7-[18F]Fluorotryptophan as a Novel Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Probe for the Visualization of Tryptophan Metabolism in Vivo. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlovskaya, V.; Fedorova, O.; Kuznetsova, O.; Krasikova, R. Cu-Mediated Radiofluorination of Aryl Pinacolboronate Esters: Alcohols as Solvents with Application to 6-L-[18F]FDOPA Synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 7079–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovskaya, V.V.; Craig, A.S.; Fedorova, O.S.; Kuznetsova, O.F.; Neumaier, B.; Krasikova, R.N.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Production of 6-L-[18F] Fluoro-m-tyrosine in an Automated Synthesis Module for 11C-Labeling. Molecules. 2021, 26, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, V.W.; Aigbirhio, F.I. Reactions of cyclotron-produced [18F]fluoride with diaryliodonium salts—A novel single-step route to no-carrier-added [18F]fluoroarenses. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1995, 21, 2215–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richarz, R.; Krapf, P.; Zarrad, F.; Urusova, E.A.; Neumaier, B.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Neither azeotropic drying, nor base nor other additives: A minimalist approach to 18F-labeling. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8094–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiishi, N.; Brooks, A.F.; Topczewski, J.J.; Rodnick, M.E.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Copper-Catalyzed [18F]Fluorination of (Mesityl)(aryl)iodonium Salts. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlovskaya, V.V.; Modemann, D.J.; Kuznetsova, O.F.; Fedorova, O.S.; Urusova, E.A.; Kolks, N.; Neumaier, B.; Krasikova, R.N.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Alcohol-supported Cu-mediated 18F-fluorination of iodonium salts under “minimalist” conditions. Molecules. 2019, 24, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.H.; Lu, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Pike, V.W. Fast and high-yield microreactor syntheses of ortho-substituted [(18)F]fluoroarenes from reactions of [(18)F]fluoride ion with diaryliodonium salts. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 10–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; de Vicente, J.; Bonnert, R.V. A Novel One-Pot Method for the Preparation of Pyrazoles by 1,3-Dipolar Cycloadditions of Diazo Compounds Generated in Situ. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 5381–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, L.K.; Cantacuzene, D.; Nimitkitpaisan, Y.; McCulloh, D.; Padgett, W.L.; Daly, J.W.; Creveling, C.R. Synthesis and biological properties of 2-, 5-, and 6-fluoronorepinephrines. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Couture, A.; Deniau, E.; Grandclaudon, P.; Lebrun, S. A new approach to isoindoloisoquinolinones. A simple synthesis of nuevamine. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 6169–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entry | 2a/Cu(py)4(OTf)2, µmol | Radiofluorination Conditions | RCC, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10/20 | 2-PrOH/DMA a | 0; 5 |
| 2 | 10/20 | 2-PrOH/acetone a | 13; 26 |
| 3 | 10/20 | 2-PrOH a | 29 ± 20 (n = 3) |
| 4 | 20/20 | 2-PrOH a | 32 ± 22 (n = 3) |
| 5 | 20/20 | 2-PrOH/CH3CN b | 96 ± 2 (n = 6) |
| 6 | 10/10 | 2-PrOH/CH3CN b | 48 (n = 1) |
| 7 | 15/15 | 2-PrOH/CH3CN b | 86 (n = 1) |
| 8 | 20/15 | 2-PrOH/CH3CN b | 64 (n = 1) |
| Entry | Eluent Composition | Evaporation Step | Precursor/µmol | (CH3CN)4 CuOTf, µmol | Radiofluorination | RCC, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent, mL | T, °C/t, min | ||||||
| 1 | 3 (20 µmol) in 20% MeOH/DMF (0.72 mL) | - | - | 20 | MeOH/DMF (0.72) | 90/20 | 10 |
| 2 | 3 (20 µmol) in MeOH (1 mL) | + | - | 20 | DMF (0.5) | 90/20 | 0 |
| 3 | Et4NHCO3/MeOH (1 mL) | + | 3/20 | 20 | DMF (0.5) | 90/20 | 35 |
| 4 | Et4NHCO3/MeOH (1 mL) | + | 3/30 | 30 | DMF (0.5) | 90/20 | 43 |
| 5 | Bu4NOTs/MeOH (1 mL) | + | 3/20 | 20 | DMF (0.5) | 90/20 | 27 |
| 6 | Bu4NOTs/MeOH (1 mL) | + | 3/30 | 30 | DMF (0.5) | 90/20 | 52 |
| 7 | 4a (20 µmol) in 20% MeOH/DMF (0.72 mL) | - | - | - | MeOH/DMF (0.72) | 100/20 | 3 |
| 8 | 4a (20 µmol) in 20% MeOH/DMF (0.72 mL) | - | - | - | MeOH/DMF (0.72) | 140/20 | 11 |
| 9 | 4a (20 µmol) in MeOH (1 mL) | - | - | - | MeOH/DMSO (1/0.5) | 160/15 | 5 |
| 10 | 4a (20 µmol) in MeOH (1 mL) | + | - | - | DMSO (0.5) | 160/15 | 0 |
| 11 | Et4NHCO3/ MeOH (1 mL) | + | 4a/20 | - | DMSO (0.5) | 130/15 | 4 |
| 12 | Et4NHCO3/ MeOH (1 mL) | + | 4a/20 | - | DMSO (0.5) CH3CN (0.5) | 160/15 | 3 |
| 13 | Et4NHCO3/ MeOH (1 mL) | + | 4a/20 | - | DMSO (0.5) CH3CN (0.5) | 80/20 | 3 |
| 14 | 4a (20 µmol) in 44% MeOH/PC (0.9 mL) | - | - | - | MeOH/PC (0.9) | (1) 75–85/10 (2) 120/20 | 3 ± 1 (n = 3) |
| 15 | 4b (20 µmol) in MeOH (0.8 mL) | + | - | - | PC (0.6) | 110/15 | 0 |
| 16 | 4b (20 µmol) in 44% MeOH/PC (0.9 mL) | - | - | - | MeOH/PC (0.9) | (1) 75–85/10 (2) 120/20 | 84 ± 5 (n = 6) |
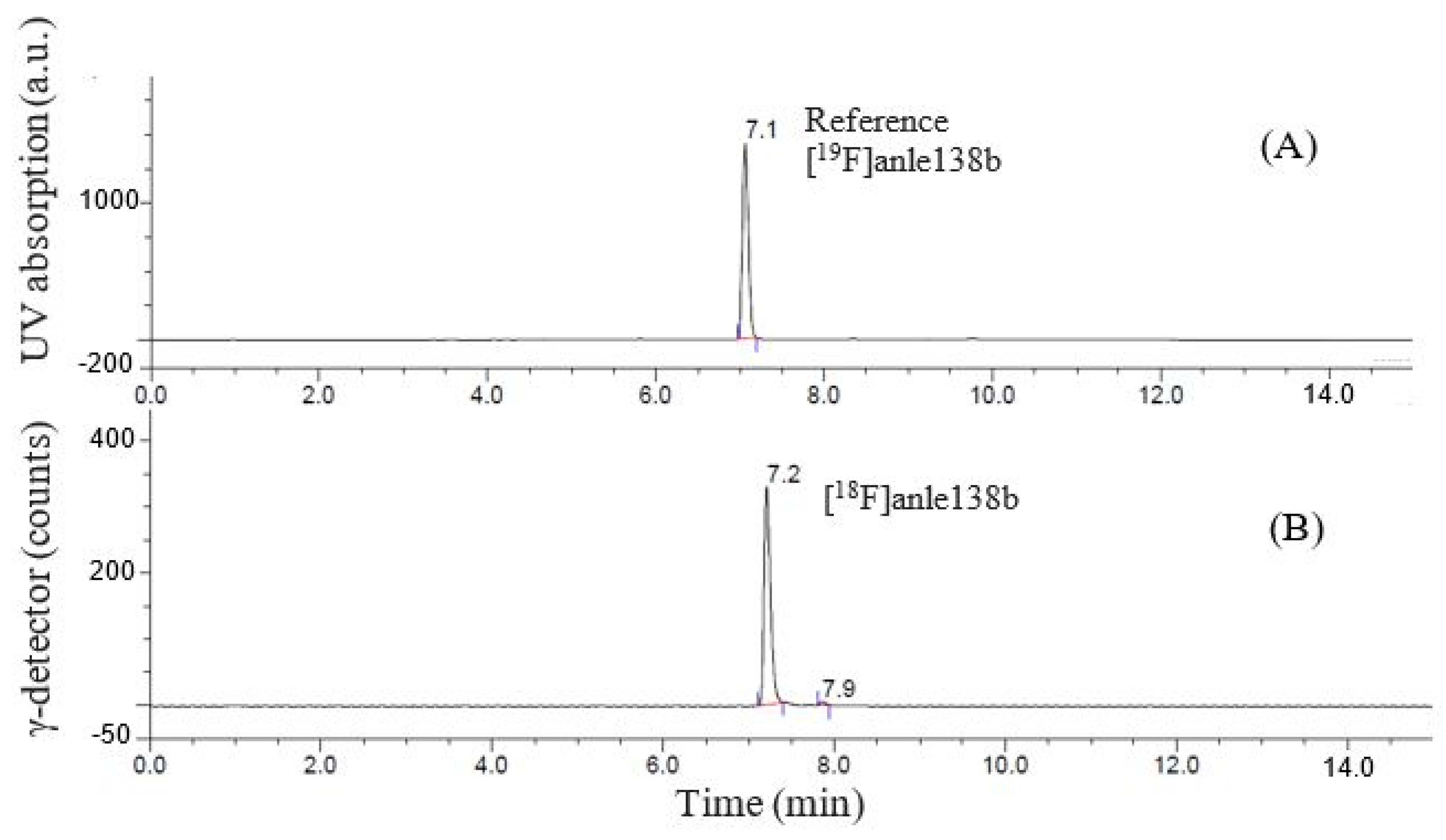
| Synthesis Step | Compound | Retention Time by γ-Detector, min | Retention Time by UV-254, min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor 4b | 2.9 | ||
| Step 1 | 6-[18F]FP | 4.7 | |
| 6-[19F]FP | 4.6 | ||
| Step 2 | 6-[18F]FTH | 6.1 | |
| Step 3 | [18F]anle138b | 7.1 | |
| Reference | [19F]anle138b | 7.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlovskaya, V.V.; Fedorova, O.S.; Viktorov, N.B.; Vaulina, D.D.; Krasikova, R.N. One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b—5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[18F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole—A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregates. Molecules 2023, 28, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062732
Orlovskaya VV, Fedorova OS, Viktorov NB, Vaulina DD, Krasikova RN. One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b—5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[18F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole—A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregates. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062732
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlovskaya, Viktoriya V., Olga S. Fedorova, Nikolai B. Viktorov, Daria D. Vaulina, and Raisa N. Krasikova. 2023. "One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b—5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[18F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole—A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregates" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062732
APA StyleOrlovskaya, V. V., Fedorova, O. S., Viktorov, N. B., Vaulina, D. D., & Krasikova, R. N. (2023). One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [18F]Anle138b—5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[18F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole—A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting α-Synuclein Aggregates. Molecules, 28(6), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062732





