Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitation and Identification of Caulerpa racemosa Carotenoids Content
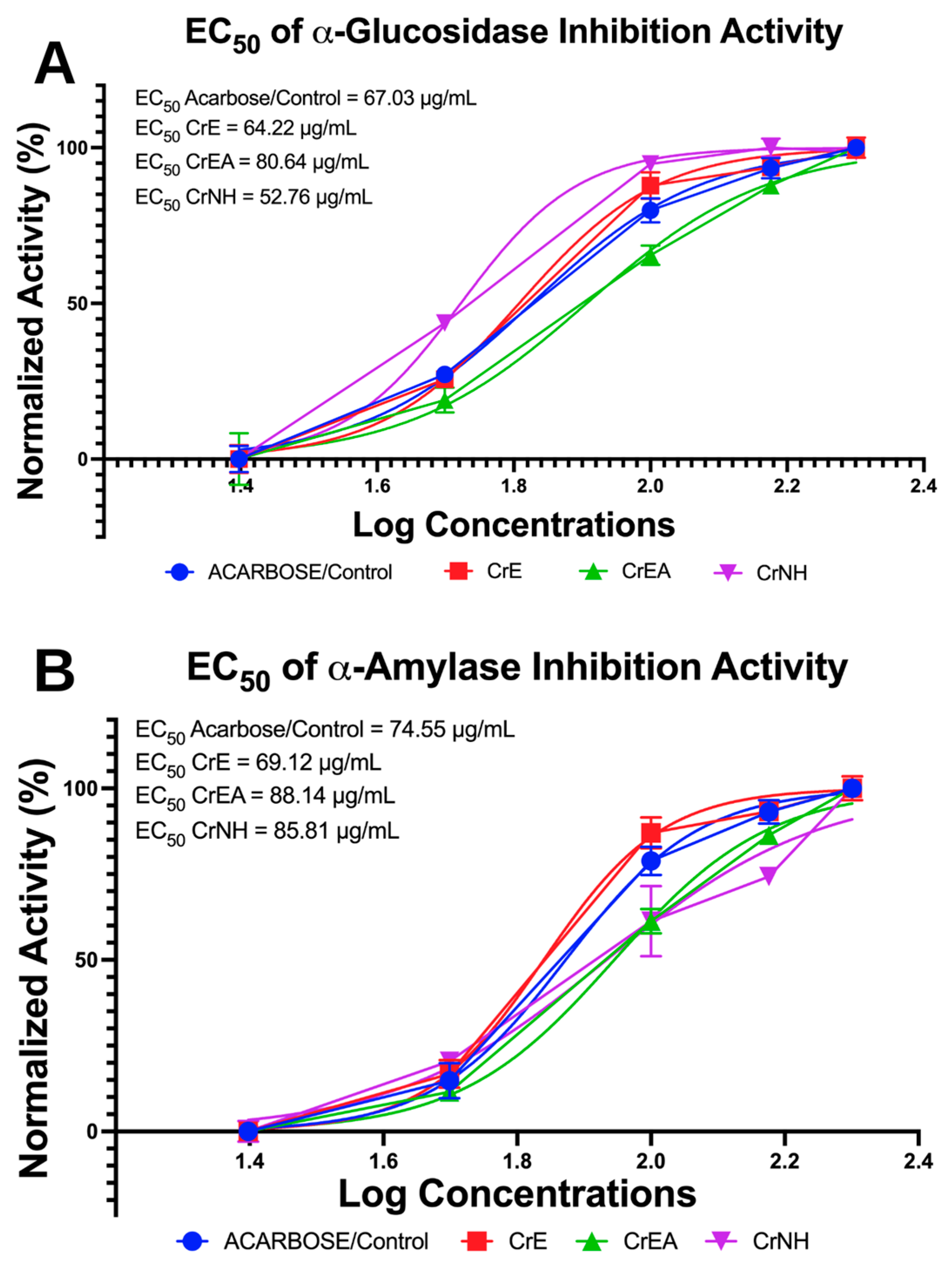
2.2. In Vitro Antidiabetic Evaluation via Carbohydrate (α-Glucosidase, α-Amylase) Hydrolyzing Enzyme Inhibition
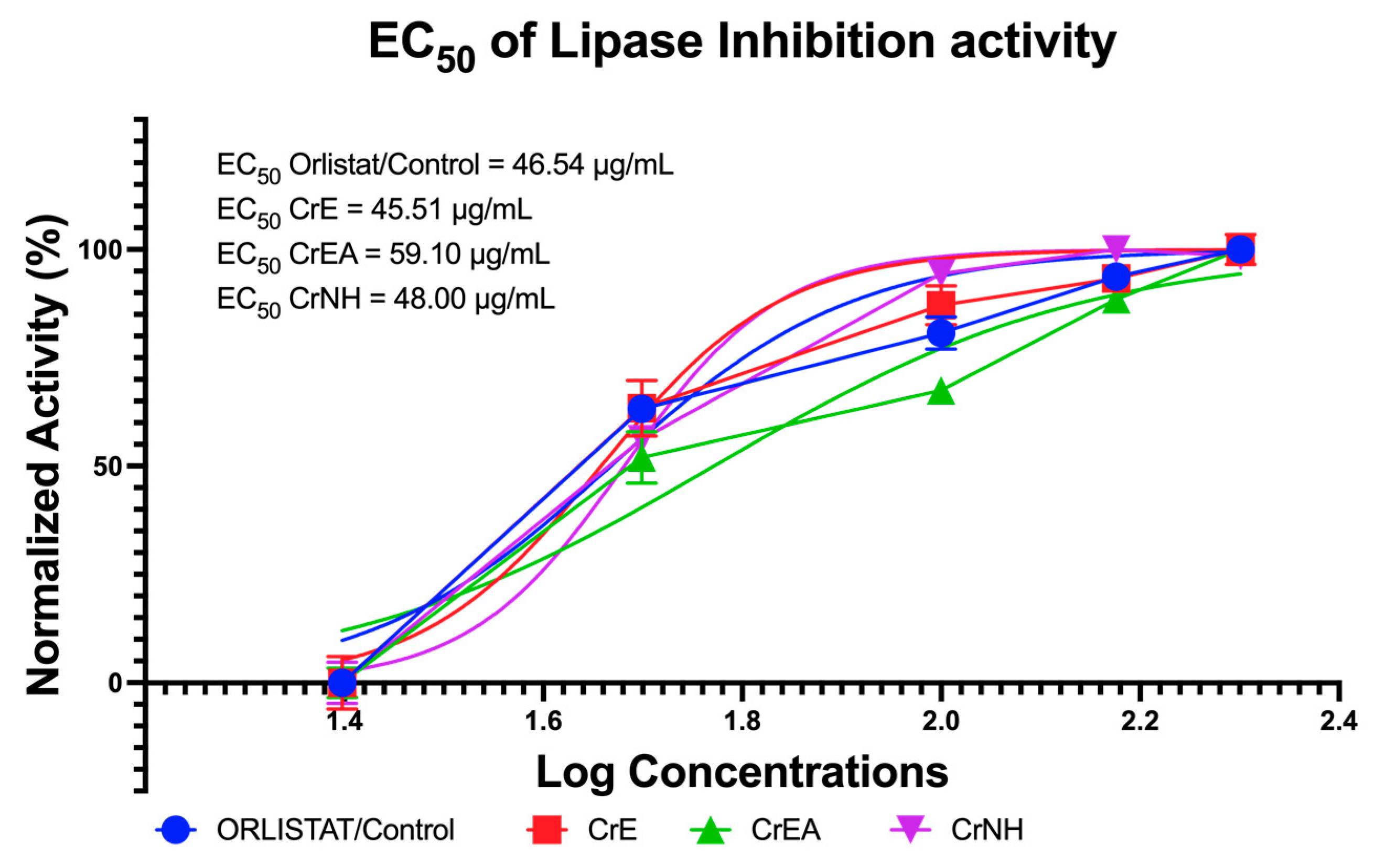
2.3. In Vitro Anti-Obesity Evaluation via Lipid (Lipase) Hydrolyzing Enzyme Inhibition
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation via MTT Assay in Normal Cell Lines
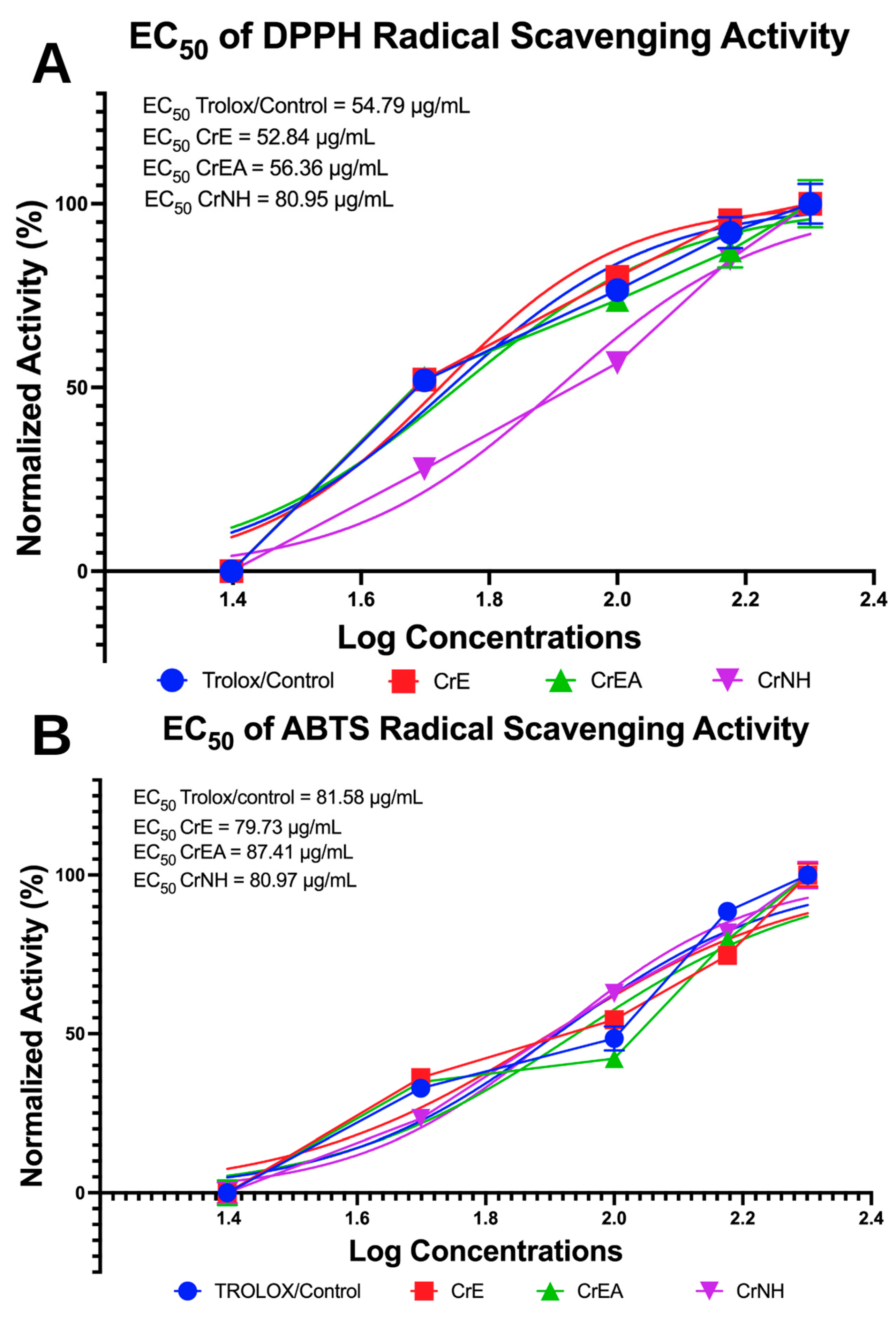
2.5. Antioxidant Capabilities Evaluation via DPPH and ABTS Inhibition Assays
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of Carotenoid Extract of C. racemosa
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
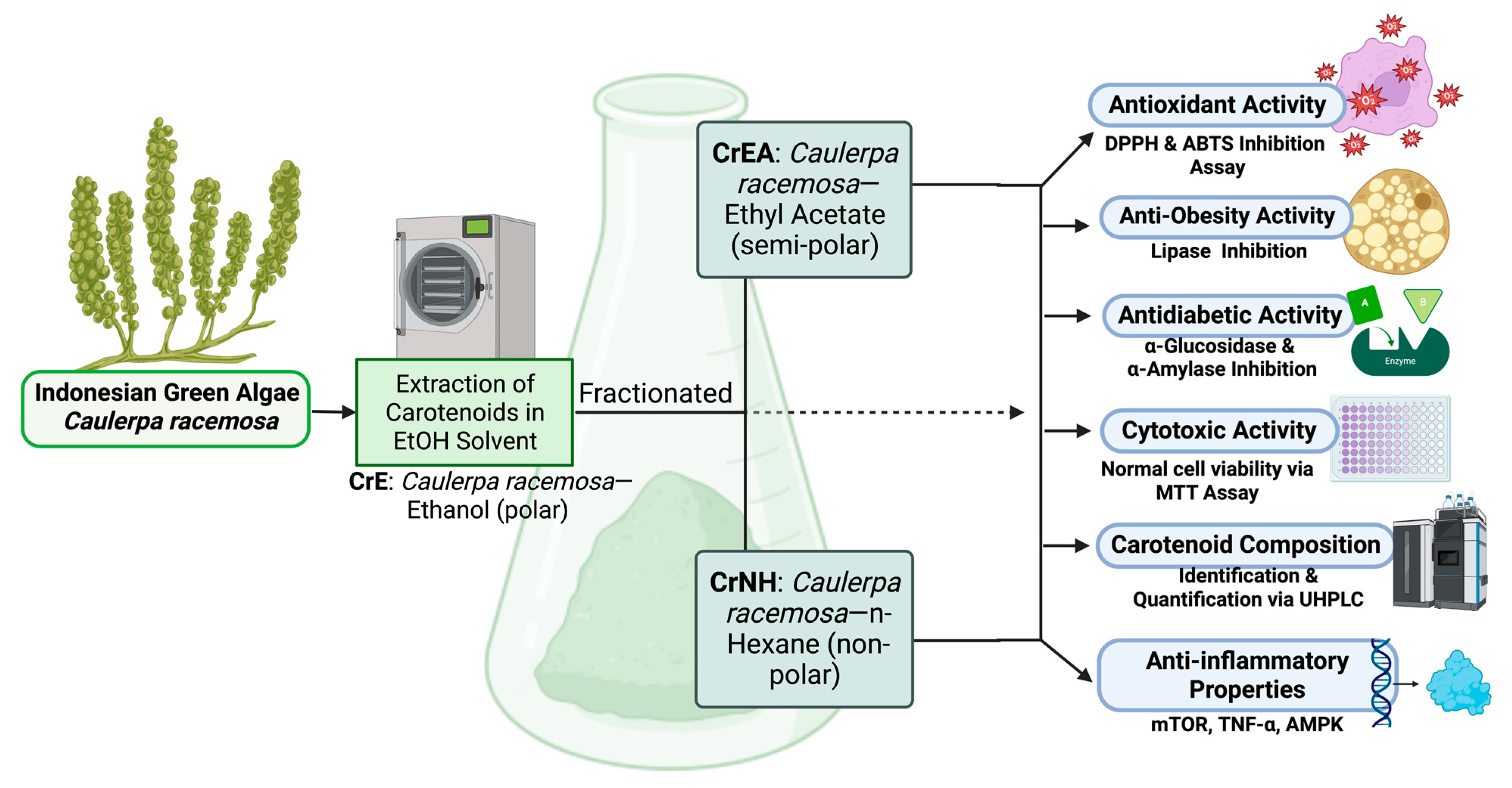
4.1. Preparation of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa
4.2. Extraction of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa
4.3. Carotenoid Identification and Analysis of Caulerpa racemosa via UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS
4.4. In Vitro Antidiabetic Assay via α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibition (%)
4.5. In Vitro Anti-Obesity Evaluation via Lipase Inhibition Assay (%)
4.6. Cytotoxicity Evaluation via MTT Assay
4.7. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assays via Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Kinase, AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK), and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) Expressions
4.8. Antioxidant Activity by DPPH and ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity Assay
4.9. Management Data and Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hoogeveen, E.K. The Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Wareham, N.J. Epidemiology of diabetes. Medicine 2022, 50, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman Asif, A.; Jürjens, J.; Chou, C.-Y.; Hsu, D.-Y.; Chou, C.-H. Predicting the Onset of Diabetes with Machine Learning Methods. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimäki, M.; Kuosma, E.; Ferrie, J.E.; Luukkonen, R.; Nyberg, S.T.; Alfredsson, L.; Batty, G.D.; Brunner, E.J.; Fransson, E.; Goldberg, M.; et al. Overweight, obesity, and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity: Pooled analysis of individual-level data for 120 813 adults from 16 cohort studies from the USA and Europe. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e277–e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Azevedo, I. Chronic inflammation in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 289645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jose, P.A. Coordinated Contribution of NADPH Oxidase- and Mitochondria-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic Syndrome and Its Implication in Renal Dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, D.; Seiglie, J.A.; Dunn, M.; Tschida, S.; Theilmann, M.; Marcus, M.E.; Brian, G.; Norov, B.; Mayige, M.T.; Gurung, M.S.; et al. The state of diabetes treatment coverage in 55 low-income and middle-income countries: A cross-sectional study of nationally representative, individual-level data in 680 102 adults. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e340–e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurwadjedi; Hartini, S.; Rosalina, L. Developing one map of national marine resources of Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 162, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widayanti, A.W.; Green, J.A.; Heydon, S.; Norris, P. Health-seeking behavior of people in Indonesia: A narrative review. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Prieto Lage, M.A.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. The potential of seaweeds as a source of functional ingredients of prebiotic and antioxidant value. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Nutrients and bioactive potentials of edible green and red seaweed in Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Kang, S.; Moon, M.; Choi, J.; Choi, M.; Park, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Kim, B. Ulvophyte Green Algae Caulerpa lentillifera: Metabolites Profile and Antioxidant, Anticancer, Anti-Obesity, and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, I.H.; Bandaranayake, U.; Keerthirathna, L.R.; Manawadu, C.; Silva, R.M.; Mohamed, B.; Rizwan, A.; Peiris, D.C. Integration of in vitro and in-silico analysis of Caulerpa racemosa against antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Hardinsyah, H.; Taslim, N.A.; Sabrina, N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Visnu, J.; Kumalawati, D.A.; Febriana, S.A.; Sudargo, T.; et al. Metabolomic Assay, Computational Screening, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Caulerpa racemosa as an Anti-obesity with Anti-aging by Altering Lipid Profile and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator 1-α Levels. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 939073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Augusta, P.S.; Mayulu, N.; Kuswari, M.; Taslim, N.A.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Batubara, S.C.; Ben Gunawan, W. Kombucha tea from seagrapes (Caulerpa racemosa) potential as a functional anti-ageing food: In vitro and in vivo study. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Firani, N.K.; Prijadi, B.; Irnandi, D.F.; Riawan, W.; Yusuf, M.; Amar, N.; Chandra, L.A.; Yusuf, V.M.; Subali, A.D.; et al. Kombucha drink enriched with sea grapes (Caulerpa racemosa) as potential functional beverage to contrast obesity: An in vivo and in vitro approach. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Sirisha, V.L. Algal Carotenoids. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohibbullah, M.; Haque, M.N.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Hossain, M.T.; Zahan, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Hannan, M.A.; Moon, I.S.; Choi, J.S. A Systematic Review on Marine Algae-Derived Fucoxanthin: An Update of Pharmacological Insights. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Nishikawa, S.; Beppu, F.; Tsukui, T.; Abe, M.; Hosokawa, M. The allenic carotenoid fucoxanthin, a novel marine nutraceutical from brown seaweeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, K.; Hosokawa, M. Biosynthetic pathway and health benefits of fucoxanthin, an algae-specific xanthophyll in brown seaweeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13763–13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçln, S.; Karakaş, Ö.; Okudan, E.S.; Başkan, K.S.; Çekiç, S.D.; Apak, R. HPLC Detection and Antioxidant Capacity Determination of Brown, Red and Green Algal Pigments in Seaweed Extracts. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, V.; June Chelyn, L.; Vimala, S.; Mohd Fairulnizal, M.N.; Brownlee, I.A.; Amin, I. Carotenoid composition and antioxidant potential of Eucheuma denticulatum, Sargassum polycystum and Caulerpa lentillifera. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butnariu, M. Methods of Analysis (Extraction, Separation, Identification and Quantification) of Carotenoids from Natural Products. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2016, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. Nutraceutical effects of fucoxanthin for obesity and diabetes therapy: A review. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbia, D.; De Martin, S. Brown Seaweeds for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.W.; Hauser, J.; Nakamura, Y.; Kanaya, S. Dietary seaweeds and obesity. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lem, D.W.; Davey, P.G.; Gierhart, D.L.; Rosen, R.B. A systematic review of carotenoids in the management of age-related macular degeneration. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gersh, B.J.; Sliwa, K.; Mayosi, B.M.; Yusuf, S. Novel therapeutic concepts: The epidemic of cardiovascular disease in the developing world: Global implications. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, K.; Tousoulis, D.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Stefanadi, E.; Stefanadis, C. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: From pathophysiology to risk stratification. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 138, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Remón, A.; Kirwan, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Dietary patterns and the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and neurodegenerative diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 262–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, E.; Chen, F.; Xiao, J.; Wang, M. Neuroprotective Phytochemicals in Experimental Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms and Potential Clinical Applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6687386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gateau, H.; Solymosi, K.; Marchand, J.; Schoefs, B. Carotenoids of Microalgae Used in Food Industry and Medicine. Mini-Reviews Med. Chem. 2016, 17, 1140–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin promotes translocation and induction of glucose transporter 4 in skeletal muscles of diabetic/obese KK-Ay mice. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Valko, M. Health protective effects of carotenoids and their interactions with other biological antioxidants. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 70, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordi, R.C.; Ademosun, O.T.; Ajanaku, C.O.; Olanrewaju, I.O.; Walton, J.C. Free radical mediated oxidative degradation of carotenes and xanthophylls. Molecules 2020, 25, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Update on natural food pigments—A mini-review on carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains. Food Res. Int. 2019, 124, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, V.; Deep, G.; Singh, R.K.; Palle, K.; Yadav, U.C.S. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, O.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Hu, L.; Lei, X. Antioxidant for treatment of diabetic complications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.C.; Lin, L.X.; Hu, X.F.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.P.; Zhang, R.Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, W.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shu, Y.; et al. AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, F.; Iblhoulen, Y.; Issaadi, H.; Elsebai, M.F.; Madani, K.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants of bejaia localities from algeria to prevent and treat coronavirus (COVID-19) infection shortened title: Phytomedicine to manage COVID-19 pandemic. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Hardinsyah, H.; Gunawan, W.B.; Kusuma, R.J.; Yusuf, V.M.; Pramono, A.; Kang, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yu, G.; Liang, Y.; Song, T.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Inhibitory effects of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from edible red alga Bangia fusco-purpurea on α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, L.; Bianchi, S. Role of nutraceutical SIRT1 modulators in AMPK and mTOR pathway: Evidence of a synergistic effect. Nutrition 2017, 34, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Gunawan, W.B.; Yusuf, V.M.; Yusuf, M.; Kusuma, R.J.; Sabrina, N.; Muharram, F.R.; Taslim, N.A.; Mayulu, N.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota and markers of metabolic syndrome in mice on cholesterol and fat enriched diet by butterfly pea flower kombucha. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Observed Compounds | RT (min) | Selected Ion | Observed MW | Peak | PubChem CID | Molecular Formula | * CAS Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fucoxanthin | 16.55 | [M + H–H2O]+ | 658.8780 | 1 | 5281239 | C42H58O6 | 3351-86-8 |
| Lutein | 19.20 | [M + H–H2O]+ | 568.4237 | 2 | 5281243 | C40H56O2 | 127-40-2 |
| Astaxanthin | 20.15 | [M + H]+ | 596.5901 | 3 | 5281224 | C40H52O4 | 472-61-7 |
| Canthaxanthin | 22.31 | [M + H]+ | 564.7006 | 4 | 5281227 | C40H52O2 | 514-78-3 |
| Zeaxanthin | 21.18 | [M]+ | 568.7206 | 5 | 5280899 | C40H56O2 | 144-68-3 |
| β-Cryptoxanthin | 23.70 | [M]+ | 552.8836 | 6 | 5281235 | C40H56O | 472-70-8 |
| Samples | β-Carotene | β-Cryptoxanthin | Fucoxanthin | Astaxanthin | Canthaxanthin | Zeaxanthin | Lutein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrE | 20.50 ± 0.10 x | 2.30 ± 0.10 x | 1.40 ± 0.01 x | 4.60 ± 0.10 x | 15.70 ± 0.50 x | 4.70 ± 0.01 x | 1.50 ± 0.50 x |
| CrEA | 11.70 ± 0.00 y | 4.00 ± 0.50 y | 2.70 ± 0.01 y | 3.00 ± 0.50 y | 9.55 ± 0.05 y | 6.50 ± 0.10 y | 4.50 ± 0.05 y |
| CrNH | 6.50 ± 0.55 z | 7.00 ± 0.01 z | 5.50 ± 0.50 z | 7.90 ± 0.05 z | 3.50 ± 0.01 z | 9.00 ± 0.05 z | 5.50 ± 0.55 y |
| Hours of Incubation | LC50 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CrE | CrEA | CrNH | |
| 24 h | 2314.00 | 2835.11 | 1351.29 |
| 48 h | 1568.00 | 1916.50 | 1001.54 |
| 6 h | 24 h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markers | CrE | CrEA | CrNH | CrE | CrEA | CrNH | |
| % Increase | AMPK | 30.96 | 21.16 | 25.00 | 54.20 | 41.76 | 38.46 |
| % Decrease | TNF-α | 28.73 | 16.13 | 15.83 | 49.70 | 41.40 | 39.46 |
| % Decrease | mTOR | 25.63 | 24.53 | 24.96 | 41.90 | 39.93 | 38.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurniawan, R.; Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Surya, R.; Gunawan, W.B.; Alisaputra, D.; Mayulu, N.; Salindeho, N.; Kim, B. Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073267
Kurniawan R, Nurkolis F, Taslim NA, Subali D, Surya R, Gunawan WB, Alisaputra D, Mayulu N, Salindeho N, Kim B. Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073267
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurniawan, Rudy, Fahrul Nurkolis, Nurpudji Astuti Taslim, Dionysius Subali, Reggie Surya, William Ben Gunawan, Darmawan Alisaputra, Nelly Mayulu, Netty Salindeho, and Bonglee Kim. 2023. "Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073267
APA StyleKurniawan, R., Nurkolis, F., Taslim, N. A., Subali, D., Surya, R., Gunawan, W. B., Alisaputra, D., Mayulu, N., Salindeho, N., & Kim, B. (2023). Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules, 28(7), 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073267













