Description of Chemical Synthesis, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization and Biological Activity of Estrane-Based Inhibitors/Activators of Steroidogenesis
Abstract
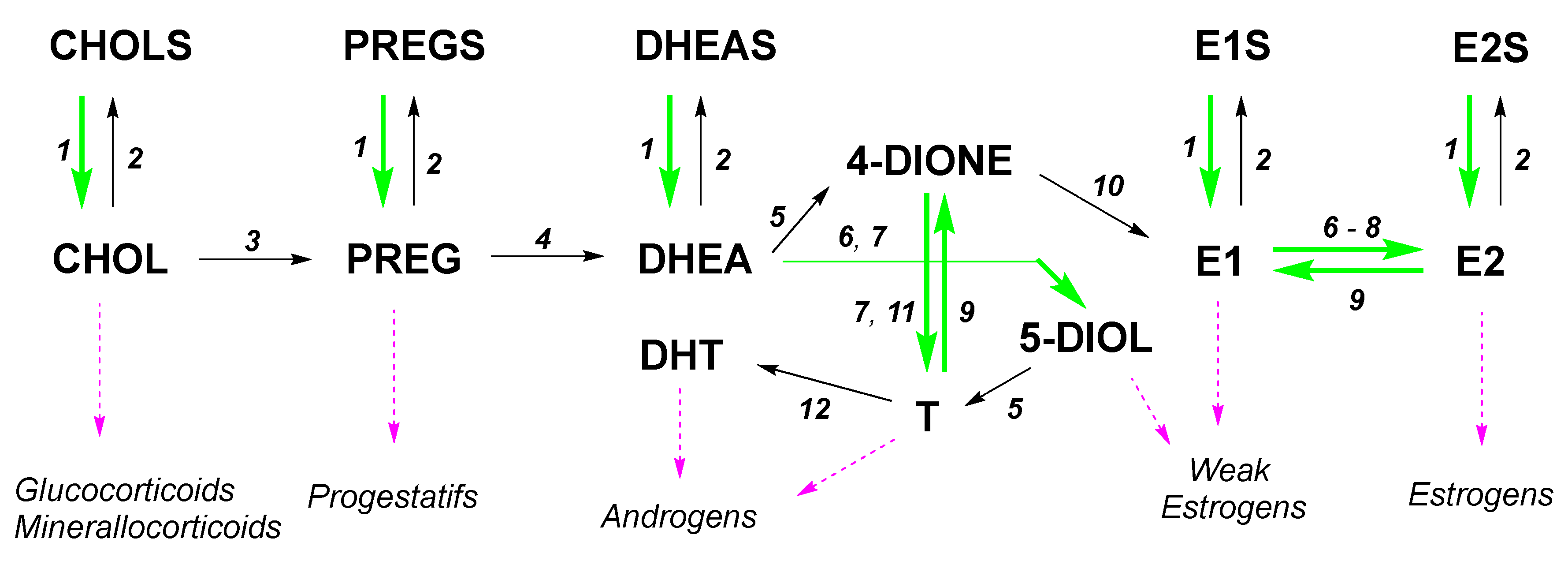
:1. Introduction
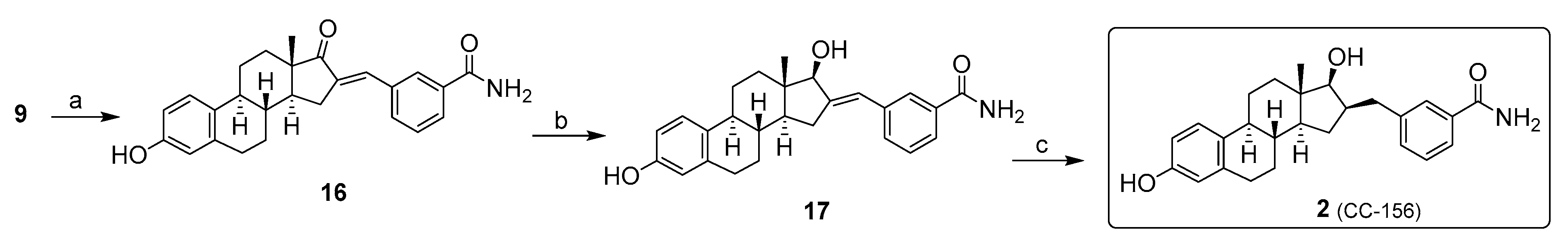
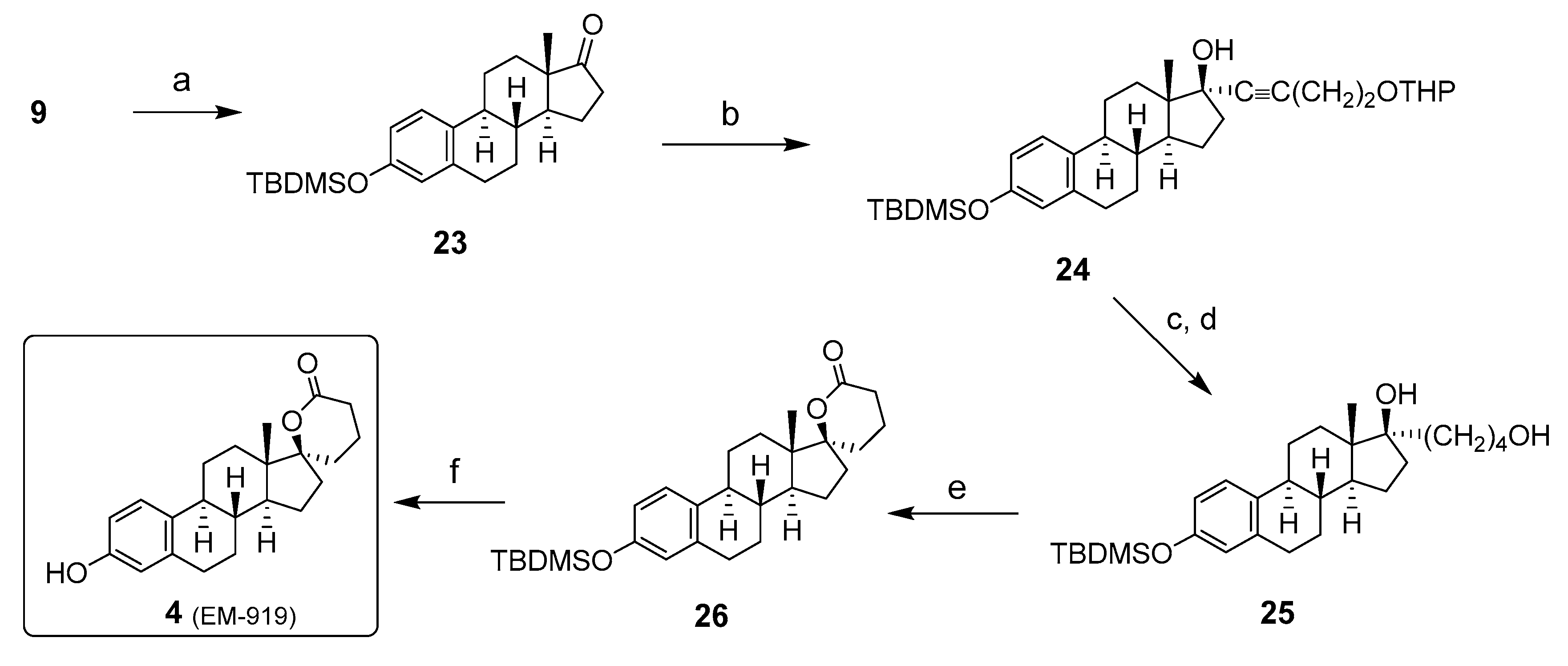
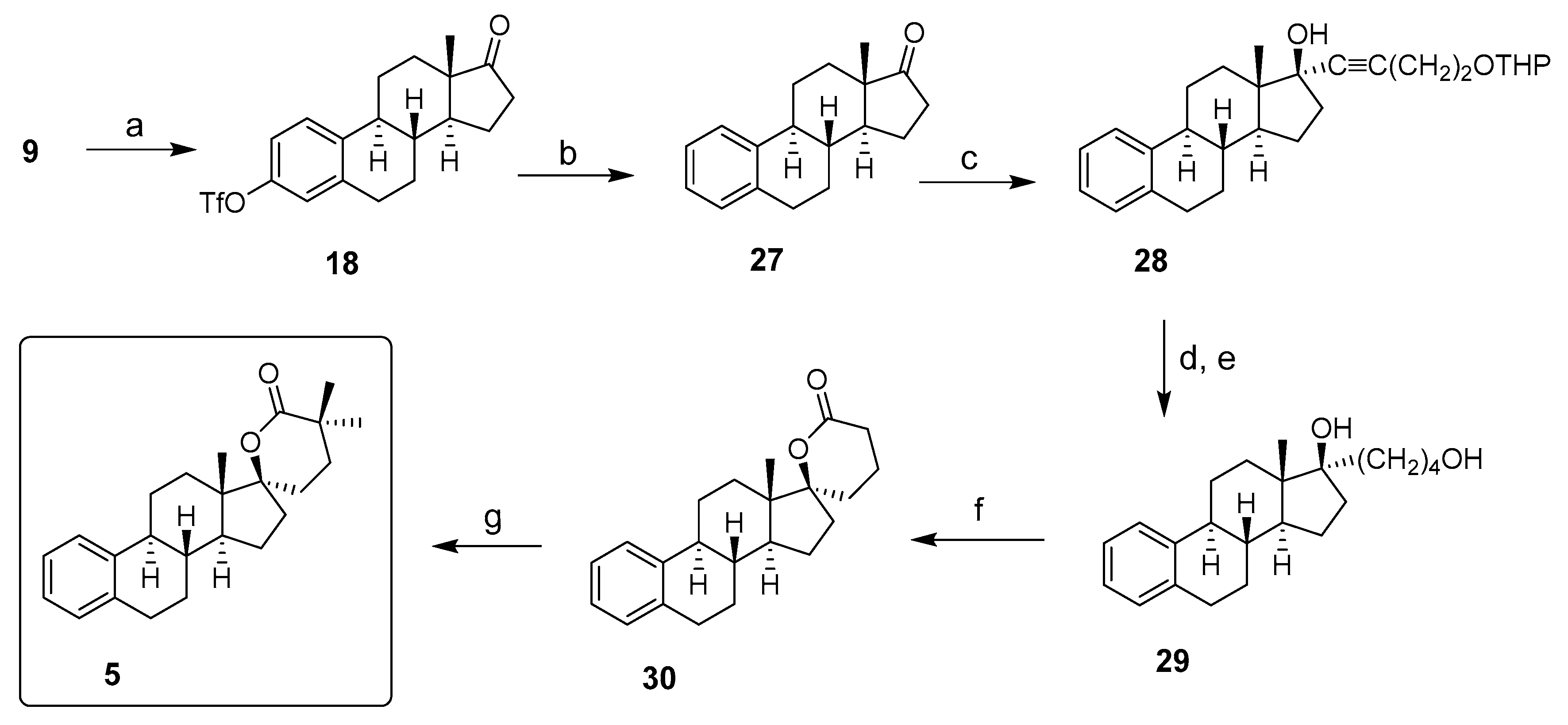
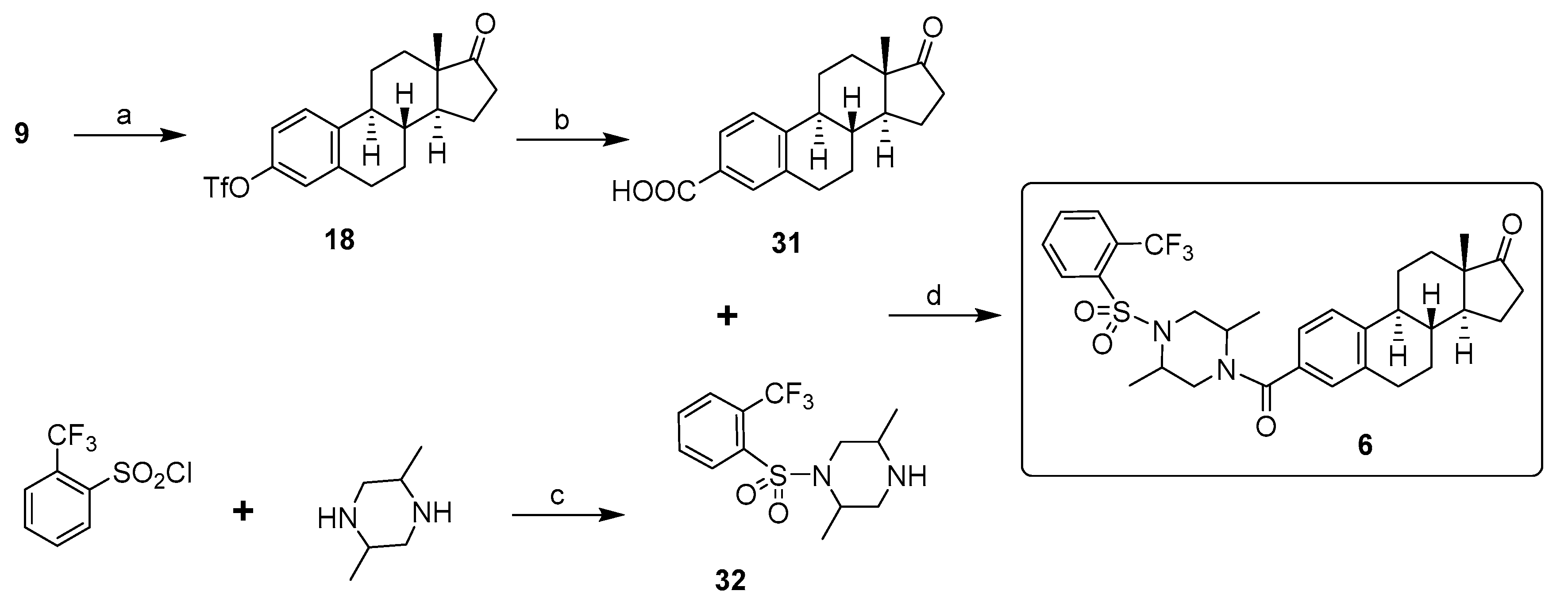
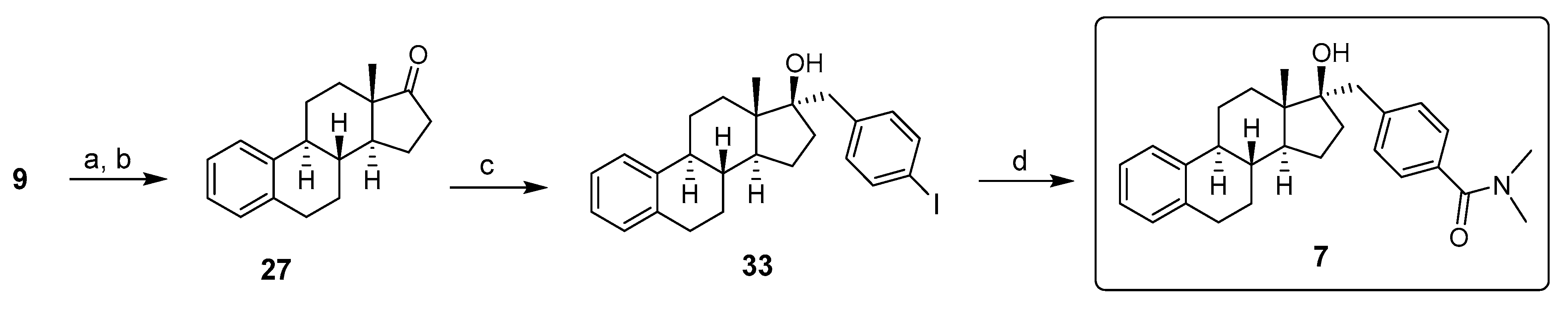
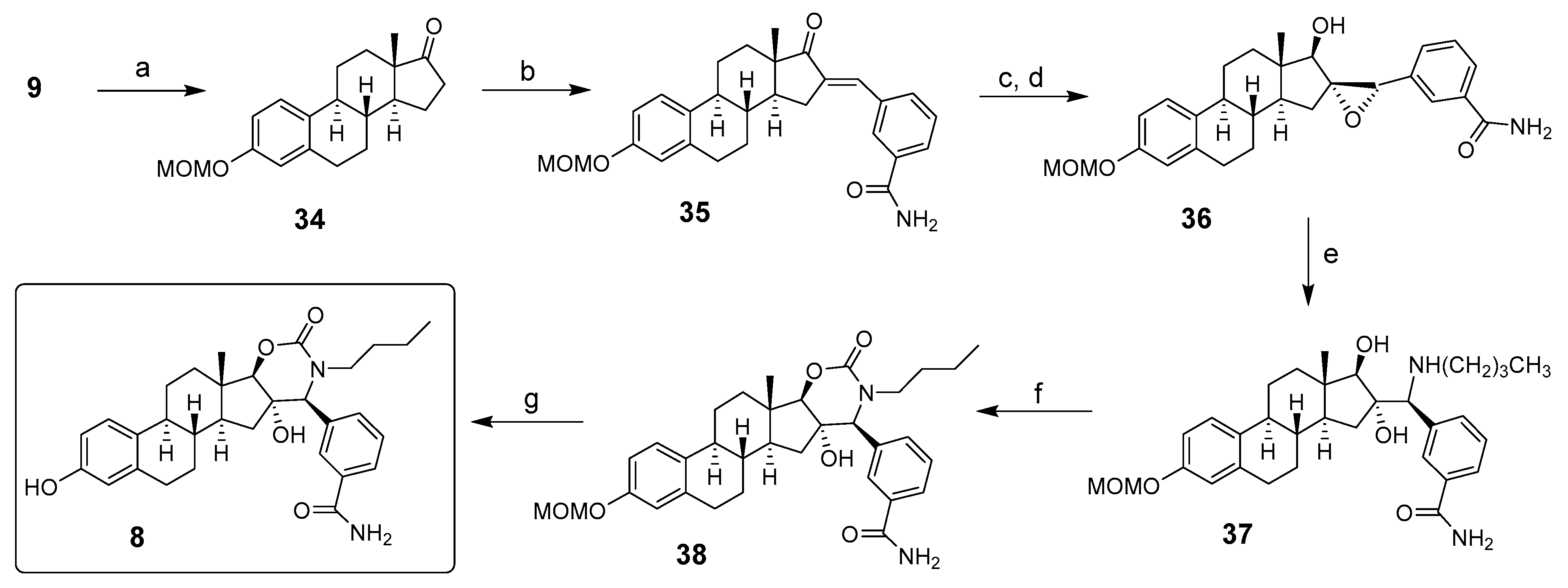
2. Chemical Synthesis of Inhibitors 1–7 and Activator 8
3. NMR Characterization of Inhibitors 1–7 and Activator 8
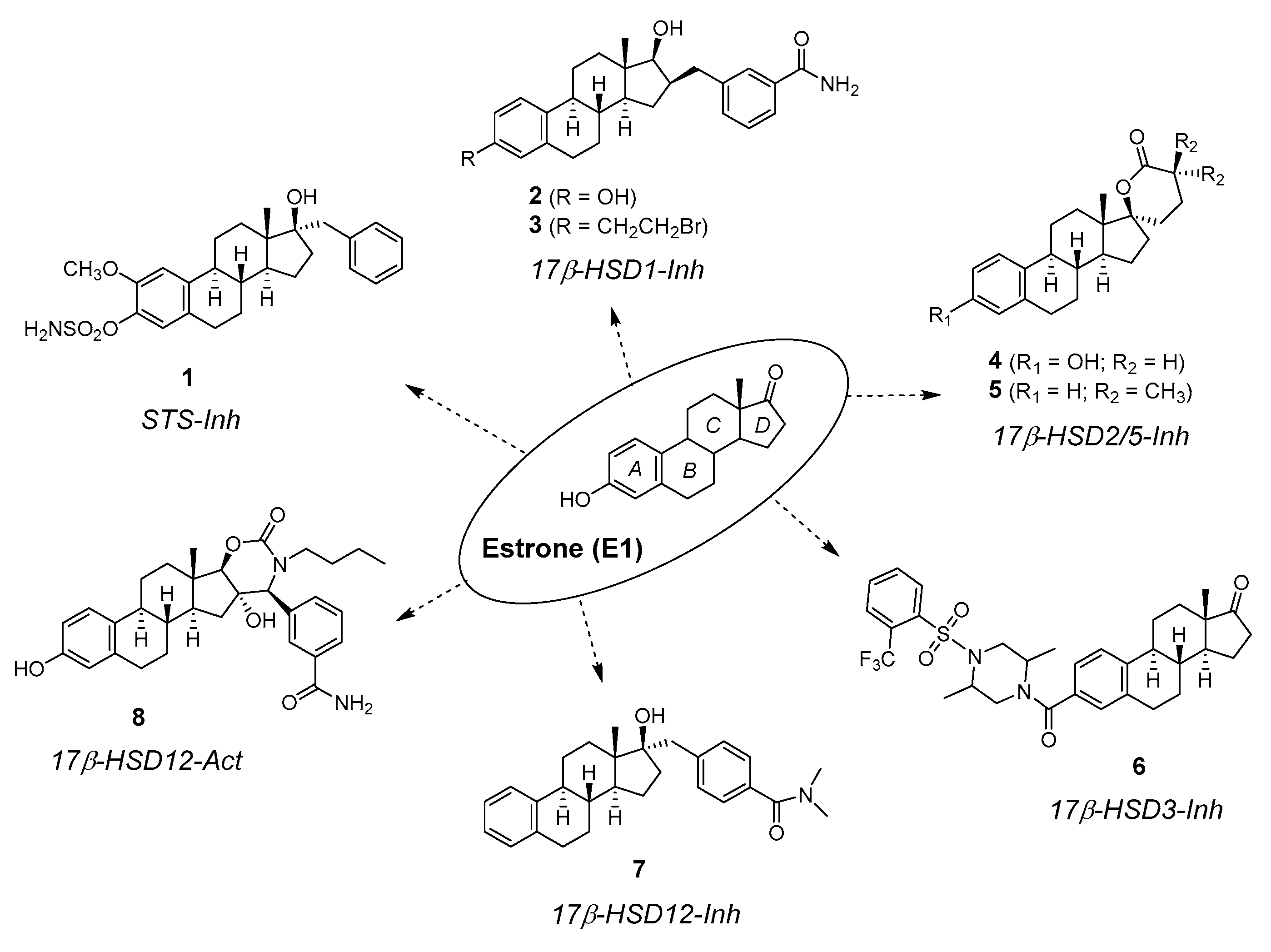
4. Biological Activity of Inhibitors 1–7 and Activator 8
| Cpd | Type | Enzyme | IC50 (Ki) in nM | EC50 in nM | Other 1 | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inh | STS | 0.024 2 | -- | Irreversible Inh; Not estrogenic and not androgenic in mice and rats; Blocks E1S, E2S, and DHEAS transformations in cells and mouse/rat tissues | [27,52,53] |
| 2 | Inh | 17β-HSD1 | 27–44 3 (0.9) | -- | Reversible Inh; Weakly estrogenic in cells and mice | [29,57] |
| 3 | Inh | 17β-HSD1 | 68–83 3 (368) | -- | Irreversible Inh (Kinact = 0.087 min−1); Not estrogenic in cells and mice; Blocks E1- and DHEA-tumor growth in mice; Orally active | [58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| 4 | Inh | 17β-HSD2 | 63 4 (29) | -- | Reversible Inh; Potentially estrogenic; NTAM | [35] |
| 5 | Inh | 17β-HSD5 (AKR1C3) | 2.9 5 | -- | Not androgenic and weakly estrogenic in cells; NTAM | [36] |
| 6 | Inh | 17β-HSD3 | 100–110 6 | -- | Reduces androgen (AR+)-dependent cells; NTAM | [38] |
| 7 | Inh | 17β-HSD12 | 560 7 | -- | NTAM | [75] |
| 8 | Act | 17β-HSD12 | -- | 7500 8 | NTAM | [42] |
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Baulieu, E.E. Hormones, a complexe communication network. In Hormones, from Molecules to Disease; Baulieu, E.E., Kelly, P.A., Eds.; Hermann, Publishers in Arts and Science: Paris, France, 1990; pp. 3–149. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, A.H.; Hales, D.B. Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 947–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luu-The, V. Assessment of steroidogenesis and steroidogenic enzyme functions. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J. Aromatase Inhibitors for Breast Cancer: Exemestane (Aromasin), Anastrozole (Arimidex), and Letrozole (Femara). In The Art of Drug Synthesis; Johnson, D.S., Li, J.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, A.; Trudeau, M.; Shelley, W.; Messersmith, H.; Pritchard, K.I. Aromatase inhibitors in adjuvant therapy for hormone receptor positive breast cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, J.A.R.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Silvestre, S.M. Steroidal 5α-reductase and 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17) inhibitors useful in the treatment of prostatic diseases. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Thareja, S.; Verma, A.; Bhardwaj, T.R.; Kumar, M. An overview on 5α-reductase inhibitors. Steroids 2010, 75, 109–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.M.; Salvador, J.A.R.; Vasaitis, T.S.; Njar, V.C.O. CYP17 Inhibitors for prostate cancer treatment—An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 868–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Scher, H.I.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Staffurth, J.N.; North, S.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone acetate for treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Final overall survival analysis of the COU-AA-301 randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, B.V.L. SULFATION PATHWAYS: Steroid sulphatase inhibition via aryl sulphamates: Clinical progress, mechanism and future prospects. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T233–T252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmieri, C.; Stein, R.C.; Liu, X.; Hudson, E.; Nicholas, H.; Sasano, H.; Guestini, F.; Holcombe, C.; Barrett, S.; Kenny, L.; et al. IRIS study: A phase II study of the steroid sulfatase inhibitor Irosustat when added to an aromatase inhibitor in ER-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.; Singh, J.; Singh, D.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N. Sulfatase inhibitors for recidivist breast cancer treatment: A chemical review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 114, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, Y.A.; Taylor, S.D. Steroid derivatives as inhibitors of steroid sulfatase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, A.; Foster, P.A. Steroid sulfatase inhibitors for estrogen- and androgen-dependent cancers. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 212, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. Steroid sulfatase inhibitors: A review covering the promising 2000–2010 decade. Steroids 2011, 76, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchais-Oberwinkler, S.; Henn, C.; Möller, G.; Klein, T.; Negri, M.; Oster, A.; Spadaro, A.; Werth, R.; Wetzel, M.; Xu, K.; et al. 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (17β-HSDs) as therapeutic targets: Protein structures, functions, and recent progress in inhibitor development. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 125, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.M.; Tutill, H.J.; Purohit, A. 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors. Minerva Endocrinol. 2010, 35, 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, D. 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2010, 20, 1123–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrns, M.C.; Jin, Y.; Penning, T.M. Inhibitors of type 5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C3): Overview and structural insights. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 125, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rižner, T.L.; Penning, T.M. Aldo-keto reductase 1C3—Assessment as a new target for the treatment of endometriosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, J.; Wells, J. Turning enzymes ON with small molecules. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, G.; Casnati, G.; Puglia, G.; Sartori, G.; Terenghi, G. Selective reactions between phenols and formaldehyde. A novel route to salicylaldehydes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1980, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, R.P.; Luu-The, V.; Lachance, R.; Labrie, F.; Poirier, D. Structure−activity relationships of 17α-derivatives of estradiol as inhibitors of steroid sulfatase. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4465–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Singh, S.M.; Labrie, F. Highly efficient nucleophilic addition of alkyl Grignard reagents to 17-ketosteroids in the presence of cerium(III) chloride: Synthesis of 17α-propyl-17β-hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one, an androgen receptor antagonist. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winum, J.-Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Montero, J.-L.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfamates and their therapeutic potential. Med. Res. Rev. 2004, 25, 186–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbar, H.S.; Isa, Z.; Elounais, J.J.; Jameel, M.A.; Zib, J.H.; Samer, A.M.; Jawad, A.F.; El-Gamal, M.I. Steroid sulfatase inhibitors: The current landscape. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2021, 31, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, L.C.; Luu-The, V.; Martel, C.; Labrie, F.; Poirier, D. Inhibition of estrone sulfate-induced uterine growth by potent non-estrogenic steroidal inhibitors of steroid sulfatase. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6442–6446. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, A.; Mohsenzadeh, F.; Mojtahedi, M.M.; Saidi, M.R.; Balalaie, S. Microwave-promoted transformation of nitriles to amides with aqueous sodium perborate. Synth. Commun. 2001, 31, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, Y.; Cadot, C.; Fournier, M.-A.; Poirier, D. Estradiol and estrone C-16 derivatives as inhibitors of type 1 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: Blocking of ER+ breast cancer cell proliferation induced by estrone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. Development of a gram-scale synthesis of PBRM, an irreversible inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury-Brégeot, N.; Presset, M.; Beaumard, F.; Colombel, V.; Oehlrich, D.; Rombouts, F.; Molander, G.A. Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling of potassium alkoxyethyltrifluoroborates: Access to aryl/heteroarylethyloxy motifs. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 10399–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearlman, W.M. Noble metal hydroxides on carbon nonpyrophoric dry catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967, 8, 1663–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, J.-H.; Xiao, J.-C. Halogenation through deoxygenation of alcohols and aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3061–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltais, R.; Ayan, D.; Poirier, D. Crucial role of 3-bromoethyl in removing the estrogenic activity of 17β-HSD1 inhibitor 16β-(m-carbamoylbenzyl)estradiol. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bydal, P.; Auger, S.; Poirier, D. Inhibition of type 2 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase by estradiol derivatives bearing a lactone on the D-ring: Structure–activity relationships. Steroids 2004, 69, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bydal, P.; Luu-The, V.; Labrie, F.; Poirier, D. Steroidal lactones as inhibitors of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5: Chemical synthesis, enzyme inhibitory activity, and assessment of estrogenic and androgenic activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchi, S.; Lupi, A. Palladium-catalysed hydroxycarbonylation of vinyl and aryl triflates: Synthesis of α,β-unsaturated and aromatic carboxylic acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 3939–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Benítez, F.; Roy, J.; Perreault, M.; Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. A- and D-ring structural modifications of an androsterone derivative inhibiting 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3: Chemical synthesis and structure–activity relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7070–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannberg, J.; Larhed, M. Microwave-Promoted Carbonylations. In Modern Carbonylation Methods; Kollar, L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, M.-A.; Poirier, D. Synthesis and evaluation of amido-deoxyestradiol derivatives as inhibitors of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 12. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2011, 7, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. Diversity-oriented synthesis of spiro- and fused azacycles from ketone molecular templates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5435–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, A.; Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. Identification of a first enzymatic activator of a 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Stothers, J.B. 13C n.m.r. spectra of steroids—A survey and commentary. Org. Magn. Reson. 1977, 9, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Duclos, R.I.; Vemuri, V.K.; Makriyannis, A. The conformations of 17β-estradiol (E2) and 17α-estradiol as determined by solution NMR. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 3465–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dionne, P.; Ngatcha, B.T.; Poirier, D. D-ring allyl derivatives of 17β- and 17α-estradiols: Chemical synthesis and 13C NMR data. Steroids 1997, 62, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D. Human sulfatases: A structural perspective to catalysis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, S.R.; Best, M.D.; Wong, C.-H. Sulfatases: Structure, mechanism, biological activity, inhibition, and synthetic utility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5736–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rižner, T.L. The important roles of steroid sulfatase and sulfotransferases in gynecological diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maltais, R.; Fournier, D.; Poirier, D. Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study with a series of 17α-derivatives of estradiol: Model for the development of reversible steroid sulfatase inhibitors. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2009, 28, 1284–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.P.; Potter, B.V.L. Discovery and development of the aryl O-sulfamate pharmacophore for oncology and women’s health. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7634–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciobanu, L.C.; Boivin, R.P.; Luu-The, V.; Labrie, F.; Poirier, D. Potent inhibition of steroid sulfatase activity by 3-O-sulfamate 17α-benzyl(or 4‘-tert-butylbenzyl)estra-1,3,5(10)-trienes: Combination of two substituents at positions C3 and C17α of estradiol. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Lefebvre, J.; Maltais, R.; Poirier, D. Inhibition of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate action in androgen-sensitive tissues by EM-1913, an inhibitor of steroid sulfatase. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 376, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Roy, J.; Maltais, R.; Ayan, D. A Potent inhibitor of steroid sulfatase (EM-1913) blocks tumor growth in nude mice (MCF-7 xenograft). Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2015, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.R.; Poirier, D. Overview of a rational approach to design type I 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors without estrogenic activity: Chemical synthesis and biological evaluation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 66, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobec, S.; Brozic, P.; Rizner, T. Inhibitors of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-X.; Poirier, D.; Adamski, J. A challenge for medicinal chemistry by the 17-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase superfamily: An integrated biological function and inhibition study. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, M.; Fournier, D.; Zhu, D.-W.; Cadot, C.; Poirier, D.; Lin, S.-X. Binary and ternary crystal structure analyses of a novel inhibitor with 17β-HSD type 1: A lead compound for breast cancer therapy. Biochem. J. 2009, 424, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayan, D.; Maltais, R.; Roy, J.; Poirier, D. A New Nonestrogenic steroidal inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I blocks the estrogen-dependent breast cancer tumor growth induced by estrone. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maltais, R.; Ayan, D.; Trottier, A.; Barbeau, X.; Lagüe, P.; Bouchard, J.-E.; Poirier, D. Discovery of a non-estrogenic irreversible inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 from 3-substituted-16β-(m-carbamoylbenzyl)-estradiol derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Maltais, R.; Poirier, D.; Lin, S.-X. Combined biophysical chemistry reveals a new covalent inhibitor with a low-reactivity alkyl halide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 5275–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, A.; Maltais, R.; Ayan, D.; Barbeau, X.; Roy, J.; Perreault, M.; Poulin, R.; Lagüe, P.; Poirier, D. Insight into the mode of action and selectivity of PBRM, a covalent steroidal inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 144, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, D.; Roy, J.; Maltais, R. A Targeted-covalent inhibitor of 17β-HSD1 blocks two estrogen-biosynthesis pathways: In vitro (metabolism) and in vivo (xenograft) studies in T-47D breast cancer models. Cancers 2021, 13, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Nyachieo, A.; Romano, A.; Roy, J.; Maltais, R.; Chai, D.; Delvoux, B.; Tomassetti, C.; Vanhie, A. An irreversible inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibits estradiol synthesis in human endometriosis lesions and induces regression of the non-human primate endometriosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 222, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Bydal, P.; Tremblay, M.R.; Sam, K.-M.; Luu-The, V. Inhibitors of type II 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 171, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniji, A.O.; Chen, M.; Penning, T.M. AKR1C3 as a target in castrate resistant prostate cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Detlefsen, A.J.; Paulukinas, R.D.; Penning, T.M. Germline mutations in steroid metabolizing enzymes: A focus on steroid transforming aldo-keto reductases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohler, M.L.; Narayanan, R.; He, Y.; Miller, D.D.; Dalton, J.T. Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17β-HSD3, 17β-HSD5, and 3α-HSD3) inhibitors: Extragonadal regulation of intracellular sex steroid hormone levels. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immun. Drug Discov. 2007, 1, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, W.M.; Davis, D.L.; Wu, L.; Bradshaw, K.D.; Patel, S.; Mendonca, B.; Elliston, K.; Wilson, J.D.; Russell, D.; Andersson, S. Male pseudohermaphroditism caused by mutations of testicular 17β–hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghrabi, N.; Andersson, S. 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: Physiological roles in health and disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 9, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Yang, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, S. Development of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 as a target in hormone-dependent prostate cancer therapy. Steroids 2017, 121, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Fournier, M.-A.; Maltais, R.; Kenmogne, L.C.; Poirier, D. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a 3β-androsterone derivative as inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 141, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, R.; Fournier, M.-A.; Poirier, D. Development of 3-substituted-androsterone derivatives as potent inhibitors of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4652–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-A.; Horton, J.D. Identification of two mammalian reductases involved in the two-carbon fatty acyl elongation cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7335–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luu-The, V.; Tremblay, P.; Labrie, F. Characterization of type 12 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, an isoform of type 3 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase responsible for estradiol formation in women. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farhane, S. Synthèse de Lactones, de Furanes et D’amides à Noyau Estratriène Comme Inhibiteurs des 17β-Hydroxystéroïdes Déshydrogénases Type 1 et Type 12. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada, 2009. Available online: https://corpus.ulaval.ca/entities/publication/47dc367e-bcd7-4a8f-aa1c-3908998c6644 (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Laplante, Y.; Rancourt, C.; Poirier, D. Relative involvement of three 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (types 1, 7 and 12) in the formation of estradiol in various breast cancer cell lines using selective inhibitors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 301, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



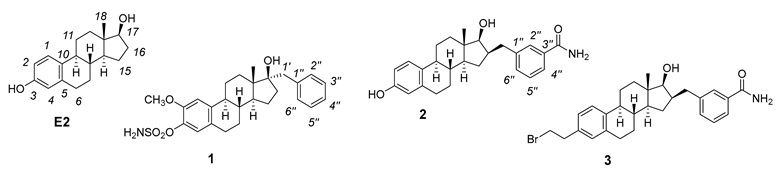
| E2 [41] 1 | E2 [42] 2 | E2 [42] 2 | 1 3 | 1 3 | 2 4 | 2 4 | 3 4 | 3 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/H | 13C | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H |
| 1 | 126.9 | 126.0 | 7.00d | 110.4 | 7.06s | 127.1 | 7.07d | 126.4 | 7.22d |
| 2 | 113.5 | 112.7 | 6.47dd | 148.9 | -- | 113.7 | 6.52dd | 127.2 | 6.97d |
| 3 | 155.6 | 154.8 | -- | 140.4 | -- | 155.8 | -- | 137.4 | -- |
| 4 | 115.9 | 114.9 | 6.39d | 124.1 | 6.96s | 116.0 | 6.45d | 130.1 | 6.91s |
| 5 | 138.4 | 137.1 | -- | 130.2 | -- | 138.7 | -- | 137.8 | -- |
| 6 | 30.2 | 29.1 | 2.67m | 28.6 | 2.82m | 33.0 | 2.72m | 33.0 | 2.82m |
| 7 | 28.7 | 26.9 | na | 26.4 | na | 28.6 | na | 28.5 | na |
| 8 | 39.8 | 38.7 | na | 39.1 | na | 39.8 | na | 39.6 | na |
| 9 | 44.8 | 43.5 | na | 44.3 | na | 45.3 | na | 45.7 | na |
| 10 | 132.3 | 130.4 | -- | 136.8 | -- | 132.6 | -- | 140.0 | -- |
| 11 | 27.1 | 26.0 | na | 27.3 | na | 27.5 | na | 27.3 | na |
| 12 | 37.6 | 36.5 | na | 31.4 | na | 38.9 | na | 38.9 | na |
| 13 | 43.9 | 42.8 | -- | 46.7 | -- | 45.4 | -- | 45.4 | -- |
| 14 | 50.8 | 49.5 | na | 49.5 | na | 49.8 | na | 50.0 | na |
| 15 | 23.7 | 22.7 | na | 23.3 | na | 30.6 | na | 30.5 | na |
| 16 | 31.0 | 29.8 | na | 33.7 | na | 43.3 | 3.14d | 43.3 | 3.17m |
| 17 | 81.9 | 80.0 | 3.48 | 83.0 | -- | 83.0 | 3.81d | 83.0 | 3.84d |
| 18 | 11.5 | 11.2 | 0.63s | 14.4 | 0.98s | 13.3 | 0.89s | 13.3 | 0.91s |
| 1′ | -- | -- | -- | 42.3 | 2.68d/ 2.94d | 38.8 | na | 38.8 | na |
| 1″ | -- | -- | -- | 138.1 | -- | 144.3 | -- | 144.3 | -- |
| 2″ | -- | -- | -- | 131.0 | 7.33m | 129.1 | 7.73s | 129.1 | 7.75s |
| 3″ | -- | -- | -- | 128.1 | 7.33m | 134.7 | -- | 134.8 | -- |
| 4″ | -- | -- | -- | 126.4 | 7.33m | 125.9 | 7.67m | 126.0 | 7.69d |
| 5″ | -- | -- | -- | 128.1 | 7.33m | 129.4 | 7.37m | 129.4 | 7.40m |
| 6″ | -- | -- | -- | 131.0 | 7.33m | 133.5 | 7.37m | 133.5 | 7.40m |
| CH3O | -- | -- | -- | 56.4 | 3.89s | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| CH2Ar | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 40.1 | 3.06t |
| BrCH2 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 33.9 | 3.55t |
| NH2 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.96s | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| CONH2 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 172.7 | -- | 172.7 | -- |
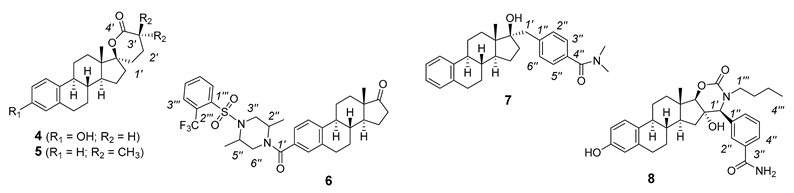
| 4 1 | 4 1 | 5 2 | 5 2 | 6 2 | 6 2 | 7 2 | 7 2 | 8 3 | 8 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H | 13C | 1H |
| 1 | 126.0 | 7.06d | 125.6 | 7.13m | 125.5 | 7.28m | 125.6 | 7.15m | 126.9 | 7.04d |
| 2 | 112.7 | 6.52dd | 125.5 | 7.13m | 124.0 | 7.06m | 125.6 | 7.15m | 113.6 | 6.56dd |
| 3 | 154.9 | -- | 125.2 | 7.13m | 141.5 | -- | 125.3 | 7.15m | 156.0 | -- |
| 4 | 114.9 | 6.44d | 129.0 | 7.30d | 126.9 | 7.06m | 129.0 | 7.35m | 115.9 | 6.48d |
| 5 | 137.1 | -- | 139.9 | -- | 137.0 | -- | 140.2 | -- | 138.2 | -- |
| 6 | 29.5 | 2.73m | 29.4 | 2.88m | 29.2 | 2.91m | 29.6 | 2.93m | 30.7 | 2.68m |
| 7 | 27.2 | na | 27.4 | na | 26.2 | na | 27.5 | na | 28.5 | na |
| 8 | ~38 4 | na | 38.9 | na | 37.9 | na | 39.4 | na | 38.2 | na |
| 9 | 43.0 | na | 44.2 | na | 44.3 | na | 44.4 | na | 44.6 | na |
| 10 | 130.1 | -- | 135.5 | -- | 136.4 | -- | 136.7 | -- | 131.5 | -- |
| 11 | 25.8 | na | 25.8 | na | 25.6 | na | 26.1 | na | 27.1 | na |
| 12 | 31.4 | na | 31.5 | na | 31.5 | na | 31.5 | na | 38.6 | na |
| 13 | 46.7 | -- | 47.3 | -- | 47.9 | na | 46.9 | -- | 45.1 | -- |
| 14 | 47.8 | na | 48.8 | na | 50.4 | na | 49.7 | na | 48.4 | ma |
| 15 | 23.0 | na | 23.3 | na | 21.5 | na | 23.3 | na | 38.6 | ma |
| 16 | 33.3 | na | 32.0 | na | 35.8 | na | 33.9 | na | 82.8 | -- |
| 17 | 92.4 | -- | 93.6 | -- | 220.6 | -- | 83.2 | -- | 97.9 | 4.12s |
| 18 | 14.1 | 0.90s | 14.4 | 1.02s | 13.8 | 0.91s | 14.4 | 0.99s | 12.5 | 0.39s |
| 1′ | -- | -- | -- | -- | 171.5 | -- | 42.3 | 2.72d/2.99d | 72.0 | 4.77s |
| 1″ | 27.0 | na | 25.6 | na | -- | -- | 140.2 | -- | 139.6 | -- |
| 2″ | 15.3 | na | 34.8 | na | 43.5/50.0 | 3.98m/ 4.95m | 126.9 | 7.39d | 127.5 | 7.88d |
| 3″ | 29.0 | na | 37.8 | na | 46.9 | 3.30m/ 3.40m | 131.0 | 7.39d | 134.0/ 135.2 | -- |
| 4″ | 171.1 | -- | 177.8 | -- | -- | -- | 134.3 | -- | 127.5 | 7.88d |
| 5″ | -- | -- | -- | -- | 48.6 | 4.06m/ 4.19m | 131.0 | 7.39d | 129.1 | 7.48t |
| 6″ | -- | -- | -- | -- | 40.5/44.0 | 3.50m/ 4.90m | 126.9 | 7.39 | 129.1 | 7.40d |
| OCON/ CH3 | -- | -- | 27.5 | 1.28s | 14.4/14.6 | 1.06d | 35.4w | 3.05s | 156.4 | -- |
| CONH2/ CH3 | -- | -- | 27.8 | 1.28s | 15.8 | 1.12m/ 1.19m | 39.7w | 3.13s | 167.1/ 168.7 | 6.76s 7.55s |
| 1‴ | -- | -- | -- | 138.8 | -- | 171.7 | -- | 49.2 | 2.90m/3.68m | |
| 2‴ | -- | -- | -- | 127.2q | -- | -- | -- | 30.1 | na | |
| 3‴ | -- | -- | -- | 128.6q | 7.89m | -- | -- | 20.5 | na | |
| 4‴ | -- | -- | -- | 132.8 | 7.70m | -- | -- | 14.1 | 0.84t | |
| 5‴ | -- | -- | -- | 132.2 | 7.70m | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 6‴ | -- | -- | -- | 132.1 | 8.18m | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| CF3/OH | -- | 9.01s | -- | -- | 122.5q | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poirier, D. Description of Chemical Synthesis, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization and Biological Activity of Estrane-Based Inhibitors/Activators of Steroidogenesis. Molecules 2023, 28, 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083499
Poirier D. Description of Chemical Synthesis, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization and Biological Activity of Estrane-Based Inhibitors/Activators of Steroidogenesis. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083499
Chicago/Turabian StylePoirier, Donald. 2023. "Description of Chemical Synthesis, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization and Biological Activity of Estrane-Based Inhibitors/Activators of Steroidogenesis" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083499
APA StylePoirier, D. (2023). Description of Chemical Synthesis, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization and Biological Activity of Estrane-Based Inhibitors/Activators of Steroidogenesis. Molecules, 28(8), 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083499






