Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16
Abstract
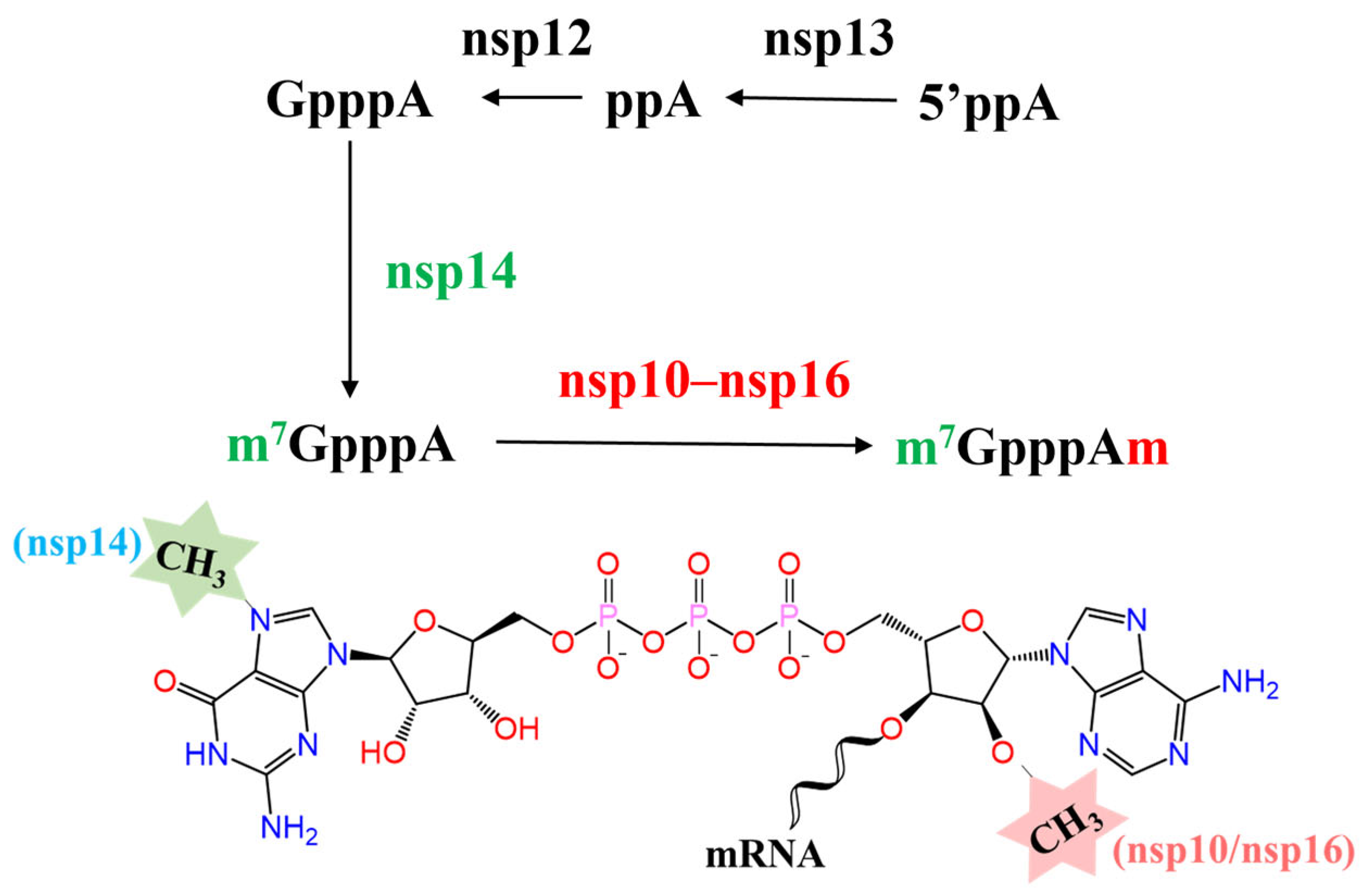
:1. Introduction
2. Results
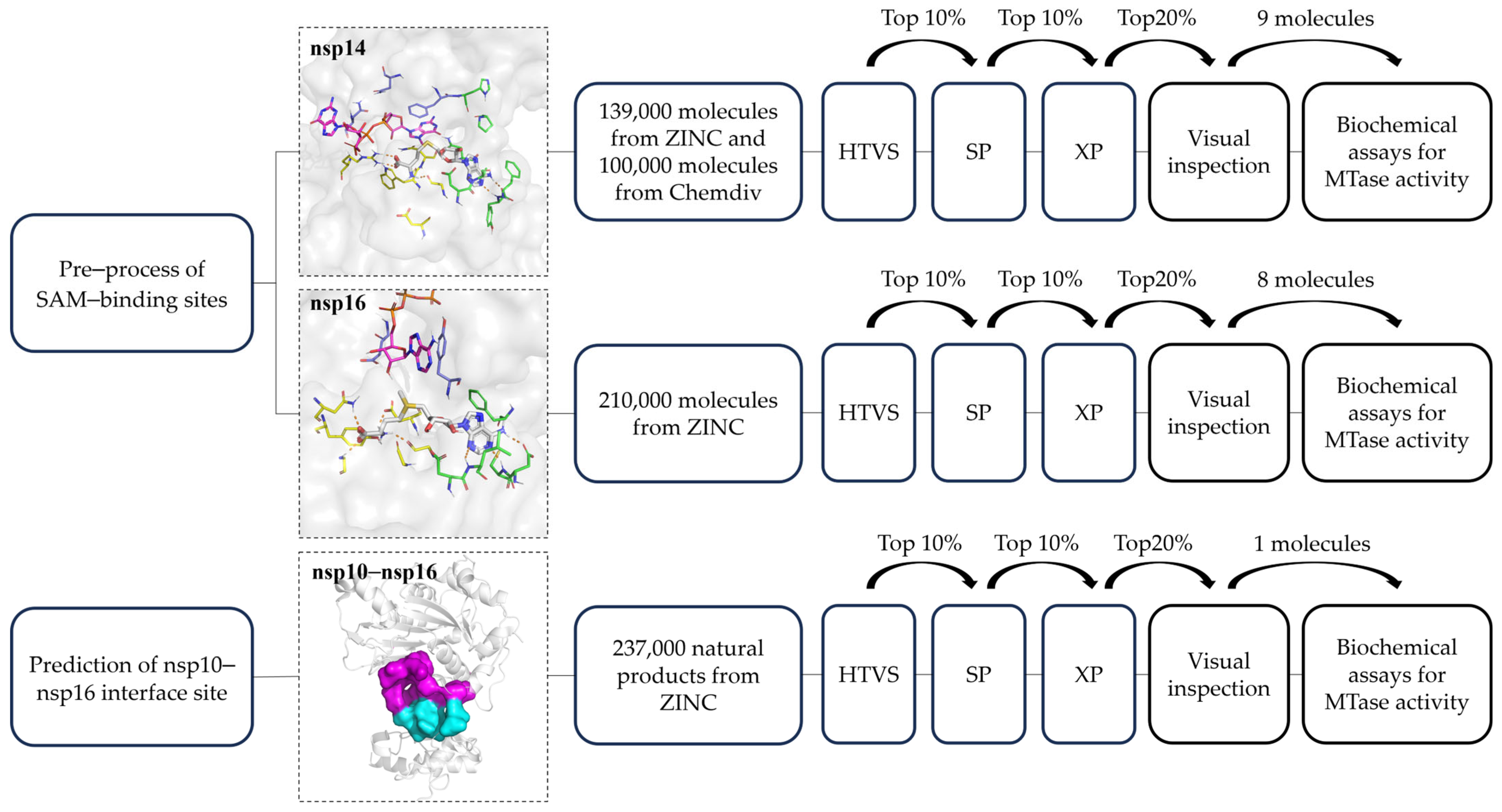
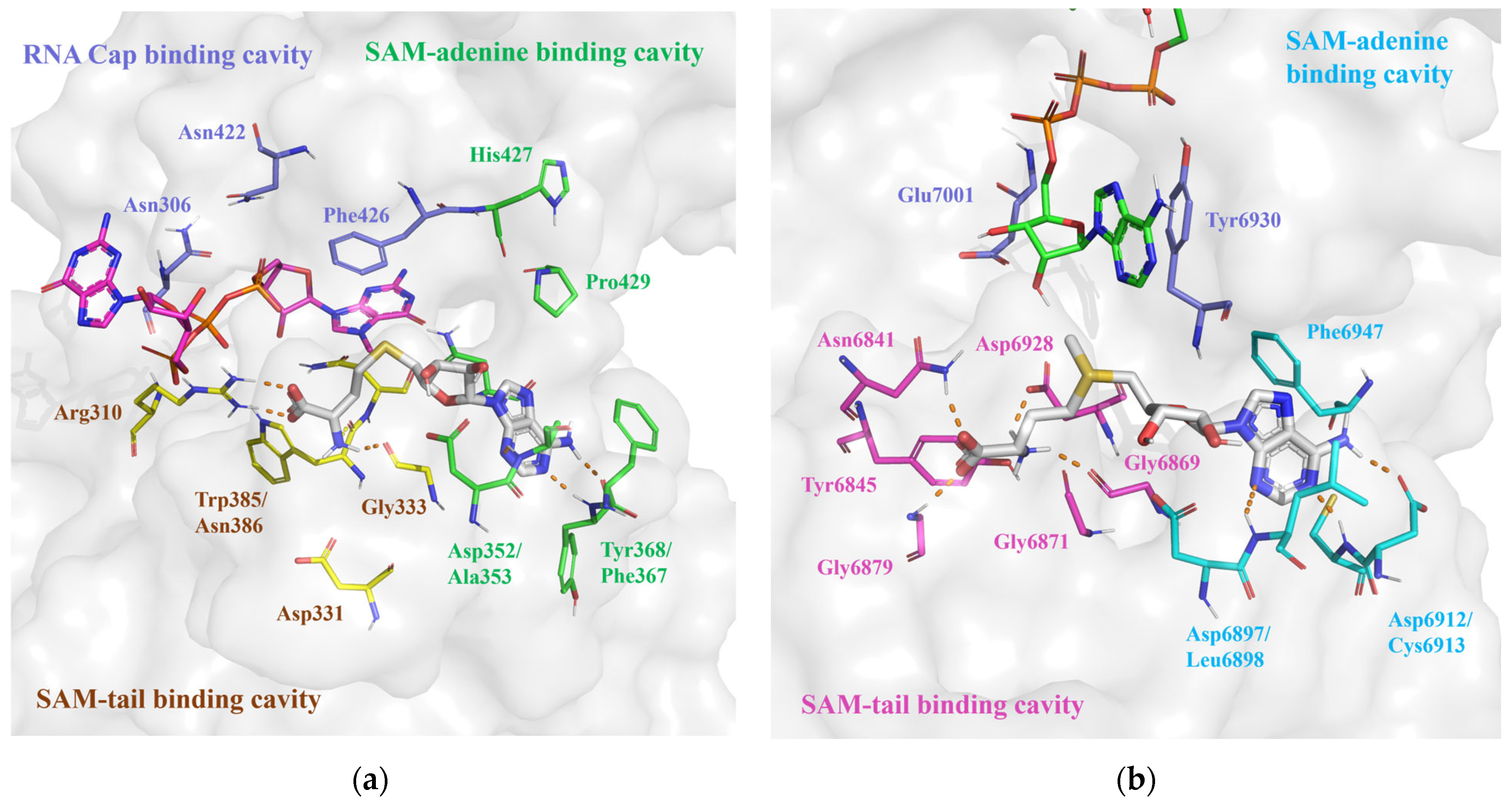
2.1. Binding Site Processing of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16
2.2. Structure-Based Virtual Screening
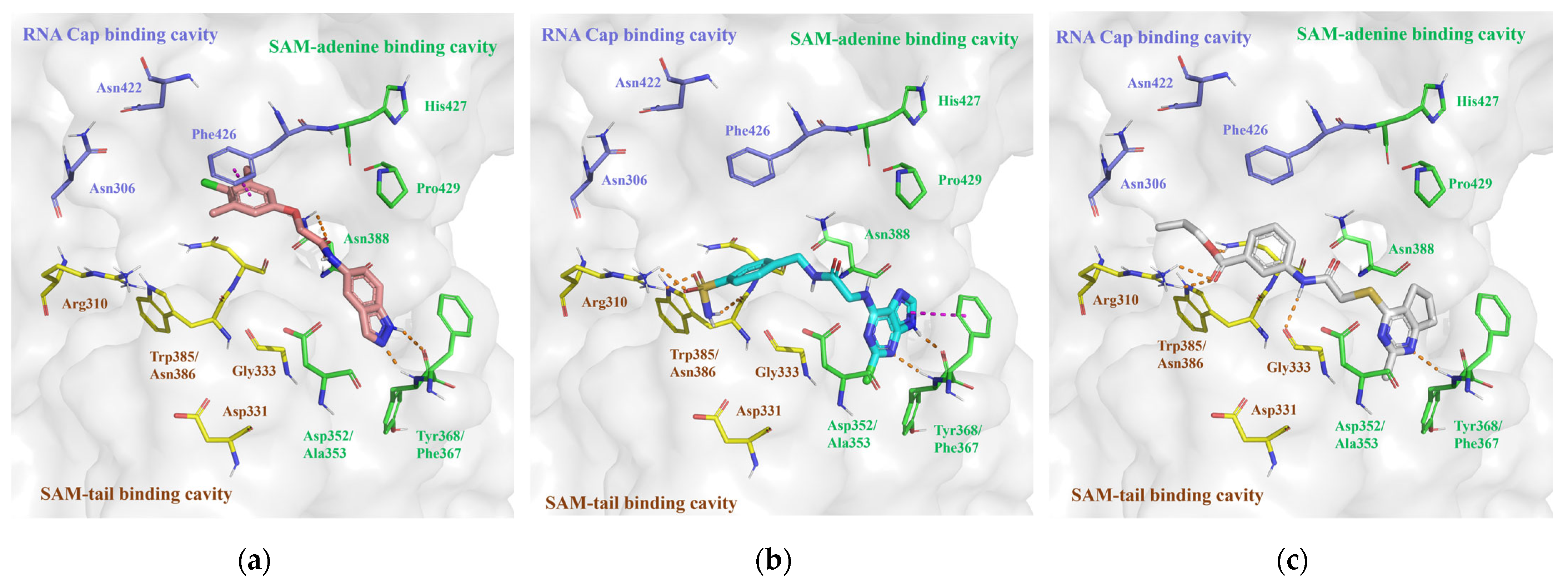
2.2.1. SBVS Results of nsp14 Inhibitors
2.2.2. SBVS Results of nsp16 Inhibitors
2.2.3. ADMET Properties of the Selected Potential MTase Inhibitors
2.3. Biochemical Assays for MTase Inhibition Activity
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Processing of nsp14 and nsp16 Structures
4.2. Processing of Small Molecules
4.3. Structure-Based Virtual Screening
4.4. Biochemical Assays
4.4.1. RNA Substrate Preparation
4.4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.4.3. Radioactive Biochemical Assays for MTase Activity
4.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gogoi, B.; Chowdhury, P.; Goswami, N.; Gogoi, N.; Naiya, T.; Chetia, P.; Mahanta, S.; Chetia, D.; Tanti, B.; Borah, P.; et al. Identification of potential plant-based inhibitor against viral proteases of SARS-CoV-2 through molecular docking, mm-pbsa binding energy calculations and molecular dynamics simulation. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1963–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maunder, R.; Hunter, J.; Vincent, L.; Bennett, J.; Peladeau, N.; Leszcz, M.; Sadavoy, J.; Verhaeghe, L.M.; Steinberg, R.; Mazzulli, T. The immediate psychological and occupational impact of the 2003 SARS outbreak in a teaching hospital. Cmaj 2003, 168, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Haque, S.; Sah, R.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Dhama, K.; Yatoo, M.I.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV: A comparative overview. Infez. Med. 2020, 28, 174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Qu, J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A clinical update. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen Espinosa-Gongora, C.B.M.R. Early detection of the emerging SARS-CoV-2 ba.2.86 lineage through integrated genomic surveillance of wastewater and COVID-19 cases in sweden, weeks 31 to 38 2023. Eurosurveillance 2023, 46, 2300595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-ncov). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chang, J. Azvudine (fnc): A promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, D. Cost-effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in china. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1174879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Khoi Quan, N.; Tran, V.P.; Nguyen, D.; Tao, N.P.H.; Linh, N.N.H.; Tien Huy, N. Molnupiravir as the COVID-19 panacea: False beliefs in low- and middle-income countries. Pathog. Glob. Health 2023, 117, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, A.B. In silico structure modelling of SARS-CoV-2 nsp13 helicase and nsp14 and repurposing of fda approved antiviral drugs as dual inhibitors. Gene Rep. 2020, 21, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, Y.; Mizrahi, O.; Nachshon, A.; Weingarten-Gabbay, S.; Morgenstern, D.; Yahalom-Ronen, Y.; Tamir, H.; Achdout, H.; Stein, D.; Israeli, O.; et al. The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 589, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, A.; Robb, G.B.; Chan, S. Mrna capping: Biological functions and applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7511–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafcikova, P.; Silhan, J.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. Structural analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex involved in rna cap creation bound to sinefungin. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Chen, H.; Ye, F.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, G. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nsp10/nsp16 2′-o-methylase and its implication on antiviral drug design. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogstam, A.; Nyblom, M.; Christensen, S.; Sele, C.; Talibov, V.O.; Lindvall, T.; Rasmussen, A.A.; André, I.; Fisher, Z.; Knecht, W.; et al. Crystal structure of non-structural protein 10 from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, M.; Lugari, A.; Posthuma, C.C.; Zevenhoven, J.C.; Bernard, S.; Betzi, S.; Imbert, I.; Canard, B.; Guillemot, J.; Lécine, P.; et al. Coronavirus nsp10, a critical co-factor for activation of multiple replicative enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25783–25796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovs, R.; Kanepe, I.; Narvaiss, N.; Patetko, L.; Kalnins, G.; Sisovs, M.; Bula, A.L.; Grinberga, S.; Boroduskis, M.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16 methyltransferase inhibitors by high-throughput virtual screening. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, M.; Khalili Yazdi, A.; Li, F.; Chau, I.; Hajian, T.; Bolotokova, A.; Kaniskan, H.Ü.; Han, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, D.; et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nsp10–nsp16 in complex with small molecule inhibitors, ss148 andwz16. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, e4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottur, J.; Rechkoblit, O.; Quintana-Feliciano, R.; Sciaky, D.; Aggarwal, A.K. High-resolution structures of the SARS-CoV-2 n7-methyltransferase inform therapeutic development. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulimov, A.; Kutov, D.; Ilin, I.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Sulimov, V. Novel inhibitors of 2′-o-methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Molecules 2022, 27, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Chan, S.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Li, P.; Huang, W. Recent insights into emerging coronavirus: SARS-CoV-2. Acs Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1369–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning-Stierand, K.; Diedrich, K.; Fährrolfes, R.; Flachsenberg, F.; Meyder, A.; Nittinger, E.; Steinegger, R.; Rarey, M. Proteinsplus: Interactive analysis of protein–ligand binding interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W48–W53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. Molprobity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Lemus, M.; Minasov, G.; Shuvalova, L.; Inniss, N.L.; Kiryukhina, O.; Brunzelle, J.; Satchell, K. High-resolution structures of the SARS-CoV-2 2′-o-methyltransferase reveal strategies for structure-based inhibitor design. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eabe1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarna, A.; Plewka, J.; Kresik, L.; Matsuda, A.; Karim, A.; Robinson, C.; O Byrne, S.; Cunningham, F.; Georgiou, I.; Wilk, P.; et al. Refolding of lid subdomain of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 upon nsp10 interaction releases exonuclease activity. Structure 2022, 30, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed-Belkacem, R.; Hausdorff, M.; Delpal, A.; Sutto-Ortiz, P.; Colmant, A.M.G.; Touret, F.; Ogando, N.S.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B.; Coutard, B.; et al. Potent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14n 7-methyltransferase by sulfonamide-based bisubstrate analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6231–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.; Soto-Acosta, R.; Xie, J.; Wilson, D.J.; Dreis, C.D.; Majima, R.; Edwards, T.C.; Geraghty, R.J.; Chen, L. Bisubstrate inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 nsp14 methyltransferase. Acs Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, R.; Delpal, A.; Canard, B.; Vasseur, J.J.; Decroly, E.; Debart, F.; Clave, G.; Smietana, M. Facile access to 4′-(n-acylsulfonamide) modified nucleosides and evaluation of their inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 rna cap n7-guanine-methyltransferase nsp14. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 7582–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobileva, O.; Bobrovs, R.; Sirma, E.E.; Kanepe, I.; Bula, A.L.; Patetko, L.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; Grinberga, S.; Jirgensons, A.; Jaudzems, K. 3-(adenosylthio)benzoic acid derivatives as SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 methyltransferase inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrat, S.K.; Bashir, Q.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Brown, T.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A universal fluorescence polarization high throughput screening assay to target the sam-binding sites of SARS-CoV-2 and other viral methyltransferases. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2204164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobiļeva, O.; Bobrovs, R.; Kaņepe, I.; Patetko, L.; Kalniņš, G.; Aišovs, M.; Bula, A.L.; Grīnberga, S.; Borodušķis, M.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; et al. Potent SARS-CoV-2 mrna cap methyltransferase inhibitors by bioisosteric replacement of methionine in sam cosubstrate. Acs Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sk, M.F.; Jonniya, N.A.; Roy, R.; Poddar, S.; Kar, P. Computational investigation of structural dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase-stimulatory factor heterodimer nsp16/nsp10 bound to the cofactor sam. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 590165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahham, B.J.M.; Al-Khafaji, K.; Saleh, M.Y.; Abdelhakem, A.M.; Alanazi, A.M.; Islam, M.A. Identification of naphthyridine and quinoline derivatives as potential nsp16-nsp10 inhibitors: A pharmacoinformatics study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3899–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Alshawaf, E.; Marafie, S.K.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Abubaker, J. Molecular simulation-based investigation of highly potent natural products to abrogate formation of the nsp10–nsp16 complex of SARS-CoV-2. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkamer, A.; Kuhn, D.; Grombacher, T.; Rippmann, F.; Rarey, M. Combining global and local measures for structure-based druggability predictions. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, Y.; Dawid, M.; Samantha, E.Z.; Krysten, A.J. Bisindolylmaleimide ix: A novel anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent targeting viral main protease 3clpro demonstrated by virtual screening pipeline and in-vitro validation assays. Methods 2021, 195, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, V.; Czyzyk, D.J.; Valhondo, M.; Jorgensen, W.L.; Anderson, K.S. Novel allosteric covalent inhibitors of bifunctional cryptosporidium hominis ts-dhfr from parasitic protozoa identified by virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, K.; Xu, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Che, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X. Virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation study of influenza polymerase pb2 inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. Pkcsm: Predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottur, J.; White, K.M.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Rechkoblit, O.; Quintana-Feliciano, R.; Nayar, A.; García-Sastre, A.; Aggarwal, A.K. Structures of SARS-CoV-2 n7-methyltransferase with dot1l and prmt7 inhibitors provide a platform for new antivirals. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, H.; Rashmi, K.M.; Nandi, S. Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (m(pro)) and rdrp targets by updating current structure-based drug design utilizing co-crystals to combat COVID-19. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Li, F.; Fink, E.A.; Chau, I.; Li, A.; Rodriguez-Hernández, A.; Glenn, I.; Zapatero-Belinchón, F.J.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Devkota, K.; et al. Structure-based discovery of inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 n7-methyltransferase. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7785–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Mak, T.; Ulferts, R.; Wu, M.; Deegan, T.; Fujisawa, R.; Tan, K.W.; Lim, C.T.; Basier, C.; Canal, B.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2 antiviral compounds by screening for small molecule inhibitors of nsp14 rna cap methyltransferase. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Pan, J.; Xiang, N.; Tien, P.; Ahola, T.; Guo, D. Functional screen reveals SARS coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp14 as a novel cap n7 methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3484–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, C.; Ke, M.; Jin, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tien, P.; et al. Biochemical and structural insights into the mechanisms of SARS coronavirus rna ribose 2′-o-methylation by nsp16/nsp10 protein complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.Z.H. Automatically constructed neural network potentials for molecular dynamics simulation of zinc proteins. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 692200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Y. Mechanistic insights into a classic wonder drug—Aspirin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Sheng, G.; Cheung, P.P.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Two symmetric arginine residues play distinct roles inthermus thermophilus argonaute dna guide strand-mediated dna target cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräutler, V.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hünenberger, P.H. A fast shake algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peramo, A. Solvated and generalised born calculations differences using gpu cuda and multi-cpu simulations of an antifreeze protein with amber. Mol. Simulat. 2016, 45, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. Ptraj and cpptraj: Software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
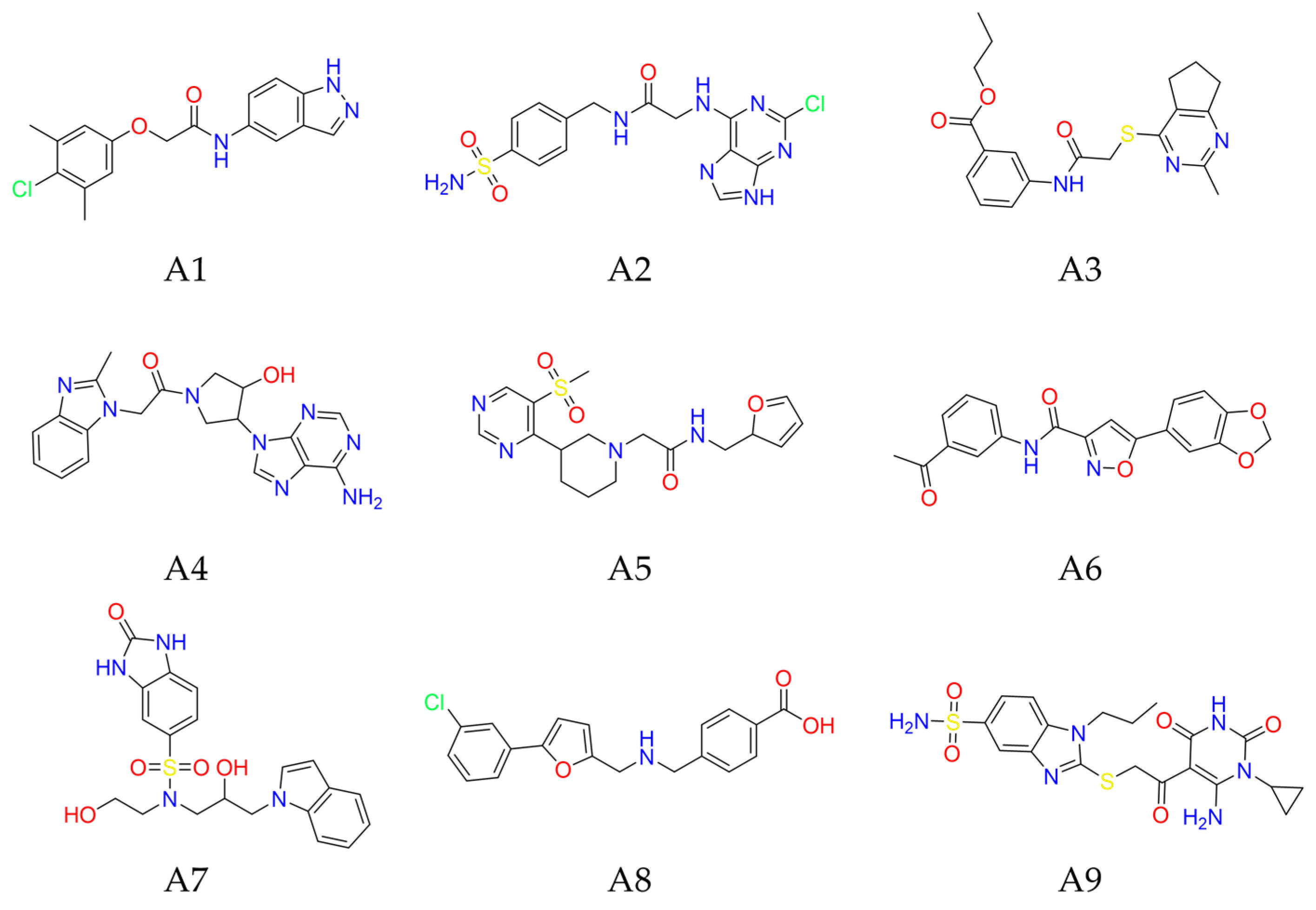


| Code | Compound | Molecular Weight | LogP | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | H-Bond Interaction | π-π Stacking Interaction | Inhibition Rate (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Y207-3841 | 329.78 | 3.78 | −10.40 | Tyr368(2) 1, Asn388(2) | Phe426 | 68.40 |
| A2 | ZINC000009481760 | 395.83 | 0.38 | −9.80 | Arg310(2), Ala353, Tyr368(2), Trp385 | Phe367 | 64.25 |
| A3 | D306-0032 | 385.48 | 3.78 | −9.17 | Arg310(2), Asn386, Ala353, Tyr368 | \ | 69.15 |
| A4 | ZINC000257219502 | 392.42 | 0.51 | −9.15 | Ala353, Tyr368(2) | Phe426 | 47.16 |
| A5 | ZINC000012154664 | 378.45 | 0.97 | −8.95 | Ala353, Tyr368, Asn388 | Phe426 | 20.79 |
| A6 | C226-1222 | 350.33 | 2.70 | −8.85 | Ala353, Tyr368, Asn386 | Phe426 | 46.92 |
| A7 | ZINC000257316872 | 430.49 | 0.86 | −8.79 | Gly333, Tyr368, Asn388 | Phe426 | 4.07 |
| A8 | D665-0380 | 378.25 | 1.42 | −8.69 | Tyr368 | Phe426 | 33.39 |
| A9 | ZINC000008892924 | 478.56 | 0.84 | −8.58 | Arg310, Gly333, Asn388 | Phe426 | 11.20 |
| Code | Compound | Molecular Weight | LogP | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | H-Bond Interaction | Salt Bridge Interaction | Inhibition Rate (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | ZINC55183218 | 397.6 | 2.50 | −8.70 | Gly6871, Cys6913 | Asp6897, Asp6928, | 49.06 |
| B2 | ZINC4073149 | 400.5 | 3.69 | −8.60 | Leu6898, Asp6928 | Asp6897 | 48.82 |
| B3 | ZINC95190922 | 386.9 | 3.52 | −8.30 | Gly6869(2) 1, Ala6870, Gly6871, Gly6879, Asp6928 | Asp6897, Asp6928 | 54.91 |
| B4 | ZINC60349570 | 395.5 | 4.63 | −8.26 | Leu6898, Cys6913, Lys6968, Asp6928 | Asp6897 | 0 |
| B5 | ZINC1127559 | 384.8 | 3.31 | −8.06 | Asn6841, Asp6897, Cys6913, Tyr6930 | \ | 26.82 |
| B6 | ZINC65164617 | 397.9 | 3.42 | −7.76 | Asp6873, Asp6897 | Asp6897 | 0.78 |
| B7 | ZINC215527498 | 378.9 | 3.74 | −7.57 | Tyr6830, Gly6871, Asp6897, Cys6913 | Asp6897 | 0 |
| B8 | ZINC20477654 | 393.3 | 3.11 | −7.51 | Gly6869, Ala6870, Gly6879, Asp6928(2) | Asp6928 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.; Huang, W.; Guo, D.; Cao, L.; Lei, J. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16. Molecules 2024, 29, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102312
Wu K, Guo Y, Xu T, Huang W, Guo D, Cao L, Lei J. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102312
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kejue, Yinfeng Guo, Tiefeng Xu, Weifeng Huang, Deyin Guo, Liu Cao, and Jinping Lei. 2024. "Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102312
APA StyleWu, K., Guo, Y., Xu, T., Huang, W., Guo, D., Cao, L., & Lei, J. (2024). Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16. Molecules, 29(10), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102312





