Antifungal Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.: An Analysis of In Silico Enzymatic Inhibition and In Vitro Efficacy against Candida Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Extraction and Isolation
2.2. Antifungal Activities
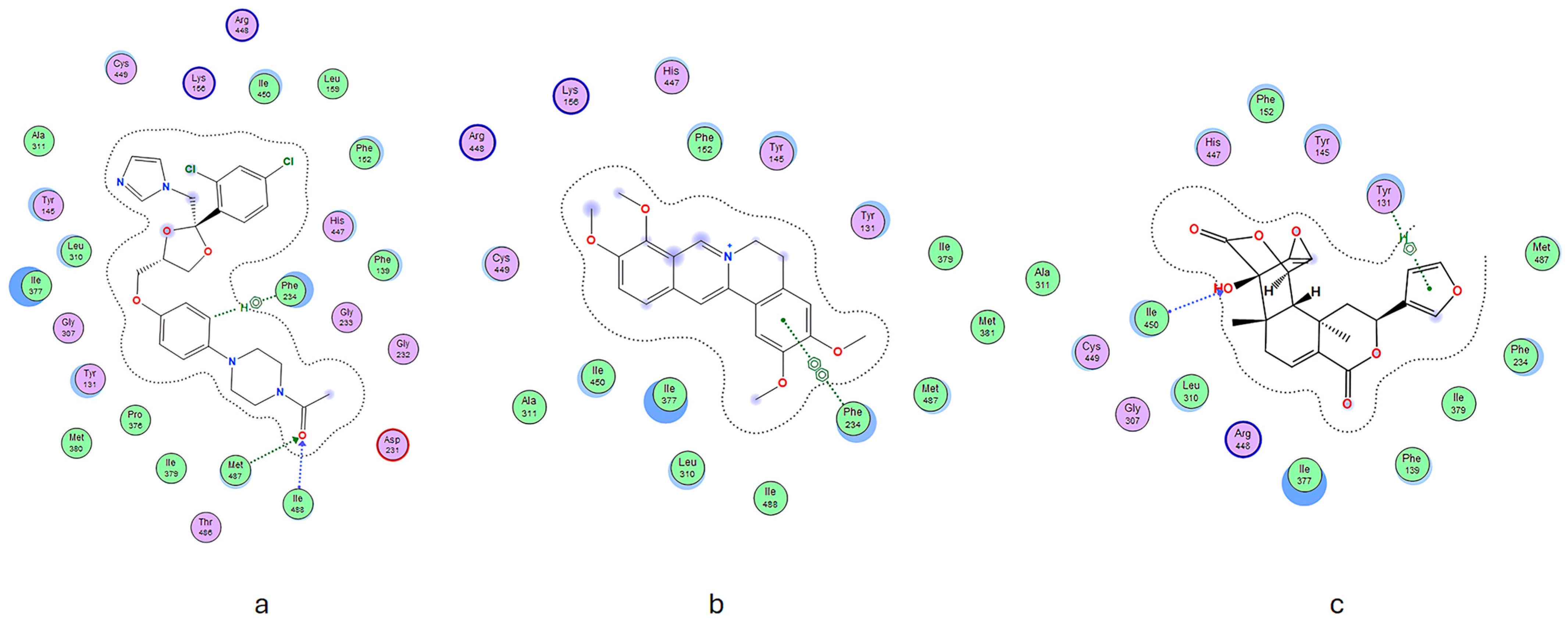
2.3. Molecular Docking
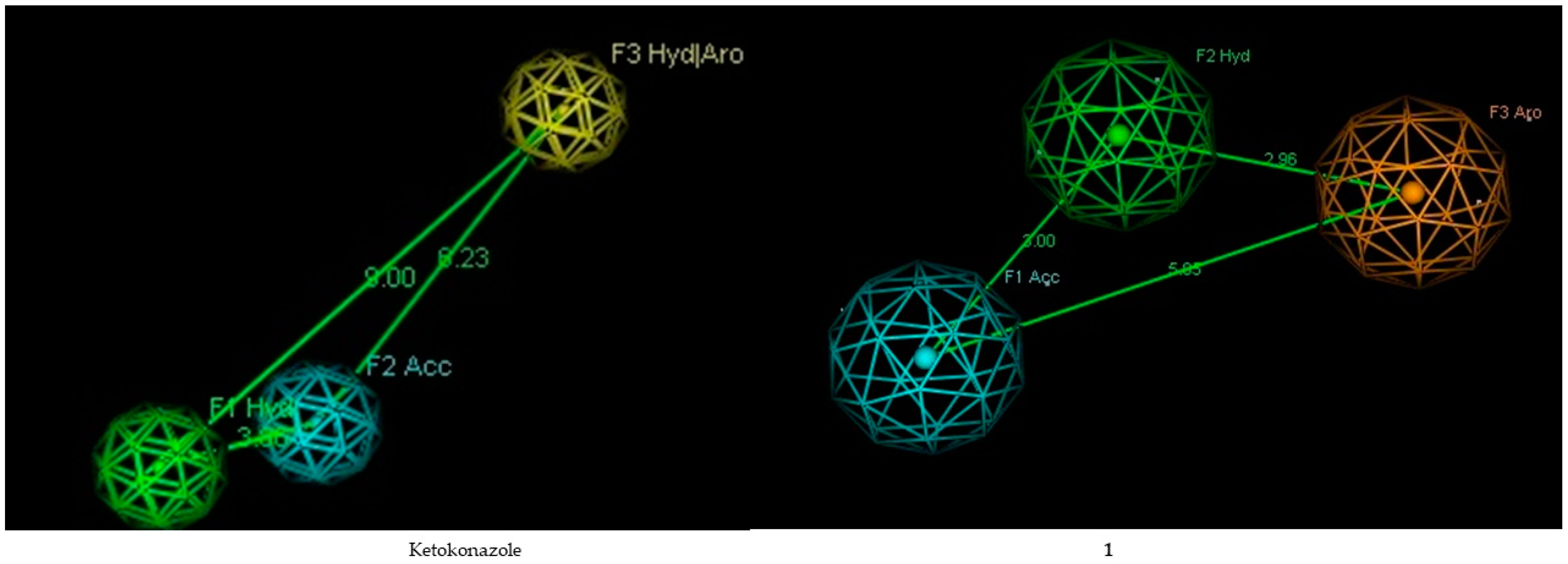
2.4. Pharmacophore
2.5. Density Functional Theory
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Collection
4.2. Extraction and Isolation
4.3. In Silico Studies
4.3.1. Protein Preparation
4.3.2. Ligand Preparation
4.3.3. Molecular Docking
4.3.4. Generation of Pharmacophore
4.3.5. Density Functional Theory
4.4. In Vitro Antifungal Activity
4.4.1. Preparation of Media
4.4.2. Cultivating Fungi
4.4.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.4.4. Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heard, S.C.; Wu, G.; Winter, J.M. Antifungal natural products. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, F.; Yan, X.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; Li, Z. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on the genus Arcangelisia: A mini review. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyowati, R.; Sudarsono, S.; Setyowati, E. The Effect of Water-Soluble Stem Extract “Kayu Kuning” (Arcangelisia flava L. Merr) on the Growth Inhibition of Candida albicans ATCC 10231 and Trichophyton mentagrophytes in vitro. Biol. Med. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2014, 3, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Nguyen, T.K.; Pham, P.T.V.; Tran, L.T.T.; Pham, H.K.T.; Truong, P.C.H.; Tran, L.T.; Tran, M.H. Anti-Staphylococcus aureus potential of compounds from Ganoderma sp.: A comprehensive molecular docking and simulation approaches. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, A.M.d.R.; de Oliveira, C.M.S.; Silva-Silva, J.V.; de Jesus, S.C.A.; Siqueira, J.E.S.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Auzier, J.F.; Soares, L.N.; Pinheiro, M.L.B.; Silva, S.C. Antimicrobial Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of the Biotransformation of Diterpene Acanthoic Acid Using the Fungus Xylaria sp. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, M.R.F.; Suratno, S.; Mulyani, E. Antibacterial activity of akar kuning (Arcangelisia flava) secondary metabolites: Molecular docking approach. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeuku, S.O.; Pang, K.-L.; Chin, K.-Y. Palmatine as an agent against metabolic syndrome and its related complications: A review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 34, 4963–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kiyotani, T.; Maeda, M.; Katayama, T.; Tomita-Yokotani, K.; Syafii, W.; Muladi, S. Furanoditerpenes from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr. and their antifungal activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustha, A.; Fadhillah, S.; Teruna, H.Y.; Hendra, R. Comparative Analysis of Antifungal Properties in Diverse Extracts of Arcangelisia flava (L.). J. Pharm. Educ. 2024, 24, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-M.; Kamnaing, P.; Kiyota, T.; Watchueng, J.; Kubo, T.; Jarussophon, S.; Konishi, Y. One-step purification of palmatine and its derivative dl-tetrahydropalmatine from Enantia chlorantha using high-performance displacement chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1208, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordá, T.; Puig, S. Regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes 2020, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.K.; Khan, P.K.; Karuppayil, S.M. Phytochemicals as potential inhibitors of lanosterol 14 α-demethylase (CYP51) enzyme: An in silico study on sixty molecules. Int. J. App. Pharm. 2020, 12, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.C.; Sagatova, A.A.; Hosseini, P.; Ruma, Y.N.; Wilson, R.K.; Keniya, M.V. Fungal Lanosterol 14α-demethylase: A target for next-generation antifungal design. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frimayanti, N.; Yaeghoobi, M.; Ikhtiarudin, I.; Putri, D.; Namavar, H.; Bitaraf, F. Insight on the in silico study and biological activity assay of chalcone-based 1, 5-benzothiazepines as potential inhibitor for breast cancer MCF7. CMUJ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 20, e2021019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswari, P.; Devika, R. In silico molecular docking studies of quercetin compound against anti-inflammatory and anticancer proteins. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 5305–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, R.R.; Sholikhah, I.; Sahu, R.K.; Widyowati, R. Phytochemical Compounds Identification From 70% Ethanol Extract of Arcangelesia flava (L.) Merr Stems Using LC-MS/MS and In-Silico Molecular Docking Approach as Inhibitor Interleukin-1β. Pharmacogn. J. 2023, 15, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.G. A unifying review of bioassay-guided fractionation, effect-directed analysis and related techniques. Sensors 2012, 12, 9181–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malviya, N.; Malviya, S. Bioassay guided fractionation-an emerging technique influence the isolation, identification and characterization of lead phytomolecules. Int. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2017, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, C.-R.; Chen, Y.-F.; Liou, M.-J.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Chang, W.-S.; Wu, T.-S. Anti-inflammatory activities of furanoditerpenoids and other constituents from Fibraurea tinctoria. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9603–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Kong, X.; Mai, W.; Sun, G.; Zhao, S. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 9-O-substituted palmatine derivatives. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volleková, A.; Košt’álová, D.; Kettmann, V.; Tóth, J. Antifungal activity of Mahonia aquifolium extract and its major protoberberine alkaloids. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keawpradub, N.; Dej-adisai, S.; Yuenyongsawad, S. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Thai medicinal plants named Khaminkhruea: Arcangelisia flava, Coscinium blumeanum and Fibraurea tinctoria. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2005, 27, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.-L.; Li, R.-T.; Ai, Y.-B.; Liu, W.; Deng, Z.-S.; Zou, Z.-M. Protoberberine isoquinoline alkaloids from Arcangelisia gusanlung. Molecules 2014, 19, 13332–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarabasz, D.; Kukula-Koch, W. Palmatine: A review of pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Zou, G.; Fan, J.; Yuan, Z. Identification of palmatine as an inhibitor of West Nile virus. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-C.; Kim, J.-K.; Kang, J.-W.; Oh, W.-Y.; Jung, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.-M. Palmatine attenuates D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Song, J.; Zhong, L.; Liao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Palmatine: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Biochimie 2019, 162, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Ali, H. Assessment of DNA damage and cytotoxicity of palmatine on human skin epithelial carcinoma cells. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y. Potential bioactive compounds and mechanisms of Fibraurea recisa Pierre for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease analyzed by network pharmacology and molecular docking prediction. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1052249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.-Y.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Lin, F.-J.; Zhou, W.-L.; Gan, R.-Y. Bioactive compounds, therapeutic activities, and applications of Ficus pumila L. Agronomy 2021, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimayanti, N.; Yaeghoobi, M.; Ashrafi, S.J.; Haghirosadat, B.F.; Octaviani, M.; Rahmi, A. Identification of compounds from Zingiber officinale as Novel Inhibitor for Dengue DEN2 NS2B/NS3 Serine Protease through Molecular Docking and DFT approaches. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2024, 17, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, C.; Gümüş, H.; Şimşek, M.; Tosun, M. DFT and Molecular Docking Study of 1-(2-Thiophen)-2-propen-1-one-3-(2,3,5-trichlorophenyl) (TTCP) Molecule as Antiviral to COVID-19 Main Protease. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouassi, K.A.R.; Ganiyou, A.; Benié, A.; Koné, M.G.-R.; Nobel, N.; Bohoussou, K.; Coulibaly, W. Identification of Potential C-kit Protein Kinase Inhibitors Associated with Human Liver Cancer: Atom-based 3D-QSAR Modeling, Pharmacophores-based Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Studies. Am. J. Pharmacol. Sci 2021, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhtiarudin, I.; Agistia, N.; Frimayanti, N.; Harlianti, T.; Jasril, J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one and its activities as an antioxidant, sunscreen, and antibacterial. J. Kim. Sains Apl. 2020, 23, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursch, M.; Mewes, J.M.; Hansen, A.; Grimme, S. Best-practice DFT protocols for basic molecular computational chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Army, M.K.; Khodijah, R.; Haryani, Y.; Teruna, H.Y.; Hendra, R. Antibacterial in vitro screening of Helminthostachys zeylanica (L.) Hook. root extracts. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2023, 11, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | MIC (µg/mL) | MFC (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | C. glabrata | C. krusei | C. albicans | C. glabrata | C. krusei | |
| F1 | 250 | >250 | 125 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F2 | 250 | 250 | >250 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F3 | 250 | >250 | 125 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F4 | 250 | >250 | 125 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F5 | 125 | 125 | 125 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F6 | 62.5 | 125 | 62.5 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| F7 | 250 | 125 | 125 | >250 | 250 | 250 |
| F8 | 250 | 250 | 125 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| F9 | 250 | 125 | 125 | >250 | 250 | 250 |
| 1 | 62.5 | 15.62 | 31.25 | 125 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| 2 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 62.5 | 125 | 125 |
| Ketoconazole | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Compound | Binding Free Energy (kcal/mol) | RMSD | H Bond | Hydrophobic Interaction | Van der Waals Interaction | Other Interactions | Binding Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketoconazole | −1.6989 | 1.1078 | Phe234, Met487, Ile488 | Lys156, Arg448 | Asp231 | Ala311, Tyr145, Leu310, Ile377, Gly307, Tyr131, Met380, Pro376, Ile379, Thr486, Gly232, Gly233, Phe139, His447, Phe152, Leu159, Ile450, Cys449 | 24 |
| 1 | −6.6377 | 1.1398 | Phe234 | Lys156, Arg448 | - | Cys449, Ala311, Ile450, Ile377, Leu310, Ile488, Met487, Met381, Ile379, Tyr131, Tyr145, Phe152, His447 | 15 |
| 2 | −6.7075 | 0.6158 | Tyr131, Ile450 | Arg448 | - | Ala311, Cys449, Gly307, Leu310, Ile377, Phe139, Ile379, Phe234, Met487, Tyr145, Phe152, His447 | 15 |
| Compound | Energy | Electronic Structure | Energy Gap | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOMO | LUMO | |||
| 1 | −1597.23 | −0.189 | −0.092 | 0.097 |
| 2 | −1803.12 | −0.210 | −0.198 | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendra, R.; Agustha, A.; Frimayanti, N.; Abdulah, R.; Teruna, H.Y. Antifungal Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.: An Analysis of In Silico Enzymatic Inhibition and In Vitro Efficacy against Candida Species. Molecules 2024, 29, 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102373
Hendra R, Agustha A, Frimayanti N, Abdulah R, Teruna HY. Antifungal Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.: An Analysis of In Silico Enzymatic Inhibition and In Vitro Efficacy against Candida Species. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102373
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendra, Rudi, Aulia Agustha, Neni Frimayanti, Rizky Abdulah, and Hilwan Yuda Teruna. 2024. "Antifungal Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.: An Analysis of In Silico Enzymatic Inhibition and In Vitro Efficacy against Candida Species" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102373
APA StyleHendra, R., Agustha, A., Frimayanti, N., Abdulah, R., & Teruna, H. Y. (2024). Antifungal Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.: An Analysis of In Silico Enzymatic Inhibition and In Vitro Efficacy against Candida Species. Molecules, 29(10), 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102373







