Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biosurfactants: Properties, Synthesis and Classification
2.1. Properties of Biosurfactants
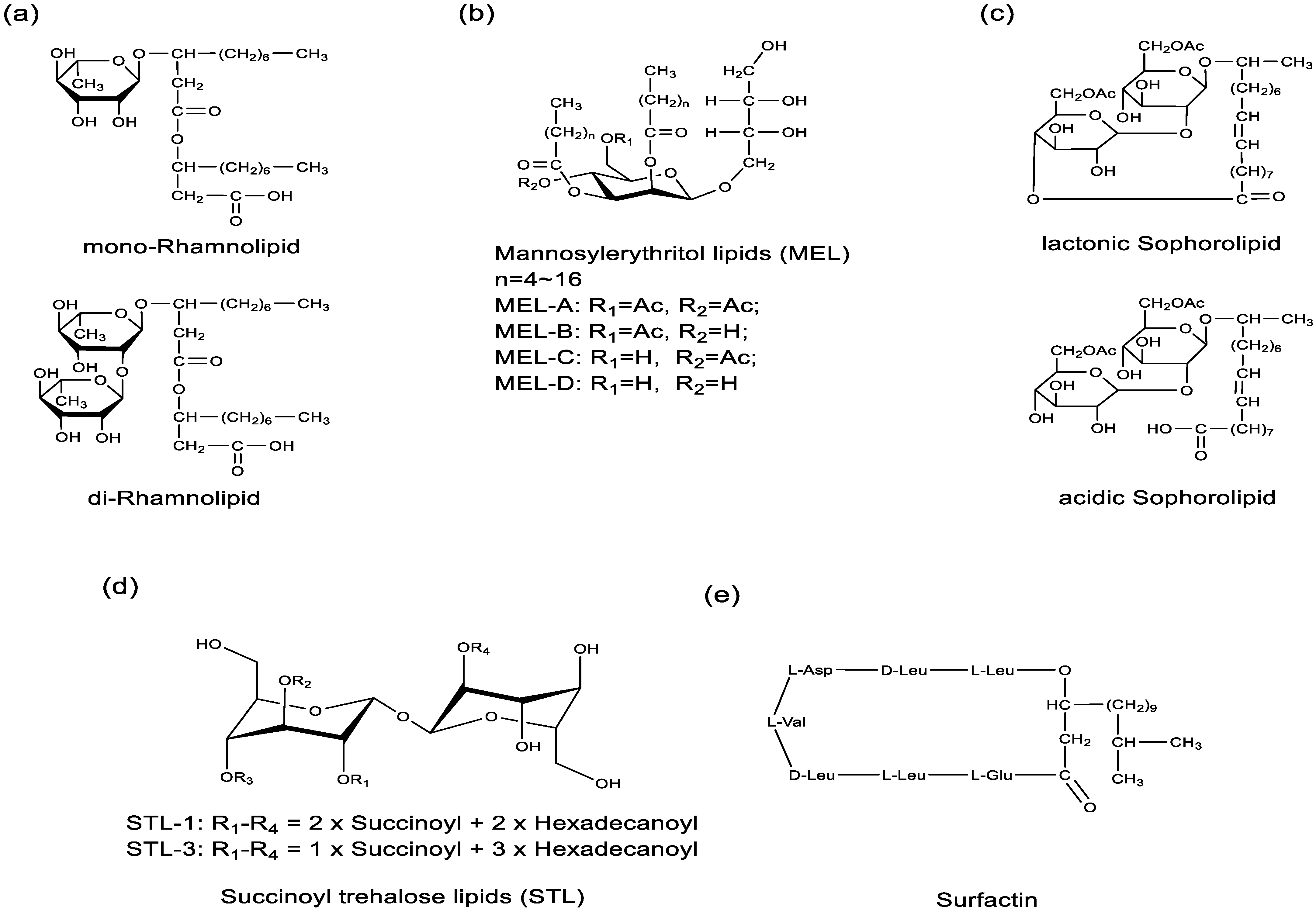
2.2. Classification, Bacterial Strains, and Responsible Genes of Biosurfactants
| Classification | Examples | Bacterial Strains | Responsible Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolipids | Rhamnolipids | P. aeruginosa | RhlA, RhlB, RhlC [59] |
| Sophorolipids | Torulopsis bombicola, S. bombicola | cyp52m1, ugtA1, at, SL transporter, ugB1, SBLE [62] | |
| Mannosylerythritol lipids | C. bombicola, Schizonella melanogramma, Geotrichum candidum | emt1, mac1, mac2, mat1, mmf1 [72] | |
| Trehalose lipids | Rhodococcus erythropolis, Mycobacterium sp., Gordonia sp. | otsA, otsB, treY, treZ [73] | |
| Exopolysaccharide | Lactobacillus spp. | epsABCDE, gt, Wzx, Wzy [74] | |
| Lipopeptides | Surfactin | B. subtilis | sfp, srfA-A, srfA-B, srfA-C, srfA-C-TE, srfA-TE [67,68] |
| Lichenysin | B. licheniformis | licAA, licAB, licAC, licAD [75] | |
| Iturin | B. subtilis | ItuD, ItuA, ItuB, ItuC [76] | |
| Arthrofactin | Pseudomonas sp. MIS38 | ArfA, ArfB, ArfC [77] | |
| Polymixins | Bacillus polymyxia | pmxA, pmxB, pmxC, pmxD, pmxE [78] | |
| Nisin | Lactococcus lactis spp. | nisZBTCIPRKFEG [79] | |
| Neutral lipids, Phospholipids and Fatty acids | Neutral lipids | Rhodotorula, Rhodosporidium, Lipomyces, Trichosporon, Candida genera of yeasts | ACCase, ACL, DAG, PDAT, GPAT, LPAAT, DGAT [80,81] |
| Phospholipids | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | INO1, INO2, INO4, CHO1, CHO2, OPI1, OPI3, PIS1, SIN3, UME6, PSD1/2, INM1 [82,83] | |
| Fatty acids | P. aeruginosa, Corynebacterium lepus, B. subtilis | accABCD, fabD, fabH, fabB, fabF, fabG, fabA, fabI, TE [84] |
3. Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences
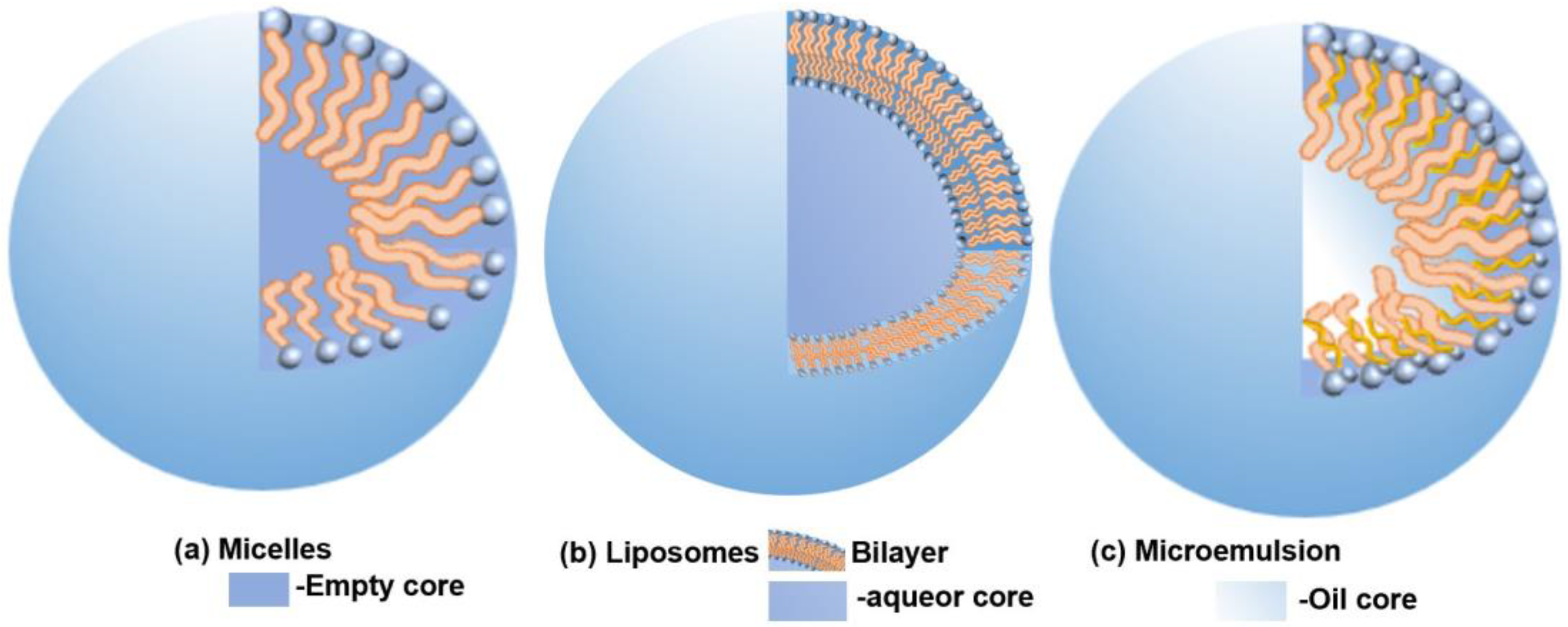
3.1. Drug Carrier Components
3.2. Inducing Tumor Cell Death and Differentiation
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
3.4. Antiviral Activity
3.5. Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
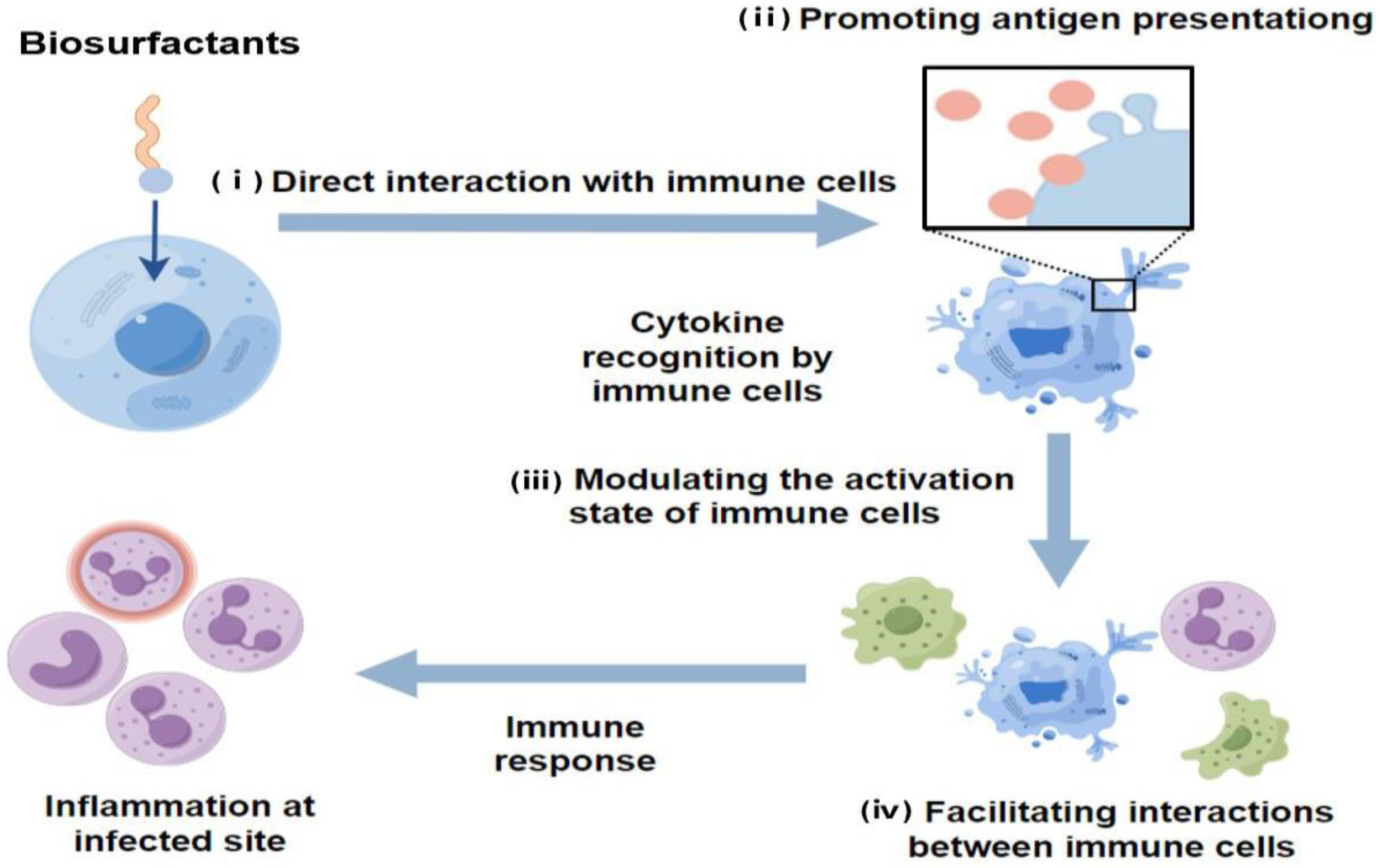
3.6. Immunomodulatory Effects
3.7. Modifiers and Functional Active Components
4. Challenges and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-López, L.; López-Prieto, A.; Lopez-Álvarez, M.; Pérez-Davila, S.; Serra, J.; González, P.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Characterization and Cytotoxic Effect of Biosurfactants Obtained from Different Sources. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31381–31390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.S.; Ghadi, R.; Kushwah, V.; Dora, C.P.; Jain, S. Lipid and Biosurfactant Based Core–Shell-Type Nanocapsules Having High Drug Loading of Paclitaxel for Improved Breast Cancer Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. 2020, 6, 6760–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Verma, V.; Saran, R.; Bhagyawant, S.S.; Srivastava, N. Natural Biosurfactant as Antimicrobial Agent: Strategy to Action Against Fungal and Bacterial Activities. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 80, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyol McKenna, P.; Naughton, P.J.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Ternan, N.G.; Lemoine, P.; Banat, I.M. Microbial Biosurfactants: Antimicrobial Activity and Potential Biomedical and Therapeutic Exploits. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofeal, M.; El-Malek, F.A. Valorization of Lipopeptides Biosurfactants as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.K.; Manickam, N. Microbial Biosurfactants: Production and Applications in Circular Bioeconomy. In Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals; Pandey, A., Tyagi, R.D., Varjani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 353–378. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Rational Strain Improvement for Surfactin Production: Enhancing the Yield and Generating Novel Structures. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, M.A.; Wang, Q.; Dai, Z. Sophorolipids Bioproduction in the Yeast Starmerella Bombicola: Current Trends and Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soberón-Chávez, G.; González-Valdez, A.; Soto-Aceves, M.P.; Cocotl-Yañez, M. Rhamnolipids Produced by Pseudomonas: From Molecular Genetics to the Market. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, S.A.; Twigg, M.S.; Naughton, P.J.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Characterisation of Cytotoxicity and Immunomodulatory Effects of Glycolipid Biosurfactants on Human Keratinocytes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabani, M.; Esmaeili-Tarzi, M.; Forootanfar, H.; Nematollahi, M.H.; Banat, I.M.; Ohadi, M.; Dehghannoudeh, G. Lipopeptide Biosurfactant from Acinetobacter junii B6: A Promising Natural Surfactant for Promoting Angiogenesis. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassenberger, A.; Scheberl, A.; Batchu, K.C.; Cristiglio, V.; Grillo, I.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Reimhult, E.; Baccile, N. Biocompatible Glyconanoparticles by Grafting Sophorolipid Monolayers on Monodispersed Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saimmai, A.; Riansa-Ngawong, W.; Maneerat, S.; Dikit, P. Application of Biosurfactants in the Medical Field. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresa, C.; Fracchia, L.; Sansotera, A.C.; De Rienzo, M.A.D.; Banat, I.M. Harnessing the Potential of Biosurfactants for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, F.; Farooq, M.; Wani, T.A.; Ahmad, H.; Javed, I.; Iqbal, M.; Sheikh, F.A.; Siddique, F.; Zargar, S.; Sheikh, S. Itraconazole Loaded Biosurfactin Micelles with Enhanced Antifungal Activity: Fabrication, Evaluation and Molecular Simulation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, E.; Abruzzo, A.; Giordani, B.; Cerchiara, T.; Bigucci, F.; Vitali, B.; di Cagno, M.P.; Luppi, B. Human Lactobacillus Biosurfactants as Natural Excipients for Nasal Drug Delivery of Hydrocortisone. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, T.; Yu, Z.; Shao, J.; Chu, J.; Zhu, H.; Yao, R. Formulation and Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Etoposide-Loaded Submicron Emulsions with Biosurfactant of Sophorolipids. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, T.; Chu, J.; Ma, X.; Yin, D. Lactonic Sophorolipid-Induced Apoptosis in Human HepG2 Cells through the Caspase-3 Pathway. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Y.-B.; Miao, J.-Y. Sophorolipid Produced from the New Yeast Strain Wickerhamiella domercqiae Induces Apoptosis in H7402 Human Liver Cancer Cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.; Khan, M.S.A.; AlQurashi, N. ROS-Mediated Necrosis by Glycolipid Biosurfactants on Lung, Breast, and Skin Melanoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 622470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuser, P.E.; Coelho, A.L.S.; de Melo, M.E.; Scussel, R.; Carciofi, B.A.M.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; de Oliveira, D.; de Andrade, C.J. Apoptosis Induction in Murine Melanoma (B16F10) Cells by Mannosylerythritol Lipids-B.; A Glycolipid Biosurfactant with Antitumoral Activities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 3855–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-H.; Wang, A.-H.; Wang, C.-L.; Mao, D.-Z.; Lu, M.-F.; Cui, Y.-Q.; Jiao, R.-Z. Surfactin Induces Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells through a ROS/JNK-Mediated Mitochondrial/Caspase Pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, C.; Day, N.; Shibahara, M.; Nomura, N.; Nakahara, T.; Murata, T.; Yokoyama, K.K. Mannosylerythritol Lipid Induces Characteristics of Neuronal Differentiation in PC12 Cells through an ERK-Related Signal Cascade. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, T.; Zhao, X.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Shibahara, M.; Nomura, N.; Nakahara, T.; Suzuki, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Jin, C.; Murata, T.; et al. Induction of the Differentiation of Human HL-60 Promyelocytic Leukemia cell Line by Succinoyl Trehalose Lipids. Cytotechnology 2000, 33, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, T.; Yanagihara, T.; Ito, S.; Imura, T.; Morita, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Kitamoto, D. Mannosylerythritol Lipid Is a Potent Inducer of Apoptosis and Differentiation of Mouse Melanoma Cells in Culture. J. Oleo. Sci. 2012, 61, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraszkiewicz, K.; Moryl, M.; Plaza, G.; Bhagat, D.; Satpute, K.S.; Bernat, P. Surfactants of Microbial Origin as Antibiofilm Agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 31, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Park, B.K.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.C.; Hwang, M.H.; Yun, H.I. Lipopolysaccharide-Binding and Neutralizing Activities of Surfactin C in Experimental Models of Septic Shock. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 556, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, R.; Kawano, A.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ariyoshi, W. Rhamnolipids and Surfactin Inhibit the Growth or Formation of Oral Bacterial Biofilm. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, C.O.; Olaniyan, O.T.; Anani, O.A.; Inobeme, A.; Samson, A.O.; Oloke, J.K.; Palnam, W.D.; Ali, S. Role of Biosurfactant in the Destruction of Pores and Destabilization of the Biological Membrane of Pathogenic Microorganisms. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Inamuddin Adetunji, C.O., Ahamed, M.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, V.K.; Tripathi, V.; Gupta, P.; Dhiman, N.; Regar, R.K.; Gautam, K.; Srivastava, J.K.; Patnaik, S.; Patel, D.K.; Manickam, N. Rhamnolipids from Planococcus spp. and Their Mechanism of Action Against Pathogenic Bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhou, S.; Sha, Z.; Sun, C. Characterization of Antifungal Lipopeptide Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Bacterium Bacillus sp. CS30. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, G.E.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Abou-Elela, G.M.; Ghozlan, H.; Sabry, S.A.; Soliman, N.A.; Teleb, M.; Abdel-Fattah, Y.R. Bioprocess Development for Biosurfactant Production by Natrialba sp. M6 with Effective Direct Virucidal and Anti-Replicative Potential Against HCV and HSV. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daverey, A.; Dutta, K.; Joshi, S.; Daverey, A. Sophorolipid: A Glycolipid Biosurfactant as a Potential Therapeutic Agent against COVID-19. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9550–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merghni, A.; Dallel, I.; Noumi, E.; Kadmi, Y.; Hentati, H.; Tobji, S.; Ben Amor, A.; Mastouri, M. Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Potential of Biosurfactants Isolated from Lactobacillus casei and Their Anti-Biofilm Effect in Oral Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 104, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Varshney, R.; Banat, I.M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pruthi, P.A.; Pruthi, V. Accelerated in Vivo Wound Healing Evaluation of Microbial Glycolipid Containing Ointment as a Transdermal Substitute. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stipcevic, T.; Piljac, A.; Piljac, G. Enhanced Healing of Full-Thickness Burn Wounds Using Di-Rhamnolipid. Burns 2006, 32, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y. Surfactin Inhibits Immunostimulatory Function of Macrophages through Blocking NK-κB, MAPK and Akt Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gein, S.V.; Kuyukina, M.S.; Ivshina, I.B.; Baeva, T.A.; Chereshnev, V.A. In Vitro Cytokine Stimulation Assay for Glycolipid Biosurfactant from Rhodococcus ruber: Role of Monocyte Adhesion. Cytotechnology 2011, 63, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccile, N.; Noiville, R.; Stievano, L.; Van Bogaert, I.N.A. Sophorolipids-Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Joshi, K.; Guin, D.; Prabhune, A.A. Chemically Conjugated Sophorolipids on CdTe QDs: A Biocompatible Photoluminescence Nanocomposite for Theranostic Applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E. Biosurfactants and Surfactants Interacting with Membranes and Proteins: Same but Different? Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, A.; Le Griel, P.; Perez, J.; Baccile, N. Cation-Induced Fibrillation of Microbial Glycolipid Biosurfactant Probed by Ion-Resolved In Situ SAXS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 10528–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andretto, V.; Taurino, G.; Guerriero, G.; Guerin, H.; Laine, E.; Bianchi, M.G.; Agusti, G.; Briancon, S.; Bussolati, O.; Clayer-Montembault, A.; et al. Nanoemulsions Embedded in Alginate Beads as Bioadhesive Nanocomposites for Intestinal Delivery of the Anti-Inflammatory Drug Tofacitinib. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 2892–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Aranda, F.J.; Teruel, J.A.; Espuny, M.J.; Marqués, A.; Manresa, Á.; Ortiz, A. Permeabilization of Biological and Artificial Membranes by a Bacterial Dirhamnolipid Produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchbhai, A. Chapter 15—Hemolysis and Formation of Ion Channels in Lipid Membrane. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Inamuddin Adetunji, C.O., Ahamed, M.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- López Hernández, M.; Pedersen, J.S.; Otzen, D.E. Proteins and Biosurfactants: Structures, Functions, and Recent Applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 68, 101746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imura, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Kitamoto, D. Coacervate Formation from Natural Glycolipid: One Acetyl Group on the Headgroup Triggers Coacervate-to-Vesicle Transition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10804–10805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binot, C.; Sadoc, J.-F.; Chouard, C.-H. Oncogenesis, Lipids Rafts and Liquid Crystals: A Nanoscopic Supplementary Field for Applied Researches and a New Hope of Advances in Cancer. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.; Kurdi, M.; Heerklotz, H. Classifying Surfactants with Respect to Their Effect on Lipid Membrane Order. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balleza, D.; Alessandrini, A.; Beltrán García, M.J. Role of Lipid Composition, Physicochemical Interactions, and Membrane Mechanics in the Molecular Actions of Microbial Cyclic Lipopeptides. J. Membr. Biol. 2019, 252, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marega Motta, A.; Donato, M.; Mobbili, G.; Mariani, P.; Itri, R.; Spinozzi, F. Unveiling the Mono-Rhamnolipid and Di-Rhamnolipid Mechanisms of Action upon Plasma Membrane Models. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 624, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasaiyan, P.; Pandey, P.R.; Visaveliya, N.R.; Roy, S.; Prasad, B.L.V. Vesicle Structures from Bolaamphiphilic Biosurfactants: Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies on the Effect of Unsaturation on Sophorolipid Self-Assemblies. Chemistry 2014, 20, 6246–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tao, X.; Zou, A.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mu, B. Effect of the Microbial Lipopeptide on Tumor Cell Lines: Apoptosis Induced by Disturbing the Fatty Acid Composition of Cell Membrane. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutchelvi, J.I.; Bhaduri, S.; Uppara, P.V.; Doble, M. Mannosylerythritol Lipids: A Review. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, D.; Ghosh, S.; Ourisson, G.; Nakatani, Y. Formation of Giant Vesicles from Diacylmannosylerythritols, and Their Binding to Concanavalin A. Chem. Commun. 2000, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaparoli, M.; Kreling, N.E.; Colla, L.M. Increasing the Production of Extracellular Biosurfactants from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Environ. Qual. Manage. 2020, 29, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyousif, N.; Al-Tamimi, W.; Al-Sahib, M.A.A. Evaluation of the Effect of Various Nutritional and Environmental Factors on Biosurfactant Production by Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Biodiversitas. 2022, 23, 3533–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouassida, M.; Mnif, I.; Ghribi, D. Enhanced Biosurfactant Production by Bacillus subtilis SPB1 Using Developed Fed-Batch Fermentation: Effects of Glucose Levels and Feeding Systems. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 46, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittgens, A.; Kovacic, F.; Müller, M.M.; Gerlitzki, M.; Santiago-Schübel, B.; Hofmann, D.; Tiso, T.; Blank, L.M.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R.; et al. Novel Insights into Biosynthesis and Iptake of Rhamnolipids and Their Precursors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhandono, S.; Kusuma, S.H.; Meitha, K. Characterization and Production of Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant in Recombinant Escherichia coli Using Autoinduction Medium and Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2021, 64, e21200301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, F.; Shen, J.-d.; Huang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Highly Efficient Production of Rhamnolipid in P. putida Using a Novel SacB-Based System and Mixed Carbon Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, X.; Chu, J. Advances in Sophorolipid-Producing Strain Performance Improvement and Fermentation Optimization Technology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10325–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Song, X. Sophorolipid Production Using Lignocellulosic Biomass by Co-culture of Several Recombinant Strains of Starmerella bombicola with Different Heterologous Cellulase Genes from Penicillum oxalicum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, G.; Fang, X.; Song, X. A Cumulative Effect by Multiple-Gene Knockout Strategy Leads to a Significant Increase in the Production of Sophorolipids in Starmerella bombicola CGMCC 1576. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 818445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewald, S.; Josephs, K.; Bolker, M. Genetic Analysis of Biosurfactant Production in Ustilago maydis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msanne, J.; Ashby, R.D.; Olanya, O.M. Heterologous eExpression of a Yeast Lipid Transporter Promotes Accumulation of Storage Compounds in Chlamydomonas. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 52, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.B.; Sarkar, B.; Moni, R.; Rahman, M.S. Molecular Genetics of Surfactin and Its Effects on Different Sub-Populations of Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 32, e00686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théatre, A.; Cano-Prieto, C.; Bartolini, M.; Laurin, Y.; Deleu, M.; Niehren, J.; Fida, T.; Gerbinet, S.; Alanjary, M.; Medema, M.H.; et al. The Surfactin-Like Lipopeptides From Bacillus spp.: Natural Biodiversity and Synthetic Biology for a Broader Application Range. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 623701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Huo, K.; Song, X.; Quan, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Yang, C. Engineering of a Genome-Reduced Strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Enhancing Surfactin Production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Efficient Production of Surfactin from Xylose-Rich Corncob Hydrolysate Using Genetically Modified Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhi, Y.; Xu, Y. Systematically Engineering the Biosynthesis of a Green Biosurfactant Surfactin by Bacillus subtilis 168. Metab. Eng. 2019, 52, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, F.; Stehlik, T.; Linne, U.; Bolker, M.; Freitag, J.; Sandrock, B. Engineering Ustilago Maydis for Production of Tailor-Made Mannosylerythritol Lipids. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2021, 12, e00165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delegan, Y.; Sargsyan, A.; Hovhannisyan, N.; Babayan, B.; Petrikov, K.; Vainstein, M. Analysis of Genome Sequence and Trehalose Lipid Production Peculiarities of the Thermotolerant Gordonia Strain. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, D.; Davray, D.; Kulkarni, R. A Diverse Repertoire of Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis Gene Clusters in Lactobacillus Revealed by Comparative Analysis in 106 Sequenced Genomes. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, S. Transcription Factor DegU-Mediated Multi-pathway Regulation on Lichenysin Biosynthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. Metab. Eng. 2022, 74, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, C.A.; Bowman, M.J.; Rooney, A.P. Iturinic Lipopeptide Diversity in the Bacillus subtilis Species Group—Important Antifungals for Plant Disease Biocontrol Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roongsawang, N.; Hase, K.; Haruki, M.; Imanaka, T.; Morikawa, M.; Kanaya, S. Cloning and Characterization of the Gene Cluster Encoding Arthrofactin Synthetase from Pseudomonas sp. MIS38. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.K.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, R.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.F.; Park, S.H. Identification of a Polymyxin Synthetase Gene Cluster of Paenibacillus polymyxa and Heterologous Expression of the Gene in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3350–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Liu, F.; Wan, X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, Z.; Saris, P.E.J.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. Genomic Features and Construction of Streamlined Genome Chassis of Nisin Z Producer Lactococcus lactis N8. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mitra, M.; Maiti, M.K. Recent Advances in Lipid Metabolic Engineering of Oleaginous Yeasts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q. Regulatory Mechanisms of Lipid biosynthesis in Microalgae. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2373–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.S.; Kanipes, M.I.; Jackson, J.C.; Yates, J.; Henry, S.A.; Lopes, J.M. Physical Map Locations of the Phospholipid Biosynthetic Structural and Regulatory Genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 1995, 11, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hancock, L.C.; Lopes, J.M. Transcriptional Regulation of Yeast Phospholipid Biosynthetic Genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1771, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Liang, S.; Zong, M.H.; Yang, J.G.; Lou, W.Y. Microbial Synthesis of Functional Odd-Chain Fatty Acids: A Review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Banerjee, T.; Totsingan, F.; Woody, K.; Gross, R.A.; Santra, S. Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactonic Sophorolipids: Nanoceria-Assisted Combination Therapy of NSCLC Using HDAC and Hsp90 Inhibitors. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohadi, M.; Shahravan, A.; Dehghannoudeh, N.; Eslaminejad, T.; Banat, I.M.; Dehghannoudeh, G. Potential Use of Microbial Surfactant in Microemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Systematic Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Aranda, F.J.; Teruel, J.A.; Ortiz, A. New pH-Sensitive Liposomes Containing Phosphatidylethanolamine and a Bacterial Dirhamnolipid. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niaz, T.; Shabbir, S.; Noor, T.; Imran, M. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Bacteriocin Loaded Nano-Vesicles Functionalized with Rhamnolipids Against Foodborne Pathogens. LWT 2019, 116, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Inoh, Y.; Kitamoto, D.; Furuno, T. Nano Vectors with a Biosurfactant for Gene Transfection and Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoh, Y.; Furuno, T.; Hirashima, N.; Kitamoto, D.; Nakanishi, M. The Ratio of Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Biosurfactants Affects the Efficiency of Gene Transfection. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 398, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imura, T.; Masuda, Y.; Ito, S.; Worakitkanchanakul, W.; Morita, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Kitamoto, D. Packing Density of Glycolipid Biosurfactant Monolayers Give a Significant Effect on Their Binding Affinity Toward Immunoglobulin G. J. Oleo. Sci. 2008, 57, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q. Synthesis, Characterization of Liposomes Modified with Biosurfactant MEL-A Loading Betulinic Acid and Its Anticancer Effect in HepG2 Cell. Molecules 2019, 24, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worakitkanchanakul, W.; Imura, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Morita, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Rujiravanit, R.; Chavadej, S.; Minamikawa, H.; Kitamoto, D. Aqueous-Phase Behavior and Vesicle Formation of Natural Glycolipid Biosurfactant, Mannosylerythritol Lipid-B. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 65, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Sánchez, A.d.J.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Jaramillo-Flores, M.E. Biological Activity of Glycolipids Produced by Microorganisms: New Trends and Possible Therapeutic Alternatives. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoda, H.; Shinmoto, H.; Matsumura, M.; Nakahara, T. The Neurite-Initiating Effect of Microbial Extracellular Glycolipids in PC12 Cells. Cytotechnology 1999, 31, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Hajikhani, B.; Faghihloo, E.; Goudarzi, H. Increased Expression of Caspase Genes in Colorectal Cancer Cell Line by Nisin. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 15, e97734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Ashtiani, H.-R.; Baldisserotto, A.; Cesa, E.; Manfredini, S.; Sedghi Zadeh, H.; Ghafori Gorab, M.; Khanahmadi, M.; Zakizadeh, S.; Buso, P.; Vertuani, S. Microbial Biosurfactants as Key Multifunctional Ingredients for Sustainable Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, M.K.; Padhi, S.; Patel, L.D.; Rath, G.; Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K. Theranostic Efficiency of Biosurfactants Against COVID-19 and Similar Viruses—A Review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayathullah, M.G.; Parekh, Y.; Banu, S.; Ram, S.; Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, B.K.; Idris, M.M. Gramicidin S and Melittin: Potential Anti-Viral Therapeutic Peptides to Treat SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Sogabe, A.; Yanagidani, S.; Imura, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Kitamoto, D. A Yeast Glycolipid Biosurfactant, Mannosylerythritol Lipid, Shows Potential Moisturizing Activity toward Cultured Human Skin Cells: The Recovery Effect of MEL-A on the SDS-damaged Human Skin Cells. J. Oleo. Sci. 2009, 58, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryll, R.; Kumazawa, Y.; Yano, I. Immunological Properties of Trehalose Dimycolate (Cord Factor) and Other Mycolic Acid-Containing Glycolipids--A Review. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Nakane, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Ikegami, T.; Kitamoto, D. Mannosylerythritol Lipid, a Yeast Extracellular Glycolipid, Shows High Binding Affinity towards Human Immunoglobulin G. BMC Biotechnol. 2001, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, M.; Smith-Norowitz, T.A.; Chice, S.; Wallner, S.R.; Viterbo, D.; Mueller, C.M.; Gross, R.; Nowakowski, M.; Schulze, R.; Zenilman, M.E.; et al. Sophorolipids Decrease IgE Production in U266 Cells by Downregulation of BSAP (Pax5), TLR-2, STAT3 and IL-6. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Tadokoro, S.; Sasai, M.; Kitamoto, D.; Hirashima, N. Biosurfactant Mannosyl-Erythritol Lipid Inhibits Secretion of Inflammatory Mediators from RBL-2H3 Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Mukherji, R.; Joshi-Navare, K.; Banerjee, A.; Gokhale, R.; Nagane, S.; Prabhune, A.; Ogale, S. Fluorescent Sophorolipid Molecular Assembly and its Magnetic Nanoparticle Loading: A Pulsed Laser Process. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardouri, M.; Bettencourt, A.; Martin, V.; Carvalho, F.A.; Santos, C.; Monge, N.; Santos, N.C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gomes, P.S.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Using Plasma-Mediated Covalent Functionalization of Rhamnolipids on Polydimethylsiloxane towards the Antimicrobial Improvement of Catheter Surfaces. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Application | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Carrier Components | Enhance drug delivery capabilities and bioavailability | [15,16,17] |
| Inducing Tumor Cell Death and Differentiation | Activate enzyme pathway | [18,19] |
| Effect mitochondria pathway | [20,21,22] | |
| Regulation cell cycle | [23,24,25] | |
| Antibacterial Activity | Disruption of cell membrane and proteins responsible for essential function | [26,27] |
| Changing the external environment of bacteria | [28,29] | |
| Effect the mitochondria pathway | [30,31] | |
| Antiviral Activity | Damage the viral envelope and hinder the virus’s ability to penetrate host cells | [32] |
| Dissolve the lipid envelope | [33] | |
| Wound Healing and Tissue Repair | Effect the inflammatory phase | [34] |
| Endorse cellular migration and proliferation | [11,35] | |
| Fostering tissue remodeling | [10,36] | |
| Immunomodulatory Effects | Direct interaction with immune cells Promoting antigen presentation Modulating the activation state of immune cells Facilitating interactions between immune cells | [10,37,38] |
| Modifiers and Functional Active Components | Modifiers of functional ingredients Broadens the prospective utility of glycolipid biosurfactants within the sphere of drug diagnosis | [12,39,40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; An, J.; Cao, T.; Guo, M.; Han, F. Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences. Molecules 2024, 29, 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112606
Wang X, An J, Cao T, Guo M, Han F. Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112606
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoyan, Jiachen An, Tianyu Cao, Mingmin Guo, and Fu Han. 2024. "Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112606
APA StyleWang, X., An, J., Cao, T., Guo, M., & Han, F. (2024). Application of Biosurfactants in Medical Sciences. Molecules, 29(11), 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112606







