Bicolor Tuning and Hyper-Reflective Color Switching Based on Two Stacked Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Cells with Asymmetric Electrothermal Optical Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
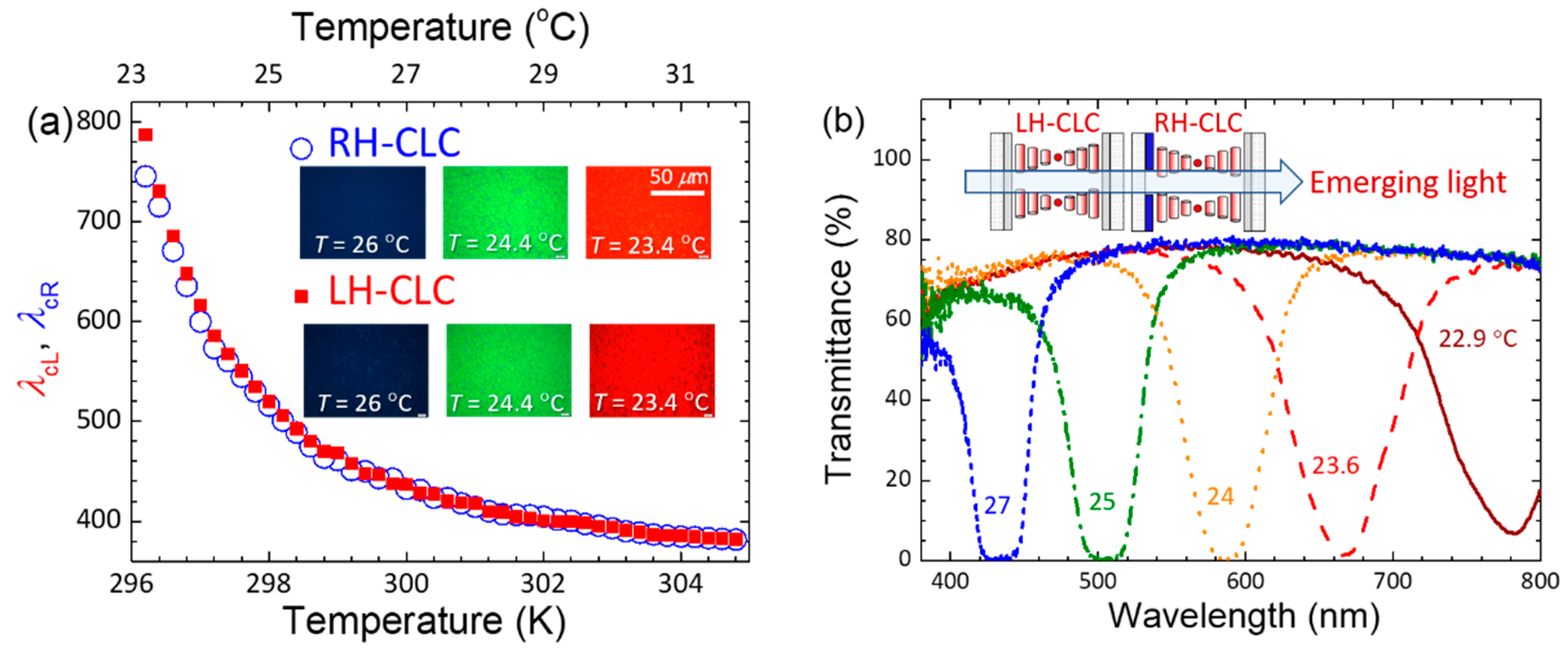
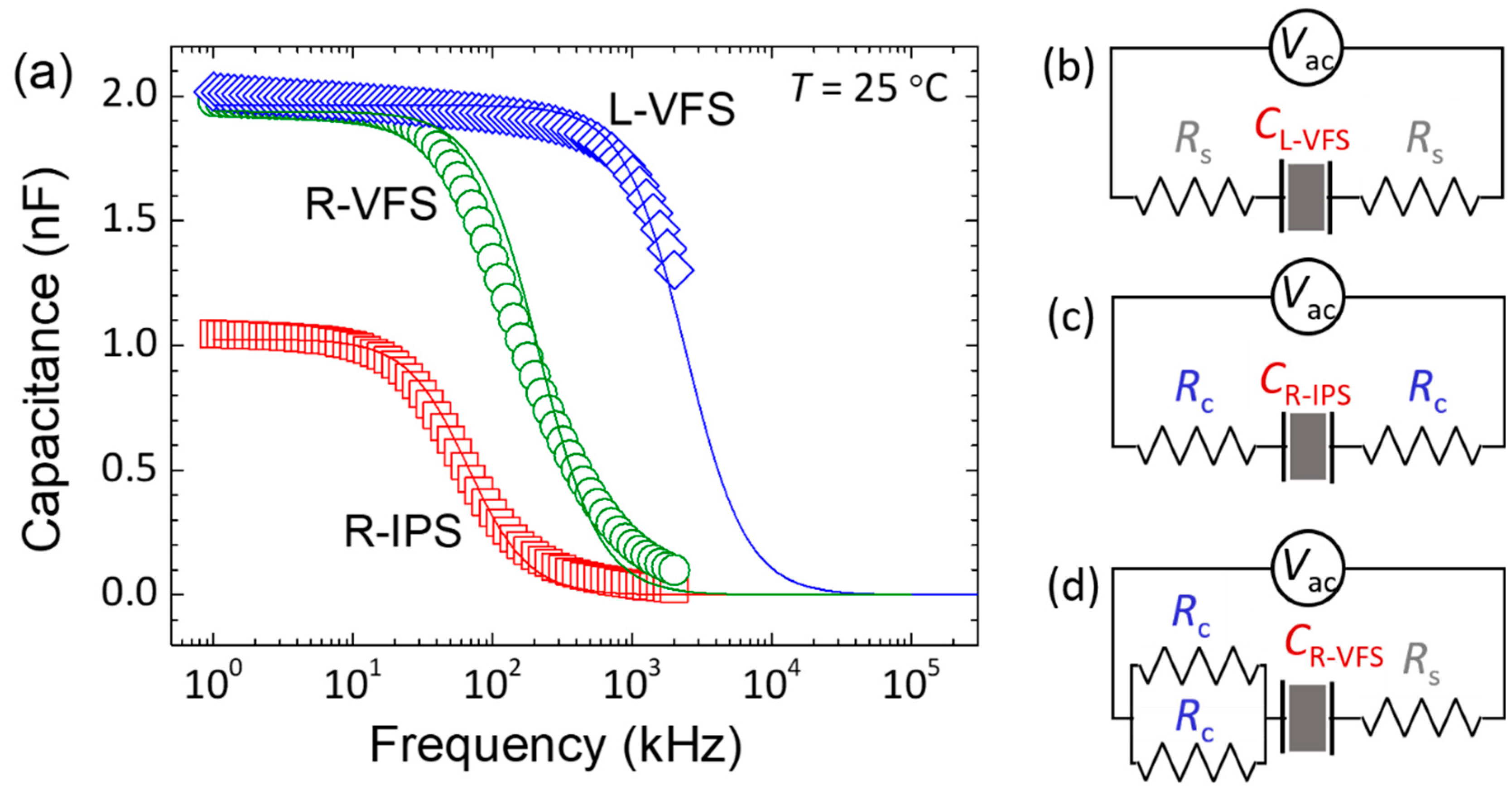
2.1. Passively Thermal and Actively Electrothermal Modulation of the Hyper-Reflective Bandgap
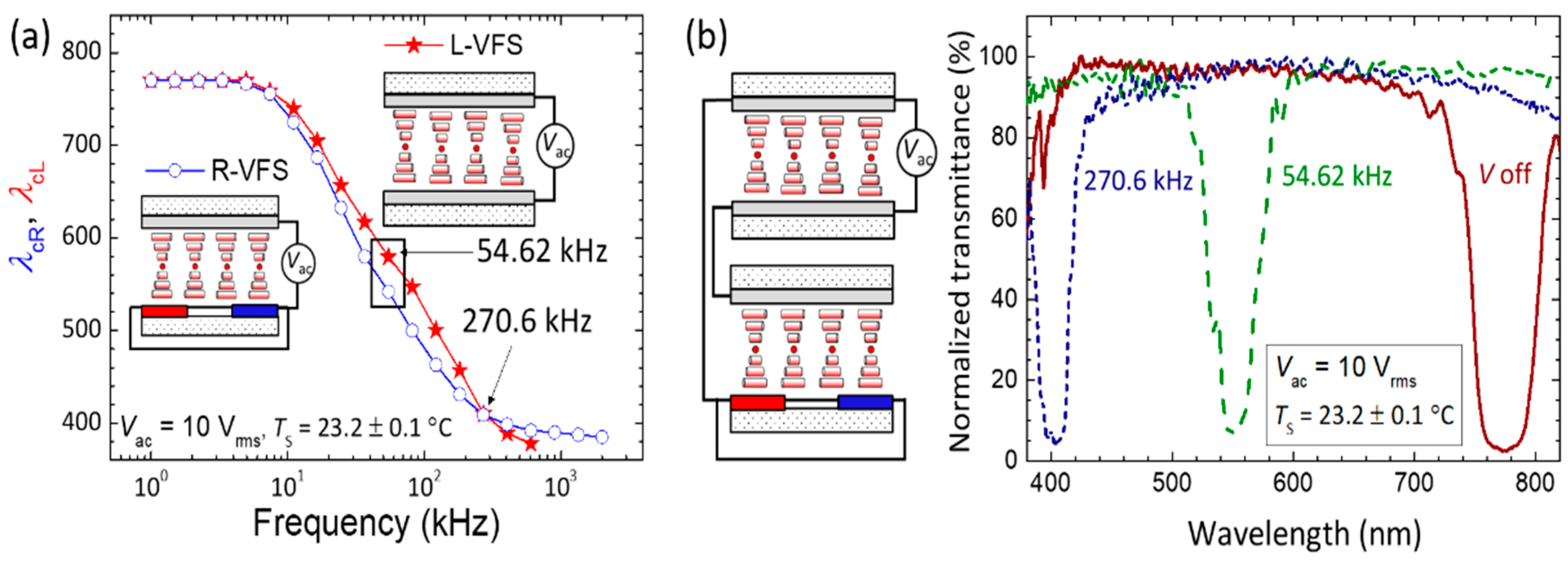
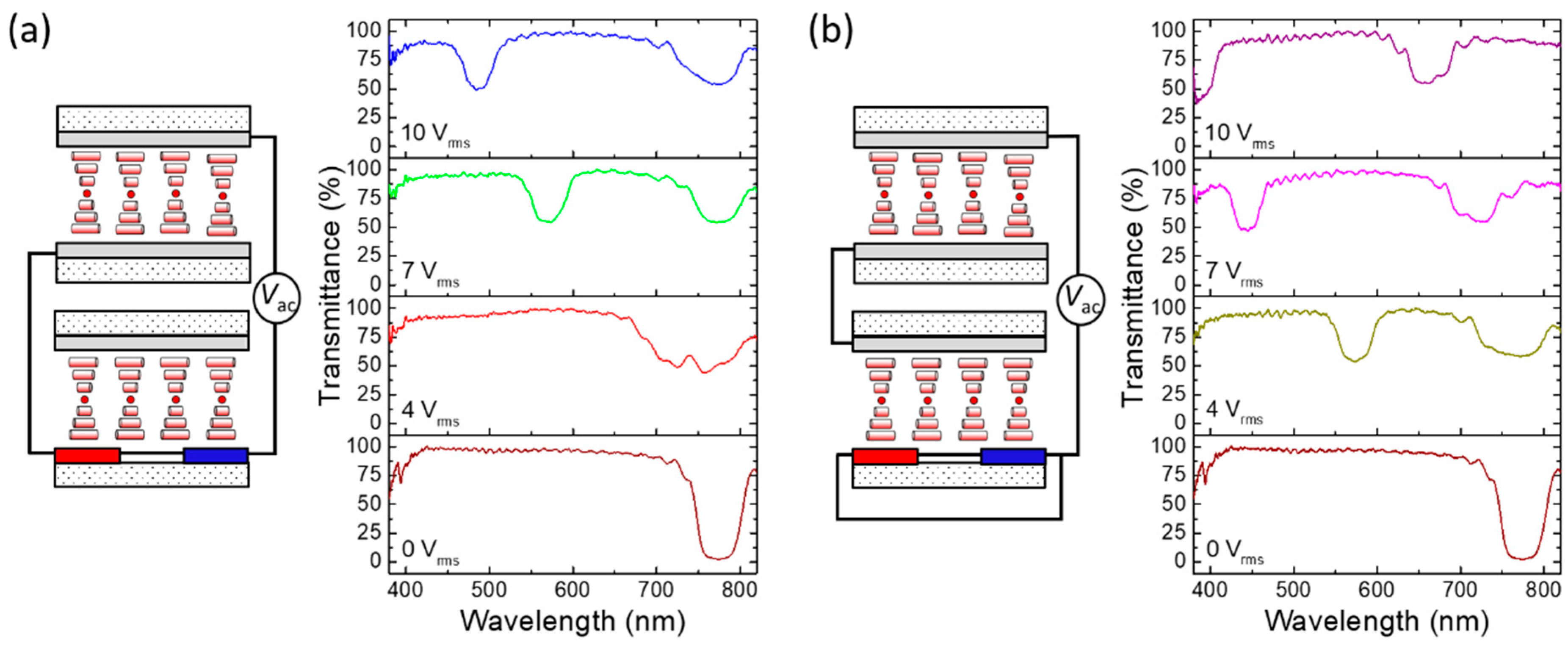
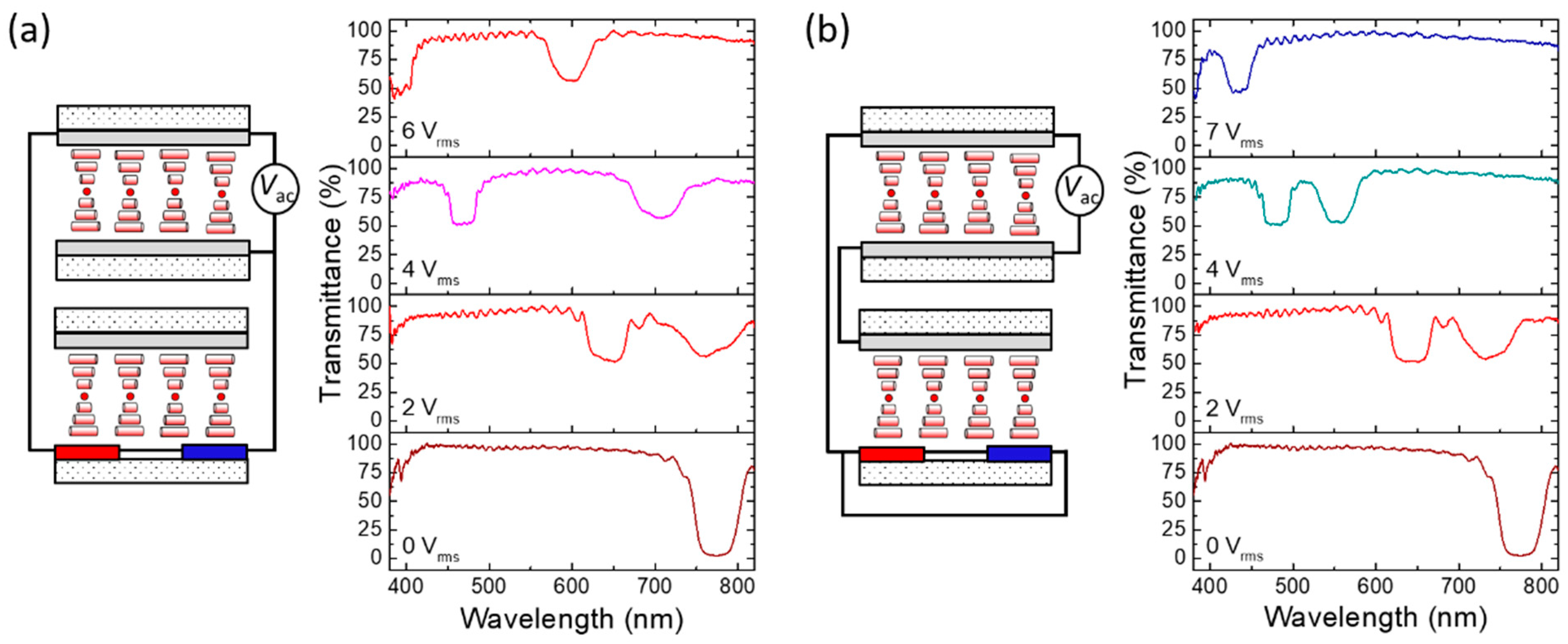
2.2. Electrothermal Tunability of Bi-Reflected Color from Staked LH- and RH-Bandgaps
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Sample Preparations
3.2. Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzeng, S.Y.; Chen, C.N.; Tzeng, Y. Thermal tuning band gap in cholesteric liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Doyle, C.; Wu, S.T. Tuning the photonic band gap in cholesteric liquid crystals by temperature-dependent dopant solubility. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrovsky, A.Y.; Boiko, N.I.; Shibaev, V.; Wendorff, J.H. Cholesteric mixtures with photochemically tunable, circularly polarized fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bricker, R.L.; Natarajan, L.V.; Tabiryan, N.V.; Green, L.; Li, Q.; Bunning, T.J. Phototunable azobenzene cholesteric liquid crystals with 2000 nm range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3484–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; McConney, M.E.; Bunning, T.J. Dynamic color in stimuli-responsive cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9832–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Morris, S.M.; Coles, H.J.; Huck, W.T. Wavelength tuning the photonic band gap in chiral nematic liquid crystals using electrically commanded surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 231110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Morris, S.M.; Huck, W.T.S.; Coles, H.J. Liquid crystals: Electrically tuneable liquid crystal photonic bandgaps. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3817–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.; Imrie, C.T.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Electrically tunable selective reflection of light from ultraviolet to visible and infrared by heliconical cholesterics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.-C.; Yang, Z.-H.; Shen, D.; Lee, W. Red, green, and blue reflections enabled in an electrically tunable helical superstructure. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1701128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Wu, G.-W.; Timofeev, I.V.; Zyryanov, V.Y.; Lee, W. Electrothermally tunable reflective colors in a self-organized cholesteric helical superstructure. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Wu, G.-W.; Yu, C.-H.; Lee, W. Voltage-induced pseudo-dielectric heating and its application for color tuning in a thermally sensitive cholesteric liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.-C.; Yang, S.-H.; Lee, W. Color tuning in thermo-sensitive chiral photonic liquid crystals based on the pseudo-dielectric heating effect. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.V.; Wofford, J.M.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Sutherland, R.L.; Koerner, H.; Vaia, R.A.; Bunning, T.J. Electrothermal tuning in a negative dielectric cholesteric liquid crystal material. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 093107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Tondiglia, V.; Natarajan, L.; Duning, M.; Bricker, R.; Sutherland, R.; White, T.; Durstock, M.; Bunning, T. Electromechanical tuning of cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 013105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-H.; Jau, H.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wei, T.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Fuh, A.Y.-G. Electrically controllable laser based on cholesteric liquid crystal with negative dielectric anisotropy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 061122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Park, H.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoon, D.K. Optical Rotation-Based Tunable Color Filter Using Chiral Photonic Crystal. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.G.; Beom, T.W.; Cui, H.; Park, J.R.; Hwang, S.J.; Lim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H. Reduction of viewing-angle dependent color shift in a reflective type cholesteric liquid crystal color filter. Appl. Phys. Express 2008, 1, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chemingui, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Drevensek-Olenik, I.; Hassan, F.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Saadaoui, L.; Xu, J. Dual-wavelength lasing with orthogonal circular polarizations generated in a single layer of a polymer–cholesteric liquid crystal superstructure. Polym. J. 2023, 15, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuhisa, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.T.; Ozaki, R.; Takao, Y.; Fujii, A.; Ozaki, M. Low-threshold and high efficiency lasing upon band-edge excitation in a cholesteric liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 091114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.C.; Lee, W. Color-reflective dual-frequency cholesteric liquid crystal displays and their drive schemes. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-K.; West, J.L.; Chien, L.-C.; Doane, J.W. Control of reflectivity and bistability in displays using cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, D.; Lub, J.; Mol, G. Wide-band reflective polarizers from cholesteric polymer networks with a pitch gradient. Nature 1995, 378, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Cao, H.; He, W.; Ma, Z.; Geng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, H. Wide-band reflective polarizers from cholesteric liquid crystals with stable optical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Chiu, S.W.; Kuo, H.L.; Tang, K.T. Cholesteric liquid crystal-carbon nanotube hybrid architectures for gas detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 043501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, D.; Schenning, A.; Bastiaansen, C. Chiral-nematic liquid crystals as one dimensional photonic materials in optical sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 6695–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-C.; Sung, Y.-C.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive color-indicating and quantitative biosensor based on cholesteric liquid crystal. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 5033–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Pai, C.-P.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, W. Label-free single-substrate quantitative protein assay based on optical characteristics of cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, W. Photocontrolled capacitive biosensor based on photoresponsive azobenzene-doped liquid crystals for label-free protein assay. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Wang, C.-T.; Jau, H.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hsu, W.-H.; Lin, T.-H. Versatile energy-saving smart glass based on tristable cholesteric liquid crystals. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 7601–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Ji, S.M.; Han, C.H.; Yoon, T.H. A cholesteric liquid crystal smart window with a low operating voltage. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 197, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, G.-F.; Wu, P.-C.; Zyryanov, V.Y.; Lee, W. Electrically active and thermally passive liquid-crystal device toward smart glass. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makow, D.M. Peak reflectance and color gamut of superimposed left-and right-handed cholesteric liquid crystals. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.H.; Park, B.; Shin, K.C.; Ohta, T.; Tsunoda, Y.; Hoshi, H.; Takanishi, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Watanabe, J.; Nishimura, S. Effect of phase retardation on defect-mode lasing in polymeric cholesteric liquid crystals. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radka, B.P.; King, B.E.; McConney, M.E.; White, T.J. Electrically induced splitting of the selective reflection in polymer stabilized cholesteric liquid crystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, F.; Wei, J.; Yang, H. Realisation of cholesteric liquid-crystalline materials reflecting both right-and left-circularly polarised light using the wash-out/refill technique. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lu, J. High-Reflective Templated Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Filters. Molecules 2021, 26, 6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Han, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; He, W. Cholesteric liquid crystal films with adjustable wavelength band and reflectance by using wash-out/refill technique and light-responsive compounds. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froyen, A.A.; Wübbenhorst, M.; Liu, D.; Schenning, A.P. Electrothermal color tuning of cholesteric liquid crystals using interdigitated electrode patterns. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2000958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, W. All-electrical switching and electrothermo-optical response of a tristable smectic-A liquid crystal. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 114566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, W. Electrothermal formation of uniform lying helix alignment in a cholesteric liquid crystal cell. Crystals 2019, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, P.N. A theory of the cholesteric mesophase. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1969, 8, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkowski, P. Dielectric spectroscopy of liquid crystals. Theoretical model of ITO electrodes influence on dielectric measurements. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2009, 17, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Wu, G.-W.; Lee, W. Pseudo-dielectric relaxation-enabled electrothermal tuning of reflective color in a soft chiral photonic crystal. In Liquid Crystals XXIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; p. 1109202. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, H.-K.; Wu, P.-C.; Lee, W. Bicolor Tuning and Hyper-Reflective Color Switching Based on Two Stacked Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Cells with Asymmetric Electrothermal Optical Responses. Molecules 2024, 29, 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112607
Tseng H-K, Wu P-C, Lee W. Bicolor Tuning and Hyper-Reflective Color Switching Based on Two Stacked Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Cells with Asymmetric Electrothermal Optical Responses. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112607
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Hsin-Kai, Po-Chang Wu, and Wei Lee. 2024. "Bicolor Tuning and Hyper-Reflective Color Switching Based on Two Stacked Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Cells with Asymmetric Electrothermal Optical Responses" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112607
APA StyleTseng, H.-K., Wu, P.-C., & Lee, W. (2024). Bicolor Tuning and Hyper-Reflective Color Switching Based on Two Stacked Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Cells with Asymmetric Electrothermal Optical Responses. Molecules, 29(11), 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112607








