Computational Docking as a Tool in Guiding the Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
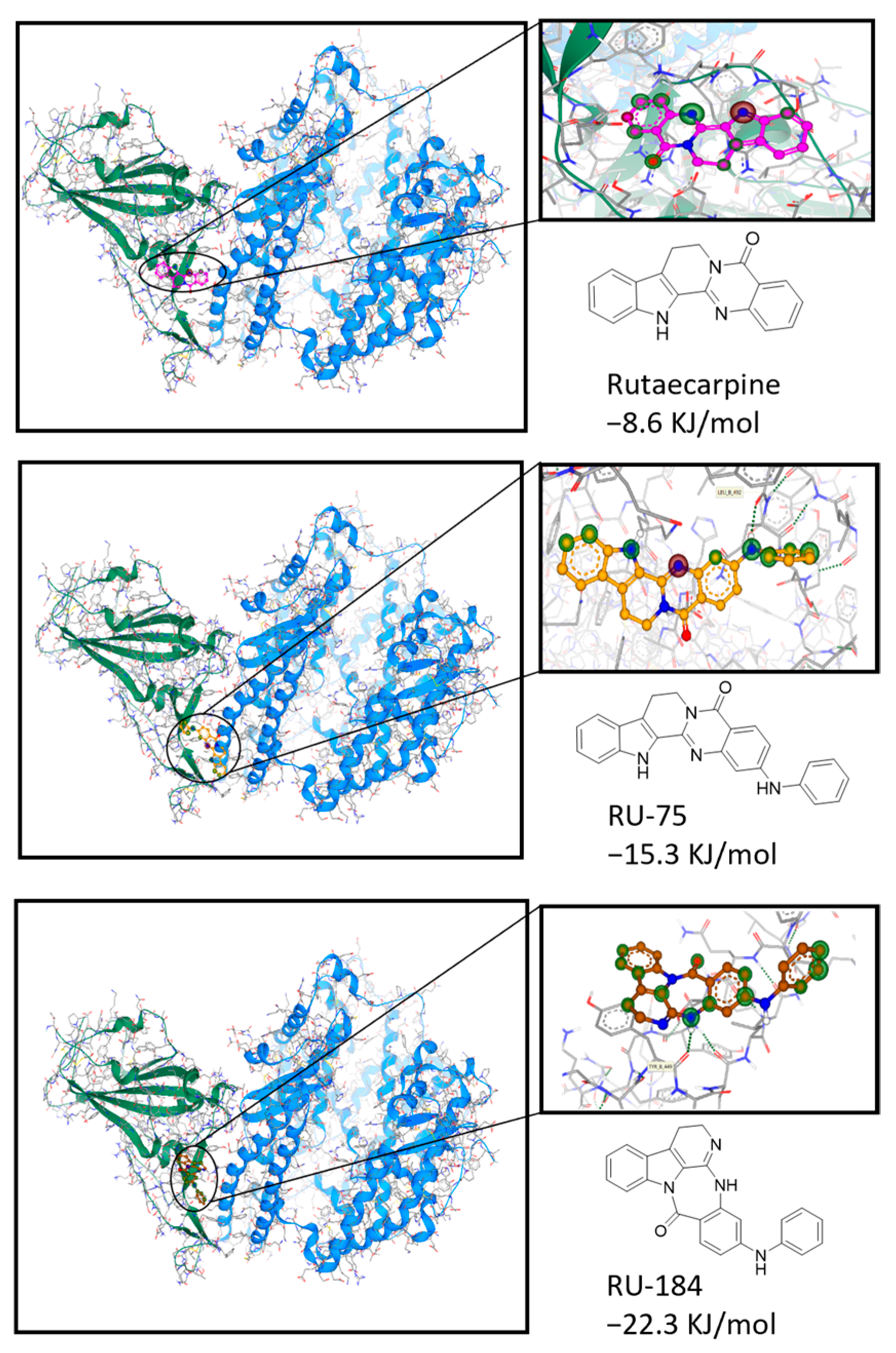
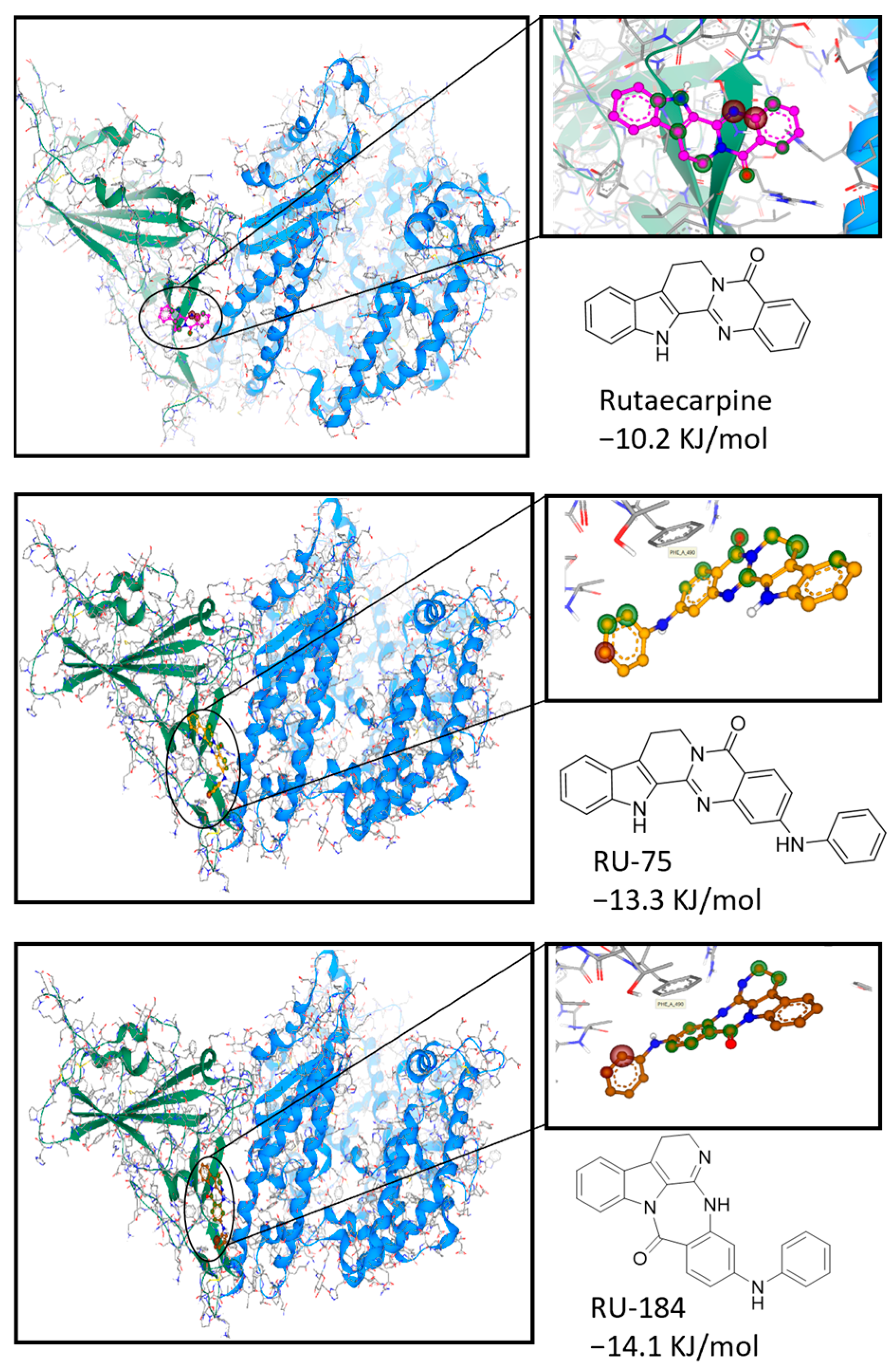
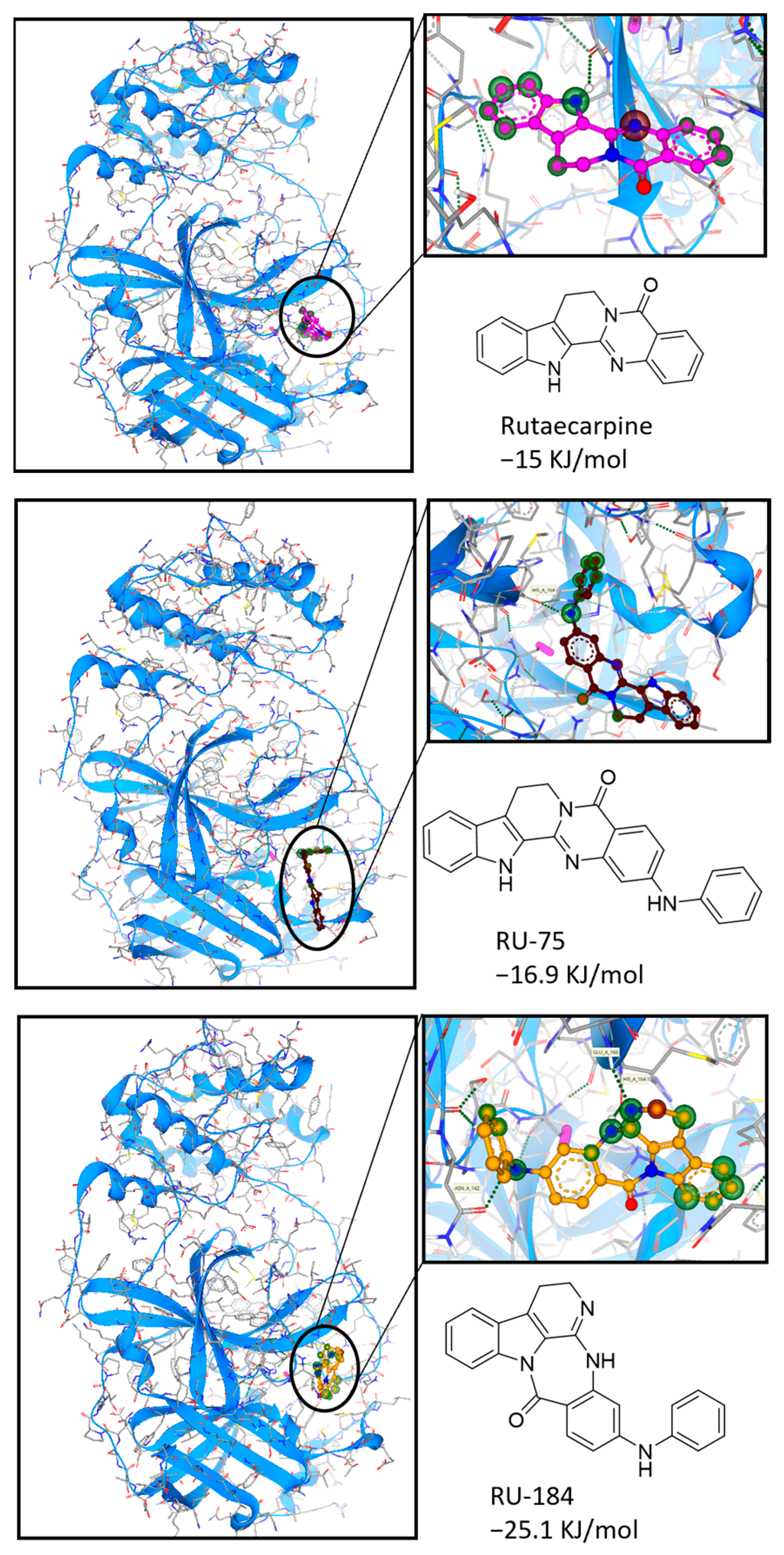
2.1. In Silico-Guided Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives
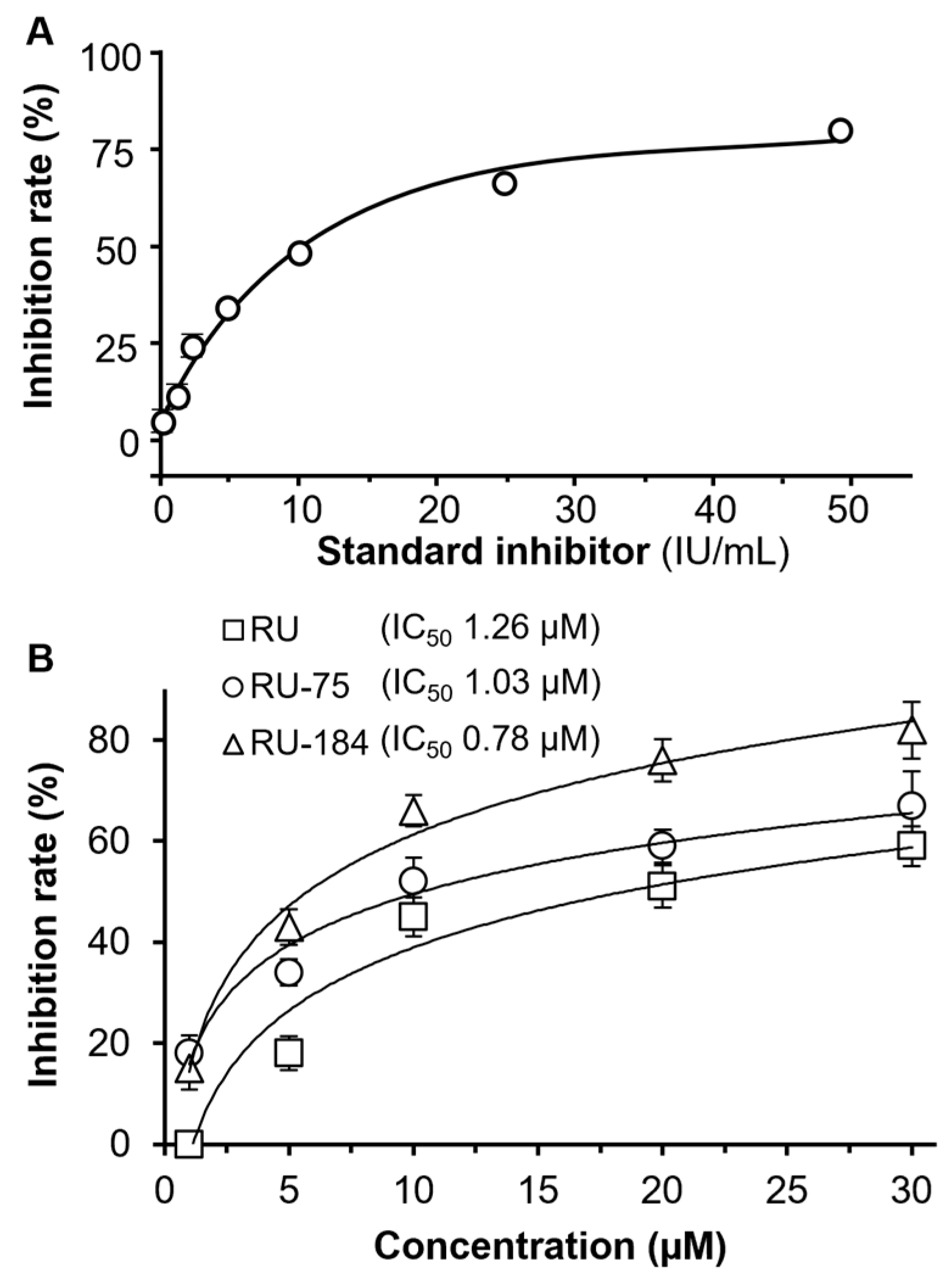
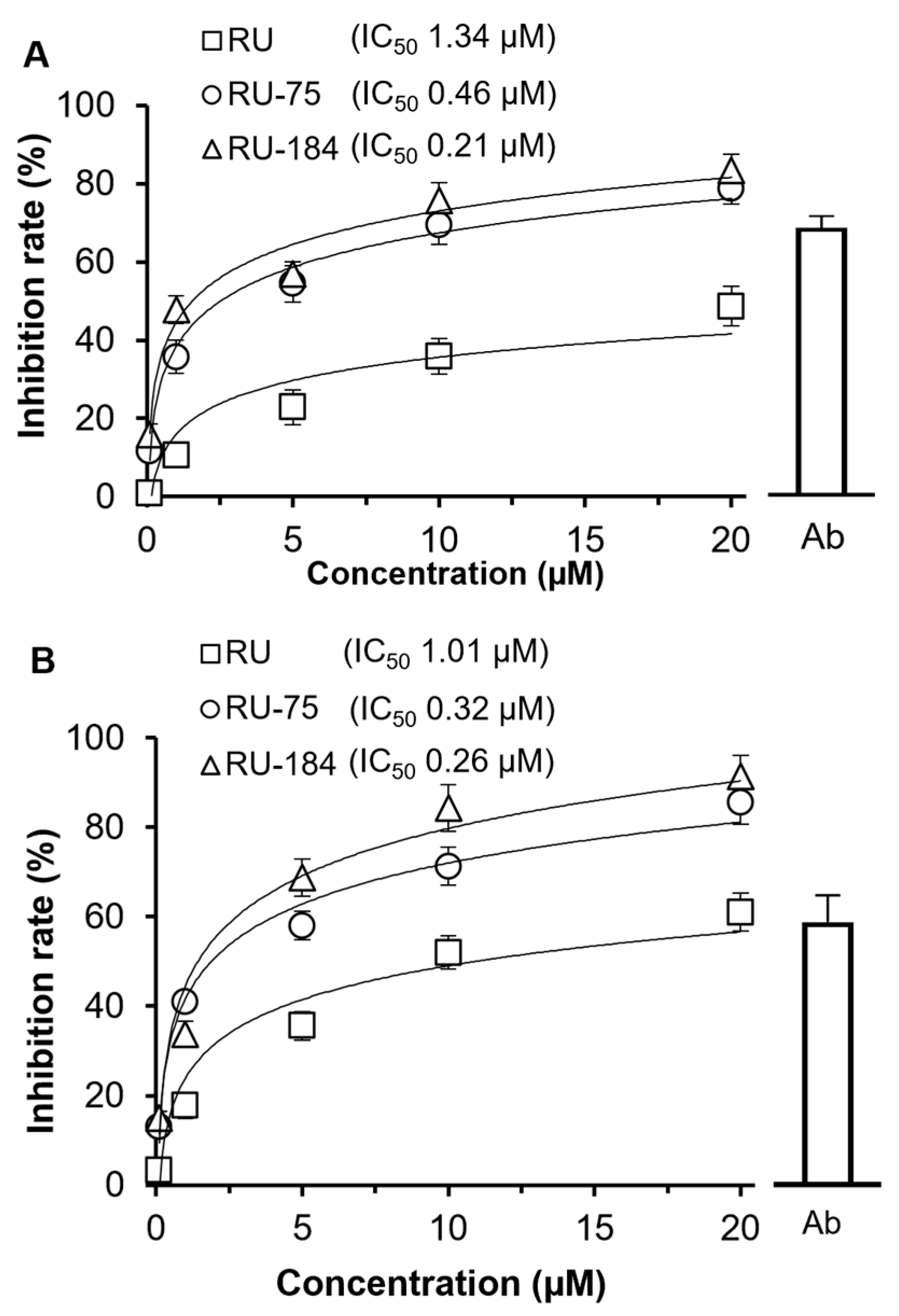
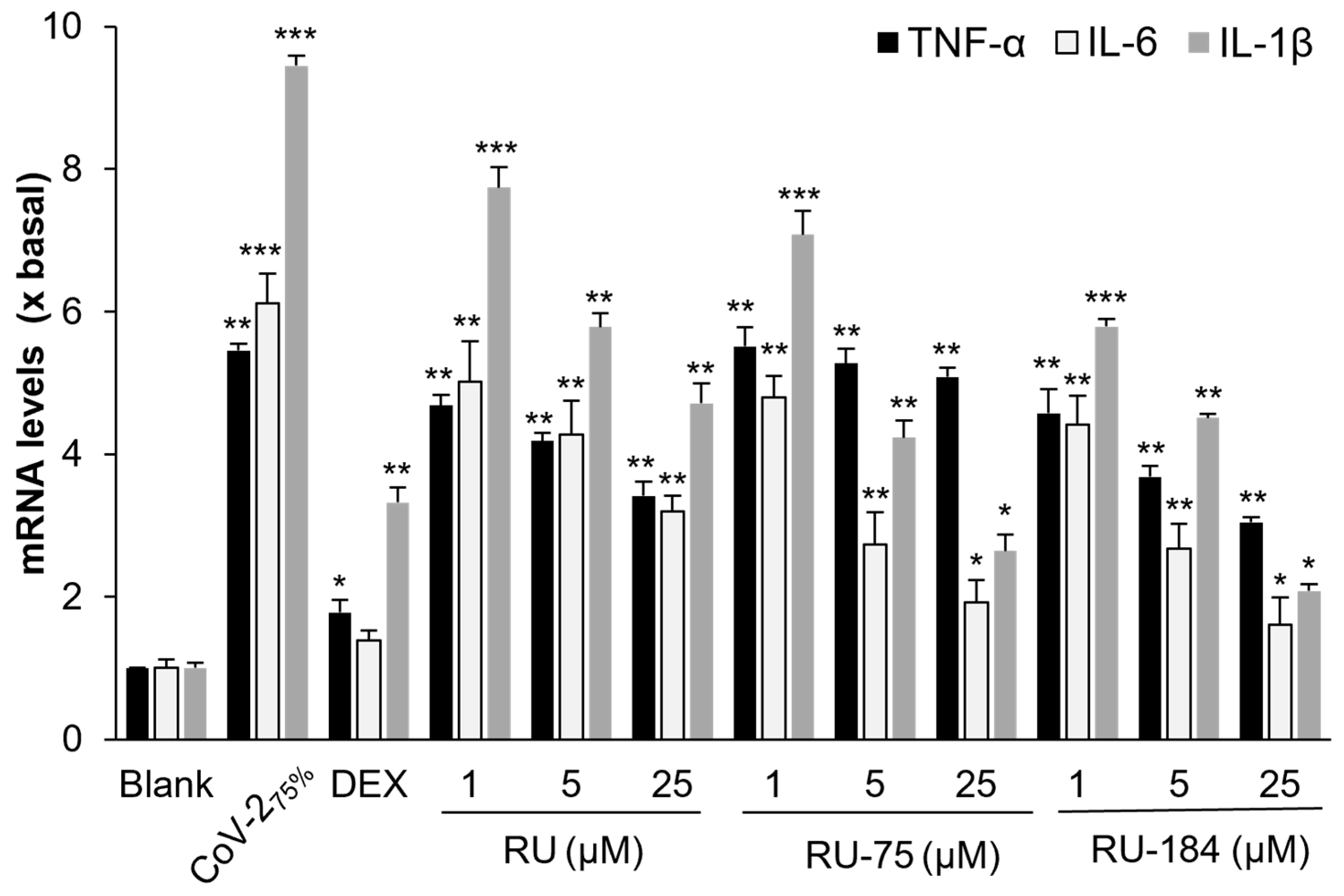
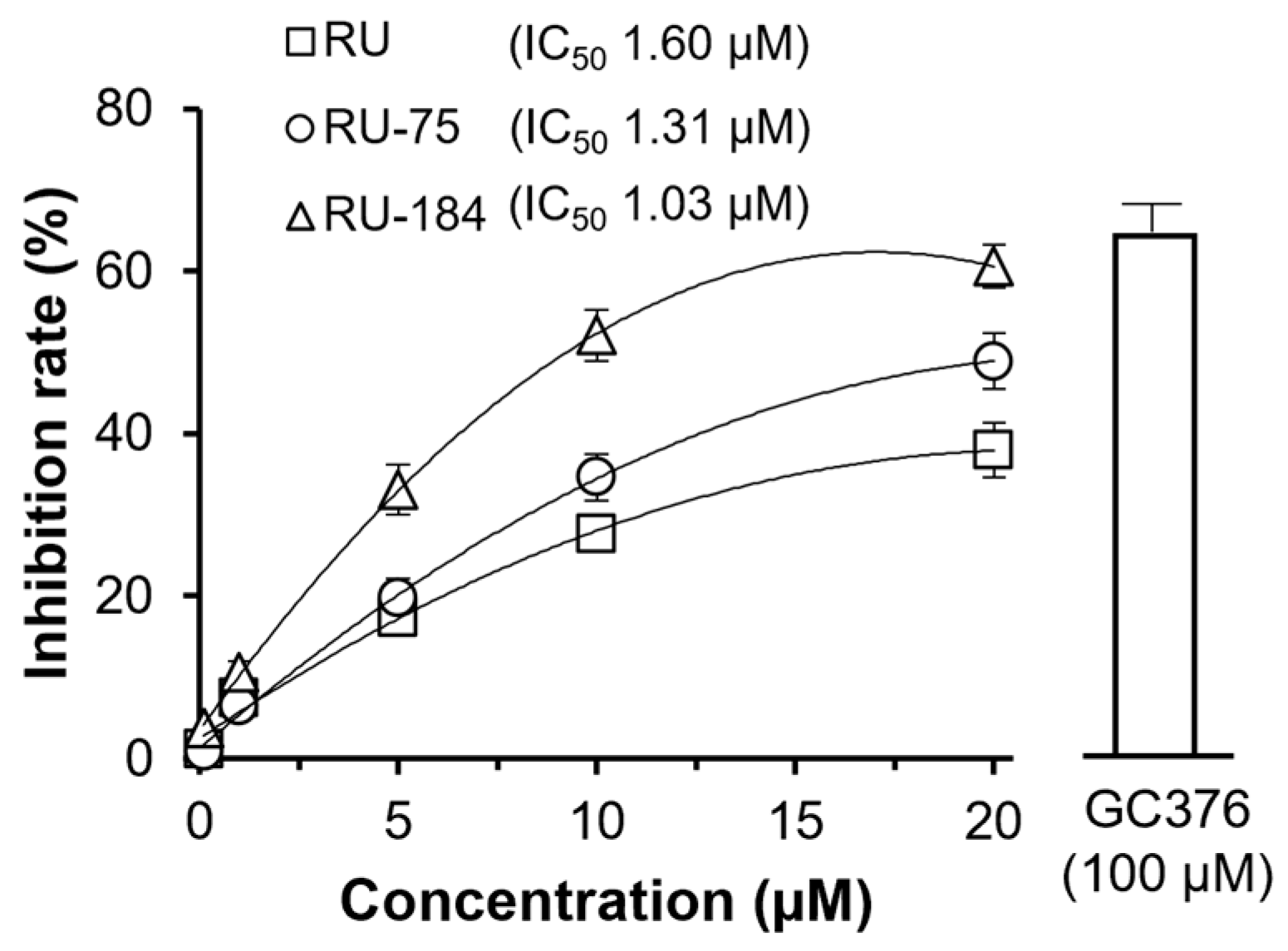
2.2. In Vitro Evaluations of the Rutaecarpine Analogs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Production of SARS-CoV-2 Pseudotyped Virus
4.3. Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Entry
4.4. Luciferase Assay
4.5. Inflammation Test
4.6. S-Protein Inhibition
4.7. 3CL Protease Assay
4.8. Computational Docking Analysis
4.9. Chemistry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Chinta, S.; Rodriguez-Guerra, M.; Shaban, M.; Pandey, N.; Jaquez-Duran, M.; Vittorio, T.J. COVID-19 therapy and vaccination: A clinical narrative review. Drugs Context 2023, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiao, B.; Qu, L.; Yang, D.; Liu, R. The development of COVID-19 treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1125246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Smith, D.M. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. eLife 2020, 9, e61312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping neutralizing and immunodominant sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain by structure-guided high-resolution serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Lacko, L.A.; Chen, S. Druggable targets and therapeutic development for COVID-19. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 963701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021, 372, eabg3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Hilton, S.K.; Ellis, D.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.S.; Navarro, M.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Tortorici, M.A.; Walls, A.C.; et al. Deep mutational scanning of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain reveals constraints on folding and ACE2 binding. Cell 2020, 182, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.E.; Zhang, X.; Case, J.B.; Winkler, E.S.; Liu, Y.; Van Blargan, L.A.; Liu, J.; Errico, J.M.; Xie, X.; Suryadevara, N.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, C.; Ginex, T.; Maestro, I.; Nozal, V.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.; Urquiza, J.; Ramírez, D.; Alonso, C.; Campillo, N.E.; et al. COVID-19: Drug Targets and Potential Treatments. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12359–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jencks, W.P. On the attribution and additivity of binding energies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 4046–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, P.; Hartman, A.M.; Hirsch, A.K.H.; Empting, M. Concepts and core principles of fragment-based drug design. Molecules 2019, 24, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q. Application of fragment-based drug discovery to versatile targets. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular docking: Shifting paradigms in drug discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Dai, N.; Tang, R.W.-L.; Lee, H.C.; Leung, K.W.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Webb, S.E.; Miller, A.L.; et al. The Ethanol Extract of Evodiae Fructus and Its Ingredient, Rutaecarpine, Inhibit Infection of SARS-CoV-2 and Inflammatory Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneller, D.W.; Phillips, G.; O’Neill, H.M.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Stols, L.; Langan, P.; Joachimiak, A.; Coates, L.; Kovalevsky, A. Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Mpro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, M.M.; Zadsirjan, V.; Malmir, M.; Mohammadi, L. Buchwald–Hartwig reaction: An update. Monatsh. Chem. 2021, 152, 1127–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Masum, H.U.; Wajed, S.; Talukder, A. A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: Development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges. VirusDisease 2022, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Whitley, R.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: Progress and lessons learned. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaicha, K.; Khenhrani, R.R.; Veer, M.; Devi, S.; Shahbaz, U.; Salah, Q.M.; Hammad, M.; Palleti, S.K. Efficacy of Molnupiravir for the Treatment of Mild or Moderate COVID-19 in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) Consortium; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Fan, C.; Lv, Y.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y.; Ye, X.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter randomized controlled study. Lancet. Reg. Health. West Pac. 2023, 33, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhi, B.; Niraj, N.; Mahajan, S.; Prakash, A.; Sarma, P. Paxlovid: A promising drug for the challenging treatment of SARS-CoV-2 in the pandemic era. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2022, 54, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Vayer, P.; Tanwar, S.; Poyet, J.-L.; Tsaioun, K.; Villoutreix, B.O. Drug discovery and development: Introduction to the general public and patient groups. Front. Drug Discov. 2023, 3, 1201419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limban, C.; Nuţă, D.C.; Chiriţă, C.; Negreș, S.; Arsene, A.L.; Goumenou, M.; Karakitsios, S.P.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Sarigiannis, D.A. The use of structural alerts to avoid the toxicity of pharmaceuticals. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 5, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keserű, G.M.; Makara, G.M. Hit discovery and hit-to-lead approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 11, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.-S.; Lee, C.-S.; Jahng, Y. New Topoisomerases Inhibitors: Synthesis of Rutaecarpine Derivatives and Their Inhibitory Activity against Topoisomerases. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2012, 35, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Li, N.; Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Si, S. Optimization of Rutaecarpine as ABCA1 Up-Regulator for Treating Atherosclerosis. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.-K.; Chang, H.W.; Jahng, Y. Progress in Studies on Rutaecarpine. II.—Synthesis and Structure-Biological Activity Rela-tionships. Molecules 2015, 20, 10800–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Tang, R.W.-L.; Lee, H.C.; Chan, H.-H.; Choi, S.S.; Leung, K.W.; Webb, S.E.; Miller, A.L.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Polygoni multiflori radix extracts inhibit SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus entry in HEK293T cells and zebrafish larvae. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, R.W.-L.; Lee, H.C.; Chan, H.H.; Choi, S.S.A.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Leung, K.W.; Webb, S.E.; Miller, A.L.; et al. The Extracts of Polygonum cuspidatum Root and Rhizome Block the Entry of SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type and Omicron Pseudotyped Viruses via Inhibition of the S-Protein and 3CL Protease. Molecules 2022, 27, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolli, G.; Massignan, T.; Astolfi, A.; Biggi, S.; Rigoli, M.; Brunelli, P.; Libergoli, M.; Ianeselli, A.; Orioli, S.; Boldrini, A.; et al. Pharmacological inactivation of the prion protein by targeting a folding intermediate. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, R.W.-L.; Duan, R.; Leung, K.W.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Webb, S.E.; Miller, A.L.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Computational Docking as a Tool in Guiding the Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112636
Lin S, Wang X, Tang RW-L, Duan R, Leung KW, Dong TT-X, Webb SE, Miller AL, Tsim KW-K. Computational Docking as a Tool in Guiding the Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112636
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shengying, Xiaoyang Wang, Roy Wai-Lun Tang, Ran Duan, Ka Wing Leung, Tina Ting-Xia Dong, Sarah E. Webb, Andrew L. Miller, and Karl Wah-Keung Tsim. 2024. "Computational Docking as a Tool in Guiding the Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112636
APA StyleLin, S., Wang, X., Tang, R. W.-L., Duan, R., Leung, K. W., Dong, T. T.-X., Webb, S. E., Miller, A. L., & Tsim, K. W.-K. (2024). Computational Docking as a Tool in Guiding the Drug Design of Rutaecarpine Derivatives as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors. Molecules, 29(11), 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112636






