Valorization of Sour Cherry Kernels: Extraction of Polyphenols Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Comparison of Different Extraction Techniques
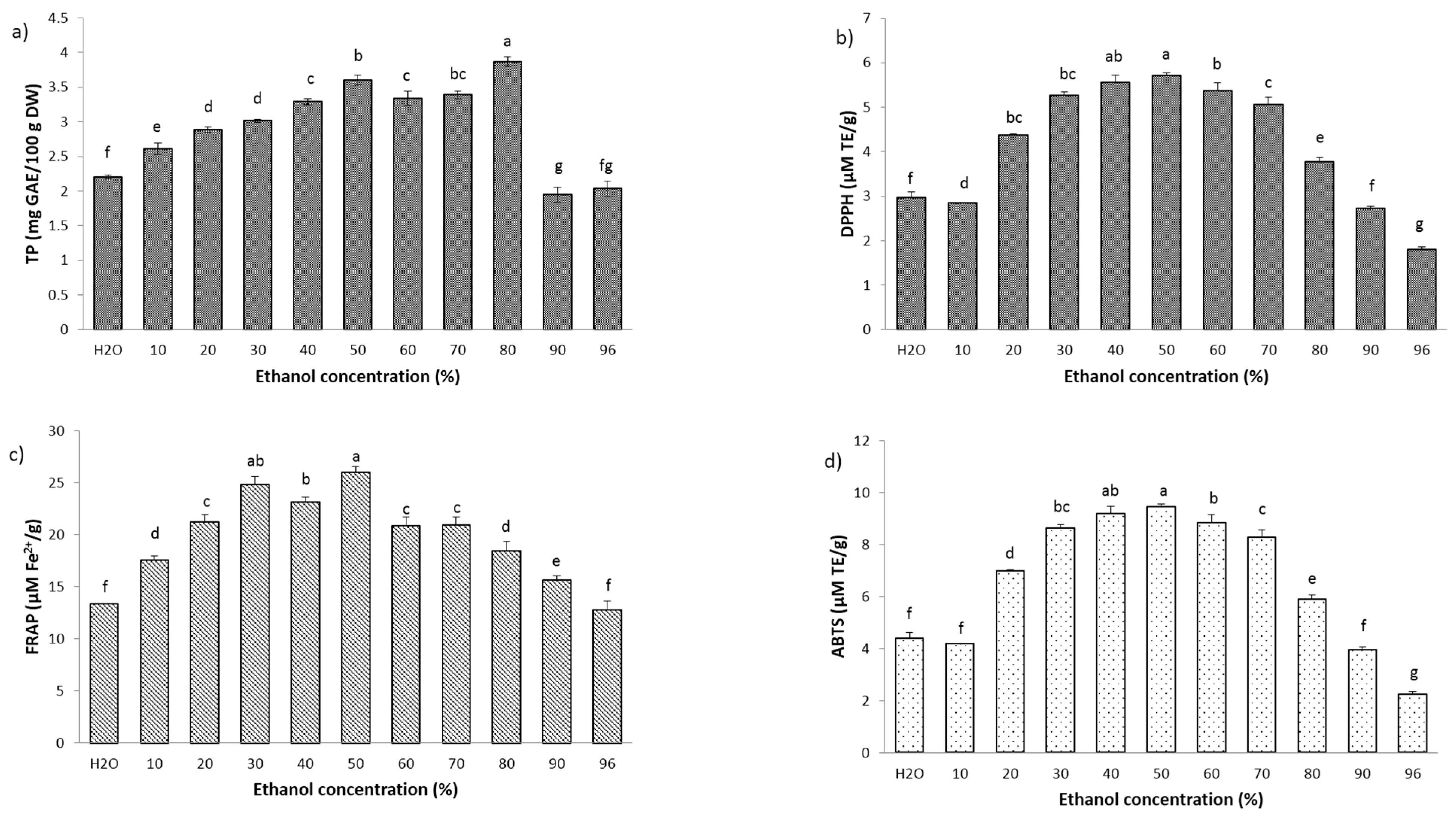
2.2. Total Phenol Content and Antioxidant Activity
2.3. Confirmation of Adequacy of Fit and Influence Analysis
2.4. Influence of NADES Extraction Parameters
2.5. Optimization with Multi-Response Surface Methodology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Sample Preparation
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Solid–Liquid Extraction (SLE)
3.4. Preparation of NADES
3.5. NADES Extraction
3.6. Determination of the Total Phenol Yield (TP)
3.7. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Assays
3.7.1. DPPH-Radical-Scavenging Assay
3.7.2. ABTS+-Radical-Scavenging Assay
3.7.3. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
3.8. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, L.C.; Barbosa, J.R.; da Costa, A.L.C.; Bezerra, F.W.F.; Pinto, R.H.H.; de Carvalho Junior, R.N. From waste to sustainable industry: How can agro-industrial wastes help in the development of new products? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Romaní, A.; Rocchetti, G.; Lorenzo, J.M. Smart advanced solvents for bioactive compounds recovery from agri-food by-products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišan, A.; Nađpal, J.; Stupar, A.; Pojić, M.; Mandić, A.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H.H. The perspectives of natural deep eutectic solvents in agri-food sector. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 2564–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, L.L.D.R.; Flórez-López, E.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. The potential of selected agri-food loss and waste to contribute to a circular economy: Applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Molecules 2021, 26, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomičić, Z.; Spasevski, N.; Popović, S.; Banjac, V.; Đuragić, O.; Tomičić, R. By-products of the oil industry as sources of amino acids in feed. Food Feed Res. 2020, 47, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batinić, P.; Milošević, M.; Lukić, M.; Prijić, Ž.; Gordanić, S.; Filipović, V.; Marinković, A.; Bugarski, B.; Marković, T. In vitro evaluation of antioxidative activities of the extracts of petals of Paeonia lactiflora and Calendula officinalis incorporated in the new forms of biobased carriers. Food Feed. Res. 2022, 49, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryjecka, M.; Michalak, M.; Cymerman, J.; Kiełtyka-Dadasiewicz, A. Comparative assessment of phytochemical compounds and antioxidant properties of kernel oil from eight sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) cultivars. Molecules 2022, 27, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, C.; Gökmen, V. Compositional characteristics of sour cherry kernel and its oil as influenced by different extraction and roasting conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Parastouei, K.; Khodaiyan, F. Simultaneous extraction optimization and characterization of pectin and phenolics from sour cherry pomace. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaovanalikit, A.; Wrolstad, R.E. Anthocyanin and polyphenolic composition of fresh and processed cherries. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, FCT73–FCT83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo-Llamosas, A.; del Río, P.G.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; Yáñez, R.; Garrote, G.; Gullón, B. Recent advances to recover value-added compounds from avocado by-products following a biorefinery approach. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot-Allain, C.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Ak, G.; Zengin, G. Conventional versus green extraction techniques—A comparative perspective. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, S.; Soltanipour, F.; Ferrari, G.; Pataro, G.; Donsì, F. Emerging green techniques for the extraction of antioxidants from agri-food by-products as promising ingredients for the food industry. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teslić, N.; Santos, F.; Oliveira, F.; Stupar, A.; Pojić, M.; Mandić, A.; Pavlić, B.; Kljakić, A.C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A.; et al. Simultaneous Hydrolysis of Ellagitannins and Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Defatted Raspberry Seeds Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for green-solvent design: From hydrophilic to hydrophobic (deep) eutectic solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosiljkov, T.; Dujmić, F.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Hribar, J.; Vidrih, R.; Brnčić, M.; Zlatic, E.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jokić, S.; Bubalo, M.C.; et al. Natural deep eutectic solvents and ultrasound-assisted extraction: Green approaches for extraction of wine lees anthocyanins. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamčević Razboršek, M.; Ivanović, M.; Krajnc, P.; Kolar, M.; Razborsek, M.; Ivanovic, M.; Krajnc, P.; Kolar, M. Choline chloride based natural deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for extracting phenolic compounds from chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa). Molecules 2020, 25, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan D’Alessandro, L.; Kriaa, K.; Nikov, I.; Dimitrov, K. Ultrasound assisted extraction of polyphenols from black chokeberry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 93, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Liu, Z.T.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhang, Y. Deep eutectic solvent combined with ultrasound technology: A promising integrated extraction strategy for anthocyanins and polyphenols from blueberry pomace. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Marques, C.; de Oliveira, A.; de Almeida dos Santos, A.; do Amaral, W.; Ineu, R.P.; Leimann, F.V.; Peron, A.P.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Mafra, M.R. Extraction of bioactive compounds from Curcuma longa L. using deep eutectic solvents: In vitro and in vivo biological activities. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 70, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulyanska, Y.; Cruz-Lopes, L.P.; Esteves, B.; Ferreira, J.V.; Domingos, I.; Lima, M.J.; Correia, P.M.R.; Ferreira, M.; Fragata, A.; Barroca, M.J.; et al. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Cherry Seeds: A Preliminary Study. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, S.; Oliveira, I.V.; Meyer, A.S.; Aires, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Gonçalves, B. Phenolic profile and bioactive potential of stems and seed kernels of sweet cherry fruit. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannou, O.; Koca, I. Greener extraction of anthocyanins and antioxidant activity from blackberry (Rubus spp.) using natural deep eutectic solvents. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 113184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Martín, M.; Cubero-Cardoso, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Cortés-Triviño, E.; Sayago, A.; Urbano, J.; Fernández-Recamales, Á. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from blueberry leaves using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) for the valorization of agrifood wastes. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 175, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, A.; Daničić, T.; Horecki, A.T.; Šumić, Z.; Kovačević, D.B.; Putnik, P.; Pavlić, B. Maximizing Contents of Phytochemicals Obtained from Dried Sour Cherries by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Separations 2021, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.P.; Pham, T.V.; Weina, K.; Tran, T.N.H.; Vo, L.T.V.; Nguyen, P.T.; Bui, T.L.H.; Phan, T.H.; Nguyen, D.Q. Green extraction of phenolics and flavonoids from black mulberry fruit using natural deep eutectic solvents: Optimization and surface morphology. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianni, F.; Scandar, S.; Mangiapelo, L.; Blasi, F.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Cossignani, L. NADES-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Coriander Seeds: A Systematic Optimization Study. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimić, I.; Pavlić, B.; Rakita, S.; Cvetanović Kljakić, A.; Zeković, Z.; Teslić, N. Isolation of cherry seed oil using conventional techniques and supercritical fluid extraction. Foods 2022, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zang, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z. Green and efficient removal of heavy metals from Porphyra haitanensis using natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang Yao, H.Y.; Zang YuanYuan, Z.Y.; Yang Xi, Y.X.; Chen ZhiGang, C.Z. Effects of natural deep eutectic solvents on removal of heavy metal cadmium from rice flour and its mechanism. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2018, 41, 939–945. [Google Scholar]
- Shikov, A.N.; Shikova, V.A.; Whaley, A.O.; Burakova, M.A.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Whaley, A.K.; Terninko, I.I.; Generalova, Y.E.; Gravel, I.V.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. The ability of acid-based natural deep eutectic solvents to co-extract elements from the roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. and associated health risks. Molecules 2022, 27, 7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.Y.; Yiin, C.L.; Lock, S.S.M.; Chin, B.L.F.; Zauzi, N.S.A.; Sar-Ee, S. A review on natural based deep eutectic solvents (NADESs): Fundamentals and potential applications in removing heavy metals from soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 116878–116905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabetic, N.; Todorovic, V.; Malenovic, A.; Sobajic, S.; Markovic, B. Optimization of Extraction and HPLC–MS/MS Profiling of Phenolic Compounds from Red Grape Seed Extracts Using Conventional and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, N.; Algan Cavuldak, O.; Anlı, R.E. Multi response optimisation of polyphenol extraction conditions from grape seeds by using ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE). Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldiken, B.; Boyacioglu, D.; Capanoglu, E. Optimization of Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Black Carrot Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, E.; Rouger, C.; Griffault, E.; Ferrer, A.; Renouf, E.; Cluzet, S. Optimization of polyphenols extraction from grapevine canes using natural deep eutectic solvents. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, S.; Markovinović, A.B.; Teslić, N.; Mišan, A.; Pojić, M.; Karačonji, I.B.; Jurica, K.; Lasić, D.; Putnik, P.; Kovačević, D.B. Use of natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) as a green extraction of antioxidant polyphenols from strawberry tree fruit (Arbutus unedo L.): An optimization study. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airouyuwa, J.O.; Mostafa, H.; Riaz, A.; Stathopoulos, C.; Maqsood, S. Natural deep eutectic solvents and microwave-assisted green extraction for efficient recovery of bioactive compounds from by-products of date fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.) processing: Modeling, optimization, and phenolic characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 824–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Boiteux, J.; Espino, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural deep eutectic solvents-mediated extractions: The way forward for sustainable analytical developments. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, P.L.; Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Silva, M.F.; Olivieri, A.C. Structural analysis of natural deep eutectic solvents. Theoretical and experimental study. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity appliying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorizatio assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.F.; Strain, J.J.; Straint, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Input Factors | Response 1 | Response 2 | Response 3 | Response 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | A: Temperature [°C] | B: Extraction Time [min] | C:S/L Ratio [g/g] | TP [mg GAE/g DW] | DPPH [µM TE/g] | FRAP [µM Fe2+/g] | ABTS [µM TE/g] |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8.17 | 10.09 | 72.54 | 16.78 |
| 2 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 3.42 | 9.80 | 55.94 | 9.22 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.94 | 9.87 | 60.97 | 14.05 |
| 4 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 5.50 | 8.08 | 63.46 | 14.91 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.16 | 11.66 | 61.55 | 13.38 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 6.59 | 12.46 | 80.10 | 19.96 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.03 | 10.85 | 57.99 | 16.73 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 10.09 | 8.38 | 62.34 | 21.10 |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7.72 | 10.44 | 55.38 | 16.37 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.92 | 10.84 | 56.78 | 16.00 |
| 11 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 3.86 | 6.65 | 41.57 | 7.68 |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10.27 | 11.84 | 63.86 | 20.16 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 4.04 | 7.80 | 40.03 | 10.31 |
| 14 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 4.85 | 9.87 | 47.89 | 12.61 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 5.30 | 9.81 | 46.19 | 13.03 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4.61 | 12.08 | 54.42 | 13.39 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.97 | 11.39 | 60.71 | 18.26 |
| 18 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 5.20 | 8.26 | 49.97 | 15.17 |
| 19 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 4.79 | 10.08 | 56.51 | 12.46 |
| Response | Source | SS | df | MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | Model | 63.00 | 9 | 7.00 | 13.65 | 0.0003 |
| Residual | 4.62 | 9 | 0.5128 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 1.71 | 5 | 0.3412 | 0.4692 | 0.7860 | |
| Pure Error | 2.91 | 4 | 0.7273 | |||
| Cor Total | 67.61 | 18 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9317 | |||||
| CV [%] | 11.69 | |||||
| DPPH | Model | 41.99 | 9 | 4.67 | 11.63 | 0.0006 |
| Residual | 3.61 | 9 | 0.4013 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 1.72 | 5 | 0.3450 | 0.7312 | 0.6366 | |
| Pure Error | 1.89 | 4 | 0.4718 | |||
| Cor Total | 45.60 | 18 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9208 | |||||
| CV [%] | 6.33 | |||||
| FRAP | Model | 1451.25 | 9 | 161.25 | 5.24 | 0.0107 |
| Residual | 276.89 | 9 | 30.77 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 259.47 | 5 | 51.89 | 11.92 | 0.0162 | |
| Pure Error | 17.42 | 4 | 4.36 | |||
| Cor Total | 1728.14 | 18 | ||||
| R2 | 0.8398 | |||||
| CV [%] | 9.68 | |||||
| ABTS | Model | 202.07 | 9 | 22.45 | 5.54 | 0.0089 |
| Residual | 36.49 | 9 | 4.05 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 20.72 | 5 | 4.14 | 1.05 | 0.4944 | |
| Pure Error | 15.77 | 4 | 3.94 | |||
| Cor Total | 238.55 | 18 | ||||
| R2 | 0.8471 | |||||
| CV [%] | 13.59 |
| Response | Equation |
|---|---|
| TP | TP = 6.13 + 1.81A + 1.39B+ 0.6943AB + 0.9544A2 − 1.46C2 |
| DPPH | DPPH = 10.72 + 0.6264A + 1.71C |
| FRAP | FRAP = 56.27 + 9.21A + 5.35C + 7.26A2 |
| ABTS | ABTS = 14.83 + 3.54A + 2.09B |
| Input and Output Parameters | Predicted Values |
|---|---|
| Temperature [°C] | 70 |
| Extraction time [min] | 161 |
| S/L ratio [g NADES/g] | 1:25 |
| TP [mg GAE/g DW] | 10.27 |
| DPPH [µM TE/g] | 11.50 |
| FRAP [µM Fe2+/g] | 70.48 |
| ABTS [µM TE/g] | 20.57 |
| Mark | Sample | Molar Ratio | Water Content [%] | NADES Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | Hydrogen Bond Donor | ||||
| N1 | Choline chloride (ChCl) | Malonic acid (MA) | 1:1 | 20 | Hydrophilic |
| N2 | Betaine (Bet) | Citric acid (CA) | 1:3 | 20 | Hydrophilic |
| N3 | Betaine (Bet) | Glycerol (Gly) | 1:2 | 20 | Hydrophilic |
| N4 | Glucose (Glu) | Lactic acid (LA) | 5:1 | 20 | Hydrophilic |
| N5 | Choline chloride (ChCl) | 1,2-Propanediol (PD) | 1:1 | 20 | Hydrophilic |
| N6 | Octanoic acid (OA) | Lauric acid (LA) | 3:1 | / | Hydrophobic |
| N7 | Decanoic acid: (DA) | Lauric acid (LA) | 3:1 | / | Hydrophobic |
| N8 | Menthol (Menthol) | Lactic acid (LA) | 1:2 | / | Hydrophobic |
| N9 | Menthol (Menthol) | Decanoic acid (DA) | 7:2 | / | Hydrophobic |
| N10 | Menthol (Menthol) | Lauric acid (LA) | 3:1 | / | Hydrophobic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Božović, D.; Dimić, I.; Teslić, N.; Mišan, A.; Pojić, M.; Stupar, A.; Mandić, A.; Milošević, S.; Zeković, Z.; Pavlić, B. Valorization of Sour Cherry Kernels: Extraction of Polyphenols Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs). Molecules 2024, 29, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122766
Božović D, Dimić I, Teslić N, Mišan A, Pojić M, Stupar A, Mandić A, Milošević S, Zeković Z, Pavlić B. Valorization of Sour Cherry Kernels: Extraction of Polyphenols Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs). Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122766
Chicago/Turabian StyleBožović, Danica, Ivana Dimić, Nemanja Teslić, Aleksandra Mišan, Milica Pojić, Alena Stupar, Anamarija Mandić, Sanja Milošević, Zoran Zeković, and Branimir Pavlić. 2024. "Valorization of Sour Cherry Kernels: Extraction of Polyphenols Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs)" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122766
APA StyleBožović, D., Dimić, I., Teslić, N., Mišan, A., Pojić, M., Stupar, A., Mandić, A., Milošević, S., Zeković, Z., & Pavlić, B. (2024). Valorization of Sour Cherry Kernels: Extraction of Polyphenols Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs). Molecules, 29(12), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122766










