Abstract
The targeted stimulation of micropores based on the transformation of coal’s molecular structure is proposed due to the chemical properties and difficult-to-transform properties of micropores. Carbon disulfide (CS2) extraction is used as a targeted stimulation to reveal the internal evolution mechanism of micropore transformation. The variations of microcrystalline structures and micropores of bituminous coal and anthracite extracted by CS2 were analyzed with X-ray diffraction (XRD), low-temperature carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorption, and molecular simulation. The results show that CS2 extraction, with the broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic ring rearrangement effect, can promote micropore generation of bituminous coal by transforming the microcrystalline structure. Furthermore, CS2 extraction on bituminous coal can decrease the average micropore size and increase the micropore volume and area. The aromatic layer fragmentation effect of CS2 extraction on anthracite, compared to the micropore generation effect of the broken chain effect and swelling effect, can enlarge micropores more remarkably, as it induces an enhancement in the average micropore size and a decline in the micropore volume and area. The research is expected to provide a theoretical basis for establishing reservoir stimulation technology based on CS2 extraction.
1. Introduction
Coal is a classical porous medium containing fractures and pores of different sizes. These fractures and pores are the channels for coalbed methane (CBM) migration [1,2,3,4]. Pores primarily influence CBM desorption and diffusion capacity [5,6,7], while fractures mainly affect CBM seepage capacity [8,9,10]. Currently, most reservoir stimulation methods mainly focus on enhancing the permeability of coal by improving its fracture connectivity [11,12,13]. However, the adsorbed methane stored in micropores accounts for the total content of CBM (80–90%) [14,15,16]. Therefore, to further improve the CBM migration and development efficiency, more and more studies are paying attention to the pore stimulation of coal.
A series of reservoir stimulation technologies, mainly including hydraulic fracturing [17,18], CO2 phase change fracturing [19,20,21], electrical pulse [22], liquid nitrogen freeze–thaw [23], acid treatment [24,25], supercritical CO2 extraction [26,27], and solvent extraction [28], have been explored to transform pore connectivity. These technologies exert different effects on pore transformation due to their different action mechanisms. Furthermore, the pores with different sizes are divided into micropores, mesopores, and macropores based on the IUPAC [29]. Although hydraulic fracturing can transform mesopores and macropores [30], its water lock effect is inevitable. CO2 phase change fracturing only has an excellent transformation effect on mesopores and macropores rather than micropores [31,32]. Electrical pulse and liquid nitrogen freeze–thaw are only effective for pores with sizes of over 100 nm [33,34]. In short, these physical stimulation methods underperform in transforming micropores with chemical properties [35,36]. Also, acid treatment fails to exhibit any noticeable transformation effects on micropores by dissolving minerals in coal [37]. As for supercritical CO2 extraction, although it can transform micropores by extracting those small coal molecules over a long time (240 h), its influence on micropores with sizes of below 0.46 nm is relatively weak [38]. Besides, supercritical CO2 extraction requires rigorous temperature and pressure conditions to transform micropores [39].
By contrast, solvent extraction is superior in transforming micropores of coal because it can remarkably transform the coal molecular structure [40,41], and the walls of the micropores are made of atoms in the molecular structure of coal [36]. Therefore, micropores in coal have difficult-to-transform properties and chemical properties. Carbon disulfide (CS2), N-methylpyrrolidone, tetrahydrofuran, etc., are commonly applied to extract coal [42,43]. Therefore, the targeted stimulation of micropores based on the transformation of coal’s molecular structure is proposed because of the difficult-to-transform properties and chemical properties of micropores. The solvent extraction is used as a targeted stimulation to reveal the internal evolution mechanism of micropore transformation. The coal with different coalification indicates significant differences in terms of micropore and molecular structure [44,45], and different solvents also exert different extraction effects on them. Our previous research indicated that CS2 extraction on anthracite can increase the microfracture volume and permeability [46], but there is still a lack of comprehensive understanding of the evolution characteristics and mechanism on micropores of bituminous coal and anthracite by CS2 extraction targeted stimulation, which restricts the application of CS2 extraction in reservoir stimulation.
In this paper, CS2 extraction experiments were conducted on bituminous coal and anthracite. Next, the effects of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline and micropore structures of the two coals were analyzed with the aid of XRD, low-temperature CO2 adsorption, and molecular structure simulation. Moreover, the stimulation mechanism of CS2 extraction on the micropore structure of coal was further revealed. The research is expected to provide a theoretical basis for establishing reservoir stimulation technology based on CS2 extraction.
2. Experiment and Methodology
2.1. Samples
The samples used in the experiments were bituminous coal from Pingdingshan No. 8 Coal Mine, named PDS, and anthracite from Zhongma Coal Mine in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China, named JZ. After being collected, they were sealed for the subsequent testing and analysis. The basic analyses of the coal are listed in Table 1. The basic analyses indicate that PDS and JZ belong to bituminous coal and anthracite, respectively.

Table 1.
Results of the basic analyses on coal samples.
2.2. CS2 Extraction Experiment
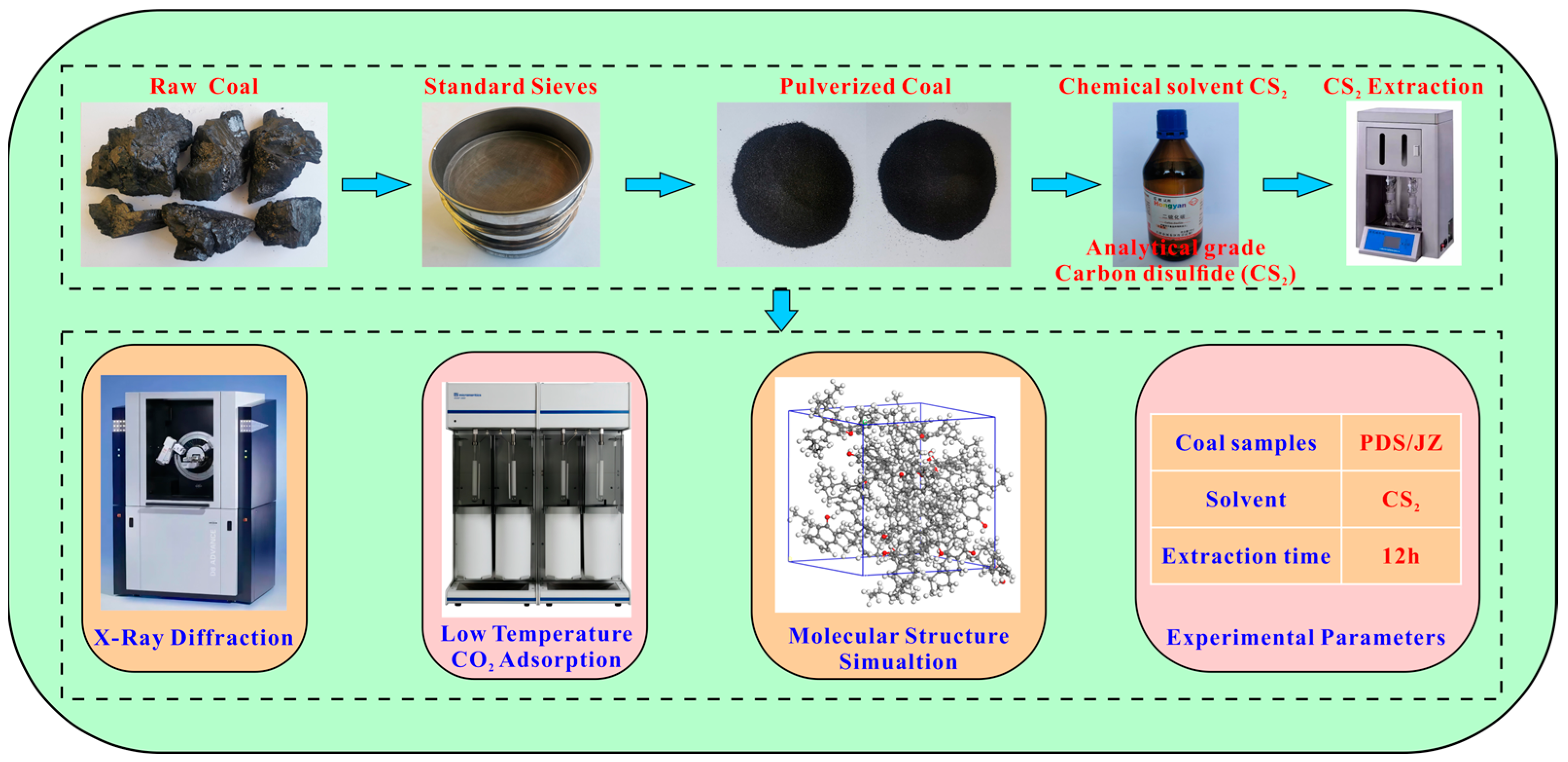
The raw coal (PDS and JZ) was pulverized into 60–80 mesh and dried at 105 °C for 12 h. Then, it was subjected to the CS2 extraction experiments with a soxhlet extractor. In the experiment, 10 mL CS2 solvent were consumed per gram of coal sample, and the extraction time lasted 12 h. After the CS2 solvent-extracted treatment, the extracted coal samples were labeled PDST and JZT. The extracted coal samples were placed in a drying oven at a drying temperature of 105 °C. The coal sample was weighed every four hours until the weight change of the coal samples was less than 0.01 g and the samples were considered dry to constant weight. The extracted coal was measured by XRD and low-temperature CO2 adsorption. The experimental and measuring procedures are shown in Figure 1.
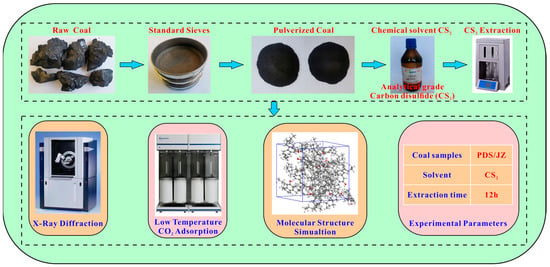
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the experimental and measuring process.
2.3. XRD Measurement
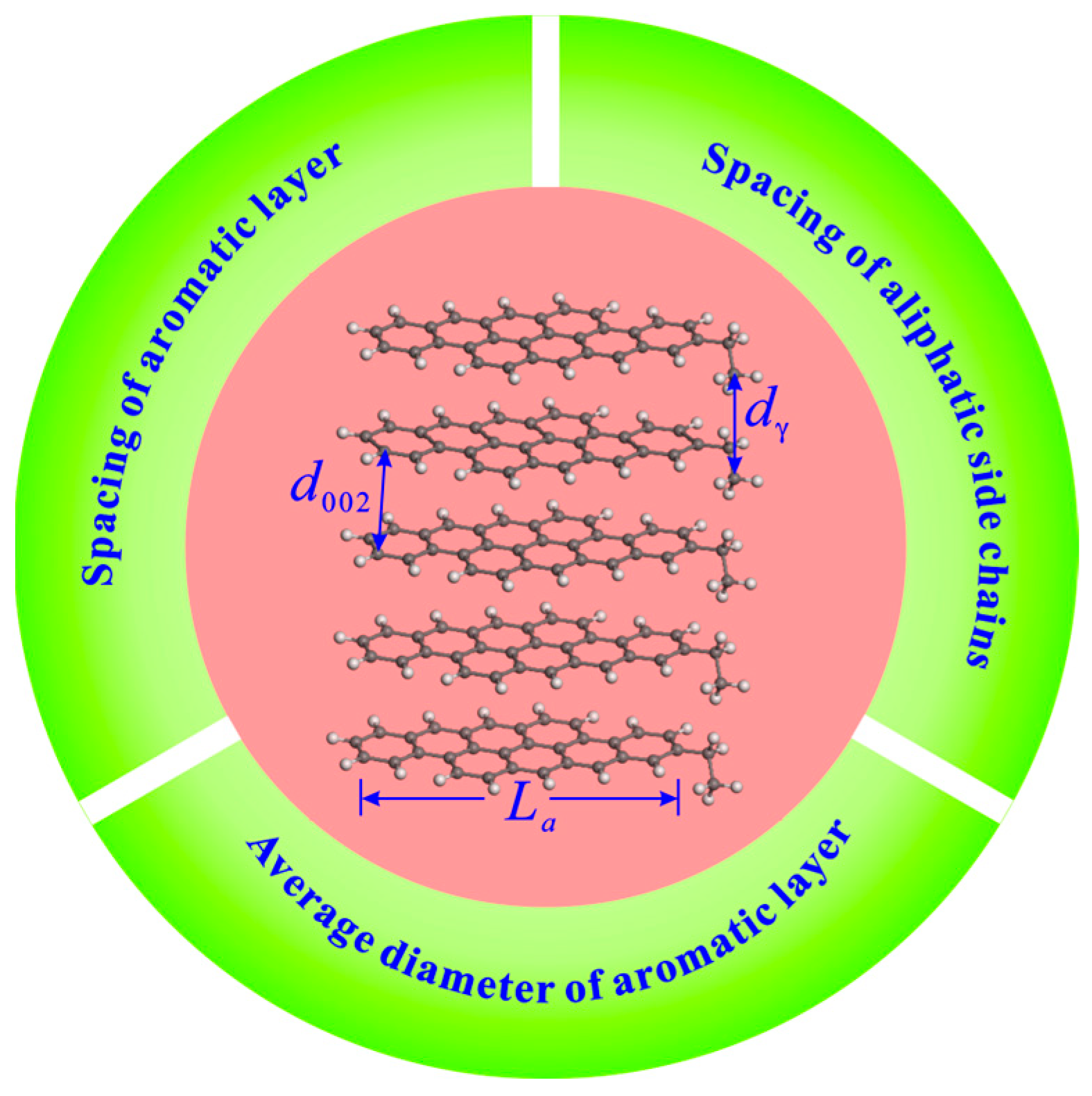
XRD measurement with copper Ka radiation (40 kV, 40 mA) was performed on raw and extracted coal samples with particle sizes of below 200 mesh by a D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer. The scanning range was 10–80°, the scanning speed was 2.0° per minute, and the step size was 0.02°. The coal microcrystalline parameters, including the chain spacing of aliphatic side chains (dγ), spacing of aromatic layers (d002), and average diameter of aromatic layers (La), can be obtained through the XRD analysis (Figure 2). The calculation formulas of these parameters are follows.
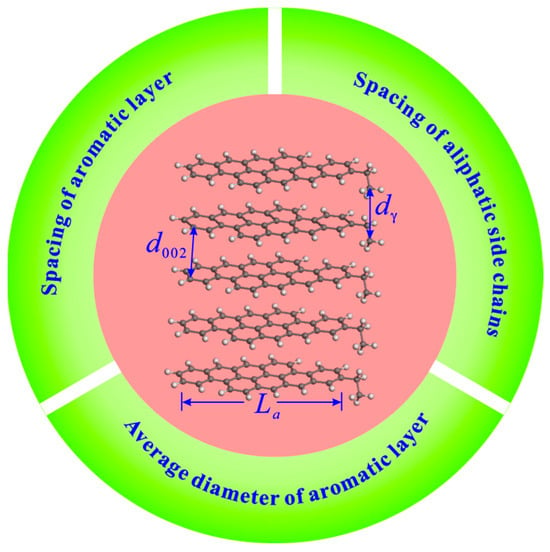
Figure 2.
Diagram of microcrystalline structure parameters.
The parameters dγ and d002 can be calculated from the positions of peak γ and peak 002 by Equations (1) and (2), respectively [46,47,48].
where λ is the X-ray wavelength, and θ002 and θγ are the peak positions of peak 002 and peak γ.
The relevant research has demonstrated that the parameter La can also be approximately calculated by Equation (3) [49,50].
where Ba is the full width at the half maximum of peak 100, and Ka is 1.84 for peak 100.
2.4. Low-Temperature CO2 Adsorption Measurement
The low-temperature CO2 adsorption measurement was conducted on raw and extracted coal samples with sizes of 60–80 meshes at 273.15 K with the aid of an ASAP 2460 made by Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA. The micropore volume and area of the samples were estimated by the D-A model and the D-R model, respectively, and their pore diameter distribution was analyzed by DFT analysis [51].
2.5. Molecular Structure Simulation
Materials Studio 2019 software was employed to construct the conceptual models of coal’s molecular structure before and after CS2 extraction. The basic structural units of bituminous coal and anthracite, which were based on those of Wender et al. [52], were adjusted and modified by the Geometry Optimization and Anneal in Forcite module, which minimized the energy of the basic structural unit [53,54]. Furthermore, the conceptual models of bituminous coal and anthracite were constructed using the Amorphous Cell module and the modified basic structural units. Finally, micropores in the two coals were visualized using the Connolly surface [55,56,57].
3. Results
Variation of Microcrystalline Structure Parameters
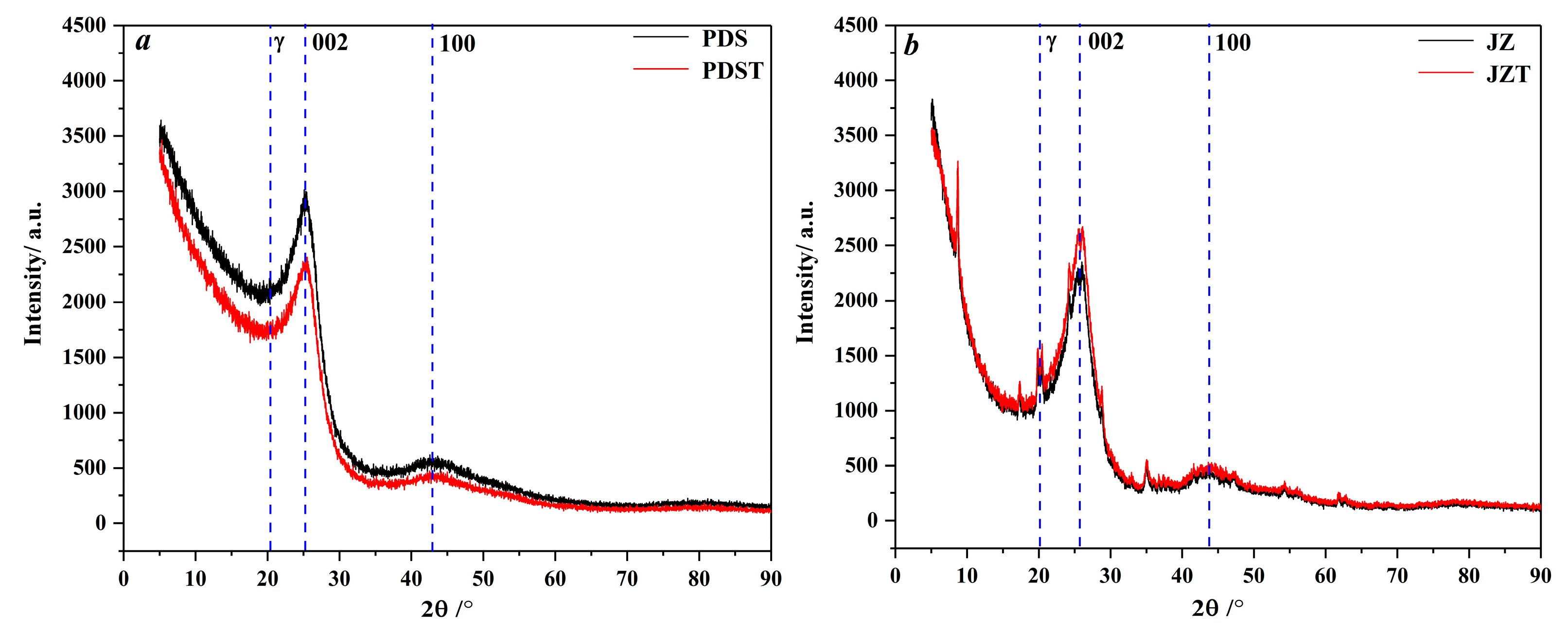
As illustrated in Figure 3, peaks 002 and peak 100 of the raw and extracted coal are located in the angle (2θ) ranges of 20–30° and 40–50°, respectively. Peak γ is located to the left of peak 002 and overlaps with peak 002, which induces the asymmetrical shape of peak 002 [58,59,60].
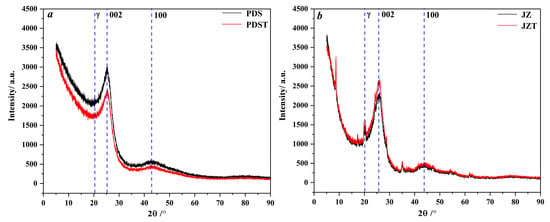
Figure 3.
XRD spectra of raw and extracted coal: (a) PDS and PDST samples, (b) JZ and JZT samples.
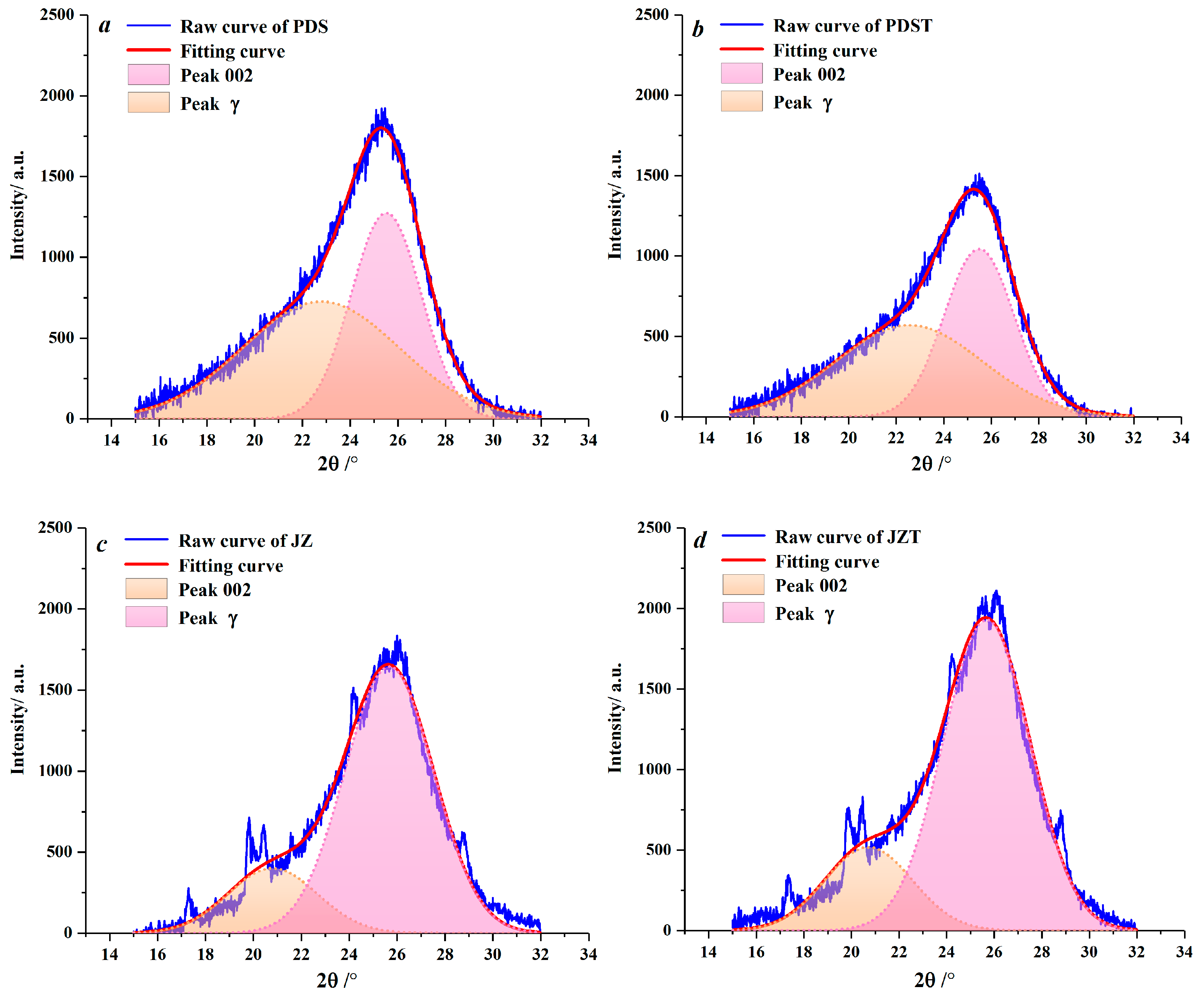
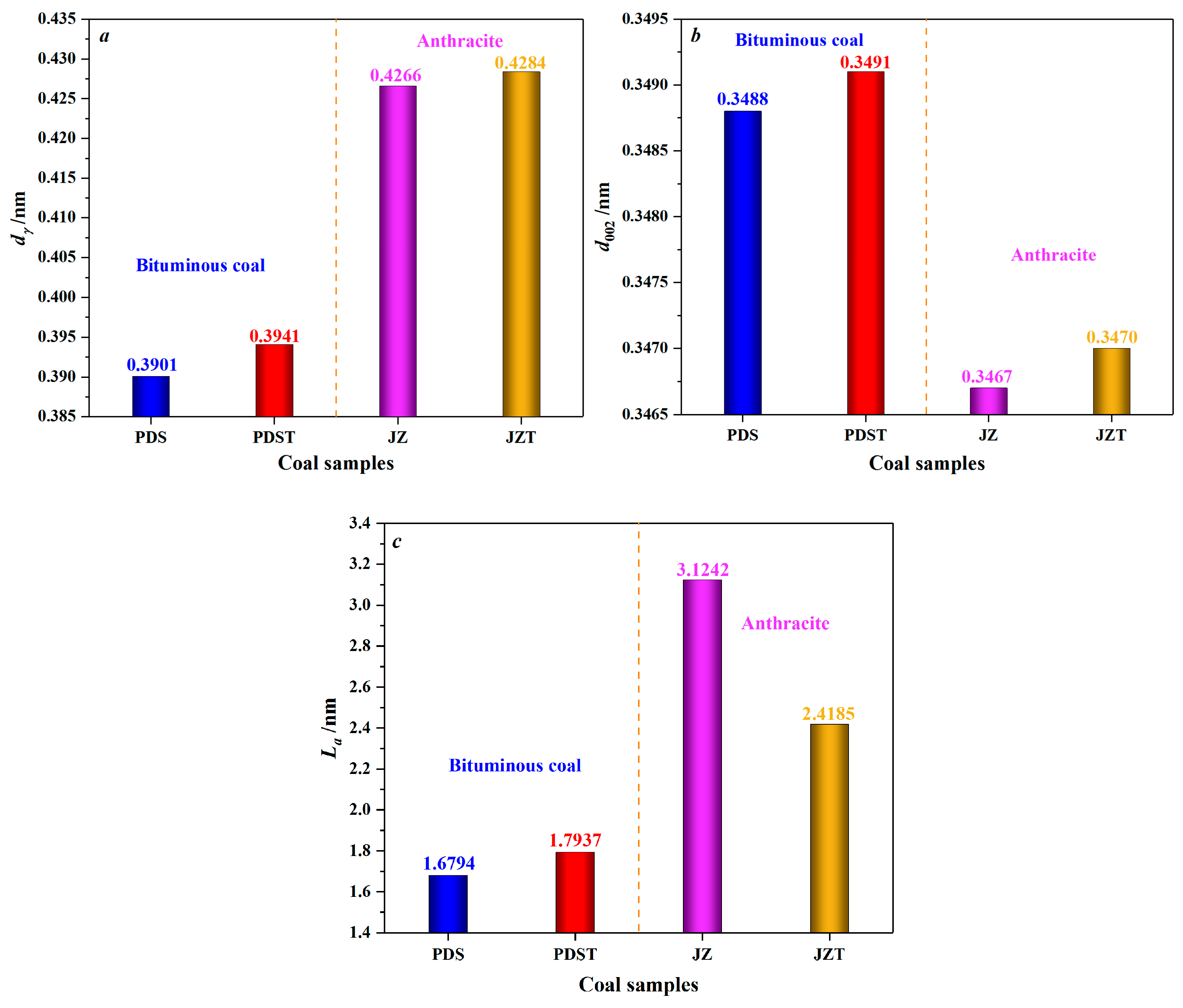
Peaks 002 and γ in XRD spectra were fitted by Peakfit 4.12 software (Figure 4). With he aid of this software, the microcrystalline parameters of the raw and extracted coal samples were derived (Table 2). Compared to PDS, JZ has larger dγ and La values and smaller d002 values. During the coalification from bituminous coal to anthracite, the aliphatic side chains fall off [61,62], and the aromatic ring condensation effect becomes enhanced [63], which contributes to an increase in the dγ and La. By combining with previous XRD and Raman spectroscopy studies of coal [64,65], the reduction in d002 reflects that the microcrystalline structure of coal continuously tends to graphitize during coalification [60,66].
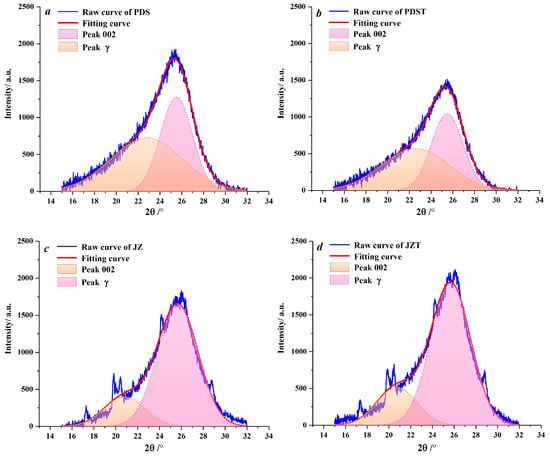
Figure 4.
Peak fitting for peaks 002 and γ: (a) sample PDS, (b) sample PDST, (c) sample JZ, (d) sample JZT.

Table 2.
Microcrystalline parameters of raw and extracted coal.
As displayed in Figure 5, after being extracted by CS2, bituminous coal experiences an increase in dγ from 0.3901 to 0.3941 nm and an increase in d002 from 0.3488 to 0.3491 nm, indicating an enhancement in the spacing of aliphatic side chains and the spacing of aromatic layers. That is to say, CS2 extraction significantly reduces the microcrystalline structure cross-linking degree [67]. Moreover, after the CS2 extraction treatment, the La value of bituminous coal increases from 1.6794 nm to 1.7937 nm. Such a result indicates that the extracted bituminous coal has larger aromatic layers and higher condensation of aromatic rings. The primary reason is that the low degree of cross-linking of the bituminous coal molecular structure around the second coalification jump [68] makes it easier for CS2 to contact the molecular structure fully. It is discovered that the CS2-extracted coal contains much more aliphatic hydrocarbons than aromatic hydrocarbons, from the previous analysis of its extracts [69]. This further reflects that CS2 will extract the aliphatic structures of coal preferentially. Moreover, bituminous coal has a large number of aliphatic structures [70,71]. Therefore, the extraction of aliphatic structures and partial aromatic structures can create favorable conditions for rearranging aromatic rings by reducing the degree of cross-linking of molecular structures [72] and increasing the La.
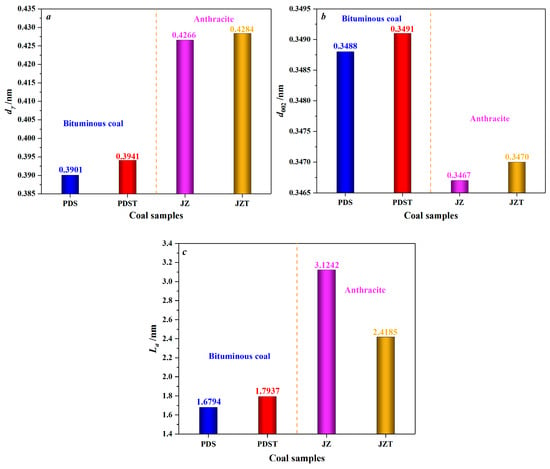
Figure 5.
Variation in microcrystalline structure parameters of coal by CS2 extraction: (a) variation in the chain spacing of aliphatic side chains (dγ), (b) variation in the spacing of aromatic layers (d002), (c) variation in the average diameter of aromatic layers (La).
As for anthracite, its dγ increases from 0.4266 to 0.4284 nm after CS2 extraction (Figure 5), which indicates an increase in the spacing of aliphatic side chains. However, such an increase is inferior to that of the dγ of CS2-extracted bituminous coal, mainly because anthracite has a low content of aliphatic structures [70,71]. Moreover, anthracite’s d002 increases from 0.3467 to 0.3470 nm after CS2 extraction, marking an increase in aromatic layer spacing. The decrease in La of CS2-extracted anthracite reflects a reduction in the aromatic layers’ average diameter. In addition, the La of THF-extracted anthracite also shows a decrease [67], but this decrease is less than that of CS2-extracted anthracite. What causes the above difference can be explained as follows: THF, a polar solvent, mainly affects the oxygen-containing functional groups [73,74], but anthracite, with a high degree of coalification, has few oxygen-containing functional groups and aliphatic structures [70,75]. By contrast, CS2, as a non-polar solvent [46], has excellent extraction and transformation effects on the aromatic structures of anthracite, causing a significant decrease in La.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of CS2 Extraction on Microcrystalline Structure of Coal
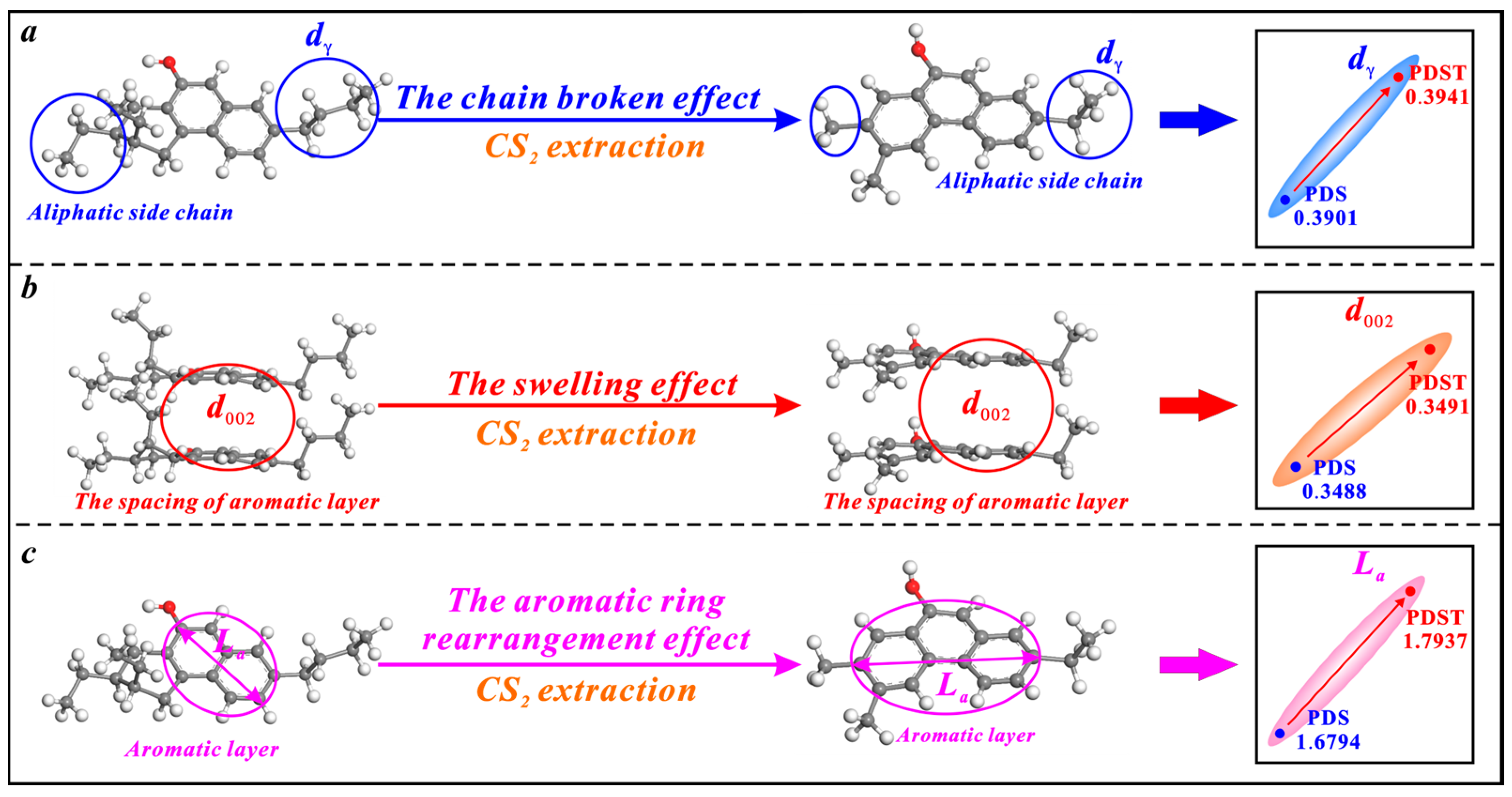
CS2 extraction has triple effects on the microcrystalline structure of bituminous coal, i.e., the broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic ring rearrangement effect (Figure 6). Bituminous coal contains a large number of chemical aliphatic structures [71,76], and CS2 extraction increases the dγ by breaking and shortening them (Figure 6a). The previous research demonstrates the irreversible swelling effect of cyclohexanone (CYC) extraction on the microcrystalline structure of bituminous coal. The molecules of CYC solvent tend to continuously penetrate the aromatic layers of coal and increase their spacing [77]. In this study, the solvent CS2 also displays an irreversible swelling effect on the microcrystalline structure of bituminous coal. When CS2 molecules penetrate the aromatic layers of bituminous coal, the d002 is promoted (Figure 6b). The microcrystalline structure cross-linking degree is reduced under the broken chain effect and the swelling effect, which causes an aromatic ring rearrangement effect to increase the La (Figure 6c).
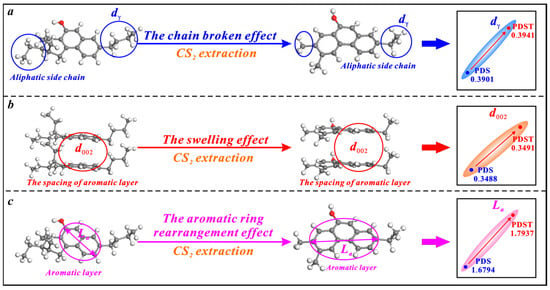
Figure 6.
Effects of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline structure of bituminous coal: (a) the broken chain effect, (b) the swelling effect, (c) the aromatic ring rearrangement effect.
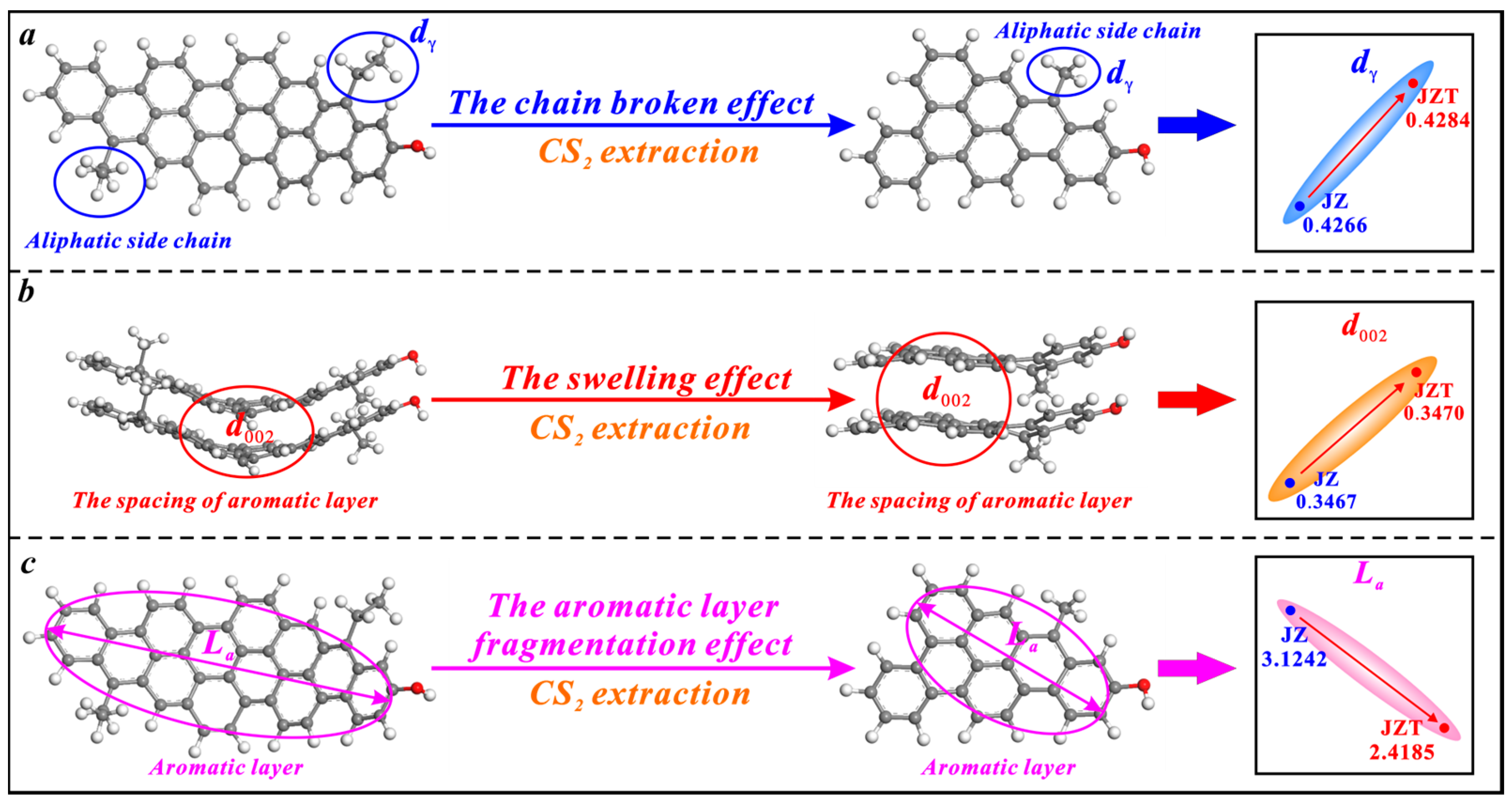
CS2 extraction also has triple effects on the microcrystalline structure of anthracite, i.e., the broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic layer fragmentation effect (Figure 7). However, its broken chain effect on anthracite is weaker than on bituminous coal. The effect only causes a slight increase in the spacing of anthracite’s aliphatic side chains (dγ) (Figure 7a), since anthracite contains fewer aliphatic side chains than bituminous coal [36,78]. Similarly, CS2 extraction causes an irreversible swelling effect on anthracite to increase the spacing of its aromatic layers (d002) (Figure 7b). Most of the CS2 molecules strongly extract the aromatic layers of anthracite due to its low content of aliphatic structures and further fragment the aromatic layers. Ultimately, this causes a decrease in the average diameter of anthracite’s aromatic layers (La) (Figure 7c).
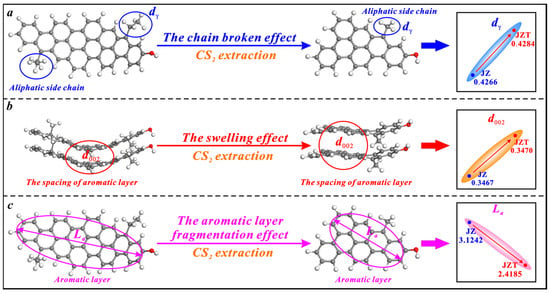
Figure 7.
Effects of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline structure of anthracite: (a) the broken chain effect, (b) the swelling effect, (c) the aromatic layer fragmentation effect.
4.2. Effects of CS2 Extraction on Micropores
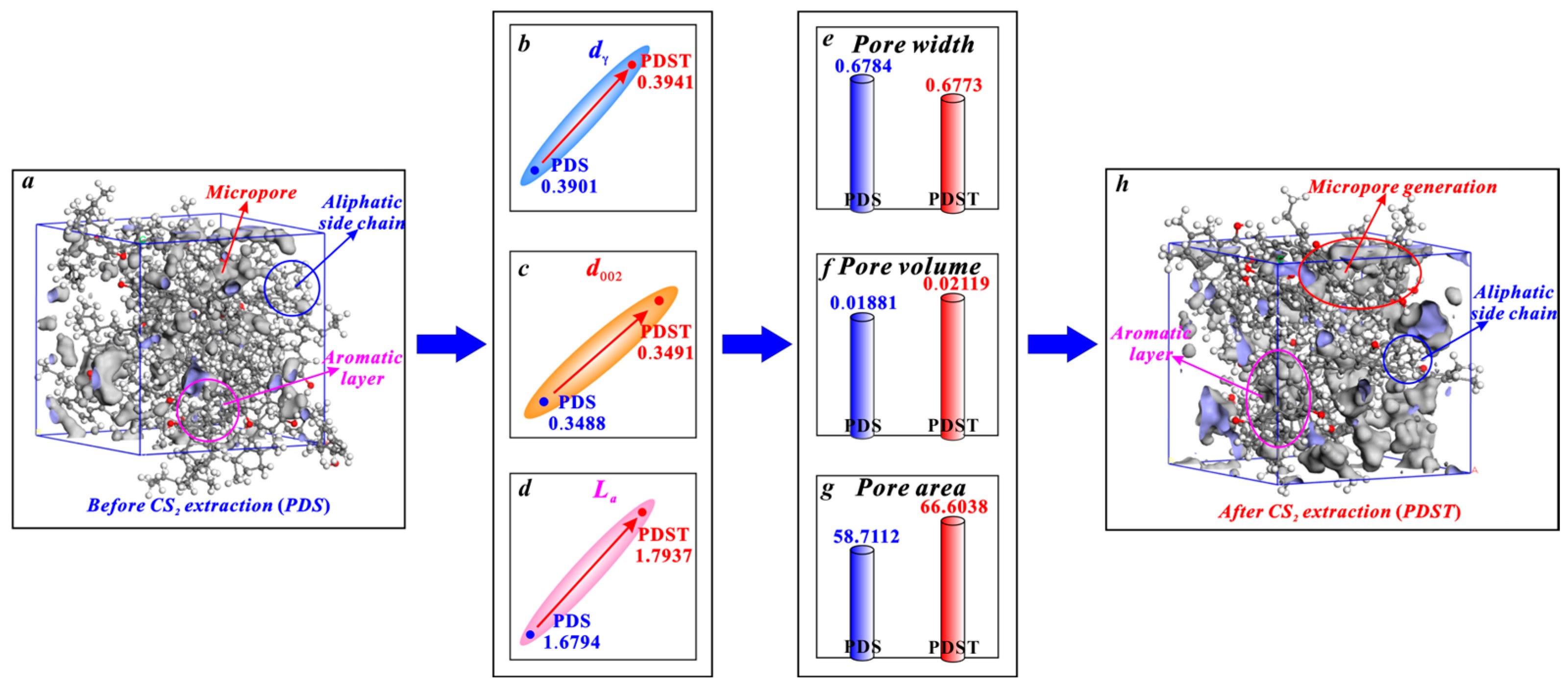
The micropores of bituminous coal mainly arise from the spacing between the aliphatic structure and aromatic structure (Figure 8). CS2 extraction enlarges the spacing of aliphatic side chains (dγ) with its broken chain effect (Figure 8b) and enlarges the spacing of aromatic layers (d002) with its swelling effect (Figure 8c), providing space for micropore generation [38,79]. Moreover, with its aromatic ring rearrangement effect, CS2 extraction increases the average diameter of aromatic layers (La) (Figure 8d). This promotes the generation of micropores since micropores are mostly formed between the layers of two microcrystallites [36,80]. In this way, the above triple effects of CS2 extraction jointly promote the micropore generation of bituminous coal, among which the aromatic ring rearrangement effect plays a dominant role in controlling micropore generation. In detail, after a CS2 extraction treatment, bituminous coal experiences an average pore width decrease from 0.6784 to 0.6773 nm (Figure 8e), a micropore volume growth from 0.01881 to 0.02119 cm3/g (Figure 8f), and a micropore area growth from 58.7112 to 66.6038 m2/g (Figure 8g).
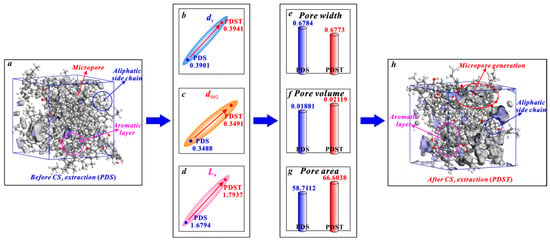
Figure 8.
Effects of CS2 extraction on micropores of bituminous coal: (a) molecular structure of coal sample PDS, (b) variation in dγ, (c) variation in d002, (d) variation in La, (e) variation in average pore width, (f) variation in pore volume, (g) variation in pore area, (h) molecular structure of coal sample PDST.
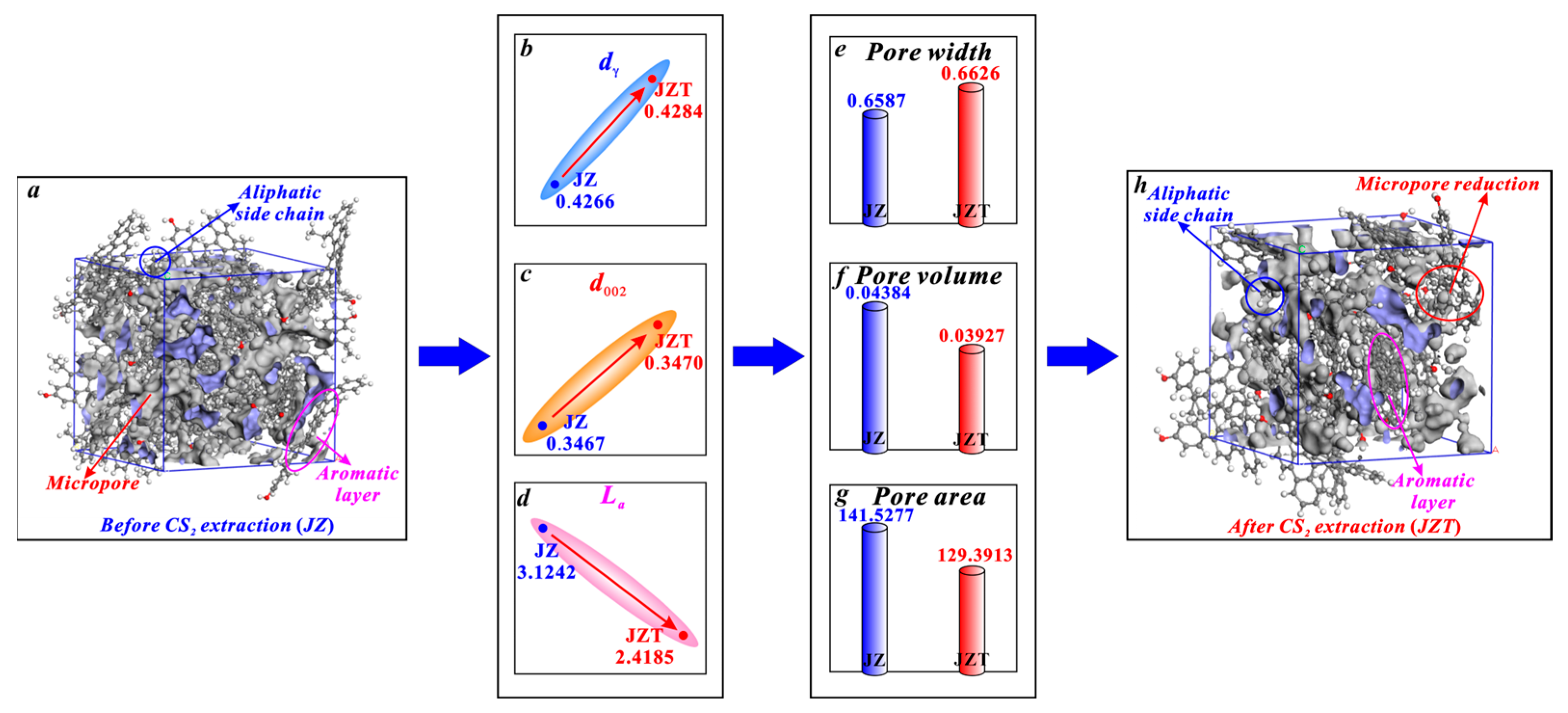
It can be seen in Figure 9 that the micropores of anthracite mainly arise from the spacing between aromatic layers. Similarly, according to the research of Liu et al. [36] on micropore evolution with coalification, the micropores of anthracite are mainly controlled by aromatic structures. First, it is noteworthy that anthracite contains few aliphatic structures [61,78], which are not the main structure for micropore generation in anthracite. Therefore, the increase in the dγ of anthracite (Figure 9b) caused by the broken chain effect cannot significantly promote micropore generation. Although the increase in the spacing of its aromatic layers (d002) (Figure 9c) caused by the swelling effect can promote micropore generation, the increasing rate of its d002 (0.0864%) is far less than the decreasing rate of its La (22.5881%) after CS2 extraction. Noticeably, micropores are mostly formed between the layers of two microcrystallites [36,80]. Furthermore, Alvira et al. [81] concluded that fragmenting large carbon layers into small sheets produces a mesoporous structure. Similarly, the aromatic layer fragmentation effect will decrease the La (Figure 9d) and thus improve the mesopore generation. Zhang et al. [46] put forward that the mesopores of anthracite become larger in volume after a CS2 extraction. Therefore, the reduction in La caused by the aromatic layer fragmentation effect can promote the transformation of micropores into mesopores, which causes a reduction in the micropore number and an enlargement in the micropore size. Obviously, this micropore enlargement effect caused by the aromatic layer fragmentation effect is stronger than the micropore generation effect by the broken chain effect and the swelling effect. The aromatic layer fragmentation effect plays a dominant role in controlling the micropore enlargement. Therefore, it is the micropore enlargement effect that causes the variation in the structure parameters of anthracite micropores. In detail, after being extracted by CS2, anthracite undergoes an average pore width increase from 0.6587 to 0.6626 nm (Figure 9e), a micropore volume decrease from 0.04384 to 0.03927 cm3/g (Figure 9f), and a micropore area decrease from 141.5277 to 125.3913 m2/g (Figure 9g).
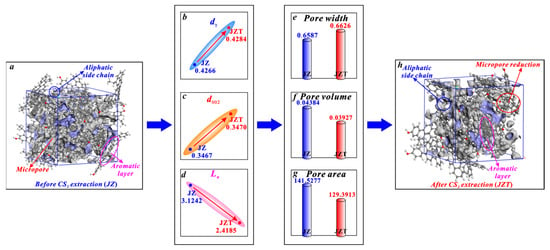
Figure 9.
Effects of CS2 extraction on micropores of anthracite: (a) molecular structure of coal sample JZ, (b) variation in dγ, (c) variation in d002, (d) variation in La, (e) variation in average pore width, (f) variation in pore volume, (g) variation in pore area, (h) molecular structure of coal sample JZT.
4.3. Implication and Limitation
Our recent research analyzed the micropore (<2 nm), mesopore (2–50 nm), and macropore (>50 nm) variation characteristics of CS2-extracted anthracite. The macropore and mesopore volume increased significantly, while the micropore volume decreased [82]. However, the mechanism by which the microcrystalline structure evolution of CS2-extracted coal controls the evolution of micropores has not been effectively revealed, especially for bituminous coal. This study explored the triple effects of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline structures of bituminous coal (i.e., the broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic ring rearrangement effect) and anthracite (i.e., the broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic layer fragmentation effect). Moreover, it also investigated the micropore generation effect of CS2 extraction on bituminous coal and the micropore enlargement effect of it on anthracite. The results revealed that CS2 extraction boasts unique advantages of chemical transformation of micropores compared with conventional reservoir stimulation technologies, including hydraulic fracturing, CO2 phase change fracturing (CO2-PTF), liquid nitrogen freeze–thaw, etc.
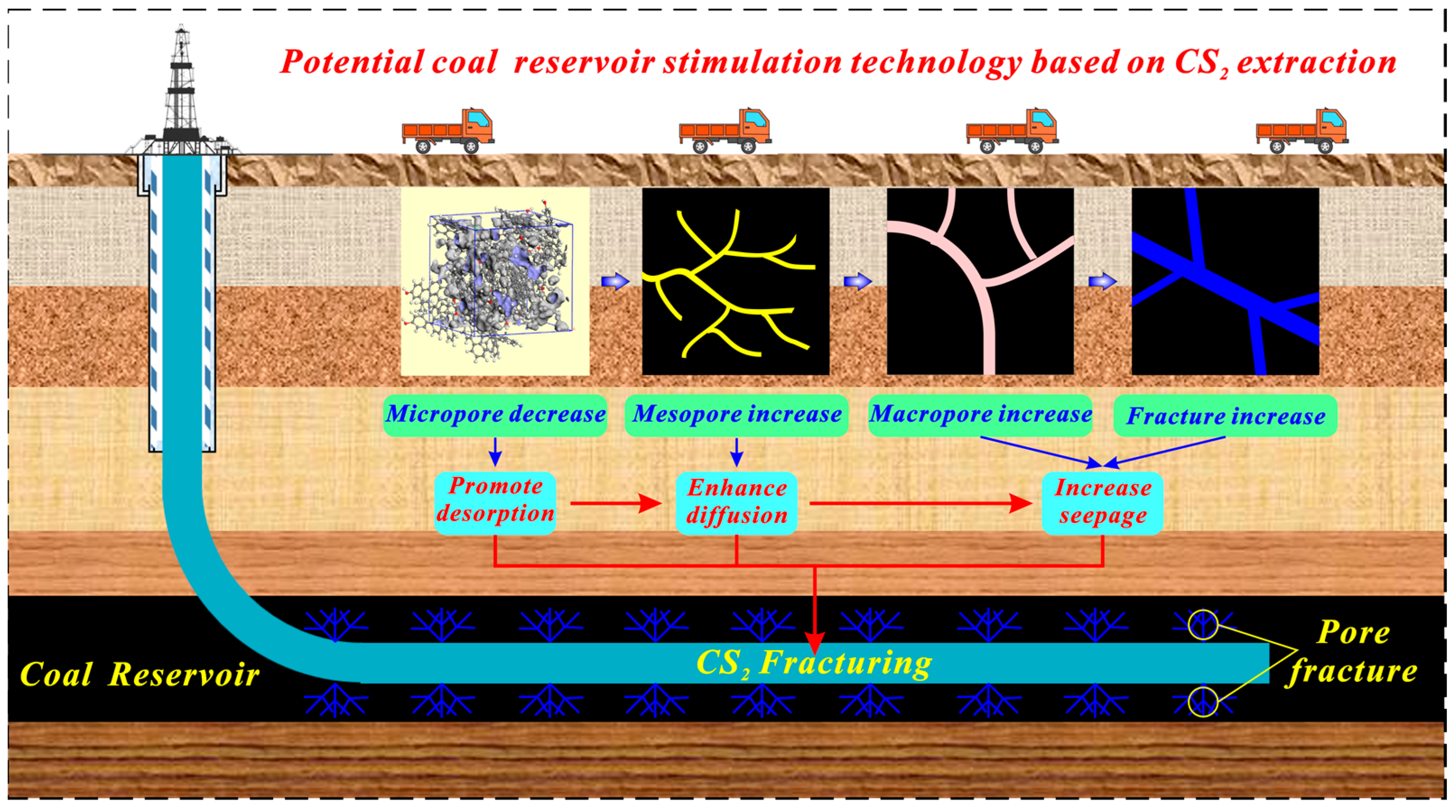
Figure 10 indicates the diagram of potential reservoir stimulation technology–CS2 fracturing of a horizontal well in anthracite reservoirs. Coal reservoirs contain multi-scale pore and fracture structures, which influence the desorption–diffusion–seepage capabilities of coalbed methane [83]. The micropore is the major space where CBM is adsorbed and stored [84,85]. CS2 extraction, with a micropore enlargement effect on anthracite, can increase its average micropore size and decrease its micropore volume and area, which is conducive to gas desorption. Besides, as proven in our previous research, CS2 extraction can increase the mesopore and macropore volume significantly and generate a large number of microfractures in anthracite [46,82], which is conducive to gas diffusion and seepage. Therefore, CS2 extraction is conducive to “promote desorption–enhance diffusion–increase seepage” for improving the gas migration ability for anthracite. Further, CS2 can be considered the fracturing fluid to establish the novel reservoir stimulation technology, which has effective transformation and stimulation effects to avoid the water-locking effect of water-based fracturing fluid. However, the micropore generation effect of CS2 extraction on bituminous coal may enhance the adsorption capacity of coal reservoirs, which may be not conducive to gas desorption. Significantly, our previous study demonstrated that CS2 transformation microfractures in coal reservoirs have a time effect [46]. Extending the extraction time for CS2 to transform micropores in bituminous coal may have a potential micropore enlargement effect. Such a transformation effect on bituminous coal remains uncertain and requires further research.
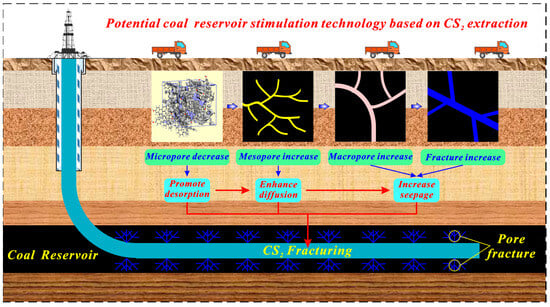
Figure 10.
Diagram of potential reservoir stimulation technology based on CS2 extraction.
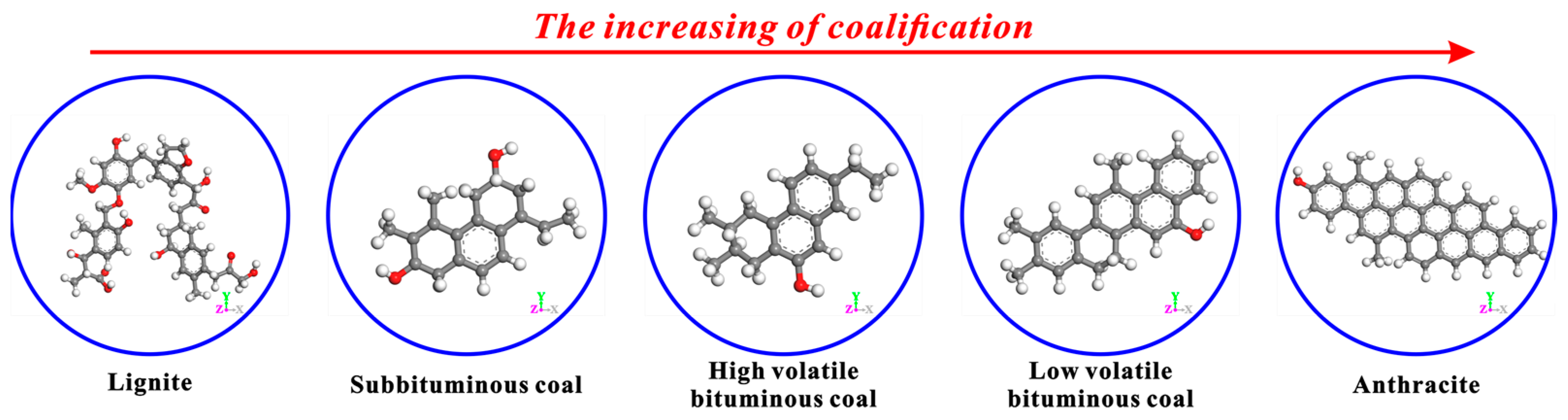
In addition, the apparent differences in the basic structural units of coals with different coalification degrees can be observed in Figure 11. From lignite to anthracite, the basic structural unit of coal’s molecular structure shows regular changes with the increase in coalification degree. Specifically, the numbers of side chains and functional groups keep decreasing, and that of condensed aromatic rings keeps increasing. In the anthracite stage, the condensed aromatic rings mount rapidly, while the side chains and functional groups almost disappear. In this study, only the effects of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline structures and micropores of bituminous coal and anthracite were discussed. In fact, the influence of CS2 extraction on the microcrystalline structures and micropores of other coals with different coalification degrees needs to be further explored.
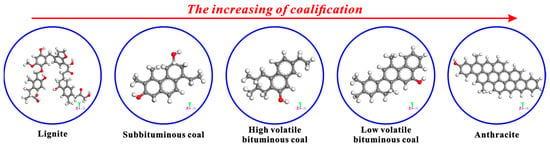
Figure 11.
Basic structural units of coals with different coalification degrees [52].
5. Conclusions
This research discussed the influence of CS2 extraction targeted stimulation on the microcrystalline and micropore structures of bituminous coal and anthracite. The related conclusions are as follows:
(1) CS2 extraction exerts a broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic ring rearrangement effect on the microcrystalline structure of bituminous coal, increasing the spacing of its aliphatic side chains (dγ), the spacing of its aromatic layers (d002), and the average diameter of its aromatic layers (La).
(2) CS2 extraction exerts a broken chain effect, swelling effect, and aromatic layer fragmentation effect on the microcrystalline structure of anthracite, increasing the spacing of its aliphatic side chains (dγ) and the spacing of its aromatic layers (d002), and reducing the average diameter of its aromatic layers (La).
(3) CS2 extraction, which has a micropore generation effect on bituminous coal, can decrease its average micropore size and significantly increase its micropore volume and area.
(4) The micropore enlargement effect caused by the aromatic layer fragmentation effect on CS2-extracted anthracite, which is prominently stronger than the micropore generation effect caused by the broken chain effect and the swelling effect, can expand the average micropore size and significantly reduce the micropore volume and area.
(5) This research provides a theoretical reference for improving reservoir stimulation technology on micropores in coal reservoirs based on CS2 extraction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L. and P.C.; data curation, Z.Z., X.W., J.L. and G.B.; formal analysis, Z.Z., X.W., J.L. and G.B.; funding acquisition, G.L.; methodology, Z.Z., X.W., J.L., G.B. and P.C.; supervision, G.L. and P.C.; visualization, Z.Z.; writing—original draft, Z.Z. and G.L.; writing—review and editing, G.L. and P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42230814 and No. 42372204), the China Scholarship Council (No. 202308410549), the Henan Province International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (No. 242102520034), the Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project (No. 242102320365), and the Key Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (No. 24B170005).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Karacan, C.Ö.; Mitchell, G.D. Behavior and effect of different coal microlithotypes during gas transport for carbon dioxide sequestration into coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2003, 53, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-D.; Liu, D.-M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Che, Y. Evolution of pore structure, submaceral composition and produced gases of two Chinese coals during thermal treatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 156, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Si, N.; Guan, W. An Analogical Method On Fractal Dimension for Three-Dimensional Fracture Tortuosity in Coal Based on Ct Scanning. Fractals 2023, 31, 2350072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Li, B.; Liu, H. Fractal Characterization on Three-Dimensional Fractur Tortuosity in Coal Based On Ct Scanning. Fractals 2023, 31, 2350034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, R.; Clarkson, C. Geological controls on coalbed methane reservoir capacity and gas content. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 38, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, S. Gas diffusion in coal particles: A review of mathematical models and their applications. Fuel 2019, 252, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, S.; Elsworth, D. Re-evaluating adsorbed and free methane content in coal and its ad-and desorption processes analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Tao, S.; Liu, Z.; Tian, W.; Chen, S. Experimental study on gas mass transfer process in a heterogeneous coal reservoir. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 216, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan, C.Ö.; Ruiz, F.A.; Cotè, M.; Phipps, S. Coal mine methane: A review of capture and utilization practices with benefits to mining safety and to greenhouse gas reduction. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 86, 121–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Liu, H. Fractal Characterization on Fracture Volume in Coal Based on Ct Scanning: Principle, Methodology, and Implication. Fractals 2022, 30, 2250124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, I. Coalbed methane completions: A world view. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 82, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Connell, L.D.; Camilleri, M. Laboratory characterisation of coal reservoir permeability for primary and enhanced coalbed methane recovery. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 82, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Lv, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C. Research progress on permeability improvement mechanisms and technologies of coalbed deep-hole cumulative blasting. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chu, W. Methane adsorption behavior on coal having different pore structures. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, Y.; Wen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, X. Effect of water occurrences on methane adsorption capacity of coal: A comparison between bituminous coal and anthracite coal. Fuel 2020, 266, 117102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Lv, R.; Liu, H.; Lin, J.; Barakos, G.; Chang, P. A fractal Langmuir adsorption equation on coal: Principle, methodology and implication. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, C.T.; Smith, M.B. Hydraulic fracturing: History of an enduring technology. J. Pet. Technol. 2010, 62, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Lv, R.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. Coalbed Methane Enhancement in Low-Permeability Reservoirs by Hydraulic Fracturing with Coated Ceramsite. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 9023–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nie, B.; Guo, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Permeability enhancement and porosity change of coal by liquid carbon dioxide phase change fracturing. Eng. Geol. 2021, 287, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X. Effects of Liquid CO2 Phase Transition Fracturing on Methane Adsorption of Coal. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Lin, J.; Barakos, G.; Chang, P. Fractal Evolution Characteristics on the Three-Dimensional Fractures in Coal Induced by CO2 Phase Transition Fracturing. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Zhong, L.; Gao, Y. Experimental study on the effect of high-voltage electrical pulses on the nanoscale pore structure of coal. Fuel 2021, 306, 121621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Qin, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Tang, Z.; Wu, S. Pore structure in coal: Pore evolution after cryogenic freezing with cyclic liquid nitrogen injection and its implication on coalbed methane extraction. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6009–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.; Li, S.; Rahman, S.; Xun, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Xie, H. Effect of nitric acid on the pore structure and fractal characteristics of coal based on the low-temperature nitrogen adsorption method. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ni, G.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Dong, K.; Xie, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. The influence of surfactant on pore fractal characteristics of composite acidized coal. Fuel 2019, 253, 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Gathitu, B.B.; Chen, W.-Y.; McClure, M. Effects of coal interaction with supercritical CO2: Physical structure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5024–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, K.; Sin, I.; Perera, M.; Matthai, S.; Ranjith, P.; Dong-Yin, L. Effect of supercritical-CO2 interaction time on the alterations in coal pore structure. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 76, 103214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Mao, Y.; Su, H. Effects of organic micromolecules in bituminous coal on its microscopic pore characteristics. Fuel 2020, 262, 116529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Mou, P.; Ju, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Ge, T.; Yu, K. Micro-nano-scale pore stimulation of coalbed methane reservoirs caused by hydraulic fracturing experiments. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 214, 110512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Si, N.; Guan, W.; Lin, J. Effects of Liquid CO2 Phase Transition Fracturing on Mesopores and Micropores in Coal. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 10016–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Si, N.; Guan, W. Transformed effect of nano-pores in coal by CO2 phase transition fracturing. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2023, 42, 672–684. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Xu, J.; Lin, B.; Peng, S.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, X. Changes in pore structure and permeability of anthracite coal before and after high-voltage electrical pulses treatment. Powder Technol. 2019, 343, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, S.; Zhai, C.; Lin, H.; Zhao, P.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Y. Changes in the pore structure of lignite after repeated cycles of liquid nitrogen freezing as determined by nitrogen adsorption and mercury intrusion. Fuel 2020, 267, 117214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Ultra micropores in macromolecular structure of subbituminous coal vitrinite. Fuel 2017, 210, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Molecular structure controls on micropore evolution in coal vitrinite during coalification. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 199, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; He, X. Effects of composition changes of coal treated with hydrochloric acid on pore structure and fractal characteristics. Fuel 2021, 294, 120506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sang, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, T.; Du, Y.; Fang, H. Effects of supercritical CO2 on micropores in bituminous and anthracite coal. Fuel 2019, 242, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, D.; Liu, Z. Influence of supercritical CO2 on pore structure and functional groups of coal: Implications for CO2 sequestration. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 40, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Peng, X.; Yao, J.; Mao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Sheng, Z. Insight into the influence of small organic molecules on the wettability of coal. Fuel 2021, 294, 120537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkova, V.; Czaplicka, M. Changes in the structure of plasticized coals caused by extraction with dichloromethane. Fuel 2012, 96, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanohashi, T.; Terao, Y.; Iino, M. Sorption behaviors of methanol vapor by coal extracts and residues. Fuel 2000, 79, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; Xu, Y.; Mo, W.; Wei, X.; Ma, F. Structural elucidation for soluble organic oxygenated compounds in soft and hard coals using advanced extraction methods. Fuel 2022, 322, 124069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousige, C.; Ghimbeu, C.M.; Vix-Guterl, C.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Suleimenova, A.; Vaughan, G.; Garbarino, G.; Feygenson, M.; Wildgruber, C.; Ulm, F.-J. Realistic molecular model of kerogen’s nanostructure. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Chang, P.; Wang, X.; Lin, J. Fractal characteristics for coal chemical structure: Principle, methodology and implication. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 173, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y.; Lin, J.; Jin, Y.; Xian, B.; Lv, R.; Zhang, Z. Experimental Investigation of CS2 Extraction to Enhance the Permeability of Coal. Transp. Porous Media 2021, 136, 899–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, G.N.; Neomagus, H.W.; Everson, R.C.; Roberts, M.J.; Bunt, J.R.; Sakurovs, R.; Mathews, J.P. Chemical–structural properties of South African bituminous coals: Insights from wide angle XRD–carbon fraction analysis, ATR–FTIR, solid state 13C NMR, and HRTEM techniques. Fuel 2015, 158, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, T.F.; Erdman, J.G.; Pollack, S.S. Investigation of the structure of petroleum asphaltenes by X-ray diffraction. Anal. Chem. 1961, 33, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Lv, M.; Hou, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, K. Coal microcrystalline structural changes related to methane adsorption/desorption. Fuel 2019, 239, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Dhamelincourt, P.; Laureyns, J.; Martinez-Alonso, A.; Tascon, J.M. Comparative performance of X-ray diffraction and Raman microprobe techniques for the study of carbon materials. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2875–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Pan, Z.; Chen, S.; Tang, S. Coal seam porosity and fracture heterogeneity of marcolithotypes in the Fanzhuang Block, southern Qinshui Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 66, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, I. Catalytic synthesis of chemicals from coal. Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng. 1976, 14, 97–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S. Molecular mechanisms of hydrogen leakage through caprock in moisture and residual gas conditions: A molecular dynamics–Monte Carlo study. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S. Molecular insights into the carbon dioxide sequestration in kerogen: An accelerated algorithm coupling molecular dynamics simulations and Monte Carlo methods. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 185, 1336–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.L. Analytical molecular surface calculation. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1983, 16, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Baiquan, L.; Tong, L. Construction of Pingdingshan coal molecular model based on FT-IR and 13C-NMR. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1262, 132992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ji, H. Control mechanism of small organic molecules on methane adsorption capacity of coal. Fuel 2023, 331, 125904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Guet, J. Characterization of coals and macerais by X-ray diffraction. Fuel 1990, 69, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, K. Molecular structure characterization of middle-high rank coal via XRD, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy: Implications for coalification. Fuel 2019, 239, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Quantitative investigation on the structural characteristics of thermally metamorphosed coal: Evidence from multi-spectral analysis technology. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, J.; Munoz, E.; Moliner, R. FTIR study of the evolution of coal structure during the coalification process. Org. Geochem. 1996, 24, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Wang, G.; Jiang, B. Characterization of coalification jumps during high rank coal chemical structure evolution. Fuel 2016, 185, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z. HRTEM observation of morphological and structural evolution of aromatic fringes during the transition from coal to graphite. Carbon 2022, 187, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, B.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, K.; Teppen, B.J. Structural evolution of high-rank coals during coalification and graphitization: X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and reactive force field molecular dynamics simulation study. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zeng, F.; Li, C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, P. Insight into the molecular structural evolution of a series of medium-rank coals from China by XRD, Raman and FTIR. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Lei, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, X.; Shui, H. Molecular structure characterization of low-medium rank coals via XRD, solid state 13C NMR and FTIR spectroscopy. Fuel 2020, 268, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Ding, Z.; Hao, Z. Investigation on solubility of multicomponents from semi-anthracite coal and its effect on coal structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 174, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zeng, F. Molecular Structure Characterization of CS2–NMP Extract and Residue for Malan Bituminous Coal via Solid-State 13C NMR, FTIR, XPS, XRD, and CAMD Techniques. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 12142–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Du, Z. The FTIR characteristics of extracted coking coal in different macrolithotype. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, J.P.; Chaffee, A.L. The molecular representations of coal—A review. Fuel 2012, 96, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z. New advances in coal structure model. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.P.; Burgess-Clifford, C.; Painter, P. Interactions of Illinois No. 6 bituminous coal with solvents: A review of solvent swelling and extraction literature. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Ultrasonic extraction and oxidation characteristics of functional groups during coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 2019, 242, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, X. Solvent Extraction of Superfine Pulverized Coal. Part 2. Free-Radical Characteristics. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 15555–15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D. Experimental study on temperature response of different ranks of coal to liquid nitrogen soaking. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, A. Macromolecular and molecular model of coal structure. Fuel Process. Technol. 1986, 14, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Qiao, Y.-Y.; Tian, Y.-Y.; Xie, K.-C.; Li, D.-W. Effect of heat reflux extraction on the structure and composition of a high-volatile bituminous coal. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, R.; Guo, Y. Abrupt changes (jumps) in reflectance values and chemical compositions of artificial charcoals and inertinite in coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 38, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Cao, L.; Sang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, W.; Ji, Z.; Chang, J.; Li, M. Experimental study on the softening effect and mechanism of anthracite with CO2 injection. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 138, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Bhatia, S.K. Variation of the pore structure of coal chars during gasification. Carbon 2003, 41, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvira, D.; Antorán, D.; Manyà, J.J. Plant-derived hard carbon as anode for sodium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review to guide interdisciplinary research. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, N.; Liu, G.; Lin, J.; Chang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H. Effects of CS2 Solvent Extraction on Nanopores in Coal. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 13799–13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Xian, B.; Gao, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Fuzzy pattern recognition model of geological sweetspot for coalbed methane development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Webley, P.A. Preparation of activated carbons from corncob with large specific surface area by a variety of chemical activators and their application in gas storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.D.; Tan, B.; Trewin, A.; Su, F.; Rosseinsky, M.J.; Bradshaw, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cooper, A.I. Microporous organic polymers for methane storage. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1916–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).