Phytochemistry and Biological Profile of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Botanical Description
2.1. Botanical Systematics
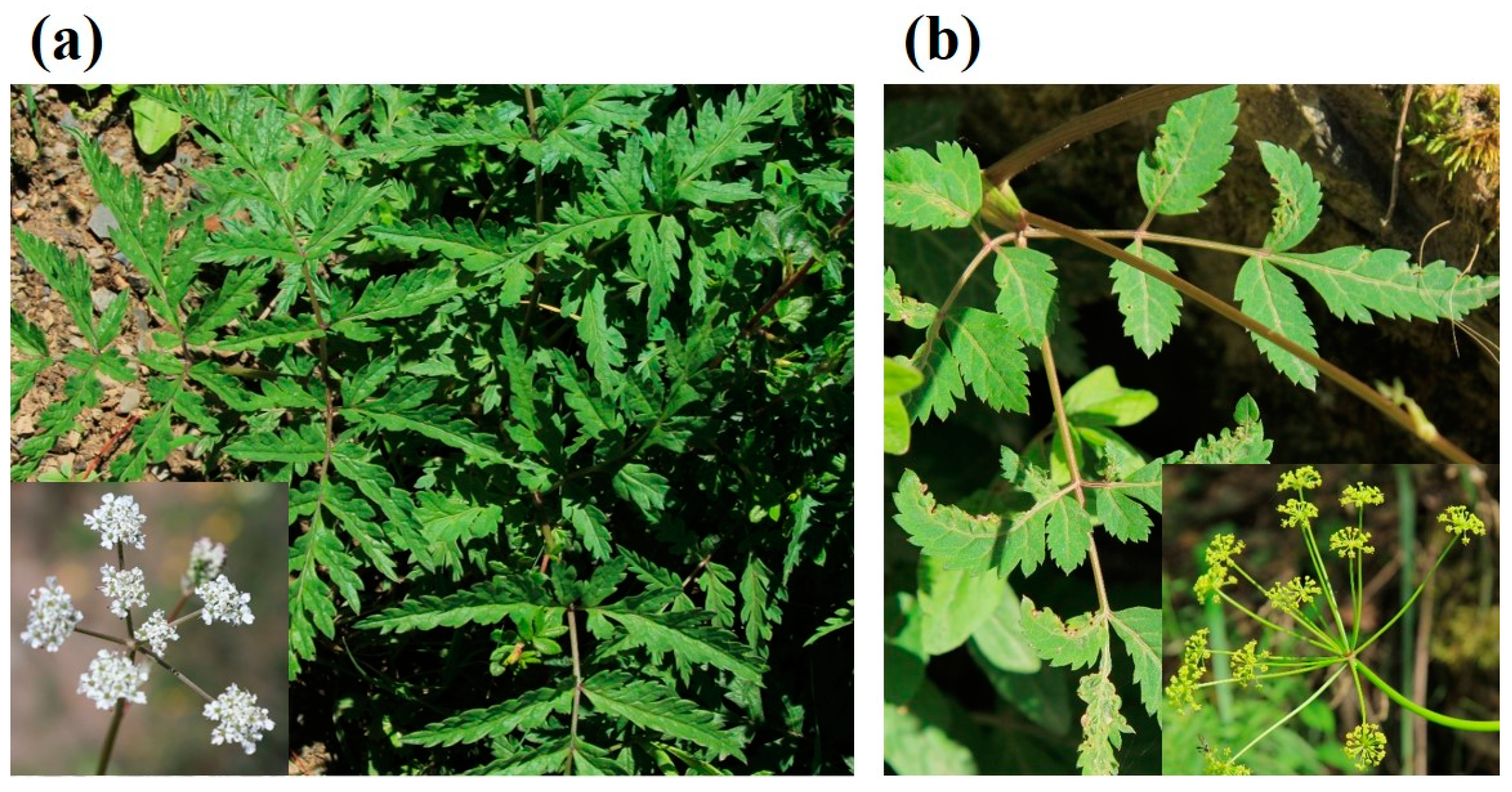
2.2. Botanical Characteristics
3. Phytochemical Composition
3.1. Volatile Oils
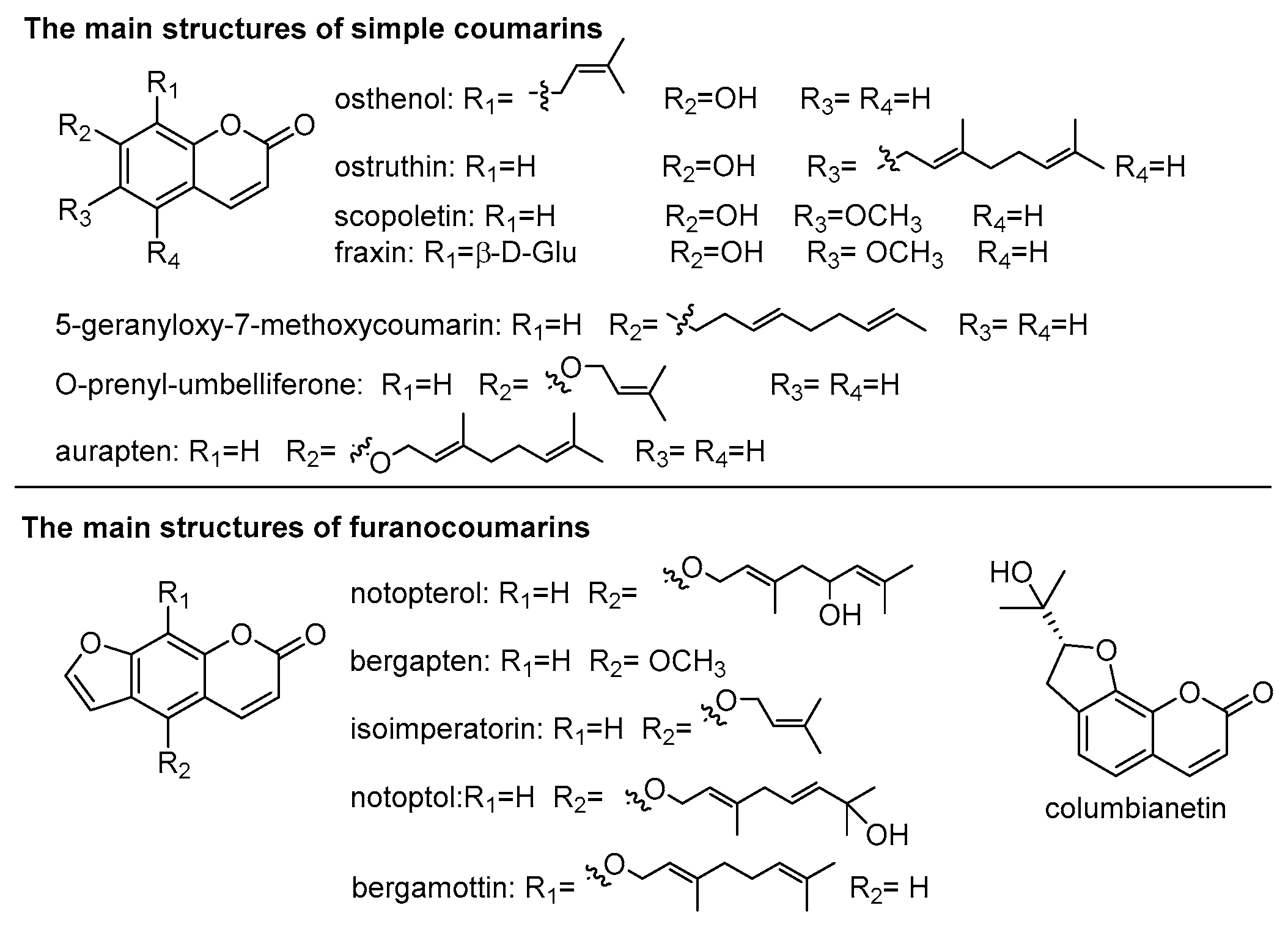
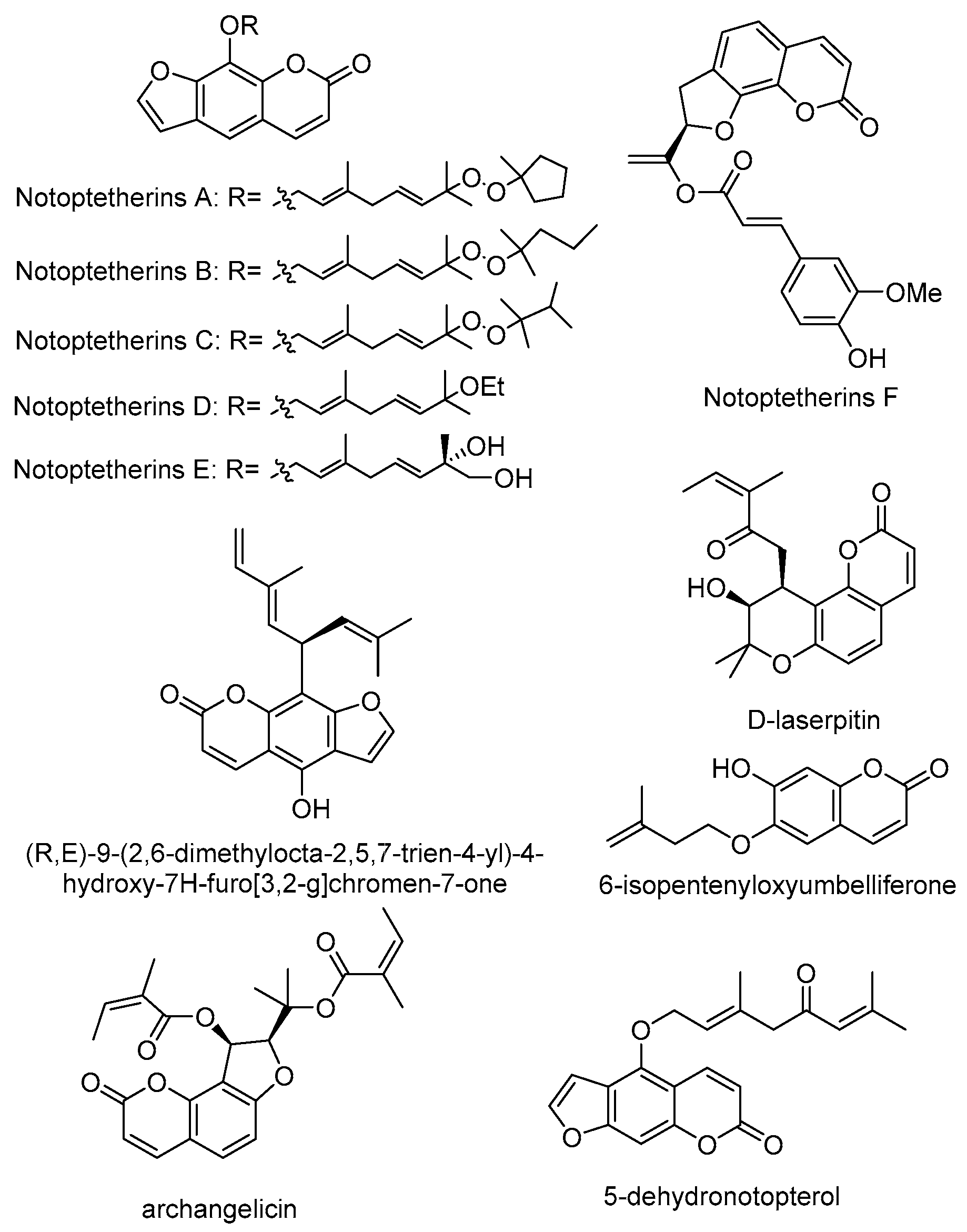
3.2. Coumarins
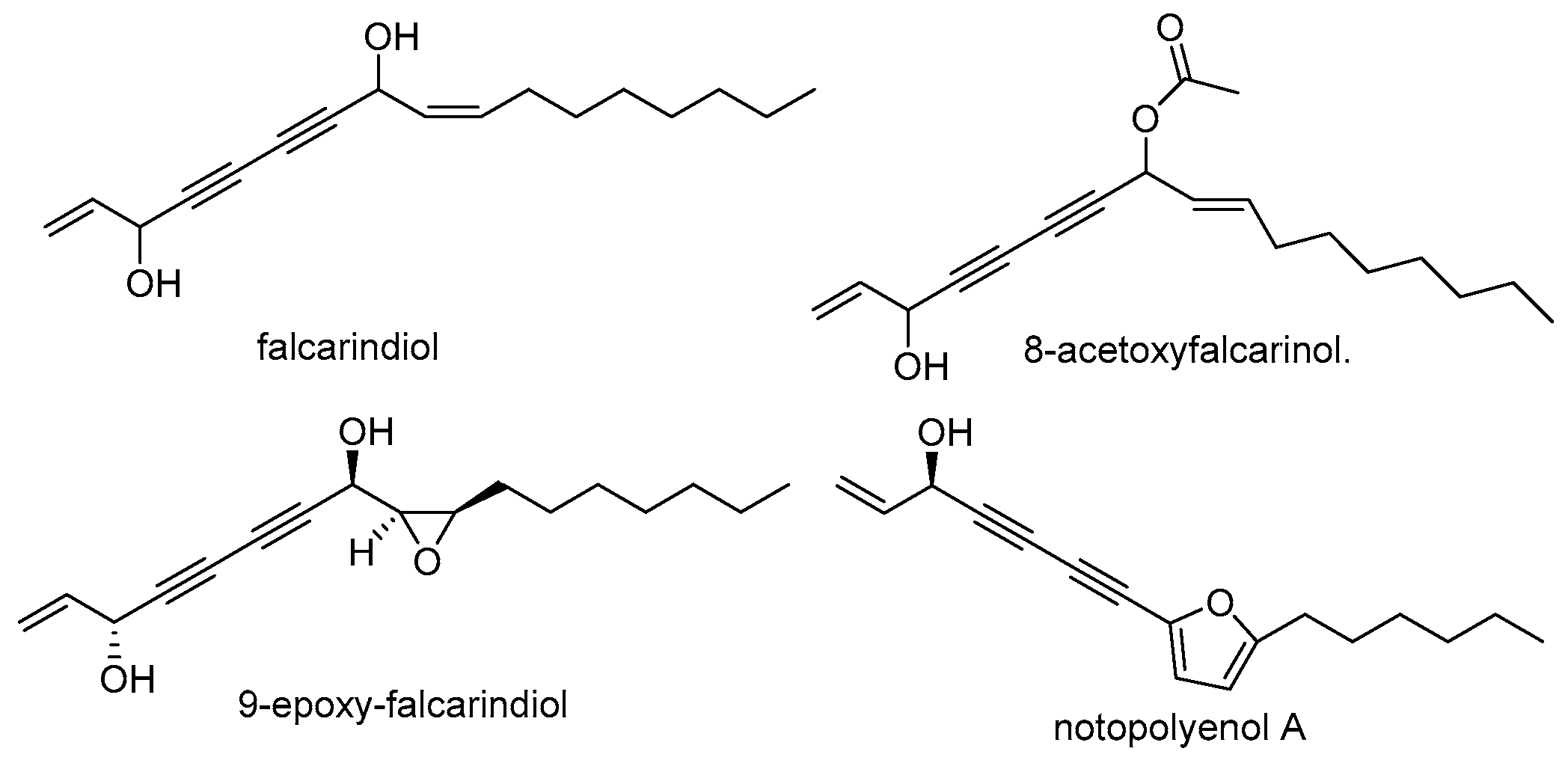
3.3. Polyene-Alkyne
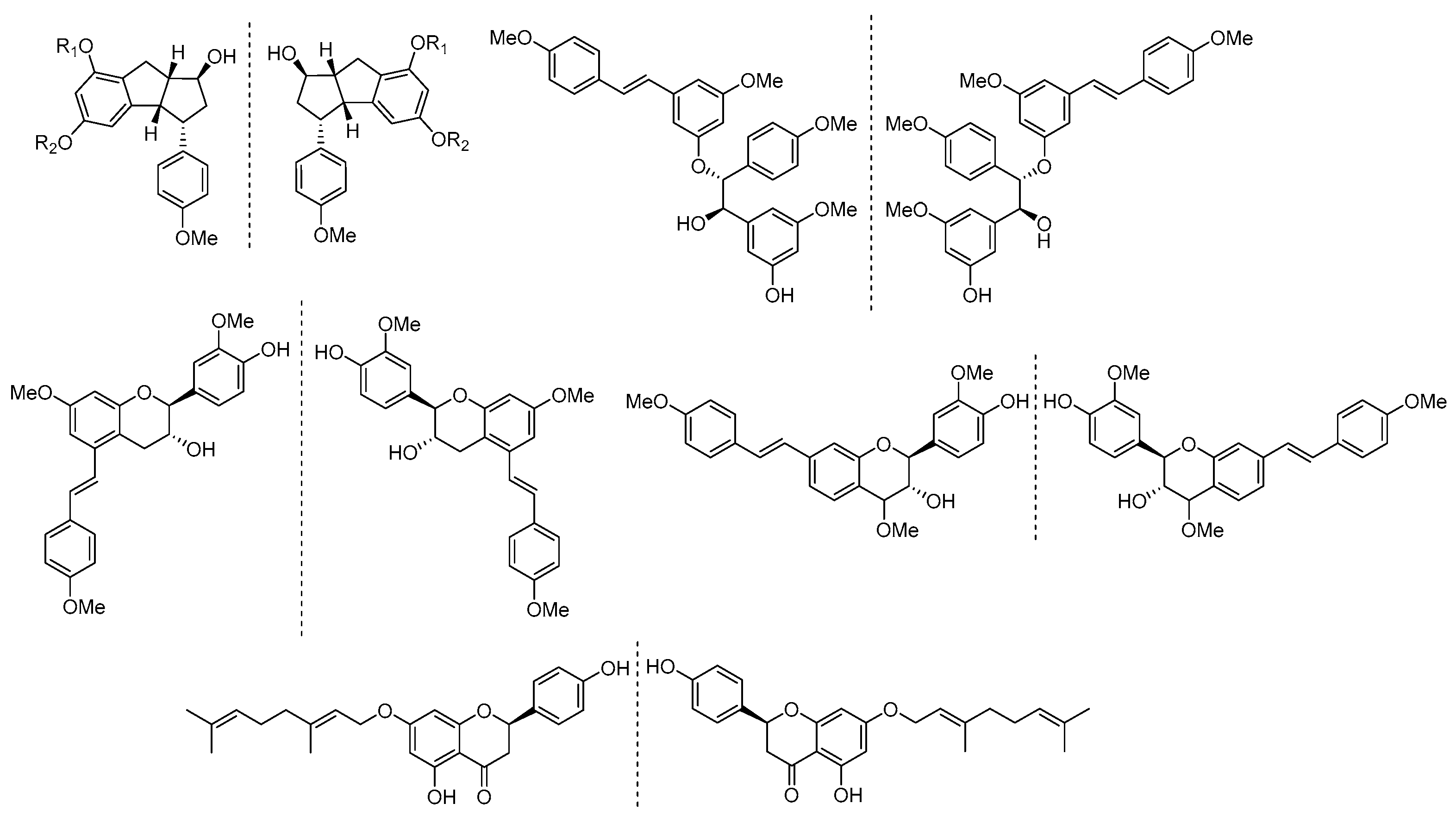
3.4. Phenolics and Flavonoids
3.5. Others
4. Biological Activity
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory
4.2. Anti-Tumor
4.3. Antibacterial and Antifungal
4.4. Other Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Communication. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2020th ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Z. Rapid Discrimination of Notopterygium incisum and Notopterygium franchetii Based on Characteristic Compound Profiles Detected by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Analysis. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azietaku, J.T.; Ma, H.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Oppong, M.B.; Cao, J.; An, M.; Chang, Y. A Review of the Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Notopterygium incisum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 202, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-R.; Tang, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Shu, L.-X.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Yao, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-B. Systematic Characterization of the Chemical Constituents in Vitro and in Vivo of Qianghuo by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Fitoterapia 2024, 172, 105758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M. The Pharmacological Mechanism Analysis of Qianghuo Shengshi Tang in the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Minerva Surg. 2024, 79, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, M.-L.; López-Pujol, J.; Jia, R.-W.; Kou, Y.-X.; Yue, M.; Guan, T.-X.; Li, Z.-H. The Hybridization Origin of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium (Apiaceae): Evidence from Population Genomics and Ecological Niche Analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2023, 182, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Raven, P.H.; Hong, D.Y. Flora of China Volume 14: Apiaceae through Ericaceae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; ISBN 1-930723-41-5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-L.; He, Y.-L.; López-Pujol, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.-H. Complex Population Evolutionary History of Four Cold-Tolerant Notopterygium Herb Species in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Adjacent Areas. Heredity 2019, 123, 242–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Yue, M.; He, Y.-L.; Zhao, G.-F.; Li, Z.-H. Species Delimitation and Interspecific Relationships of the Endangered Herb Genus Notopterygium Inferred from Multilocus Variations. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 133, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-L.; Shang, Q.-H.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Wang, N.; Sa, W.; Li, B.-G.; Li, Z.-H. Drivers of Intraspecific Differentiation of an Alpine Cold-Tolerant Herb, Notopterygium Oviforme: Roles of Isolation by Distance and Ecological Factors. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, T.; Gu, Z.M.; Zhou, G.C.; Wang, T.Z.; Huo, M.; Komatsu, K. Pharmacognostical Study on the Chinese “Qiang-Huo”: On the Anatomical Characteristics of the Underground Parts of Notopterygium incisum and N. forbesii. Nat. Med. 1995, 49, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Lu, X.; Pang, T.; Zhu, S.; Kong, H.; Xu, G. Study of Traditional Chinese Medicine Volatile Oils from Different Geographical Origins by Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (GCxGC-TOFMS) in Combination with Multivariate Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, J.; Huo, G.; Ding, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Wang, R. Constituents, Antibacterial Effect, and Cytotoxicity of Essential Oil from Aerial Parts of Notopterygium incisum. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedge, D.; Gao, Z.; Tabanca, N.; Demirci, B.; Baser, K.; Pridgeon, J.; Becnel, J.; Sampson, B.; Werle, C. The Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Notopterygium incisum and Notopterygium Forbesii Essential Oils from China. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, H.; King, J.W.; Ehsani, A.; Yousefi, M. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Seed Oils—A Short Review of Current Trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjare, S.D.; Dhingra, K. Supercritical Fluids in Separation and Purification: A Review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, A.-D.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.-J.; Wu, R. Quantitative analysis of volatile oils and isoimperatorin in rhizoma et Radix notopterygii. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2007, 32, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, X.; Yin, H.; Jin, X.; He, Y. Extraction of Notopterygium Forbesii by Surercritical CO2 Extraction. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2009, 29, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Poumale, H.M.P.; Hamm, R.; Zang, Y.; Shiono, Y.; Kuete, V. 8—Coumarins and Related Compounds from the Medicinal Plants of Africa. In Medicinal Plant Research in Africa; Kuete, V., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 261–300. ISBN 978-0-12-405927-6. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.L.A.R.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Rocha, J.E.; Farias, P.A.M.; Freitas, T.S.; de Lemos Caldas, F.R.; Figueredo, F.G.; Sampaio, N.F.L.; de Morais Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.; Tintino, S.R.; et al. Unlocking Bacterial Defense: Exploring the Potent Inhibition of NorA Efflux Pump by Coumarin Derivatives in Staphylococcus Aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 190, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Two New Isocoumarins Isolated from the Marine-Sponge-Derived Fungus Setosphaeria sp. SCSIO41009. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202302069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Singh, M.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.C.; Mujwar, S.; Kapoor, M.; Mishra, K.K.; Wani, T.A. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Coumarin Analogs Targeted against SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2024, 29, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Hussain, S.A.; Luo, M. Columbianadin Ameliorates Experimental Acute Reflux Esophagitis in Rats via Suppression of NF-κB Pathway. Acta Cir. Bras. 2024, 39, e391824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Khan, H.; Aschner, M.; Mirzae, H.; Küpeli Akkol, E.; Capasso, R. Anticancer Potential of Furanocoumarins: Mechanistic and Therapeutic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjeh, M.S.; Mazlomifar, A.; Shahvelayti, A.S.; Moghaddam, S.K. Coumarin Linked to 2-Phenylbenzimidazole Derivatives as Potent α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wei, G.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y.; Hou, B.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Su, M.; Guo, Z.; et al. Angelica Keiskei Water Extract Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2024, 29, 2305036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; López-Jornet, P.; Lopez, E.P.-F.; Harun, N.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Sytar, O.; Shaheen, S.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Natural Coumarins: Exploring the Pharmacological Complexity and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6492346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, X.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 2D6 by Notopterol. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 322, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozawa, M.; Fukumoto, M.; Matsuyama, Y.; Baba, K. Chemical Studies on the Constituents of the Chinese Crude Drug “Quiang Huo”. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 2712–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-W.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.-W. Simultaneous Quantification of 33 Active Components in Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix Using Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Okamura, Y.; Dibwe, D.F.; Awale, S.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Anti-Austerity Agents from Rhizoma et Radix Notopterygii (Qianghuo). Planta Med. 2012, 78, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Hu, Y.-H.; Hamann, M.T.; Peng, J.-N.; Starks, C.M.; O’Neil-Johnson, M.; Hu, J.-F. New Guaiane Sesquiterpenes and Furanocoumarins from Notopterygium incisum. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, S.-B.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.-F. Glycosides from the Methanol Extract of Notopterygium incisum. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, B.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Ding, L. Discrimination of the Seeds of Notopterygium incisum and Notopterygium franchetii by Validated HPLC-DAD–ESI-MS Method and Principal Component Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Coumarins from the Roots and Rhizomes of Notopterygium incisum. Fitoterapia 2018, 131, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Río, J.A.D.; Díaz, L.; García-Bernal, D.; Blanquer, M.; Ortuño, A.; Correal, E.; Moraleda, J.M. Chapter 5—Furanocoumarins: Biomolecules of Therapeutic Interest. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, F.R.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 43, pp. 145–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Lee, D.Y.W. Novel Coumarin Glycoside and Phenethyl Vanillate from Notopterygium Forbesii and Their Binding Affinities for Opioid and Dopamine Receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3218–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, K.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, W.; Ding, L.; Peng, S. Chemical constituents contained in seeds of Notopterygium franchetii. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2012, 37, 941–945. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. Studies on the Chemical Constituents of Notopterygium incisum Ting. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1994, 19, 421–422+447. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.M.; Zhang, D.X.; Yang, X.W.; Hattori, M.; Namba, T. Isolation of Two New Coumarin Glycosides from Notopterygium forbesii and Evaluation of a Chinese Crude Drug, Qiang-Huo, the Underground Parts of N. incisum and N. forbesii, by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.-S.; Wang, Q.; Leung, K.S.-Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Z.-H. Quality Assessment of Rhizoma et Radix Notopterygii by HPTLC and HPLC Fingerprinting and HPLC Quantitative Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Ling, L. Studies on the chemical constituents of not opterygium forbesii boiss. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1988, 30, 562–564. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Lian, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Z. Quality Control of Notopterygii rhizoma et Radix Using near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 111, 103181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Different Post-Harvest Processing Methods on the Chemical Constituents of Notopterygium franchetii by an UHPLC-QTOF-MS-MS Metabolomics Approach. Molecules 2019, 24, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y. Coumarins from Notopterygium incisum and Their Inhibitory Effect against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Nitric Oxide Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 3383–3392. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Zhang, X.-F.; Du, F.-Y. Notopterygium incisum Extract and Associated Secondary Metabolites Inhibit Apple Fruit Fungal Pathogens. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 150, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q. Chemical constituents of coumarins compounds from Notopterygium incisum and their anti-oxidant activity. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2019, 50, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; You, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, C.; Suo, Y. Analysis of Free Fatty Acids in Notopterygium forbesii Boiss by a Novel HPLC Method with Fluorescence Detection. Talanta 2012, 98, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lv, J.-M.; Hu, D.; Abe, I. Biosynthesis of Alkyne-Containing Natural Products. RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Q.-Y.; Yang, Z.; Lin, H.-W.; Han, B.-N. Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Blunder, M.; Fakhrudin, N.; Liu, X.; Noha, S.M.; Malainer, C.; Kramer, M.P.; Cocic, A.; Kunert, O.; Schinkovitz, A.; et al. Polyacetylenes from Notopterygium incisum—New Selective Partial Agonists of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kunert, O.; Blunder, M.; Fakhrudin, N.; Noha, S.M.; Malainer, C.; Schinkovitz, A.; Heiss, E.H.; Atanasov, A.G.; Kollroser, M.; et al. Polyyne Hybrid Compounds from Notopterygium incisum with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Agonistic Effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Cytotoxic Polyacetylenes Isolated from the Roots and Rhizomes of Notopterygium incisum. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungmunnithum, D.; Thongboonyou, A.; Pholboon, A.; Yangsabai, A. Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants for Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects: An Overview. Med. Basel Switz. 2018, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant Flavonoids: Classification, Distribution, Biosynthesis, and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, A.; Umar, N.; Rabail, R.; Butt, M.S.; Kieliszek, M.; Hassoun, A.; Aadil, R.M. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Potential of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wen, R.; Liu, Y.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Phenolic Constituents Isolated from the Roots and Rhizomes of Notopterygium incisum. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 128, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Jiang, S.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Peng, S.; Ding, L. New Alkaloids from the Seeds of Notopterygium incisum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, T.; Takata, M.; Nishino, H.; Nishino, A.; Takayasu, J.; Iwashima, A. Studies on the Antitumor-Promoting Activity of Naturally Occurring Substances. II. Inhibition of Tumor-Promoter-Enhanced Phospholipid Metabolism by Umbelliferous Materials. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1084–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-S.; Tan, Q.-W.; Guan, L.-P. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Antibacterial, and Analgesic Activities and Mechanisms of Quinolines, Indoles and Related Derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiranvand, M. A Review of the Most Common in Vivo Models of Stomach Ulcers and Natural and Synthetic Anti-Ulcer Compounds: A Comparative Systematic Study. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the Immune System in Cancer: From Tumor Initiation to Metastatic Progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, E.; Nishimura, S.; Ohmori, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Satake, M.; Yamazaki, M. Analgesic Component of Notopterygium incisum Ting. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Urzúa, S.; Briones-Valdivieso, C.; Chichiarelli, S.; Saso, L.; Rodrigo, R. Potential Role of Natural Antioxidants in Countering Reperfusion Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-A.; Li, J.; Azietaku, J.T.; Liu, W.; He, J.; Chang, Y.-X. A Single Standard to Determine Multi-Components Method Coupled with Chemometric Methods for the Quantification, Evaluation and Classification of Notopterygii Rhizoma et Radix from Different Regions. Molecules 2019, 24, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-S.; Xu, X.-X.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Jiang, S.-Q.; Wang, T.; Li, P.; Li, F. System Pharmacology Analysis to Decipher the Effect and Mechanism of Active Ingredients Combination from Herb Couple on Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 288, 114969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Qiu, H.; Shen, Y.; Tang, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q. Notopterol Alleviates the Progression of Osteoarthritis: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Shi, P.; Ma, R.; Xie, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Notopterol Inhibits the NF-κB Pathway and Activates the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathway in Periodontal Tissue. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Gan, S.; Fu, G.; Zou, P.; Chen, G.; et al. Notopterol Attenuates Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rat. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 859422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-T.; Yeh, C.-T.; Yadav, V.K.; Pikatan, N.W.; Fong, I.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Chiu, Y.-S. Notopterol Mitigates IL-1β-Triggered Pyroptosis by Blocking NLRP3 Inflammasome via the JAK2/NF-kB/Hsa-miR-4282 Route in Osteoarthritis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Ding, N.; Zhang, S.; Hutchinson, S.Z.; Zhang, X. Adiponectin Protects Rat Myocardium against Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Injury via Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-W.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.-W.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.-F.; Zhong, G.-Y.; Liu, H.-N.; Yang, S.-L. Anti-Inflammatory Phenolic Acid Esters from the Roots and Rhizomes of Notopterygium Incisium and Their Permeability in the Human Caco-2 Monolayer Cell Model. Molecules 2017, 22, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunder, M.; Liu, X.; Kunert, O.; Winkler, N.A.; Schinkovitz, A.; Schmiderer, C.; Novak, J.; Bauer, R. Polyacetylenes from Radix et Rhizoma Notopterygii Incisi with an Inhibitory Effect on Nitric Oxide Production In Vitro. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, S. Nodakenetin Alleviates Inflammatory Pain Hypersensitivity by Suppressing NF-κB Signal Pathway. Neuroimmunomodulation 2022, 29, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, T.; Komatsu, T.; Nakayama, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiratsuka, A. Induction of Antioxidant and Phase 2 Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes by Falcarindiol Isolated from Notopterygium incisum Extract, Which Activates the Nrf2/ARE Pathway, Leads to Cytoprotection against Oxidative and Electrophilic Stress. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 488, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Yang, C.; Qiu, S. Distributive Differences of P2Xs between the Forelimb and Hind Limb of Adjuvant Arthritis Rats and Intervention by Notopterygh Rhizoma et Radix. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Mitochondrion-NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages: A Novel Mechanism of the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Notopterygium in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Xing, B.; Liang, X.; Wang, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Q. Notopterygium incisum Root Extract (NRE) Alleviates Epileptiform Symptoms in PTZ-Induced Acute Seizure Mice. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2023, 22, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Cheng, T.-F.; Jia, Y.-R.; Li, P.; Li, F. Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Effects of Traditional Chinese Herb Couple in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, W. Application of Omics Technology to Investigate the Mechanism Underlying the Role of San Hua Tang in Regulating Microglia Polarization and Blood-Brain Barrier Protection Following Ischemic Stroke. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 314, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-B.; Pang, F.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, H.-F.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, J.-F. Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Activities of Linear Furocoumarins from Notopterygium incisum on Cancer Cell Lines. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Yang, C.-K.; Chen, M.-Y.; Yadav, V.K.; Fong, I.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Cherng, Y.-G. Furanocoumarin Notopterol: Inhibition of Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis through Suppression of Cancer Stemness Signaling and Induction of Oxidative Stress-Associated Cell Death. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chew, Z.; Xiao, J.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, Q.; et al. The Natural Compound Notopterol Binds and Targets JAK2/3 to Ameliorate Inflammation and Arthritis. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthanon, S.; Dejkriengkraikul, P.; Yodkeeree, S. Notopterol Suppresses IL-17-Induced Proliferation and Invasion of A549 Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Modulation of STAT3, NF-κB, and AP-1 Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, M.; Jiang, J.; Yan, M.; Xiang, W.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Notopterol Improves Cognitive Dysfunction and Depression-like Behavior via Inhibiting STAT3/NF-ĸB Pathway Mediated Inflammation in Glioma-Bearing Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Ojika, M.; Sakagami, Y. Differentiation in a Rat PC12 Cell Line Induced by Ostruthin and (-)-Bornyl Ferulate, Constituents of a Chinese Herbal Medicine. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lu, H.; Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Q. Notopterygium incisum Extract (NRE) Rescues Cognitive Deficits in APP/PS1 Alzhneimer’s Disease Mice by Attenuating Amyloid-Beta, Tau, and Neuroinflammation Pathology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lai, D.; Liu, Q.Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.L. Identification of Nematicidal Constituents of Notopterygium incisum Rhizomes against Bursaphelenchus Xylophilus and Meloidogyne Incognita. Molecules 2016, 21, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Chang, W.; Yao, J.; Liu, F.; Zeng, Q.; He, Z. Anti-Osteoporosis Effect of Notopterygium incisum Ting Ex H. T. Chang Extract in Rats. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 18, 2051–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.-C. Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia and Hypertension: A Review of Systemic Inflammation and Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2013, 19, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y.-F.; Zahoor, A.; Shaukat, A.; Chen, Y.; Umar, T.; Deng, P.G.; Guo, M. Upregulated-Gene Expression of pro-Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) via TLRs Following NF-κB and MAPKs in Bovine Mastitis. Acta Trop. 2020, 207, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, P.; Liang, R.; Tu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Law, M.-K.; Chen, M. Reactive Oxygen Species and Nitric Oxide Scavenging Nanoparticles Alleviating Rheumatoid Arthritis through Adjusting the Seeds and Growing Soils. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 5016–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J. Efficient Extraction, Antioxidant Activities and Anti-Inflammation of Polysaccharides from Notopterygium franchetii Boiss. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-Y.; Xie, L.; Wang, W.-Y.; Zou, X.-S.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Chen, M.-H. Pomelo Peel Volatile Oil Alleviates Neuroinflammation on Focal Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Rats via Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1878–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Han, J.; Duan, L.; Fan, J.; Lv, Z.; Guo, M.; Hu, G.; Chen, L.; et al. The Role of Interleukin-17 in Lung Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8494079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Błajet, M.; Feder-Kubis, J. Monoterpenes and Their Derivatives—Recent Development in Biological and Medical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Xiong, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, W.; Duan, X. Species Quantification in Complex Herbal Formulas-Vector Control Quantitative Analysis as a New Method. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 488193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Jin, X.; Ji, H.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, C.; Tang, Z. Water Extract of Notopterygium incisum Alleviates Cold Allodynia in Neuropathic Pain by Regulation of TRPA1. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 305, 116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari-Khanamiri, F.; Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M. A Hypothesis That Notopterol May Be Effective in COVID-19 via JAK/STAT and Other Signaling Pathways. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 34, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Dowerah, D.; Basumatary, M.; Phonglo, A.; Deka, R.C. Inhibitory Potential of Furanocoumarins against Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4 Using Integrated Docking, Molecular Dynamics and ONIOM Methods. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biological Activity | Component/Compound | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | Notopterol | Down-regulated the hypersecretion of inflammatory mediators and alleviated the degradation of the extracellular matrix. | [68] |
| Inhibited synthesis of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β, IL-32, and IL-8 in LPS-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts. | [69] | ||
| Enhanced the survival rate and improved the functioning of the right ventricle. | [70] | ||
| Acted as therapeutic agent in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA.) | [71] | ||
| Pterostilbene and notopterol | Exhibited potential therapeutic effects on obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). | [72] | |
| 4-methyl-3-trans-hexenylferulate, (-)-boroylferulate, 4-methoxyphenyl ferulate, and phenylyl ferulate | Inhibited NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. | [73] | |
| 3-hydroxy allyl polyacetylenes | [74] | ||
| Notoflavinols A and B, and (2R)-5,4′-dihydroxy-7-O-[(E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl]flavanone | [35,57] | ||
| Nodakenetin | Reduced CFA-induced inflammatory pain, but did not have a substantial therapeutic impact. | [75] | |
| Falcarindiol | Activated the Nrf2/ARE pathway and induced cytoprotective enzymes. | [76] | |
| Polyacetylenes | Acted as selective partial PPARγ agonist in the luciferase reporter model. | [51] | |
| Volatile oils | Exhibited strong antioxidant activity in vitro and potent anti-inflammatory activity in zebrafish embryos. | [13] | |
| Extract of NI or the formula containing NI | Down-regulated P2X1, P2X3, P2X4, P2X5, and P2X7 to inhibit FCA-induced RA in rats. | [77] | |
| Regulated NLRP3, pro-Caspase-1, Caspase-1, and CD11b in the ankle joint of AA rats. | [78] | ||
| Improved cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. | [79] | ||
| Reduced levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and VEGF—possessed evident anti-arthritic effects in AIA rats. | [80] | ||
| Regulated gut microbiota, inhibited pro-inflammatory factors in rats with IS. | [81] | ||
| Anti-tumor | Notopol, notopterol, 5-[(2 E,5 Z)-7-hydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2,5-octadienoxy]psoralene, and 5-[(2,5)-epoxy-3-hydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-6-octenoxy]psoralene | Exhibited antiproliferative activity against hepg-2 and C6 cancer cell lines. | [82] |
| Notopterol | Suppressed the viability, migration, and invasion capacity of the human HCC hepj5 and Mahlavu cell lines. | [83] | |
| Bound Janus kinase (JAK)2 and JAK3 kinase domains to inhibit JAK/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) activation. | [84] | ||
| Suppressed IL-17-induced proliferation and invasion of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells via modulation of STAT3, NF-κB, and AP-1 activation. | [85] | ||
| Exhibited anti-glioma effects and alleviated neuropsychiatric symptoms. | [86] | ||
| Strustin | Exhibited activity on PANC-1 (PC50 = 7.2 μmol/L) and PSN-1 (PC50 = 7.8 μmol/L). | [87] | |
| Ostruthin and (-)-bornyl ferulate | Induced comparable neurite-like structures in twenty percent of rat PC12 cells at 2 mg/mL, and showed cytotoxicity at concentrations higher than 3 mg/mL. | [87] | |
| Antibacterial | Volatile oils | The diameters of inhibition zone (dizs) of NI-EO against E. coli and S. aureus were 14.63 and 11.25 mm and the minimum inhibitory concentrations were 3.75 and 7.5 μL/mL, respectively. | [13] |
| Antifungal | Ethyl acetate extract of NI | Exhibited antifungal activities against apple fruit pathogens of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Botryosphaeria dothidea with MIC values ranging from 8 to 250 mg L−1. | [46] |
| The others | Extract of NI | Showed potential therapeutic effects on ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic and thrombus rats. | [88] |
| Columbianetin, falcarindiol, falcarinol, and isoimperatorin | Showed strong nematicidal activity against the two species of nematodes. | [89] | |
| Extract of NI | Mitigated ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Chen, P.; Li, L. Phytochemistry and Biological Profile of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium. Molecules 2024, 29, 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143252
Tang Z, Zheng R, Chen P, Li L. Phytochemistry and Biological Profile of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143252
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhikang, Renlin Zheng, Ping Chen, and Liangchun Li. 2024. "Phytochemistry and Biological Profile of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143252
APA StyleTang, Z., Zheng, R., Chen, P., & Li, L. (2024). Phytochemistry and Biological Profile of the Chinese Endemic Herb Genus Notopterygium. Molecules, 29(14), 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143252







