Abstract
Dimeric forms of flavonoids, known as biflavonoids, are much less studied compared to monomeric forms. It is estimated that nearly 600 different natural biflavonoids have been described to date, containing various subtypes that can be subdivided according to the position of their combinations and the nature of the subunits. The group in which two monomers are linked by a 3′-8″-C atom includes the first isolated biflavonoid ginkgetin, derivatives of amentoflavone, and several other compounds. 3′-8″-biflavones recently attracted much attention as potential molecules with biological activity such as antiviral and antimicrobial activity and as effective molecules for the treatment of neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases and in cancer therapies. With the growing interest in them as pharmacologically active molecules, there is also increasing interest in finding new natural sources of 3′-8″-biflavones and optimizing methods for their extraction and identification. Herein, we have summarized the available data on the structural diversity, natural occurrence, role in plants, extraction, and identification of 3′-8″-biflavones.
1. Introduction
Flavonoids are undoubtedly the best known and most studied specialized metabolites. They are produced by plants primarily through two distinct pathways: the acetate pathway (ring A) and the shikimate pathway (ring B), along with the connecting chain (ring C) that forms the C6-C3 component [1]. In a plant, they are essential for plant–environment interaction, but in science, they have come into focus as potential natural compounds to treat various diseases due to their antioxidant [2], antimicrobial [3], anti-inflammatory [4], neuroprotective [5], anticancer [6], and other activities [7]. Although some of the activities are often associated with the presence of flavonoids in general, their roles in plants and biological activity are largely dependent on the molecular structure [8]. Flavonoids include several subclasses of compounds, such as flavones, isoflavones, flavonols, flavanols, flavanones, flavanonols, chalcones and dihydrochalcones, aurones, and anthocyanidins [3], which can be further modified by glycolization, esterification, or polymerization. They can occur in free form, but in plants, plant foods, and pharmaceutical preparations, they are mostly present in conjugated form, with one or more sugar residues attached by β-glycosidic bonds to a hydroxyl group (O-glycosides) or a carbon atom of the aromatic ring (C-glycosides) [9]. Flavonoids can be polymerized, with two, three, or more monomers forming a new molecule that has a different biological activity than the monomers.
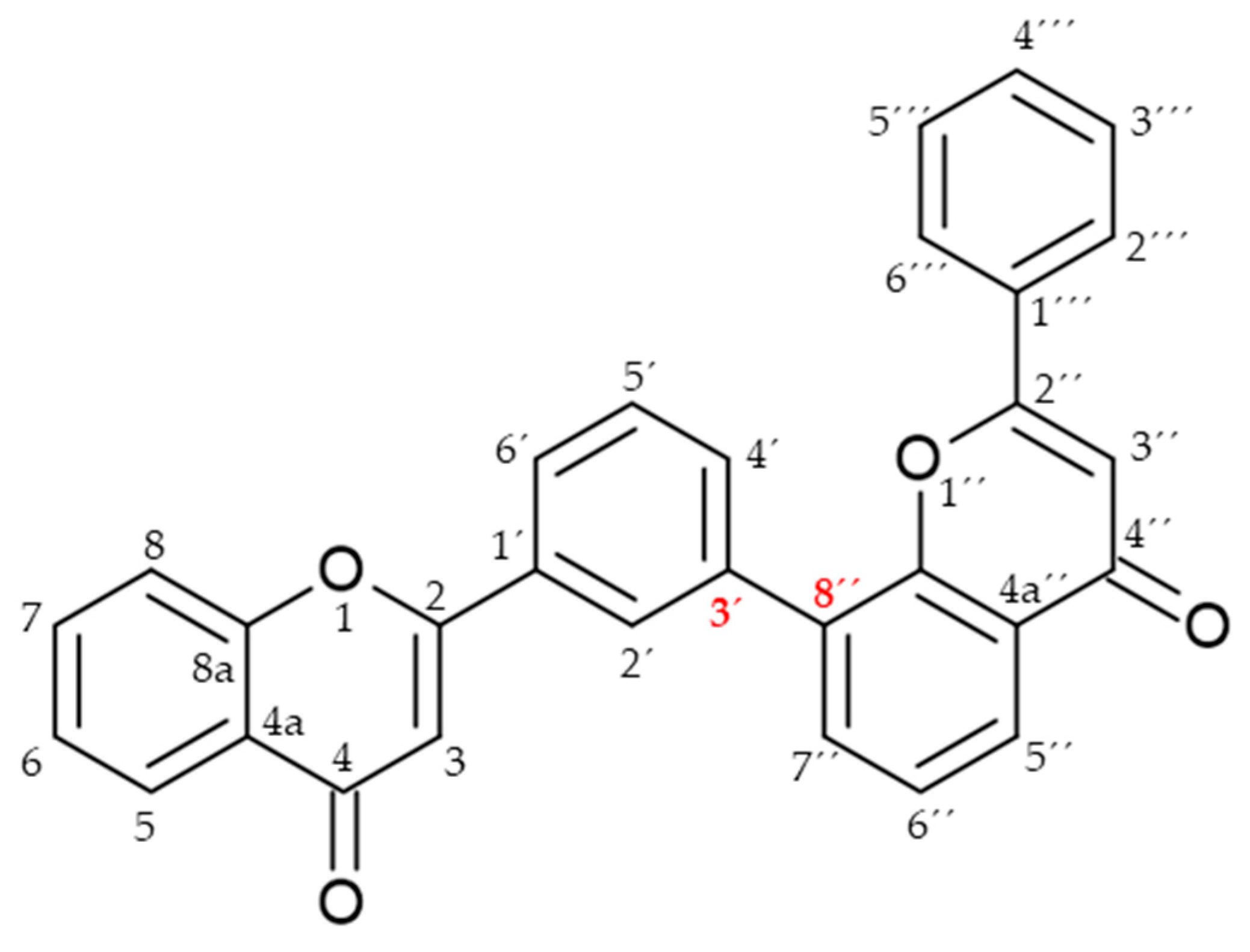
Biflavonoids or flavonoid dimers are a class of flavonoids that have been known for almost 100 years, since the first biflavonoid–ginkgetin was isolated from yellow ginkgo leaves in 1929 [10]. Biflavonoids are much less studied compared to monomeric flavonoids, although studies show a wide range of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, antiviral, antidiabetic, antitumor, cytotoxic, and neuroprotective properties [11]. According to He et al. [11] nearly 600 different biflavonoid structures have been described, which can be divided into two groups: C-C and C-linear fragments-C biflavonoids, depending on whether the linker between the two residues contains an atom. The C-C type contains different subtypes, which can be divided according to the position of their combinations into: 2-3″, 2′-2‴, 2′-6″, 2′-8″, 3-3″, 3-3‴, 3′-3‴, 3′-4‴, 3′-5″, 3-6″, 3′-6″, 3-7″, 3′-7″, 3-8″, 3′-8″, 4-6″, 4-8″, 4′-8″, 5-5″, 6-6″, 6-γ, 6-8″, 7-7″, and 8-8″. The group of biflavonoids in which two flavones are linked by a 3′-8″ C atom (Figure 1) includes the first isolated biflavonoid ginkgetin, derivatives of amentoflavone, and various other compounds that possess biological activity.
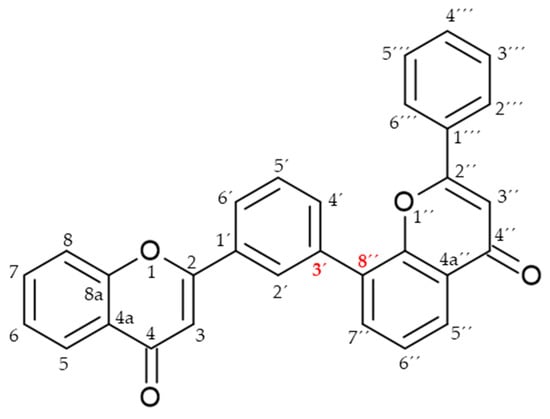
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of 3′-8″-biflavones.
Most notably, during the coronavirus pandemic, they became known as potential antiviral agents against SARS-CoV2 viruses [12], but they also may be beneficial in the treatments of other conditions. Recently, several review papers have focused on biflavones’ antiviral and other antimicrobial activity [12,13], neurodegenerative effects [14,15,16], and roles in metabolism-related diseases and in cancer therapies [17,18]. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no review summarizing the occurrence, possible role in plants, extraction of, or identification technique for amentoflavone and their derivatives, known as 3′-8″ -biflavones.
2. Structural Diversity of 3′-8″-Biflavones
Monomeric subunits of biflavones are, as the name implies, flavones a subclass of flavonoids that differ from other flavonoids in that they have a double bond between C2 and C3 in the flavonoid skeleton, there is no substitution at the C3 position, and they are oxidized at the C4 position [19] Flavones may contain various number of hydroxy group and form molecules with distinct biological activity such as chrysin (5,7-dihydroxyflavone) [20], apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone) [21], baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone), luteolin (3′,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) [22], norwogonin (5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone), tangeritin (4′,5,6,7,8-pentamethoxyflavone) [23], etc. The hydroxy group in the structure may be methylated, and O-methylated flavones, ones that obtain a methyl group through hydroxyl group and C-methylated flavonones, in which the methyl group is directly bound to C atoms of the basic skeleton, may be formed. Methylated biflavones are acacetin (5,7-dihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone), genkwanin (4′,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone), echioidinin (5,2′-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone), negletein (5,6-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone), wogonin (5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone), echtochrysin (5-hydroxy-7-methoxyflavone), chrysoeriol (4′,5,7-trihydroxy-3′-methoxyflavone), and many others. Methylated derivatives usually show higher bioactivity, but bioactivity depends on the position of methylated group and the number of methylated and hydroxy groups [24,25]. Another modification that affects biological activity is prenylation, which can form prenylated flavones with different biological activity, but only a few prenylated flavones have been studied in detail [26].
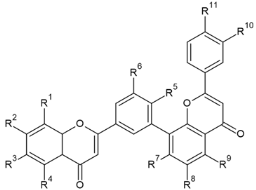
Flavones may be present in plant material in free form or may be glycolyzed, but also, they can form dimers at different positions. Among them, those forming dimers at 3′-8″ (Figure 1) stand out as molecules with different biological activity [15,27,28]. The formulas of the naturally occurring 3′-8″-biflavones and their methylated forms which are known to date are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical formula of naturally occurring 3′-8″-biflavones.
It should be noted that most of the known 3′-8″-biflavones were isolated and characterized 50 or more years ago, and many of them were not subsequently explored. Thus, there is a possibility that some of the compounds were inadvertently misidentified because of the lack of commercial standards and modern high-sensitivity instruments for identification at that time. In addition, the nomenclature of (bi-)flavonoids was not standardized at that time, so the same compound could be referred to in different ways, especially in the case of isomers, where isomeric structures can be referred to as the same molecule in different publications.
As can be noticed from Table 1, 3′-8″-biflavones contain two flavone subunits, and, like their monomeric subunits, may differ in a number of hydroxyl and methylated groups. For monomers, methylation is known to increase metabolic stability by preventing the formation of glucuronic acid and sulfate conjugates, resulting in increased membrane transport that facilitates absorption and greatly increases bioavailability [25]. Also, methylated monomeric derivatives usually show higher bioactivity, and the site as well as extent of methylation play an important role [24,25]. In the case of biflavonoids, including biflavones, how dimerization and the degree of methylation affect metabolism and biological activity is not yet well documented.
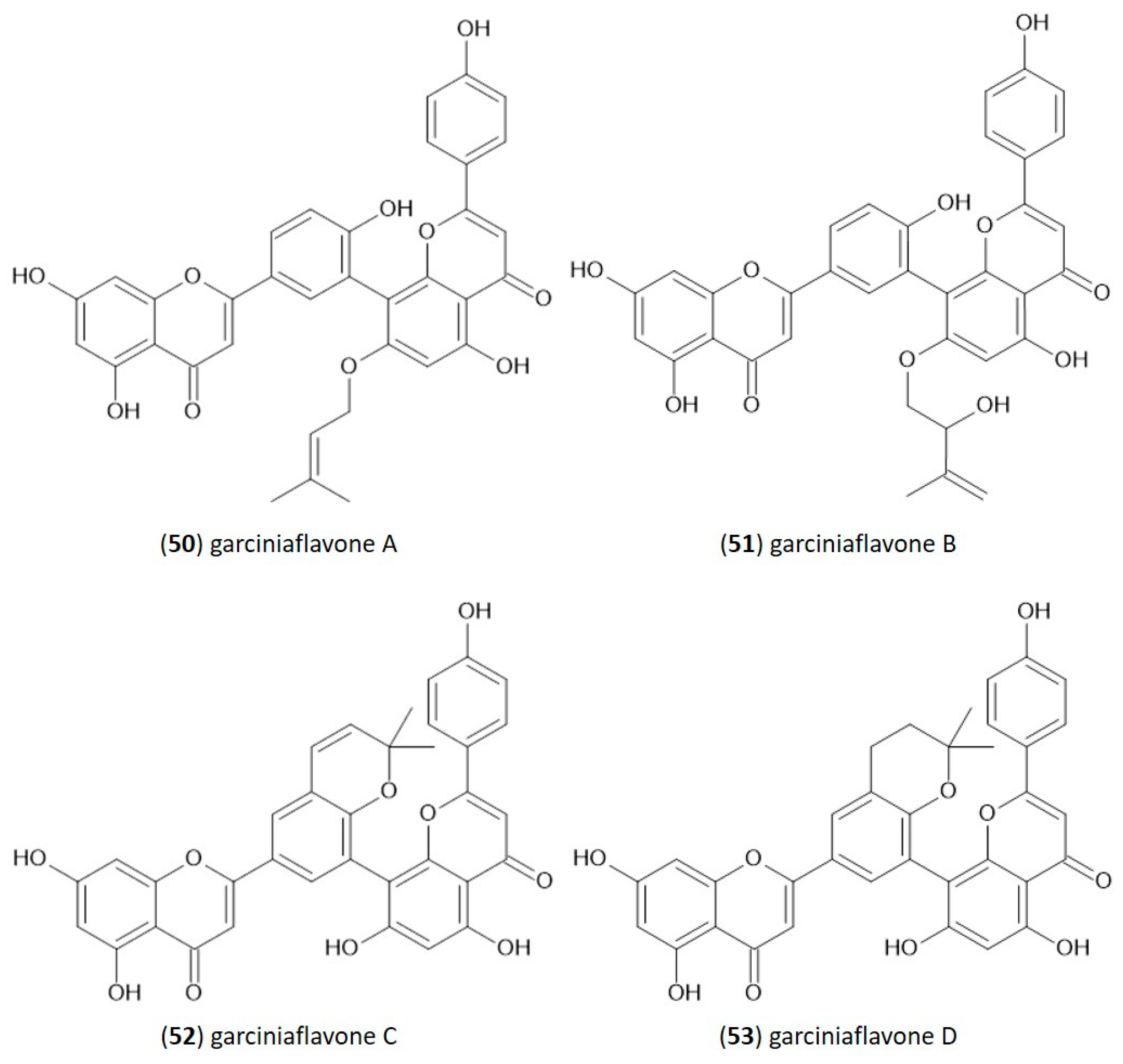
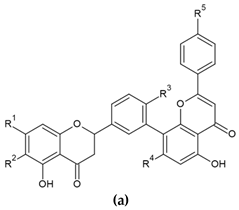
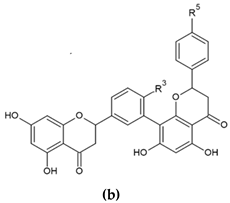
In the structure of 3′-8″-biflavones, the carbon–carbon double bonds C2-C3 and C2″-C3″ can be readily hydrogenated, resulting in a wide range of naturally occurring hydrogenation products (Table 2). Similarly to monomeric flavones, biflavones can also occur in a prenylated form, such as in plants of the genus Garcinia, from which several different prenylated 3′-8″-biflavones have been reported [29], and the structure of which is shown in Figure 2. Prenylated forms of biflavonoids are considered very rare in nature, and data have been reported only in Garcinia sp.

Table 2.
Naturally occurring hydrogenation derivatives of 3′-8″ -biflavones.
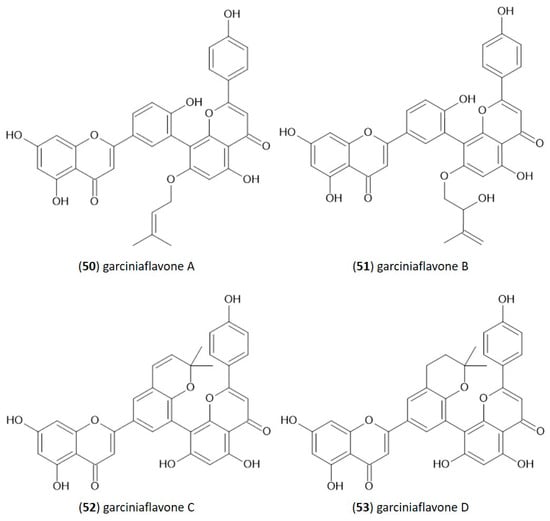
Figure 2.
Molecular structure of naturally occurring prenylated 3′-8″-biflavones.
In the vast majority of reports, 3′-8″-biflavones are described as aglycones, but, for example, in whisk fern (Psilotum nudum L.), amentoflavone has also been detected in a glycoside form with one to three sugars attached [30,31] Amentoflavone, ginkgetin, and isoginkgetin glycosides have also been detected in ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) (summarized by Liu et al. [32]) This shows similar behaviour to the monomeric forms, but according to the available data, the biflavone glycosides are present in much lower concentrations than the free biflavones, which is in contrast to the monomeric forms, where the glycoside forms are normally more abundant.
3. Distribution in the Plant Kingdom
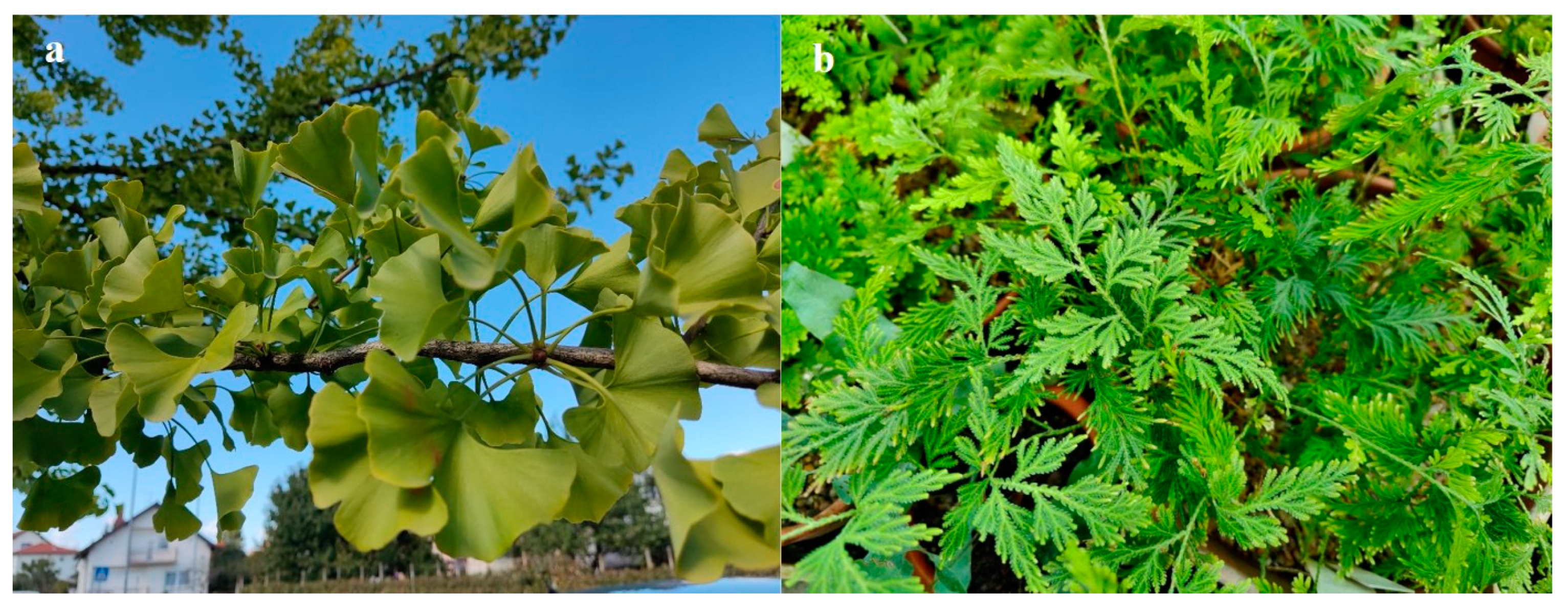
The first isolated 3′-8″-biflavone, and biflavonoid altogether, was isolated in 1932 as a yellow flavonoid pigment from the yellowed leaves of G. biloba L. (Figure 3a), and it was later named ginkgetin [33]. Isoginkgetin and bilobetin were also named after ginkgo, but several other 3′-8″-biflavones were named after the plants from which they were first isolated (Table 3).

Figure 3.
Plants abundant in 3′-8″-biflavones: (a) G. biloba L. and (b) Selaginella sp.

Table 3.
Examples of the 3′-8″-biflavones named after the plants from which they were first isolated.
Later, other biflavones from ginkgo leaves were also characterized [40], and to date, ginkgo is commonly mentioned and studied as a plant containing various 3′-8″-biflavones. Eight different 3′-8″ biflavone aglycones and three glycosides have been detected in ginkgo leaves [21,32], with amentoflavone, bilobetin, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin, and sciadopitysin being the most commonly detected. Older studies considered biflavonoid compounds to be characteristic of gymnosperms [41], with 3′-8″-biflavones most frequently detected in the gymnosperm families Cupressaceae, Taxaceae, and Podocarpaceae, where they occurred in 22, 16, and 12 different species (Table 4). Although most of the older studies reported their occurrence only in gymnosperms, 3′-8″-biflavons were later also found in various angiosperm families such as Euphorbiaceae, Clusiaceae, Nartheciaceae, Primulaceae, Phyllanthaceae, Oxalidaceae, Malpighiaceae, Fabaceae, Calophyllaceae, Burseraceae, Capparaceae, Salicaceae, Connaraceae, Cyperaceae, Moraceae, Putranjivaceae, Ericaceae, Hypericaceae, Lanariaceae, Caprifoliaceae, Anacardiaceae, Ranunculaceae, Thymelaeceae, Viburnaceae, and Ochnaceae. In addition, 3′-8″-biflavones were detected in pteridophytes from the families Psilotaceae and Selaginellaceae. They were particularly abundant in various spikemosses (Selaginella sp.) (Figure 3b, in which 71 different species of biflavonoids were detected, 24 of which were 3′-8″-biflavones represented mainly by amentoflavone and isoginkgetin [18]. The list of plants in which the presence of 3′-8″-biflavones was reported is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The list of the plants in which 3′-8″ biflavones have been identified.
The accumulation of 3′-8″-biflavones is highly dependent on the tissue type studied and other environmental conditions. For example, ginkgo leaves are rich in bilobetin, isoginkgetin, ginkgetin, and sciadopytisin [177,178], but their content is highly dependent on the growing location of the ginkgo plant [179] and the developmental stage of the leaves [177,178], so these parameters should be taken into account when ginkgo leaves are used as a source of 3′-8″-biflavones for pharmaceutical purposes. According to currently available data, the yellow autumn leaves are more abundant in 3′-8″-biflavones than the green leaves used in traditional medicine and for extract preparations [27]. In addition to the leaves, 3′-8″-biflavones have also been detected in other parts of the ginkgo plant, but their content depends strongly on the tissue type, with the leaves having the highest content, followed by the sarcotesta [178].
4. Role in Plants
In general, flavonoids in plants have a protective function against biotic and abiotic stress conditions. They accumulate when plants are exposed to UV-B radiation and act as sunscreens due to their absorption in the UV range. They also act as scavengers of reactive oxygen species (ROS) due to the phenolic hydroxyl groups in their structure and are often accumulated in plants exposed to various stress factors [177]. However, flavonoids are a large group of molecules that have 6000 different structures and, depending on their structure, can play different roles in plants growth, development, and protection from stress [27]. Although flavonoids are often considered as good antioxidants, biflavonoids, including 3′-8″-biflavones, have significantly lower antioxidant activity than monomeric flavonoids [136], and their role in plants is probably different from that of monomeric flavonoids.
The role of biflavonoids in plants is still largely unexplored. Their localization in plant tissues may indicate roles in plant–environment interactions. Tissue-specific profiling of five 3′-8″-biflavones, amentoflavone, bilobetin, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin, and sciadopitysin, in ginkgo showed that they are accumulated only in plant parts that are in direct contact with the environment [178]. A similar result was observed in MALDI imaging studies. Li et al. [180] used MALDI imaging to investigate the spatio-chemical localization of metabolites in ginkgo leaves and found that the 3′-8″-biflavones amentoflavone, bilobetin/sequioflavone, isoginkgetin/ginkgetin, sciadopytisyn, and methoxybilobetin accumulate in the upper and lower epidermis. The accumulation of ginkgetin/isoginkgetin on the surfaces of the ginkgo leaves was also shown by Beck and Stengel [179]. They reported an increased concentration on the lower side of the leaf compared to the upper side, which might be related to the proposed functions of biflavonoids in plants as fungitoxins and predators, because for both fungi and insects, the lower side of the leaf seems to be a preferred site of invasion. Amentoflavone in whisk fern is also accumulated in the outer part of the above-ground rhizome, according to MALDI imaging [31].
This accumulation of 3′-8″-biflavones, as we already mentioned, might be related to defence against biotic stress. 3′-8″-biflavones showed strong antimicrobial effects against pathogenic fungi in several studies. Krauze-Baranowska and Witwart [103] studied the antifungal activity of bilobetin, 4‴-O-methylamentoflavone, amentoflavone, 7-O-methylamentoflavone, ginkgetin, sciadopitysin, and 2,3-dihydrosciadopitysin against the fungi Alternaria alternata, Fusarium culmorum, and Cladosporium oxysporum. Bilobetin completely inhibited the growth of C. oxysporum and F. culmorum at a concentration of 100 mmol/L, but the activity of ginkgetin and 7-O-methylamentoflavone towards A. alternata was stronger than that of bilobetin. Amentoflavone, along with other biflavonoids, has been shown to affect the production of aflatoxins in Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus [181]. In this study, the authors found that biflavonoids were generally more active in inhibiting aflatoxin production at lower concentrations than the monomeric flavonoids, which may indicate that the dimeric structure would cause stronger activity. According to the authors [181], biflavonoids can be used to develop compounds to control aflatoxin production.
There is evidence that the role of biflavonoids in plants may be related to their role in photosynthesis, more precisely in inhibiting photosynthesis. Aguilar et al. [182] reported in their study with spinach chloroplasts that biflavonoids isolated from Selaginella lepidophylla inhibited ATP synthesis and several other photosynthetic processes, including electron flow, PSII, PSI, and their partial reactions on chloroplasts. Céspedes et al. [183] also reported that biflavonoids can case a concentration-dependent inhibition of photophosphorylation. In an experiment with cyanobacteria, Microcystis aeruginosa, a harmful cyanobacterial bloom, lost its original shape and chlorophylls after treatment with extracts containing high levels of amentoflavone [184]. In this study, the authors show that amentoflavone selectively kills only M. aeruginosa strains without harming other non-cyanobacteria, which may be related to the photosynthetic capacity of cyanobacteria. Few studies have also shown that amentoflavone has an allelopathic effect. De Almeida et al. [185] studied the in vitro effects of Byrsonima crassa extract, rich in amentoflavone, on tomato seedlings and showed that all doses tested had stimulatory effects on root length and inhibitory effects on the length of the aboveground parts of the tomato. Interestingly, biflavonoids are used as taxonomic markers in species of Ochnaceae, known to exhibit allelopathic activity against Lactuca sativa [186]. However, the exact mechanisms of action are unknown, and further studies should explain the above effects and clarify the role of 3′-8″-biflavones and biflavonoids in plants as a whole.
5. Extraction
As mentioned earlier, biflavonoids are much less studied compared to monomeric flavonoids, and most of the older work dealing with biflavonoids merely reports the presence of individual 3′-8″-biflavones in plant material without optimizing extraction or identification/quantification methods. As biflavones, 3′-8″-biflavones are of interest for industrial application, and progress has also been made in the development of extraction methods. Because of their beneficial properties, especially when it comes to medical and food applications, effective, controlled, and safe extraction methods are needed [187]. Before extraction, plant samples typically undergo freeze drying, convection drying, or microwave vacuum drying, followed by milling, grinding, and homogenization, after which an appropriate solvent and extraction method are selected [188,189]. Traditionally, most extraction procedures for 3′-8″-biflavones extraction are based on conventional methods such as organic solvent extraction, reflux extraction, percolation extraction, and Soxhlet extraction [104] (Table 5). Although these methods are widely used, they are time- and energy-consuming, inefficient [190,191,192] and require large volumes of possibly toxic solvents [192,193]. New solvents, ionic liquids (IL), and deep eutectic solvents (DES) are being researched more and more [191,192,193]. The main advantages of DESs are their versatility, tunability, wide temperature range, high polarity, low vapor pressure, non-flammability, and potential as eco-friendly solvents that reduce extraction costs, environmental impact, and degradation of temperature-sensitive molecules [193].
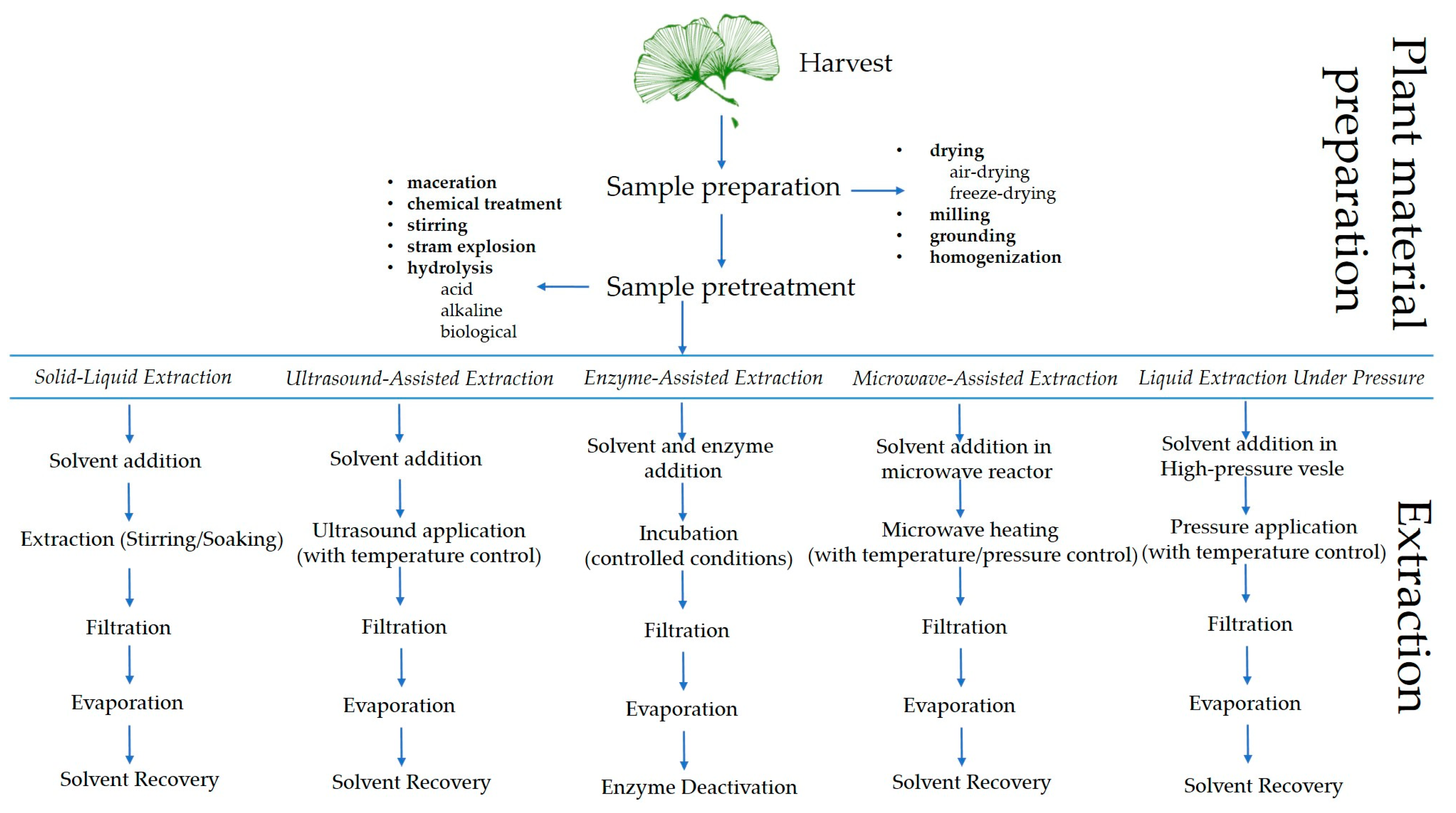
To develop a successful extraction method, formulation and optimization, evaluation, and standardization of process variables are required. This is the only way to achieve a reproducible and efficient extraction process [192]. When it comes to extraction processes, the choice of solvent, liquid/solid ratio, temperature, extraction time, and plant material size are likely to be the starting point for process design and optimization [188]. When using novel methods such as ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), enzyme-assisted extraction (EAE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), and liquid extraction under pressure (PLE), some additional variables such as ultrasound frequency and power, microwave power, solvent amount, pressure, etc., should be considered [188]. To find the optimal conditions, it is necessary to optimize each process individually due to the different characteristics of biflavonoids and the sources [192,193,194,195]. Figure 4 illustrates the biflavonoid extraction process from plant material, highlighting the various steps involved in the procedure.
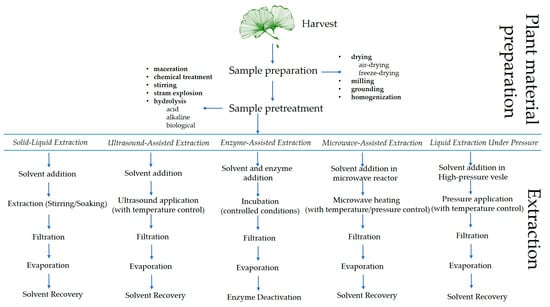
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the biflavonoid extraction process from plant material, highlighting key extraction steps.
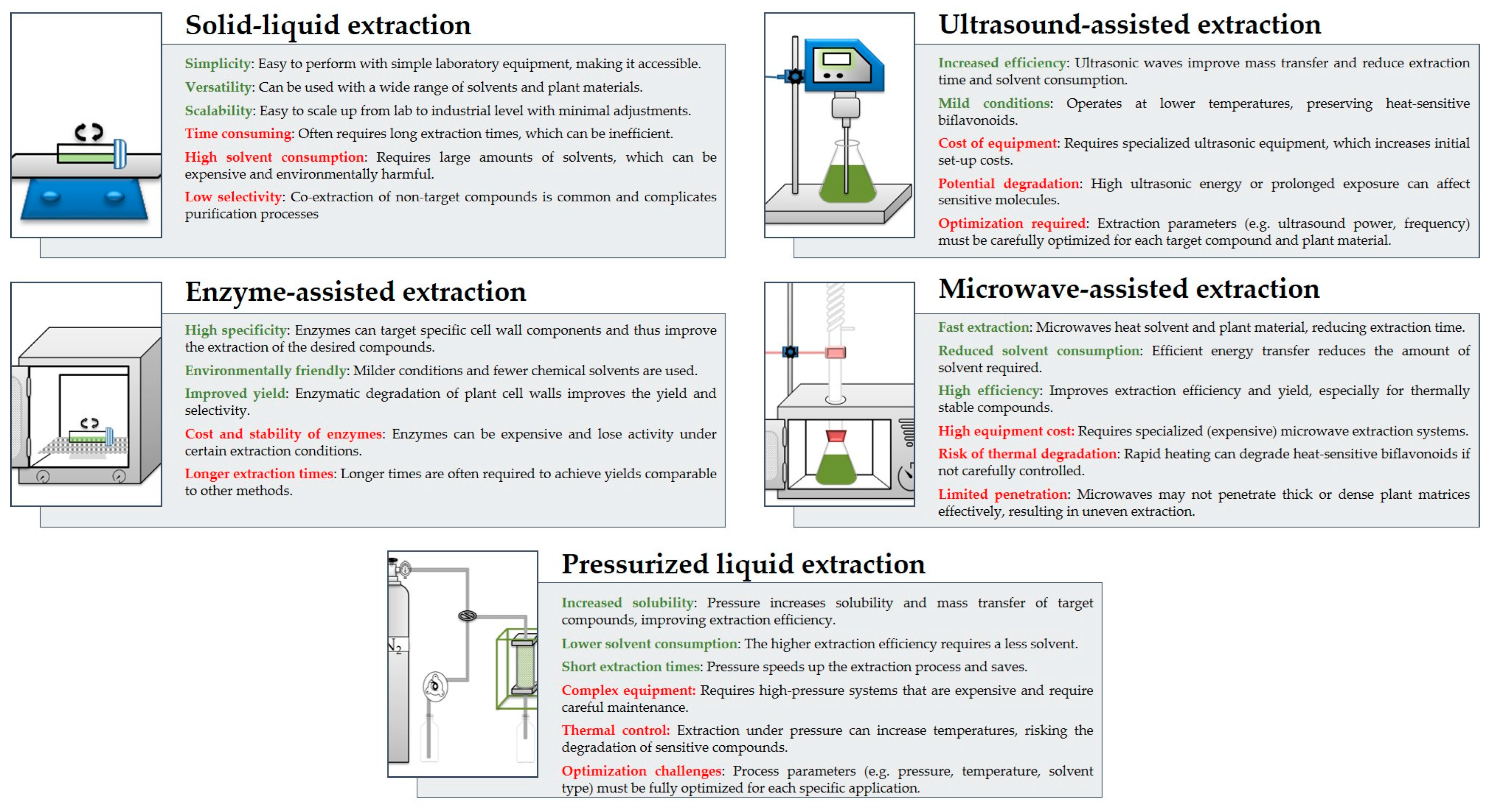
The most effective extraction methods often involve a combination of several approaches, as each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, as illustrated in Figure 5.
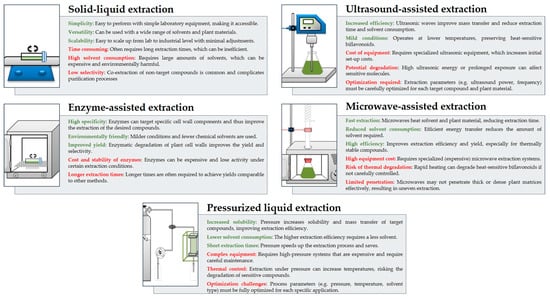
Figure 5.
Comparison of extraction methods used for biflavonoids—advantages (green) and disadvantages (red).
The UAE-DES extraction process has the advantages such as short extraction time, low solvent and energy consumption, and high extraction efficiency [193]. In the paper presented by Liu et al. [196], the authors described the UAE-DES extraction of total biflavonoids (including heveaflavone and amentoflavone) from S. chaetoloma. Comparing the effect of UAE-DES extraction with conventional methods (maceration and percloration with 95% ethanol), the authors observed that by using UAE-DES, the extraction rate increased by 1.5–3-fold compared to conventional methods. In the paper by Li et al. [193] the authors combined MAE-IL for the extraction of amentoflavone (and hinokiflavone) from S. sinensis. Under optimal conditions, the content of amentoflavone was 1.96 mg/g dry weight. Compared with the conventional extraction methods, MAE-IL achieved a higher yield in a shorter time, but also reduced the consumption of the solvent. Lei et al. [188] extracted four main biflavonoids (bilobetin, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin, and sciadopitysin) from G. biloba L. using UAE-IL. Compared with UAE-ethanol, infiltration extraction, and percolation extraction, by applying UAE-IL, more biflavonoids were obtained in less time. In addition, the results of the recovery test indicated that the recovered IL could be repeatedly extracted six times. A comparison of different methods for 3′-8″-biflavonoid extraction is given in the Table 5.
Once the extraction is performed, unfortunately, 3′-8″-biflavonoids are not the only components present in the extract. Since neither of mentioned methods is selective to extract only 3′-8″-biflavonids, the extract is a mixture of different phytochemicals. Due to this, and in order for 3′-8″-biflavonoids to be used in pharmacology, they need to be isolated with high purity. The most common methods used for 3′-8″-biflavonoid isolation are liquid–liquid extraction, macroporous resin adsorption, antisolvent crystallization, and chromatography, with chromatography being the primary technique to obtain high-purity compounds. Column chromatography, using silica gel, polyamide, and sephadex LH 20 as packing materials, has been successfully employed for this purpose. Although this method is widespread, it is time-consuming, expensive, and not environmentally friendly since it requires large amounts of organic solvents. To obtain high purity, this method has to be repeated multiple times, thus leading to low recovery. The additional problem is the selectivity of traditional chromatography methods. Isolating isomers such as ginkgetin and isoginkgetin from G. biloba L. poses even greater challenges with traditional column chromatography [197]. As a possible solution, two-dimensional preparative HPLC methods have been proposed and applied for isolating high-purity compounds on a large scale [198]. But, as for the extraction methods, the combination of approaches is also crucial for efficient isolation of biflavonoids. In the paper presented by Shen et al. [199] the authors proposed an efficient and industrially viable protocol for large-scale targeted isolation of high-purity bioactive biflavonoids from industrial waste G. biloba L. exocarp. The process involved several key steps to achieve high purity and substantial yields. Firstly, macroporous adsorption resin was employed to enrich the bioflavonoids from the G. biloba L. waste. This step ensured the concentration of the target compounds for further processing. Next, a targeted on-line recognition method based on their characteristic UV absorption at 210 nm, 270 nm, and 330 nm was applied to identify and isolate the biflavonoids selectively. This recognition process facilitated the efficient separation of the desired compounds from the mixture. The core technique used in the protocol was the two-dimensional preparative normal phase/reversed phase HPLC-DAC system. This state-of-the-art system allowed for the precise and reliable isolation of the biflavonoids. Within a remarkably short period of 30 min, a total of three biflavonoids, namely, bilobetin, ginkgetin, and isoginkgetin, were isolated with purity exceeding 99.0%. The yield from each isolation run reached dozens or even hundreds of milligrams, making it highly suitable for large-scale production.

Table 5.
Comparison of different extraction methods for 3′-8″ biflavone extraction.
Table 5.
Comparison of different extraction methods for 3′-8″ biflavone extraction.
| Source | Conventional Method | Novel Methods | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biflavonoid | Extraction Conditions | Yield mg/g | Extraction Conditions | Yield mg/g | |||||
| Amentoflavone | T. chinensis leaves | Soxhlet extractor, methanol, textraction = 7 h | 4.08 ± 0.03 | Supercritical CO2 extraction plus co-solvent (78% ethanol), textraction = 2 h, T = 48 °C, p = 25 Mpa, qCO2 = 2 L/min | 4.47 ± 0.06 | [104] | |||
| G. biloba L. | tree bark | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.06 ± 0.004 | - | - | [178] | |||
| twig bark | 0.08 ± 0.007 | - | - | ||||||
| buds | 0.04 ± 0.002 | - | - | ||||||
| leaf blades | 0.09 ± 0.001 | - | - | ||||||
| petioles | 0.18 ± 0.005 | - | - | ||||||
| seed petioles | 0.03 ± 0.002 | - | - | ||||||
| sarcotesta | 0.02 ± 0.002 | - | - | ||||||
| S. tamariscina (Beauv) Spring | Solvent extraction, sonification, textraction = 2 h, T = 25 °C | 70% ethanol | 14.05 | Supercritical CO2 fluid extraction extractor T = 60 °C, p = 200 bar, static, textraction static = 0.5 h, textraction dynamic = 1 h, 70% ethanol | 20.18 | [200] | |||
| 70% hexane | 0.40 | ||||||||
| 70% n-butanol | 1.72 | Accelerated solvent extraction, 70% ethanol, textraction = 4 min, elution is flushed with 60% volume, the nitrogen purge lasts 60 s, and extraction is performed three times. The extraction T = 80 °C, and p < 1500 psi | 27.77 | ||||||
| 70% ethyl acetate | 1.71 | ||||||||
| Reflux extraction, 70% ethanol, textraction = 1 h, T = 90 °C | 33.00 | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction, textraction = 2 h, T = 40 °C | 14.73 | ||||||||
| S. uncinata | Maceration extraction, DES, textraction = 3 h | 0.05 ± 0.01 | Ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction, 33% (w/w), textraction = 0.5 h | 0.71 ± 0.01 | [201] | ||||
| Percolation extraction, textraction = 4 h, T = 40 °C | 0.60 ± 0.01 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 70% ethanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.064 ± 0.004 | Enzyme-assisted extraction(Viscozyme L), textraction = 4 h, T = 50 °C and 200 rpm | 0.066 ± 0.003 | [202] | ||||
| Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 24 h, T = 50 °C and 200 rpm | 0.069 ± 0.002 | ||||||||
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction, 20 kHz, 62% amplitude, textraction = 10 min, T = 0 °C | 0.064 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Mechanically assisted extraction, textraction = 20 min, T = 25 °C and 600 rpm | 0.065 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Chemically assisted extraction, 0.1% TritonX and 10% NaClO solution, T = 25 °C and 200 rpm. | 0.044 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.081 ± 0.002 | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; DES, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.061 ± 0.009 | [178] | |||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.053 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Bilobetin | G. biloba L. leaves | Ethanol-based Ultrasound Assisted Extraction, 70% ethanol textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 2.00 * | Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L,textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 2.44 | [188] | |||
| Infiltration extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 48 h | 1.60 * | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 30 min, percolate: q = 2 drops/min | 1.40 * | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. | twig bark | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min); 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.03 ± 0.002 | - | - | [178] | |||
| petioles | 0.98 ± 0.006 | - | - | ||||||
| leaf blades | 1.38 ± 0.01 | - | - | ||||||
| seed petioles | 0.25 ± 0.02 | - | - | ||||||
| sarcotesta | 0.14 ± 0.05 | - | - | ||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min; 70% ethanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.164 ± 0.014 | Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 4 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 0.166 ± 0.003 | [202] | ||||
| Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 24 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 0.172 ± 0.002 | ||||||||
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction, 20 kHz, 62% amplitude, textraction = 10 min, T = 0 °C | 0.167 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Mechanically assisted extraction, textraction = 20 min, T = 25 °C, and 600 rpm | 0.177 ± 0.012 | ||||||||
| Chemically assisted extraction, 0.1% TritonX and 10% NaClO solution, T = 25 °C, and 200 rpm. | 0.108 ± 0.023 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.471 ± 0.013 | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; DES, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.107 ± 0.008 | [203] | |||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.171 ± 0.029 | ||||||||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.118 ± 0.013 | ||||||||
| Betaine: sucrose 1:4 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.063 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Betaine: glycerol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.092 ± 0.013 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.065 ± 0.002 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.072 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.066 ± 0.003 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea: ethylene glycol 1:2:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.077 ± 0.003 | ||||||||
| Ginkgetin | T. chinensis leaves | Soxhlet extractor; extraction solvent, methanol; textraction = 7 h | 2.17 ± 0.02 | Supercritical CO2 extraction Plus co-solvent (78% ethanol) textraction = 2 h, T = 48 °C, p = 25 Mpa; qCO2 = 2 L/min | 3.39 ± 0.02 | [104] | |||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Ethanol-based ultrasound-assisted extraction, 70% ethanol textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 3.90 * | Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 4.33 | [183] | ||||
| Infiltration extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 48 h | 2.60 * | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 30 min, percolate: q = 2 drops/min | 2.00 * | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. | twig bark | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min, 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.03 ± 0.002 | - | - | [178] | |||
| buds | 0.01 ± 0.001 | - | - | ||||||
| petioles | 0.63 ± 0.003 | ||||||||
| leaf blades | 1.33 ± 0.005 | - | - | ||||||
| seed petioles | 0.15 ± 0.01 | - | - | ||||||
| sarcotesta | 0.12 ± 0.007 | - | - | ||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min; 70% ethanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.607 ± 0.050 | Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 4 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 0.627 ± 0.010 | [202] | ||||
| Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 24 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 0.646± 0.007 | ||||||||
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction, 20 kHz, 62% amplitude, textraction = 10 min, T = 0 °C | 0.622 ± 0.003 | ||||||||
| Mechanically assisted extraction, textraction = 20 min, T = 25 °C, and 600 rpm | 0.634 ± 0.009 | ||||||||
| Chemically assisted extraction, 0.1% TritonX and 10% NaClO solution, T = 25 °C, and 200 rpm. | 0.466 ± 0.055 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.367 ± 0.004 | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; DES, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.110 ± 0.010 | [203] | |||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.105 ± 0.016 | ||||||||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.074 ± 0.03 | ||||||||
| Betaine: glycerol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.073 ± 0.004 | ||||||||
| Isoginkgetin | G. biloba L. leaves | Ethanol-based ultrasound-assisted extraction, 70% ethanol textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 5.20 * | Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 6.50 | [188] | |||
| Infiltration extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 48 h | 5.00 * | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 30 min, percolate: q = 2 drops/min | 3.50 * | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. | twig bark | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min, 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.03 ± 0.003 | - | - | [178] | |||
| buds | 0.005 ± 0.001 | - | - | ||||||
| petioles | 0.88 ± 0.005 | - | - | ||||||
| leaf blades | 1.90 ± 0.01 | - | - | ||||||
| seed petioles | 0.38 ± 0.03 | - | - | ||||||
| sarcotesta | 0.31 ± 0.02 | - | - | ||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, t sonification = 10 min; 70% ethanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.945 ± 0.090 | Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 4 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 0.974 ± 0.018 | [202] | ||||
| Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 24 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 1.007 ± 0.013 | ||||||||
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction, 20 kHz, 62% amplitude, textraction = 10 min, T = 0 °C | 0.969 ± 0.004 | ||||||||
| Mechanically assisted extraction, textraction = 20 min, T = 25 °C and 600 rpm | 0.994 ± 0.015 | ||||||||
| Chemically assisted extraction, 0.1% TritonX and 10% NaClO solution, T = 25 °C, and 200 rpm. | 0.631 ± 0.123 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.543 ± 0.005 | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; DES, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.146 ± 0.016 | [203] | |||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.124± 0.006 | ||||||||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.094 ± 0.006 | ||||||||
| Betaine: sucrose 1:4 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.063 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Betaine: glycerol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.082 ± 0.009 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.062 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.061 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.061 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea: ethylene glycol 1:2:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.062 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Ethanol-based ultrasound-assisted extraction, 70% ethanol textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 10.00 * | Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 25 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:14 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 280 W | 13.97 | [188] | ||||
| Infiltration extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 48 h | 9.10 * | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction c[Epy]BF4 = 0.148 mol/L, textraction = 30 min, percolate: q = 2 drops/min | 9.00 * | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. | twig bark | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min, 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.04 ± 0.004 | - | - | [178] | |||
| buns | 0.01 ± 0.003 | - | - | ||||||
| petioles | 0.73 ± 0.003 | - | - | ||||||
| leaf blades | 2.40 ± 0.006 | - | - | ||||||
| seed petioles | 0.29 ± 0.02 | ||||||||
| sarcotesta | 0.22 ± 0.004 | - | - | ||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 70% ethanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 1.387 ± 0.105 | Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 4 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 1.430 ± 0.021 | [203] | ||||
| Enzyme-assisted extraction (Viscozyme L), textraction = 24 h, T = 50 °C, and 200 rpm | 1.461 ± 0.105 | ||||||||
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction, 20 kHz, 62% amplitude, textraction = 10 min, T = 0 °C | 1.419 ± 0.006 | ||||||||
| Mechanically assisted extraction, textraction = 20 min, T = 25 °C, and 600 rpm | 1.450 ± 0.018 | ||||||||
| Chemically assisted extraction, 0.1% TritonX and 10% NaClO solution, T = 25 °C, and 200 rpm. | 1.054 ± 0.099 | ||||||||
| G. biloba L. leaves | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; 80% methanol, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | 0.344 ± 0.026 | Sonification, tsonification = 10 min; DES, textraction = 45 min, T = 25 °C | Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.154 ± 0.019 | [203] | |||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.077± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Betaine: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.071 ± 0.005 | ||||||||
| Betaine: sucrose 1:4 with 30% H2O (w/w) | 0.054 ± 0.002 | ||||||||
| Betaine: glycerol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.059 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.051 ± 0.002 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: ethylene glycol 1:2 with 20% H2O (w/w) | 0.050 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea 1:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.050 ± 0.000 | ||||||||
| Choline chloride: urea: ethylene glycol 1:2:2 with 10% H2O (w/w) | 0.050 ± 0.001 | ||||||||
| Total biflavonoids | |||||||||
| Amentoflavone, ginkgetin, hinokiflavone and heveaflavone | S. helvetica | Ethanol-based ultrasound-assisted extraction, 95% ethanol, ultrasonic power 250 W,T = 45 °C, textraction = 40 min | 11.00 * | Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction c[C6mim]PF6 = 0.78 mol/L, textraction = 40 min, solid–liquid ratio of 1:12.72 g/mL, and ultrasonic power of 250 W, T = 47.27 °C | 18.69 | [190] | |||
| Heat-reflux extraction, 95% ethanol, textraction = 120 min | 6.50 * | ||||||||
| Soxhelt extraction, 95% ethanol, textraction = 120 min | 7.00 * | ||||||||
| Percolation extraction, 95% ethanol, textraction = 24 min | 10.00 * | ||||||||
| Amentoflavone, robustaflavone, and hinokiflavone | S. doederleinii | Soxhlet extraction, 70% ethanol, textraction = 2 h, T = 95 °C | 4.97 ± 0.08 | Microwave-assisted extraction; 70% ethanol, 460 W microwave power, T = 45 °C, textraction = 45 min | 8.91 ± 0.13 | [193] | |||
| Ionic liquid microwave-assisted extraction, c(Hmim) (PF6) = 2 mmol/L, solvent–material ratio = 1:15 g/mL, microwave power 460 W, T = 45 °C, textraction = 40 min | 16.83 ± 1.51 | ||||||||
| Myricitrin, isoquercitrin, quercitrin, amentoflavone and hinokiflavone | P. cacumen | - | - | Deep eutectic solvents (choline chloride:1,4-butanediol-lactic acid 1:3) and ultrasonic extraction, ultrasonic time: 60 min, liquid/solid ratio: 20:1, and water content: 35% | 23.11 ± 0.35 | [204] | |||
* Most Abundant.
6. Identification, Quantification, and Localization within Tissue
Progress in developing methods to identify and quantify some natural compounds depends on several factors, such as whether a compound is recognized as having biological activity, whether regulatory agencies require control of the amount in a product, or whether appropriate tools are simply available. If standards are not commercially available, identification is usually performed by NMR. In most studies reporting 3′-8″-biflavones for the first time, such as those in a Table 1, identification is performed using NMR. In the 1H NMR spectrum, aromatic proton signals typically appear between 6.0–8.0 ppm, while hydroxyl protons resonate as broad singlets around 10.0–12.0 ppm. 13C NMR spectra display aromatic carbon signals between 100 and 160 ppm, with carbonyl carbons around 175–180 ppm [43]. Carbons involved in the 3′-8″ linkage, such as C3′ and C8″, generally exhibit downfield shifts compared to non-linked carbons [43]. Due to the dimeric nature of 3′-8″-biflavones, duplicate or split signals may occur, reflecting the slightly different chemical environments of the two flavonoid units, especially near the linkage [205]. NMR spectroscopy of dimeric flavonoids is often complicated by hindered rotation of the monomers around the C–C axis (atropisomerism), leading to high spectral complexity. Several approaches have been proposed to accelerate identification, such as 1,1-ADEQUATE [206], while two-dimensional NMR techniques (HSQC, HMBC, and COSY) may help in resolving duplicate signals and confirming structural connectivity [206]. However, these techniques have not found widespread application in studies of 3′-8″-biflavones. Problems with the low sensitivity of NMR compared to other spectroscopic techniques are well known and pose a significant challenge in identifying biflavonoids, which are often present at low concentrations [205]. Over the past few decades, most advances in NMR spectroscopy have focused on increasing sensitivity. However, an even greater challenge remains: the lack of a comprehensive NMR database for the identification of 3′-8′- biflavones [205]. Many NMR databases lack information on these compounds, but the Spektraris database [207] stands out as an exception, having integrated data on biflavones and having been successfully used for the identification of biflavonoids in P. nudum [31]. However, the structure of some possible methyl-biflavones reported earlier should be corrected because structural elucidation in the 1960s and 1970s was based on co-chromatography with isolated authentic compounds, which may lead to misidentification [208].
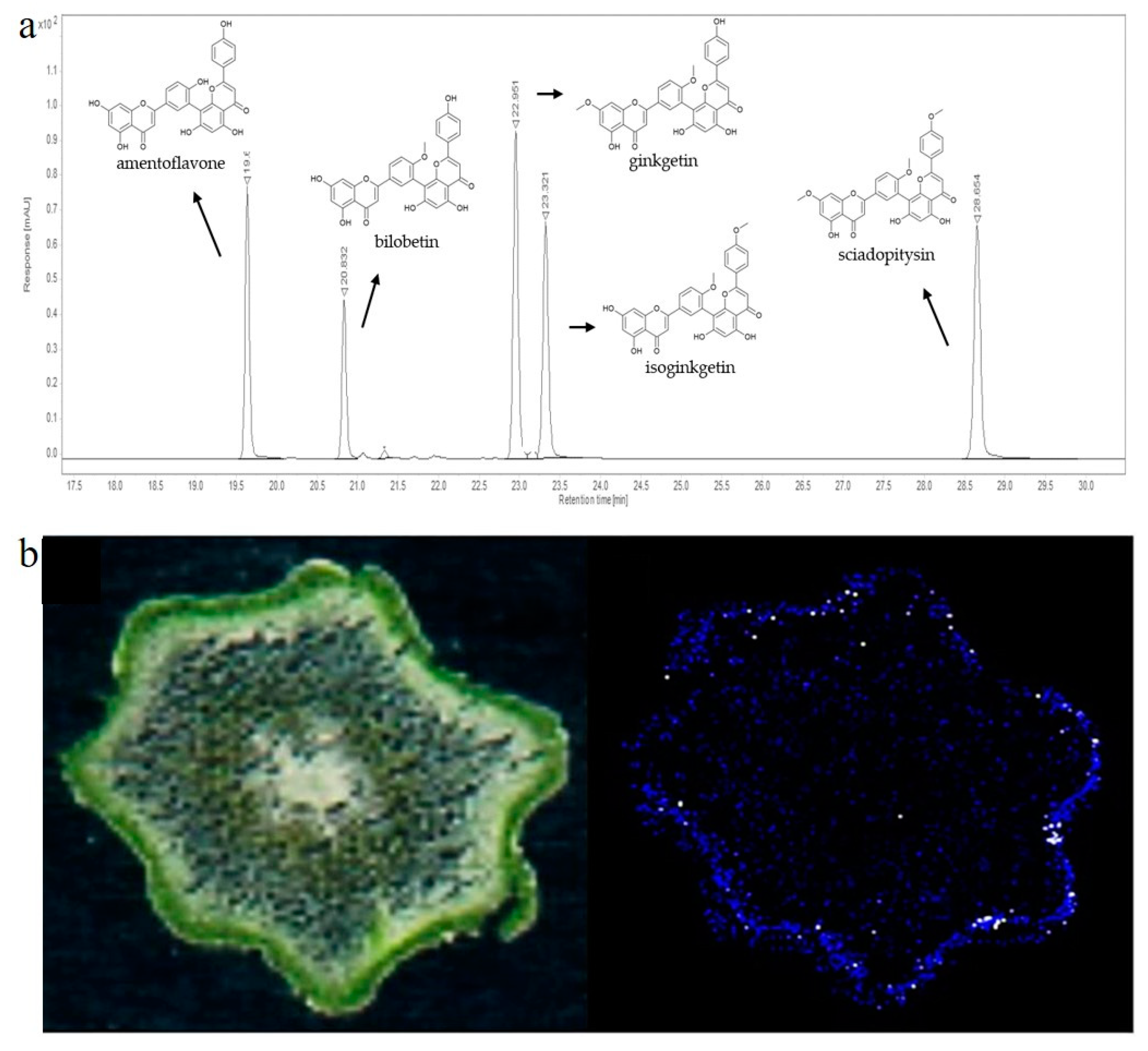
Later, when liquid chromatography and suitable detectors became available, these methods became methods of choice for the separation and detection of 3′-8″-biflavones, especially when standards and suitable databases became commercially available. Usually, liquid chromatography is coupled with DAD or MS detectors [27]. The first report on separation and quantification of biflavones by liquid chromatography and spectrophotometric detector was reported in the early 1980s. In this publication, the authors separated four biflavones from ginkgo leaves, bilobetin, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin and sciadopitysin, using the LiChrosorb® HPLC column and quantified them using a spectrophotometric detector. Today, the most commonly used detectors are mass detectors, but 3′-8″-biflavones have a strong signal at 330 nm, making the DAD detector in combination with standards a compelling, rapid, and accessible method for identification and quantification [178]. An example of a 330 nm chromatogram separating five 3′-8″-biflavones is presented in Figure 6a.
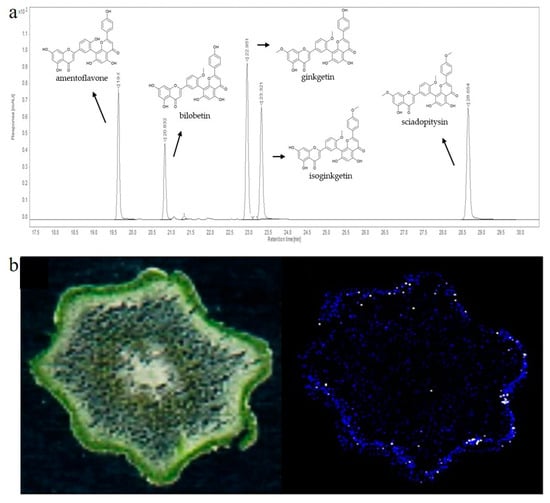
Figure 6.
(a) Representative HPLC-DAD chromatogram of five biflavones recorded at 330 nm [179]; (b) MALDI-MS imaging of amentoflavone in cross sections of P. nudum above-ground rhizomes [31].
Over the past 20 years, MS-dependent imaging techniques have been developed to study the small-scale localization of compounds from complex biological systems. The most significant advances have been made with Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization–Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS) imaging, which can be applied at both the tissue and single-cell level and provides information on the spatial distribution of specific molecules [209]. After tissue preparation and matrix application, the instrument acquires a series of mass spectra, each of which represents the profile of a specific region in the sample on a predefined x,y coordinate grid. This allows the gradients of individual analytes in the tissue to be visualized using specialized computer programs. The most commonly used ionization techniques besides MALDI are desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) and secondary ionization MS (SIMS). In the literature, ginkgo leaves in which 3′-8″-biflavones had been detected and localized were frequently used for method optimization [179,180]. Most of the available literature data showed that 3′-8″-biflavones, such as amentoflavone, bilobetin/sequioflavone, isoginkgetin/ginkgetin, sciadopytisyn, and methoxybilobetin, accumulate in the epidermis of ginkgo leaves [179,180]. The application of MALDI imaging in the study of the above-ground rhizome of P. nudum provided evidence for preferential accumulation of amentoflavone in cells of the chlorenchyma [31] (Figure 6b). The application of MALDI matrices to tissues sometimes complicates tissue preparation for imaging and can interfere with the native distribution of the metabolites under study. Therefore, a matrix-free laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry method (LDI-MSI) was proposed in the study by Holscher et al. [210], which successfully detected amentoflavone in Hypericum perforatum pollen. MS-based imaging techniques provide valuable information not only on the presence of metabolites, but also on their localization, but are not widely used because of their high cost.
7. Conclusions and Further Directions
In recent years, 3′-8″-biflavones have become of interest as potential new compounds with pharmaceutical applications. Most studies have focused on their biological activity, with less information being available on their new natural sources and their role in plants. Most of the naturally occurring 3′-8″-biflavones have been elucidated as part of a larger screening study of natural products in specific plants, with few studies focusing specifically on biflavones. According to the available data, they are common in Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms, and so far, G. biloba and Selaginella sp. contain a variety of different 3′-8″-biflavones. Further studies to screen different species for the presence of 3′-8″-biflavones are needed and are likely to reveal their presence in more plant species and help to elucidate their role in plants and possible plant evolution. The content of 3′-8″-biflavones is highly dependent on the tissue type studied and other environmental factors, as shown by several studies on ginkgo. Although their exact role in plants is not clear, their localization in plants and tissues suggests their possible role in plant–environment interactions, especially biotic interactions, as they exhibit antimicrobial activity. Several studies suggest a possible role in the inhibition of photosynthesis, but more studies are needed to explain this statement and also other possible role in plants.
To study the role of 3′-8″-biflavones in plants, as well as their potential pharmaceutical use, efficient methods for their extraction and identification are being developed. Traditionally, most extraction methods for the extraction of 3′-8″-biflavones have been based on conventional methods such as organic solvent extraction, reflux extraction, percolation extraction, and Soxhlet extraction, but novel methods such as UAE, EAE, MAE, PLE, and new green solvents IL and DES are also being increasingly explored. In particular, extraction using environmentally friendly methods should be the focus in the future. It is challenging to conclude that a single method is suitable for extraction all 3′-8″-biflavones. When optimizing extraction methods, it is important to consider both the plant part used and the specific biflavone of interest, as their structures can vary significantly.
For the identification of new 3′-8″-biflavone structures, NMR was used, but for routine separation, identification, and quantification, especially when standards are available, HPLC coupled with MS or DAD is the method of choice. Great progress has also been made in the development of MALDI imaging methods for the identification and localization of 3′-8″-biflavones in tissues, particularly in G. biloba leaves. However, most of the studies performed are targeted analyses that are likely to miss some 3′-8″-biflavones. Therefore, more untargeted analyses using high-resolution mass spectrometry should be performed in the future to identify additional 3′-8″-biflavones.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Š.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Š. and A.Š.; I.J.Š., E.K., B.Š. and B.Z. writing—review and editing, D.Š., A.Š. and B.Z.; visualization, D.Š.; supervision, D.Š.; project administration, D.Š.; funding acquisition, D.Š. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation project “Biflavonoids role in plants: Ginkgo biloba L. as a model system” under Project No. UIP-2019-04-1018.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nabavi, S.M.; Šamec, D.; Tomczyk, M.; Milella, L.; Russo, D.; Habtemariam, S.; Suntar, I.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; et al. Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathways in Plants: Versatile Targets for Metabolic Engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant Flavonoids: Classification, Distribution, Biosynthesis, and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive Review of Antimicrobial Activities of Plant Flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.G.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putteeraj, M.; Lim, W.L.; Teoh, S.L.; Yahaya, M.F. Flavonoids and Its Neuroprotective Effects on Brain Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Yuan, B.; Hu, X.; Okazaki, M. Chemopreventive and Anticancer Activity of Flavonoids and Its Possibility for Clinical Use by Combining with Conventional Chemotherapeutic Agents. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1517–1535. [Google Scholar]
- González-Paramás, A.M.; Ayuda-Durán, B.; Martínez, S.; González-Manzano, S.; Santos-Buelga, C. The Mechanisms Behind the Biological Activity of Flavonoids. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6976–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šamec, D.; Karalija, E.; Šola, I.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Salopek-Sondi, B. The Role of Polyphenols in Abiotic Stress Response: The Influence of Molecular Structure. Plants 2021, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, V.S.; dos Santos, M.H.; Viegas, C., Jr. Biological and Chemical Aspects of Natural Biflavonoids from Plants: A Brief Review. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 834–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, F.; Huang, X. Proceedings of Chemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Synthesis of Biflavonoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, M.; Shang, H.; Zou, Z. Natural Biflavones Are Potent Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease. Phytochemistry 2022, 193, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.C.J.M.D.S.; Campos, V.R. Natural Biflavonoids as Potential Therapeutic Agents against Microbial Diseases. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Kabir, M.T.; Tewari, D.; Mathew, B.; Aleya, L. Emerging Signal Regulating Potential of Small Molecule Biflavonoids to Combat Neuropathological Insults of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatlı Çankaya, İ.İ.; Devkota, H.P.; Zengin, G.; Šamec, D. Neuroprotective Potential of Biflavone Ginkgetin: A Review. Life 2023, 13, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, A.; Chi, E.Y. Biflavonoids as Potential Small Molecule Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. In Natural Compounds as Therapeutic Agents for Amyloidogenic Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, J.C.J.M.D.S.; Diederich, M.F. Bioactivity of Natural Biflavonoids in Metabolism-Related Disease and Cancer Therapies. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Li, S.; Gao, Q.; Qiao, L.; Cao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Fu, S. Advances in the Anti-Tumor Activity of Biflavonoids in Selaginella. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, G.L.; Ralston, R.A.; Schwartz, S.J. Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.; Natesan, V. Chrysin: Sources, Beneficial Pharmacological Activities, and Molecular Mechanism of Action. Phytochemistry 2018, 145, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Khan, H.; D’onofrio, G.; Šamec, D.; Shirooie, S.; Dehpour, A.R.; Argüelles, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E. Apigenin as Neuroprotective Agent: Of Mice and Men. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; Chen, J.; He, Z. Dietary Luteolin: A Narrative Review Focusing on Its Pharmacokinetic Properties and Effects on Glycolipid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Siddique, Y.H. Role of Flavonoids in Neurodegenerative Disorders with Special Emphasis on Tangeritin. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Channakesavula, C.N.; Stone, S.R.; Kaur, P. Synthetic Biology towards Improved Flavonoid Pharmacokinetics. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T. Methylation of Dietary Flavones Increases Their Metabolic Stability and Chemopreventive Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5002–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Song, S.-J. A Comprehensive Review: Biological Activity, Modification and Synthetic Methodologies of Prenylated Flavonoids. Phytochemistry 2021, 191, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šamec, D.; Karalija, E.; Dahija, S.; Hassan, S.T.S. Biflavonoids: Important Contributions to the Health Benefits of Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.). Plants 2022, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Tang, N.; Lai, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Insights Into Amentoflavone: A Natural Multifunctional Biflavonoid. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, e768708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, I.; Phongpaichit, S.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P.; Mahabusarakam, W. Prenylated Biflavonoids from the Green Branches of Garcinia Dulcis. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 23, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, K.R. The Structures of Amentoflavone Glycosides Isolated from Psilotum Nudum. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2053–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Pierz, V.; Srividya, N.; Wüst, M.; Lange, B.M. Assessing Chemical Diversity in Psilotum Nudum (L.) Beauv., a Pantropical Whisk Fern That Has Lost Many of Its Fern-Like Characters. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Advances in the Chemical Constituents and Chemical Analysis of Ginkgo Biloba Leaf, Extract, and Phytopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasawa, S. History of Japanese Natural Product Research. Pure Appl. Chem. 1964, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.S.; Mitra, C.R. Putraflavone, a New Biflavonoid from Putranjiva Roxburghii. Phytochemistry 1971, 10, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Kawano, N. Sequoiaflavone in the Leaves of Sequoia Sempervirens and Cunninghamia Lanceolata Var. Konishii and Its Formation by Partial Demethylation. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1968, 88, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Kihara, T.; Kawano, N. Studies on Bisflavones in the Leaves of Podocarpus Macrophylla and P. Nagi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1969, 17, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madhav, R. Heveaflavone—A New Biflavonoid from Hevea Braseliensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969, 10, 2017–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyone, T.; Nobuske, K. Studies on the Structure of Sciadopitysin, a Flavonoid from the Leaves of Sciadopitys Verticillata Sieb. et Zucc. VII. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1956, 76, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhong-wu, M.; Guan-fu, H.; Wan-fen, Y. Oliveriflavone, a New Biflavonoid from Cephalotaxus Oliveri Mast. Acta Bot. Sin. 1986, 28, 641–645. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, K.; Wada, K.; Haga, M. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Ginkgo Biloba. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 165–198. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, H.; Quinn, C. Biflavonoids. In The Flavonoids; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 692–742. [Google Scholar]
- Kunert, O.; Swamy, R.C.; Kaiser, M.; Presser, A.; Buzzi, S.; Appa Rao, A.V.N.; Schühly, W. Antiplasmodial and Leishmanicidal Activity of Biflavonoids from Indian Selaginella Bryopteris. Phytochem. Lett. 2008, 1, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-C.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-J. Cytotoxic Biflavonoids from Selaginella delicatula. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sáez, J.A.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Negueruela, A.V. The Biflavonoid Pattern of Selaginella Selaginoides. Z. Naturforsch. C 1994, 49, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, P.; Ma, W.; Feng, X.; Chen, K. Antitumor Activities of Ethyl Acetate Extracts from Selaginella Doederleinii Hieron In Vitro and In Vivo and Its Possible Mechanism. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-F.; Sun, H.-H.; Tan, J.-B.; Huang, Q.; Cheng, F.; Xu, K.-P.; Zou, Z.-X.; Tan, G.-S. New Cytotoxic Biflavones from Selaginella doederleinii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, L. Identification of Biflavones in Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Ethanol Extract of Selaginella doederleinii Hieron. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 550–553, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Seguin, E.; Tillequin, F.; Koch, M. Phenolic Constituents of Selaginella doederleinii. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.-J.; Xu, J.-C.; Li, L.; Chen, K.-L. Bioactive Compounds of Inhibiting Xanthine Oxidase from Selaginella labordei. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Tan, N.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Zeng, G.-Z.; Ma, Y.-B.; Wu, Y.-P.; Yan, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.-F.; Wang, Q. Bioactive Flavones and Biflavones from Selaginella Moellendorffii Hieron. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-M.; Syu, W.-J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Ou, J.-C. Selective Cytotoxicity of Ginkgetin from Selaginella moellendorffii. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.I.; Benítez, W.V.; Colín, A.; Bye, R.; Ríos-Gómez, R.; Calzada, F. Evaluation of the Diuretic Activity in Two Mexican Medicinal Species: Selaginella Nothohybrida and Selaginella Lepidophylla and Its Effects with Ciclooxigenases Inhibitors. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 163, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, B.; Rao, Y.; Gambhir, S.; Gode, K. Isolation of Amentoflavone from Selaginella Rupestris and Its Pharmacological Activity on Central Nervous System, Smooth Muscles and Isolated Frog Heart Preparations. Planta Med. 1981, 43, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K. Target-Guided Isolation and Purification of Antioxidants from Selaginella Sinensis by Offline Coupling of DPPH-HPLC and HSCCC Experiments. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuang-Cheng, M.; Paul Pui-Hay, B.; Vincent Eng-Choon, O.; Yue-Hua, H.; Spencer Hon-Sun, L.; Song-Fong, L.; Rui-Chao, L. Antiviral Amentoflavone from Selaginella Sinensis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.S.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, X.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, L.G.; Li, Y.L. Chemical Constituents of Selaginella Stautoniana. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 9, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.-L.; Ma, S.-C.; Yu, J.-D.; Yang, S.-Y.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Hu, J.-Y.; Lu, Y.; Shaw, P.-C.; But, P.P.-H.; Lin, R.-C. Selaginellin A and B, Two Novel Natural Pigments Isolated from Selaginella Tamariscina. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-W.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Chang, I.-S.; Moon, H.T.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, W.K.; Woo, E.-R. Biflavonoids Isolated from Selaginella Tamariscina Regulate the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Luo, H.; Fischer, D.; Sutherland, I.A.; Wei, Y. How to Realize the Linear Scale-up Process for Rapid Purification Using High-Performance Counter-Current Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1194, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Tai, B.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory Constituents from Selaginella Tamariscina. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2015, 36, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, N.-L.; Fang, Y.-X.; Du, Z.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, M.-M.; Wu, L.-Y.; et al. New 3′,8″-Linked Biflavonoids from Selaginella Uncinata Displaying Protective Effect against Anoxia. Molecules 2011, 16, 6206–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.L.; Chai, H.; Gupta, M.P.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Cordell, G.A.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Douglas Kinghorn, A. Cytotoxic Biflavonoids from Selaginella Willdenowii. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Niu, X.M.; Yao, P.; Sun, H.D.; Fong, H.H.S. Chemical Constituents from Amentotaxus Yunnanensis and Torreya Yunnanensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, L.F.; Kato, M.J.; Di Mascio, P. Biflavonoids from Araucaria Angustifolia Protect against DNA UV-Induced Damage. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.M.; Almeida, M.T.R.; Andrighetti-Fröhner, C.R.; Cardozo, F.T.G.S.; Barardi, C.R.M.; Farias, M.R.; Simões, C.M.O. Antiviral Activity-Guided Fractionation from Araucaria Angustifolia Leaves Extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulerie, P.; Nour, M.; Maciuk, A.; Eydoux, C.; Guillemot, J.-C.; Lebouvier, N.; Hnawia, E.; Leblanc, K.; Lewin, G.; Canard, B.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Biflavonoids on the Dengue Virus Polymerase DENV-NS5 RdRp. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, S. The Chemical Constituents in Dacrydium Pierrei. Acta Bot. Sin. 1991, 33, 646–648. [Google Scholar]
- Chaabi, M.; Antheaume, C.; Weniger, B.; Justiniano, H.; Lugnier, C.; Lobstein, A. Biflavones of Decussocarpus Rospigliosii as Phosphodiesterases Inhibitors. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1284–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negm, W.A.; Abo El-Seoud, K.A.; Kabbash, A.; Kassab, A.A.; El-Aasr, M. Hepatoprotective, Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Dioon Spinulosum Leaves Dyer Ex Eichler and Its Isolated Secondary Metabolites. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, S.-C.; Liu, H.-K.; Kuo, Y.-H. Two New Compounds from the Leaves of Calocedrus Microlepic Var. Formosana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Morita, N. Mechanism of Action of the Antiherpesvirus Biflavone Ginkgetin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-N.; Yu, M.-Y.; Kong, L.-M.; Wang, W.-H.; Yang, Y.-F.; Liu, J.-Q.; Qiu, M.-H.; Li, Y. Biflavone Ginkgetin, a Novel Wnt Inhibitor, Suppresses the Growth of Medulloblastoma. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect 2015, 5, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiratta (Nee Chugh), A.; Dayal, R.; Bartley, J.P.; Smith, G. A Phenylpropanoid and Biflavonoids from the Needles of Cephalotaxus Harringtonia Var. Harringtonia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1934578X1701201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Miki, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Koyama, K.; Juliawaty, L.D.; Achmad, S.A.; Hakim, E.H.; Kaneda, M.; Takahashi, K. β-Secretase (BACE-1) Inhibitory Effect of Biflavonoids. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4558–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Lim, S.W.; Yang, H.; Sung, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, M.J.; Kim, Y.C. Osteoblast Differentiation Stimulating Activity of Biflavonoids from Cephalotaxus Koreana. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2850–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Mu, Z.-Q.; Cheng, C.-R.; Ding, J. Three New Biflavonoids from the Branches and Leaves of Cephalotaxus Oliveri and Their Antioxidant Activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Dai, R.; Yu, Y.; Saeed, M.K.; Li, L.; Meng, W.; Zhang, X. Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Cephalotaxus Sinensis from Various Sources by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Diodearray Detection–Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Shen, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-L.; Li, S.-Y. A Novel Cytotoxic C-Methylated Biflavone from the Stem of Cephalotaxus Wilsoniana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Cisowski, W.; Wiwart, M.; Madziar, B. Antifungal Biflavones from Cupressocyparis leylandii. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, A.; Galardi, C.; Pinelli, P.; Mulinacci, N.; Heimler, D. HPLC Quantification of Flavonoids and Biflavonoids in Cupressaceae Leaves. Chromatographia 2002, 56, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenweber, E.; Kraut, L.; Mues, R. External Accumulation of Biflavonoids on Gymnosperm Leaves. Z. Naturforsch. C 1998, 53, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Mahender, G.; Koteswara Rao, Y.; Prabhakar, A.; Jagadeesh, B. Biflavonoids from Cycas Beddomei. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, A.; Hetta, M.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Jacob, M.R.; Hifnawy, M.; Marais, J.P.J.; Ferreira, D. Phytochemical Investigation of Cycas Circinalis and Cycas Revoluta Leaflets: Moderately Active Antibacterial Biflavonoids. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, N.G.M.; Al-Fakhrany, O.M.; Elekhnawy, E.; Hussein, I.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Altwaijry, N.; Alqahtani, M.J.; Negm, W.A. Anti-Biofilm and Antibacterial Activities of Cycas Media, R. Br Secondary Metabolites: In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Approaches. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laishram, S.; Sheikh, Y.; Moirangthem, D.S.; Deb, L.; Pal, B.C.; Talukdar, N.C.; Borah, J.C. Anti-Diabetic Molecules from Cycas Pectinata Griff. Traditionally Used by the Maiba-Maibi. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Pobłocka, L.; El Helab, A.A. Biflavones from Chamaecyparis Obtusa. Z. Naturforsch. C 2005, 60, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Inatomi, Y.; Murata, H.; Iida, N.; Inada, A.; Lang, F.A.; Murata, J. Phytochemical Study on American Plants, I. Two New Phenol Glucosides, Together with Known Biflavones and Diterpene, from Leaves of Juniperus Occidentalis HOOK. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Seo, H.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Anti-Inflammatory Phenolics Isolated from Juniperus Rigida Leaves and Twigs in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Mardarowicz, M.; Wiwart, M. The Chemical Composition of Microbiota Decussata. Z. Naturforsch. C 2002, 57, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvik, O.J.; Nguyen, X.H.T.; Andersen, H.L.; Fossen, T. Growing with Dinosaurs: Natural Products from the Cretaceous Relict Metasequoia Glyptostroboides Hu & Cheng—A Molecular Reservoir from the Ancient World with Potential in Modern Medicine. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.E.F.; da Silva, M.S.; Schindler, E.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; El-Bachá, R. dos S.; Castello-Branco, M.V.S.; Agra, M. de F.; Tavares, J.F. 3′,8”-Biisokaempferide, a Cytotoxic Biflavonoid and Other Chemical Constituents of Nanuza Plicata (Velloziaceae). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndongo, J.T.; Issa, M.E.; Messi, A.N.; Ngo Mbing, J.; Cuendet, M.; Pegnyemb, D.E.; Bochet, C.G. Cytotoxic Flavonoids and Other Constituents from the Stem Bark of Ochna schweinfurthiana. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, J.R.; de Carvalho, M.G.; Braz-Filho, R.; Werle, A.A. Biflavonoids and a Glucopyranoside Derivative from Ouratea semiserrata. Phytochemical Analysis 2002, 13, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Baczek, T.; Glod, D.; Kaliszan, R.; Wollenweber, E. HPLC Separation of O-Acylated Flavonoids and Biflavones from Some Species of Gymnospermae. Chromatographia 2004, 60, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagla, V.P.; McGaw, L.J.; Elgorashi, E.E.; Eloff, J.N. Antimicrobial Activity, Toxicity and Selectivity Index of Two Biflavonoids and a Flavone Isolated from Podocarpus Henkelii (Podocarpaceae) Leaves. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiella, L.; Temraz, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Braca, A. Diterpenes, Ionol-Derived, and Flavone Glycosides from Podocarpus Elongatus. Phytochemistry 2012, 76, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Sun, W.W.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, J.D. Flavonoids from Podocarpus Macrophyllus and Their Cardioprotective Activities. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, S. The Chemical Constituents from Podocarpus Nagi (II). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1991, 33, 406–408. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, P.H.; Shieh, Y.D.; Hsu, L.C.; Kuo, L.M.; Lin, J.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H. Naturally Occurring Cytotoxic [3′→8″]-Biflavonoids from Podocarpus Nakaii. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012, 2, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haider, S.; Rizvi, M.; Rahman, W.; Okigawa, M.; Kawano, N. Biflavones from Podocarpus Neriifolius. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fang, S. The Chemical Constituents from Podocarpus Imbricatus. Acta Bot. Sin. 1990, 32, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.G. Terpenoids and Flavonoids From Podocarpus Wallichiana. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Wiwart, M. Antifungal Activity of Biflavones from Taxus Baccata and Ginkgo Biloba. Z. Naturforsch. C 2003, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Yan, L.Y.; Li, X.X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q. Optimization of Process Parameters of Extraction of Amentoflavone, Quercetin and Ginkgetin from Taxus Chinensis Using Supercritical CO2 plus Co-Solvent. Molecules 2014, 19, 17682–17696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-S.; Kwak, S.-S.; Liu, J.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, M.-K.; An, N.-H. Taxol and Related Compounds in Korean Native Yews (Taxus cuspidata). Planta Med. 1995, 61, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Guo, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Q.; Song, Y.-B.; Zhang, L.; Dong, M.; Shen, C. Comparative Proteomic Analyses of Two Taxus Species (Taxus x Media and Taxus Mairei) Reveals Variations in the Metabolisms Associated with Paclitaxel and Other Metabolites. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1878–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, Z.-S.; Cheng, F.; Ruan, X.; Jiang, D.-A.; Pan, C.-D.; Wang, Q. Seasonal Dynamics of Metabolites in Needles of Taxus Wallichiana Var. Mairei. Molecules 2016, 21, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.H.; Ryoo, I.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Choo, S.J.; Yoo, I.D. Free Radical Scavenging and Antielastase Activities of Flavon Ids from the Fruits of Thuja Orientalis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, Y.B.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, D.; Naguyen, T.T.H.; Park, S.-J.; Chang, J.S.; Park, K.H. Biflavonoids from Torreya Nucifera Displaying SARS-CoV 3CLpro Inhibition. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7940–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro-Luis, J.M.; Amesty, Á.; Bahsas, A.; Montealegre, R. Biflavones from the Leaves of Retrophyllum Rospigliosii. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleńsk, M.; Włodarczyk, M.; Stefanowicz, P.; Kucharska, A. Biflavonoids from the Wollemi Pine, Wollemia Nobilis (Araucariaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 46, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, T.R.; Lima, Z.P.; Silva, J.S.; Ballesteros, K.V.R.; Pellizzon, C.H.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A.; Tamashiro, J.; Brito, A.R.M.S.; Takahira, R.K.; Vilegas, W. Constituents and Antiulcer Effect of Alchornea Glandulosa: Activation of Cell Proliferation in Gastric Mucosa during the Healing Process. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, T.R.; Demarco, D.; Santos, F.V.; Moraes, H.P.; Bauab, T.M.; Varanda, E.A.; Cólus, I.M.S.; Vilegas, W. Phenolic Compounds in Leaves of Alchornea Triplinervia: Anatomical Localization, Mutagenicity, and Antibacterial Activity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1934578X1000500816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azebaze, A.G.B.; Dongmo, A.B.; Meyer, M.; Ouahouo, B.M.W.; Valentin, A.; Nguemfo, E.L.; Nkengfack, A.E.; Vierling, W. Antimalarial and Vasorelaxant Constituents of the Leaves of Allanblackia Monticola (Guttiferae). Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2007, 101, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Z.; Wang, M.H.; Sun, J.B.; Liang, J.Y. Flavonoids and Other Constituents from Aletris Spicata and Their Chemotaxonomic Significance. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Lei, J.; Xiao, J.C.; Xi, Z.; Yu, M.; Huang, J. The Separation and Indentification of Biflavonoids from Androsace Umbellata. West. China J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 26, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, D.T.; Huyen, L.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Hang, D.T.T.; Yen, P.H.; Tai, B.H.; Anh, H.L.T.; Binh, N.Q.; Van Minh, C.; et al. Tirucallane Glycoside from the Leaves of Antidesma Bunius and Inhibitory NO Production in BV2 Cells and RAW264.7 Macrophages. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1934578X1601100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchinda, A.; Teshome, A.; Dagne, E.; Arnold, N.; Wessjohann, L.A. Squalene and Amentoflavone from Antidesma Laciniatum. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2006, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, K.I.; Alviarez, P.F.; Compagnone, R.S.; Suárez, A.I. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Chemical Constituents of Amanoa Almerindae. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 47, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucar1, F.; Jackak1, S.M.; Noreen2, Y.; Kartnig1, T.; Perera2, P.; Bohlin, L.; Schubert-Zsilavecz3, M. Amentoflavone from Biophytum Sensitivum and Its Effect on COX-1 j COX-2 Catalysed Prostaglandin Biosynthesis. Planta Medica 1998, 64, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannomiya, M.; Fonseca, V.B.; da Silva, M.A.; Rocha, L.R.M.; dos Santos, L.C.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A.; Souza Brito, A.R.M.; Vilegas, W. Flavonoids and Antiulcerogenic Activity from Byrsonima Crassa Leaves Extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannomiya, M.; Cardoso, C.R.P.; Figueiredo, M.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.; dos Santos, L.C.; dos Santos, F.V.; Serpeloni, J.M.; Cólus, I.M.S.; Vilegas, W.; Varanda, E.A. Mutagenic Evaluation and Chemical Investigation of Byrsonima Intermedia A. Juss. Leaf Extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahia, M.V.; David, J.P.; David, J.M. Occurrence of Biflavones in Leaves of Caesalpinia Pyramidalis Specimens. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman Aminudin, N.; Taher, M.; Zulkifli, R. Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Activities of Constituents from Calophyllum Ferrugineum Ridley. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2016, 5, 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Ferchichi, L.; Derbré, S.; Mahmood, K.; Touré, K.; Guilet, D.; Litaudon, M.; Awang, K.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Le Ray, A.M.; Richomme, P. Bioguided Fractionation and Isolation of Natural Inhibitors of Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs) from Calophyllum Flavoramulum. Phytochemistry 2012, 78, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminudin, N.I.; Ahmad, F.; Taher, M.; Zulkifli, R.M. α-Glucosidase and 15-Lipoxygenase Inhibitory Activities of Phytochemicals from Calophyllum symingtonianum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1934578X1501000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.H.; Jantan, I.; Waterman, P.G. Neoflavonoid and Biflavonoid Constituents of Calophyllum Inophylloide. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, A.B.; Cuesta-Rubio, O.; Pérez, J.C.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Rastrelli, L. Constituents of the Cuban Endemic Species Calophyllum pinetorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubada, A.; Garca, M.; BelloAlarcon, A.; CuestaRubio, O.; Monzote, L. Antileishmanial Activity of Leaf Extract from Calophyllum Rivulare against Leishmania Amazonensis. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2014, 26, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.-G.; Sim, K.-Y.; Goh, S.-H. Biflavonoids of Calophyllum venulosum. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elo-Manga, S.S.; Tih, A.E.; Ghogomu, R.T.; Blond, A.; Bodo, B. Chemical Constituents of the Leaves of Campylospermum elongatum. Z. Naturforsch. C 2017, 72, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njock, G.B.B.; Bartholomeusz, T.A.; Bikobo, D.N.; Foroozandeh, M.; Shivapurkar, R.; Christen, P.; Pegnyemb, D.E.; Jeannerat, D. Structure and Dynamic of Three Indole Alkaloids from the Campylospermum Genus (Ochnaceae). Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elo Manga, S.S.; Tih, A.E.; Ghogomu, R.T.; Blond, A.; Bodo, B. Biflavonoid Constituents of Campylospermum Mannii. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liaf, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R. Study on Chemical Constituents of the Leaves of Canarium Album (Lour.) Raeusch. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2007, 27, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Helene, T.; Serge, F.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Etienne, D.; Abegaz, B.M. Phenolic Metabolites from the Seeds of Canarium schweinfurthii. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2000, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, E.; Tatli, I.I.; Khan, R.A.; Zhao, J.; Takamatsu, S.; Walker, L.A.; Goldman, P.; Khan, I.A. Biologically Active Secondary Metabolites from Ginkgo biloba. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3150–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaari, K.; Waterman, P.G. Podophyllotoxin-Type Lignans as Major Constituents of the Stems and Leaves of Casearia Clarkei. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, P.; Garcia, M.R.; Hernandez, B.E.; Torres, B.A.; Anaya, A.L.; Mata, R. Effects of Some Compounds Isolated from Celaenodendron Mexicanum Standl (Euphorbiaceae) on Seeds and Phytopathogenic Fungi. J. Chem. Ecol. 1992, 18, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rayo Camacho, M.; Mata, R.; Castaneda, P.; Kirby, G.C.; Warhurst, D.C.; Croft, S.L.; Phillipson, J.D. Bioactive Compounds from Celaenodendron Mexicanum. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, H.M.; Almowallad, F.M.; Esmat, A.; Shehata, I.A.; Abdel-Sattar, E.A. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Flavonoids from Chrozophora Tinctoria. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishola, I.O.; Agbaje, O.E.; Narender, T.; Adeyemi, O.O.; Shukla, R. Bioactivity Guided Isolation of Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Constituents of Cnestis Ferruginea Vahl Ex DC (Connaraceae) Root. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, C. A New Flavanone and Other Constituents from the Rhizomes of Cyperus Rotundus and Their Antioxidant Activities. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 48, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Ngameni, B.; Kuete, V.; Simo, I.K.; Ambassa, P.; Roy, R.; Bezabih, M.; Etoa, F.X.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Abegaz, B.M.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of the Crude Extracts and Five Flavonoids from the Twigs of Dorstenia Barteri (Moraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng′ang′a, M.M.; Hussain, H.; Chhabra, S.; Langat-Thoruwa, C.; Irungu, B.N.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Riaz, M.; Krohn, K. Antiplasmodial Activity of Compounds from Drypetes Gerrardii. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattamadilok, D.; Suttisri, R. Seco-Terpenoids and Other Constituents from Elateriospermum tapos. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shagdari, A.; Alarcón, A.B.; Cuesta-Rubio, O.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Rastrelli, L. Biflavonoids, Main Constituents from Garcinia Bakeriana Leaves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1934578X1300800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroni Arwa, P.; Zeraik, M.L.; Farias Ximenes, V.; da Fonseca, L.M.; da Silva Bolzani, V.; Siqueira Silva, D.H. Redox-Active Biflavonoids from Garcinia Brasiliensis as Inhibitors of Neutrophil Oxidative Burst and Human Erythrocyte Membrane Damage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderamane, B.; Tih, A.E.; Ghogomu, R.T.; Blond, A.; Bodo, B. New Flavonoid C-O-C Dimers and Other Chemical Constituents from Garcinia Brevipedicellata Stem Heartwood. Z. Naturforsch. C 2016, 71, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, F.; Nagafuji, S.; Okabe, H.; Akahane, H.; Estrada-Muñiz, E.; Huerta-Reyes, M.; Reyes-Chilpa, R. Trypanocidal Constituents in Plants 3. Leaves of Garcinia Intermedia and Heartwood of Calophyllum Brasiliense. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Figueroa, M.; To, S.; Baggett, S.; Jiang, B.; Basile, M.J.; Weinstein, I.B.; Kennelly, E.J. Benzophenones and Biflavonoids from Garcinia Livingstonei Fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4749–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikabo, A.A.; Eloff, J.N. Antibacterial Activity of Two Biflavonoids from Garcinia Livingstonei Leaves against Mycobacterium Smegmatis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Hormaza, L.; Ramírez, A.M.; Quintero-Ortiz, C.; Cossio, M.; Medina, S.; Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Osorio, E. Comprehensive Characterization and Antioxidant Activities of the Main Biflavonoids of Garcinia Madruno: A Novel Tropical Species for Developing Functional Products. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Phongpaichit, S.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N. Tetraoxygenated Xanthones and Biflavanoids from the Twigs of Garcinia Merguensis. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Anderson, H.; Flavin, M.T.; Pai, Y.-H.S.; Mata-Greenwood, E.; Pengsuparp, T.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Hughes, S.H.; Chen, F.-C. In Vitro Anti-HIV Activity of Biflavonoids Isolated from Rhus succedanea and Garcinia multiflora. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Yokota, R.; Watarai, T.; Mori, K.; Oyama, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Matsuda, H.; Iinuma, M. Isolation of Six Isoprenylated Biflavonoids from the Leaves of Garcinia subelliptica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggett, S.; Protiva, P.; Mazzola, E.P.; Yang, H.; Ressler, E.T.; Basile, M.J.; Weinstein, I.B.; Kennelly, E.J. Bioactive Benzophenones from Garcinia Xanthochymus Fruits. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; LI, F.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Su, X.-J.; Huang, C.-P.; Lu, X.-W. A New Dilactone from the Seeds of Gaultheria Yunnanensis. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, D.; Venturi, C.R.; Cargnin, S.; Schripsema, J.; Roehe, P.M.; Montanha, J.A.; von Poser, G.L. Herpes Virus Inhibitory Substances from Hypericum Connatum Lam., a Plant Used in Southern Brazil to Treat Oral Lesions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghöfer, R.; Hölzl, J. Biflavonoids in Hypericum Perforatum 1; Part 1. Isolation of I3, II8-Biapigenin. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroshima, K.N.; Campos-Buzzi, F.; Yunes, R.A.; Delle Monache, F.; Cechinel Filho, V. Chemical Composition and Antinociceptive Properties of Hyeronima alchorneoides Leaves. Pharm. Biol. 2005, 43, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, G.; Edwards, J.M. Taxonomic Status of Lanaria Lanata and Isolation of a Novel Biflavone. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Feng, X.; Yin, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Y. A Biflavonoid from Stems and Leaves of Lonicera Macranthoides. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.C.C.; Carvalho, M.G.d.; Silva, C.J.d.; Werle, A.A. New Biflavonoid and Other Constituents from Luxemburgia Nobilis (EICHL). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2002, 13, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, D.; Deng, J. New Flavonoids from Lysimachia Christinae HANCE. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yi, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; He, X. Bioactive Phenolics from Mango Leaves (Mangifera indica L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, M.F.; dos Santos, C.B.; Cavalcanti, J.F.; Pereira, F.S.; Mendes, G.S.; Werle, A.A.; Romanos, M.T.V.; de Carvalho, M.G. Proposed Active Compounds from Ouratea Parviflora. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2011, 5, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Fidelis, Q.C.; Castro, R.N.; Guilhon, G.M.S.P.; Rodrigues, S.T.; De Salles, C.M.C.; De Salles, J.B.; De Carvalho, M.G. Flavonoids and Other Compounds from Ouratea Ferruginea (Ochnaceae) as Anticancer and Chemopreventive Agents. Molecules 2012, 17, 7989–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonezi, C.A.; Hamerski, L.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L.; Cavalheiro, A.; Castro-Gamboa, I.; Silva, D.H.S.; Furlan, M.; Young, M.C.M.; Lopes, M.N.; Bolzani, V. da S. Bioactive Flavone Dimers from Ouratea Multiflora (Ochnaceae). Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2007, 17, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegnyemb, D.E.; Mbing, J.N.; de Théodore Atchadé, A.; Tih, R.G.; Sondengam, B.L.; Blond, A.; Bodo, B. Antimicrobial Biflavonoids from the Aerial Parts of Ouratea Sulcata. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1922–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Sun, J.; Zhao, P.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P. Cytotoxic Metabolites from the Roots of Ranunculus Ternatus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 50, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenningsen, A.B.; Madsen, K.D.; Liljefors, T.; Stafford, G.I.; van Staden, J.; Jäger, A.K. Biflavones from Rhus Species with Affinity for the GABAA/Benzodiazepine Receptor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cai, L. Flavonoids from Speranskia tuberculata. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 6, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, S.; Zink, D.L.; Mohn, K.; Powell, J.S.; Brown, C.M.; Murphy, T.; Brand, R.; Pretorius, S.; Stevenson, D.; Thompson, D.; et al. Flavones from Struthiola Argentea with Anthelmintic Activity in Vitro. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, M.Y.; González-Morales, A.; Villarreal, M.L. Sterols, Triterpenes and Biflavonoids of Viburnum Jucundum and Cytotoxic Activity of Ursolic Acid. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, L.; Gao, J.; Foddai, S.; Serafini, M.; Ventrone, A.; Nicoletti, M. Iridoid Glucosides from Viburnum chinshanense. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Lee, J.W.; Jin, Q.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, B.Y. Biflavones and Furanone Glucosides from Zabelia tyaihyonii. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreyra, M.L.F.; Serra, P.; Casati, P. Recent Advances on the Roles of Flavonoids as Plant Protective Molecules after UV and High Light Exposure. Physiol. Plant 2021, 173, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovač Tomas, M.; Jurčević, I.; Šamec, D. Tissue-Specific Profiling of Biflavonoids in Ginkgo (Ginkgo Biloba L.). Plants 2022, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.; Stengel, J. Mass Spectrometric Imaging of Flavonoid Glycosides and Biflavonoids in Ginkgo biloba L. Phytochemistry 2016, 130, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Neumann, E.K.; Ge, J.; Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; Sweedler, J.V. Interrogation of Spatial Metabolome of Ginkgo Biloba with High-resolution Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization and Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalez, E.; Felicio, J.D.; Pinto, M.M. Biflavonoids Inhibit the Production of Aflatoxin by Aspergillus Flavus. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.I.; Romero, M.G.; Chávez, M.I.; King-Díaz, B.; Lotina-Hennsen, B. Biflavonoids Isolated from Selaginella Lepidophylla Inhibit Photosynthesis in Spinach Chloroplasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6994–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, C.L.; Achnine, L.; Lotina-Hennsen, B.; Salazar, J.R.; Gómez-Garibay, F.; Calderón, J.S. Inhibition of Photophosphorylation and Electron Transport by Flavonoids and Biflavonoids from Endemic Tephrosia Spp. of Mexico. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 69, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Jeong, S.E.; Park, H.Y.; Jeon, C.O.; Park, W. Amentoflavone, a Novel Cyanobacterial Killing Agent from Selaginella Tamariscina. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, L.F.R.; Sannomiya, M.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Delachiave, M.E.; Dos Santos, L.C.; Vilegas, W.; De Feo, V. In Vitro Allelopathic Effects of Extracts and Amenthoflavone from Byrsonima Crassa (Malpighiaceae). J. Plant Interact. 2007, 2, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; da Silva, M.A.; Queiroz, G.S.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Brighente, I.M.C. Antioxidant, Allelopathic and Toxic Activity of Ochna Serrulata. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2011, 30, 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Šamec, D.; Šalić, A. Modern Techniques for Flavonoid Extraction—To Optimize or Not to Optimize? Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sun, C.; Linghu, L.; Qin, C.; Gang, W. Ultrasonic-Assisted Ionic Liquid Extraction of Four Biflavonoids from Ginkgo biloba L. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 3297–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Feng, Q.; Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, Z. Deep Eutectic Solvent Combined with Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction as High Efficient Extractive Media for Extraction and Quality Evaluation of Herba Epimedii. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, X.; Jiang, F.; He, Q.; Qiu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, G. Ionic Liquid–Ultrasound-Based Extraction of Biflavonoids from Selaginella Helvetica and Investigation of Their Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Hormaza, L.; Duque, L.; López-Parra, S.; Osorio, E. High-Intensity Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Garcinia Madruno Biflavonoids: Mechanism, Kinetics, and Productivity. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 161, 107676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extraction Media for Valuable Flavonoids from Natural Sources. Applied Sciences 2019, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qian, Y.; Tian, Y.-J.; Yuan, S.-M.; Wei, W.; Wang, G. Optimization of Ionic Liquid-Assisted Extraction of Biflavonoids from Selaginella Doederleinii and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant and Antitumor Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.J.; Díaz, I.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Sueiras, A. On the Behavior of Imidazolium versus Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Extractants of Phenolic Compounds from Water: Experimental and Computational Analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 201, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Hadinoto, K. Deep Eutectic Solvent as Green Solvent in Extraction of Biological Macromolecules: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Qiao, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Lei, J.; Ren, M.; Xiao, S.; Kuang, J.; Deng, S.; et al. Total Biflavonoids Extraction from Selaginella Chaetoloma Utilizing Ultrasound-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvent: Optimization of Conditions, Extraction Mechanism, and Biological Activity in Vitro. Ultrason. Sonochem 2023, 98, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.-L.; Park, J.-G.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, W.; Cho, M.J.; Jang, J.-H.; Kwon, M.-G.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.; et al. Ginkgetin, a Biflavone from Ginkgo Biloba Leaves, Prevents Adipogenesis through STAT5-Mediated PPARγ and C/EBPα Regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Qu, L.; Li, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Liang, X. Isolation and Bioactive Evaluation of Flavonoid Glycosides from Lobelia Chinensis Lour Using Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Combined with Label-Free Cell Phenotypic Assays. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Xin, H. Large-scale targetedly isolation of biflavonoids with high purity from industrial waste Ginkgo biloba exocarp using two-dimensional chromatography coupled with macroporous adsorption resin enrichment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 175, 114264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.M. Chromatography of Separation and Qualitative, Quantitative Analysis Biflavonoids from Crude Extract of Selaginella Tamariscina. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 658–663. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, G.; Lei, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Ren, M.; Gao, Q.; Song, C.; Fu, S.; Zhou, J.; et al. Efficient, Green Extraction of Two Biflavonoids from Selaginella Uncinata with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šalić, A.; Šepić, L.; Turkalj, I.; Zelić, B.; Šamec, D. Comparative Analysis of Enzyme-, Ultrasound-, Mechanical-, and Chemical-Assisted Extraction of Biflavonoids from Ginkgo Leaves. Processes 2024, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šalić, A.; Bajo, M.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radović, M.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Zelić, B.; Šamec, D. Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds from Ginkgo Leaves Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Potential Solution for the Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Isolation of Biflavonoids. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, G.; Wu, G.; Bo, Y.; Yang, D.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; An, M. An Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Using an Alcohol-Based Hydrophilic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Determination of Five Flavonoids from Platycladi Cacumen. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrous, E.A.; Farag, M.A. Two Dimensional NMR Spectroscopic Approaches for Exploring Plant Metabolome: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, T.D.; Lösch, S.; Salger, M.; Balemba, O.B.; Wakamatsu, J.; Frank, O.; Hofmann, T. A New NMR Approach for Structure Determination of Thermally Unstable Biflavanones and Application to Phytochemicals from Garcinia buchananii. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischedick, J.T.; Johnson, S.R.; Ketchum, R.E.B.; Croteau, R.B.; Lange, B.M. NMR Spectroscopic Search Module for Spektraris, an Online Resource for Plant Natural Product Identification—Taxane Diterpenoids from Taxus×media Cell Suspension Cultures as a Case Study. Phytochemistry 2015, 113, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, A.; Amir, D. Ginkgetin or Isoginkgetin: The Dimethylamentoflavone of Dioon Edule Lindl. Leaves. European J. Med. Plants 2016, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, S.; Peukert, M.; Svatos, A.; Matros, A.; Mock, H. MALDI-imaging Mass Spectrometry—An Emerging Technique in Plant Biology. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, D.; Shroff, R.; Knop, K.; Gottschaldt, M.; Crecelius, A.; Schneider, B.; Heckel, D.G.; Schubert, U.S.; Svatoš, A. Matrix-free UV-laser desorption/ionization (LDI) mass spectrometric imaging at the single-cell level: Distribution of secondary metabolites of Arabidopsis thaliana and Hypericum species. Plant J. 2009, 60, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).