Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing ONS-Type Pincer Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
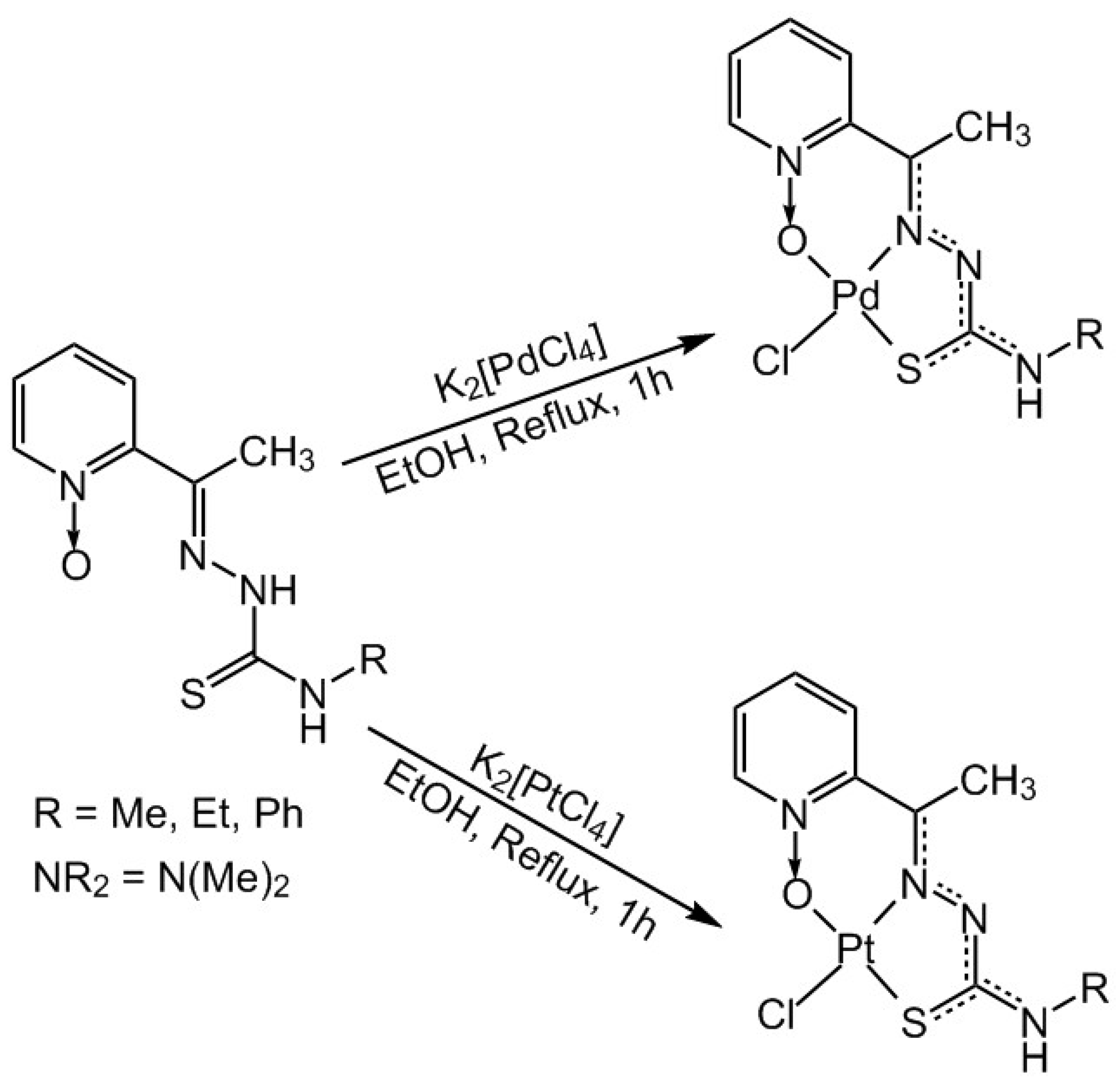
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. FT-IR Spectra
2.3. UV–Visible Spectra
2.4. NMR Spectra of the Complexes
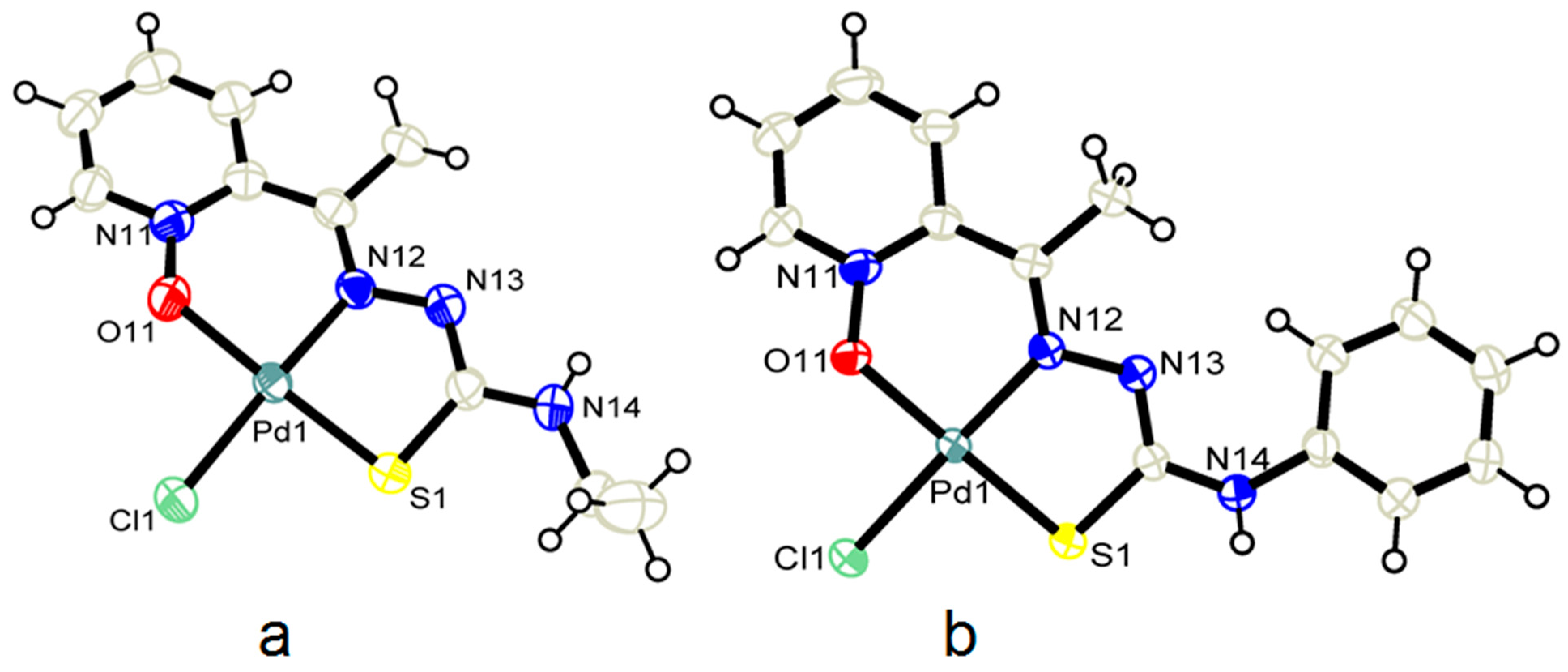
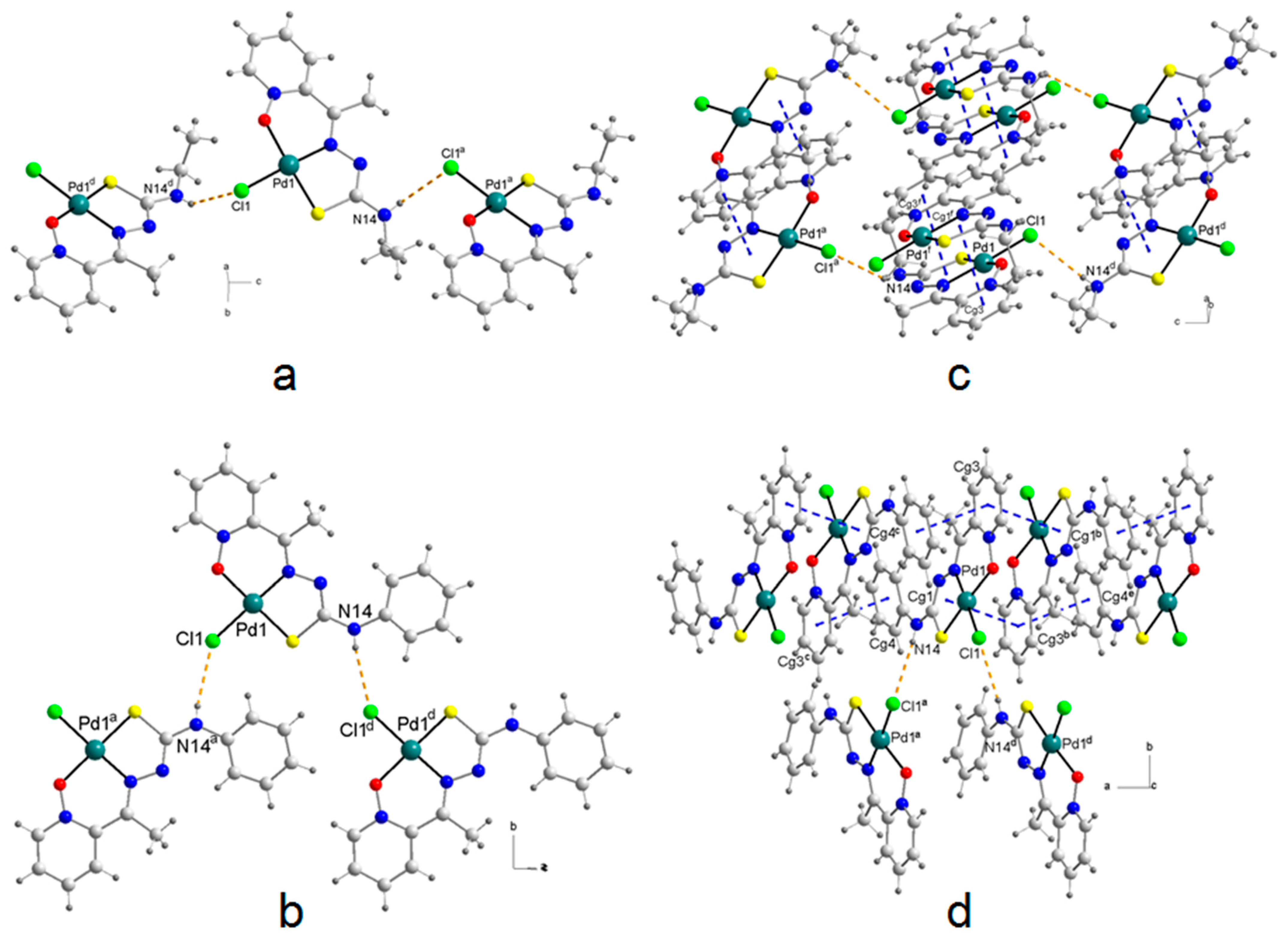
2.5. Molecular Structures and Supramolecular Analysis
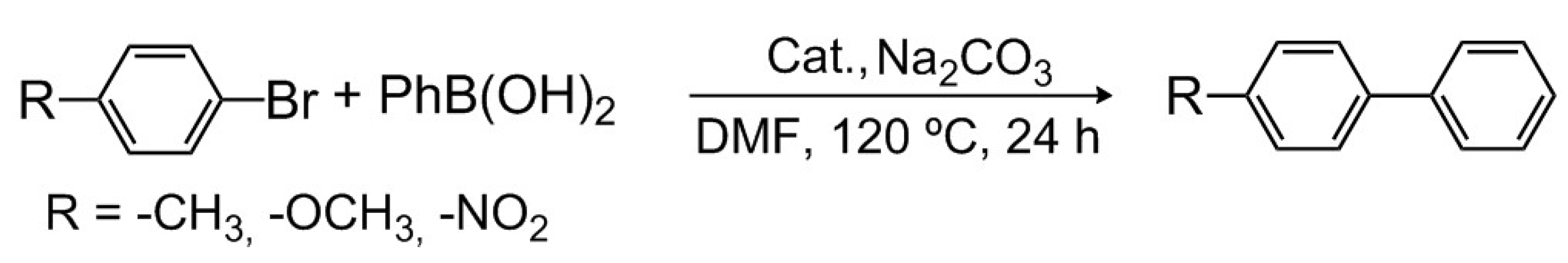
2.6. Catalysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Physical Measurements
3.2. Synthesis of Thiosemicarbazone Ligands
3.3. Synthesis and Crystallization of the Complexes
3.4. Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction
3.5. General Procedure for the Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warner, C.J.; Cannon, A.S.; Dye, K.M. Green Chemistry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2004, 24, 775–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dub, P.A.; Gordon, J.C. The Role of the Metal-Bound N-H Functionality in Noyori-Type Molecular Catalysts. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, S.; Topf, C.; Fischer, S.; Jiao, H.; Spannenberg, A.; Baumann, W.; Ludwig, R.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Selective Catalytic Hydrogenations of Nitriles, Ketones, and Aldehydes by Well-Defined Manganese Pincer Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8809–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maser, L.; Vondung, L.; Langer, R. The ABC in Pincer Chemistry- From Amine- to Borylene- and Carbon-Based Pincer-Ligands. Polyhedron 2018, 143, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Van Koten, G. Platinum Group Organometallicals Based on “Pincer” Complexes: Sensors, Switches, and Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3750–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Hu, X. Recent Developments of Iron Pincer Complexes for Catalytic Applications. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 741–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.-H.; Chen, J.-C.; Lin, G.-L.; Lin, T.-T.; Sun, M.-H. Novel synthesis of palladium (II) complexes derived from 3-arylsydnone-4-carbaldehyde n(4)-phenylthiosemicarbazones and biological activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 66, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyarega, S.; Haribabu, J.; Karvembu, R. Development of thiosemicarbazone-based transition metal complexes as homogeneous catalysts for various organic transformations. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 532, 120742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.; Pathak, T.P.; Sigman, M.S. Advances in Transition Metal (Pd,Ni,Fe)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions Using Alkyl-organometallics as Reaction Partners. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1417–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, H. Heterocyclic Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction of metalla-aromatics and mechanistic analysis of site selectivity. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alterio, M.C.; Casals-Cruañas, È.; Tzouras, N.V.; Talarico, G.; Nolan, S.P.; Poater, A. Mechanistic Aspects of the Palladium-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 13481–13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, I.D.; Steele, B.R. Thiosemicarbazone Complexes of Transition Metals as Catalysts for Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Datta, S.; Halder, S.; Acharyya, R.; Basuli, F.; Butcher, R.J.; Peng, S.-M.; Lee, G.-H.; Castineiras, A.; Drewe, M.G.B.; et al. Syntheses, structures and efficient catalysis for C–C coupling of some benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone complexes of palladium. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 344, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiñeiras, A.; Fernández-Hermida, N.; García-Santos, I.; Gómez-Rodríguez, L. Neutral NiII, PdII and PtII ONS-pincer complexes of 5-acetylbarbituric-4Ndimethylthiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13486–13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, W.J. The Use of Conductivity Measurements in Organic Solvents for the Characterisation of Coordination Compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, E.; Castiñeiras, A.; Domínguez, A.; Carballo, R.; Maichle-Mössmer, C.; Strähle, J.; Liberta, A.E.; West, D.X. Complexes of Group 12 Metal Dihalides with 2-Acetylpyridine-N-oxide 4N-methylthiosemicarbazone (H4MLO). The Crystal Structures and Organization of [Zn(H4MLO)X2] (X = Br, I). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2000, 626, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, E.; Carballo, R.; Castiñeiras, A.; Domínguez, R.; Maichle-Mössmer, C.; Strähle, J.; West, D.X. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal activity of group 12 metal complexes of 2-acetylpyridine- 4N-ethylthiosemicarbazone (H4EL) and 2-acetylpyridine-n-oxide- 4N-ethylthiosemicarbazone (H4ELO). Polyhedron 1999, 18, 3695–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, E.; Castiñeiras, A.; Domínguez, R.; Carballo, R. Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Antifungal Activities of Complexes of Group 12 Metals with 2-Acetylpyridine- and 2-Acetylpyridine-n-oxide-4N-phenyl-thiosemicarbazones. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1999, 625, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, E.; Carballo, R.; Castiñeiras, A.; Domínguez, R.; Liberta, A.E.; Maichle-Mössmer, C.; West, D.X. Complexes of Group 12 Metals with 2-Acetylpyridine 4N-Dimethyl-thiosemicarbazone and with 2-Acetylpyridine-n-oxide 4N-Dimethyl-thiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, Structure and Antifungal Activity. Z. Naturforsch. 1999, 54, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlein, J.; Müller, U.; Dehnicke, K. Schwingungsspektroskopie, 2nd ed.; G. Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lever, A.B.P. Inorganic Electronic Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, W.R.; Gray, H.B. Electronic Structures of Square-Planar Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 5721–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Cryst. 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovala-Demertzi, D.; Yadav, P.N.; Demertzis, M.A.; Jasiski, J.P.; Andreadaki, F.J.; Kostas, I.D. First use of a palladium complex with a thiosemicarbazone ligand as catalyst precursor for the Heck reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, N.; Szabó, K.J. Catalysis by Palladium Pincer Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2048–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, T.; Uetake, Y.; Isoda, M.; Takimoto, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Hashizume, D.; Sakurai, H.; Hosoya, T. Lewis acid-mediated Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Agarwal, M.; Singh, A.K.; Butcher, R.J. Palladium(II), platinum(II), ruthenium(II) and mercury(II) complexes of potentially tridentate Schiff base ligands of (E, N, O) type (E = S, Se, Te): Synthesis, crystal structures and applications in Heck and Suzuki coupling reactions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonius, B.V. CAD4-Express Software, version 5.1/1.2; Enraf Nonius: Delft, The Netherlands, 1994.
- North, A.C.T.; Phillips, D.C.; Mathews, F.S. A semi-empirical method of absorption correction. Acta Cryst. 1968, 24, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal structure Determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.J.C. International Tables for Crystallography; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume C. [Google Scholar]
- Putz, H.; Brandenburg, K. Diamond—Crystal and Molecular Structure Visualization, version 5.0.2 (Build 47); Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.; Seth, D.K.; Butcher, R.J.; Bhattacharya, S. Mixed-ligand thiosemicarbazone complexes of nickel: Synthesis, structure and catalytic activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2011, 377, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, C. A critical account on π–π stacking in metal complexes with aromatic nitrogen-containing ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 3885–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | (3) | (5) |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C10H13ClN4OPdS | C14H13ClN4OPdS |
| Formula weight | 379.15 | 427.19 |
| Temperature/K | 293(2) | 293(2) |
| Wavelength/Å | 0.71073 (Mo-Kα) | 0.71073 (Mo-Kα) |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c (No. 14) | P21/n (No. 14) |
| Unit cell dimensions | ||
| a/Å | 7.820(1) | 8.516(2) |
| b/Å | 10.140(1) | 17.756(2) |
| c/Å | 16.471(3) | 10.004(3) |
| α/° | - | - |
| β/° | 91.457(8) | 92.496(14) |
| γ/° | - | - |
| Volume/Å−3 | 1305.5(3) | 1511.3(6) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Calc. density/Mg/m3 | 1.929 | 1.878 |
| Absorp. Coefc./mm−1 | 1.778 | 1.548 |
| F(000) | 752 | 848 |
| Crystal size | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.15 | 0.27 × 0.18 × 0.11 |
| θ range/° | 3.19–27.07 | 3.07–27.02 |
| Limiting indices/h, k, l | −1/9, 0/12, −21/21 | −1/10, 0/22, −12/12 |
| Refl. collect/unique | 3467/2843 (Rint = 0.0168) | 3948/3288 (Rint = 0.0183) |
| Completeness θ/° | 27.07 (99.1%) | 27.02 (99.2%) |
| Absorp. correct. | ψ-scans | ψ-scans |
| Max./min. transm. | 0.7763 / 0.6175 | 0.8481/0.6799 |
| Data/parameters | 2843/163 | 3288/199 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.108 | 1.089 |
| Final R indices | R1 = 0.0305/wR2 = 0.0783 | R1 = 0.0287/wR2 = 0.0628 |
| R indices (alla data) | R1 = 0.0374/wR2 = 0.0815 | R1 = 0.0425/wR2 = 0.0673 |
| Largest dif. peak/hole | 0.939/−0.466 | 0.376/−0.487 |
| CCDC number | 2367114 | 2367115 |
| Compound | (3) | (5) |
|---|---|---|
| Distances [Å] | ||
| Pd(1)–O(11) | 2.007(2) | 2.009(2) |
| Pd(1)–N(12) | 1.971(3) | 1.976(2) |
| Pd(1)–S(1) | 2.2221(9) | 2.2221(8) |
| Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 2.3107(9) | 2.3226(8) |
| Angles [°] | ||
| N(12)–Pd(1)–O(11) | 92.75(10) | 92.57(9) |
| N(12)–Pd(1)–S(1) | 86.53(8) | 85.94(7) |
| O(11)–Pd(1)–S(1) | 175.46(8) | 174.80(8) |
| N(12)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 177.38(8) | 177.53(7) |
| O(11)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 89.44(7) | 89.01(7) |
| S(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 91.18(3) | 92.64(3) |
| Reac. | R | Cat. | % Conv. | TON | TOF (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -OCH3 | 3 | 50.4 | 5040 | 3.5 |
| 2 | -CH3 | 3 | 72.1 | 7210 | 5.0 |
| 3 | -NO2 | 3 | 91.1 | 9110 | 6.3 |
| 4 | -OCH3 | 5 | 64.3 | 6430 | 4.5 |
| 5 | -CH3 | 5 | 82.3 | 8230 | 5.7 |
| 6 | -NO2 | 5 | 93.0 | 9300 | 6.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castiñeiras, A.; García-Santos, I. Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing ONS-Type Pincer Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Investigations. Molecules 2024, 29, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143425
Castiñeiras A, García-Santos I. Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing ONS-Type Pincer Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Investigations. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143425
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastiñeiras, Alfonso, and Isabel García-Santos. 2024. "Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing ONS-Type Pincer Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Investigations" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143425
APA StyleCastiñeiras, A., & García-Santos, I. (2024). Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Bearing ONS-Type Pincer Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Investigations. Molecules, 29(14), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143425







