Abstract
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is a key neuropeptide hormone that is secreted from the hypothalamus. It is the master hormone of the HPA axis, which orchestrates the physiological and behavioral responses to stress. Many disorders, including anxiety, depression, addiction relapse, and others, are related to over-activation of this system. Thus, new molecules that may interfere with CRF receptor binding may be of value to treat neuropsychiatric stress-related disorders. Also, CRF1R antagonists have recently emerged as potential treatment options for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Previously, several series of CRF1 receptor antagonists were developed by our group. In continuation of our efforts in this direction, herein we report the synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of CRF1R antagonists. Representative compounds were evaluated for their binding affinities compared to antalarmin. Four compounds (2, 5, 20, and 21) showed log IC50 values of −8.22, −7.95, −8.04, and −7.88, respectively, compared to −7.78 for antalarmin. This result indicates that these four compounds are superior to antalarmin by 2.5, 1.4, 1.7, and 1.25 times, respectively. It is worth mentioning that compound 2, in terms of IC50, is among the best CRF1R antagonists ever developed in the last 40 years. The in silico physicochemical properties of the lead compounds showed good drug-like properties. Thus, further research in this direction may lead to better and safer CRF receptor antagonists that may have clinical applications, particularly for stress-related disorders and the treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
1. Introduction
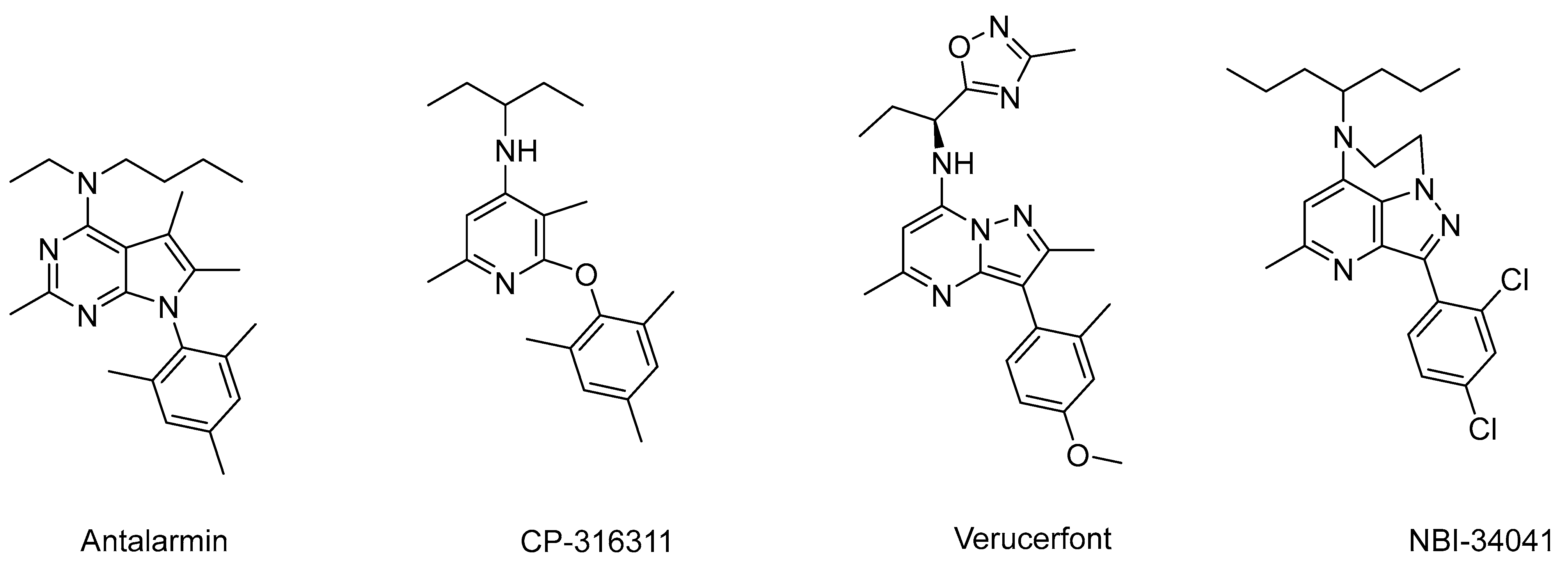
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is a pivotal hormonal player in the physiology of stress. It was first discovered in the ovine hypothalamus in 1981 [1,2]. CRF is secreted from the hypothalamus region known as the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). It plays a major role in the regulation of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenocortical (HPA) axis. Despite variation in sequence, CRF peptides compromise 41 amino acids across all examined species, and they exhibit notable homologies between humans and other species with 76–95% similarities [3]. In response to stressful stimuli, hypothalamic CRF release triggers a cascade, prompting the secretion of corticotropin, which is also known as the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Subsequent transport of corticotropin via the blood to the adrenal gland cortex instigates cortisol (hydrocortisone) release. Once cortisol reaches the normal physiological concentration, it then causes a classical negative feedback inhibition on the hypothalamus, which is very important for the regulation and homeostasis of the stress system [4]. Dysregulation of the HPA system occurs in many stress-related disorders where this negative feedback system may be impaired, resulting in elevated levels of CRF [5]. Depression is associated with CRF hypersecretion, and studies revealed that CRF mRNA has higher expression in the PVN of patients with depression and also found elevated CRF in the CSF of drug-free depressed patients [6,7] Several analogs of CRF exist in different species, and they include urocortin, sauvagine, and urotensin. They all exert their physiological and biological functions through binding to membrane-bound G-protein couple receptors (GPCRs). Two CRF receptor subtypes exist, including CRF1 and CRF2 [8,9,10]. The binding affinity of CRF to CRF1R is almost eight times higher relative to its binding to CRF2R [11]. Abnormally high levels of CRF are often implicated in a variety of stress-related diseases, including anxiety, depression, suicidal tendencies, Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety-induced relapses of drug addiction, and several other psychiatric and mental disorders [6,12]. CRF also modulates many other physiological and pathological processes of the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, behavioral, immune, and reproductive systems [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. The total economic burden of these diseases and disorders in the US exceeds USD 1 trillion annually. This heavy economic impediment highlights the urgency for new and effective therapeutic interventions. Thus, antagonists of the CRF receptors hold promise as potential drug candidates for ameliorating stress-related disorders such as anxiety, depression, and addictive disorders [12,26,27,28] as well as treating peripheral disorders such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome, inflammation, peptic ulcer, and many others [29,30,31,32]. Some of the recent studies demonstrated that CRF1R antagonists can prevent the expression of anxiety-like behavior in mice [33], improve the HPA axis negative feedback mechanism in stressed mice [34], and reduce stress-induced addictive behavior [35]. There are literally hundreds of non-peptide small-molecule CRF1 receptor antagonists available in the literature. Many of these compounds have demonstrated promise in animal models of stress-related disorders. Several molecules, including antalarmin, CP-326311, verucefont, and NBI-34041 (Figure 1), have been evaluated in multiple subclinical studies and also clinical studies in patients suffering from anxiety, depression, stress disorders, endometriosis, and drug addiction [36,37,38,39,40,41]. Unfortunately, none of them has been approved as a drug because they have failed in clinical trials for different reasons, including lack of proper efficacy and elevation of liver enzymes, which may indicate hepatic toxicity [42]. Because anxiety and depression are major problems affecting hundreds of millions of people and have been associated with chronic over-activation of the HPA axis, it was expected that these conditions would be the first to be treated by CRF1R antagonists.
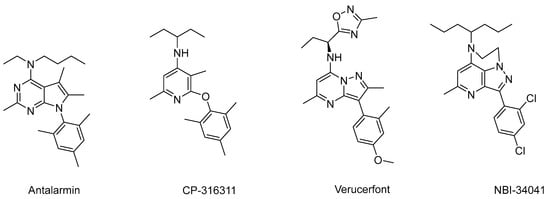
Figure 1.
Important CRF1R antagonists.
However, the first clinical application of CRF1R antagonists was in the treatment of classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Yet, the potential of CRF1R antagonists as a treatment option for anxiety, depression, and other stress-related disorders is still an open chapter.
Recently, the recognition of CRF1R antagonists as a potential treatment option for congenital adrenal hyperplasia, also known as CAH [43], marks a significant advancement. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an autosomal recessive disorder, and it is most commonly associated with 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency (21OHD). This enzymatic defect leads to a decreased production of the endogenous glucocorticoid cortisol, resulting in a lack of negative feedback towards CRF secretion from the hypothalamus and ACTH from the anterior pituitary gland [44]. CAH due to 21OHD occurs in approximately 1:15,000 births, and it is associated with a myriad of devastating complications, such as atypical genitalia in female infants. Continued androgen excess during childhood and adolescence in females causes sexual precocity and virilization. Continued excessive androgen production during adulthood causes hirsutism and irregular menses in women. Both sexes with 21OHD also suffer from reduced fertility and psychiatric disorders [45]. Until recently, treatment of CAH mainly aimed to substitute the deficient steroid hormones. To suppress adrenal androgen synthesis, higher doses of glucocorticoids are required, which can often lead to growth suppression in children, iatrogenic Cushing syndrome, and metabolic disorders such as obesity, insulin resistance, and hypertension, which can increase cardiovascular risk [46,47,48].
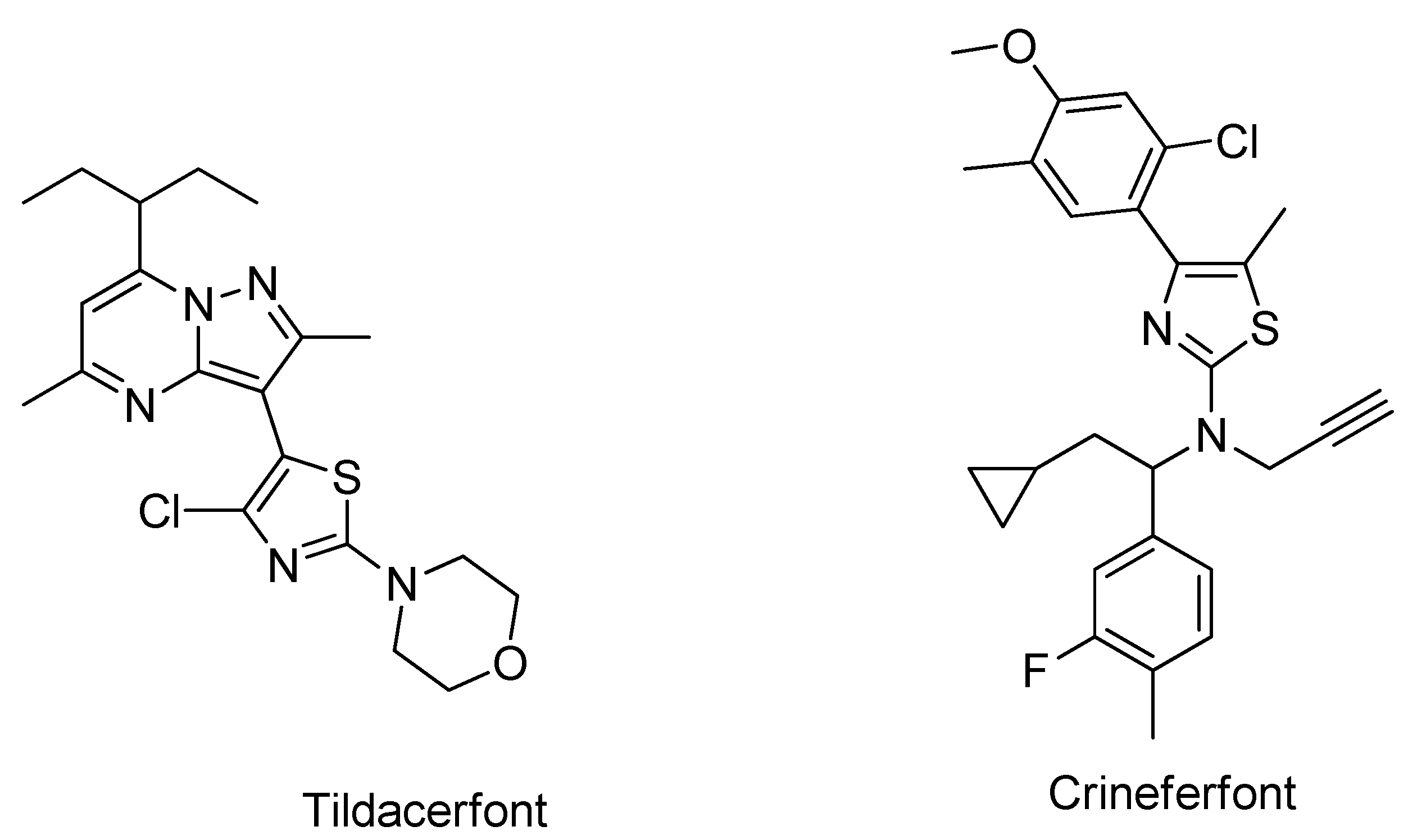
Recently, two CRF1 receptor antagonists, tildacerfont and crinecerfont (Figure 2), were developed and are in clinical trials on Phase 2 and Phase 3, respectively. They have shown excellent promise in managing CAH by lowering elevated adrenal androgens [43,49,50], and this discovery has opened a new era for CRF1R antagonist researchers as potential drug candidates [51]. Both molecules, tildacerfont and crinecerfontare, are classified as orphan drugs [52]. Tildacerfont also showed promising effects in treating polycystic ovary syndrome. On 5 December 2023, Neurocrine Biosciences announced that it had received a breakthrough therapy designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for crinecerfont in congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
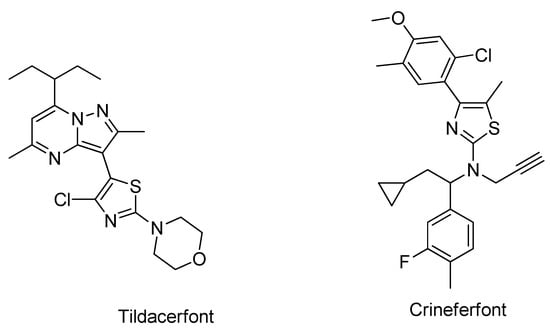
Figure 2.
Structure of Tildacerfont and Crinecerfont.
Hence, developing new molecules with diverse structural scaffolds as CRF1 receptor antagonists and further clinical investigations are still an active area of research that may shed more light on potential new treatment options for CAH. This new approach could help ameliorate the negative consequences of long-term supra physiological glucocorticoid treatment.
In the last decade, our group has published several papers describing the synthesis of several series of substituted pyrimidines and fused pyrimidine compounds that retained the main structural features of CRF1 receptor antagonists. Those series of compounds were evaluated, and several compounds have demonstrated promising binding affinity to the CRF1 receptors [53,54,55,56]. To continue our work in this direction, we have synthesized new analogs of our previously published lead compounds. In this manuscript, we report the synthesis, characterization, biological evaluation, and structural-activity relationship (SAR) of our most recent synthesized compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design Rationale
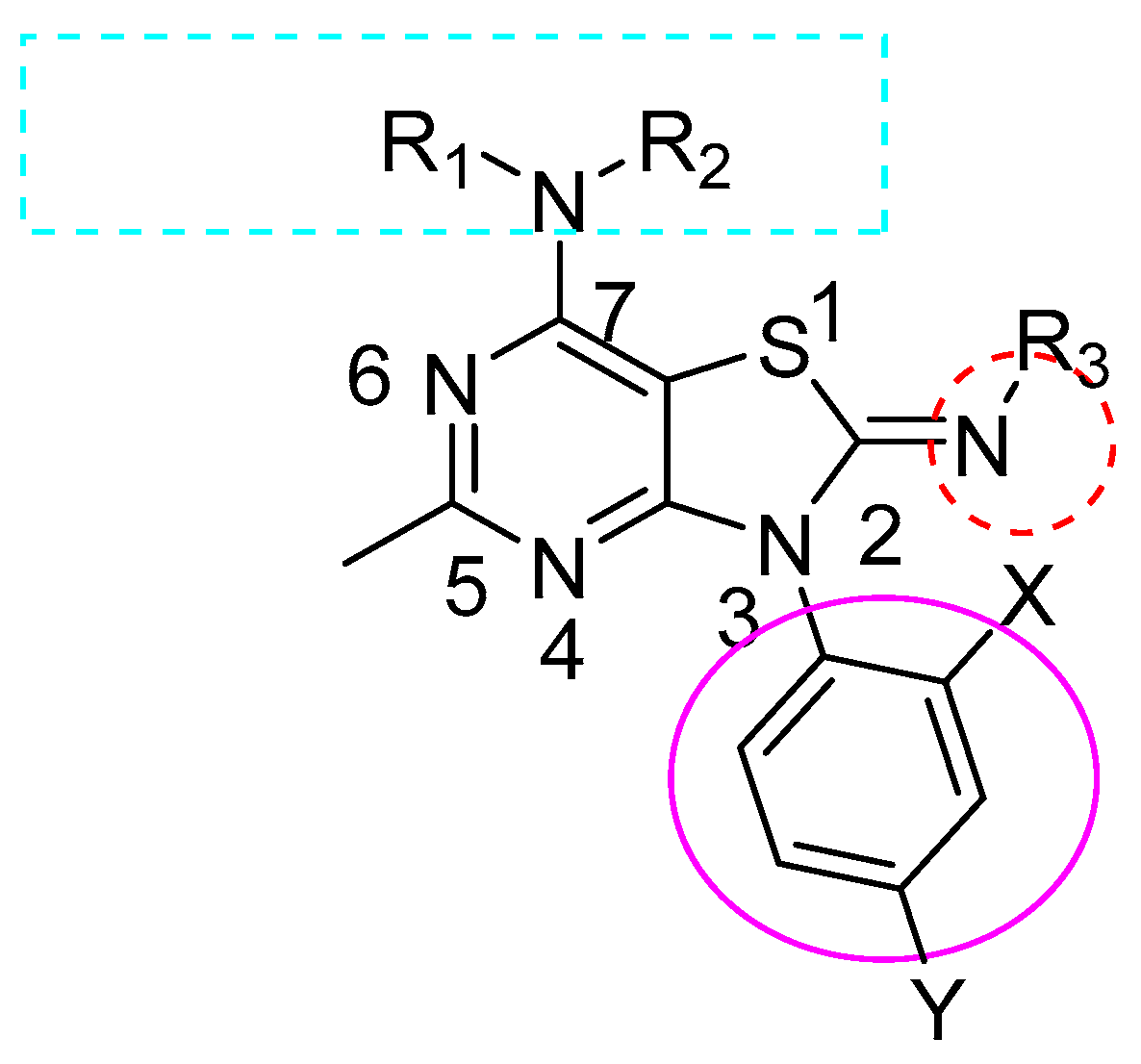
The new set of analogs reported in this work was designed based on SAR studies of our previously prepared published compounds from the same research project [56], while keeping the basic pharmacophore. The general structure (Figure 3) was modified using 2,4-di substituted phenyl group at position-3. At least one side of the alkyl amino group at C-7 contained more than two carbons in the chain, and the N-CH3 group at the N-2 position had superior binding affinity to CRF1R.
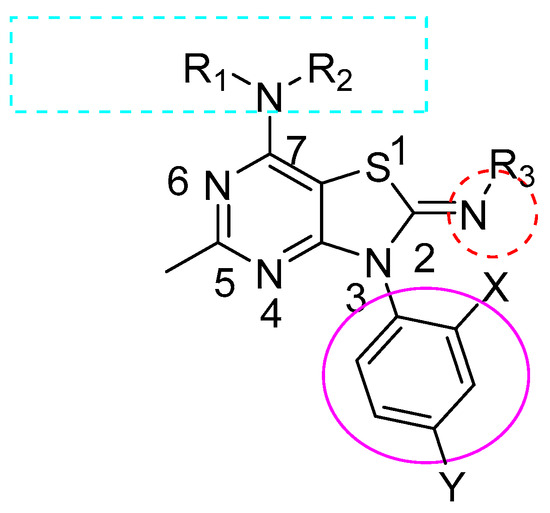
Figure 3.
General structure of synthesized analogs.
2.2. Chemistry
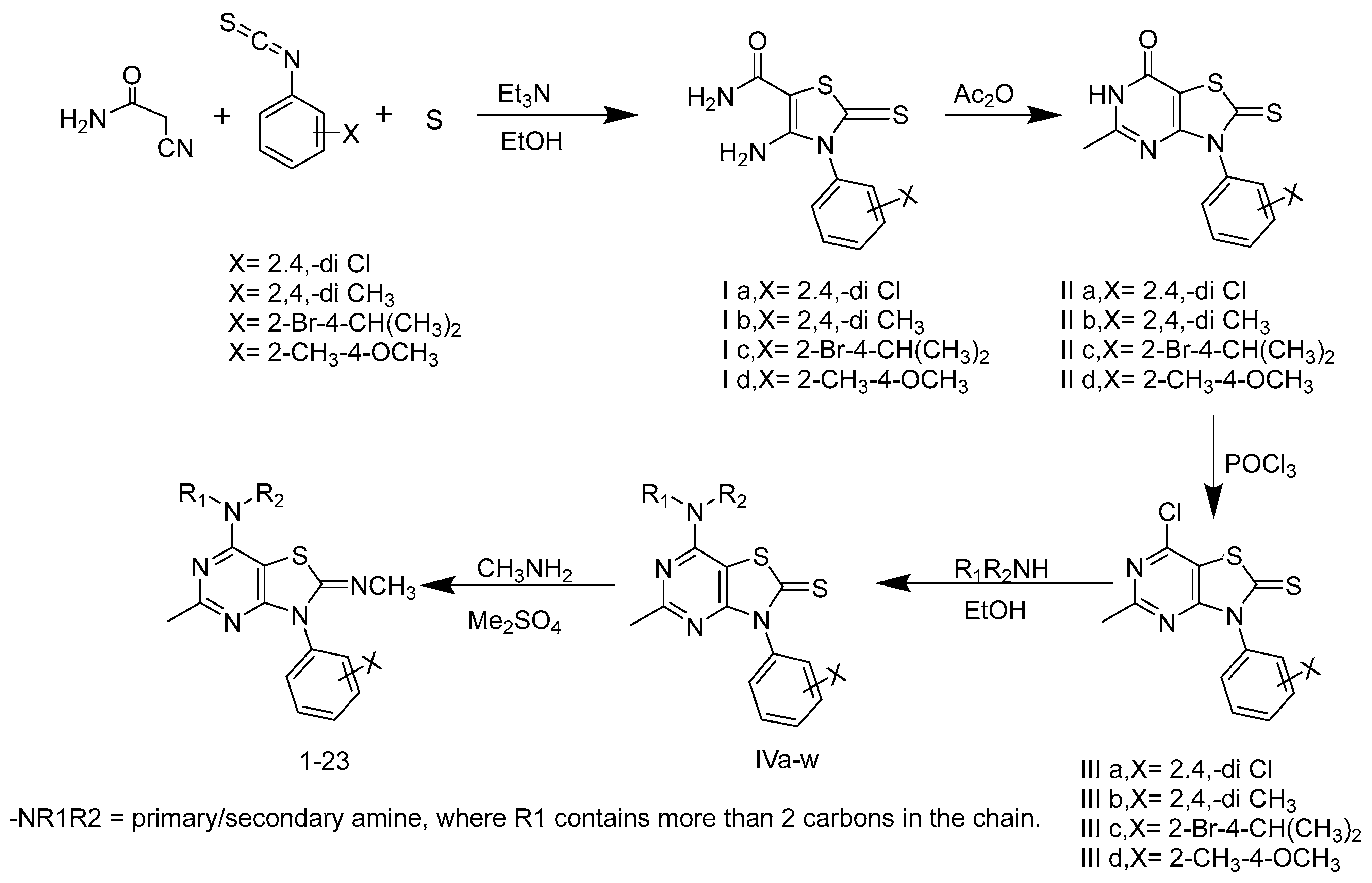
The general synthetic scheme for the designed target compounds is described in Figure 4. The synthetic procedures for the synthesis of intermediates I–IV are reported in our previously published papers [53,54,55,57]. In brief, the selected 2,4-disubstituted phenyl isothiocyanates were allowed to react with cynoacetamide and sulfur in the presence of triethylamine following a Gewald-reaction to give the intermediate 4-amino-3-substituted phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydrothiazole-5-carboxamide (Ia-d) [58,59]. These intermediates (Ia-d) were heated in acetic anhydride at reflux temperature to undergo cyclization into the 5-methyl-3-substituted phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7(7aH)-ones (IIa-d), as previously described by Fahmy et al. [60]. Compounds IIa-d were then subjected to a chlorination reaction using phosphorus oxychloride at reflux temperature [53,60,61] to produce the 7-chloro-5-methyl-3-substituted phenylthiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2(3H)-thione derivatives (IIIa-d). These chloro derivatives were then treated with two equivalents of the selected dialkylamine/alkylamine to give the 7-(dialkylamino/alkylamino)-5-methyl-3-substituted phenylbenzo[4,5-d]thiazole-2(3H)-thiones (IVa-w).
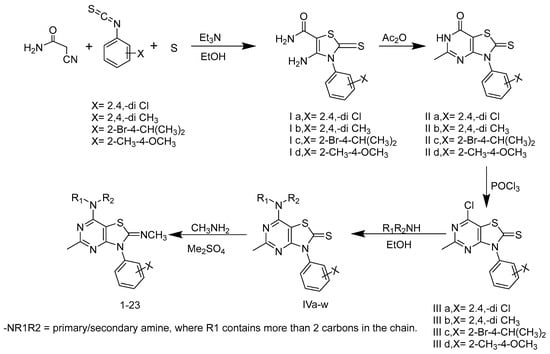
Figure 4.
General synthetic scheme for intermediate and final target compounds.
The final target compounds (1–23) were prepared from the 7-amino derivatives IVa-w by reaction with dimethyl sulphate, followed by reaction of the 2-methylthiazolium intermediate with methylamine to yield the 2-methylimino target compounds according to previously reported procedures [56]. By using different groups at three different positions, including substituted phenyl isothiocyanate at N-3, the alkylimino group at C-2, and the alkylamino group at C-7 (Figure 3), a series of final target compounds were synthesized as described in the methods section.
Structure details of target final compounds with different substitutions of general structure (Figure 3) and molecular weight of those compounds are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of substitutions of the final target compounds (1–23).
2.3. Biological Evaluation
An investigation of the specific binding was carried out in membrane homogenates extracted from human embryonic kidney (HEK 293) cells stably expressing CRF1 receptors, a standard methodology previously detailed in several of our published works [53,55]. This experimental approach closely adheres to the original Gkountelias et al. procedure [62].
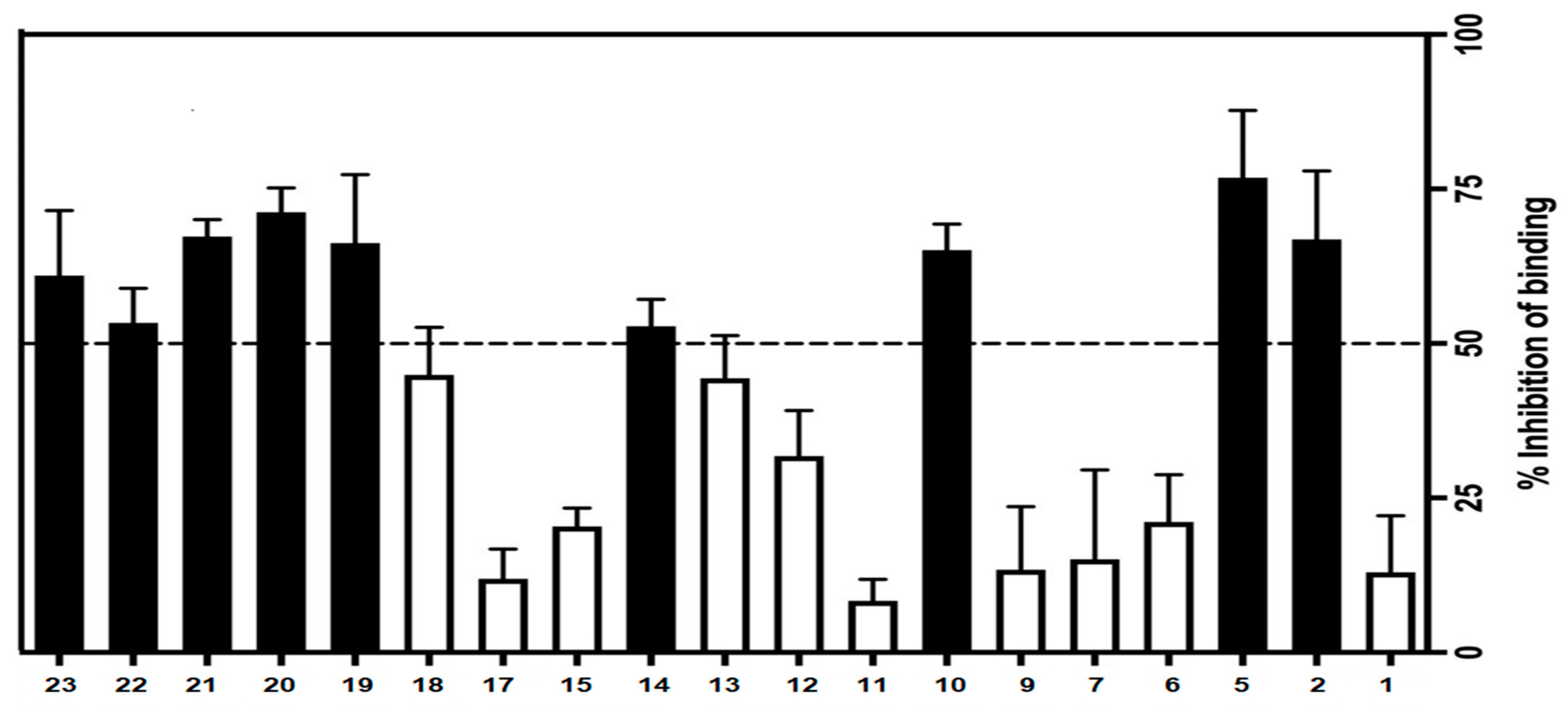
The CRF1 receptor binding affinities for final target compounds 1–23 were evaluated. First, the ability of the entire test compounds to inhibit the specific binding of the radiolabelled ligand [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine to membranes from HEK 293 cells stably expressing the CRF1 receptors was evaluated at a single concentration of 100 nM. In this primary screening experiment, nine compounds (compounds 2, 5, 10, 14, and 19–23) have shown their ability to inhibit more than 50% of [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine-specific binding, while the remaining compounds showed the ability to inhibit [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine specific binding but not more than 50% (Figure 5).
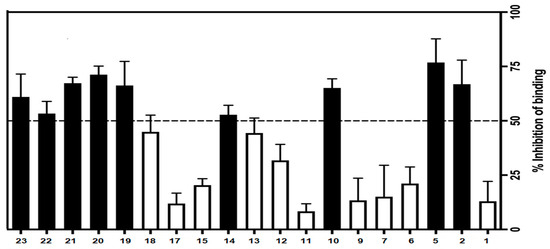
Figure 5.
% inhibition of [125I]-Try0 sauvagine-specific binding by 100 nM of test compounds on membranes from HEK293 stably expressing human CRF1 receptors. In the absence of the test compound, the inhibition is 0%.
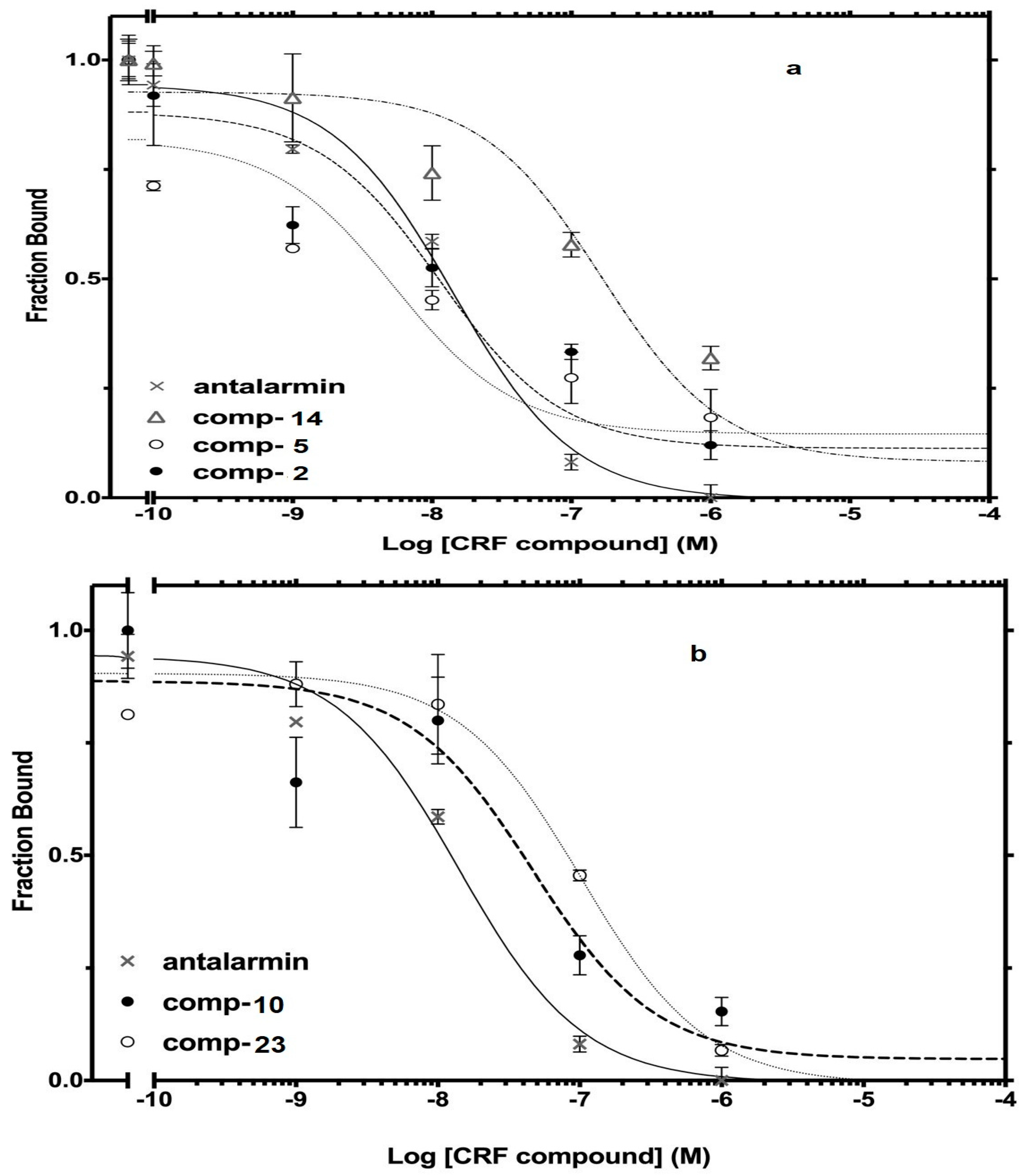
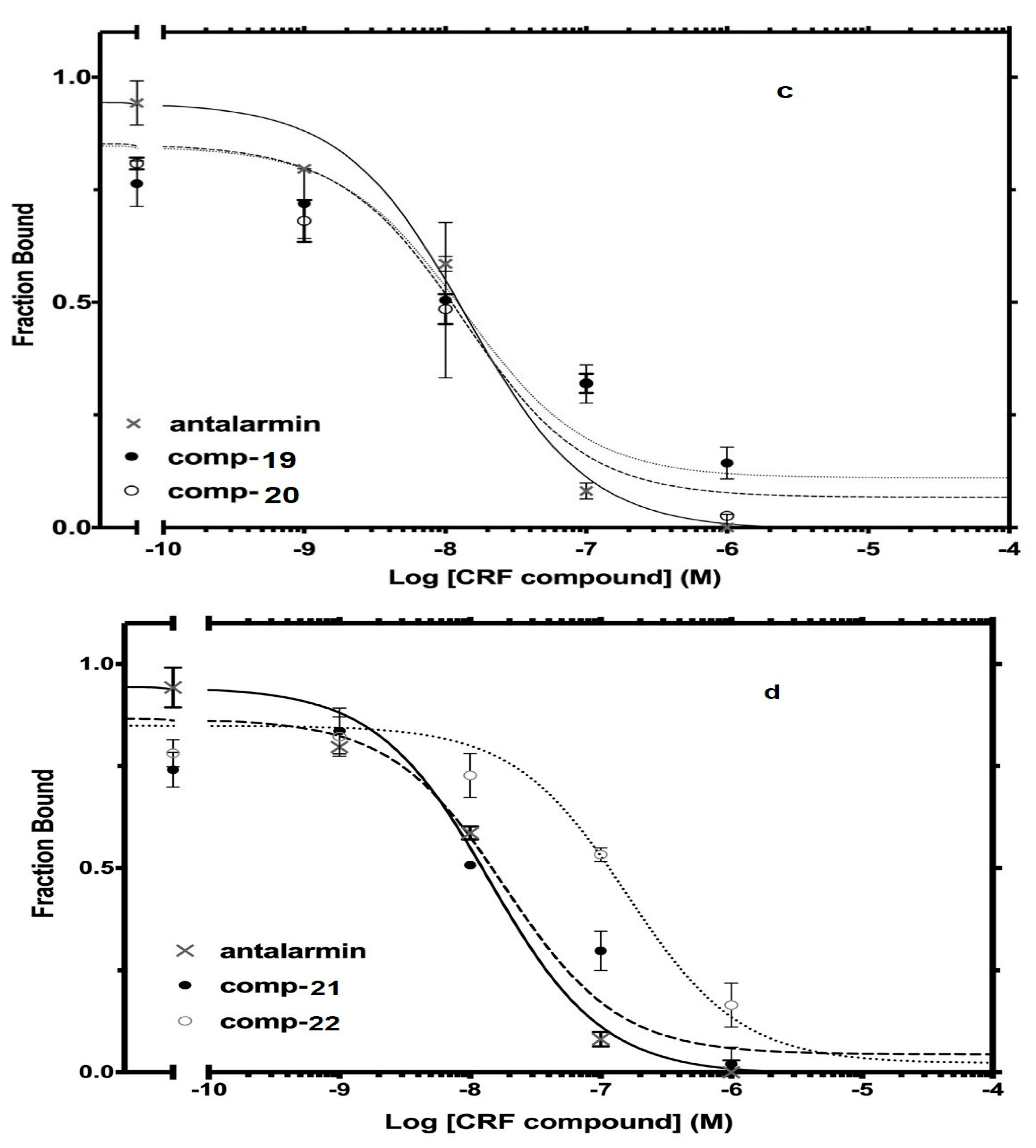
The best nine compounds (lead compounds) resulting from the primary screening (compounds 2, 5, 10, 14, and 19–23) were subjected to a second pharmacological characterization by determining their inhibitory ability (Log IC50) in competition experiments performed under equilibrium conditions in membranes from HEK 293 cells stably expressing CRF1 receptors. In the second assay, the inhibitory effects measured by the lead compounds were compared to those of the standard drug antalarmin. These nine lead compounds were found to inhibit [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine binding to CRF1 receptors in a dose-dependent manner, with Log IC50 ± SE values of −8.22 ± 0.33, −7.95 ± 0.26, −7.51 ± 0.15, −6.84 ± 0.09, −7.39 ± 0.34, −8.04 ± 0.16, −7.88 ± 0.09, −7.04 ± 0.24, and −6.95 ± 0.12 for the compounds 2, 5, 10, 14, 19, 20, 21, 22 and 23, respectively, compared to the Log IC50 ± SE value of −7.78 ± 0.21 for the standard drug antalarmin (Figure 6). The corresponding IC50 (nM) values are shown in Table 2.
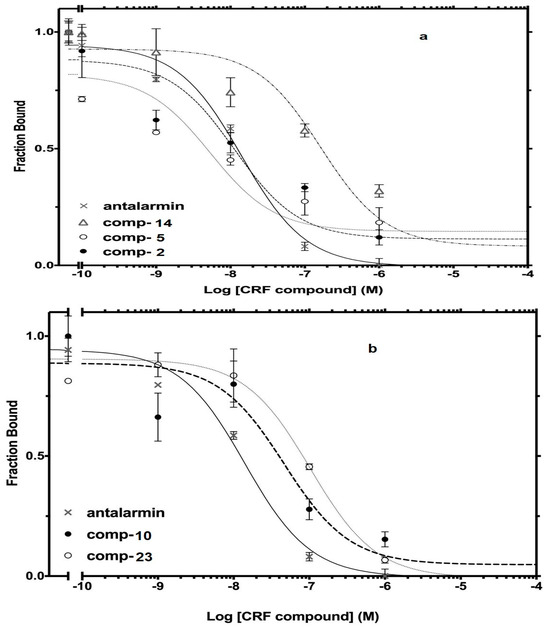
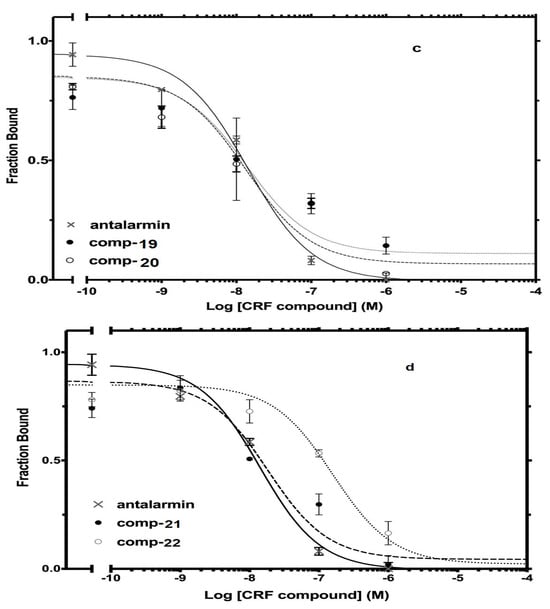
Figure 6.
Competitive binding isotherms of compounds 2, 5, and 14 (a), compounds 10 and 23 (b), compounds 19 and 20 (c) and 21 and 22 (d) to human CRF1 receptors. Antalarmin was used as a standard drug.

Table 2.
IC50 (nM) values of the lead compounds in comparison to antalarmin.
2.4. Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) of the Lead Compounds
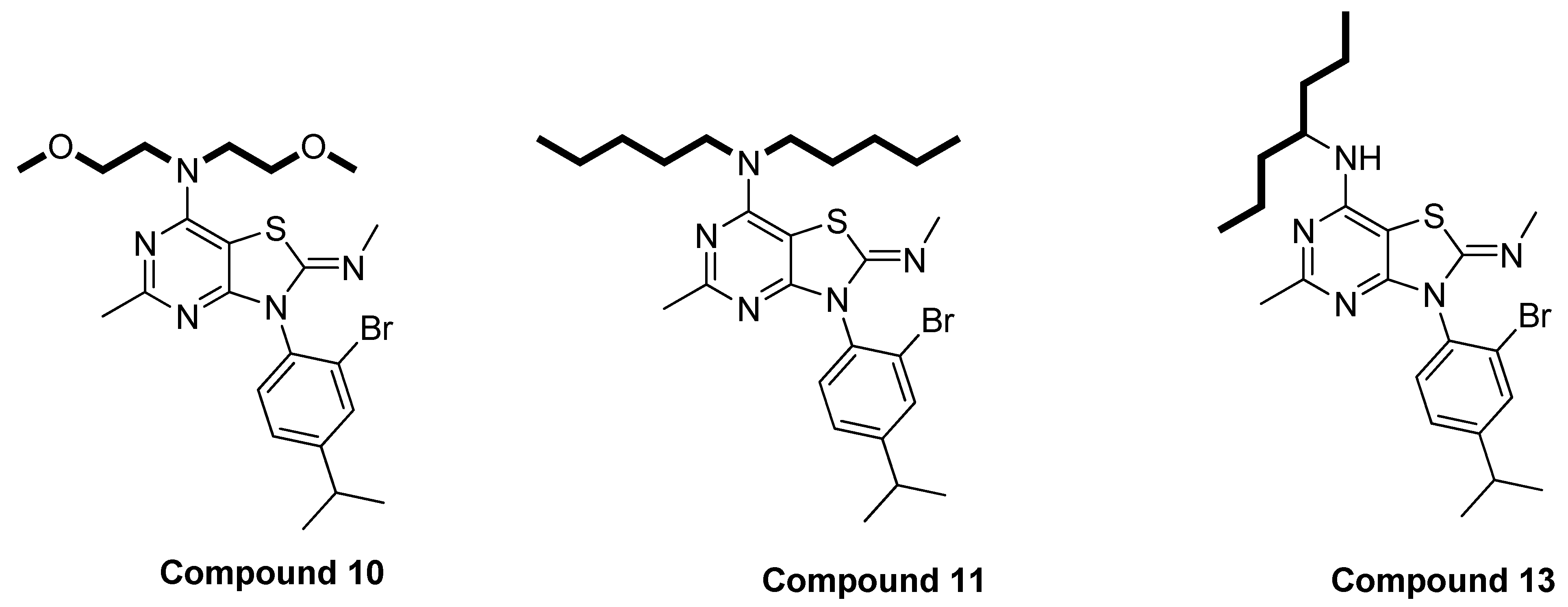
The compounds prepared in this study were designed based on the SAR studies of compounds mentioned in a previously published paper [56]. This SAR aimed to narrow down the diversity of structures of compounds and to focus on definite features, hoping to obtain more potent compounds. In this series of compounds, two different positions (C-7 and N-3) were modified. The preliminary screening indicates that the groups on one side or both sides of the alkylamino group in the C-7 position should be 3–4 carbons in length for optimum inhibitory effects. Extending the carbon chain length at the C-7 position with more than four carbons can diminish the activity of the compounds in this class. For example, compound 11, which contains five carbons on each side of the alkylamino group at the C-7 position, showed reduced activity compared to compounds 10 and 13 (Figure 7).
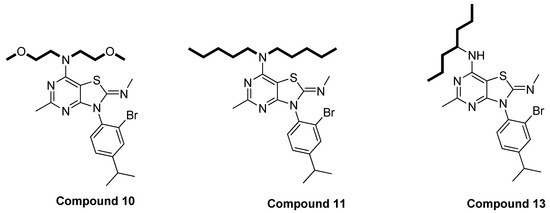
Figure 7.
Structure of compound 11 with more than four carbons at C-7 versus other two compounds (10 and 13) with 3–4 carbons in the side chain at C-7 position.
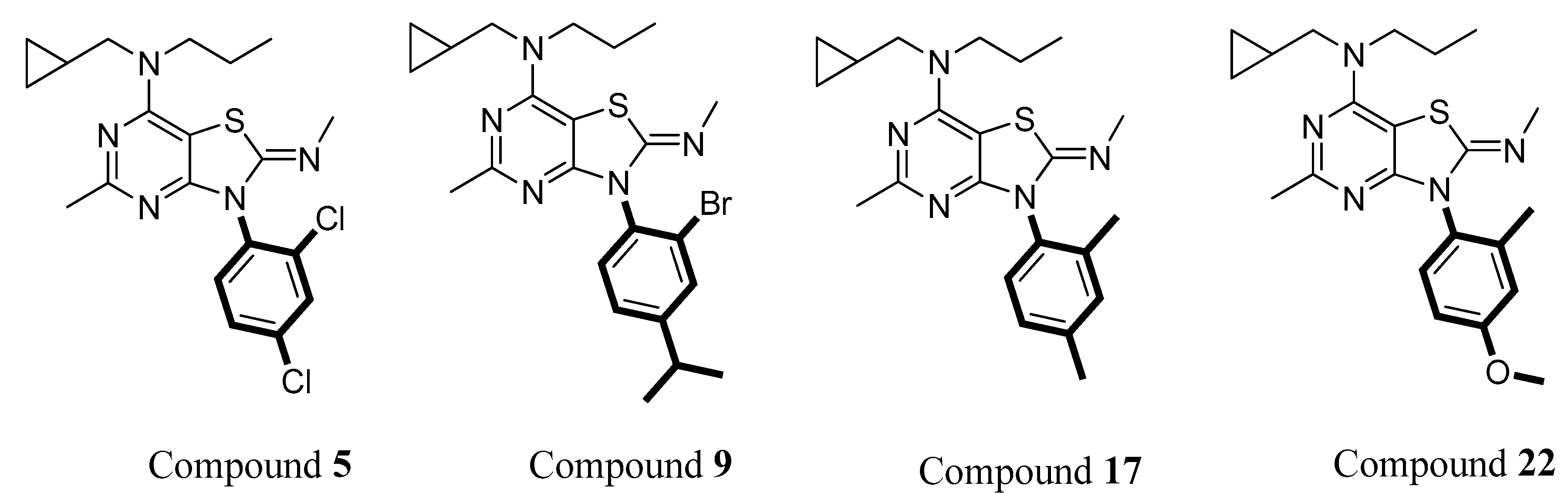
The study results also revealed that 2,4-dichlorophenyl and 4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl groups at the N-3 position showed better inhibitory effects than 2,4-dimethylphenyl and 2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl. For example, compounds 5 and 22, which have 2,4-dichlorophenyl and 4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl groups at the N-3 position, respectively, showed significantly higher inhibitory effects than compounds 9 and 17, which contain 2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl and 2,4-dimethylphenyl, respectively (Figure 8). Most of the compounds with a 4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl group at N-7 exhibited a better inhibitory effect, although the best active compound (compound 2) contains 2,4-dichlorophenyl at N-3.
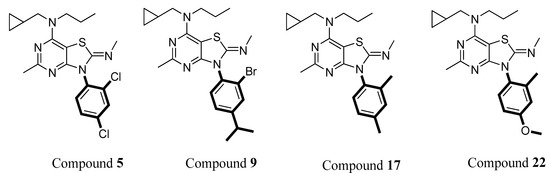
Figure 8.
Representative compounds with different substituted phenyl groups at the N-3 position.
Based on the SAR studies of this series of compounds as well as studies of our previously published paper, it can be concluded that 2,4-dichlorophenyl or 4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl at the N-3 position, both sides of the alkylamino group at the C-7 position having 3–4 carbons, and a small group such as N-CH3 at the C-2 position can be optimum for this class of compound for better inhibitory effect.
2.5. Prediction of Physicochemical Parameters and BBB Permeability
In recent decades, in silico modeling of the physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of designed and synthesized compounds has been considered one of the key tools available in rational drug design and development [63]. The in silico ADME prediction permits the parallel optimization of compound efficacy and drug-like properties. This helps not only to improve the overall quality of drug candidates and the probability of their success but also to lower the cost.
To examine the possible drug-likeness of the best five compounds (compounds 2, 5, 19, 20, and 21), in silico evaluation of some physicochemical properties such as molecular weight (MW), number of rotating bonds (RBs), number of hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs), number of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs), calculated partition coefficient (clog P), violations of Lipinski’s rule (Vio LR), and BBB permeability were performed according to the methods described in Section 3.3.
From the five predictive models available to be used to predict the lipophilicity in the Swiss ADME software (http://www.swissadme.ch/, accessed on 30 March 2022), which are XLOGP3, WLOGP, MLOGP, SILICOS-IT, and iLOGP, we have only used MLOGP in our prediction of lipophilicity with the Swiss ADME software since it is the archetype of the topological method that is adopted from Moriguchi’s and Lipinki’s work [64]. The online “Light BBB” tool complies with most CNS drugs with an accuracy of 90% and a specificity of 0.94 [65].
The theoretical calculations of physicochemical parameters as well as the BBB permeability of the selected compounds as well as antalarmin are shown in Table 3. The theoretical results indicate that all five of the best compounds do not violate Lipinski’s rule, whereas the standard drug antalarmin has one violation.

Table 3.
Physicochemical parameters and BBB permeability of the best five compounds.
2.6. Significance
CRF intricately regulates neuroendocrine functions and behavioral as well as autonomic adaptation in response to stress [66,67,68]. Chronic and overproduction of CRF could explain the pathogenesis of several severe chronic diseases, including anorexia, depression, anxiety, hypogonadism, peptic ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, drug addiction, suicidal tendency, immunosuppression, and many other disorders [67,69].
Currently, different classes of antidepressant drugs are available for treating MDD. These drugs include tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), and serotonin receptor antagonists with serotonin reuptake inhibition (SARI) [70]. Despite a large number of anxiolytics and anti-depressant drugs on the market, the number of patients with MDD has not only remained large but is also increasing. The annual economic burden of only MDD on society was USD 326 billion in 2018. More than 20% of patients with MDD exhibit treatment resistance to the current medications [71], and in some cases, the side effects of the current antidepressant medications may make the condition worse [72]. So, new antidepressant drugs that work through different mechanisms may represent other options for treating MDD. Several studies have revealed that CRF1R antagonists can be potential candidates for the treatment of MDD. CRFR antagonists can also be a novel alternative treatment option for abdominal and pelvic pain [73].
Perhaps the most important advance related to CRF1R antagonists was the fact that they have recently been recognized as a potential treatment option for congenital adrenal hyperplasia CAH [43], and two molecules were advanced to phase-II and phase-III clinical trials with highly promising results [74,75], with one receiving FDA approval and the second underway. In the Phase-III crinical trial, CRF1R antagonist crinecerfont is also a promising drug candidate for pediatric CAH [76]. The emerging therapies for CAH with CRF1R antagonists opened up a novel concept that can reduce the dose of glucocorticoids significantly, which helps to improve quality of life [77].
Both peptide and non-peptide molecules may be developed as CRF1R antagonists. However, most research focuses on small non-peptide molecules due to several reasons. Small-molecule non-peptide CRF1R antagonists are stable, cost-effective, easy to prepare, non-immunogenic, and have enhanced pharmacokinetic profiles and blood brain permeability because of their low molecular weight [78]. Peptide drugs in general suffer serious drawbacks, such as a lack of oral bioavailability and the risk of illiciting an immune response.
Some of the major pharmaceutical companies have developed many promising molecules, and some of them have advanced to clinical trials. Neurocrine Biosciences, Bristol Mayers Squibb, Pfizer, and GSK developed compounds that were advanced to clinical trials for major depression, suicidal tendency, irritable bowel syndrome, and alcoholism. But those compounds failed mainly due to a lack of efficacy or hepatotoxicity [42,79]. Some of the prominent CRF1R antagonists, including antalarmin and verucerfont (Figure 1), contain a bicyclic core ring system where the five-membered ring (pyrrolo/pyrazolo) has an un-modifiable methyl group at C-5 (antalarmin) or C-3 (verucerfont). To compare those compounds with our compounds that are presented in this paper, the best compounds reported in this paper (compounds 2, 5, and 19–21) have N–CH3 group at C-2, which may facilitate metabolism through N-dealkylation followed by conjugation, and thus it may be less hepatotoxic than the other compounds that were advanced to clinical trials. However, further studies are needed to evaluate the hepatotoxicity of our compounds. Thus, the chemical scaffold we developed may potentially have an advantage over existing compounds that were advanced to clinical trials by having a modifiable C-2 position. The receptor binding studies clearly showed that some of our compounds showed superior binding affinity to CRF receptors, and the best one has 2.5-folds higher affinity than antalarmin. It is worth mentioning that, by comparing the binding kinetics of the most renowned CRF1 receptor antagonists evaluated by Fleck et al. [79], it appears that the best one, compound 2, is possibly one of the top CRF1R antagonists ever synthesized in the history of small-molecule CRF1R antagonists in terms of binding affinity. In addition to this, preliminary predictions of drug-able properties demonstrated that most of our best compounds have excellent drug-able properties without violating any basic parameters of Lipinski’s rules of five.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Materials and General Information
All chemicals used in the manuscript were purchased or sourced from chemical companies including Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA), Fisher (Waltham, MA, USA), Oakwood Chemicals (West Columbia, SC, USA), and TCI (Portland, OR, USA). Flash column chromatographic separation and purification were carried out using silica gel 40–60 mm, 60 Å as the stationary phase and different ratios of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether (hexanes) as the eluent. TLC plates (Sigma (Kawasaki, Japan) TLC-99577) were used for thin-layer chromatography. For visualization, the universal visualization systems of UV fluorescence at 254 nm or iodine vapor were used. Mel-Temp Laboratory apparatus was used for melting point determination. A Bruker (Billerica, MA, USA) Avance 600 MHz NMR spectrometer was utilized for 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Deuterated solvents for NMR spectroscopy include DMSO-d6 and CDCl3. Order, multiplicity, number of protons, and signals of NMR were recorded as s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublet of doublet), t (triplet), dt (doublet of triplet), td (triplet of doublet), m (multiplet), br s (broad signal), q (quartet), quin (quintet), tquin (triplet of quintet), sxt (sextet), spt (septet). Chemical shifts were recorded relative to TMS, which was used as the internal standard. MestReNova 6.0.2 and Topspin 4.0.5 NMR software were used for NMR spectra analysis. Mass spectra were recorded using a Bruker Solari X MRMS (Magnetic Resonance Mass Spectrometry) instrument using the electro-spray ionization method, and Bruker Compass Data Analysis 4.2 software was utilized for data reporting.
3.1.2. General Synthetic Procedure for Preparation of Intermediate Compounds (I–IV)
The intermediate compounds I–IV were obtained through four steps: First, the selected 2,4-disubstituted phenyl isothiocyanates were allowed to react with cynoacetamide and sulfur in the presence of triethylamine following the established Gewald-reaction to give the 4-amino-3-substituted phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydrothiazole-5-carboxamide compounds (Ia-d) [58,59]. Second, the thiazoline derivatives (Ia-d) were heated in acetic anhydride at reflux temperature, where they underwent cyclization into the 5-methyl-3-substituted phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7(7aH)-ones (IIa-d), as previously described by Fahmy et al. [60]. Third, the cyclized compounds IIa-d were then subjected to a chlorination reaction using phosphorus oxychloride at reflux temperature [53,60,61] to produce the 7-chloro-5-methyl-3-substituted phenylthiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2(3H)-thione derivatives (IIIa-d). Fourth, these chloro derivatives were then treated with two equivalents of the selected dialkylamine/alkylamine to give the 7-(dialkylamino/alkylamino)-5-methyl-3-substituted phenylbenzo[4,5-d]thiazole-2(3H)-thiones (IVa-w) [53,60,61].
Since most of the intermediate compounds I-III were reported in our previously published papers, in this manuscript, we are reporting the characterization of only intermediates IVa-w (13 compounds).
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4,-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVa)
Yield: Solid 67%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, Acetone) δ 7.79 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.58–7.56 (m, 1H), 3.71 (tt, J = 8.1, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 3.65–3.61 (m, 2H), 2.29 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 3H), 1.71 (tt, J = 7.9, 6.9 Hz, 2H), 1.47–1.40 (m, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.99 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, Acetone) δ 206.17, 189.44, 166.26, 160.33, 155.80, 136.73, 134.72, 134.43, 133.47, 130.95, 129.49, 96.59, 49.11, 44.50, 31.78, 25.77, 20.66, 14.25, 14.17.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVb)
Yield: Solid 70%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.20 (m, 1H), 3.45–3.41 (m, 4H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.65–1.61 (m, 4H), 0.91 (dd, J = 9.3, 5.5 Hz, 6H).
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVc)
Yield: Solid 76%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.61 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.29–7.26 (m, 1H), 3.90–3.85 (m, 4H), 3.63 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 4H), 3.37 (s, 6H), 2.35 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.59, 165.60, 159.47, 155.36, 136.36, 133.96, 132.85, 131.65, 130.67, 128.48, 96.78, 71.04, 59.12, 49.54, 25.70.
7-(N,N-Dipentylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVd)
Yield: Solid 57%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.52 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.20–7.17 (m, 1H), 3.51–3.37 (m, 4H), 2.26 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 3H), 1.69–1.49 (m, 4H), 1.33–1.24 (m, 6H), 0.92–0.88 (m, 2H), 0.84 (tt, J = 7.2, 2.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.73, 165.72, 159.33, 155.01, 136.34, 133.99, 132.95, 131.65, 130.68, 128.46, 96.10, 49.27, 28.93, 25.73, 22.67, 22.51, 14.10.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVe)
Yield: Solid 74%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.36 (m, 1H), 7.23–7.20 (m, 1H), 3.52–3.44 (m, 4H), 2.28 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 3H), 1.69–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.08–1.01 (m, 1H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.54–0.49 (m, 2H), 0.29–0.24 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.85, 165.70, 159.37, 155.25, 136.40, 133.98, 132.87, 131.60, 130.72, 128.47, 96.28, 53.15, 50.99, 25.73, 22.32, 11.09, 10.29, 3.84.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVf)
Yield: Solid 62%;1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 1H), 4.18 (ddd, J = 183.6, 78.0, 45.8 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 1.74–1.66 (m, 2H), 1.58–1.50 (m, 2H), 0.97 (td, J = 7.4, 3.5 Hz, 6H).
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVg)
Yield: Solid 65%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.38 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 4.07 (s, 1H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 1.55–1.27 (m, 8H), 0.87 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.65, 166.62, 155.16, 136.56, 133.99, 132.53, 131.58, 130.78, 128.52, 51.96, 37.90, 25.65, 19.07, 14.06, 14.04.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVh)
Yield: Solid 81%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.56 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.15 (m, 1H), 3.47–3.40 (m, 4H), 2.92 (dq, J = 13.8, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1.67–1.60 (m, 4H), 1.25 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.91 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.97, 165.67, 159.59, 155.08, 152.16, 133.31, 131.84, 130.25, 127.02, 122.47, 96.22, 50.97, 33.84, 25.83, 23.70, 23.66, 22.06, 11.16.
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVi)
Yield: semisolid 77%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.54 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.16–7.14 (m, 1H), 3.80 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 4H), 3.56 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 4H), 3.29 (s, 6H), 2.95–2.86 (m, 1H), 2.27 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 1.23 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.75, 165.54, 159.74, 155.32, 152.18, 133.26, 131.80, 130.28, 127.02, 122.47, 96.80, 71.12, 59.11, 49.51, 33.82, 25.78, 23.71, 23.67.
7-(N,N-Dipentylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVj)
Yield: Semisolid 57%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.53 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.55–3.36 (m, 4H), 2.90 (dt, J = 13.8, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.26 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 3H), 1.63–1.25 (m, 12H), 1.22 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.85 (dd, J = 8.4, 5.9 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.88, 165.64, 159.60, 155.00, 152.09, 133.37, 131.79, 130.29, 126.99, 122.49, 96.16, 77.41, 77.20, 76.99, 49.22, 33.83, 28.94, 25.80, 23.71, 23.67, 22.66, 22.50, 14.09.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVk)
Yield: Solid 78%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.15 (m, 1H), 3.51–3.45 (m, 4H), 2.92 (dt, J = 13.8, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1.70–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.25 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 1.09–1.02 (m, 1H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.53–0.49 (m, 2H), 0.27 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.99, 165.62, 159.64, 155.22, 152.17, 133.30, 131.84, 130.25, 127.03, 122.47, 96.37, 53.13, 50.98, 33.84, 25.82, 23.70, 23.66, 22.34, 11.11, 10.31, 3.84.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVl)
Yield: Solid 58%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.56 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.16 (m, 1H), 5.27–4.09 (m, 1H), 3.84 (s, 1H), 2.92 (dq, J = 13.8, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 1.66–1.58 (m, 2H), 1.51–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.25 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.90 (td, J = 7.4, 4.5 Hz, 6H).
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVm)
Yield: Solid 55%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.56 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.19–7.16 (m, 1H), 4.04 (s, 1H), 2.92 (hept, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 1.56–1.29 (m, 8H), 1.25 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H), 0.87 (td, J = 7.3, 4.2 Hz, 6H).
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVn)
Yield: Solid 79%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.22 (s, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (dd, J = 7.9, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 3.64 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.56–3.51 (m, 2H), 2.41 (s, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 2.04 (s,3H), 1.67 (tt, J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz, 2H), 1.45–1.38 (m, 2H), 1.27 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.00 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.94, 165.77, 159.86, 154.91, 139.75, 135.89, 132.99, 132.10, 128.27, 127.99, 96.27, 48.44, 43.72, 31.15, 31.14, 25.86, 21.43, 20.03, 17.66, 13.93.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVo)
Yield: Solid 74%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.21 (d, J = 0.4 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (dd, J = 7.9, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 3.54–3.48 (m, 4H), 2.40 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 2.04 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 3H), 1.74–1.67 (m, 4H), 0.99 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.91, 165.71, 159.86, 155.09, 139.74, 135.88, 132.99, 132.09, 128.26, 127.98, 96.28, 50.92, 25.86, 22.04, 21.42, 17.66, 11.13.
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVp)
Yield: Solid 82%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.22 (dd, J = 2.6, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (ddd, J = 4.9, 1.6, 0.5 Hz, 1H), 7.06–7.04 (m, 1H), 3.91–3.86 (m, 4H), 3.64 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 4H), 3.38 (s, 6H), 2.41 (s, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 2.04 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.80, 165.61, 160.02, 155.31, 139.81, 135.89, 132.91, 132.11, 128.25, 128.01, 96.89, 59.09, 49.47, 25.81, 21.42, 17.66.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVq)
Yield: Solid 76%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.14 (s, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.00–6.97 (m, 1H), 3.48 (dd, J = 15.8, 7.4 Hz, 4H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96 (s,3H), 1.69–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.08–1.01 (m, 1H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.51 (q, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 0.27 (q, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.97, 165.67, 159.91, 155.22, 139.80, 135.92, 133.00, 132.14, 128.30, 128.03, 96.48, 53.14, 50.98, 25.86, 22.36, 21.47, 17.70, 11.12, 10.34, 3.85.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVr)
Yield: Solid 58%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.15 (s, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 4.06–3.58 (m, 1H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 1.97 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 3H), 1.66–1.58 (m, 2H), 1.51–1.43 (m, 2H), 0.90 (td, J = 7.4, 2.8 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 188.89, 166.37, 159.42, 155.07, 139.98, 135.94, 132.64, 132.19, 128.29, 128.08, 54.75, 27.83, 25.66, 21.46, 17.70, 10.23.
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVs)
Yield: Solid 61%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.14 (s, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.00–6.98 (m, 1H), 4.36–3.70 (m, 1H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 1.98 (s, 3H), 1.56–1.49 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.28 (m, 6H), 0.86 (td, J = 7.3, 2.8 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.84, 167.45, 160.44, 150.55, 139.98, 135.95, 132.64, 132.39, 132.19, 128.29, 128.08, 37.90, 25.63, 21.46, 19.09, 17.71, 14.07, 14.05.
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethyl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVt)
Yield: Solid 73%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.09 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (dt, J = 8.5, 2.8 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.64 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.56–3.51 (m, 2H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.67 (tt, J = 7.9, 6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.42 (dq, J = 14.8, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 1.27 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.00 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.25, 165.78, 160.19, 159.95, 154.93, 137.68, 129.57, 128.25, 116.42, 112.45, 96.19, 55.32, 48.45, 43.72, 31.13, 25.87, 20.03, 18.07, 13.93.
7-(N,N-Dipropyl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVu)
Yield: Solid 70%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.01 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85–6.84 (m, 1H), 6.83–6.80 (m, 1H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 3.47–3.39 (m, 4H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.97 (s,, 3H), 1.67–1.59 (m, 4H), 0.91 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.24, 165.73, 160.21, 159.97, 155.12, 137.69, 129.59, 128.27, 116.43, 112.47, 96.24, 55.35, 50.96, 25.89, 22.07, 18.09, 11.16.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVv)
Yield: Solid 82%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.09 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.56 (dd, J = 15.8, 7.4 Hz, 4H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.77–1.70 (m, 2H), 1.16–1.09 (m, 1H), 1.00 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.61–0.56 (m, 2H), 0.34 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.26, 165.69, 160.21, 160.04, 155.27, 137.68, 129.59, 128.27, 116.43, 112.48, 96.37, 55.36, 53.12, 50.96, 25.90, 22.36, 18.10, 11.12, 10.34, 3.85.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-thioxo-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (IVw)
Yield: Solid 55%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 4.97–4.12 (m, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.06 (s, 3H), 1.74–1.65 (m, 2H), 1.58–1.50 (m, 2H), 0.97 (td, J = 7.4, 3.2 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.20, 166.62, 160.30, 155.31, 137.73, 129.60, 127.92, 116.48, 112.53, 55.36, 44.95, 27.85, 25.85, 18.10, 10.22.
3.1.3. General Synthetic Procedure for the Preparation of Final Targeted Compounds
1 mmole solution of the selected IV in 20 mL of acetonitrile was allowed to react at reflux temperature with 3.0 mmoles of dimethyl sulfate for a period of ten hours. Additional dimethyl sulfate (3.0 mmol) was then added, and the mixture was stirred under reflux while the reaction was monitored by TLC till completion. After the reaction mixture was left to cool down to room temperature, triethylamine (12 equivalents) was added, followed by the addition of methylamine hydrochloride (12 equivalents), and the reaction mixture was continuously stirred for ten hours. After confirming the reaction completion by TLC, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Water was then added to the residue, and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate. After several extractions, the ethyl acetate was combined, washed with water and brine solution, and then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Finally, the ethyl acetate was removed by evaporation in a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure. The remaining residue was then subjected to chromatographic purification using flash column chromatography. The solvent mixture used was ethyl acetate and hexane. Finally, the pure final 2-alkylamino compounds (1–23) were characterized by a variety of spectroscopic tools, including proton and carbon NMR and high-resolution mass spectroscopy, as listed below.
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (1)
Yield: Solid 44%; MP: 66 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.44 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.19 (m, 1H), 3.53 (dt, J = 8.3, 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.47–3.43 (m, 2H), 2.95 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.58–1.53 (m, 2H), 1.33–1.27 (m, 2H), 1.14 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.89 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.34, 158.49, 155.15, 153.45, 135.34, 134.54, 133.05, 132.34, 130.56, 128.31, 89.08, 48.19, 43.50, 40.38, 31.44, 25.82, 20.13, 14.40, 14.06; HRMS (ES+) calculated C19H24Cl2N5S for [M + H]+ 424.1123; found: 424.1128.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (2)
Yield: Solid 48%; MP: 66 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.44 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.26 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.44–3.40 (m, 4H), 2.95 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.62–1.56 (m, 4H), 0.87 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.27, 158.44, 155.30, 153.55, 135.36, 134.49, 132.94, 132.25, 130.58, 128.32, 89.10, 50.73, 40.32, 25.78, 22.37, 11.18..; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C19H24Cl2N5S [M + H]+: 424.1123; found: 424.1133.
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (3)
Yield: Solid 50%; MP: 88–89 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.48 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 3.81 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 4H), 3.56 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 4H), 3.31 (s, 6H), 2.97 (s, 3H), 2.22 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.27, 158.65, 155.28, 153.14, 135.43, 134.44, 132.85, 132.14, 130.69, 130.54, 128.28, 89.64, 71.79, 59.18, 49.48, 40.44, 25.82; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C19H24Cl2N5O2S [M + H]+: 456.1022; found: 456.1028.
7-(N,N-Dipentylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (4)
Yield: Solid 49%; MP: 72–74 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.43 (m, 1H), 7.27–7.24 (m, 1H), 7.21 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 3.52–3.40 (m, 4H), 2.97–2.94 (m, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.61–1.43 (m, 4H), 1.33–0.89 (m, 8H), 0.84 (ddd, J = 7.5, 5.4, 3.3 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.30, 158.49, 155.25, 153.46, 135.32, 134.54, 133.06, 132.31, 130.56, 128.30, 89.08, 49.01, 40.36, 29.00, 25.75, 22.53, 14.14; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C23H32Cl2N5S [M + H]+: 480.1749; found: 480.1754.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (5)
Yield: Solid 52%; MP: 54–56 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.47 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.51 (dd, J = 9.1, 6.7 Hz, 2H), 3.45 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 1.67–1.61 (m, 2H), 1.08–1.01 (m, 1H), 0.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.50–0.46 (m, 2H), 0.24 (q, J = 4.9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.25, 158.53, 155.44, 153.50, 135.37, 134.49, 132.96, 132.26, 130.58, 128.32, 89.31, 52.91, 50.67, 40.35, 25.78, 22.56, 11.14, 10.64, 3.77; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C20H24Cl2N5S [M + H]+: 436.1123; found: 436.1131.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (6)
Yield: Solid 44%; MP: 88–89 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.49 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.93 (s, 1H), 2.99 (s, 3H), 2.79 (dd, J = 21.2, 17.3 Hz, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.64–1.56 (m, 2H), 1.48–1.41 (m, 2H), 0.89 (td, J = 7.2, 3.2 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.26, 157.86, 155.41, 153.07, 135.54, 134.47, 132.66, 132.15, 130.63, 128.36, 89.81, 54.14, 40.85, 27.88, 25.79, 10.13, 10.12; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C18H22Cl2N5S [M + H]+: 410.0967; found: 410.0977.
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (7)
Yield: Solid 42%; MP: 106 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.48 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (s, 1H), 2.97 (s, 3H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 1.53–1.46 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.25 (m, 7H), 0.86 (td, J = 7.2, 3.0 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.27, 157.81, 155.32, 153.08, 135.51, 134.49, 132.70, 132.18, 130.62, 128.34, 89.72, 60.43, 40.86, 38.43, 38.11, 25.80, 19.06, 19.04, 14.15, 14.13; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C20H26Cl2N5S [M + H]+: 438.1280; found: 438.1288.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (8)
Yield: Solid 55%; MP: 60–62 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.44 (s, 1H), 7.17–7.14 (m, 2H), 3.44–3.35 (m, 4H), 2.94 (s, 3H), 2.83–2.77 (m, 1H), 2.17 (s, 3H), 1.60–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.15 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.83 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.18, 158.91, 155.29, 153.73, 150.91, 133.53, 131.75, 131.23, 126.99, 123.41, 89.12, 53.67, 50.75, 40.50, 33.80, 25.82, 23.77, 22.47, 11.25; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C22H31BrN5S [M + H]+: 476.1478; found: 476.1484.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (9)
Yield: Solid 50%; MP: 83–84 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.48 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.53–3.47 (m, 2H), 3.46–3.40 (m, 2H), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.87–2.81 (m, 1H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.67–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.19 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H), 1.07–1.00 (m, 1H), 0.88 (dd, J = 13.8, 6.3 Hz, 3H), 0.49–0.44 (m, 2H), 0.23 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.18, 158.94, 155.42, 153.92, 150.99, 133.41, 131.78, 131.01, 126.99, 123.32, 89.36, 52.90, 50.66, 40.54, 33.79, 25.88, 23.75, 23.72, 22.59, 11.18, 10.68, 3.81; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C23H31BrN5S [M + H]+: 488.1478; found: 488.1487.
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (10)
Yield: Solid 47%; MP: 76–77 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.49 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.20–7.17 (m, 1H), 3.81 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 4H), 3.56 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 4H), 3.30 (s, 6H), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.85 (dt, J = 18.3, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 1.20 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.23, 159.02, 155.24, 153.73, 151.13, 147.88, 133.21, 131.74, 130.97, 127.07, 123.23, 89.65, 71.71, 58.78, 49.29, 40.53, 33.77, 26.13, 23.79; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C22H31BrN5O2S [M + H]+: 508.13763554; found: 508.1384.
7-(N,N-Dipentylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (11)
Yield: Solid 60%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.49 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.24–7.21 (m, 1H), 7.20 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 3.53–3.42 (m, 4H), 3.00–2.98 (m, 3H), 2.86 (dt, J = 13.8, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.22 (d, J = 0.7 Hz, 3H), 1.63–1.45 (m, 4H), 1.34–1.24 (m, 6H), 1.20 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.92–0.89 (m, 2H), 0.88–0.84 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.22, 158.85, 155.21, 154.07, 150.97, 133.39, 131.81, 130.94, 127.01, 123.27, 89.12, 48.94, 40.54, 33.77, 28.99, 28.94, 28.79, 26.25, 25.88, 25.85, 23.72, 23.69, 22.72, 22.51, 16.92, 14.12; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C26H39BrN5S [M + H]+: 532.2104; found: 532.2107.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (12)
Yield: Solid 48%; MP: 77–78 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.49 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.93 (s, 1H), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.88–2.83 (m, 1H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 1.62–1.53 (m, 2H), 1.47–1.39 (m, 2H), 1.19 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H), 0.88 (td, J = 7.5, 4.6 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.19, 158.22, 155.37, 153.64, 151.23, 133.09, 131.83, 130.93, 127.02, 123.27, 89.88, 53.87, 40.99, 33.78, 27.86, 25.85, 23.71, 23.69, 10.17, 10.14; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H29BrN5S [M + H]+: 462.1321; found: 462.1329.
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-bromo-4-isopropylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (13)
Yield: Solid 46%; MP: 65–66 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.49 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.19 (m, 2H), 4.12 (s, 1H), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.87–2.82 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.52–1.44 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.27 (m, 6H), 1.19 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H), 0.85 (td, J = 7.2, 4.3 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.19, 158.18, 155.28, 153.64, 151.16, 133.13, 131.87, 131.82, 130.98, 130.93, 130.88, 127.06, 127.01, 126.96, 123.29, 89.74, 41.03, 38.07, 33.78, 26.22, 26.04, 25.77, 23.92, 23.72, 23.53, 19.07, 14.17; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C23H33BrN5S [M + H]+: 490.1634; found: 490.1639.
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (14)
Yield: Semisolid 44%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.23 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.7 Hz, 2H), 3.77 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.71–3.68 (m, 2H), 3.19 (s, 3H), 2.47 (s, 3H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 1.83–1.77 (m, 2H), 1.57–1.50 (m, 2H), 1.38 (dd, J = 8.5, 5.6 Hz, 3H), 1.13 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.38, 159.39, 155.18, 154.31, 138.65, 136.38, 133.07, 132.08, 132.00, 129.17, 127.88, 89.08, 48.21, 43.52, 40.63, 40.60, 31.56, 25.70, 20.21, 17.96, 17.53, 14.29; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H30N5S [M + H]+: 384.2216; found: 384.2229.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (15)
Yield: Semisolid 42%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.26–7.22 (m, 2H), 3.71–3.63 (m, 4H), 3.20 (s, 3H), 2.47 (s, 3H), 2.45 (s, 3H), 2.23 (s, 3H), 1.87–1.80 (m, 4H), 1.14–1.08 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.33, 159.42, 155.36, 154.21, 138.63, 136.39, 133.09, 132.03, 129.16, 127.88, 89.12, 60.37, 50.83, 40.59, 26.01, 22.56, 21.42, 21.04, 17.98, 14.36, 11.31; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H29N5NaS [M + Na]+: 406.2035; found: 406.2048.
7-(N,N-Bis(2-methoxyethyl)amino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (16)
Yield: Solid 30%; MP: 103–104 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.07 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 4H), 3.56 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 4H), 3.31 (s, 6H), 2.96 (s, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.99 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.30, 159.46, 155.22, 154.07, 138.79, 136.26, 132.75, 132.04, 128.93, 127.89, 89.60, 71.75, 59.09, 49.28, 40.60, 25.90, 21.37, 17.88; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H29N5NaO2S [M + Na]+: 438.1934; found: 438.1936.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (17)
Yield: Solid 50%; MP: 61–63 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.01 (s, 1H), 7.00–6.96 (m, 2H), 3.50–3.44 (m, 2H), 3.41 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 2.93 (s, 3H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 1.96 (s, 3H), 1.60 (dq, J = 15.1, 7.3 Hz, 2H), 1.04–0.97 (m, 1H), 0.85 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 0.45–0.40 (m, 2H), 0.20 (q, J = 4.9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.28, 159.43, 155.45, 154.25, 138.67, 136.38, 133.03, 132.04, 129.12, 127.89, 89.31, 52.97, 50.74, 40.62, 25.98, 22.70, 21.43, 17.96, 11.26, 10.82, 3.91, 3.90; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C22H30N5S [M + H]+: 396.2216; found: 396.2227.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (18)
Yield: Solid 48%; MP: 66 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.04 (s, 1H), 7.02–6.98 (m, 2H), 4.24 (s, 1H), 3.93 (s, 1H), 2.94 (s, 3H), 2.23 (s, 6H), 1.99 (s, 3H), 1.54 (td, J = 13.5, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.39 (dtd, J = 12.4, 7.3, 5.1 Hz, 2H), 0.85 (td, J = 7.4, 4.2 Hz, 6H); HRMS (ES+) calculated for C20H28N5S [M + H]+: 370.2059; found: 370.2072.
7-(N-Heptan-4-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (19)
Yield: Semisolid 46%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.05 (d, J = 0.7 Hz, 1H), 7.03–6.99 (m, 2H), 4.22–3.99 (m, 2H), 2.95 (s, 3H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.23 (s, 3H), 2.00 (s, 3H), 1.54–1.24 (m, 8H), 0.84 (td, J = 7.2, 3.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.25, 158.60, 155.26, 154.07, 138.84, 136.33, 132.67, 132.06, 128.97, 127.88, 89.66, 60.43, 41.04, 38.19, 38.17, 25.94, 21.37, 19.11, 19.09, 17.92, 14.19, 14.17; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C22H32N5S [M + H]+: 398.2372; found: 398.2383.
7-(N-Butyl-N-ethylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (20)
Yield: Semisolid 36%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.02 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.65 (s, 3H), 3.52 (dd, J = 14.1, 6.9 Hz, 2H), 3.47–3.41 (m, 2H), 2.94 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.98 (s, 3H), 1.55 (dt, J = 15.2, 7.7 Hz, 2H), 1.33–1.25 (m, 2H), 1.13 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.88 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.34, 159.60, 159.43, 155.13, 154.57, 138.03, 130.26, 128.30, 116.37, 112.41, 88.99, 55.25, 48.16, 43.47, 40.56, 31.50, 25.97, 20.15, 18.28, 14.44, 14.09; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H30N5OS [M + H]+: 400.2165; found: 400.2176.
7-(N,N-Dipropylamino)-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (21)
Yield: Semisolid 51%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.01 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.73 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 3.65 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 3H), 3.45–3.37 (m, 4H), 2.93 (s, 3H), 2.19 (s, 3H), 1.97 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H), 1.57 (dq, J = 15.1, 7.4 Hz, 4H), 0.85 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.27, 159.60, 159.44, 155.29, 154.48, 138.01, 130.25, 128.29, 116.34, 112.39, 89.01, 55.23, 50.75, 40.51, 25.95, 22.47, 18.26, 11.24; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C21H30N5OS [M + H]+: 400.2165; found: 400.2176.
7-(N-Propyl-N-(cyclopropylmethyl))amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (22)
Yield: Solid 54%; MP: 89–91 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.02 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 3.65 (s, 3H), 3.51–3.46 (m, 2H), 3.42 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 2.94 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.98 (s, 3H), 1.61 (dq, J = 15.1, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.05–0.98 (m, 1H), 0.86 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 0.46–0.41 (m, 2H), 0.21 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.24, 159.60, 159.50, 155.41, 154.48, 138.02, 130.25, 128.28, 116.36, 112.41, 89.22, 55.26, 52.93, 50.69, 40.57, 25.95, 22.64, 18.28, 11.21, 10.76, 3.86, 3.84; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C22H30N5OS [M + H]+: 412.2165; found: 412.2175.
7-(N-Pentan-3-yl)amino-2-(methylimino)-5-methyl-3-(2-methyl-4-methoxylphenyl)-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine (23)
Yield: Solid 48%; MP: 41 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.03 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 4.35 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.94 (m, 1H), 3.64 (s, 3H), 2.92 (s, 3H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 1.98 (s, 3H), 1.57–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.41–1.32 (m, 2H), 0.88–0.78 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.19, 159.67, 158.65, 155.40, 154.37, 138.06, 130.24, 128.02, 116.35, 112.37, 89.79, 60.40, 40.93, 27.83, 25.92, 21.02, 18.22, 14.25, 10.25; HRMS (ES+) calculated for C20H28N5OS [M + H]+: 386.2009; found: 386.2021.
3.2. Biological Evaluation
In this protocol, a radiolabeled agonist, which is [125I]-Tyr0-sauvagine is used. The cell culture medium that was used to grow these cells consisted of DMEM/F12 (1:1) supplemented with 10% bovine calf serum, 3.15 g/L glucose, and 300 mg/mL of the antibiotic geneticin. The cells were then incubated at a temperature of 37 °C with 5% CO2. After a suitable time was given to grow the expected number of cells to the required cell density, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a neutral pH of 7.2–7.3. This was followed by treatment with 2 mM EDTA containing PBS (PBS/EDTA). The suspension of cells was pitted under centrifugation at a speed of 1000× g for a period of 5 min, after which the resulting pellets were allowed to be homogenized in 1.5 mL of buffer H with the following composition: 20 mM HEPES, 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM EGTA, 0.2 mg/mL bacitracin antibiotic, and 0.93 mg/mL aprotinin at pH 7.2 at 4 °C. The homogenizer used was a Janke & Kunkel IKA Ultra Turrax T25 homogenizer (IKA Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen, Germany). The homogenates were then put into a centrifuge to be centrifuged at a speed of 16,000× g, for a period of 10 min, at 4 °C. The resulting membrane pellets were again suspended in a homogenizer in 1 mL of buffer B, which is buffer H containing BSA (0.1%) at a pH of 7.2 at 20 °C. After that, the membrane suspensions were diluted using buffer B and 50 μL aliquots of the suspensions and 20–25 pM of the radiolabeled ligand [125I]-Tyr0sauvagine with (test) and then without (positive control) the compounds to be evaluated at a single concentration of 100 nM.
A secondary assay was carried out to determine the competitive binding affinities of the best compounds chosen from the first assay. In this competitive binding assay, different and increasing concentrations of the test compounds were used. The final volume of the tubes was adjusted to 0.2 mL using buffer B (the composition mentioned earlier). The test mixtures were then incubated at a temperature of 21 °C for a period of two hours. Then it was filtered through presoaked Whatman 934AH filter papers (in a solution of 0.3% polyethylene imine for 1 h at a temperature of 4 °C). The filter papers were then washed with a solution of 0.5 mL of ice-cold PBS containing 0.01% Triton X-100, and the washing process was repeated three times at pH 7.1. To measure the radioactivity, a gamma radiation counter was utilized. The quantity of membranes used was adjusted to make sure that the specific binding is always equal to or less than 10% of the total concentration of the added radiolabeled sauvagine. The specific [125I]-Tyr0-sauvagine binding was defined as the total binding minus the non-specific binding in the presence of 1000 nM of the standard antagonist Antalarmin. Non-linear regression analysis was used for data analysis, and Log IC50 values for the test compounds in comparison to the standard antagonist antalarmin were calculated by fitting the data from the competition studies into a one-site competition model. The statistical analysis was performed using Prism 4.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3.3. Physicochemical Properties and ADME Analysis
The physicochemical properties and BBB permeability of our designed and synthesized compounds were predicted using the Swiss ADME online tool (http://www.swissadme.ch/, accessed on 30 March 2022) and Light BBB (http://bioanalysis.cau.ac.kr:7030/, accessed on 30 March 2022), respectively. The structures of compounds were drawn using ChemDraw Ultra 12.0 software.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 4.0 (Graph Pad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Non-linear regression analysis was used in the competitive binding studies. Log IC50 values were calculated by fitting the data from the competition studies to a one-site competition model.
4. Conclusions
Based on SAR studies of our previously published work, a series of 2,3-dihydrothiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives were synthesized. Some representative compounds were evaluated for their binding affinity to the CRF1 receptors as a part of our ongoing research to develop CRF1 receptor antagonists with superior binding affinity. These compounds were designed to have a basic pharmacophore for optimum binding affinity to CRF1 receptors, including a substituted phenyl at position N-3, a methyl group at position C-5, and a dialkylamino group at position C-7. The binding affinity of newly synthesized compounds was evaluated in two different experiments. The compounds were screened in a primary assay by measuring their ability to inhibit the specific binding of [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine to membranes from HEK 293 cells stably expressing the CRF1 receptors. A secondary assay was performed by determining the competitive binding affinity of select compounds in comparison to the standard drug, antalarmin. Nine compounds (compounds 2, 5, 10, 14, and 19–23) from the synthesized compounds have shown their ability to inhibit more than 50% of [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine binding. These nine compounds were able to inhibit [125I]-Tyr0 sauvagine binding to CRF1 receptors in a dose-dependent manner, with Log IC50 ± SE values of −8.22 ± 0.33, −7.95 ± 0.26, −7.51 ± 0.15, −6.84 ± 0.09, −7.39 ± 0.34, −8.04 ± 0.16, −7.88 ± 0.09, −7.04 ± 0.24, and −6.95 ± 0.12 for the compounds 2, 5, 10, 14, 19, 20, 21, 22, and 23, respectively, compared to the Log IC50 ± SE value of −7.78 ± 0.21 for the standard drug antalarmin.
Four compounds (compounds 2, 5, 20, 21) from the synthesized compounds have shown better inhibitory effects than antalarmin. The best compound (compound 2) is 2.5 times more potent than antalarmin in terms of IC50, which is a great achievement. It can be argued that compound 2 may be one of the top small-molecule non-peptide CRF1R antagonists (in terms of IC50) ever developed. In silico prediction of physicochemical properties showed that all of our best lead compounds (compounds 2, 5, 19, 20) are predicted to have better drug-like properties (no violation of Lipinski’s rule) than the standard drug antalarmin (one violation of Lipinski’s rule), and these compounds are also predicted to have the ability to cross BBB. It can be concluded that this study resulted in the development of four compounds with excellent binding affinity and inhibitory effects and better druggable properties. This excellent binding affinity is not only compared to our previous compounds [53,54], but also compared to any other compound developed in the last 40 years of the history of small molecule CRF1R antagonists. Thus, further research in this direction may lead to the development of compounds that can be drug candidates for stress-related disorders and congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29153647/s1, Compounds characterization: 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HRMS spectrum of all the target compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: H.F. and G.L.; Methodology, M.R.I., C.M., I.P., M.P. and V.K.; Formal analysis: M.R.I., C.M. and V.K.; Data curation; G.L.; Writing-original draft: M.R.I.; Writing, review and editing: H.F.; Supervision and Project administration: H.F. and G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Spiess, J.; Rivier, J.; Rivier, C.; Vale, W. Primary structure of corticotropin-releasing factor from ovine hypothalamus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6517–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, M.J.; Nemeroff, C.B. Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin-releasing factor. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 425–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amano, M. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone. In Handbook of Hormones: Comparative Endocrinology for Basic and Clinical Research; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.L.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, M.; Kori, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Yano, T.; Sako, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kanzaki, N.; Gyorkos, A.C. Design and Synthesis of Benzimidazoles As Novel Corticotropin-Releasing Factor 1 Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2551–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raadsheer, F.C.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; Stam, F.C.; Tilders, F.J.; Swaab, D.F. Increased numbers of corticotropin-releasing hormone expressing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of depressed patients. Neuroendocrinology 1994, 60, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossey, M.D.; Lydiard, R.B.; Ballenger, J.C.; Laraia, M.T.; Bissette, G.; Nemeroff, C.B. Cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin-releasing factor concentrations in patients with anxiety disorders and normal comparison subjects. Biol. Psychiatry 1996, 39, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, T.L.; Vale, W.W. CRF and CRF receptors: Role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, E.B. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors: Physiology, pharmacology, biochemistry and role in central nervous system and immune disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1995, 20, 789–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautzenberg, F.M.; Hauger, R.L. The CRF peptide family and their receptors: Yet more partners discovered. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Liaw, C.W.; Grigoriadis, D.E.; Clevenger, W.; Chalmers, D.T.; De Souza, E.B.; Oltersdorf, T. Cloning and characterization of a functionally distinct corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadis, D.E. The corticotropin-releasing factor receptor: A novel target for the treatment of depression and anxiety-related disorders. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 651–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, P.W.; Chrousos, G.P. Organization of the stress system and its dysregulation in melancholic and atypical depression: High vs low CRH/NE states. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, M.E.; Holsboer, F. Hyperactivity of CRH neuronal circuits as a target for therapeutic interventions in affective disorders. Peptides 2001, 22, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reul, J.M.; Holsboer, F. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors 1 and 2 in anxiety and depression. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautzenberg, F.M.; Kilpatrick, G.J.; Hauger, R.L.; Moreau, J. Molecular biology of the CRH receptors—In the mood. Peptides 2001, 22, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behan, D.P.; Heinrichs, S.C.; Troncoso, J.C.; Liu, X.J.; Kawas, C.H.; Ling, N.; De Souza, E.B. Displacement of corticotropin releasing factor from its binding protein as a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 1995, 378, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrigiannakis, A.; Zoumakis, E.; Kalantaridou, S.; Coutifaris, C.; Margioris, A.N.; Coukos, G.; Rice, K.C.; Gravanis, A.; Chrousos, G.P. Corticotropin-releasing hormone promotes blastocyst implantation and early maternal tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.; Rivier, J.; Wang, L.; Tache, Y. Central injection of a new corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) antagonist, astressin, blocks CRF- and stress-related alterations of gastric and colonic motor function. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Torpy, D.J.; Gold, P.W. Interactions between the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the female reproductive system: Clinical implications. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.N. Corticotropin-releasing hormone in humans. Endocr. Rev. 1992, 13, 164–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, D.G.; Weisinger, R.S.; May, C.N. Cardiovascular actions of CRH and urocortin: An update. Peptides 2001, 22, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venihaki, M.; Majzoub, J.A. Animal models of CRH deficiency. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1999, 20, 122–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venihaki, M.; Dikkes, P.; Carrigan, A.; Karalis, K.P. Corticotropin-releasing hormone regulates IL-6 expression during inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoumakis, E.; Margioris, A.N.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Stournaras, C.; Gravanis, A. Human endometrium as a neuroendocrine tissue: Expression, regulation and biological roles of endometrial corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and opioid peptides. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1997, 20, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolber, B.J.; Roberts, M.S.; Howell, M.P.; Wozniak, D.F.; Sands, M.S.; Muglia, L.J. Central amygdala glucocorticoid receptor action promotes fear-associated CRH activation and conditioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12004–12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.A.; Kucenas, S.; Bowman, T.A.; Ruhlman, M.; Knuepfer, M.M. Angiotensin II and CRF receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala mediate hemodynamic response variability to cocaine in conscious rats. Brain Res. 2010, 1309, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnyai, Z.; Biro, E.; Gardi, J.; Vecsernyes, M.; Julesz, J.; Telegdy, G. Brain corticotropin-releasing factor mediates ‘anxiety-like’ behavior induced by cocaine withdrawal in rats. Brain Res. 1995, 675, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofford, L.J.; Sano, H.; Karalis, K.; Webster, E.L.; Goldmuntz, E.A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Wilder, R.L. Local secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone in the joints of Lewis rats with inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 2555–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofford, L.J.; Sano, H.; Karalis, K.; Friedman, T.C.; Epps, H.R.; Remmers, E.F.; Mathern, P.; Chrousos, G.P.; Wilder, R.L. Corticotropin-releasing hormone in synovial fluids and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikanza, I.C.; Petrou, P.; Kingsley, G.; Chrousos, G.; Panayi, G.S. Defective hypothalamic response to immune and inflammatory stimuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.K.; Woods, J.H. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-1: A therapeutic target for cardiac autonomic disturbances. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, S.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Xue, B.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Hyperexcitation of ovBNST CRF neurons during stress contributes to female-biased expression of anxiety-like avoidance behaviors. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarguen-Vargas, Y.; Leman, S.; Palme, R.; Belzung, C.; Surget, A. CRF-R1 Antagonist Treatment Exacerbates Circadian Corticosterone Secretion under Chronic Stress, but Preserves HPA Feedback Sensitivity. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xiang, S.; Jiang, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhou, W.; Lian, Q.; Wu, B. The Antagonism of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor-1 in Brain Suppress Stress-Induced Propofol Self-Administration in Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 775209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Reveron, A.; Rivera-Lopez, L.L.; Flores, I.; Appleyard, C.B. Antagonizing the corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1 with antalarmin reduces the progression of endometriosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Fitzgerald, L.; Wong, H.; Lelas, S.; Zhang, G.; Lindner, M.D.; Wallace, T.; McElroy, J.; Lodge, N.J.; Gilligan, P.; et al. The pharmacology of DMP696 and DMP904, non-peptidergic CRF1 receptor antagonists. CNS Drug Rev. 2005, 11, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelas, S.; Wong, H.; Li, Y.W.; Heman, K.L.; Ward, K.A.; Zeller, K.L.; Sieracki, K.K.; Polino, J.L.; Godonis, H.E.; Ren, S.X.; et al. Anxiolytic-like effects of the corticotropin-releasing factor1 (CRF1) antagonist DMP904 [4-(3-pentylamino)-2,7-dimethyl-8-(2-methyl-4-methoxyphenyl)-pyrazolo-[1,5-a]-pyr imidine] administered acutely or chronically at doses occupying central CRF1 receptors in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabbi, M.J.; Razaghi, E.; Moazen-Zadeh, E.; Safi-Aghdam, H.; Zarrindast, M.R.; Vousoghi, N.; Akhondzadeh, S. Pexacerfont as a CRF1 antagonist for the treatment of withdrawal symptoms in men with heroin/methamphetamine dependence: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 33, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ising, M.; Zimmermann, U.S.; Kunzel, H.E.; Uhr, M.; Foster, A.C.; Learned-Coughlin, S.M.; Holsboer, F.; Grigoriadis, D.E. High-affinity CRF1 receptor antagonist NBI-34041: Preclinical and clinical data suggest safety and efficacy in attenuating elevated stress response. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 32, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Koob, G.F. Progress in corticotropin-releasing factor-1 antagonist development. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierling, S.R.; Zorrilla, E.P. Don’t stress about CRF: Assessing the translational failures of CRF1antagonists. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auchus, R.J.; Sarafoglou, K.; Fechner, P.Y.; Vogiatzi, M.G.; Imel, E.A.; Davis, S.M.; Giri, N.; Sturgeon, J.; Roberts, E.; Chan, J.L.; et al. Crinecerfont Lowers Elevated Hormone Markers in Adults With 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, M.A.M.; Claahsen—Van der Grinten, H.L. Novel treatments for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisch, N. Review of Health Problems in Adult Patients with Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, E.; Falhammar, H. Glucocorticoid Regimens in the Treatment of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1227–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcu, A.F.; Auchus, R.J. The next 150 years of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafoglou, K.; Forlenza, G.P.; Yaw Addo, O.; Kyllo, J.; Lteif, A.; Hindmarsh, P.C.; Petryk, A.; Gonzalez-Bolanos, M.T.; Miller, B.S.; Thomas, W. Obesity in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia in the Minnesota cohort: Importance of adjusting body mass index for height-age. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 86, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, A.; Auchus, R.J.; Ross, R.J. Clinical advances in the pharmacotherapy of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 186, R1–R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newfield, R.S.; Sarafoglou, K.; Fechner, P.Y.; Nokoff, N.J.; Auchus, R.J.; Vogiatzi, M.G.; Jeha, G.S.; Giri, N.; Roberts, E.; Sturgeon, J.; et al. Crinecerfont, a CRF1 Receptor Antagonist, Lowers Adrenal Androgens in Adolescents With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrousos, G.P. Crinecerfont in a First Clinical Application of a CRH Antagonist: Further Potential Uses Are Still an Open Chapter! J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e1365–e1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800050153 (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Teleb, M.; Kuppast, B.; Spyridaki, K.; Liapakis, G.; Fahmy, H. Synthesis of 2-imino and 2-hydrazono thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines as corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) antagonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppast, B.; Spyridaki, K.; Lynch, C.; Hu, Y.; Liapakis, G.; Davies, G.E.; Fahmy, H. Synthesis of new thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines as Corticotropin releasing factor modulators. Med. Chem. 2014, 11, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuppast, B.; Spyridaki, K.; Liapakis, G.; Fahmy, H. Synthesis of substituted pyrimidines as corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Teleb, M.; Karageorgos, V.; Sakellaris, S.; Papadopoulos, M.; Pirmettis, I.; Fronczek, F.R.; Liapakis, G.; Fahmy, H. Design, synthesis, structural optimization, SAR, in silico prediction of physicochemical properties and pharmacological evaluation of novel & potent thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 169, 106084. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Obach, R.S.; Braselton, J.; Corman, M.L.; Forman, J.; Freeman, J.; Gallaschun, R.J.; Mansbach, R.; Schmidt, A.W.; Sprouse, J.S.; et al. 2-aryloxy-4-alkylaminopyridines: Discovery of novel corticotropin-releasing factor 1 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewald, K.; Hain, U. Zur Chemie der 4-aminothiazolin-2-thione. Monatshefte Fur Chem. 1981, 112, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewald, K.; Hain, U.; Schindler, R. ZurChemie der 4-Amino-thiazolin-2-thione. Mitt. Monatsh. Fur Chem. Chem. Mon. 1994, 125, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.T.; Rostom, S.A.; Saudi, M.N.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Robins, D.J. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of the anticancer activity of novel fluorinated thiazolo[4, 5-d]pyrimidines. Arch. Der Pharm. 2003, 336, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawey, E.; Rida, S.M.; Hazza, A.A.; Fahmy, H.T.; Gohar, Y.M. Potential antimicrobials.II. Synthesis and in vitro anti-microbial evaluation of some thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 28, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountelias, K.; Tselios, T.; Venihaki, M.; Deraos, G.; Lazaridis, I.; Rassouli, O.; Gravanis, A.; Liapakis, G. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of the second extracellular loop of type 1 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor revealed residues critical for peptide binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Peng, J.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, X.; Luo, X.; Luo, C.; Chen, K.; et al. In silico ADME/T modelling for rational drug design. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 48, 488–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, B.; Yu, M.S.; Song, J.S.; Ahn, S.; Ryu, J.Y.; Oh, K.S.; Na, D. LightBBB: Computational prediction model of blood-brain-barrier penetration based on LightGBM. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Gold, P.W. The concepts of stress and stress system disorders. Overview of physical and behavioral homeostasis. JAMA 1992, 267, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivier, C.; Vale, W. Modulation of stress-induced ACTH release by corticotropin-releasing factor, catecholamines and vasopressin. Nature 1983, 305, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 53, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasipe, O. Neuropharmacological classification of antidepressant agents based on their mechanisms of action. Arch. Med. Health Sci. 2018, 6, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, K.S. Treatment-resistant depression: Therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2012, 6, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, G.A. May antidepressant drugs worsen the conditions they are supposed to treat? The clinical foundations of the oppositional model of tolerance. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 10, 2045125320970325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagán-Busigó, J.E.; López-Carrasquillo, J.; Appleyard, C.B.; Torres-Reverón, A. Beyond depression and anxiety; a systematic review about the role of corticotropin-releasing hormone antagonists in diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auchus, R.J.; Hamidi, O.; Pivonello, R.; Bancos, I.; Russo, G.; Witchel, S.F.; Isidori, A.M.; Rodien, P.; Srirangalingam, U.; Kiefer, F.W.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Crinecerfont in Adult Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafoglou, K.; Barnes, C.N.; Huang, M.; Imel, E.A.; Madu, I.J.; Merke, D.P.; Moriarty, D.; Nakhle, S.; Newfield, R.S.; Vogiatzi, M.G.; et al. Tildacerfont in Adults With Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Results from Two Phase 2 Studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4666–e4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafoglou, K.; Kim, M.S.; Lodish, M.; Felner, E.I.; Martinerie, L.; Nokoff, N.J.; Clemente, M.; Fechner, P.Y.; Vogiatzi, M.G.; Speiser, P.W.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Crinecerfont in Pediatric Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisch, N. Block and Replace—A New Therapeutic Concept in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 107, e423–e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makurvet, F.D. Biologics vs. small molecules: Drug costs and patient access. Med. Drug Discov. 2021, 9, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, B.A.; Hoare, S.R.; Pick, R.R.; Bradbury, M.J.; Grigoriadis, D.E. Binding kinetics redefine the antagonist pharmacology of the corticotropin-releasing factor type 1 receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).