Metabolite Variations during the First Weeks of Growth of Immature Citrus sinensis and Citrus reticulata by Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
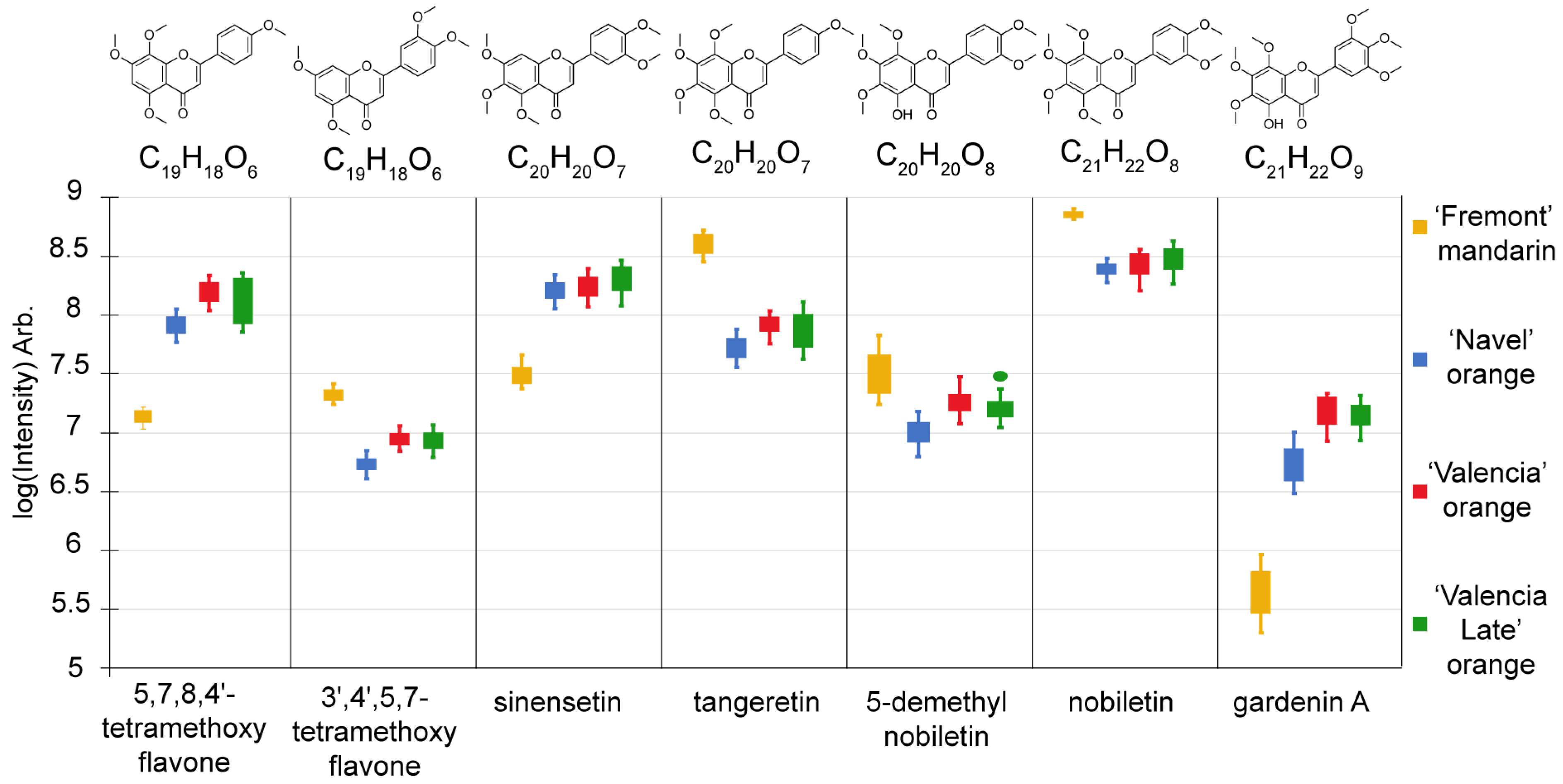
2.1. Key Metabolites Responsible for Differentiating Immature Varieties
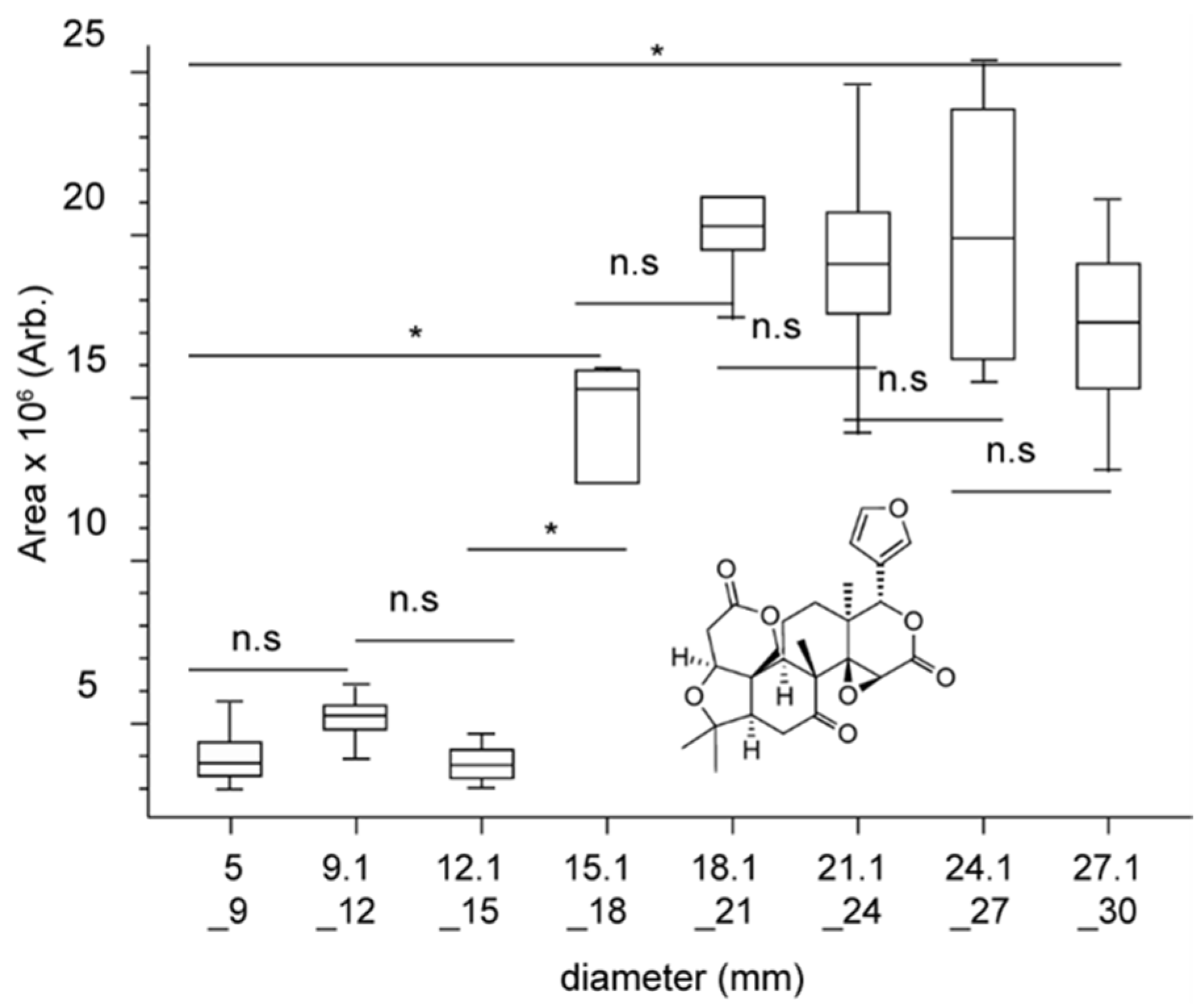
2.2. Evolution of Major Metabolites in Growing Fruits during the First Weeks of Growth
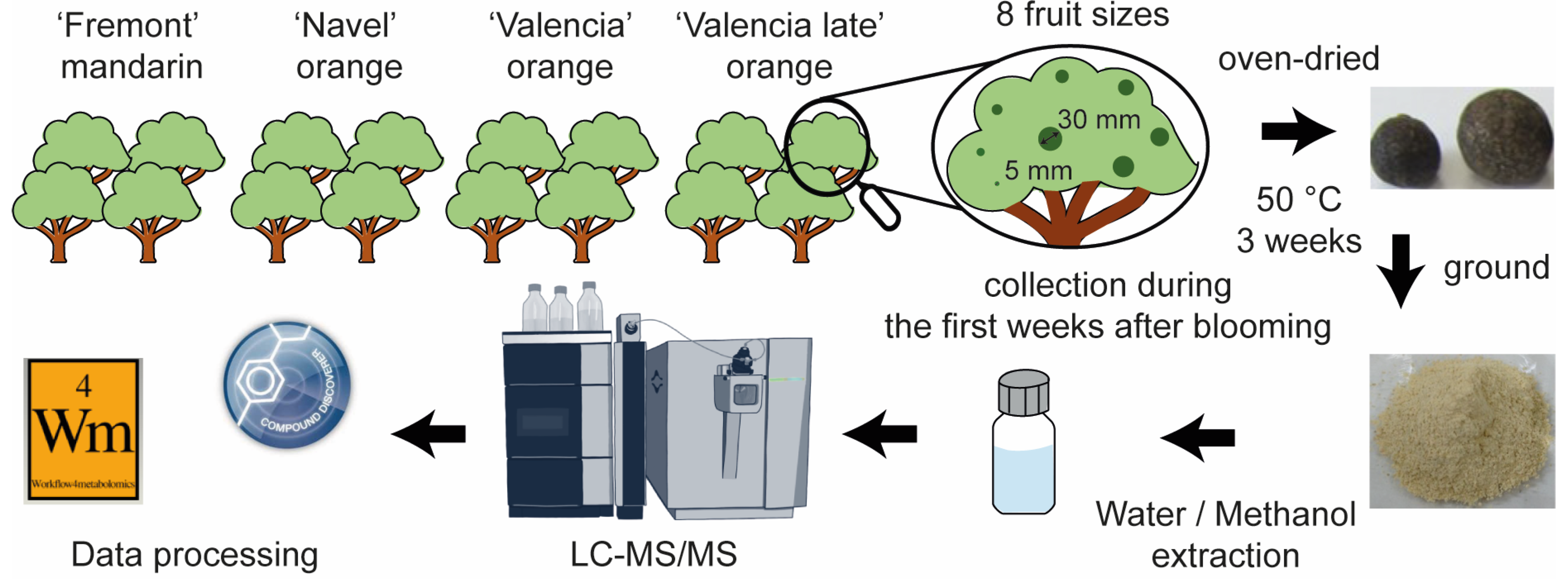
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Fruit Samples and Sample Preparation
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Data Processing and Data Analysis
3.4.1. Data Processing
3.4.2. Statistical Analysis
3.4.3. Metabolite Identifications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, R.K.; Ranjit, A.; Sharma, K.; Prasad, P.; Shang, X.; Gowda, K.G.M.; Keum, Y.-S. Bioactive Compounds of Citrus Fruits: A Review of Composition and Health Benefits of Carotenoids, Flavonoids, Limonoids, and Terpenes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favela-Hernández, J.M.J.; González-Santiago, O.; Ramírez-Cabrera, M.A.; Esquivel-Ferriño, P.C.; Camacho-Corona, M.D.R. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Citrus sinensis. Molecules 2016, 21, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorbagi, M.; Fayek, N.M.; Shao, P.; Farag, M.A. Citrus reticulata Blanco (the Common Mandarin) Fruit: An Updated Review of Its Bioactive, Extraction Types, Food Quality, Therapeutic Merits, and Bio-Waste Valorization Practices to Maximize Its Economic Value. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Yang, B.; Gu, Q. Review of Phytochemical and Nuritional Characteristics and Food Applications of Citrus L. Fruits. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 968604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, D.; Cercós, M.; Colmenero-Flores, J.; Naranjo, M.; Ríos, G.; Carrera, E.; Ruiz-Rivero, O.; Lliso, I.; Morillon, R.; Tadeo, F.; et al. Physiology of Citrus Fruiting. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 19, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An Overview of Bioactive Flavonoids from Citrus Fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Potential and Health Benefits of Citrus Peel. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Tu, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J. Characterization and Metabolic Diversity of Flavonoids in Citrus Species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogata, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Ishii, T.; Yano, M.; Ohta, H. Flavonoid Composition of Fruit Tissues of Citrus Species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, R.; Campone, L.; Pagano, I.; Carabetta, S.; Di Sanzo, R.; Rastrelli, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Russo, M. Characterisation of Nutraceutical Compounds from Different Parts of Particular Species of Citrus sinensis ‘Ovale Calabrese’ by UHPLC-UV-ESI-HRMS. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Yoshitomi, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hakamatsuka, T.; Uchiyama, N. High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomic Discrimination of Citrus -Type Crude Drugs and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy-Based Metabolomics. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Niu, L.; Suh, J.H.; Hung, W.-L.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive Metabolomics Analysis of Mandarins ( Citrus reticulata ) as a Tool for Variety, Rootstock, and Grove Discrimination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10317–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, K.J.; Kang, S.B.; Park, Y.; Han, S.-G.; Kim, M.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, D.-S. Metabolomic Profiling of Citrus unshiu during Different Stages of Fruit Development. Plants 2022, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Liao, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, G.; Xiong, B.; Wang, Z. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal Candidate Genes Involved in Tangor (Citrus reticulata × Citrus sinensis) Fruit Development and Quality Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Pu, Z.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, G.-S.; Zou, D.-Q.; Guo, S.; Li, C.; Zhan, Z.-L.; Duan, J.-A. Research on Biomarkers of Different Growth Periods and Different Drying Processes of Citrus Wilsonii Tanaka Based on Plant Metabolomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 700367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J. Metabolomics Analysis of the Peels of Different Colored Citrus Fruits (Citrus reticulata Cv. ‘Shatangju’) During the Maturation Period Based on UHPLC-QQQ-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Ladaniya, M.S.; Gurjar, M.; Kumar, S.; Mendke, S. Quantification of Flavonoids, Phenols and Antioxidant Potential from Dropped Citrus reticulata Blanco Fruits Influenced by Drying Techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Ladaniya, M.S.; Gurjar, M.; Kumar, S. Impact of Drying Methods on Natural Antioxidants, Phenols and Flavanones of Immature Dropped Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck Fruits. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and Considerations for the Use of System Suitability and Quality Control Samples in Mass Spectrometry Assays Applied in Untargeted Clinical Metabolomic Studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronningen, I.G.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of Aging-Associated Food Quality Changes in Citrus Products Using Untargeted Chemical Profiling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multari, S.; Licciardello, C.; Caruso, M.; Martens, S. Monitoring the Changes in Phenolic Compounds and Carotenoids Occurring during Fruit Development in the Tissues of Four Citrus Fruits. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.T.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, Y.F. Fast Separation and Sensitive Quantitation of Polymethoxylated Flavonoids in the Peels of Citrus Using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Pang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, J. Comparative Study of Flavonoid Production in Lycopene-Accumulated and Blonde-Flesh Sweet Oranges (Citrus sinensis) during Fruit Development. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Ye, X.; Tian, J. Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Capacities of Young Citrus Fruits Cultivated in China. Molecules 2022, 27, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, R.M.V.; Pua, A.; Ee, K.H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Lassabliere, B.; Yu, B. Investigation of Changes in Non-Traditional Indices of Maturation in Navel Orange Peel and Juice Using GC–MS and LC-QTOF/MS. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Gao, W.; Zeng, S.-L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.-H. Chemical Structures, Bioactivities and Molecular Mechanisms of Citrus Polymethoxyflavones. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Gupta, R.P. Microbiology of Fresh and Processed Fruits. In Handbook of Fruits and Fruit Processing; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 51–72. ISBN 978-1-118-35253-3. [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi, T.; Kita, M.; Tomono, Y.; Endo-Inagaki, T.; Omura, M. Gene Expression in Flavonoid Biosynthesis: Correlation with Flavonoid Accumulation in Developing Citrus Fruit. Physiol. Plant. 2001, 111, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, M.; Reig, C.; Martínez-Fuentes, A.; Mesejo, C. Advances in Citrus Flowering: A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 868831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Chao, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, M. Evaluation of Dynamic Changes in the Bioactive Components in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’) under Different Harvesting and Drying Conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3280–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Guo, X.; Abbasi, A.M.; Liu, R.H. Influence of the Stage of Ripeness on the Phytochemical Profiles, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities in Different Parts of Citrus reticulata Blanco Cv. Chachiensis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chahal, T.S.; Gill, P.S.; Grewal, S.K. Changes in Phenolics and Antioxidant Capacities in Fruit Tissues of Mandarin Cultivars Kinnow and W. Murcott with Relation to Fruit Development. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e16040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qiao, L.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Chen, J.; Ye, X. Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Physiological Drop of Citrus Fruits. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C37–C42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Xu, C.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics for Discrimination of Navel Oranges from Different Geographical Origins of China. LWT 2021, 137, 110382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and Environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durand-Hulak, M.; Dugrand, A.; Duval, T.; Bidel, L.P.R.; Jay-Allemand, C.; Froelicher, Y.; Bourgaud, F.; Fanciullino, A.-L. Mapping the Genetic and Tissular Diversity of 64 Phenolic Compounds in Citrus Species Using a UPLC–MS Approach. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomoni, F.; Le Corguillé, G.; Monsoor, M.; Landi, M.; Pericard, P.; Pétéra, M.; Duperier, C.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Martin, J.-F.; Jacob, D.; et al. Workflow4Metabolomics: A Collaborative Research Infrastructure for Computational Metabolomics. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guitton, Y.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Le Corguillé, G.; Martin, J.-F.; Pétéra, M.; Roger-Mele, P.; Delabrière, A.; Goulitquer, S.; Monsoor, M.; Duperier, C.; et al. Create, Run, Share, Publish, and Reference Your LC–MS, FIA–MS, GC–MS, and NMR Data Analysis Workflows with the Workflow4Metabolomics 3.0 Galaxy Online Infrastructure for Metabolomics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.J.; Xing, T.T.; Li, Y.F.; Jiao, B.N.; Jiang, D. Efficient Analysis of Phytochemical Constituents in the Peel of Chinese Wild Citrus Mangshanju (Citrus reticulata Blanco) by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole Time-of-Flight-Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Tian, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, W.; Ning, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of the Chemical Components of Peels from Different Pomelo Cultivars (Citrus grandis [L.] Osbeck) Based on Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS, and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Photodiode Array Detection. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6253–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.; Deng, X. Structural Diversity and Distribution of Limonoids in Pummelo (Citrus grandis) Fruit Revealed by Comprehensive UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 282, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, B.; Deng, L.; Tian, J.; Yang, G.; Zheng, G. UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS Analysis for Identification of Lipophilic Components in Citri sarcodactylis Fructus from Different Origins in China Using Supercritical CO2 Fluid Extraction Method. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11013–11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of Polymethoxylated Flavonoids in the Peels of Chinese Wild Mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco) by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, Q.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Lu, J.-Q.; Qiao, Y.-J. Rapid Screening and Identification of Target Constituents Using Full Scan-Parent Ions List-Dynamic Exclusion Acquisition Coupled to Diagnostic Product Ions Analysis on a Hybrid LTQ-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Talanta 2014, 124, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Chemical Family | Number of Up-Regulated Compounds in the ‘Fremont’ Mandarin | Number of Up-Regulated Compounds in the Oranges |
|---|---|---|
| Amino acids | 0 | 4 |
| Amines | 4 | 3 |
| Peptides | 0 | 1 |
| Amino sugars | 0 | 4 |
| Sugars | 0 | 2 |
| Lipids | 1 | 1 |
| Polyphenols | 0 | 6 |
| Polymethoxyflavones | 11 | 10 |
| Polymethoxyflavanones | 0 | 1 |
| Flavones | 2 | 5 |
| Organic phosphorous | 0 | 1 |
| Chemical Family | Number of Compounds with an Intensity Increase | Number of Compounds with an Intensity Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Organic acids | 1 | 0 |
| Amino acids | 1 | 0 |
| Peptides | 0 | 1 |
| Amines | 5 | 11 |
| Amino sugars | 10 | 1 |
| Sugars | 4 | 2 |
| Lipids | 0 | 3 |
| Polyphenols | 3 | 3 |
| Limonoids | 3 | 0 |
| Polymethoxyflavones | 3 | 10 |
| Flavones | 3 | 0 |
| Flavanones | 2 | 0 |
| Organic phosphorus | 5 | 0 |
| Variety | Citrus sinensis (L.) Obs. | Citrus sinensis (L.) Obs. | Citrus sinensis (L.) Obs. | Citrus reticulata Ten. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar | Valencia campbell | Valencia Late | Navelate | Fremont |
| SRA 17 | SRA 246 | SRA 307 | SRA 147 | |
| Rootstock | Poncirus trifoliata | Poncirus trifoliata | Poncirus trifoliata | Poncirus trifoliata |
| Plot location | Ala H1-4 | Ala H1-4 | Ala O17-20 | B3 G1-4 |
| Time (min) | Mobile Phase B (%) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 4 | 40 |
| 10 | 100 |
| 14 | 100 |
| 14.5 | 0 |
| 16 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deschamps, E.; Durand-Hulak, M.; Castagnos, D.; Hubert-Roux, M.; Schmitz, I.; Froelicher, Y.; Afonso, C. Metabolite Variations during the First Weeks of Growth of Immature Citrus sinensis and Citrus reticulata by Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Molecules 2024, 29, 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163718
Deschamps E, Durand-Hulak M, Castagnos D, Hubert-Roux M, Schmitz I, Froelicher Y, Afonso C. Metabolite Variations during the First Weeks of Growth of Immature Citrus sinensis and Citrus reticulata by Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163718
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeschamps, Estelle, Marie Durand-Hulak, Denis Castagnos, Marie Hubert-Roux, Isabelle Schmitz, Yann Froelicher, and Carlos Afonso. 2024. "Metabolite Variations during the First Weeks of Growth of Immature Citrus sinensis and Citrus reticulata by Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163718
APA StyleDeschamps, E., Durand-Hulak, M., Castagnos, D., Hubert-Roux, M., Schmitz, I., Froelicher, Y., & Afonso, C. (2024). Metabolite Variations during the First Weeks of Growth of Immature Citrus sinensis and Citrus reticulata by Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Molecules, 29(16), 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163718








