The [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex as a Catalyst for the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene with Dioxygen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oxidation of Cyclohexene
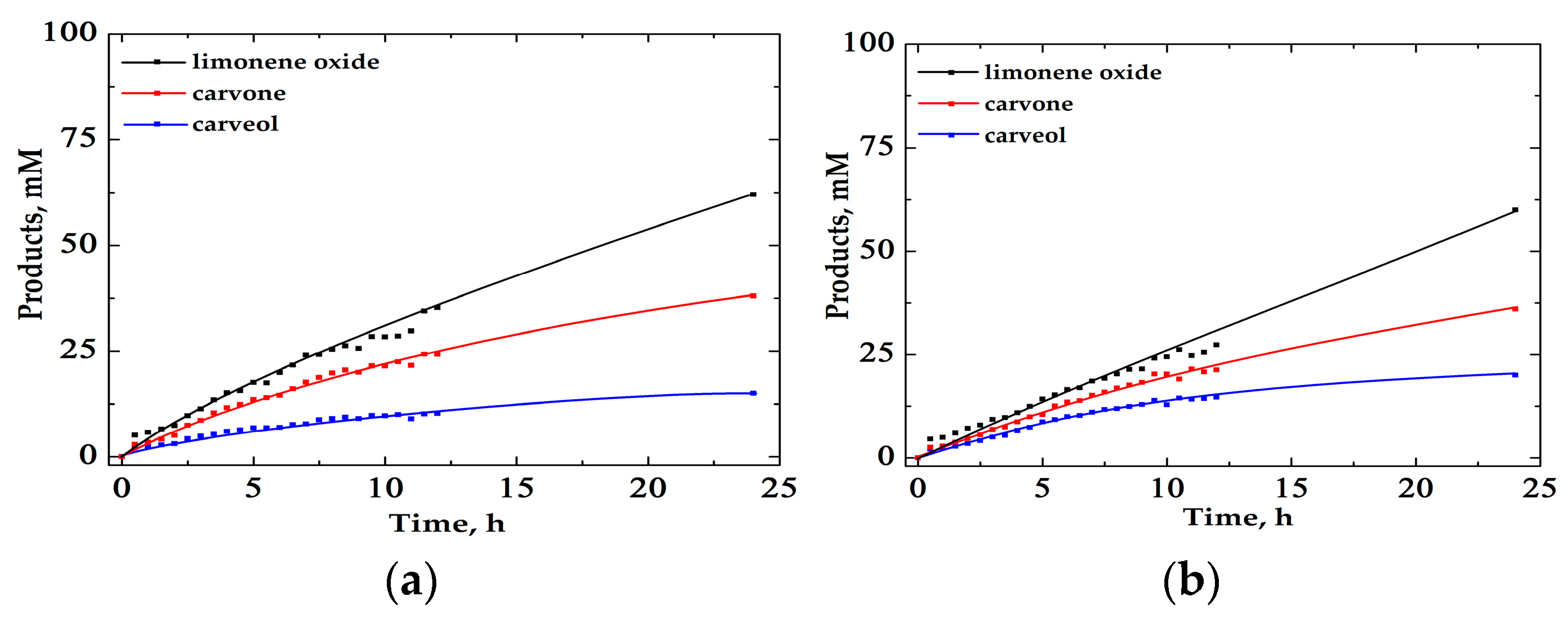
2.2. Oxidation of Limonene
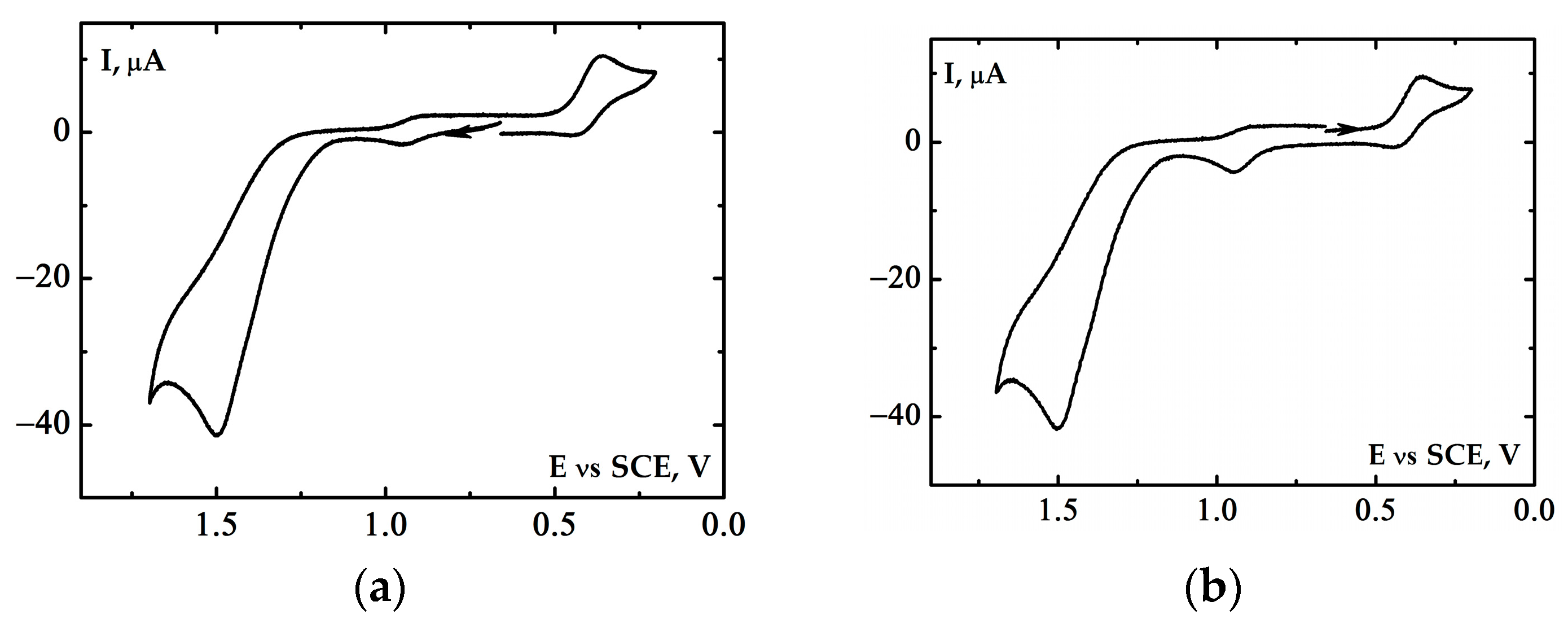
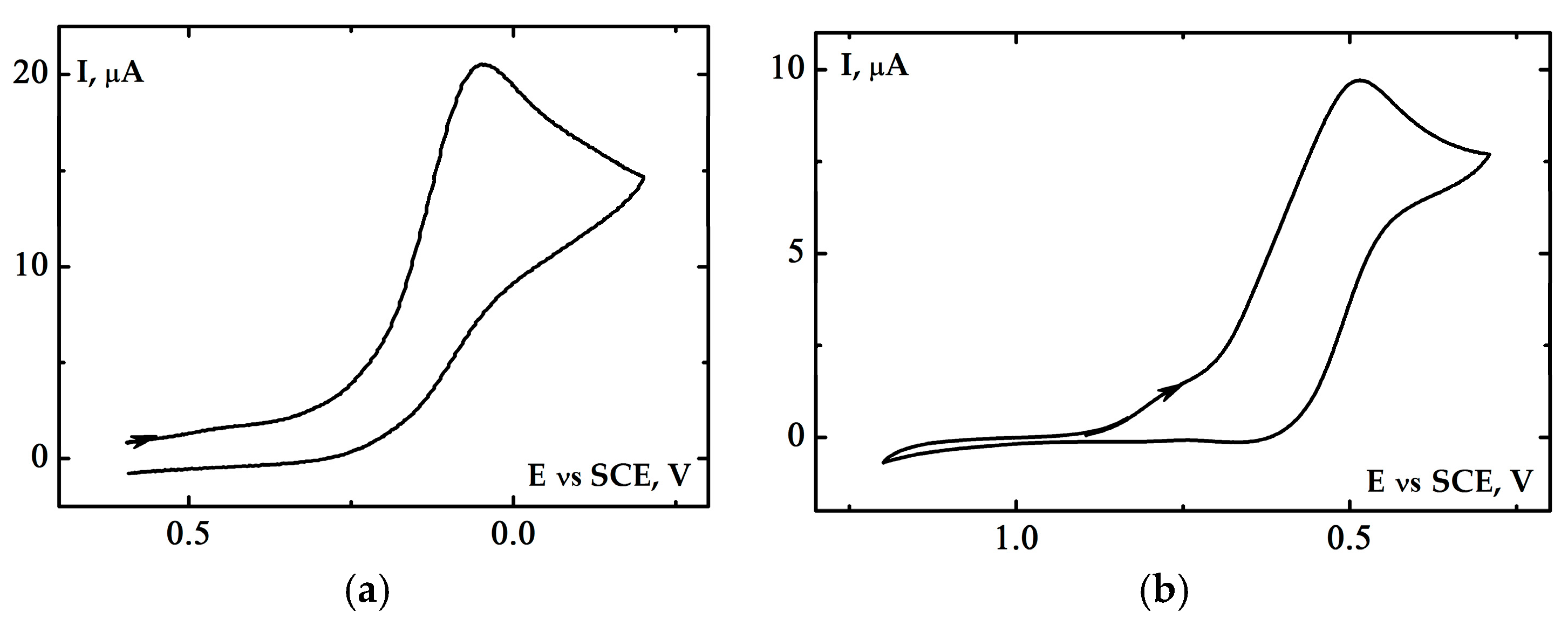
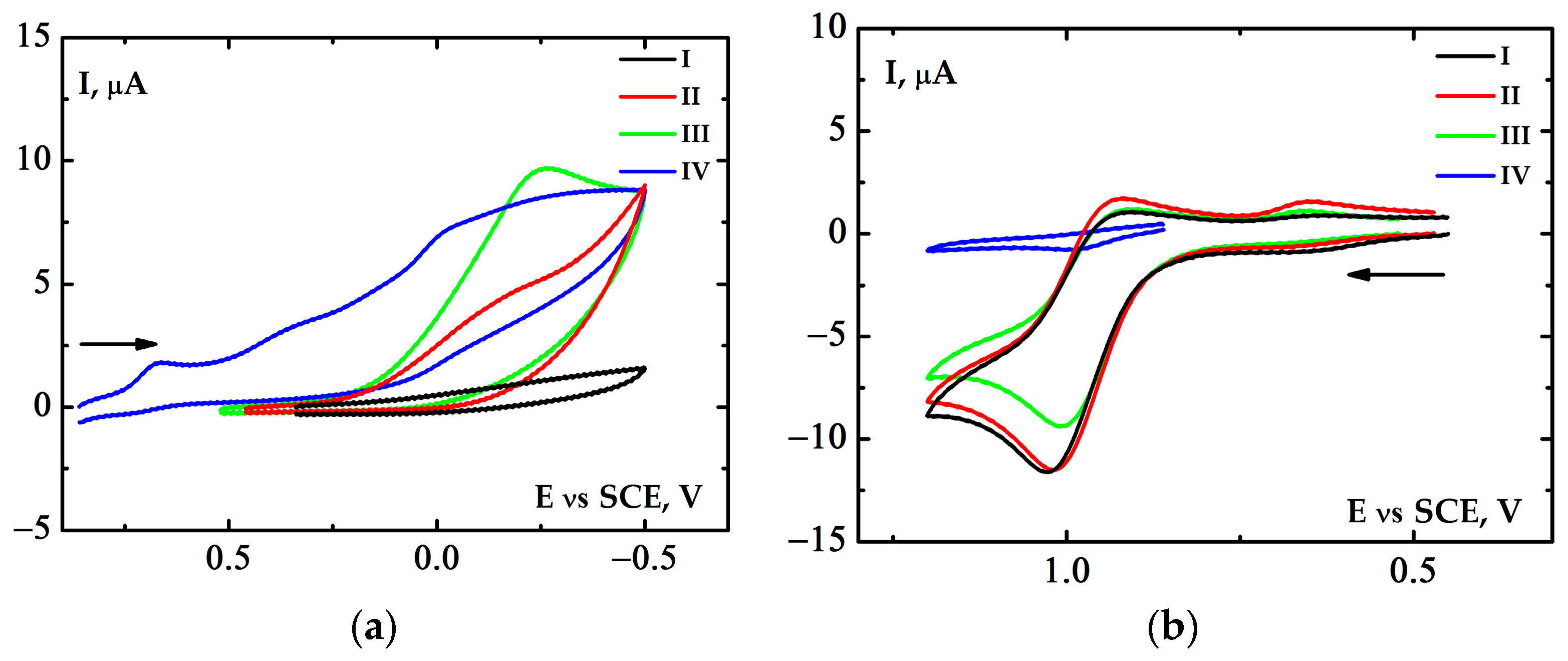
2.3. Electrochemical Properties of the [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex
2.4. Proposed Putative Oxidation Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Equipment
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rydel-Ciszek, K.; Pacześniak, T.; Chmielarz, P.; Sobkowiak, A. Bio-Inspired Iron Pentadentate Complexes as Dioxygen Activators in the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene. Molecules 2023, 28, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarso, A.; Strukul, G. Sustainability Trends in Homogeneous Catalytic Oxidations. In Handbook of Advanced Methods and Processes in Oxidation Catalysis; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 679–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Védrine, J.C. Heterogeneous Catalysis on Metal Oxides. Catalysts 2017, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canta, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Costas, M. Recent Advances in the Selective Oxidation of Alkyl C-H Bonds Catalyzed by Iron Coordination Complexes. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 372, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’pin, G.B. New Trends in Oxidative Functionalization of Carbon–Hydrogen Bonds: A Review. Catalysts 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.D.; Mewada, R.K.; Wagh, D.P.; Manyar, H.G. Advances and Future Trends in Selective Oxidation Catalysis: A Critical Review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 7245–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büker, J.; Muhler, M.; Peng, B. Concepts of Heterogeneously Catalyzed Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Cyclohexene with tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide, Hydrogen Peroxide and Molecular Oxygen. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202201216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, G.; Peñate, I.Q.; Franceschi, S.; Perez, E.; Garrigues, J.-C.; Poux, M.; Cognet, P. Sustainable Process for Adipic Acid Production from Cyclohexene in Microemulsion. Catal. Today 2020, 346, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Spada, E.; Bertani, R.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Adipic Acid Route: Oxidation of Cyclohexene vs. Cyclohexane. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, J.-U.; Torelli, S.; Shan, X.; Lim, M.H.; Klinker, E.J.; Kaizer, J.; Chen, K.; Nam, W.; Que, L., Jr. Structural Insights into Nonheme Alkylperoxoiron(III) and Oxoiron(IV) Intermediates by X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16750–16761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, A.; McKenzie, C.J.; Nielsen, L.P.; Schindler, S.; Weitzer, M. Mononuclear Non-Heme Iron(III) Peroxide Complexes: Syntheses, Characterisation, Mass Spectrometric and Kinetic Studies. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Shin, W.; Fukuzumi, S.; Nam, W. Dioxygen Activation by Mononuclear Nonheme Iron(II) Complexes Generates Iron−Oxygen Intermediates in the Presence of an NADH Analogue and Proton. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13910–13911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubben, M.; Meetsma, A.; Wilkinson, E.C.; Feringa, B.; Que Jr, L. Nonheme Iron Centers in Oxygen Activation: Characterization of an Iron(III) Hydroperoxide Intermediate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 1512–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfes, G.; Lubben, M.; Leppard, S.W.; Schudde, E.P.; Hermant, R.M.; Hage, R.; Wilkinson, E.C.; Que, L., Jr.; Feringa, B.L. Functional Models for Iron-Bleomycin. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 117, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draksharapu, A.; Li, Q.; Roelfes, G.; Browne, W.R. Photo-Induced Oxidation of [FeII(N4Py)CH3CN] and Related Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13180–13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelfes, G.; Lubben, M.; Chen, K.; Ho, R.Y.N.; Meetsma, A.; Genseberger, S.; Hermant, R.M.; Hage, R.; Mandal, S.K.; Young, V.G.; et al. Iron Chemistry of a Pentadentate Ligand that Generates a Metastable FeIII−OOH Intermediate. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaizer, J.; Klinker, E.J.; Oh, N.Y.; Rohde, J.-U.; Song, W.J.; Stubna, A.; Kim, J.; Münck, E.; Nam, W.; Que, L., Jr. Nonheme FeIVO Complexes that Can Oxidize the C−H Bonds of Cyclohexane at Room Temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.R.; Que, L., Jr. High-Valent Nonheme Iron-Oxo Complexes: Synthesis, Structure, and Spectroscopy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ray, K.; Collins, M.J.; Farquhar, E.R.; Frisch, J.R.; Gómez, L.; Jackson, T.A.; Kerscher, M.; Waleska, A.; Comba, P.; et al. Nonheme Oxoiron(IV) Complexes of Pentadentate N5 Ligands: Spectroscopy, Electrochemistry, and Oxidative Reactivity. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Singh, R.; Sinha, A.; Lisensky, G.C.; Haukka, M.; Nilsson, J.; Yiga, S.; Demeshko, S.; Gross, S.J.; Dechert, S.; et al. Nonheme FeIV=O Complexes Supported by Four Pentadentate Ligands: Reactivity toward H- and O- Atom Transfer Processes. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 18338–18356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinker, E.J.; Kaizer, J.; Brennessel, W.W.; Woodrum, N.L.; Cramer, C.J.; Que, L., Jr. Structures of Nonheme Oxoiron(IV) Complexes from X-ray Crystallography, NMR Spectroscopy, and DFT Calculations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3690–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Kotani, H.; Suenobu, T.; Nam, W.; Fukuzumi, S. Fundamental Electron-Transfer Properties of Non-Heme Oxoiron(IV) Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, G.; Lee, C.W.Z.; Nag, S.S.; Alili, A.; Cantú Reinhard, F.G.; Kumar, D.; Sastri, C.V.; de Visser, S.P. Dramatic Rate-Enhancement of Oxygen Atom Transfer by An Iron(IV)-Oxo Species by Equatorial Ligand Field Perturbations. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14945–14957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydel-Ciszek, K. The Most Reactive Iron and Manganese Complexes with N-pentadentate Ligands for Dioxygen Activation—Synthesis, Characteristics, Applications. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2021, 133, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; McKenzie, C.; Nielsen, L.; Pedersen, J.; Svendsen, H. Deprotonation of Low-Spin Mononuclear Iron(III)–Hydroperoxide Complexes give Transient Blue Species Assigned to High-Spin Iron(III)–Peroxide Complexes. Chem. Commun. 1999, 14, 1313–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, O.; Jeandey, C.; Oddou, J.-L.; Bonville, P.; McKenzie, C.J.; Latour, J.-M. Hydrogenperoxo-[(bztpen)Fe(OOH)]2+ and Its Deprotonation Product Peroxo-[(bztpen)Fe(O2)]+, Studied by EPR and Mössbauer Spectroscopy − Implications for the Electronic Structures of Peroxo Model Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 12, 3278–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfes, G.; Vrajmasu, V.; Chen, K.; Ho, R.Y.N.; Rohde, J.-U.; Zondervan, C.; la Crois, R.M.; Schudde, E.P.; Lutz, M.; Spek, A.L.; et al. End-On and Side-On Peroxo Derivatives of Non-Heme Iron Complexes with Pentadentate Ligands: Models for Putative Intermediates in Biological Iron/Dioxygen Chemistry. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 2639–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, A.; Del Giacco, T.; Di Stefano, S.; Lanzalunga, O.; Lapi, A.; Mazzonna, M.; Olivo, G. Electron Transfer Mechanism in the Oxidation of Aryl 1-Methyl-1-phenylethyl Sulfides Promoted by Nonheme Iron(IV)–Oxo Complexes: The Rate of the Oxygen Rebound Process. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 12382–12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.; Schmitt, S.M.; Dou, Q.P.; Kodanko, J.J. Inhibition of the Purified 20S Proteasome by Non-Heme Iron Complexes. Metallomics 2012, 4, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcas, R.; Kripli, B.; Attia, A.A.A.; Lakk-Bogáth, D.; Speier, G.; Giorgi, M.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R.; Kaizer, J. Catalytic and Stoichiometric Flavanone Oxidation Mediated by Nonheme Oxoiron(IV) Complexes as Flavone Synthase Mimics: Kinetic, Mechanistic and Computational Studies. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14416–14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakk-Bogáth, D.; Juraj, N.P.; Meena, B.I.; Perić, B.; Kirin, S.I.; Kaizer, J. Comparison of Nonheme Manganese- and Iron-Containing Flavone Synthase Mimics. Molecules 2021, 26, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, S. Electron-Transfer Properties of High-Valent Metal-Oxo Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draksharapu, A.; Li, Q.; Logtenberg, H.; van den Berg, T.A.; Meetsma, A.; Killeen, J.S.; Feringa, B.L.; Hage, R.; Roelfes, G.; Browne, W.R. Ligand Exchange and Spin State Equilibria of FeII(N4Py) and Related Complexes in Aqueous Media. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Draksharapu, A.; Rasheed, W.; Que, L., Jr. Acid pKa Dependence in O–O Bond Heterolysis of a Nonheme FeIII–OOH Intermediate to Form a Potent FeV═O Oxidant with Heme Compound I-Like Reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16093–16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Lee, J.; Suh, Y.; Kim, J.; Nam, W. Reactivities of Mononuclear Non-Heme Iron Intermediates Including Evidence that Iron(III)−Hydroperoxo Species Is a Sluggish Oxidant. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2630–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobkowiak, A.; Naróg, D.; Sawyer, D.T. Iron(III, II)-Induced Activation of Dioxygen for the Oxygenation of Cyclohexene and Related Unsaturated Hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 159, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacześniak, T.; Sobkowiak, A. The Influence of Solvent on the Reaction Between Iron(II), (III) and Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 194, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanik, A.; Sobkowiak, A. Manganese(II)-Induced Oxidation of Limonene by Dioxygen. Catal. Lett. 2008, 126, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Ray, K.; Nam, W. Dioxygen Activation Chemistry by Synthetic Mononuclear Nonheme Iron, Copper and Chromium Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 334, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’pin, G.B. Metal-Catalyzed Hydrocarbon Oxygenations in Solutions: The Dramatic Role of Additives: A Review. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2002, 189, 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimchuk, N.; Lee, J.S.; Ayupov, A.; Chang, J.-S.; Kholdeeva, O. Cyclohexene Oxidation with H2O2 over Metal-Organic Framework MIL-125(Ti): The Effect of Protons on Reactivity. Catalysts 2019, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greef, R.; Peat, R.; Peter, L.M.; Pletcher, D.; Robinson, J. Instrumental Methods in Electrochemistry, Southampton Electrochemistry Group; Halsted Press: Chichester, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, J. Chemistry of Iron; Silver, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, A.F.; Wilkinson, G.; Murillo, C.A.; Bochmann, M. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Bühlmann, P.; Que, L., Jr. Redox Potential and C-H Bond Cleaving Properties of a Nonheme Fe(IV)=O Complex in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7638–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.; Goldberg, D.P. Activation of Dioxygen by Iron and Manganese Complexes: A Heme and Nonheme Perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11410–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasevich, E.I.; Kulikova, V.S.; Shilov, A.E.; Al'bert, A.S. Biomimetic Alkane Oxidation Involving Metal Complexes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1998, 67, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekmouche, Y.; Duboc-Toia, C.; Ménage, S.; Lambeaux, C.; Fontecave, M. Hydroxylation of Alkanes Catalysed by a Chiral μ-Oxo Diferric Complex: A Metal-Based Mechanism. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 156, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Hong, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Shin, W.; Fukuzumi, S.; Nam, W. Dioxygen Activation by a Non-Heme Iron(II) Complex: Formation of an Iron(IV)−Oxo Complex via C−H Activation by a Putative Iron(III)−Superoxo Species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10668–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Dey, A.; Maiti, D. Mechanistic Elucidation of C–H Oxidation by Electron Rich Non-Heme Iron(IV)–Oxo at Room Temperature. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14469–14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terencio, T.; Andris, E.; Gamba, I.; Srnec, M.; Costas, M.; Roithová, J. Chemoselectivity in the Oxidation of Cycloalkenes with a Non-Heme Iron(IV)-Oxo-Chloride Complex: Epoxidation vs. Hydroxylation Selectivity. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naróg, D.; Szczepanik, A.; Sobkowiak, A. Iron(II, III)-Catalyzed Oxidation of Limonene by Dioxygen. Catal. Lett. 2008, 120, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, H.; Sharefkin, J.G. Iodosobenzene. Org. Synth. 1963, 43, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, H.; Sharefkin, J.G. Iodosobenzene Diacetate. Org. Synth. 1963, 43, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blicke, F.F.; Maxwell, C.E. Naphthylaminoalkanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemers, E.; Hiltmann, R. Pyridylalkyl-Substituierte Amine. Synthesis 1976, 9, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duelund, L.; Hazell, R.; McKenzie, C.J.; Preuss Nielsen, L.; Toftlund, H. Solid and Solution State Structures of Mono- and Di-Nuclear Iron(III) Complexes of Related Hexadentate and Pentadentate Aminopyridyl Ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2001, 2, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, D.T.; Sobkowiak, A.; Roberts, J.L. Electrochemistry for Chemists, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
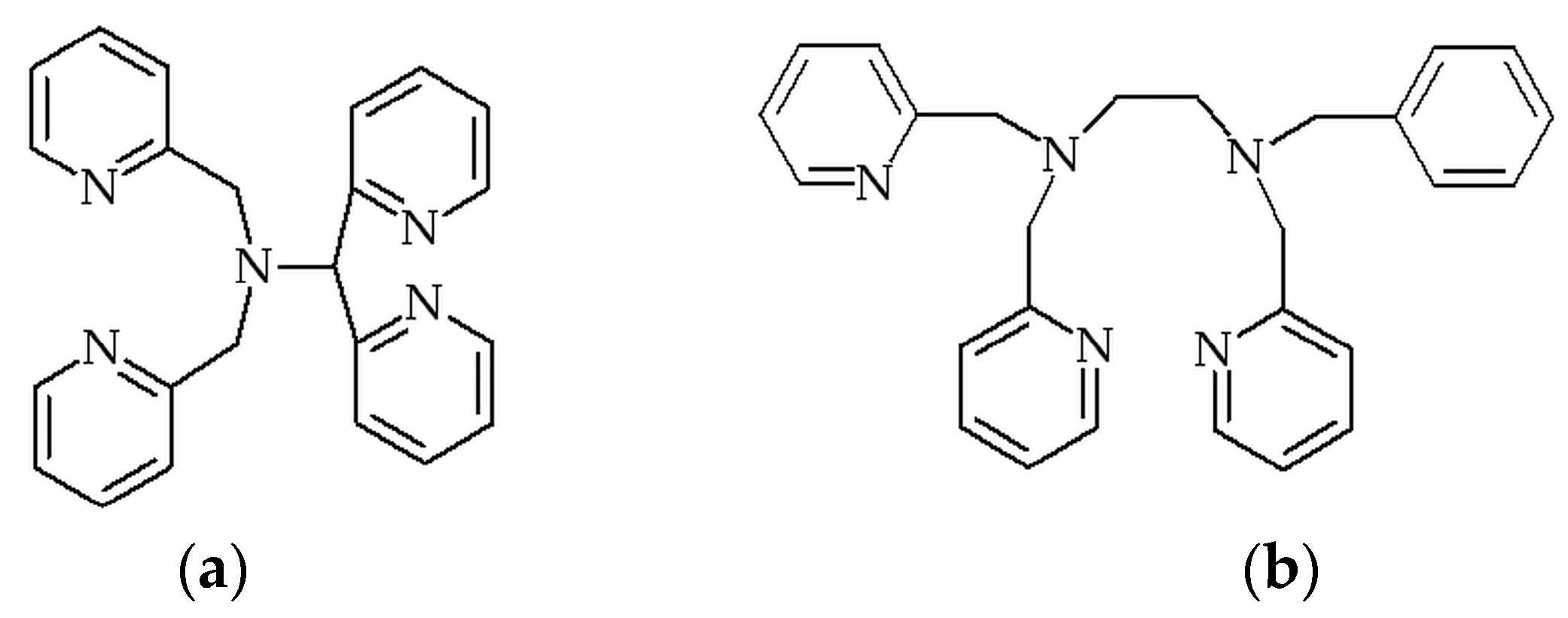
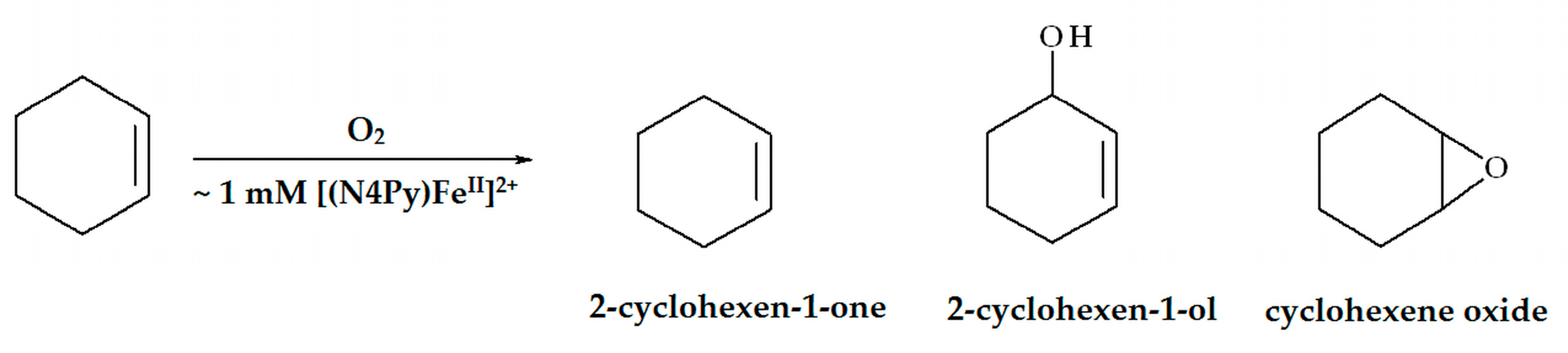
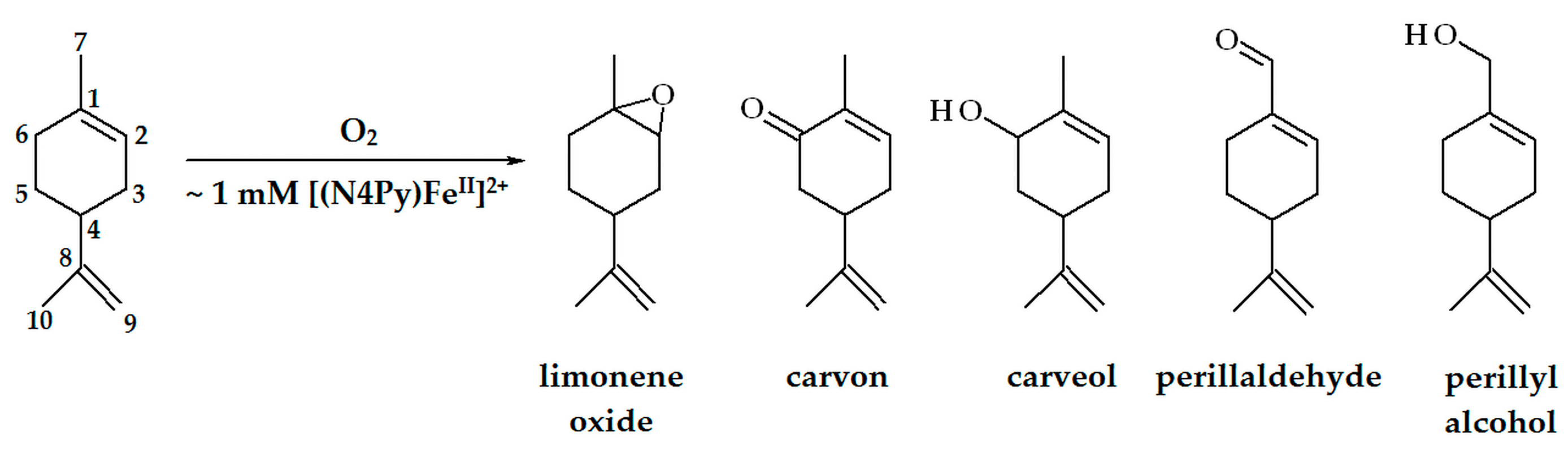
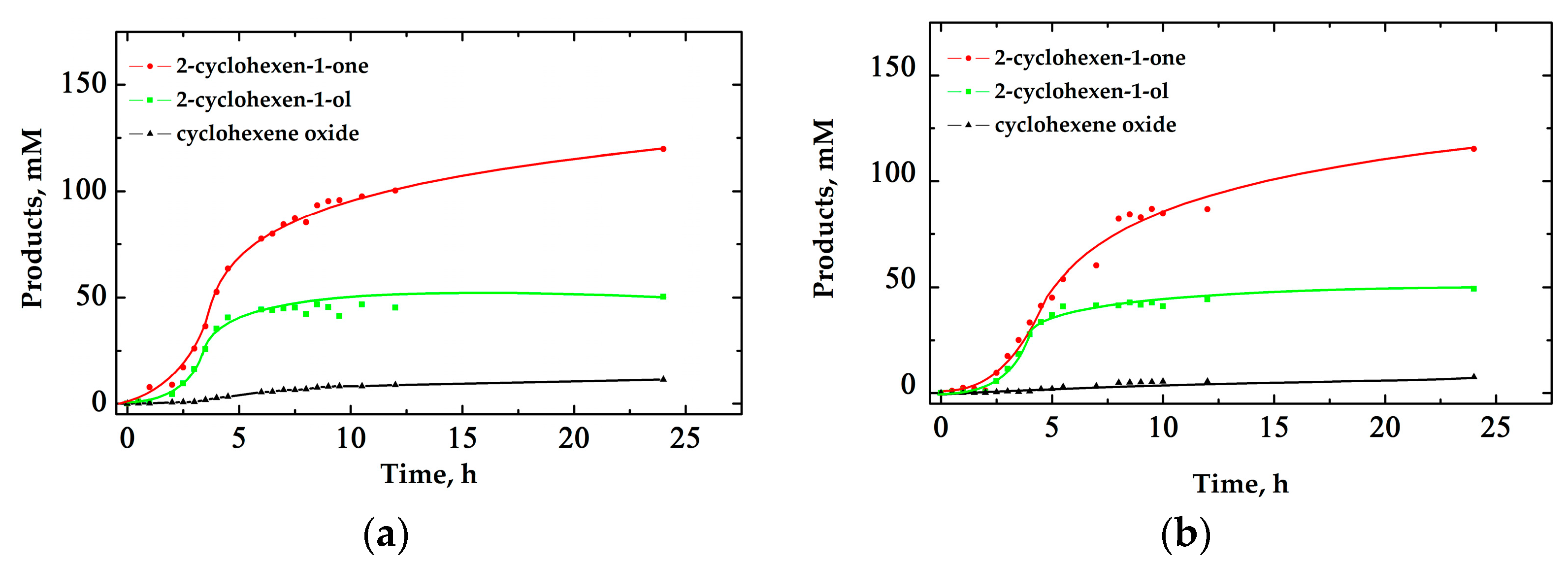



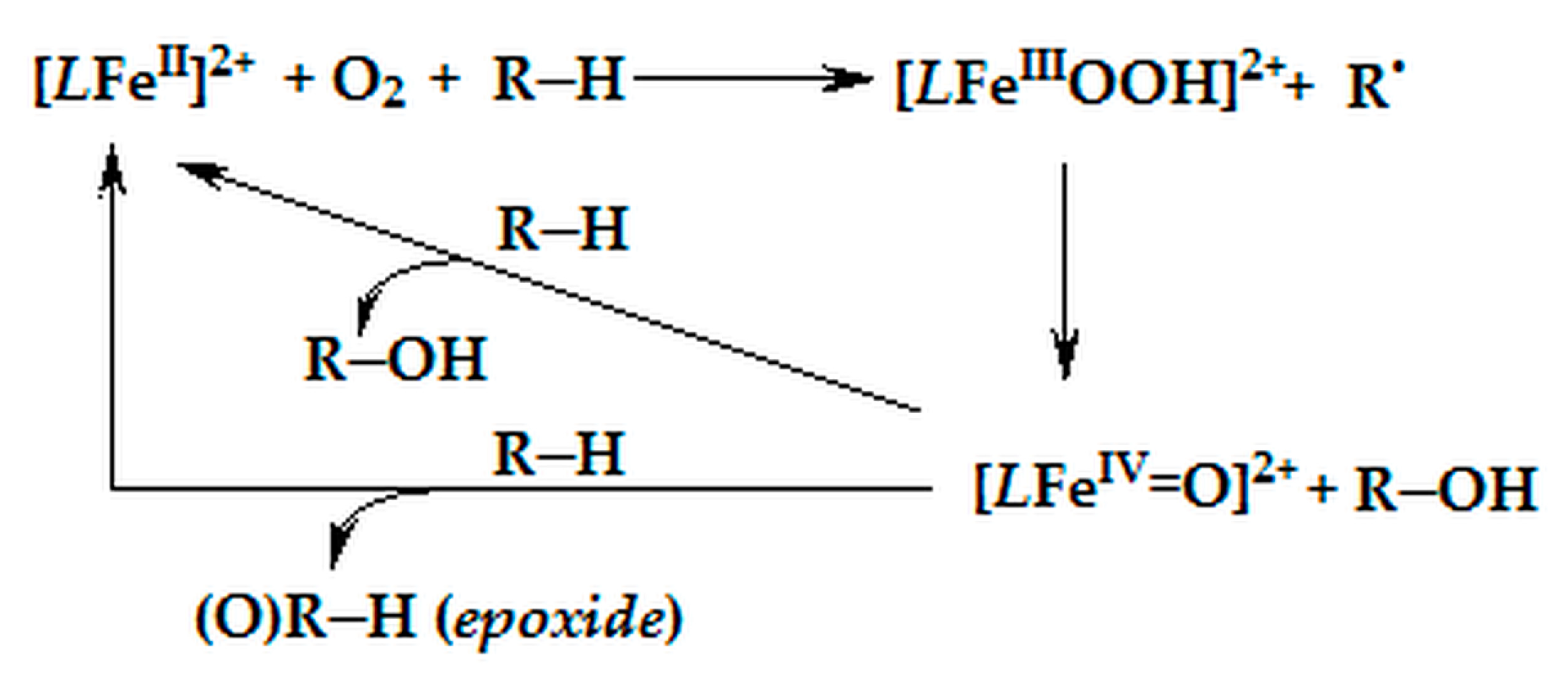
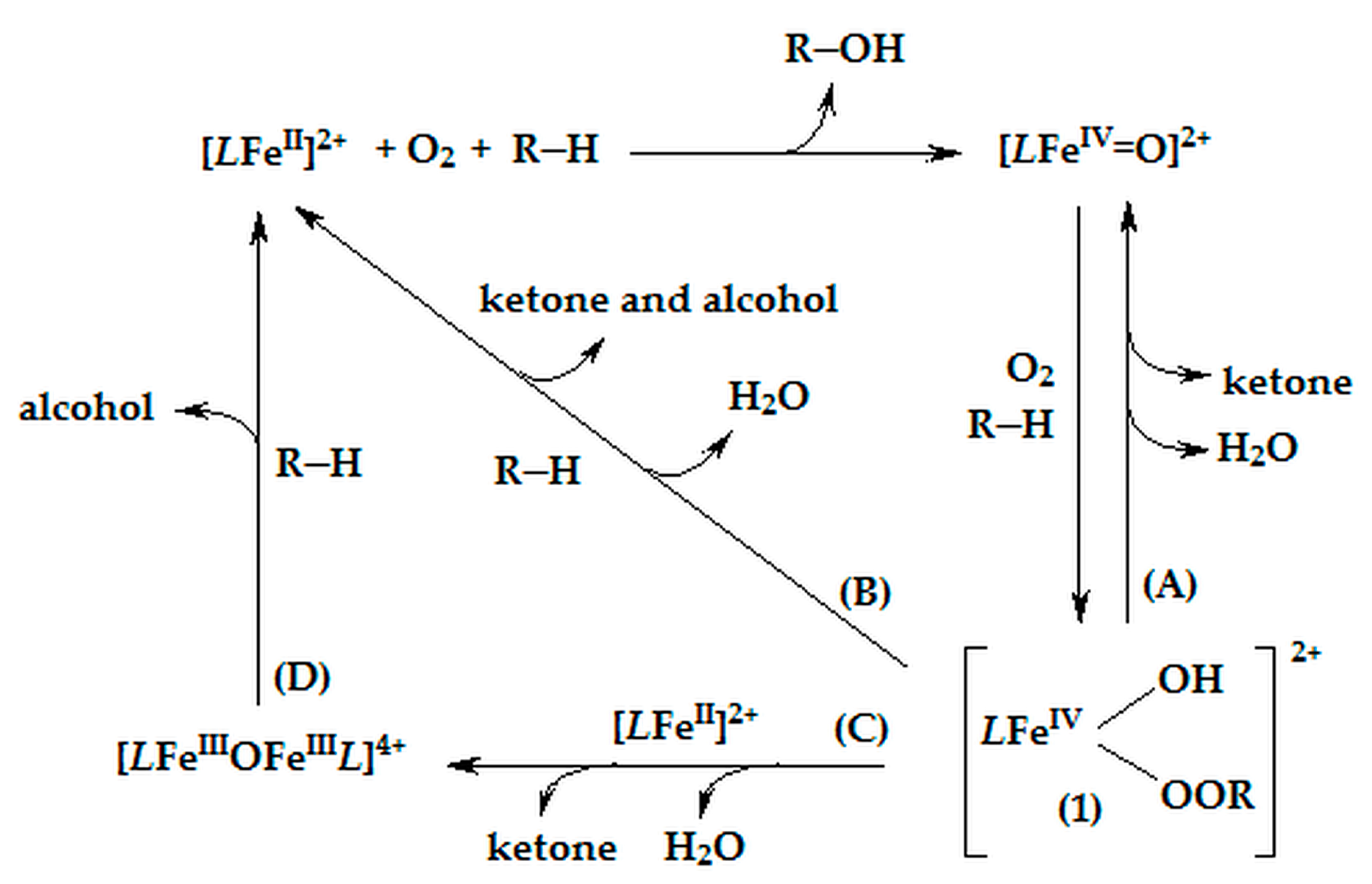
| Complexes | Analytical Methods L–Bn-tpen | Analytical Methods L–N4Py |
|---|---|---|
| [LFeII]2+ | UV–Vis [11], NMR [12], CV [12] | UV–Vis [13,14,15], NMR [12,14,16], EPR [16], EXAFS [10], CV [1,12] |
| [LFeIV=O]2+ | UV–Vis [10,17,18,19,20], EXAFS [10], NMR [21], Mössbauer [10,17,20], ESI-MS [17,19], CV [19,22] | UV–Vis [10,17,18,19,20,23], X-ray [10,21], EXAFS [10], NMR [21], Mössbauer [17,20], CV [1,19,22], ESI-MS [17] |
| [LFeIII–OOH]2+ | UV–Vis [11,12,24], EPR [12,25,26,27], ESI-MS [25], Mössbauer [26,27] | UV–Vis [12,13,14,16,27], EPR [12,13,14,16,27], EXAFS [27], Mössbauer [26,27] |
| Catalyst, mM | Substrate, M | O2, atm | Ketone a, mM | Ketone b, mM | Alcohol a, mM | Alcohol b, mM | Epoxide a, mM | Epoxide b, mM | TON a | TON b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 116 | 113 | 46 | 35 | 12 | 14 | 348 | 324 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 110 | 118 | 48 | 44 | 10 | 15 | 336 | 354 |
| 1 c | 1 | 1 | 120 | 138 | 50 | 41 | 11 | 18 | 181 | 197 |
| 1 d | 1 | 0.2 | 115 | 115 | 49 | 51 | 8 | 7 | 172 | 173 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 1 | 96 | 111 | 34 | 20 | 4 | 12 | 54 | 57 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 80 | 98 | 20 | 37 | 7 | 4 | 43 | 56 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 93 | 84 | 38 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 27 | 21 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 72 | 65 | 13 | 23 | 3 | 2 | 18 | 18 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 1 | 76 | 48 | 28 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 9 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 62 | 42 | 20 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 11 | 7 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 72 | 23 | 20 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 3 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.2 | 47 | 21 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 51 | 43 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 63 | 57 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 38 | 42 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 55 | 58 |
| 1 c | 1 | 1 | 120 | 138 | 50 | 41 | 11 | 18 | 181 | 197 |
| 1 d | 1 | 0.2 | 115 | 115 | 49 | 51 | 8 | 7 | 172 | 173 |
| 1 | 1.5 | 1 | 182 | 144 | 47 | 43 | 25 | 23 | 254 | 210 |
| 1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 145 | 143 | 44 | 54 | 26 | 20 | 215 | 217 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 218 | 174 | 94 | 70 | 30 | 28 | 342 | 272 |
| 1 | 2 | 0.2 | 196 | 170 | 138 | 56 | 22 | 21 | 356 | 247 |
| Catalyst, mM | Substrate, M | O2, atm | Limonene Oxide, mM | Carvone, mM | Carveol, mM | Perillaldehyde, mM | Perillyl Alcohol, mM | TON a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 69 | 41 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 260 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 55 | 32 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 214 |
| 1 b | 1 | 1 | 62 | 38 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 119 |
| 1 c | 1 | 0.2 | 59 | 36 | 20 | 3 | 1 | 119 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 1 | 56 | 37 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 46 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 54 | 32 | 20 | 2 | 3 | 44 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 50 | 35 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 44 | 28 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 1 | 56 | 30 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 14 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 43 | 24 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 59 | 33 | 16 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.2 | 47 | 27 | 19 | 0 | 1 | 9 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 34 | 17 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 59 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 34 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 59 |
| 1 b | 1 | 1 | 62 | 38 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 119 |
| 1 c | 1 | 0.2 | 59 | 36 | 20 | 3 | 1 | 119 |
| 1 | 1.5 | 1 | 69 | 50 | 30 | 1 | 3 | 153 |
| 1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 62 | 38 | 26 | 2 | 4 | 132 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 80 | 48 | 24 | 3 | 3 | 158 |
| 1 | 2 | 0.2 | 71 | 36 | 32 | 1 | 2 | 142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rydel-Ciszek, K.; Sobkowiak, A. The [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex as a Catalyst for the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene with Dioxygen. Molecules 2024, 29, 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163755
Rydel-Ciszek K, Sobkowiak A. The [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex as a Catalyst for the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene with Dioxygen. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163755
Chicago/Turabian StyleRydel-Ciszek, Katarzyna, and Andrzej Sobkowiak. 2024. "The [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex as a Catalyst for the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene with Dioxygen" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163755
APA StyleRydel-Ciszek, K., & Sobkowiak, A. (2024). The [(Bn-tpen)FeII]2+ Complex as a Catalyst for the Oxidation of Cyclohexene and Limonene with Dioxygen. Molecules, 29(16), 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163755







