Regulatory Effects of Chlormequat Chloride on the Yield and Chemical Composition of Angelica sinensis Radix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of CCC on the Yield of ASR
2.2. Residue of CCC in ASR
2.3. Chemical Composition Changes in ASR
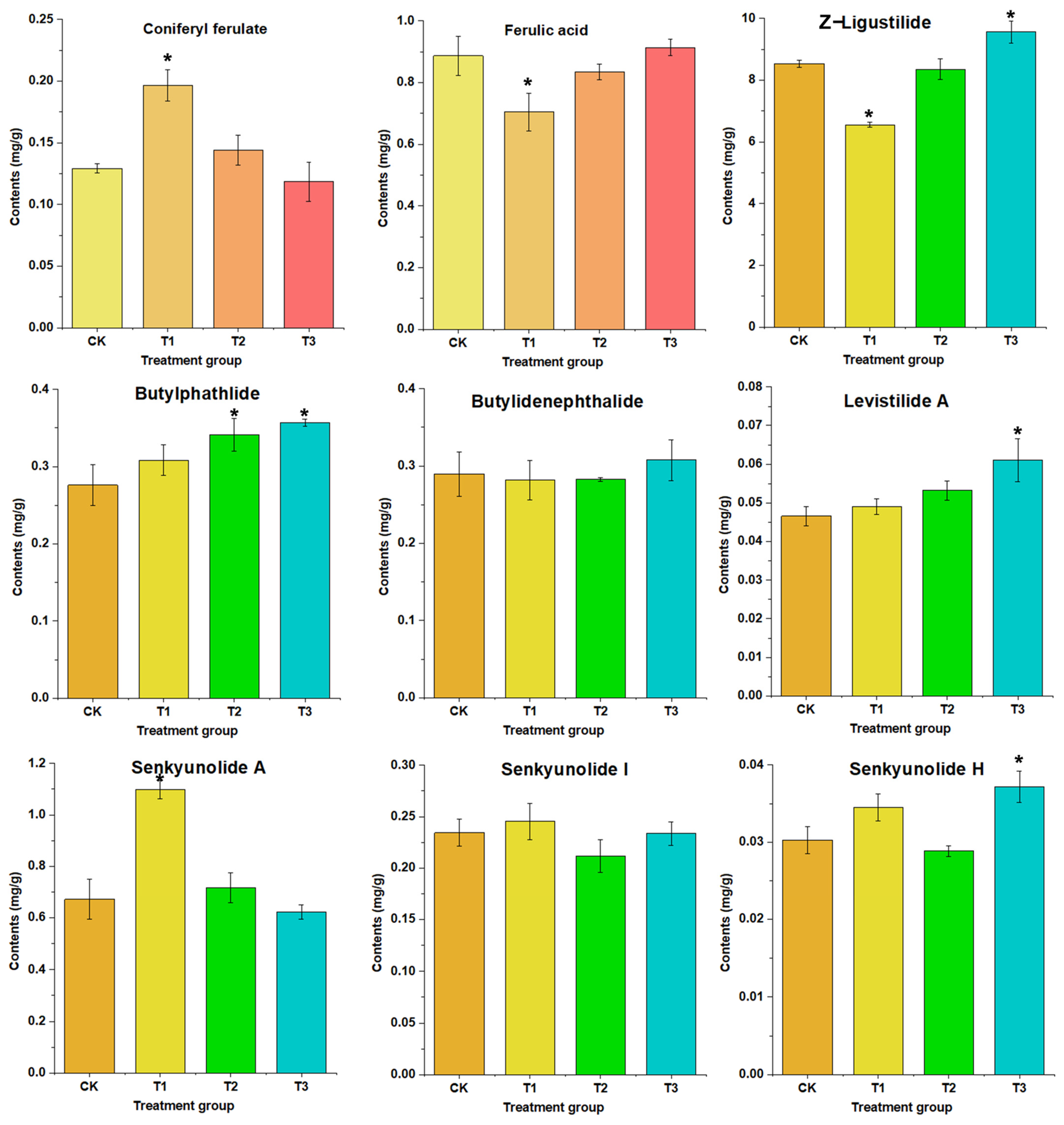
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Nine Bioactive Compounds in ASR
2.4.1. Optimization of the HPLC-MS/MS Condition
2.4.2. Sample Pretreatment
2.4.3. Method Validation
2.4.4. Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials and CCC Treatment
3.3. Instruments
3.4. Standard and Sample Solution Preparation
3.5. Chemical Composition Analysis of ASR
3.6. Quantitative Analysis of Nine Components in ASR
3.6.1. HPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS Conditions
3.6.2. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopeia of the People’s Republic of China, Part I; Chemical Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.L.; Fu, F.; Yu, B.Y.; Li, R.S. Analysis of 12 chemical compounds and pattern recognition of different parts of Angelicae Sinensis Radix by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and chemometrics methods. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 61, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Yao, W.; Ji, P.; Wei, Y. Integrated metabonomic–proteomic studies on blood enrichment effects of Angelica sinensis on a blood deficiency mice model. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhong, L.; Hua, Y.; Ji, P.; Yao, W.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, Y. Metabolomics study on promoting blood circulation and ameliorating blood stasis: Investigating the mechanism of Angelica sinensis and its processed products. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2019, 33, e4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Q.; Sun, J. Research progress in pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Angelica sinensis against cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Molecules 2024, 29, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook; Ingrid, L.I. Danggui to Angelica sinensis root: Are potential benefits to European women lost in translation? A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.W.; Zhao, Y.H. Overview of therapeutic potentiality of Angelica sinensis for ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Guan, H.; Bai, L.; Chen, P.; Gao, W.; Zhuang, G.D.; Lu, T.; Yan, G. Comparative study on Angelica sinensis after different processing with yellow rice wine in color, aromas, chemical components, and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.L.; Zeng, R.; Gu, C.M.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.F. Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.L.; Fu, F.; Jia, Y.R.; Yu, X.A.; Yu, B.Y.; Li, R.S. Quality assessment and traceability study of Angelicae sinensis Radix via binary chromatography, triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry, and multivariate statistical analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.W.; Lin, B.F. Bioactivities of major constituents isolated from Angelica sinensis (Danggui). Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yuan, D. The analysis of Radix Angelicae Sinensis (Danggui). J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.H.; Chan, K.; Chan, C.L.; Leung, K.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhao, Z.Z. Quantification of ligustilides in the roots of Angelica sinensis and related umbelliferous medicinal plants by high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1046, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.T.; Liu, W.Z.; Du, L.D.; Tuo, H.Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, M. Protective effects of Angelica sinensis volatile oil on levels of blood fats and vascular endothelial structure in hyperlipidemia rats. Chin. J. Arterioscler. 2016, 24, 989–993. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.; Wei, Y.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yang, C. A novel approach using metabolomics coupled with hematological and biochemical parameters to explain the enriching-blood effect and mechanism of unprocessed Angelica sinensis and its 4 kinds of processed products. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 211, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Banerjee, T.; Harshang, T.; Patanjali, N.; Singh, A. Development of a QuEChERS-LCMS/MS method for simultaneous estimation of tebuconazole and chlormequat chloride in wheat crop. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2021, 56, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Geng, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. The determination of underivatized chlormequat, fosetyl-aluminium and phosphonic acid residues in maize and soybean by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.L.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, F.H.; Yu, S.; Han, L.J.; Jiang, S.R. Chlormequat residues and dissipation rates in cotton crops and soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.Y.; Guo, B.L.; Cheng, M. Review on application of plant growth retardants in medicinal plants cultivation. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.F.; Yang, H.; Kong, L. Determination of chlormequat and mepiquat residues and their dissipation rates in tomato cultivation matrices by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life 2017, 1064, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedikera, S.; Obristb, H.; Vargaa, N.; Stadlera, R.H. Determination of chlormequat and mepiquat in pear, tomato, and wheat flour using on-line solid-phase extraction (Prospekt) coupled with liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 966, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.Y.; Guo, B.L.; Huang, W.H. Detection of agent “zhuanggenling” and investigation of utilization of plant growth retardants in traditional Chinese medicine cultivation. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2015, 40, 414–420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.X.; Mou, Y.; Yang, M.H.; Yu, J.; Tang, D.Y.; Guo, F.; Gu, Z.; Luo, Z.L.; Ma, X.J. Application and safety evaluation of plant growth regulators in traditional Chinese medicine. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2020, 45, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.; Chen, J.W.; Zhai, J.Y.; Shen, H.; Wu, W. Effect of different plant growth regulators on yield and quality of Angelica dahurica var. formosana development. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 2082–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Jin, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, M. An improved method for analyzing chlormequat and mepiquat in source waters by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 678, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.E.; Christensen, H.B.; SørensenV, M.T.; Leffers, H.; Andersen, J.H. Determination of chlormequat in pig serum and sow milk by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, F.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Gao, X. Study on effects of Dangshen Zhuanggenling on quality of Codondpisis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2011, 31, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Li, P.; Sun, T.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Du, B.; Yang, Z. Influence of Plant Growth Retardants on Quality of Codonopsis Radix. Molecules 2017, 22, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Guo, Y.; Yao, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, T. Impacts of cycocel and gibberellin on the biomass and flavonoid production in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2008, 24, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, W.W.; Sun, N.N.; Li, L.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of chlorocholine chloride on photosynthesis metabolism and terpene trilactones biosynthesis in the leaf of Ginkgo biloba. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2011, 38, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Sun, Z. Analysis on the research progress of early bolting of Danggui (Chinese Angelica). Guid. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2020, 26, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Z.; Liu, X.R.; Jing, Y.M. Study on the control of premature bolting of Angelica sinensis in Gansu province. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 1999, 24, 660–662. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, E. A study on inhibitory effect of plant growth retardants on earlier bolting of Chinese Angelica. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 1999, 24, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wei, J. Apiaceae medicinal plants in China: A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, bolting and flowering (BF), and BF control methods. Molecules 2023, 28, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cui, X.; Jin, L.; Li, M.; Wei, J. Bolting reduces ferulic acid and flavonoid biosynthesis and induces root lignification in Angelica sinensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.R.; Liu, Q.R.; Wu, K.Q.; Jing, Y.M. Application effect of plant growth regulator on Angelica sinensis. Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol. 1994, 11, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mou, Y.; Cui, S.; Gu, Z.; Yu, J.; Ma, X. Multi-residue analysis of plant growth regulators and pesticides in traditional Chinese medicines by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2763-2022; China National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission and Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Galea, K.S.; Maccalman, L.; Jones, K.; Cocker, J.; Teedon, P.; Cherrie, J.W.; Van Tongeren, M. Urinary biomarker concentrations of captan, chlormequat, chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin in UK adults and children living near agricultural land. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Reasoned opinion on the modification of the existing MRLs for chlormequat in pears, cereals and commodities of animal origin. Efsa J. 2014, 12, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, L.; Su, D.; Xiagedeer, B. The disrupting effect of chlormequat chloride on growth hormone is associated with pregnancy. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 395, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Kang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Wei, X.; Xiao, Q.; Hao, W. Chlorocholine chloride exposure induced spermatogenic dysfunction via iron overload caused by AhR/PERK axis-dependent ferritinophagy activation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M.T.; Danielsen, V. Effects of the plant growth regulator, chlormequat, on mammalian fertility. Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Suspected Endocrine Toxicants; National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Cai, G.; Gong, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W. Chemical composition analysis of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels and its four processed products by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry combining with nontargeted metabolomics. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sa, R.; Yan, H.; Pan, X. Metabolic fingerprinting of Angelica sinensis during growth using UPLC-TOFMS and chemometrics data analysis. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.B.; Lv, J.L.; Chen, H.L.; Duan, J.A.; Liu, J.W. Research progress of structures and pharmacological activities of phthalides from Angelica sinensis. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2016, 41, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Duan, G.; Guo, J. Research on herbal research, chemical composition and pharmacological action of different medicinal parts of Angelica sinensis. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Akkarach, B.; Supathra, L.; Siriporn, T.; Nednapis, T.; Surat, K. Ferulic acid supplementation improves lipid profiles, oxidative stress, and inflammatory status in hyperlipidemic subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.; Zheng, J. Simultaneous determination of eight components in Angelica sinensis based on UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for quality evaluation. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.L.; Li, H.H.; Shi, Y.J.; Mao, Y.J.; Gao, Q.H.; Yan, H.J.; Zhang, L.B.; Lyu, J.L. Research progress of Angelicae sinensis Radix and predictive analysis on its quality markers. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 5140–5157. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Q2 (R1): Text on Validation of Analytical Procedures; SANCO. Guidance Document Onanalytical Quality Control and Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]

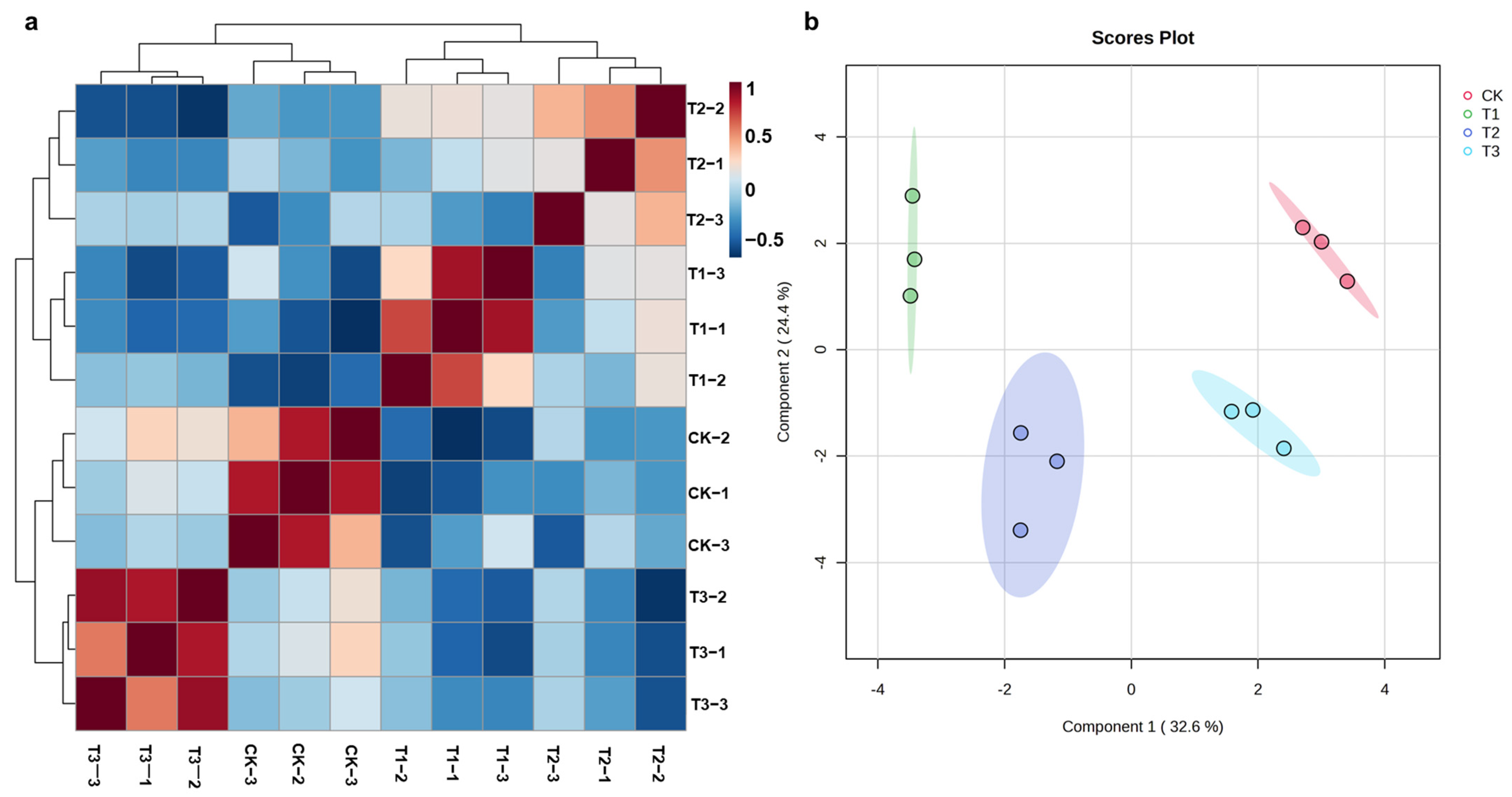

| Compound No. | Rt (min) | Formula | Expected m/z | Measured m/z | Mass Error (ppm) | Fragment Ion | Compound | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.121 | C11H12N2O2 | 205.0977 | 205.0978 | 0.49 | 188.0700, 170.0600 | Tryptophan | amino acid |
| 2 | 3.603 | C16H18O9 | 355.1029 | 355.1028 | −0.36 | 163.0392, 145.0300, 135.0439 | Chlorogenic acid | organic acids |
| 3 | 5.623 | C10H10O4 | 195.0657 | 195.0645 | −6.15 | 177.0545, 137.9867 | Ferulic acid | organic acids |
| 4 | 5.833 | C12H14O4 | 223.097 | 223.0605 | −163.39 | 209.1170, 177.0518 | Ethyl ferulate | organic acids |
| 5 | 6.944 | C12H16O4 | 225.1126 | 225.1141 | 6.66 | 207.1011, 189.0927 | Senkyunolide I | phthalides |
| 6 | 7.269 | C12H16O4 | 225.1126 | 225.1141 | 6.66 | 207.1011, 189.0927 | Senkyunolide H | phthalides |
| 7 | 8.808 | C12H12O2 | 189.0915 | 189.0917 | 1.07 | 171.0733, 161.0971, 143.0789 | Butylidenephthalide isomer | phthalides |
| 8 | 11.230 | C16H20O9 | 357.1185 | 357.1206 | 5.96 | 177.0552 | Coniferyl ferulate | organic acids |
| 9 | 14.139 | C12H16O2 | 193.1228 | 193.1230 | 0.98 | 175.1132, 147.1171, 137.0605 | Senkyunolide A | phthalides |
| 10 | 14.609 | C12H14O2 | 191.1072 | 191.1080 | 4.31 | 173.0965, 145.1014 | Butylphathlide isomer | phthalides |
| 11 | 14.667 | C18H37NO3 | 316.2851 | 316.2852 | 0.43 | 145.1014 | Dehydrophytosphingosine | fatty acids |
| 12 | 15.587 | C12H14O2 | 191.1072 | 191.1074 | 1.31 | 173.0965, 145.1014 | Butylphathlide | phthalides |
| 13 | 16.344 | C12H14O2 | 191.1072 | 191.1089 | 8.64 | 173.0965, 145.1014 | Z-ligustilide | phthalides |
| 14 | 17.661 | C12H14O2 | 191.1072 | 191.1069 | −1.57 | 173.0965, 145.1014 | Ligustilide isomer | phthalides |
| 15 | 18.437 | C24H40O6 | 425.2903 | 425.2900 | −0.60 | 345.4098, 121.1012 | 1-beta-Hydroxycholic acid | fatty acids |
| 16 | 19.147 | C12H12O2 | 189.0915 | 189.0920 | 2.43 | 171.0733, 161.0971, 143.0789 | Butylidenephthalide | phthalides |
| 17 | 20.667 | C24H28O4 | 381.2065 | 381.2065 | −0.09 | 191.1069, 149.0592 | Levistilide A isomer | phthalides |
| 18 | 20.847 | C24H28O4 | 381.2065 | 381.2065 | −0.09 | 191.1069, 149.0592 | Levistilide A isomer | phthalides |
| 19 | 21.343 | C24H28O4 | 381.2065 | 381.2064 | −0.21 | 191.1069, 149.0592 | Levistilide A | phthalides |
| 20 | 23.307 | C19H20O5 | 329.1389 | 329.1397 | 2.51 | 191.1069, 174.1264 | Columbianadin | phthalides |
| 21 | 27.371 | C18H37ON | 284.2953 | 284.2942 | −3.82 | 174.1291 | Stearamide | fatty acids |
| Compound | Rt (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ions (m/z) | Ionization Mode | DP (V) | CE (V) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For Quantification | For Identification | ||||||
| Ferulic acid | 2.95 | 192.9 | 133.8 | 177.7 | ESI− | −80 | −15/20 |
| Senkyunolide I | 3.51 | 225.2 | 207.2 | 161.1 | ESI+ | 70 | 15/30 |
| Senkyunolide H | 3.7 | 225.2 | 207.2 | 161.1 | ESI+ | 70 | 15/30 |
| Coniferyl ferulate | 7.61 | 355.3 | 192.7 | 133.7 | ESI− | −70 | −15/30 |
| Senkyunolide A | 8.18 | 193 | 137 | 146.8 | ESI+ | 20 | 20/15 |
| Butylphathlide | 8.41 | 190.9 | 144.9 | 173 | ESI+ | 20 | 15/15 |
| Z-ligustilide | 9.46 | 190.9 | 173 | 144.9 | ESI+ | 20 | 15/15 |
| Butylidenephthalide | 9.56 | 189.2 | 170.9 | 128 | ESI+ | 80 | 20/25 |
| Levistilide A | 14.52 | 381.3 | 191 | 157.2 | ESI+ | 20 | 25/35 |
| Compound | Rt (min) | Linearity | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | Precision (RSD, %) | Recovery (%) | Repeatability (RSD, %) | Stability (RSD, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (ng/mL) | r | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | ||||||
| Ferulic acid | 2.95 | 2–500 | 0.9997 | 0.6 | 2 | 2.16 | 1.15 | 105.02 | 112.86 | 109.29 | 2.34 | 3.66 |
| Senkyunolide I | 3.51 | 10–500 | 0.9992 | 5 | 10 | 2.42 | 4.37 | 101.39 | 109.46 | 110.01 | 4.31 | 5.81 |
| Senkyunolide H | 3.7 | 10–500 | 0.9998 | 5 | 10 | 2.63 | 5.56 | 105.26 | 111.07 | 112.33 | 2.04 | 2.66 |
| Coniferyl ferulate | 7.61 | 5–500 | 0.9992 | 0.6 | 2 | 3.22 | 5.72 | 100.24 | 100.91 | 102.74 | 5.01 | 4.05 |
| Senkyunolide A | 8.18 | 2–500 | 0.9996 | 0.6 | 2 | 4.20 | 2.85 | 82.35 | 83.18 | 85.14 | 1.69 | 1.89 |
| Butylphathlide | 8.41 | 2–100 | 0.9993 | 0.6 | 2 | 3.89 | 3.10 | 85.06 | 83.34 | 81.88 | 2.48 | 1.67 |
| Z-ligustilide | 9.46 | 15–500 | 0.9999 | 2 | 5 | 5.55 | 3.36 | 90.55 | 89.37 | 93.01 | 1.99 | 2.68 |
| Butylidenephthalide | 9.56 | 2–500 | 0.9998 | 0.6 | 2 | 3.74 | 4.52 | 94.22 | 87.05 | 89.76 | 4.35 | 2.15 |
| Levistilide A | 14.52 | 2–100 | 0.9992 | 0.6 | 2 | 4.49 | 2.90 | 91.17 | 90.19 | 90.03 | 2.29 | 2.38 |
| Compounds | Treatment Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Ferulic acid | 0.8867 | 0.7046 | 0.8352 | 0.9142 |
| Senkyunolide I | 0.2342 | 0.2453 | 0.2116 | 0.2335 |
| Senkyunolide H | 0.0302 | 0.0345 | 0.0288 | 0.0372 |
| Coniferyl ferulate | 0.1293 | 0.1965 | 0.1441 | 0.1185 |
| Senkyunolide A | 0.6714 | 1.0987 | 0.7171 | 0.6224 |
| Butylphathlide | 0.2763 | 0.3081 | 0.3413 | 0.3572 |
| Z-ligustilide | 8.5304 | 6.5549 | 8.3521 | 9.5662 |
| Butylidenephthalide | 0.2898 | 0.2820 | 0.2827 | 0.3076 |
| Levistilide A | 0.0466 | 0.0490 | 0.0532 | 0.0610 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Xu, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, R.; Luo, Z. Regulatory Effects of Chlormequat Chloride on the Yield and Chemical Composition of Angelica sinensis Radix. Molecules 2024, 29, 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194725
Qin H, Xu J, Ma X, Wei R, Luo Z. Regulatory Effects of Chlormequat Chloride on the Yield and Chemical Composition of Angelica sinensis Radix. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194725
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Honghan, Juan Xu, Xiaojun Ma, Rongchang Wei, and Zuliang Luo. 2024. "Regulatory Effects of Chlormequat Chloride on the Yield and Chemical Composition of Angelica sinensis Radix" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194725
APA StyleQin, H., Xu, J., Ma, X., Wei, R., & Luo, Z. (2024). Regulatory Effects of Chlormequat Chloride on the Yield and Chemical Composition of Angelica sinensis Radix. Molecules, 29(19), 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194725






