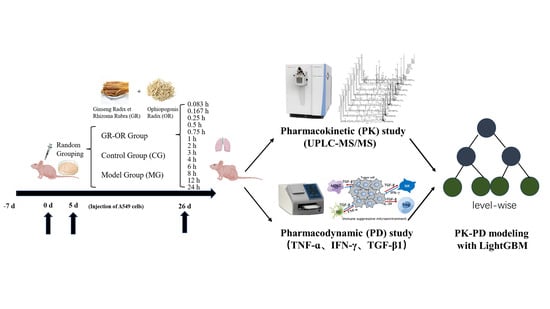
Using Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Main Active Substances of the Anticancer Effect in Mice from Panax ginseng–Ophiopogon japonicus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
2.1.1. Specificity
2.1.2. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
2.1.3. Precision and Accuracy
2.1.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.1.5. Stability
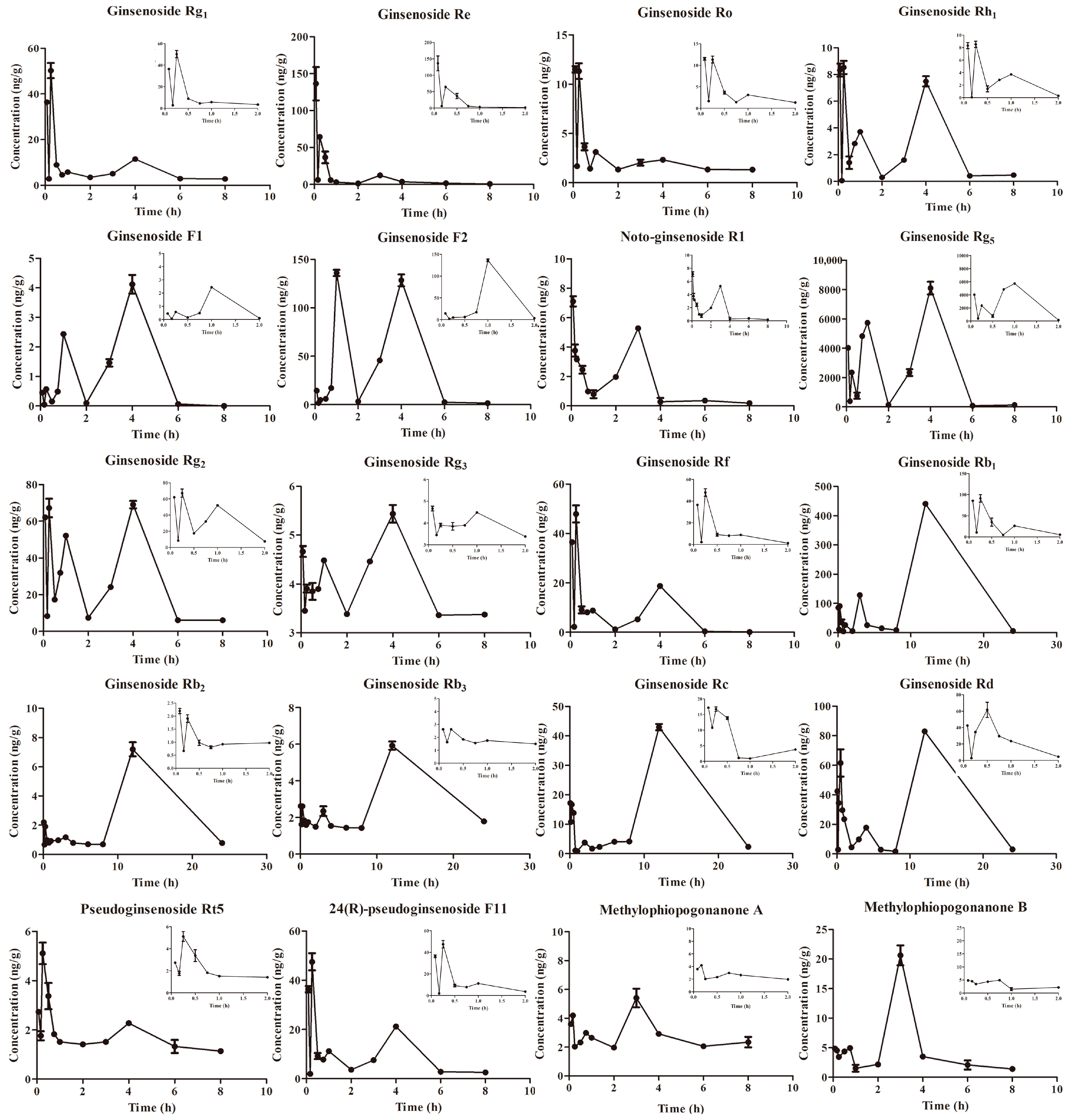
2.2. Pharmacokinetics Experiment
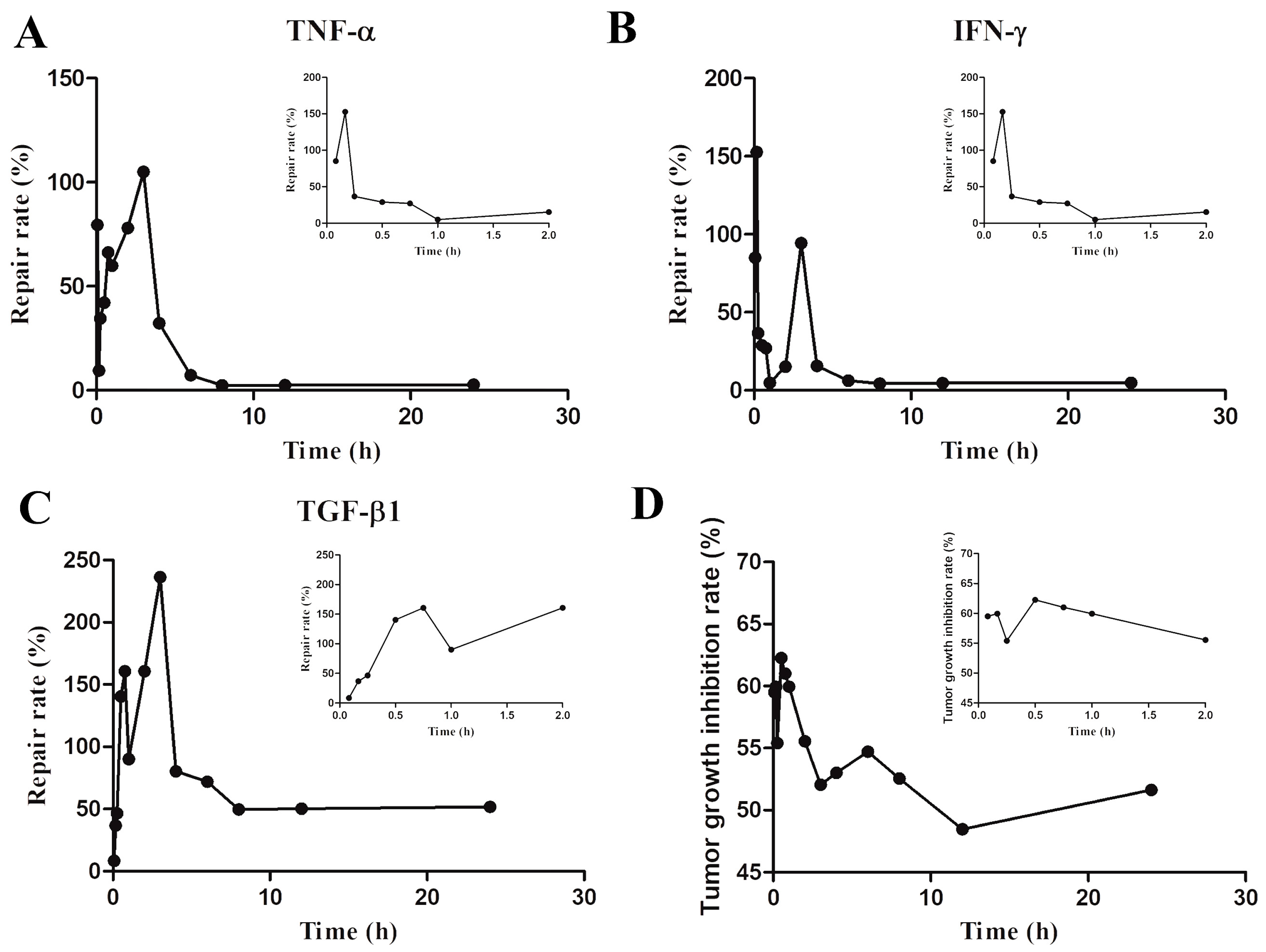
2.3. Pharmacodynamic Experiment
2.4. Related Analysis
2.4.1. Comprehensive Weighted Scoring of Efficacy Indicators
2.4.2. Feature-Sorting Algorithm Based on LightGBM Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Sample Solutions
4.3. Animal Treatments and Tissue-Sample Collection
4.4. UHPLC—Orbitrap MS Conditions
4.5. Preparation of Quality-Control (QC) Samples and Method Validation
4.6. Data Analysis of the Pharmacokinetic Study
4.7. Pharmacodynamic Experiment
4.8. PK–PD-Correlation Analysis
4.8.1. The Comprehensive Weight Method for Efficacy-Indicators Assessment
4.8.2. Feature-Ranking Based on LightGBM Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, S.Y.; Li, H.; Cao, M.M.; Sun, D.Q.; Lei, L.; Li, N.; Peng, J.; Chen, W.Q. Trends and risk factors of lung cancer in China. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.; Li, C.; Cai, P.; Qi, F. The positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for cancer. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, G. Traditional Chinese medicine and lung cancer—From theory to practice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.H.; Li, C.I.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, J.G.; Chiang, J.H.; Li, T.C. Traditional Chinese medicine as adjunctive therapy improves the long-term survival of lung cancer patients. J. Cancer. Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Commission of Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 11th ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, T.K. Panax ginseng—A non-organ-specific cancer preventive? Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.H.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, M.; Lin, L.G.; Wang, Y.T. Ophiopogon japonicus—A phytochemical, ethnomedicinal and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Lc/Ms fingerprinting of Shenmai injection: A novel approach to quality control of herbal medicines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Zhao, J.; He, L.F.; Li, L.X.; Zhu, Z.K.; Tian, M.L. Extraction, characterization and anti-oxidant activity of polysaccharide from red Panax ginseng and Ophiopogon japonicus waste. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1183096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ye, Q.; Xu, S.; Chang, Y.X.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Hua, S. Shengmai injection alleviates H2O2-induced oxidative stress through activation of AKT and inhibition of ERK pathways in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 239, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Jia, X.; Cai, E.; Zhao, Y. Comparative analysis of active ingredients and effects of the combination of Panax ginseng and Ophiopogon japonicus at different proportions on chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression mouse. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Tang, L.; Hu, S.; Tian, G.; Dong, C.; Lai, H.; Yang, H. Shengmai San-derived Compound Prescriptions: A review on Chemical constituents, Pharmacokinetic studies, Quality control, and Pharmacological properties. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukae, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Hirota, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamahashi, M.; Takayama, K.; Ieiri, I. Population pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling and model-based prediction of docetaxel-induced neutropenia in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.F.; Chen, C.; Fan, X.L.; Dong, Y.; Ge, Y.W.; Wang, S.M. Study on pharmacodynamic material basis of Naomaitong to protect neuronal cells based on PK-PD model. J. Cancer Chin. Mat. Med. 2019, 44, 2588–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, T.Y. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, H.; Oyama, A.; Kitora, S.; Toki, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Kotoku, J.I.; Moriyama, T. Gradient boosting decision tree becomes more reliable than logistic regression in predicting probability for diabetes with big data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.Y.; Shang, W.Q.; Yu, J.J.; Sun, Q.; Li, M.Q.; Sun, J.S. The antitumor activity study of ginsenosides and metabolites in lung cancer cell. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 1708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, D.H.; Nahar, J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Rupa, E.J.; Ramadhania, Z.M.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Kang, S.C. A focused review on molecular signalling mechanisms of ginsenosides anti-Lung cancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, H.; Lyu, Z.; Bai, Y.; He, J. Simultaneous Determination of 16 Saponins Contents in Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma in Rats by UHPLC-MS/MS and Pharmacokinetics. J. Cancer Chin. Mat. Med. 2023, 46, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Du, F.; Jia, W.; Xu, F.; Li, C. Molecular mechanisms governing different pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides and potential for ginsenoside-perpetrated herb–drug interactions on OATP 1 B 3. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y.L.; Yin, J.N.; Yan, W.Q.; Liu, J.G.; Li, H.J. Pharmacological activities of ginsenoside Rg5. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Wang, S. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of saponins after intravenous administration of ShenMai Injection in rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1128, 121777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zuo, Z.T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, F.R. A fast multi-source information fusion strategy based on FTIR spectroscopy for geographical authentication of wild Gentiana rigescens. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, R.W.; Stone, L.A. Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Pharmacokinetics of Chinese medicines: Strategies and perspectives. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, G.C.; Liu, Y.Q. Duality of interactions between TGF-β and TNF-α during tumor formation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 810286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Cao, D. TGF-β signaling, tumor microenvironment and tumor progression: The butterfly effect. Front. Biosci.-Landmrk 2010, 15, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojic, M.; Takeda, K.; Hayakawa, Y. The dark side of IFN-γ: Its role in promoting cancer immunoevasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Pang, Y.; Moses, H.L. TGF-β and immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.A.; Qin, J.-J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: In vitro and in vivo activities, structure–activity relationships, and molecular mechanisms of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Guan, D. Decoding the key compounds and mechanism of Shashen Maidong decoction in the treatment of lung cancer. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, J.J.; Hong, H.J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.J. Ophiopogon japonicus and its active compounds: A review of potential anticancer effects and underlying mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2023, 113, 154718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ci, Y.; Han, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 can ameliorate the key in nti-in cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 in a cancer cachexia mouse model. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.; Gao, H.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, S. Ginsenoside Rb1 is an immune-stimulatory agent with antiviral activity against enterovirus 71. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-J.; Tang, H.-T.; Jia, Y.-T.; Ma, B.; Fu, J.-F.; Wang, Y.; Lv, K.-Y.; Xia, Z.-F. Notoginsenoside R1 Attenuates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Shock 2010, 34, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline, I.H. Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis M10; ICH Harmonised Guideline: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]


| Compounds | Regression Equation | R2 | Linear Range (ng/g) | LLOQ (ng/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | y = −0.000025 + 0.00015 × x | 0.9996 | 0.10–500 | 0.10 |
| Ginsenoside Re | y = −0.0000039 + 0.0000078 × x | 0.9995 | 0.10–500 | 0.10 |
| Ginsenoside Ro | y = −0.00015 + 0.00012 × x | 0.9996 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | y = 0.000060 + 0.00011 × x | 0.9996 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Ginsenoside F1 | y = 0.0000053 + 0.00015 × x | 0.9974 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Ginsenoside F2 | y = 0.000012 + 0.000052 × x | 0.9993 | 0.50–500 | 0.50 |
| Notoginsenoside R1 | y = 0.0000060 + 0.00000026 × x | 0.9990 | 0.005–500 | 0.005 |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | y = −0.00042 + 0.000081 × x | 0.9997 | 50–10,000 | 50.00 |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | y = −0.0021 + 0.00065 × x | 0.9998 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | y = 0.000012 + 0.00014 × x | 0.9992 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Ginsenoside Rf | y = −0.000062 + 0.000029 × x | 0.9990 | 0.10–500 | 0.10 |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | y = −0.000038 + 0.000068 × x | 0.9997 | 0.10–500 | 0.10 |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | y = −0.00011 + 0.000081 × x | 0.9992 | 0.50–500 | 0.50 |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | y = 0.00016 + 0.000037 × x | 0.9993 | 0.50–500 | 0.50 |
| Ginsenoside Rc | y = −0.00022 + 0.00014 × x | 0.9998 | 0.50–500 | 0.50 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | y = −0.00020 + 0.00016 × x | 0.9997 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Pseudoginsenoside RT5 | y = 0.0052 + 0.00017 × x | 0.9990 | 0.50–500 | 0.50 |
| 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | y = 0.000044 + 0.00014 × x | 0.9991 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone A | y = −0.00034 + 0.00021 × x | 0.9997 | 0.25–500 | 0.25 |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone B | y = −0.000089 + 0.00016 × x | 0.9994 | 0.10–500 | 0.10 |
| Compounds | Nominal Concentration (ng/g) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (RSD%) | Accuracy (RE%) | Precision (RSD%) | Accuracy (RE%) | ||
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 5 | 3.67% | −0.58% | 1.97% | 2.68% |
| 50 | 3.71% | −0.31% | 3.61% | 1.03% | |
| 500 | 8.28% | −4.01% | 3.02% | −0.18% | |
| Ginsenoside Re | 5 | 5.13% | −0.10% | 13.22% | 10.71% |
| 50 | 12.09% | −14.43% | 8.16% | −14.86% | |
| 500 | 3.31% | −9.34% | 11.62% | −4.12% | |
| Ginsenoside Ro | 5 | 7.50% | 3.64% | 12.85% | 8.34% |
| 50 | 7.81% | 4.45% | 8.31% | 2.31% | |
| 500 | 12.85% | −1.01% | 7.09% | −3.14% | |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 5 | 4.94% | 8.66% | 5.90% | 10.26% |
| 50 | 11.78% | −5.02% | 8.44% | −1.37% | |
| 500 | 11.26% | 1.14% | 10.67% | −0.60% | |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 5 | 3.31% | 3.81% | 3.51% | 7.55% |
| 50 | 4.44% | 0.95% | 3.88% | 0.50% | |
| 500 | 10.39% | −3.38% | 5.70% | −1.42% | |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 5 | 1.57% | 0.05% | 3.18% | −1.82% |
| 50 | 5.54% | 1.29% | 4.95% | 2.65% | |
| 500 | 10.39% | −2.04% | 3.84% | 1.04% | |
| Notoginsenoside R1 | 5 | 10.28% | 11.96% | 6.94% | 6.76% |
| 50 | 14.25% | 9.24% | 8.37% | 10.25% | |
| 500 | 5.78% | 13.01% | 4.87% | −9.83% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 5 | 9.10% | −1.55% | 14.73% | −5.73% |
| 50 | 6.14% | −3.75% | 7.70% | −3.68% | |
| 500 | 11.80% | −7.95% | 4.94% | −0.09% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | 5 | 9.57% | 11.69% | 11.68% | 12.11% |
| 50 | 8.30% | −3.65% | 8.81% | −5.70% | |
| 500 | 10.55% | 9.49% | 10.44% | 6.54% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 5 | 3.25% | 6.73% | 3.57% | 5.42% |
| 50 | 3.24% | 0.66% | 4.73% | 2.50% | |
| 500 | 8.82% | −4.47% | 2.50% | 0.29% | |
| Ginsenoside Rf | 5 | 3.67% | −7.00% | 8.84% | −4.19% |
| 50 | 7.33% | 5.65% | 9.05% | 7.85% | |
| 500 | 8.90% | −4.17% | 4.00% | −3.07% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 5 | 8.19% | 5.68% | 5.20% | 10.27% |
| 50 | 9.10% | 7.12% | 7.53% | 5.81% | |
| 500 | 8.80% | −4.68% | 6.24% | −2.28% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 5 | 4.88% | 0.84% | 6.15% | 8.20% |
| 50 | 8.44% | 4.22% | 8.43% | 4.30% | |
| 500 | 8.86% | −1.16% | 5.00% | −2.66% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 5 | 8.90% | −7.38% | 11.52% | −7.37% |
| 50 | 7.04% | −2.91% | 5.69% | 0.04% | |
| 500 | 13.20% | −5.55% | 5.89% | 2.28% | |
| Ginsenoside Rc | 5 | 4.14% | 1.24% | 9.36% | −5.75% |
| 50 | 10.62% | −8.09% | 7.65% | −3.45% | |
| 500 | 13.66% | −2.49% | 11.64% | 0.21% | |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 5 | 9.37% | 5.41% | 1.87% | 11.06% |
| 50 | 3.58% | 1.80% | 5.40% | 4.06% | |
| 500 | 7.69% | −1.63% | 3.51% | −0.32% | |
| Pseudoginsenoside RT5 | 5 | 1.93% | 0.94% | 1.39% | 2.94% |
| 50 | 3.52% | 2.14% | 8.05% | 6.65% | |
| 500 | 8.09% | −2.43% | 3.09% | 0.94% | |
| 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | 5 | 3.25% | 4.81% | 3.48% | 4.74% |
| 50 | 3.22% | 1.09% | 4.88% | 3.17% | |
| 500 | 7.10% | −4.07% | 1.89% | −0.19% | |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone A | 5 | 4.06% | 9.29% | 3.58% | 9.21% |
| 50 | 3.60% | −1.90% | 6.43% | 0.56% | |
| 500 | 8.39% | −3.36% | 4.25% | −0.65% | |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone B | 5 | 3.59% | 5.19% | 6.61% | 2.75% |
| 50 | 4.09% | −3.82% | 6.37% | −1.21% | |
| 500 | 8.78% | −2.83% | 5.05% | 0.27% | |
| Compounds | Nominal Concentration (ng/g) | Extraction Recovery | Matrix Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (%) | RSD (%) | Mean ± SD (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 5 | 102.54 ± 5.35 | 5.22 | 91.20 ± 5.23 | 5.74 |
| 50 | 99.25 ± 3.72 | 3.74 | 97.24 ± 6.01 | 6.18 | |
| 500 | 101.85 ± 1.70 | 1.67 | 105.54 ± 5.51 | 5.22 | |
| Ginsenoside Re | 5 | 102.03 ± 4.98 | 4.88 | 105.94 ± 3.07 | 2.90 |
| 50 | 99.28 ± 4.54 | 4.58 | 99.95 ± 5.12 | 5.12 | |
| 500 | 103.82 ± 3.06 | 2.95 | 101.40 ± 3.87 | 3.82 | |
| Ginsenoside Ro | 5 | 109.20 ± 8.40 | 7.70 | 95.81 ± 3.90 | 4.07 |
| 50 | 92.95 ± 2.63 | 2.83 | 90.57 ± 5.89 | 6.50 | |
| 500 | 105.26 ± 2.48 | 2.36 | 100.70 ± 7.99 | 7.93 | |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 5 | 100.56 ± 6.15 | 6.12 | 107.55 ± 0.68 | 0.63 |
| 50 | 98.56 ± 3.36 | 3.41 | 95.99 ± 4.47 | 4.65 | |
| 500 | 104.53 ± 1.30 | 1.24 | 103.87 ± 3.29 | 3.17 | |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 5 | 100.83 ± 4.76 | 4.72 | 103.12 ± 0.50 | 0.49 |
| 50 | 99.35 ± 3.47 | 3.49 | 94.52 ± 4.62 | 4.88 | |
| 500 | 103.32 ± 0.61 | 0.59 | 101.06 ± 5.51 | 5.15 | |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 5 | 101.19 ± 4.58 | 4.52 | 103.50 ± 2.67 | 2.58 |
| 50 | 99.81 ± 8.81 | 8.83 | 102.04 ± 6.75 | 6.61 | |
| 500 | 102.48 ± 0.47 | 0.46 | 101.14 ± 5.17 | 5.11 | |
| Notoginsenoside R1 | 5 | 106.68 ± 5.63 | 5.28 | 108.68 ± 1.39 | 1.28 |
| 50 | 105.11 ± 6.07 | 5.77 | 104.17 ± 4.13 | 3.96 | |
| 500 | 90.53 ± 4.55 | 5.03 | 104.16 ± 2.47 | 2.37 | |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 5 | 88.79 ± 9.64 | 10.86 | 94.04 ± 4.37 | 4.65 |
| 50 | 102.14 ± 9.37 | 9.17 | 91.92 ± 9.32 | 10.14 | |
| 500 | 105.76 ± 4.70 | 4.44 | 88.85 ± 8.56 | 9.63 | |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | 5 | 101.42 ± 6.48 | 6.39 | 87.43 ± 3.31 | 3.79 |
| 50 | 102.51 ± 2.42 | 2.36 | 96.56 ± 5.11 | 5.29 | |
| 500 | 101.75 ± 6.75 | 6.64 | 100.94 ± 3.36 | 3.33 | |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 5 | 103.19 ± 5.52 | 5.35 | 100.84 ± 9.24 | 9.16 |
| 50 | 101.82 ± 1.71 | 1.68 | 99.60 ± 4.06 | 4.08 | |
| 500 | 101.00 ± 2.96 | 2.93 | 105.45 ± 5.09 | 4.82 | |
| Ginsenoside Rf | 5 | 101.09 ± 1.45 | 1.43 | 106.77 ± 1.76 | 1.65 |
| 50 | 96.94 ± 1.10 | 1.13 | 94.08 ± 4.43 | 4.71 | |
| 500 | 93.95 ± 0.50 | 0.53 | 95.49 ± 8.33 | 8.73 | |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 5 | 97.98 ± 1.49 | 1.53 | 104.16 ± 10.06 | 9.66 |
| 50 | 94.94 ± 3.94 | 4.15 | 91.29 ± 8.92 | 9.78 | |
| 500 | 94.63 ± 1.60 | 1.69 | 95.02 ± 3.24 | 3.41 | |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 5 | 106.83 ± 10.37 | 9.71 | 91.96 ± 3.36 | 3.65 |
| 50 | 90.20 ± 0.95 | 1.06 | 86.80 ± 3.97 | 4.57 | |
| 500 | 99.93 ± 0.21 | 0.21 | 90.85 ± 1.33 | 1.46 | |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 5 | 100.26 ± 0.12 | 0.12 | 103.25 ± 1.03 | 1.00 |
| 50 | 97.90 ± 2.76 | 2.82 | 91.06 ± 9.65 | 9.60 | |
| 500 | 105.68 ± 4.45 | 4.21 | 101.07 ± 0.79 | 0.78 | |
| Ginsenoside Rc | 5 | 106.00 ± 9.49 | 8.96 | 103.24 ± 2.19 | 2.12 |
| 50 | 105.32 ± 5.84 | 5.54 | 97.35 ± 2.63 | 2.70 | |
| 500 | 103.82 ± 3.06 | 2.95 | 89.15 ± 3.08 | 3.45 | |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 5 | 94.57 ± 2.18 | 2.31 | 101.35 ± 1.99 | 1.97 |
| 50 | 91.97 ± 9.20 | 10.01 | 90.50 ± 11.17 | 12.34 | |
| 500 | 87.71 ± 1.24 | 1.42 | 103.30 ± 3.12 | 3.02 | |
| Pseudoginsenoside RT5 | 5 | 105.81 ± 11.39 | 10.76 | 88.10 ± 1.22 | 1.38 |
| 50 | 99.32 ± 0.46 | 0.46 | 97.33 ± 2.49 | 2.56 | |
| 500 | 105.63 ± 7.06 | 6.68 | 92.97 ± 8.64 | 9.29 | |
| 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | 5 | 100.44 ± 4.78 | 4.66 | 104.37 ± 2.60 | 2.49 |
| 50 | 100.94 ± 2.78 | 2.75 | 98.85 ± 5.13 | 5.19 | |
| 500 | 96.92 ± 5.55 | 5.72 | 99.30 ± 6.58 | 6.63 | |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone A | 5 | 101.56 ± 1.45 | 1.43 | 91.33 ± 1.39 | 1.52 |
| 50 | 105.05 ± 7.10 | 6.76 | 99.85 ± 1.44 | 1.44 | |
| 500 | 88.99 ± 0.91 | 1.02 | 93.11 ± 3.34 | 3.59 | |
| Methylophiopogon flavanone B | 5 | 99.45 ± 3.02 | 3.04 | 98.99 ± 0.95 | 0.96 |
| 50 | 105.41 ± 22.49 | 2.36 | 103.36 ± 5.31 | 5.14 | |
| 500 | 97.94 ± 3.04 | 3.11 | 87.71 ± 6.06 | 6.91 | |
| Compounds | Nominal Concentration (ng/g) | Short Term | Three Freeze–Thaw Cycles | Long Term | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ||
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 5 | 3.74% | 0.49% | 10.56% | 11.24% | 6.12% | −1.70% |
| 50 | 3.94% | 1.34% | 7.41% | 13.01% | 4.32% | 17.42% | |
| 500 | 10.80% | 0.20% | 5.53% | 14.49% | 5.64% | 13.31% | |
| Ginsenoside Re | 5 | 11.05% | 4.81% | 10.92% | −1.98% | 7.39% | −19.79% |
| 50 | 12.72% | −13.15% | 0.62% | 10.81% | 2.00% | 14.21% | |
| 500 | 11.79% | 6.17% | 16.02% | 11.65% | 18.75% | 13.94% | |
| Ginsenoside Ro | 5 | 8.54% | 8.62% | 11.19% | 16.33% | 10.47% | 8.22% |
| 50 | 7.84% | 6.89% | 10.41% | 10.39% | 12.03% | 13.22% | |
| 500 | 12.82% | 0.28% | 11.66% | 15.72% | 10.51% | 11.59% | |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 5 | 5.55% | 11.68% | 6.01% | 15.36% | 4.53% | −1.41% |
| 50 | 12.06% | −3.24% | 11.28% | 18.32% | 15.41% | 18.76% | |
| 500 | 8.80% | −0.38% | 2.83% | 10.57% | 5.48% | 17.88% | |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 5 | 4.17% | 6.91% | 9.85% | 18.33% | 10.67% | −4.70% |
| 50 | 3.83% | 2.39% | 9.37% | 16.72% | 7.36% | 19.31% | |
| 500 | 11.39% | 0.31% | 6.12% | 9.29% | 9.18% | 12.65% | |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 5 | 2.23% | −1.67% | 7.94% | 7.15% | 4.74% | −2.19% |
| 50 | 5.94% | 4.33% | 6.64% | 13.85% | 7.13% | 15.28% | |
| 500 | 10.74% | 0.36% | 3.29% | −1.50% | 9.81% | 3.40% | |
| Notoginsenoside R1 | 5 | 10.26% | 11.06% | 8.95% | 14.20% | 2.96% | 4.89% |
| 50 | 8.53% | 6.89% | 2.12% | 6.22% | 2.71% | 8.60% | |
| 500 | 11.57% | −3.93% | 16.60% | −5.12% | 13.87% | −7.16% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 5 | 12.61% | −9.35% | 19.09% | 19.21% | 7.46% | 15.87% |
| 50 | 8.07% | −7.55% | 9.95% | 9.55% | 10.76% | −6.36% | |
| 500 | 10.82% | 5.42% | 5.80% | 16.06% | 6.71% | 14.05% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | 5 | 3.25% | 11.46% | 16.98% | −18.16% | 5.66% | −2.28% |
| 50 | 7.42% | 0.76% | 16.66% | 2.30% | 16.66% | 2.30% | |
| 500 | 14.04% | 2.58% | 4.29% | −3.34% | 18.65% | −17.08% | |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 5 | 2.48% | 5.07% | 11.40% | 17.95% | 4.71% | 15.74% |
| 50 | 3.60% | 2.96% | 3.46% | 0.71% | 3.46% | 0.71% | |
| 500 | 11.75% | −0.04% | 2.95% | 17.81% | 3.75% | 18.93% | |
| Ginsenoside Rf | 5 | 3.27% | −7.44% | 19.17% | 17.80% | 13.23% | −1.25% |
| 50 | 6.34% | 11.93% | 9.94% | 18.33% | 9.94% | 18.33% | |
| 500 | 11.26% | 2.59% | 5.47% | 9.47% | 5.14% | 7.20% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 5 | 7.45% | 3.93% | 17.12% | 3.07% | 5.97% | −14.73% |
| 50 | 7.74% | 12.32% | 7.54% | 17.02% | 7.43% | 16.77% | |
| 500 | 11.36% | 2.98% | 16.29% | 13.24% | 2.37% | 19.79% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 5 | 7.03% | 5.17% | 17.85% | 12.19% | 2.61% | 19.17% |
| 50 | 8.15% | 8.58% | 7.01% | 18.46% | 6.44% | 18.92% | |
| 500 | 10.19% | 0.07% | 4.70% | 17.45% | 7.06% | 19.95% | |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 5 | 7.80% | −10.06% | 5.93% | 12.30% | 2.66% | −6.18% |
| 50 | 8.50% | −1.19% | 6.94% | −7.33% | 5.26% | −5.61% | |
| 500 | 10.68% | 4.01% | 2.62% | 14.85% | 8.13% | 18.86% | |
| Ginsenoside Rc | 5 | 7.90% | −5.12% | 14.41% | −9.09% | 4.15% | −13.72% |
| 50 | 11.44% | −9.49% | 7.40% | 1.40% | 7.40% | 1.40% | |
| 500 | 18.90% | −0.11% | 9.88% | −1.45% | 8.64% | 0.82% | |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 5 | 7.45% | 7.45% | 8.21% | 12.09% | 4.08% | 4.40% |
| 50 | 4.68% | 5.45% | 7.52% | −12.02% | 8.34% | −10.53% | |
| 500 | 8.84% | −0.73% | 2.55% | 14.57% | 1.57% | 15.40% | |
| Pseudoginsenoside RT5 | 5 | 2.11% | 1.84% | 13.25% | 8.07% | 2.11% | 2.57% |
| 50 | 6.97% | 8.24% | 5.46% | 2.66% | 17.16% | 19.04% | |
| 500 | 8.85% | −1.16% | 2.06% | 12.89% | 2.37% | 13.24% | |
| 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | 5 | 2.27% | 3.05% | 11.45% | 9.60% | 4.73% | 7.63% |
| 50 | 3.64% | 3.81% | 5.78% | 8.32% | 5.78% | 8.32% | |
| 500 | 10.45% | 0.06% | 2.31% | 17.38% | 2.26% | 17.29% | |
| Methyl ophiopogon flavanone A | 5 | 3.20% | 8.50% | 18.33% | −10.97% | 3.26% | −17.92% |
| 50 | 6.69% | 0.25% | 6.76% | −14.39% | 7.63% | −13.20% | |
| 500 | 10.48% | −0.92% | 8.68% | −19.99% | 9.02% | −19.61% | |
| Methyl ophiopogon flavanone B | 5 | 3.11% | 4.61% | 18.61% | −16.54% | 8.96% | −17.22% |
| 50 | 6.34% | −2.69% | 8.47% | 15.54% | 7.37% | 12.48% | |
| 500 | 8.83% | 1.73% | 17.70% | 13.69% | 18.75% | 12.19% | |
| Components | Cmax/ng/g | Tmax/min | AUC(0–∞)/ng/g·min | AUC(0–t)/ng/g·min | MRT(0–t)/min | T1/2/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 50.24 ± 6.67 | 15.00 ± 0.00 | 2345.90 ± 212.68 | 2295.03 ± 213.32 | 135.88 ± 4.70 | 98.12 ± 2.74 |
| Ginsenoside Re | 132.49 ± 32.88 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 3933.20 ± 224.66 | 3815.68 ± 233.30 | 93.98 ± 3.79 | 105.69 ± 4.36 |
| Ginsenoside Ro | 11.95 ± 0.88 | 12.50 ± 2.89 | 1415.87 ± 57.44 | 1043.18 ± 64.96 | 184.92 ± 4.08 | 252.46 ± 11.88 |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 8.98 ± 0.20 | 12.50 ± 5.00 | 1724.14 ± 411.48 | 1303.44 ± 70.16 | 190.78 ± 1.61 | 418.21 ± 293.98 |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 4.12 ± 0.45 | 240.00 ± 0.00 | 648.77 ± 60.38 | 640.00 ± 61.94 | 197.55 ± 1.51 | 134.21 ± 14.44 |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 134.49 ± 1.58 | 60.00 ± 0.00 | 24,395.33 ± 613.30 | 21,872.62 ± 480.93 | 184.97 ± 1.87 | 349.67 ± 16.15 |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 7967.81 ± 441.77 | 240.00 ± 0.00 | 1,372,202.28 ± 48,963.33 | 1,342,117.43 ± 45,675.73 | 183.91 ± 2.00 | 126.76 ± 9.45 |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | 71.11 ± 6.20 | 15.00 ± 0.00 | 16,012.21 ± 284.14 | 13,822.64 ± 316.65 | 187.28 ± 1.45 | 214.68 ± 6.15 |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 4.75 ± 0.12 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 14,133.43 ± 3134.88 | 1879.87 ± 53.24 | 230.11 ± 2.69 | 2381.66 ± 562.33 |
| Ginsenoside Rf | 47.90 ± 6.96 | 15.00 ± 0.00 | 3678.93 ± 167.94 | 3656.82 ± 167.79 | 159.91 ± 1.98 | 76.57 ± 1.04 |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 440.68 ± 15.67 | 720.00 ± 0.00 | 283,948.70 ± 17,261.40 | 227,245.91 ± 5460.47 | 687.50 ± 1.03 | 1974.59 ± 188.71 |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 7.20 ± 0.96 | 720.00 ± 0.00 | 6076.50 ± 664.68 | 3935.63 ± 598.40 | 712.61 ± 2.29 | 1191.02 ± 262.76 |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 5.92 ± 0.45 | 720.00 ± 0.00 | 16,689.44 ± 2585.97 | 4049.29 ± 622.84 | 827.16 ± 190.05 | 3995.02 ± 516.27 |
| Ginsenoside Rc | 42.95 ± 2.11 | 720.00 ± 0.00 | 25,129.88 ± 1611.92 | 23,180.66 ± 703.80 | 698.08 ± 7.43 | 444.67 ± 101.01 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 82.95 ± 2.11 | 720.00 ± 0.00 | 56,296.57 ± 6663.99 | 46,163.94 ± 1033.00 | 667.90 ± 1.77 | 970.90 ± 220.59 |
| Pseudoginsenoside RT5 | 5.11 ± 0.88 | 15.00 ± 0.00 | 2160.58 ± 307.18 | 890.71 ± 40.23 | 224.26 ± 5.19 | 634.34 ± 141.79 |
| Notoginsenoside R1 | 7.16 ± 1.65 | 7.50 ± 3.54 | 1703.60 ± 109.17 | 1636.22 ± 104.54 | 207.16 ± 5.18 | 74.38 ± 1.47 |
| 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | 47.49 ± 6.94 | 15.00 ± 0.00 | 5604.97 ± 147.55 | 4660.97 ± 205.76 | 184.94 ± 2.87 | 227.16 ± 12.27 |
| Methylophiopogonanone A | 5.70 ± 0.88 | 150.00 ± 0.00 | 5425.63 ± 1564.22 | 1362.39 ± 36.13 | 219.18 ± 4.79 | 1219.25 ± 362.74 |
| Methylophiopogonanone B | 20.61 ± 2.38 | 150.00 ± 0.00 | 3466.12 ± 558.35 | 2331.08 ± 125.83 | 184.20 ± 10.94 | 390.53 ± 100.42 |
| Group | TNF-α (pg/g) | IFN-γ (pg/g) | TGF-β1 (pg/g) | Tumor Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 6.25 ± 1.38 *** | 541.81 ± 37.39 *** | 626.67 ± 25.88 *** | ---- |
| M | 2.30 ± 0.38 | 53.31 ± 7.41 | 316.33 ± 88.55 | 1282.09 ± 181.31 |
| 0.083 h | 5.63 ± 0.66 ** | 500.92 ± 199.42 *** | 395.33 ± 79.28 | 519.22 ± 72.02 *** |
| 0.167 h | 2.79 ± 1.38 | 697.58 ± 221.38 *** | 492.67 ± 124.69 | 513.57 ± 24.41 *** |
| 0.25 h | 3.53 ± 0.97 | 272.42 ± 71.31 | 460.83 ± 75.59 | 571.74 ± 64.86 *** |
| 0.5 h | 3.84 ± 1.11 | 206.23 ± 66.60 | 720.00 ± 23.53 *** | 483.84 ± 89.12 *** |
| 0.75 h | 5.01 ± 1.31 * | 167.15 ± 88.39 | 766.22 ± 112.59 *** | 499.70 ± 40.04 *** |
| 1 h | 4.73 ± 0.75 * | 79.58 ± 12.22 | 511.50 ± 98.52 * | 513.44 ± 16.94 *** |
| 2 h | 5.64 ± 1.47 ** | 140.73 ± 18.45 | 761.17 ± 109.49 *** | 577.87 ± 40.68 *** |
| 3 h | 6.97 ± 1.44 *** | 522.69 ± 116.26 *** | 975.00 ± 104.86 *** | 614.60 ± 39.46 *** |
| 4 h | 3.35 ± 1.43 | 132.55 ± 53.12 | 554.67 ± 20.40 ** | 611.46 ± 12.89 *** |
| 6 h | 2.86 ± 1.01 | 82.68 ± 11.38 | 510.67 ± 104.52 * | 578.167 ± 19.38 *** |
| 8 h | 2.42 ± 0.45 | 71.11 ± 7.73 | 467.11 ± 71.36 | 608.35 ± 27.81 *** |
| 12 h | 2.56 ± 0.67 | 72.67 ± 8.90 | 472.71 ± 51.56 | 660.64 ± 42.43 *** |
| 24 h | 2.65 ± 0.97 | 75.15 ± 12.45 | 487.83 ± 64.64 | 626.68 ± 23.61 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, B. Using Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Main Active Substances of the Anticancer Effect in Mice from Panax ginseng–Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules 2024, 29, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020334
Liu L, Lyu J, Yang L, Gao Y, Zhao B. Using Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Main Active Substances of the Anticancer Effect in Mice from Panax ginseng–Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020334
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Jing Lyu, Longfei Yang, Yan Gao, and Bonian Zhao. 2024. "Using Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Main Active Substances of the Anticancer Effect in Mice from Panax ginseng–Ophiopogon japonicus" Molecules 29, no. 2: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020334
APA StyleLiu, L., Lyu, J., Yang, L., Gao, Y., & Zhao, B. (2024). Using Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Main Active Substances of the Anticancer Effect in Mice from Panax ginseng–Ophiopogon japonicus. Molecules, 29(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020334