Selective Sorption of Noble Metals on Polymer Gel Modified with Ionic Liquid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
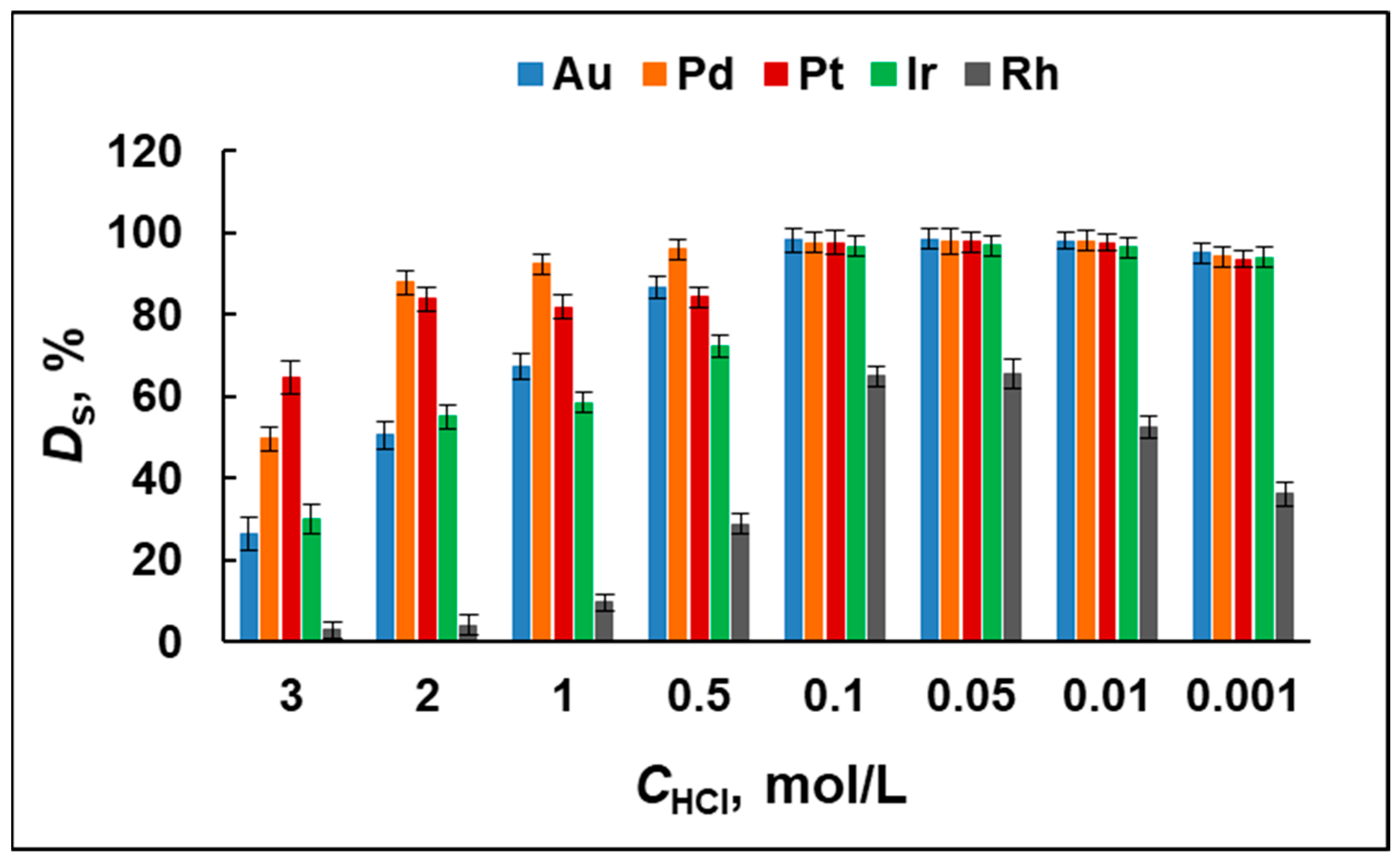
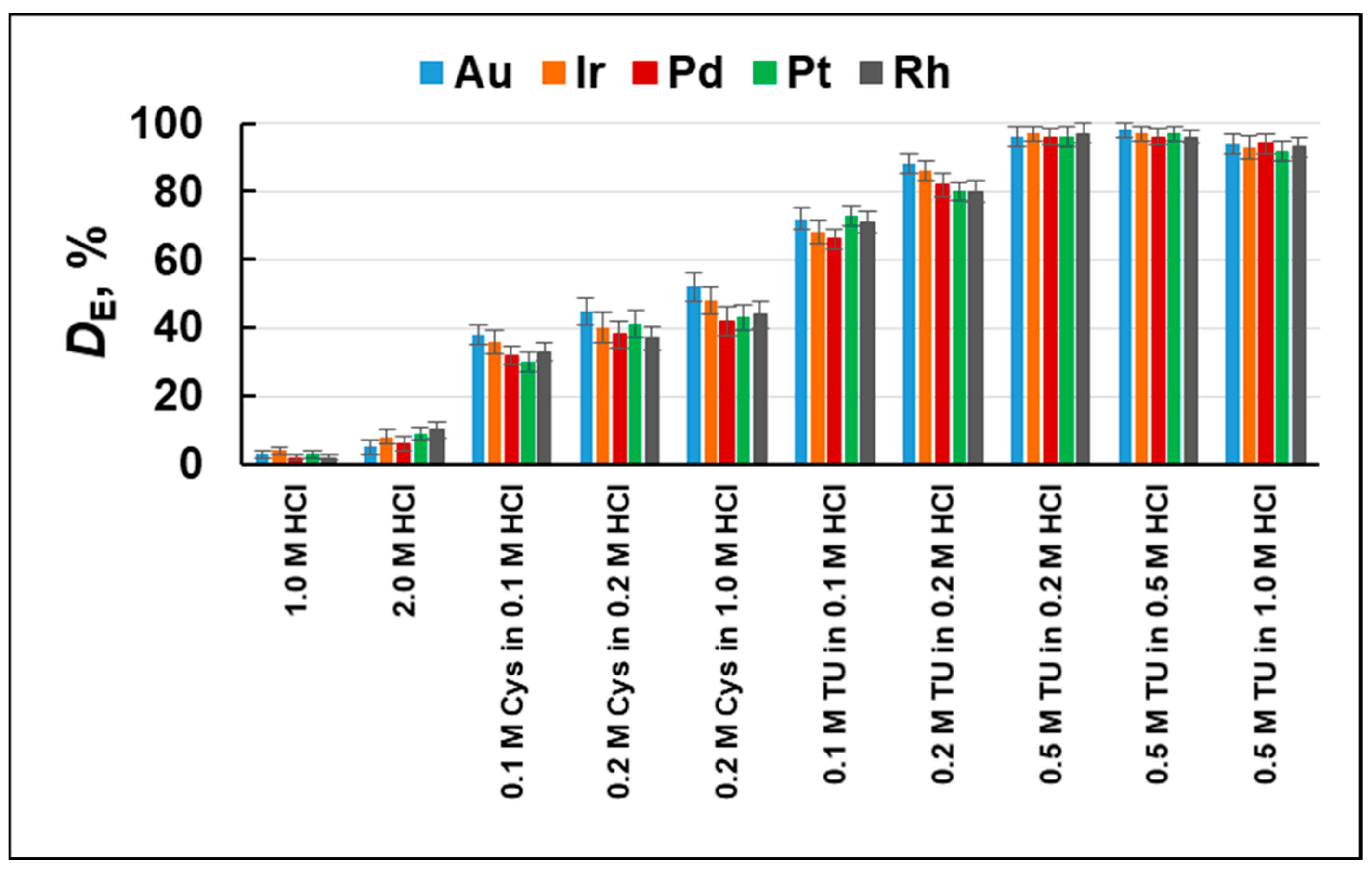
2.1. Extraction Efficiency—Optimization Studies
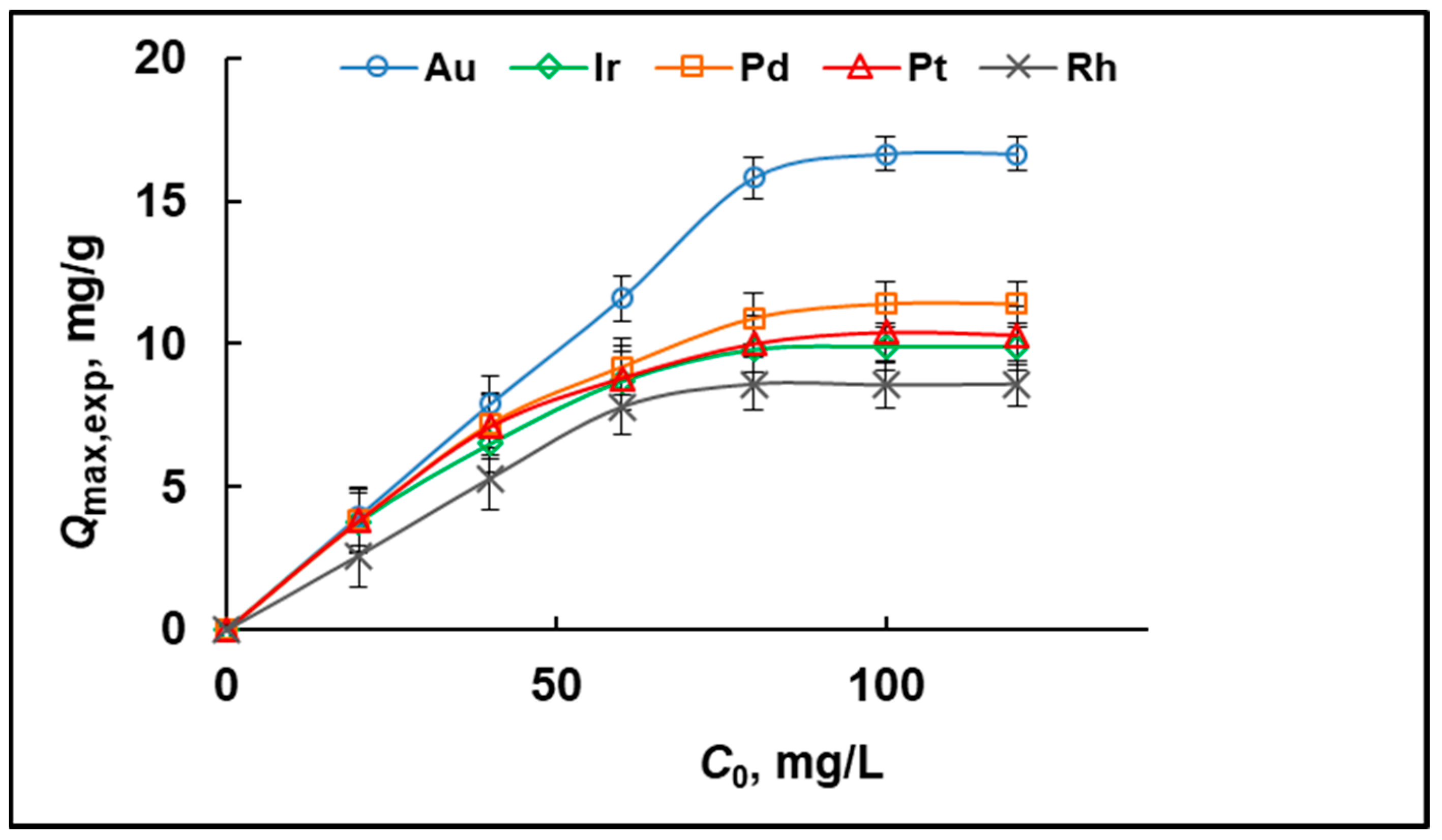
2.2. Capacity and Adsorption Isotherms
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics Studies
2.4. Analytical Application
2.4.1. Selectivity Studies
2.4.2. Determination of Pd, Pt, and Rh in Road Dust and Soils
2.4.3. Determination of Au, Pd, and Pt in Polymetallic Ore and Copper Concentrate
3. Experimental
3.1. Apparatus
3.2. Reagents and Materials
3.3. Procedures
3.3.1. Sorbent Synthesis
3.3.2. Batch Sorption Procedure
3.3.3. Desorption Studies
3.3.4. Kinetics Studies
3.3.5. Selectivity Studies
3.3.6. Procedure for Pd, Pt, and Rh Determination in Road Dust and Soils
3.3.7. Procedure for Au Determination in Cooper Concentrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlamp, G. Noble metals and noble metal alloys. In Springer Handbook of Materials Data; Warlimont, H., Martienssen, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 339–412. [Google Scholar]
- Schindl, R.; Leopold, K. Analysis of Platinum Group Elements in Environmental Samples: A Review. In Platinum Metals in the Environment; Zereini, F., Wiseman, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Pianowska, K.; Kluczka, J.; Benke, G.; Goc, K.; Malarz, J.; Ochmański, M.; Leszczyńska-Sejda, K. Solvent Extraction as a Method of Recovery and Separation of Platinum Group Metals. Materials 2023, 16, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-C.; Kurniawan, K.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Pandey, B.D. Ionic Liquids-Assisted Solvent Extraction of Precious Metals from Chloride Solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2023, 52, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaridi, O.; Platzer, S.; Nischkauer, W.; Limbeck, A.; Schnürch, M.; Bica-Schröder, K.A. Combined Deep Eutectic Solvent–Ionic Liquid Process for the Extraction and Separation of Platinum Group Metals (Pt, Pd, Rh). Molecules 2021, 26, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suoranta, T.; Zugazua, O.; Niemelä, M.; Perämäki, P. Recovery of palladium, platinum, rhodium and ruthenium from catalyst materials using microwave-assisted leaching and cloud point extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 154, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Souza, E.J.; do Amaral, C.D.B.; Nagata, N.; Grassi, M.T. Cloud point extractors for simultaneous determination of Pd and Pt in water samples by ICP OES with multivariate optimization. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulwanda, J.; Dorfling, C. Recovery of dissolved platinum group metals from copper leach solutions by precipitation. Miner. Eng. 2015, 80, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, R.; Lu, X.; Xu, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Efficient adsorption of gold ions from aqueous systems with thioamide-group chelating nanofiber membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, E.; Karadjova, I.; Tsalev, D.L. Solid-phase extraction in the determination of gold, palladium, and platinum. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1249–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Application of Solid Sorbents for Enrichment and Separation of Platinum Metal Ions. In Platinum Metals in the Environment; Zereini, F., Wiseman, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, H.V.; Buslaeva, T.M.; Maryutina, T.A. Trends in Sorption Recovery of Platinum Metals: A Critical Survey. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 62, 1797–18188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Sun, C.; Zhao, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, X. Adsorptive recovery of precious metals from aqueous solution using nanomaterials—A critical review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, A.G.; Asasian-Kolur, N.; Sharifian, S.; Golnaraghi, A. Biosorpion for sustainable recovery of precious metals from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Foley, S.R.; Wilson, L.D. An Overview of Modified Chitosan Adsorbents for the Removal of Precious Metals Species from Aqueous Media. Molecules 2022, 27, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubicki, Z.; Zinkowska, K.; Wójcik, G. A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption. Molecules 2023, 28, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.S.K.; Rajesh, N. A perspective on diverse adsorbent materials to recover precious palladium and the way forward. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52133–52142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Szczepańska, N.; de la Guardia, M.; Namieśnik, J. Modern trends in solid phase extraction: New sorbent media. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 77, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasović, A.; Marković, B.; Suručić, L.; Onjia, A. Methacrylate-Based Polymeric Sorbents for Recovery of Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Metals 2022, 12, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P. Synthesis of Adsorbents with Anion Exchange and Chelating Properties for Separation and Recovery of Precious Metals—A Review. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2020, 38, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmapriya, T.N.; Lee, D.-Y.; Huang, P.-J. Novel Reusable Hydrogel Adsorbents for Precious Metal Recycle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J. Preparation of 2-Aminothiazole-Functionalized Poly(Glycidyl Methacrylate) Microspheres and Their Excellent Gold Ion Adsorption Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinemuchi, H.; Ochiai, B. Synthesis of Hydrophilic Sulfur-Containing Adsorbents for Noble Metals Having Thiocarbonyl Group Based on a Methacrylate Bearing Dithiocarbonate Moieties. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3729580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, E.; Dakova, I.; Karadjova, I.; Karadjov, M. Column solid phase extraction and determination of ultra-trace Au, Pd and Pt in environmental and geological samples. Microchem. J. 2012, 101, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasovic, A.; Jovanovic, S.; Jakovljevic, D.; Stankovic, S.; Onjia, A. Noble Metal Binding on Macroporous Poly(GMA-Co-EGDMA) Modified with Ethylenediamine. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2004, 69, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, L. Synthesis and evaluation of 8-aminoquinoline-grafted poly(glycidyl methacrylate) for the recovery of Pd(II) from highly acidic aqueous solutions. Polymers 2018, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Kubota, F.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Separation of Gold(III) in Acidic Chloride Solution Using Porous Polymeric Ionic Liquid Gel. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2015, 48, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-X.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Liang, W.-Y.; Zhou, P.-P.; Yang, Y. A novel N-methylimidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid) to recover trace tetrachloroaurate from aqueous solution based on multiple supramolecular interactions. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xue, W.; Cheng, M.; Yang, Y. Efficient and selective gold recovery from e-waste by imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid)s. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 328, 125049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Yang, Y. Efficient gold recovery from waste SIM cards by imidazolium-based ionic liquids: Insight into structure-performance relationship. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, W.; Shi, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of N-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole-based poly(ionic liquid) as an adsorbent for the selective recovery of Au(III) ions from aqueous solutions. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20387–20395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of the length and aromaticity of N3-substituent on adsorption performance of imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquids) towards Pd (II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z. Exploring imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquids) as adsorbents for Pt(IV) removal: The impact of N3 substituents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Yan, X.; Cai, M.; Yang, Y. Extraction of Pt(IV), Pt(II), and Pd(II) from acidic chloride media using imidazolium-based task-specific polymeric ionic liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakova, I.; Karadjova, I. Ionic Liquid Modified Polymer Gel for Arsenic Speciation. Molecules 2024, 29, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoloski, A.N.; Ang, K.-L. Review of the Application of Ion Exchange Resins for the Recovery of Platinum-Group metals from Hydrochloric Acid Solutions. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2014, 35, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardis, F.L.; Grant, R.A.; Sherrington, D.C. A review of methods of separation of the platinum-group metals through their chloro-complexes. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 65, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benguerel, E.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Harris, G.B. Speciation and separation of rhodium(III) from chloride solutions: A critical review. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 40, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, C.; Barios, J.I.; Caetano, M.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Kinetic evaluation of phenol/aniline mixtures adsorption from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and hypercrosslinked polymeric resin (MN200). React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Tarley, M.; Del Pilar, C.R.T.; Sotomayo, T. Study on the cross-linked molecularly imprinted poly(methacrylic acid) and poly(acrylic acid) towards selective adsorption of diuron. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 100, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adsorption Isotherm Model | Parameters | Au | Ir | Pd | Pt | Rh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental adsorption capacity | Qmax,exp (mg/g) | 16.64 | 9.90 | 11.40 | 10.30 | 8.60 |
| Langmuir | Qmax (mg/g) | 16.37 | 10.19 | 11.95 | 10.72 | 8.33 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.08 | |
| R2 | 0.9936 | 0.9997 | 0.9989 | 0.9993 | 0.9949 | |
| Freundlich | kF | 7.42 | 5.03 | 4.33 | 4.31 | 1.44 |
| n | 4.22 | 5.30 | 3.80 | 4.29 | 2.61 | |
| R2 | 0.8736 | 0.6870 | 0.9327 | 0.9232 | 0.8952 |
| Model | Parameters | Au | Ir | Pd | Pt | Rh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | qe,exp (mg/g) | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.26 |
| qe,calc (mg/g) | 0.1107 | 0.2066 | 0.2052 | 0.1837 | 0.5878 | |
| k1 (1/min) | 0.1159 | 0.0876 | 0.156 | 0.1274 | 0.1474 | |
| R2 | 0.9168 | 0.8040 | 0.8814 | 0.9645 | 0.8667 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | qe,calc (mg/g) | 0.4097 | 0.4597 | 0.4174 | 0.4227 | 0.3411 |
| k2 (1/min) | 1.5897 | 0.3514 | 0.7822 | 1.0388 | 0.2264 | |
| R2 | 0.9996 | 0.9858 | 0.9968 | 0.9992 | 0.9945 |
| Model | Parameters | Au | Ir | Pd | Pt | Rh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-particle diffusion model, Region 1 | kdiff (mg/g min1/2) | 0.0327 | 0.0794 | 0.0550 | 0.0426 | 0.0139 |
| C (mg/g) | 0.2380 | 0.0139 | 0.1258 | 0.1936 | 0.0794 | |
| R2 | 0.9179 | 0.9401 | 0.9214 | 0.9304 | 0.9906 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model, Region 2 | kdiff (mg/g min1/2) | 0.0018 | 0.0018 | 0.0009 | 0.0036 | 0.3741 |
| C (mg/g) | 0.3805 | 0.3741 | 0.3755 | 0.3738 | 0.0018 | |
| R2 | 0.9988 | 0.9988 | 0.9988 | 0.9988 | 0.9973 | |
| Shell-progressive model, external diffusion | kF (µm/s) | 7.0 × 10−7 | 2.2 × 10−6 | 2.5 × 10−6 | 3.1 × 10−6 | 3.3 × 10−6 |
| R2 | 0.6561 | 0.6728 | 0.6353 | 0.6834 | 0.8972 | |
| Shell-progressive model, internal diffusion | De (µm2/s) | 1.2 × 10−6 | 2.3 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 4.7 × 10−6 | 3.1 × 10−6 |
| R2 | 0.8025 | 0.7941 | 0.7763 | 0.8505 | 0.9938 | |
| Shell-progressive model, chemical reaction | Ks (µm/s) | 2.1 × 10−2 | 2.4 × 10−2 | 1.6 × 10−2 | 2.5 × 10−2 | 1.8 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 0.7927 | 0.7178 | 0.7561 | 0.8469 | 0.9666 |
| Element | Degree of Sorption, DS (%) | Degree of Elution, DE (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Au | 97 ± 2 | 97 ± 2 |
| Ir | 96 ± 2 | 96 ± 2 |
| Pd | 98 ± 1 | 98 ± 1 |
| Pt | 97 ± 2 | 97 ± 2 |
| Rh | 65 ± 3 | 97 ± 3 |
| Cd | <1 | |
| Cu | <1 | |
| Fe | <3 | |
| Pb | <5 | |
| Co | <1 | |
| Ni | <1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakova, I.; Veleva, O.; Karadjova, I. Selective Sorption of Noble Metals on Polymer Gel Modified with Ionic Liquid. Molecules 2024, 29, 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204970
Dakova I, Veleva O, Karadjova I. Selective Sorption of Noble Metals on Polymer Gel Modified with Ionic Liquid. Molecules. 2024; 29(20):4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204970
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakova, Ivanka, Olga Veleva, and Irina Karadjova. 2024. "Selective Sorption of Noble Metals on Polymer Gel Modified with Ionic Liquid" Molecules 29, no. 20: 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204970
APA StyleDakova, I., Veleva, O., & Karadjova, I. (2024). Selective Sorption of Noble Metals on Polymer Gel Modified with Ionic Liquid. Molecules, 29(20), 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204970







