Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Validation of Method
2.2. Results of Drug Monitoring in Wastewater Samples
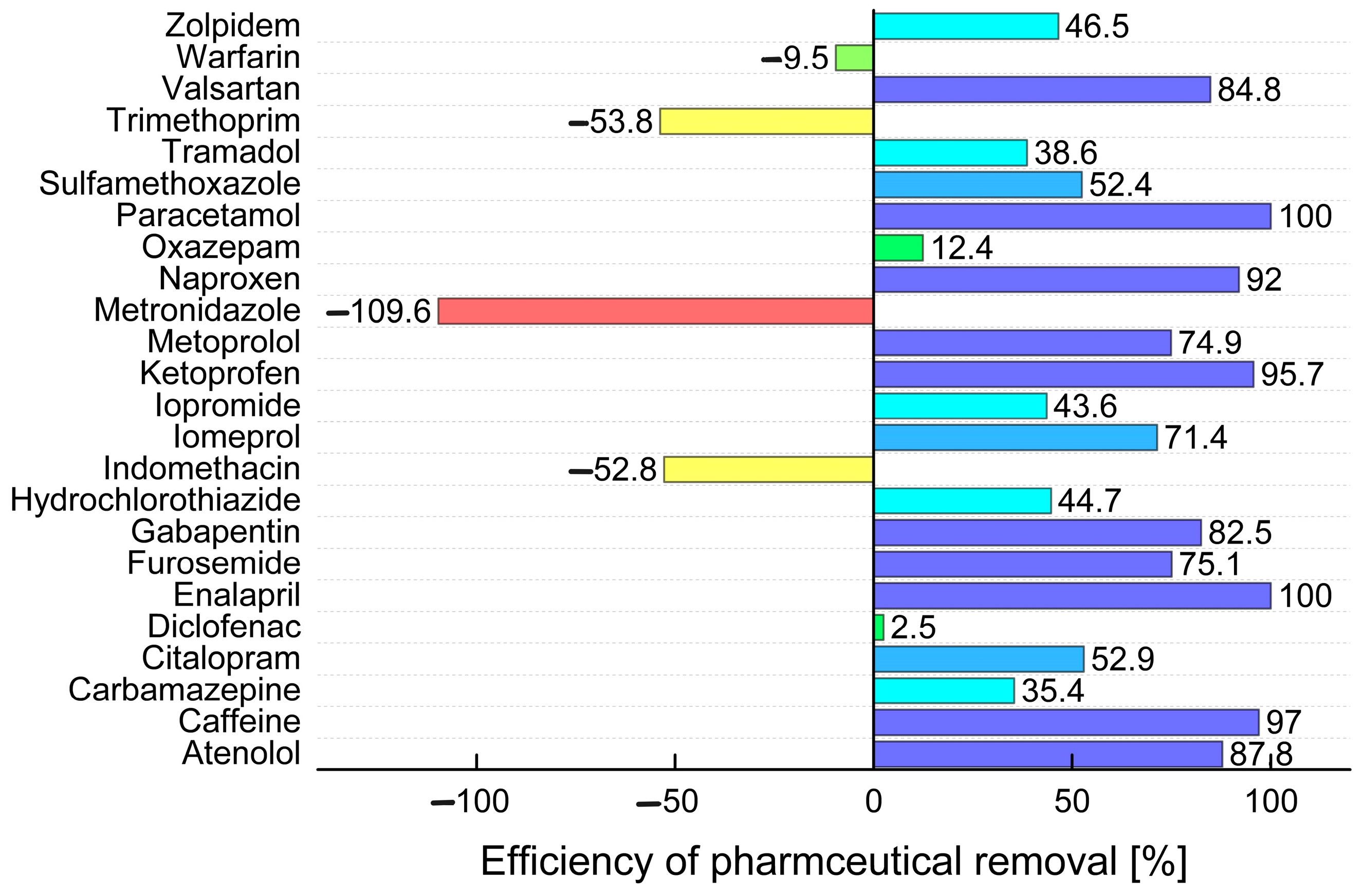
2.3. Comparison of the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants in the Czech Republic
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. Preparation of Samples and Fortified Matrices
4.4. Stock Solutions, Calibration Standards, and Quality Control (QC) Samples, and Preparation of Blank Samples and Laboratory Control Samples (LCS)
4.5. Chromatographic Conditions
4.6. Method Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nandi, A.; Pecetta, S.; Bloom, D.E. Global Antibiotic Use during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of Pharmaceutical Sales Data from 71 Countries, 2020–2022. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 57, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quireyns, M.; Boogaerts, T.; Van Wichelen, N.; Pussig, B.; De Loof, H.; Covaci, A.; Van Nuijs, A. Temporal Monitoring of Pharmaceutical Consumption Using a Wastewater-Based Epidemiologic Approach. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2022, 34, S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Persistence, Environmental Hazards, and Mitigation of Pharmaceutically Active Residual Contaminants from Water Matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.K.; Wong, C.S. Distribution and Fate of Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolite Conjugates in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water Res. 2018, 144, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.; Costa, F.; Neves, I.C.; Tavares, T. Psychiatric Pharmaceuticals as Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and Fate of Emerging Contaminants in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants from Different Geographical Regions-a Review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojemaye, C.Y.; Petrik, L. Occurrences, Levels and Risk Assessment Studies of Emerging Pollutants (Pharmaceuticals, Perfluoroalkyl and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds) in Fish Samples from Kalk Bay Harbour, South Africa. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charuaud, L.; Jardé, E.; Jaffrézic, A.; Liotaud, M.; Goyat, Q.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B. Veterinary Pharmaceutical Residues in Water Resources and Tap Water in an Intensive Husbandry Area in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielen, A.; Šimatović, A.; Kosić-Vukšić, J.; Senta, I.; Ahel, M.; Babić, S.; Jurina, T.; González Plaza, J.J.; Milaković, M.; Udiković-Kolić, N. Negative Environmental Impacts of Antibiotic-Contaminated Effluents from Pharmaceutical Industries. Water Res. 2017, 126, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Nguyen, J.; Sallach, J.B.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Boxall, A.B.; Durso, L.M.; McLain, J.E.; Singer, R.S.; Snow, D.D.; Zilles, J.L. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Agroecosystems: State of the Science. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mehmood, S.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Antibiotics Traces in the Aquatic Environment: Persistence and Adverse Environmental Impact. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 13, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Fu, L.; Tang, B.; Bin, L.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Fu, F. Occurrence, Ecotoxicological Risks of Sulfonamides and Their Acetylated Metabolites in the Typical Wastewater Treatment Plants and Receiving Rivers at the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.X.; Zhu, N.W.; Lin, Z. Trace Determination of Sulfonamide Antibiotics and Their Acetylated Metabolites via SPE-LC-MS/MS in Wastewater and Insights from Their Occurrence in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Mañas, M.C.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A.; Malato, S.; Agüera, A. Fast Determination of Pesticides and Other Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Treated Wastewater Using Direct Injection Coupled to Highly Sensitive Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1507, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, R.; Rousis, N.I.; Bijlsma, L.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F. Screening of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and Surface Waters of Spain and Italy by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Using UHPLC-QTOF MS and LC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8979–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Aguirre, A.; Romero-González, R.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Frenich, A.G. Simple and Quick Determination of Analgesics and Other Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Environmental Waters by On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1446, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso-Olivares, C.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Occurrence and Environmental Impact of Pharmaceutical Residues from Conventional and Natural Wastewater Treatment Plants in Gran Canaria (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Canela, C.; Sala-Comorera, T.; Pueyo, V.; Barata, C.; Lacorte, S. Analysis of 44 Pharmaceuticals Consumed by Elderly Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 168, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrolecco, L.; Capri, S.; Ademollo, N. Occurrence of Selected Pharmaceuticals in the Principal Sewage Treatment Plants in Rome (Italy) and in the Receiving Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5864–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Youdan, J.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Multi-Residue Analysis of 90 Emerging Contaminants in Liquid and Solid Environmental Matrices by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1431, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.H.; McEneff, G.L.; Brown, R.J.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R.; Barron, L.P. Pharmaceuticals in the Freshwater Invertebrate, Gammarus Pulex, Determined Using Pulverised Liquid Extraction, Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugajeva, I.; Rusko, J.; Perkons, I.; Lundanes, E.; Bartkevics, V. Determination of Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 133, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Reid, M.J.; Thomas, K.V. Target and Suspect Screening of Psychoactive Substances in Sewage-Based Samples by UHPLC-QTOF. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 914, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Kanda, A.; Danha, C.; Muisa-Zikali, N.; Chaukura, N. Occurrence, Human Health Risks, and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Aqueous Systems: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. In Applied Water Science Volume 1: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 63–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, A.; Wiest, L.; Fildier, A.; Libert, C.; Giroud, B.; Hammada, M.; Hervé, M.; Sibeud, E.; Vulliet, E.; Polomé, P.; et al. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Contaminants of Emerging Concern Identified by “Suspect Screening” from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents at a Territorial Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman-Sanchez, G.; Rojas-Jimenez, K. Fungi for the Bioremediation of Pharmaceutical-Derived Pollutants: A Bioengineering Approach to Water Treatment. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, M.; Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Kermanshahi-pour, A.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Water and Wastewater Using Fungal Oxidoreductase Enzymes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 190–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Aminzadeh, B.; Torabian, A.; Khatibikamal, V.; Alizadeh Fard, M. Comparison of COD Removal from Pharmaceutical Wastewater by Electrocoagulation, Photoelectrocoagulation, Peroxi-Electrocoagulation and Peroxi-Photoelectrocoagulation Processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219–220, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensano, B.M.B.; Borea, L.; Naddeo, V.; Belgiorno, V.; De Luna, M.D.G.; Ballesteros Jr, F.C. Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Wastewater by Intermittent Electrocoagulation. Water 2017, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Flowers, R.; McAvoy, D.; Dickenson, E. Biotransformation of Trace Organic Compounds by Activated Sludge from a Biological Nutrient Removal Treatment System. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandis, P.K.; Kalogirou, C.; Kanellou, E.; Vaitsis, C.; Savvidou, M.G.; Sourkouni, G.; Zorpas, A.A.; Argirusis, C. Key Points of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater, Organic Pollutants and Pharmaceutical Waste Treatment: A Mini Review. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, A. The Influence of UV Irradiation on PAHs in Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashuri, S.I.S.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Kasim, M.F.; Mastuli, M.S.; Rashid, U.; Abdullah, A.H.; Islam, A.; Asikin-Mijan, N.; Tan, Y.H.; Mansir, N.; et al. Photocatalysis for Organic Wastewater Treatment: From the Basis to Current Challenges for Society. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Cheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhang, Z. Review on Ultrasonic Technology Enhanced Biological Treatment of Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2022/1307 of 22July 2022 Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (Notified under Document C(2022) 5098) (Text with EEA Relevance), C/2022/5098. 2022. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/3887fb7f-0c86-11ed-b11c-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Molnarova, L.; Halesova, T.; Vaclavikova, M.; Bosakova, Z. Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Drinking Water Samples by the LC-MS/MS Method to Estimate Their Potential Health Risk. Molecules 2023, 28, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudreuil, M.A.; Vo Duy, S.; Munoz, G.; Sauvé, S. Pharmaceutical Pollution of Hospital Effluents and Municipal Wastewaters of Eastern Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Otomo, K.; Kunitou, M.; Shimizu, M.; Hosomaru, K.; Mikata, S.; Ishida, M.; Hisamatsu, K.; Yunoki, A.; Mino, Y.; et al. Environmental Fate of Pharmaceutical Compounds and Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria in Hospital Effluents, and Contributions to Pollutant Loads in the Surface Waters in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoudom, E.V.T.; Nguidjoe, E.; Mballa, R.N.; Tankoua, O.F.; Fokunang, C.; Anyakora, C.; Blackett, K.N. Identification and Quantification of 19 Pharmaceutical Active Compounds and Metabolites in Hospital Wastewater in Cameroon Using LC/QQQ and LC/Q-TOF. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Dvořáková Březinová, T.; Koželuh, M.; Kule, L. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Four Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands in the Czech Republic—The First Year of Monitoring. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackuľak, T.; Medvecká, E.; Vojs Staňová, A.; Brandeburová, P.; Grabic, R.; Golovko, O.; Marton, M.; Bodík, I.; Medveďová, A.; Gál, M.; et al. Boron Doped Diamond Electrode—The Elimination of Psychoactive Drugs and Resistant Bacteria from Wastewater. Vacuum 2020, 171, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Khan, E.; Chen, H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Li, Y.; Goh, S.G.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Saeidi, N.; Gin, K.Y.H. Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater, Stormwater Runoff, and Surface Water: Application as Chemical Markers for Diffuse Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.A.; Jarvis, E.; Galani, A.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Nika, M.C.; Chapman, D.V. Assessment of Selected Pharmaceuticals in Riyadh Wastewater Treatment Plants, Saudi Arabia: Mass Loadings, Seasonal Variations, Removal Efficiency and Environmental Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Díaz, E.; Ordóñez, S. A Review of the Adsorption-Biological Hybrid Processes for the Abatement of Emerging Pollutants: Removal Efficiencies, Physicochemical Analysis, and Economic Evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Show, P.L. A Review on Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Aquatic Systems: Current Trends and Scope for Further Research. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Hooda, P.S.; Barker, J.; Barton, S.; Swinden, J. Occurrence, Fate and Transformation of Emerging Contaminants in Water: An Overarching Review of the Field. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aus der Beek, T.; Weber, F.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment—Global Occurrences and Perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
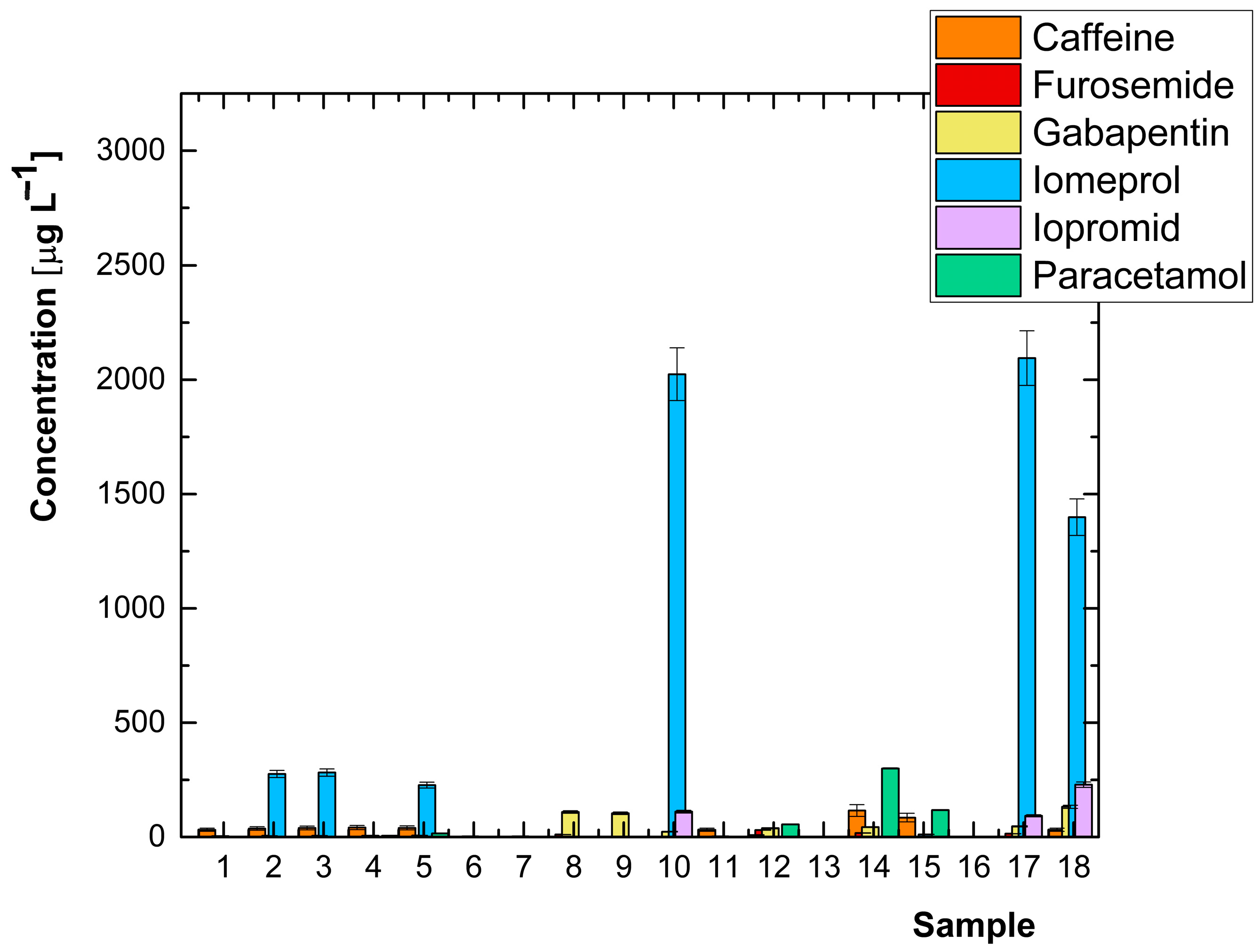
| Analyte | Concentration [μg L−1] | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| Atenolol | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.301 | 0.305 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Caffeine | 31.7 | 37.2 | 39.7 | 41.2 | 39.6 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 31.5 | 8.49 | n.d. | 116.0 | 84.8 | 0.597 | n.d. | 31.5 |
| Carbamazepine | 0.742 | 0.812 | 0.917 | 0.846 | 0.803 | 0.331 | 0.333 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.699 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.05 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Citalopram | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.205 | 0.203 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.319 | 1.04 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Cyclophosphamide | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 5.17 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Diclofenac | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.817 | 0.880 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 2.37 | n.d. | n.d. | 1.27 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Furosemide | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.378 | 0.366 | 10.8 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 30.5 | n.d. | 17.7 | 1.30 | 1.83 | 14.4 | n.d. |
| Gabapentin | 4.13 | 5.40 | 5.77 | 5.74 | 6.78 | 2.58 | 2.59 | 109 | 104 | 23.2 | 2.97 | 38.2 | 2.28 | 43.2 | 1.24 | 1.56 | 46.8 | 132 |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 1.16 | 2.09 | 1.69 | 2.58 | 2.16 | 2.39 | 2.09 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.987 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 5.91 | 2.77 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Indomethacin | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.074 | 0.065 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Iomeprol | n.d. | 276 | 282 | n.d. | 227 | 0.214 | 0.268 | n.d. | n.d. | 2024 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 11.4 | n.d. | 2095 | 1399 |
| Iopromide | n.d. | 1.20 | 1.28 | n.d. | 1.20 | 0.607 | 0.777 | n.d. | n.d. | 111 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.32 | n.d. | 92.7 | 229 |
| Ketoprofen | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 15.4 | 0.090 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Metoprolol | 0.632 | 0.740 | 0.786 | 0.902 | 0.843 | 1.31 | 1.30 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.46 | 0.708 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Metronidazole | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 15.7 | 14.1 | n.d. | 0.597 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.123 | 6.96 | n.d. |
| Naproxen | 1.21 | 1.22 | 1.17 | 1.64 | 1.25 | 0.194 | 0.169 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Oxazepam | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.117 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.27 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Paracetamol | n.d. | n.d. | 0.943 | 5.42 | 15.3 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 55.3 | n.d. | 300 | 118 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sertraline | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.207 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sotalol | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.055 | 0.052 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sulfamethoxazole | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.14 | 1.04 | 6.49 | 6.62 | n.d. | n.d. | 20.3 | n.d. | 7.86 | 1.15 | 2.78 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Tramadol | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.918 | 0.930 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 7.87 | n.d. | 6.48 | 0.291 | 4.66 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Trimethoprim | 0.441 | 0.759 | 0.846 | 0.909 | 0.877 | 0.522 | 0.511 | 11.4 | 11.5 | n.d. | 0.343 | 5.11 | n.d. | 4.83 | 1.40 | 2.30 | 3.51 | 3.71 |
| Valsartan | 0.817 | 0.900 | 0.697 | 1.10 | 0.747 | 0.242 | 0.242 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.780 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 2.81 | 0.773 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Zolpidem | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.052 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Analyte | Concentration [μg L−1] | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WWTP 1 Inflow | WWTP 1 Outflow | WWTP 2 Inflow | WWTP 2 Outflow | WWTP 3 Inflow | WWTP 3 Outflow | WWTP 4 Inflow | WWTP 4 Outflow | WWTP 5 Inflow | WWTP 5 Outflow | WWTP 6 Inflow | WWTP 6 Outflow | WWTP 7 Inflow | WWTP 7 Outflow | WWTP 8 Inflow | WWTP 8 Outflow | WWTP 9 Inflow | WWTP 9 Outflow | WWTP 10 Inflow | WWTP 10 Outflow | |
| Atenolol | 0.093 | 0.152 | n.d. | 0.014 | 0.234 | 0.214 | 0.528 | 0.025 | 1.87 | 0.102 | 3.59 | 0.088 | 0.773 | 0.025 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.421 | 0.300 |
| Caffeine | 38.5 | 2.21 | 17.1 | 1.89 | 21.4 | 0.959 | 117.3 | 1.98 | 140.7 | 4.92 | 160.4 | 2.09 | 195.7 | 1.55 | 61.6 | 1.21 | 45.7 | 5.90 | 22.1 | 2.18 |
| Carbamazepine | 0.671 | 0.849 | 0.964 | 0.179 | 0.139 | 0.265 | 0.380 | 0.432 | n.d. | 0.003 | 2.44 | 0.880 | 1.42 | 0.935 | 0.239 | 0.336 | 0.037 | n.d. | 0.135 | 0.270 |
| Citalopram | 0.206 | 0.210 | 0.164 | 0.150 | 0.186 | 0.195 | 0.825 | 0.494 | 4.44 | 1.44 | 1.86 | 0.521 | 1.35 | 0.640 | 0.493 | 0.711 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.186 | 0.222 |
| Diclofenac | 3.14 | 2.03 | 0.308 | 0.275 | 0.213 | 0.367 | 3.01 | 1.79 | 6.53 | 3.10 | 5.21 | 2.06 | 5.70 | 0.496 | 0.205 | 0.553 | 0.050 | 13.1 | 0.343 | 0.322 |
| Enalapril | 0.033 | n.d. | 0.007 | n.d. | 0.007 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.076 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Furosemide | 1.08 | 1.98 | 1.71 | 1.20 | 1.14 | 1.19 | 3.03 | 1.57 | 43.2 | 10.7 | 2.44 | 1.16 | 16.3 | 1.29 | 25.8 | 4.96 | 2.11 | 0.009 | 0.080 | 0.168 |
| Gabapentin | 10.9 | 12.6 | 2.00 | 2.16 | 4.30 | 7.33 | 27.9 | 3.16 | 51.7 | 7.79 | 19.9 | 3.92 | 69.1 | 3.79 | 109.9 | 3.67 | 2.04 | 0.372 | 4.59 | 8.23 |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 0.635 | 1.71 | 0.800 | 1.27 | 0.974 | 1.39 | 3.96 | 3.30 | 11.1 | 2.52 | 8.28 | 3.37 | 9.03 | 4.78 | 9.38 | 8.76 | 6.25 | 0.149 | 3.04 | 2.33 |
| Indomethacin | 0.104 | 0.112 | 0.020 | 0.046 | 0.056 | 0.077 | 0.049 | 0.110 | 0.121 | 0.103 | 0.012 | 0.102 | 0.164 | 0.171 | 0.009 | 0.090 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.055 | 0.088 |
| Iomeprol | 0.133 | 2.90 | 0.079 | n.d. | 4.57 | 1.12 | 0.110 | 0.122 | 222.4 | 144.0 | 6.68 | 2.33 | 298.1 | 2.05 | n.d. | 0.074 | n.d. | n.d. | 5.33 | 0.995 |
| Iopromide | n.d. | 0.077 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.052 | 0.029 | 0.019 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.071 | 0.804 | 0.112 | n.d. | 0.251 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.083 | n.d. |
| Ketoprofen | 0.089 | 0.045 | 3.88 | n.d. | 0.031 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 0.051 | 1.39 | 0.070 | 0.196 | 0.044 | 1.26 | 0.019 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.034 | 0.032 |
| Metoprolol | 0.643 | 0.985 | 0.700 | 0.438 | 0.600 | 0.800 | 2.90 | 1.76 | 30.8 | 3.63 | 12.0 | 1.82 | 8.64 | 2.77 | 2.40 | 2.53 | 3.11 | 0.026 | 0.622 | 0.902 |
| Metronidazole | 0.034 | 0.024 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.033 | 0.112 | 0.040 | 0.032 | n.d. | 0.018 | n.d. | 0.007 | n.d. | 0.011 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.042 | 0.118 |
| Naproxen | 0.265 | 0.094 | 3.49 | n.d. | 0.270 | 0.085 | 4.90 | 0.651 | 3.93 | 0.509 | 2.49 | 1.16 | 12.6 | 0.078 | 1.82 | n.d. | 2.18 | n.d. | 0.867 | 0.045 |
| Oxazepam | 0.095 | 0.183 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.037 | 0.077 | n.d. | 0.012 | n.d. | 0.020 | 0.192 | 0.151 | 0.216 | 0.150 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.202 | n.d. | 0.040 | 0.081 |
| Paracetamol | 28.7 | n.d. | 30.3 | n.d. | 11.0 | n.d. | 28.6 | n.d. | 54.5 | n.d. | 104.2 | n.d. | 83.7 | n.d. | 21.4 | n.d. | 14.7 | n.d. | 11.8 | n.d. |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.041 | 0.028 | 0.503 | 0.961 | 1.95 | 0.678 | 0.024 | 0.126 | 1.82 | 0.568 | 4.09 | 0.557 | 1.21 | 0.759 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.431 | 1.10 |
| Tramadol | 0.231 | 0.396 | 0.123 | 0.247 | 0.164 | 0.405 | 1.97 | 1.89 | 17.1 | 7.11 | 0.666 | 1.40 | 3.59 | 1.93 | n.d. | 0.839 | 0.375 | 0.022 | 0.315 | 0.782 |
| Trimethoprim | 0.009 | 0.106 | 0.030 | 0.167 | 0.152 | 0.340 | 0.333 | 0.316 | 0.408 | 0.629 | 0.206 | 0.117 | 0.333 | 0.160 | 0.099 | 0.455 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.152 | 0.357 |
| Valsartan | 0.347 | 0.946 | 0.550 | 0.038 | 0.475 | 0.142 | 5.45 | 0.146 | 29.0 | 8.11 | 4.48 | 0.134 | 11.3 | 0.109 | 8.20 | 0.145 | 5.19 | 0.011 | 0.477 | 0.145 |
| Warfarin | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.007 | 0.022 | 0.033 | 0.024 | 0.017 | 0.016 | 0.019 | n.d. | 0.016 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Zolpidem | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.055 | 0.019 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.008 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.001 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molnarova, L.; Halesova, T.; Tomesova, D.; Vaclavikova, M.; Bosakova, Z. Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method. Molecules 2024, 29, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071480
Molnarova L, Halesova T, Tomesova D, Vaclavikova M, Bosakova Z. Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071480
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolnarova, Lucia, Tatana Halesova, Daniela Tomesova, Marta Vaclavikova, and Zuzana Bosakova. 2024. "Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071480
APA StyleMolnarova, L., Halesova, T., Tomesova, D., Vaclavikova, M., & Bosakova, Z. (2024). Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method. Molecules, 29(7), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071480






