A Facile Alkali-Assisted Synthesis Strategy for Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels for Supercapacitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
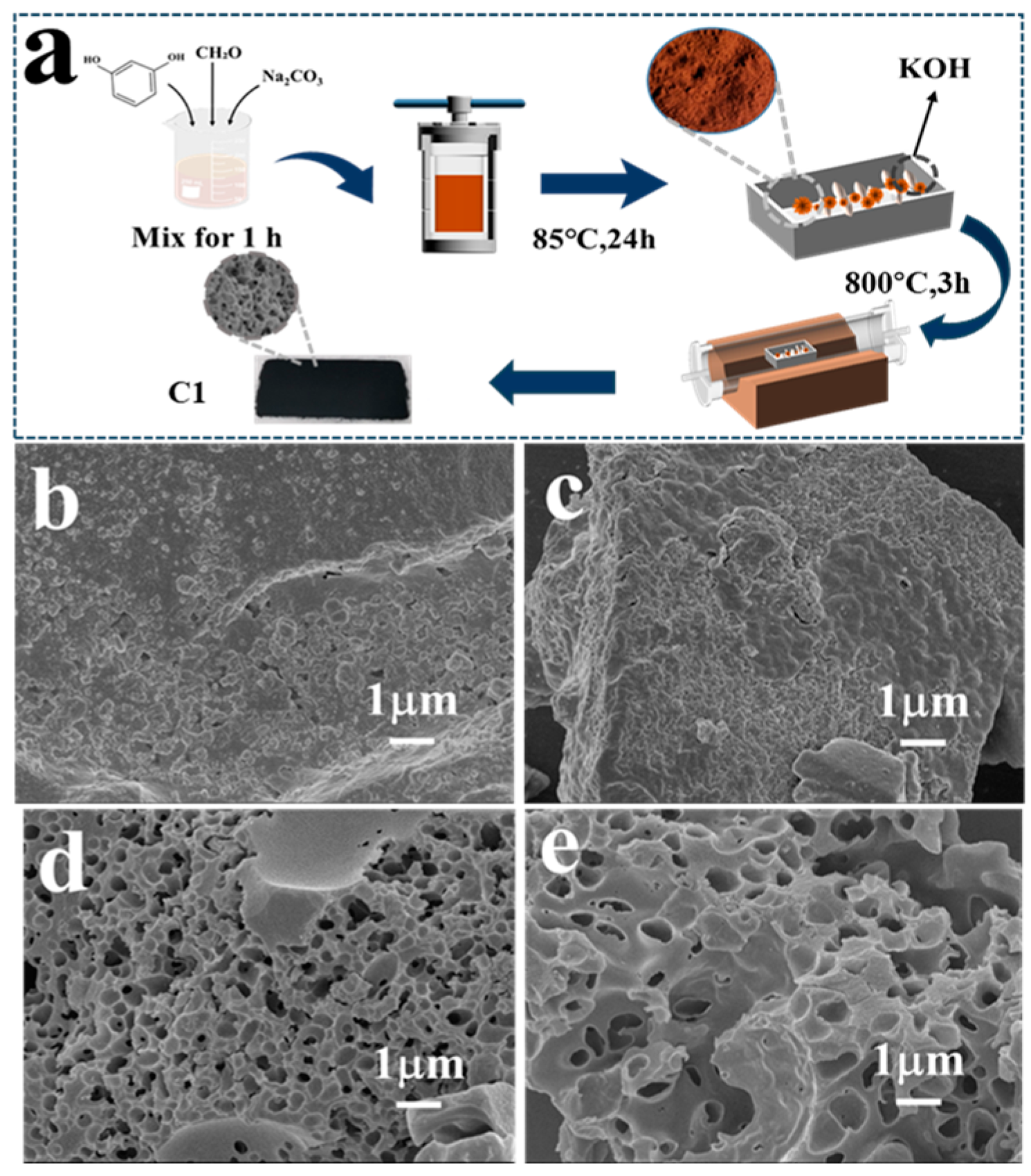
3.1. Synthesis of Hierarchical Carbon Aerogels
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Electrochemical Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giri, A.; Park, G.; Jeong, U. Layer-structured anisotropic metal chalcogenides: Recent advances in synthesis, modulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 3329–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Men, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, C.; et al. Versatile carbon-based materials from biomass for advanced electrochemical energy storage systems. eScience 2024, 4, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkar, P.K.; Sheikh, Z.A.; Chavan, V.D.; Lee, S.W. In-situ growth of 3D amorphous Ni-Co-Mn phosphate on 2D Ti3C2Tx nanocomposite for commercial-level hybrid energy storage application. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 206, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girirajan, M.; Bojarajan, A.K.; Pulidindi, I.N.; Hui, K.N.; Sangaraju, S. An insight into the nanoarchitecture of electrode materials on the performance of supercapacitors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 518, 216080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkar, P.K.; Lee, S.W. An Interfacial Engineering Approach of Flower-like Li+ Preintercalated Co–Cu Phosphate for Solid-State Hybrid Energy Storage Device. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 5927–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Z. Disorder over pore size: Boosting supercapacitor efficiency. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202411039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Kang, X.; Zhao, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, P.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Si, C.; Song, X. Regulating the properties of activated carbon for supercapacitors: Impact of particle size and degree of aromatization of hydrochar. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkar, P.K.; Naikwade, M.B.; Patil, S.A.; Lee, S.W. Self-assembly of Sr2P2O7@ 2D rGO nano/micro-architecture for highly durable and bendable solid-state supercapattery. Mater. Today Phys. 2024, 46, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Haj, Y.; Soliman, A.B.; Vapaavuori, J.; Elbahri, M. Carbon aerogels derived from anion-modified nanocellulose for adaptive supercapacitor performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Jin, J.; He, B.; Wang, R.; Gong, Y.; Fan, H.J. A dual-carbon potassium-ion capacitor enabled by hollow carbon fibrous electrodes with reduced graphitization. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, J. Progress in the synthesis of carbon aerogels for advanced energy storage applications. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 8969–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achazhiyath Edathil, A.; Rezaei, B.; Almdal, K.; Keller, S.S. In situ mineralization of biomass-derived hydrogels boosts capacitive electrochemical energy storage in free-standing 3D carbon aerogels. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 7, e12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikwade, M.B.; Katkar, P.K.; Lee, S.W. Understanding the Impact of Porosity on Li-Ion Diffusion Enhancement in Micro-sized Silicon Particles for Advanced Batteries. Ceram. Int. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, S.-J. Recent advances in preparations and applications of carbon aerogels: A review. Carbon 2020, 163, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Cai, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Du, H.; Si, C.; Zhang, K. Multifunctional superelastic, superhydrophilic, and ultralight nanocellulose-based composite carbon aerogels for compressive supercapacitor and strain sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-López, S.L.; Ramírez-Montoya, L.A.; Casal, M.D.; Montes-Morán, M.A.; Menéndez, J.A.; Arenillas, A. Tortuosity of the porous structure of carbon gels. Carbon 2021, 171, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Ge, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Application of carbon aerogel-based materials in persulfate activation for water treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Forien, J.-B.; Campbell, P.G.; Oakdale, J.S.; Mancini, J.A.; Worsley, M.A.; Biener, J. Carbon aerogels with integrated engineered macroporous architectures for improved mass transport. Carbon 2021, 179, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Orita, Y.; Shimoyama, Y. Photo-thermal CO2 desorption from amine-modified silica/carbon aerogel for direct air capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, L.; Men, J.; Feng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Qin, G.; Feng, J. Ultralow thermal conductivity of single-atom doped carbon aerogel synthesized with a facile ambient-pressure-drying strategy. Carbon 2023, 213, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momčilović, M.Z.; Nešić, A.; Gurikov, P.; Schroeter, B.; Dodevski, V.; Bojić, A.L. Atenolol uptake from pharmaceutical sources onto carbon aerogel prepared by supercritical CO2 drying. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 350, 127792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, C.; Cabanero, J.; Povia, M.; Villevieille, C. Biowaste lignin-based carbonaceous materials as anodes for Na-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A1400–A1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Jin, B.; Meng, L.Y. Effect of the SBA-15 template and KOH activation method on CO2 adsorption by N-doped polypyrrole-based porous carbons. Carbon Lett. 2018, 28, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Xing, G.; Tian, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z. Hollow carbon spheres/graphene hybrid aerogels as high-performance adsorbents for organic pollution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, N.; Barman, J.; Deka, J.; Raidongia, K.; Dutta, G.K. Microporous organic polymer-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon spheres for efficient capacitive energy storage. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 3327–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Wu, S.; Zou, Y.; Jia, M.; Zhang, W.; Yan, W.; Liu, G. Correlation between the microstructures of graphite oxides and their catalytic behaviors in air oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 421, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahani, A.A.; Motahari, S.; Nayyeri, V. Electromagnetic and microwave absorption characteristics of PMMA composites filled with a nanoporous resorcinol formaldehyde based carbon aerogel. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10855–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, B.; Guan, D.; Dong, X. Mesoporous activated carbon spheres derived from resorcinol-formaldehyde resin with high performance for supercapacitors. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeb, W.; Senthil, S.; Benny, S.; Ezhilarasi, S.; Rodney, J.D.; Joysi, M.G.; Ananthan, R.; Dinesh Raja, M.; Arulmozhi, S. Surface active sites enriched CoNiFe-Manganite: An effective electrode for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Illán, J.Á.; Sierra, L.; Guillem-Navajas, A.; Suárez, J.A.; Royuela, S.; Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Maspoch, D.; Ocón, P.; Zamora, F. β-ketoenamine-linked covalent organic frameworks synthesized via gel-to-gel monomer exchange reaction: From aerogel monoliths to electrodes for supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Zhong, F.; Song, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, H.; Niu, W.; Yao, Z. Optimization of multiscale structure and electrochemical properties of bamboo-based porous activated biochar by coordinated regulation of activation and air oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 146763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, G.; Sunil, V.; Ling, J.; Qamar, U.; Misnon, I.I.; Kuila, B.K.; Das, S.; Yang, C.-C.; Jose, R. Carbon dots as a sustainable electrolyte enhancer in aqueous alkaline electrochemical capacitors. J. Energy Storage 2024, 94, 112465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhartiya, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Balal, M.; Bhardwaj, P.; Kohli, D.K.; Singh, M.K. Nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel synthesis by solvothermal gelation for supercapacitor application. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2022, 26, 2829–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Highly porous carbon aerogels for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, X.; Meng, T.; Yang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Min, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, W.; Zhou, X. Rapid one-step preparation of hierarchical porous carbon from chitosan-based hydrogel for high-rate supercapacitors: The effect of gelling agent concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Yang, S.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, B.; Fang, P.; He, C. N-self-doped graphitic carbon aerogels derived from metal–organic frameworks as supercapacitor electrode materials with high-performance. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 380, 138237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, M.A.; Lin, L.-T.; Ko, F.; Renneckar, S. Carbon aerogels from softwood kraft lignin for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 894061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ding, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, N.; Guo, J.; Hou, S.; Tong, F.; Jia, D.; Zhang, H. Coal-based 3D hierarchical porous carbon aerogels for high performance and super-long life supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

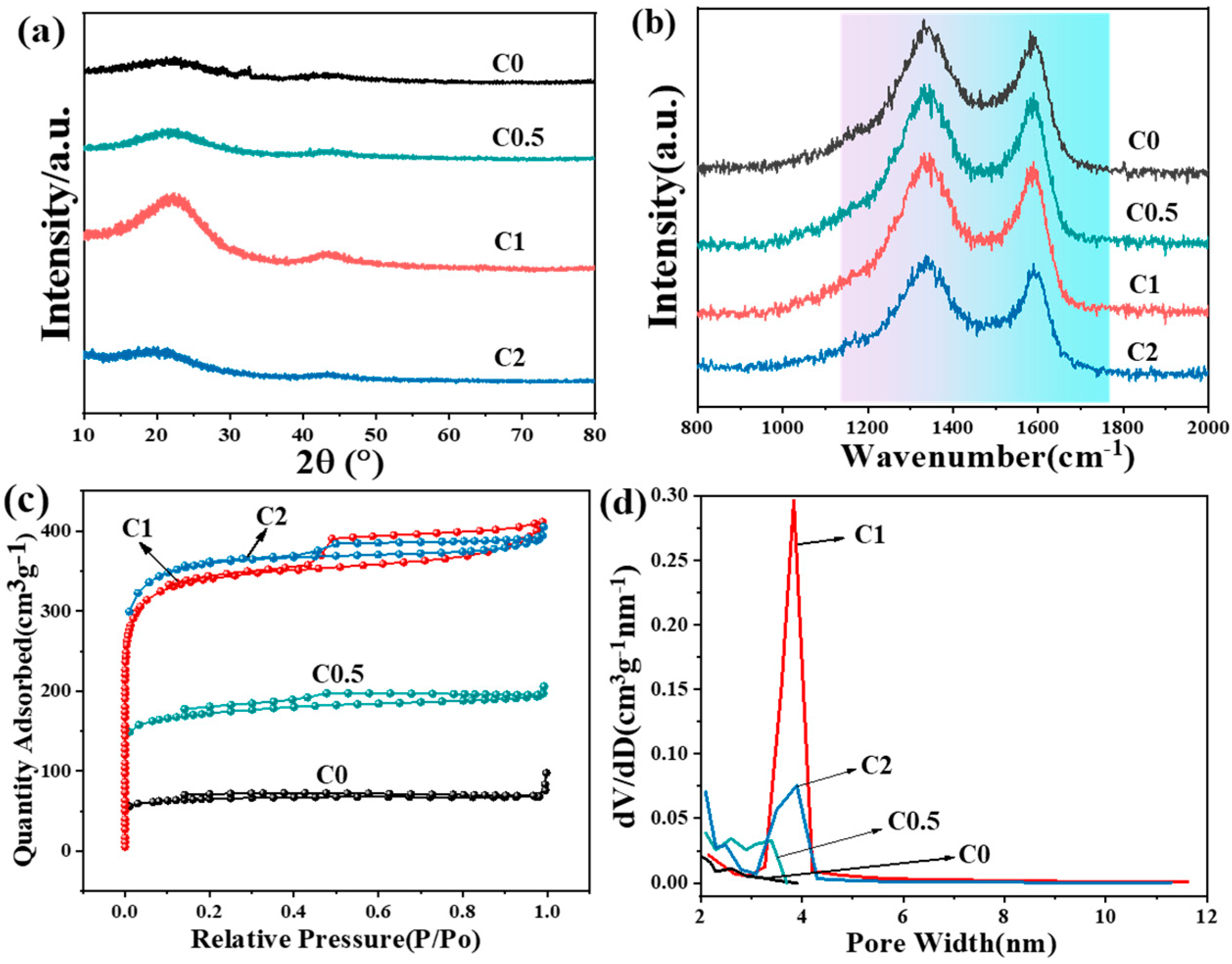
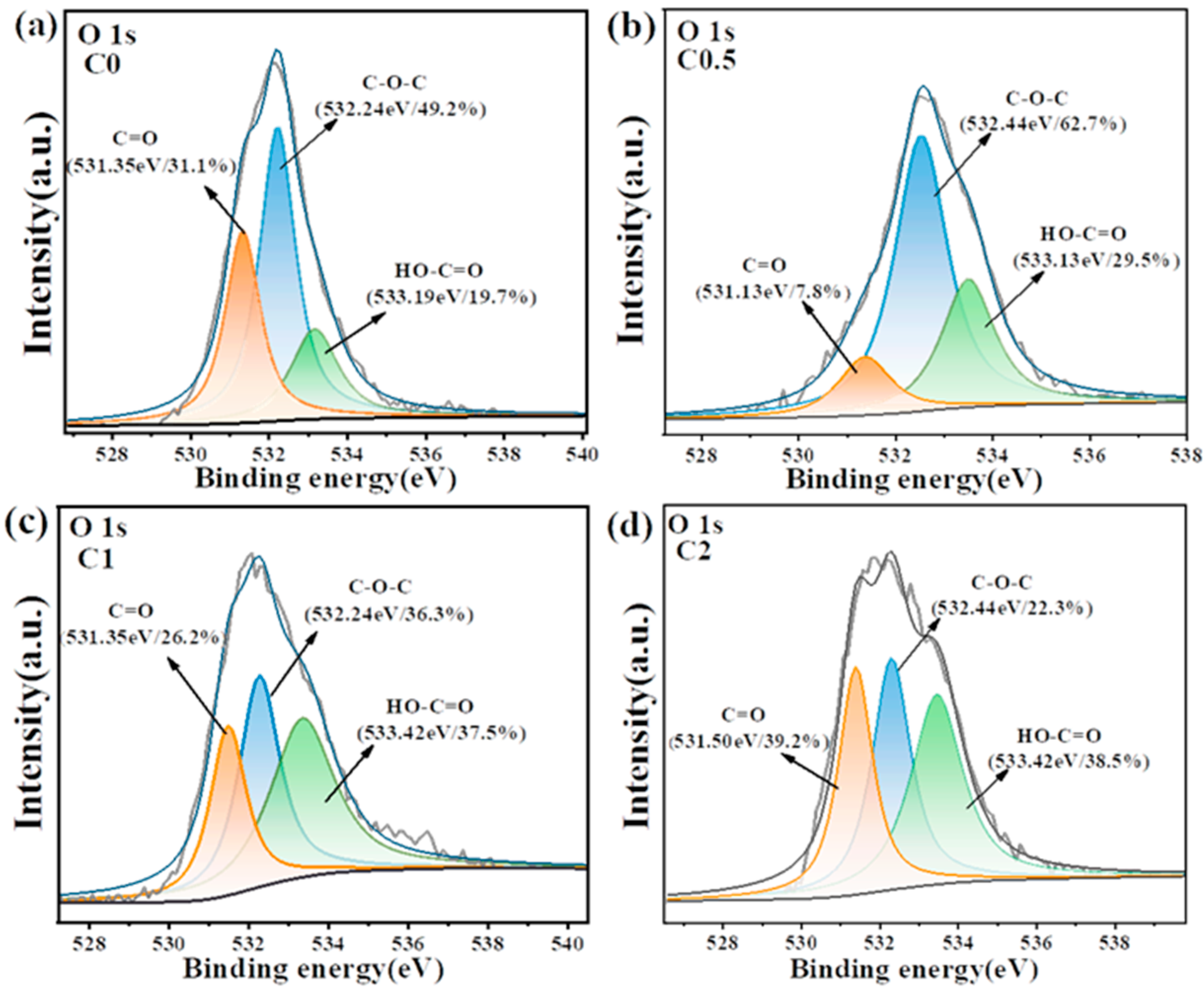
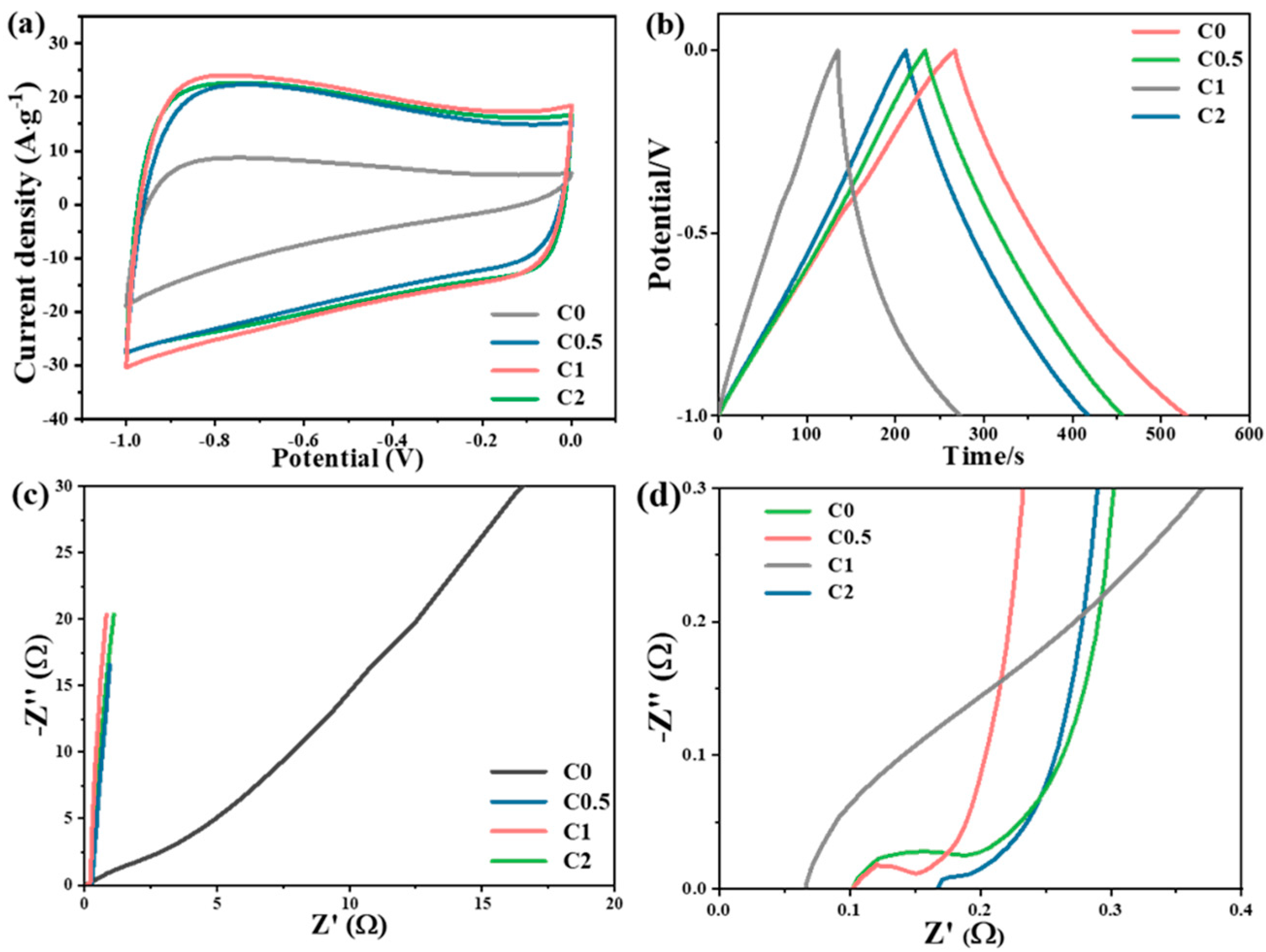

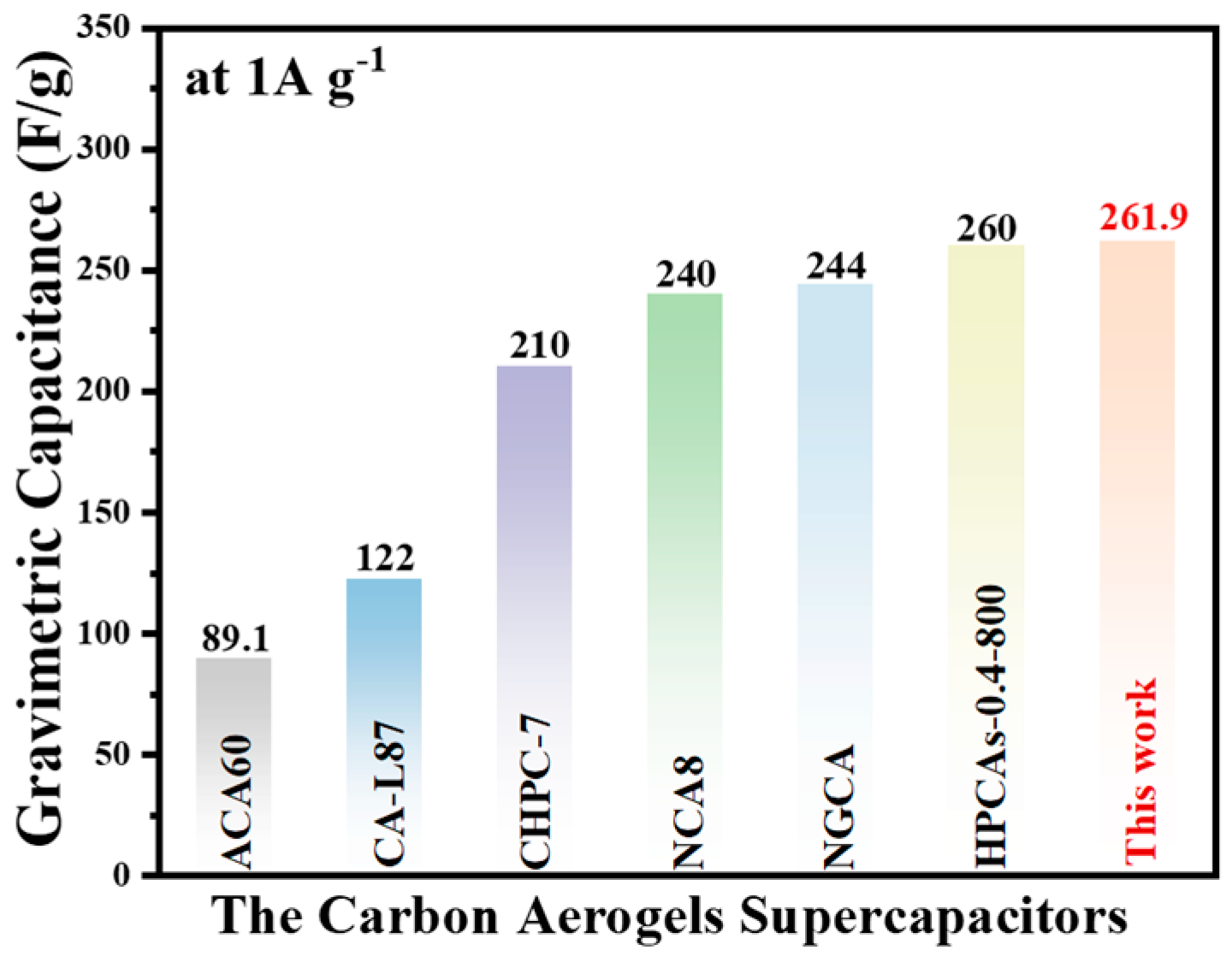
| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | Vmeso (cm3·g−1) | Vtotal (cm3·g−1) | DBJH (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 220 | 0.0114 | 0.105 | 2.6 |
| C0.5 | 582 | 0.0789 | 0.299 | 3.5 |
| C1 | 1151 | 0.167 | 0.637 | 3.8 |
| C2 | 1220 | 0.128 | 0.600 | 3.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Guan, X.; Shang, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, H.; Li, S. A Facile Alkali-Assisted Synthesis Strategy for Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels for Supercapacitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 5413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225413
Yang H, Zhang M, Guan X, Shang X, Zhu L, Xu H, Li S. A Facile Alkali-Assisted Synthesis Strategy for Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels for Supercapacitors. Molecules. 2024; 29(22):5413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225413
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Huimin, Mingfang Zhang, Xinwei Guan, Xiaogang Shang, Lingfeng Zhu, Haimei Xu, and Songbo Li. 2024. "A Facile Alkali-Assisted Synthesis Strategy for Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels for Supercapacitors" Molecules 29, no. 22: 5413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225413
APA StyleYang, H., Zhang, M., Guan, X., Shang, X., Zhu, L., Xu, H., & Li, S. (2024). A Facile Alkali-Assisted Synthesis Strategy for Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels for Supercapacitors. Molecules, 29(22), 5413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225413






