Evaluation of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives as Promising Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, In Vitro, In Silico ADMET and Molecular Docking Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
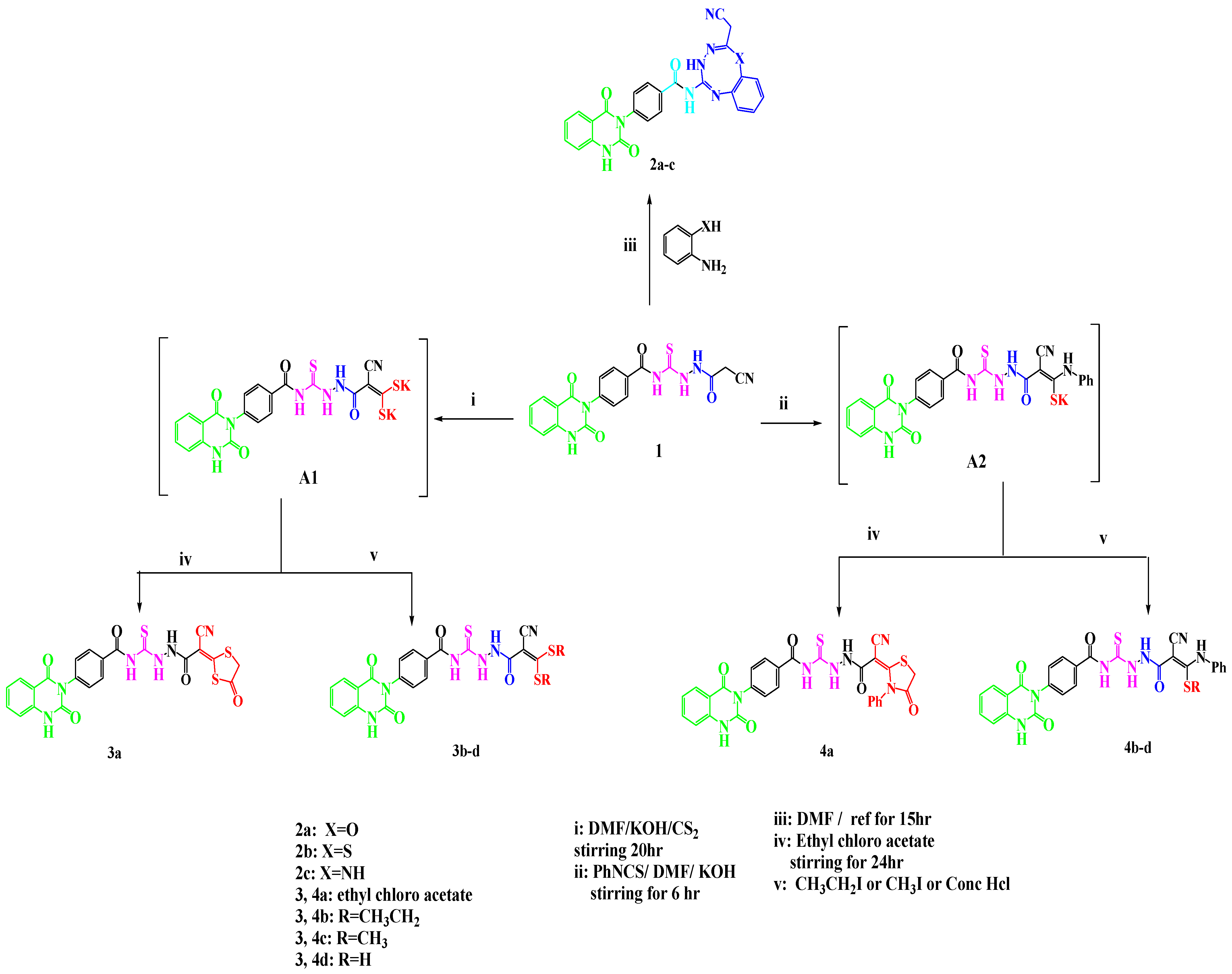
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Studies
2.3. In Silico Studies and ADMET Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Organic Synthesis
- Synthesis of N-[N′-(2-cyano-acetyl)-hydrazino-carbo-thioyl]-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydro-2H-quinazolin-3-yl)-benzamide 1
- General procedures for synthesis of oxa/thia/triazocinyl/tetrazocinyl quinazolin-2,4-diones 2a–c
- Synthesis of N-2-(cyanomethyl)-4H-benzo-[g]-[1,3,4,6]-oxatriazocin-5-yl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)-benzamide 2a
- Synthesis of N-2-(cyanomethyl)-4H-benzo-[g]-[1,3,4,6]-thiatriazocin-5-yl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)-benzamide 2b
- Synthesis of N-5-(cyanomethyl)-3,6-dihydrobenzo[e]-[1,2,4,7]-tetrazocin-2-yl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl) benzamide 2c
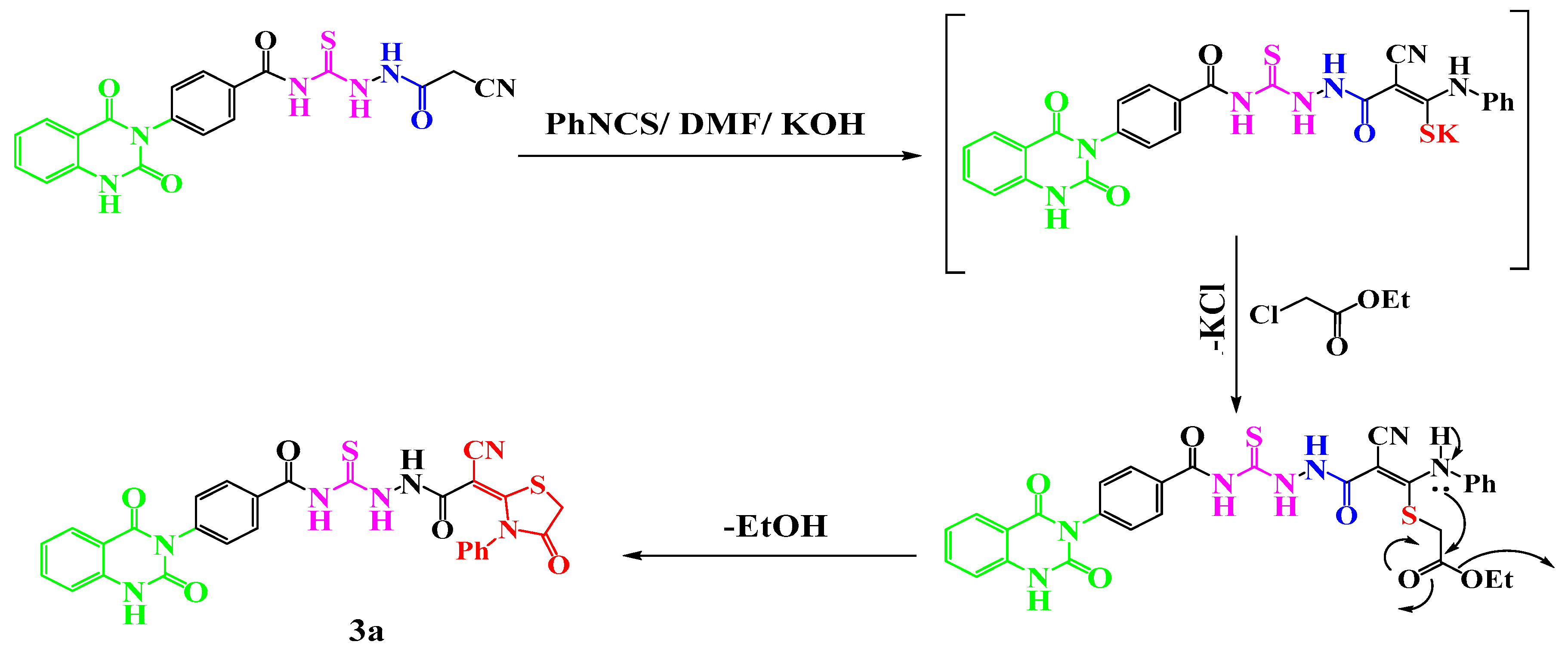
- General procedures for the synthesis of compounds 3a–d
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-2-(4-oxo-1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene)acetyl)hydrazine-1-carbono thioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 3a
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3,3-bis-(ethylthio)-acryloyl)-hydrazine-1-carbonothioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazol-in-3-(2H)-yl)benzamide 3b
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3,3-bis(methylthio)-acryloyl)-hydrazine-1-carbonothioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 3c
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3,3-dimercaptoacryloyl)-hydrazine-1-carbono-thioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 3d
- General procedures for the synthesis of compounds 4a–d
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene)-acetyl)hydrazine-1-carbonothioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 4a
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3-(ethylthio)-3-(phenylamino)-acryloyl)hydrazine-1-carbono thioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 4b
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3-(methylthio)-3-(phenylamino)-acryloyl)hydrazine-1-carbono thioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 4c
- Synthesis of N-(2-(2-cyano-3-(phenylamino)-3-thioxopropanoyl)hydrazine-1-carbono thioyl)-4-(2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)benzamide 4d
3.2. Antibacterial Susceptibility Testing
3.2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
3.2.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) by INT Assay
3.2.3. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
3.3. In Silico Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benabila, N.; Merouani, H.; Latelli, N.; May, A.A.; Morell, C.; Merzoud, L.; Chermette, H. DFT Study of the Condensation Products of 2-Chloro-3-Formylquinolines with o-Aminophenol, o-Aminothiophenol and o-Phenylenediamine. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2023, 142, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.J.; Alam, O.; Alam, J.; Bano, F.; Alam, P.; Shrivastava, N. Recent Review on Indole: A Privileged Scaffold Structure. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Uroos, M.; Ali, S.A.; Arshia; Ishtiaq, M.; Khan, K.M. Quinazoline and Quinazolinone as Important Medicinal Scaffolds: A Comparative Patent Review (2011–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebenezer, O.; Shapi, M.; Tuszynski, J.A. A Review of the Recent Development in the Synthesis and Biological Evaluations of Pyrazole Derivatives. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.D.; Kaur, R.; Arora, R.; Saini, B.; Arora, S. Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles as Anticancer Agents: An Overview. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2150–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, K.P.; Darshini, N.; Shubhavathi, T.; Mallesha, N. Biological Applications of Quinazolinone Analogues: A Review. Org. Med. Chem. Int. J. 2017, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamali, C.; Gul, H.I.; Sakarya, M.T.; Saglik, B.N.; Ece, A.; Demirel, G.; Nenni, M.; Levent, S.; Oner, A.C. Quinazolinone-Based Benzenesulfonamides with Low Toxicity and High Affinity as Monoamine Oxidase-A Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Induced-Fit Docking Studies. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 124, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, V.; Chitra, K.; Saravanan, G.; Solomon, V.R.; Sulthana, M.T.; Narendhar, B. An Overview of Quinazolines: Pharmacological Significance and Recent Developments. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 628–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.; Rashdan, H.R.M.; Abdelmonsef, A.H. Cyclization of Chalcone Derivatives: Design, Synthesis, In Silico Docking Study, and Biological Evaluation of New Quinazolin-2,4-Diones Incorporating Five-, Six-, and Seven-Membered Ring Moieties as Potent Antibacterial Inhibitors. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 27216–27230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R. Biological Significance of Nitrogen Containing Heterocyclic Compounds—A Mini Review. Int. J. Pharm. Rev. Res. 2015, 3, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, C. Recent Progress in the Construction of Eight-Membered Nitrogen-Heterocycles. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 4645–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Sperry, J. Isolation and Biological Activity of Azocine and Azocane Alkaloids. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2022, 54, 116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, N.J.; Conrow, K.; Yethon, A.E. Eight-Membered Ring Heterocycles from Primary Amines, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Formaldehyde1. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 2019–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Chang, W.; Li, J. Synthesis of Eight-Membered Nitrogen Heterocycles via a Heterogeneous PtI2-Catalyzed Cascade Cycloaddition Reaction of δ-Aminoalkynes with Electron-Deficient Alkynes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, N.A.; Vereshchagin, A.N. Piperidine Derivatives: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Pharmacological Applications Pharmacological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lv, X. Recent Advances in [4 + 4] Annulation of Conjugated Heterodienes with 1,4-Dipolar Species for the Synthesis of Eight-Membered Heterocycles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, R.M.; Kwok, N.C.; Lo, W.H.; Ng, K.W. Novel Heterocycles from 5-Methyldibenz[b,f]Azocin-6,12-Dione and Its Derivatives. J. Chem. Soc.—Perkin Trans. 1 1998, 11, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.O.A.; Hassan, A.; Mosallam, A.M.; Khodairy, A.; Rashdan, H.R.M.; Abdelmonsef, A.H. New Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives Incorporating Acylthiourea, Pyrazole and/or Oxazole Moieties as Antibacterial Agents via DNA Gyrase Inhibition. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 17158–17169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Abdelhady, H.A.; Hassain, D.Z.; Abdelmonsef, A.H.; El-Naggar, M.; Elaasser, M.M.; Mahmoud, H.K. Thiazole-Based Thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Molecular Docking Study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Wang, T.Y. Study on Antibacterial Activity and Structure of Chemically Modified Lysozyme. Molecules 2023, 28, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, W. The Applications of β-Keto Amides for Heterocycle Synthesis. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2022, 59, 1445–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.G.; Desai, K.R. Microbial Screening of Novel Synthesized Formazans Having Amide Linkages. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2006, 43, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Srivastava, S.P.; Srivastava, D.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Haq, W.; Katti, S.B. Thiazolidin-4-One and Thiazinan-4-One Derivatives Analogous to Rosiglitazone as Potential Antihyperglycemic and Antidyslipidemic Agents; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 63, ISBN 0915222620. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, H.M.; Abd El-Wahab, A.H.F.; Ahmed, K.A.; El-Agrody, A.M.; Bedair, A.H.; Eid, F.A.; Khafagy, M.M. Synthesis, Reactions and Antimicrobial Activities of 8-Ethoxycoumarin Derivatives. Molecules 2012, 17, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomha, S.M.; Badrey, M.G. A Convenient Synthesis of Some New Thiazole and Pyrimidine Derivatives Incorporating a Naphthalene Moiety. J. Chem. Res. 2013, 37, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, B.; Lv, B. Antibacterial Therapeutic Agents Composed of Functional Biological Molecules. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 6578579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonsef, A.H.; Omar, M.; Rashdan, H.R.M.; Taha, M.M.; Abobakr, A.M. Design, Synthetic Approach, in Silico Molecular Docking and Antibacterial Activity of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Hybrids Bearing Bioactive Scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2022, 13, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, S.; Marzouk, M. Utilization of Cyanoacetohydrazide and Oxadiazolyl Acetonitrile in the Synthesis of Some New Cytotoxic Heterocyclic Compounds. Molecules 2016, 21, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Wang, H.; Ding, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, X.; Chu, W. Azithromycin Reduces the Production of α-Hemolysin and Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus Aureus. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashood, S.T.; Hassan, G.S.; El-Messery, S.M.; Nagi, M.N.; Habib, E.-S.E.; Al-Omary, F.A.M.; El-Subbagh, H.I. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Study of 2-(1,3,4-Thiadiazolyl-Thio and 4-Methyl-Thiazolyl-Thio)-Quinazolin-4-Ones as a New Class of DHFR Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4557–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harer, S.; Bhatia, M.; Kawade, V. Synthesis, Antimicrobial Evaluation and Molecular Docking of Some Potential 2,6-Disubstituted 1H-Benzimidazoles; Non-Classical Antifolates. Med. Chem. 2019, 15, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Bahnan, W.; Wiley, D.J.; Barber, G.; Fields, K.A.; Schesser, K. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (EIF2) Signaling Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Bacterial Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28738–28744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. In Chemical Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1263, pp. 243–250. ISBN 9780123944474. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn, K.S.; Burda, W.N.; Fleeman, R.; Shaw, L.N.; Manetsch, R. Antibacterial Activity of a Series of N2, N4- Disubstituted Quinazoline-2,4-Diamines. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3075–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Catalano, A.; Cirillo, F.; Lappano, R.; Sinicropi, M.S. A Review on the Antimicrobial Activity of Schiff Bases: Data Collection and Recent Studies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidl, J.; Leitner, D.R.; Goessler, W.; Prassl, R.; Salem, W.; Schratter, G.; Zingl, F.G.; Schild, S. Antibacterial Activity of Silver and Zinc Nanoparticles against Vibrio Cholerae and Enterotoxic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, J.N. A Sensitive and Quick Microplate Method to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of Plant Extracts for Bacteria. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsulire, O.R.; Aibinu, I.E.; Adenipekun, T.; Adelowotan, T.; Odugbemi, T. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Crude Extracts from Plants Bryophyllum Pinnatum and Kalanchoe Crenata. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 4, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celiktas, O.Y.; Kocabas, E.E.H.; Bedir, E.; Sukan, F.V.; Ozek, T.; Baser, K.H.C. Antimicrobial Activities of Methanol Extracts and Essential Oils of Rosmarinus Officinalis, Depending on Location and Seasonal Variations. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L.; Mackerell, A.D.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The Biomolecular Simulation Program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappé, A.K.; Casewit, C.J.; Colwell, K.S.; Goddard, W.A.; Skiff, W.M. UFF, a Full Periodic Table Force Field for Molecular Mechanics and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
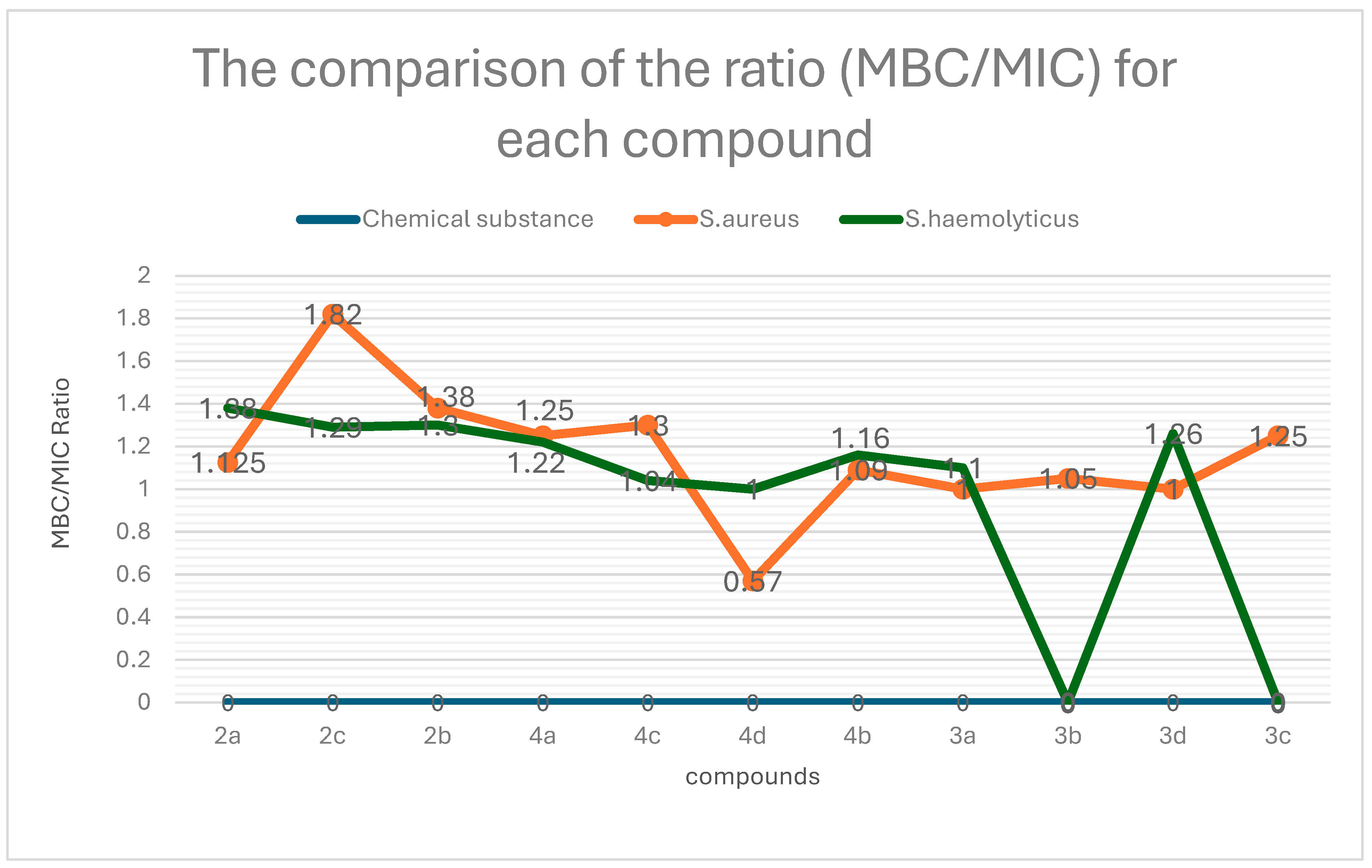
| No. | Compound | S. aureus (MIC/MBC) | S. haemolyticus (MIC/MBC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | 16 ± 2/18 ± 4.5 | 13 ± 1/18 ± 1.7 |
| 2 | 2b | 13 ± 1/18 ± 1.7 | 10 ± 1/13 ± 2.6 |
| 3 | 2c | 11 ± 1/20 ± 2.6 | 17 ± 1/22 ± 2.6 |
| 4 | 3a | 10 ± 1/10 ± 1 | 20 ± 2/22 ± 2 |
| 5 | 3b | 25.6 ± 1.6/27 ± 1.7 | N.A/N.A |
| 6 | 3c | 12 ± 1.7/15 ± 1.7 | N.A/N.A |
| 7 | 4a | 16 ± 1/18 ± 1.7 | 18 ± 1.7/22 ± 2 |
| 8 | 4b | 21 ± 1.7/23 ± 1 | 18 ± 1.7/21 ± 3 |
| 9 | 4c | 10 ± 1/13 ± 2.6 | 21 ± 1.7/22 ± 2.6 |
| 10 | 4d | 19 ± 1/11 ± 1 | 22 ± 2/22 ± 2 |
| Enzyme | Dihydrofolate Reductase Enzyme | Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 α Enzyme | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Binding Energy kcal/mol | Docked Complex (Amino Acid–Ligand) Interactions | Distance (Å) | Binding Energy kcal/mol | Docked Complex (Amino Acid–Ligand) Interactions | Distance (Å) | |
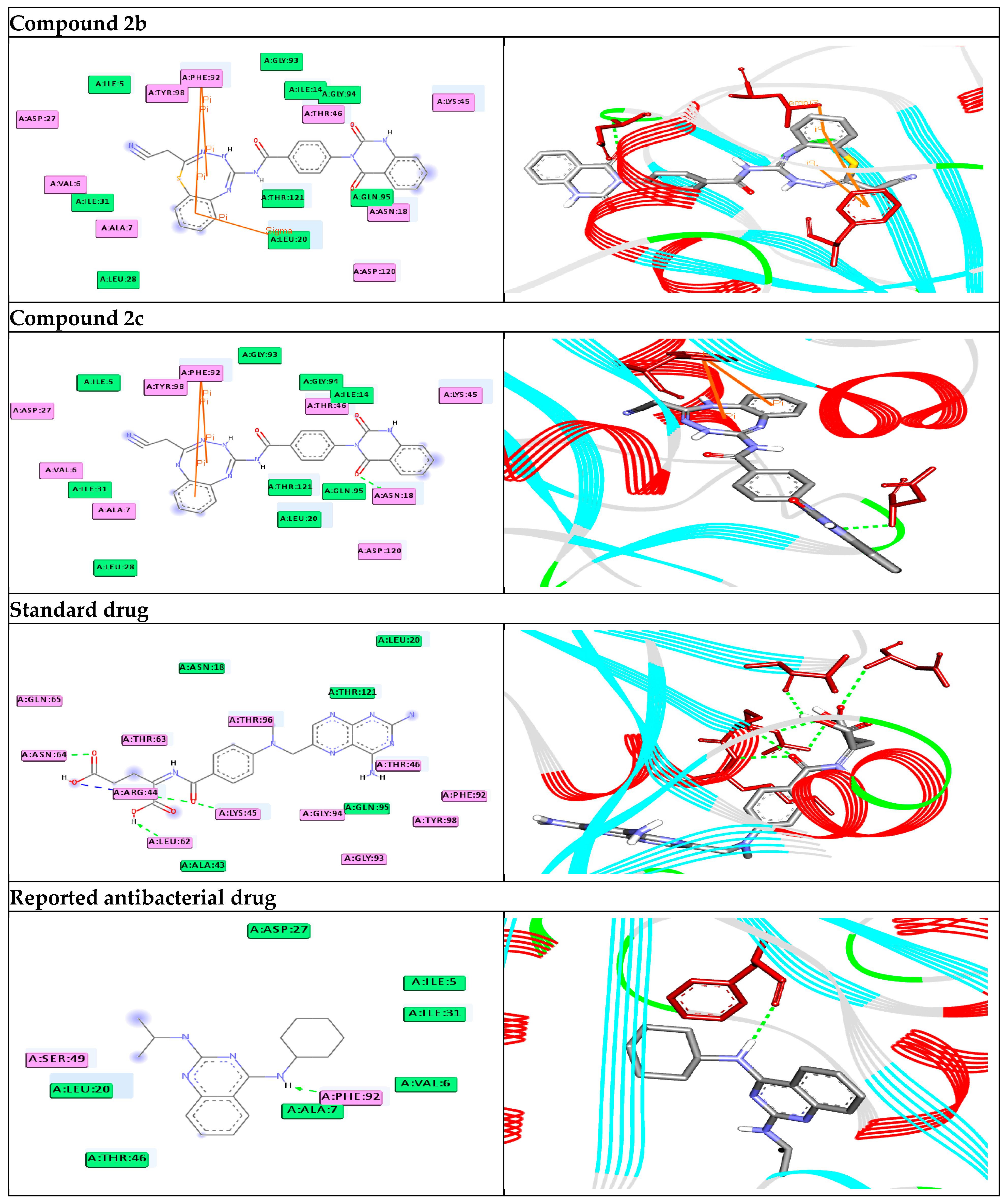
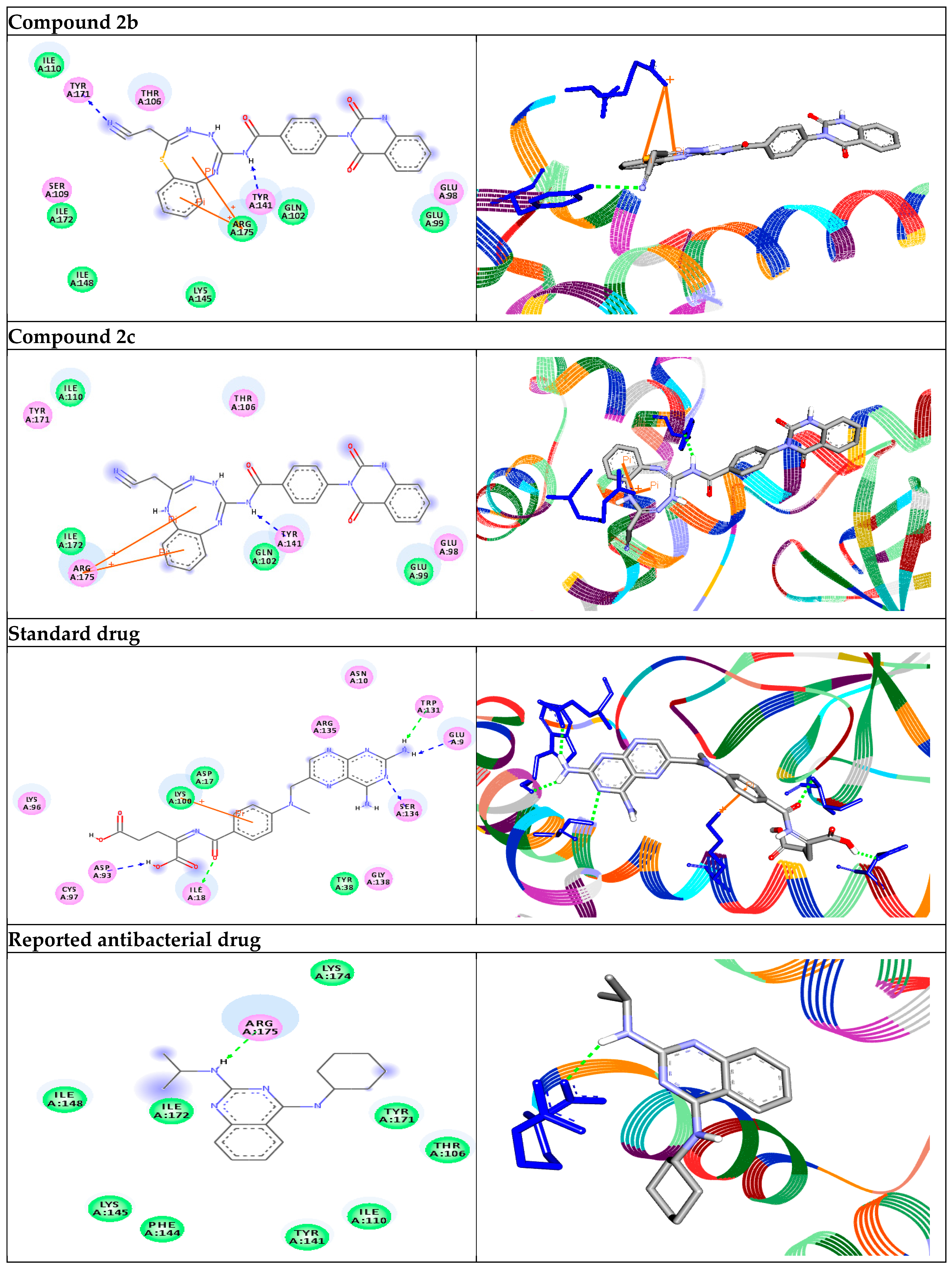
| 2a | −11.4 | H-bonds ASN18:N—compound 2a arene-arene interactions PHE92—compound 2a PHE92—compound 2a arene-sigma interactions LEU20:CD1—compound 2a | 2.95 4.92 5.61 3.99 | −7.3 | H-bonds LYS100:NZ—compound 2a | 2.95 | |
| 2b | −11.7 | H-bonds ASN18:N—compound 2b arene–arene interactions PHE92—compound 2b PHE92—compound 2b arene–sigma interactions LEU20:CD1—compound 2b | 2.91 5.01 5.92 3.82 | −9.6 | H-bonds TYR171:OH—compound 2b TYR141:OH—compound 2b arene–cation interactions ARG175:NH1--compound 2b ARG175:NH1--compound 2b | 2.91 2.21 4.75 5.12 | |
| 2c | −11.6 | H-bonds ASN18:N—compound 2c arene–arene interactions PHE92—compound 2c PHE92—compound 2c | 2.86 4.93 5.39 | −9.5 | H-bonds TYR141:OH—compound 2c arene–cation interactions ARG175:NH1—compound 2c ARG175:NH1—compound 2c | 2.20 4.76 5.69 | |
| 3a | −11.0 | H-bonds ASN18:N—compound 3a THR46:OG1—compound 3a ILE14:O—compound 3a arene–cation interactions ARG57:NH1—compound 3a ARG57:NH1—compound 3a ARG57:NH2—compound 3a ARG57:NH2—compound 3a | 2.99 2.95 2.38 5.26 5.06 5.50 5.64 | −8.1 | H-bonds LYS11:N—compound 3a ARG135:NH1—compound 3a ARG135:NH2—compound 3a arene–cation interactions ARG6:NH2—compound 3a ARG6:NH1—compound 3a LYS11:NZ—compound 3a LYS11:NZ—compound 3a | 2.96 3.00 2.89 3.93 5.86 5.13 5.09 | |
| 3b | −10.5 | H-bonds ARG44:N—compound 3b LYS45:N—compound 3b GLN95:N—compound 3b TYR98:OH—compound 3b arene–cation interactions ARG57:NH1—compound 3b ARG57:NH1—compound 3b ARG57:NH2—compound 3b ARG57:NH2—compound 3b LYS45:NZ—compound 3b | 3.00 2.98 2.97 2.83 5.25 4.63 5.36 5.23 4.81 | −8.0 | H-bonds TYR101:OH—compound 3b HIS108:ND1—compound 3b ARG112:NH1—compound 3b arene–cation interactions LYS117:NZ—compound 3b | 2.97 3.00 2.81 5.60 | |
| 3c | −11.1 | H-bonds SER49:OG—compound 3c GLN95:N—compound 3c | 2.99 2.95 | −8.7 | H-bonds SER109:OG—compound 3c TYR113:N—compound 3c TYR171:OH—compound 3c ARG175:NH1—compound 3c SER109:OG—compound 3c arene–cation interactions ARG175:NH1—compound 3c LYS145:NZ—compound 3c | 3.00 2.98 2.95 2.86 2.17 5.54 5.69 | |
| 3d | −10.4 | H-bonds SER49:OG—compound 3d | 2.95 | −7.9 | H-bonds TYR101:OH—compound 3d ARG112:NH1—compound 3d ARG112:NH1—compound 3d SER109:OG—compound 3d arene–cation interactions ARG112:NH2—compound 3d | 2.97 2.87 2.99 1.92 5.22 | |
| 4a | −10.3 | H-bonds THR46:OG1—compound 4a arene–cation interactions ARG57:NH1—compound 4a LYS45:NZ—compound 4a | 2.91 5.05 4.32 | −8.0 | H-bonds TYR171:OH—compound 4a ARG175:NH1—compound 4a TYR141:OH—compound 4a arene–cation interactions ARG175:NH1—compound 4a | 2.94 2.99 1.96 4.72 | |
| 4b | −9.7 | H-bonds ARG44:NH2—compound 4b THR46:N—compound 4b THR46:OG1—compound 4b GLY94:N—compound 4b THR46:OG1—compound 4b arene–cation interactions ARG44:NH2—compound 4b | 3.00 2.96 2.69 2.65 1.98 6.00 | −8.3 | H-bonds TYR101:OH—compound 4b LYS105:NZ—compound 4b THR106:OG1—compound 4b SER109:OG—compound 4b ARG112:NH1—compound 4b arene–cation interactions LYS105:NZ—compound 4b ARG112:NH1—compound 4b | 3.00 2.85 2.98 2.93 2.82 3.61 5.03 | |
| 4c | −10.2 | H-bonds THR46:OG1—compound 4c THR121:OG1—compound 4c SER49:OG—compound 4c arene–cation interactions PHE92—compound 4c PHE92—compound 4c | 2.83 3.00 2.46 5.88 5.33 | −8.6 | H-bonds SER109:OG—compound 4c SER109:OG—compound 4c ARG175:OXT—compound 4c arene–sigma interactions TYR113:CD1—compound 4c | 2.75 2.41 2.37 3.63 | |
| 4d | −9.5 | H-bonds SER49:OG—compound 4d PHE92:O—compound 4d arene–cation interactions LYS52:NZ—compound 4d | 1.90 2.31 5.44 | −8.5 | H-bonds SER109:OG—compound 4d SER109:OG—compound 4d ARG175:OXT—compound 4d arene–sigma interactions TYR113:CD1—compound 4d | 2.70 2.45 2.38 3.57 | |
| Standard drug | −9.3 | H-bonds ARG44:N—standard drug ARG44:NE—standard drug ARG44:NH2—standard drug LYS45:N—standard drug ASN64:N—standard drug LEU62:O—standard drug | 2.81 2.94 2.99 2.98 2.18 2.07 | −7.1 | H-bonds ILE18:N—standard drug SER134:OG—standard drug TRP131:O—standard drug GLU9:OE2—standard drug ASP93:OD1—standard drug arene–cation interactions LYS100:NZ—standard drug | 2.85 2.99 2.03 2.09 2.07 3.49 | |
| Reported antibacterial drug [34] | −9.3 | H-bonds PHE92:O—reported drug | 2.50 | −7.0 | H-bonds ARG175:O—reported drug | 2.17 | |
| # | Compound 2b | Compound 2c | Standard Drug | Reported Antibacterial Drug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (g/mol) | 495.51 | 478.46 | 454.44 | 284.40 |
| #Rotatable bonds | 5 | 5 | 10 | 4 |
| #HBA | 6 | 6 | 9 | 2 |
| #HBD | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| TPSA (Å2) | 177.56 | 165.11 | 210.54 | 49.84 |
| MLOGP | 2.64 | 2.29 | −0.46 | 3.37 |
| %ABS | 99.00 | 98.23 | 82.61 | 99.65 |
| GI absorption | Low | Low | Low | High |
| BBB permeant | No | No | No | Yes |
| Lipinski #violations | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Bioavailability Score | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.11 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelmonsef, A.H.; El-Naggar, M.; Ibrahim, A.O.A.; Abdelgeliel, A.S.; Shehadi, I.A.; Mosallam, A.M.; Khodairy, A. Evaluation of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives as Promising Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, In Vitro, In Silico ADMET and Molecular Docking Approaches. Molecules 2024, 29, 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235529
Abdelmonsef AH, El-Naggar M, Ibrahim AOA, Abdelgeliel AS, Shehadi IA, Mosallam AM, Khodairy A. Evaluation of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives as Promising Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, In Vitro, In Silico ADMET and Molecular Docking Approaches. Molecules. 2024; 29(23):5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235529
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelmonsef, Aboubakr H., Mohamed El-Naggar, Amal O. A. Ibrahim, Asmaa S. Abdelgeliel, Ihsan A. Shehadi, Ahmed M. Mosallam, and Ahmed Khodairy. 2024. "Evaluation of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives as Promising Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, In Vitro, In Silico ADMET and Molecular Docking Approaches" Molecules 29, no. 23: 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235529
APA StyleAbdelmonsef, A. H., El-Naggar, M., Ibrahim, A. O. A., Abdelgeliel, A. S., Shehadi, I. A., Mosallam, A. M., & Khodairy, A. (2024). Evaluation of Quinazolin-2,4-Dione Derivatives as Promising Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, In Vitro, In Silico ADMET and Molecular Docking Approaches. Molecules, 29(23), 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235529







