The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging
Abstract
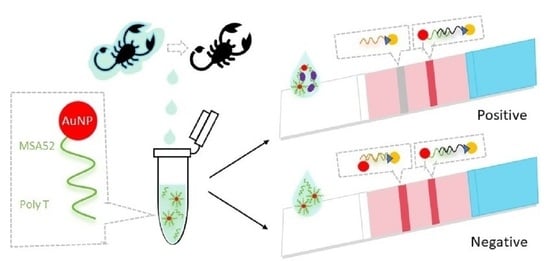
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of AuNPs and Determination of Coupling Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Test Strip Conditions
2.2.1. Optimization of SA Concentrations and Molar Ratios of SA to Biotin-DNAT
2.2.2. Optimization of NC Membranes
2.2.3. Optimization of Running Buffer
2.3. An Aptamer Engineering Approach to Selecting T-Line Complementary Sequences
2.4. Optimization of Detection Conditions
2.5. Quantitative Detection of SP by Test Strips
2.6. Specificity Test
2.7. Reproducibility Evaluation
2.8. Stability Assessment
2.9. Recovery Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles
4.3. Conjugation of Aptamer and Nanogolds
4.4. Selection of T-Line Complementary Sequences
4.5. Pre-Treatment of Test Strips
4.6. Assembly of Test Strips
4.7. Sample Test and Evaluation Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, P.; Ghosh, A.R. Environmental perspectives of COVID-19 outbreaks: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5822–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2024. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Yuen, K.S.; Ye, Z.W.; Fung, S.Y.; Chan, C.P.; Jin, D.Y. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: The most important research questions. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.L.; Liu, X.W. Can imported cold food cause COVID-19 recurrent outbreaks? A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Mao, Y.; Qi, H.C.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.R.; You, F.S.; Zhao, W.C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Real-time, selective, and low-cost detection of trace level SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein for cold-chain food quarantine. NPJ Sci. Food 2021, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavizadeh, L.; Ghasemi, S. Review Article Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 54, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikhani, A.B.; Bazaz, M.; Bamehr, H.; Fereshteh, S.; Amiri, S.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Arashkia, A.; Azadmanesh, K. The Inclusive Review on SARS-CoV-2 Biology, Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Potential Management Options. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, S.; Poma, A.B.; Kolandaivel, P. Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 3409–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.L.; Oton, J.Q.; Qu, K.; Cortese, M.; Zila, V.; McKeane, L.; Nakane, T.; Zivanov, J.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 2020, 588, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, M.; Skouridou, V.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Viéitez, I.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Alvargonzalez, J.J.C.; Poveda, E.; Bofill, C.B.; Sans, T.; Bashammakh, A.; et al. Aptamer Sandwich Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Antigen. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35657–35666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejad, Z.H.; Fatemi, F.; Siadat, S.E.R. An outlook on coronavirus disease 2019 detection methods. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Ghoshal, U.; Patel, S.S.; Singh, D.V.; Arya, A.K.; Vasanth, S.; Pandey, A.; Srivastava, N. Evaluation of seven commercial RT-PCR kits for COVID-19 testing in pooled clinical specimens. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zou, Z.Y.; Pu, Z.; Wu, M.H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Application of microfluidic technologies on COVID-19 diagnosis and drug discovery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2877–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, M.; De Falco, M.; Zappi, D.; Antonacci, A.; Scognamiglio, V. Isothermal amplification-assisted diagnostics for COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 205, 114101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, D.S.Y.; Fragkou, P.C.; Schweitzer, V.A.; Chemaly, R.F.; Moschopoulos, C.D.; Skevaki, C.; European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Study Group for Respiratory Viruses (ESGREV). How to interpret and use COVID-19 serology and immunology tests. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Tests: An Implementation Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.J.; Vyas, A.K.; Khare, P.; Gupta, S.; Nema, R.K.; Nema, S.; Gupta, S.; Chaurasiya, S.K.; Biswas, D.; Singh, A.K. Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19: Current status and challenges. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpradit, S.; Prasongtanakij, S.; Srisala, S.; Chanprasertyothin, S.; Pasomsub, E.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. The Detection of SARS-CoV2 Antigen in Wastewater Using an Automated Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, B.A.; Kandigian, S.E.; Kitchen, R.R.; Grauwet, K.; Webb, P.K.; Miller, G.A.; Jennings, C.G.; Jain, S.; Miller, S.; Kuo, Y.K.; et al. Evaluation of serological lateral flow assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.L.; Yang, S.M. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M. Blame It on the Antibodies. Nature 2015, 521, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, D.; Cui, S.S.; Li, C.; Yun, Z.G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.X. Design of a Signal-Amplified Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Test Strip for the Rapid Detection of Ochratoxin A in Red Wine. Foods 2022, 11, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Liu, L.H.; Duan, N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.P. Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Test Strip for Rapid Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.G.; Dong, Y.Y. Development of a lateral flow aptamer assay strip for facile identification of theranostic exosomes isolated from human lung carcinoma cells. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 594, 113591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Roque, M.A.; Franco-Urquijo, P.A.; García-Velásquez, V.M.; Choukeife, M.; Mayer, G.; Molina-Ramírez, S.R.; Figueroa-Miranda, G.; Mayer, D.; Alvarez-Salas, L.M. DNA aptamer selection for SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein detection. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 645, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Li, J.X.; Gu, J.; Amini, R.; Stacey, H.D.; Ang, J.C.; White, D.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Mossman, K.; Miller, M.S.; et al. A Universal DNA Aptamer that Recognizes Spike Proteins of Diverse SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202200078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Patel, D.; Pandya, A. Emerging diagnostic tools for detection of COVID-19 and perspective. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdinasab, M.; Badea, M.; Marty, J.L. Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Assays: Current Trends in Clinical Diagnostic Rapid Tests. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.H. Current Advances in Paper-Based Biosensor Technologies for Rapid COVID-19 Diagnosis. BioChip J. 2022, 16, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellipilli, S.; Wang, H.Z.; Lee, W.J.; Shu, D.; Guo, P.X. Proof-of-concept for speedy development of rapid and simple at-home method for potential diagnosis of early COVID-19 mutant infections using nanogold and aptamer. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 45, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Servos, M.R.; Liu, J.W. Surface Science of DNA Adsorption onto Citrate-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3896–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.H.; Dong, Y.Y. Development of Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Strips for Micropollutants Screening Using Colorants of Aptamer-Functionalized Nanogold Particles, Part I: Methodology and Optimization. J. Aoac Int. 2018, 101, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crampon, K.; Giorkallos, A.; Deldossi, M.; Baud, S.; Steffenel, L.A. Machine-learning methods for ligand-protein molecular docking. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.F.; Kacherovsky, N.; Panpradist, N.; Wan, R.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B.; Salipante, S.J.; Lutz, B.R.; Pun, S.H. Aptamer Sandwich Lateral Flow Assay (AptaFlow) for Antibody-Free SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7278–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, B.H.; Yu, F.Y. Novel enzyme-linked aptamer-antibody sandwich assay and hybrid lateral flow strip for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Chang, S.L.; Chen, S.J.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, S.Q.; et al. Highly sensitive and rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 via a portable CRISPR-Cas13a-based lateral flow assay. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5858–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.; Bovolato, A.L.D.; Ibáñez-Redín, G.; Brolo, A.G. Quantification of a COVID-19 Antibody Assay Using a Lateral Flow Test and a Cell Phone. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshref, Z.S.; Jalali, T.; Adriani, R.R.; Soltati, E.; Gargari, S.L.M. Aptamer-based diagnosis of various SARS-CoV2 strains isolated from clinical specimens. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chang, J.H.; Kang, H.G.; Choi, J. Colorimetric Detection of SsDNA in a Solution. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yuan, C.; Tian, T.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Xiong, E.; Zhou, X. Single-step, salt-aging-free, and thiol-free freezing construction of AuNP-based bioprobes for advancing CRISPR-based diagnostics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7506–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, T.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Luo, H.; Yen, T.M.; Chen, P.W.; Han, Y.Y.; Lo, Y.H. Nucleic Acid Aptamers: An Emerging Tool for Biotechnology and Biomedical Sensing. Sensors 2015, 15, 16281–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Wang, H.; Zhai, W.L.; Feng, X.Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, A.L.; Wang, M. A Lateral Flow Strip Based on a Truncated Aptamer-Complementary Strand for Detection of Type-B Aflatoxins in Nuts and Dried Figs. Toxins 2020, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Deng, X.; Wen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Ultrasensitive paper based nucleic acid detection realized by three-dimensional DNA-AuNPs network amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.D.; Yan, J.H.; Xiong, H.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Peng, D.M.; Liu, Z.B. Investigations on the interface of nucleic acid aptamers and binding targets. Analyst 2018, 143, 5317–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakashansky, J.A.; Imamura, A.H.; Salgado, D.F.; Mercieca, H.C.R.; Aguas, R.F.L.; Lao, A.M.; Pariser, J.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Khine, M. Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in saliva with Shrinky-Dink© electrodes. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Giroux, E.; Jovic, M.; Martic-Milne, S. Localized surface plasmon resonance aptasensor for selective detection of SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein. Analyst 2021, 146, 7207–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, W.T.; Li, J.R.; Wang, S.N.; Shen, X.J.; Wen, X.B.; Liu, L. Aptamer-based kinetically controlled DNA reactions coupled with metal-organic framework nanoprobes for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 6583–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Qian, J.C.; Chen, F.; Wan, Y.K.; Li, H.A.; Li, H.M. Atomically dispersed Mn boosting photoelectrochemical SARS-CoV-2 spike protein immunosensing on carbon nitride. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, A.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Sun, Y.N.; Du, Y.K.; Wang, X.; Ding, P.Y.; Jia, R.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, G.P. Development of a Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Strip for Rapid Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Protein. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Murray, J.; Haverstick, J.; Tripp, R.A.; Zhao, Y.P. Silver nanotriangle array based LSPR sensor for rapid coronavirus detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Seo, Y.S.; Kim, K.; Han, J.W.; Park, Y.; Cho, S. Concentration Effect of Reducing Agents on Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Size, Morphology, and Growth Mechanism. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UNA Fold Web Server. Available online: http://www.unafold.org/DNA_form.php# (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Li, X. 3dRNA/DNA Web Server. Available online: http://biophy.hust.edu.cn/new/3dRNA (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Li, X.; Qian, Z.; Chang, R.; Peng, C.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Z. Non-thiolated nucleic acid functionalized gold nanoparticle–based aptamer lateral flow assay for rapid detection of kanamycin. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Number | Energy | Aptamer Binding Site | Protein Binding Site | Aptamer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −15.89 | DA20 | Lys921 | DT18-DT22 |
| 2 | −0.9 | DT66 | Gln935 | DC65-DG71 |
| 3 | −0.72 | DT80 | Lys285 | DT77-DT84 |
| 4 | −0.64 | DT82 | Lys278 | DT77-DT84 |
| Name | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MSA-10 | Biotin-ACGCCAAGGA |
| MSA-15 | Biotin-ACGCCAAGGAGATGC |
| MSA-20 | Biotin-ACGCCAAGGAGATGCTTCGC |
| MSA-22 | Biotin-CGCCAGGCCCGGAGCCAAACCC |
| Control-line DNA | Biotin-AAAAAAAAAA |
| Target | Detection Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| S Protein | / | 100 pM | [37] |
| N Protein | 0.1–500 ng/mL | 0.1–0.5 ng/mL | [38] |
| N gene | 0.25–100 copies/mL | 0.25 copy/mL | [39] |
| IgG | 10 ng/mL–100 µg/mL | 4 ng/mL | [40] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Virus | 0–50 ng/mL | 10 ng/mL | [41] |
| S Protein | 100 ng/mL–1000 ng/mL | 91.2 ng/mL | This work |
| Batch | SP Concentration (μg/mL) | of T/C | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.2717 | 0.0398 | 14.64 |
| 0.5 | 0.4413 | 0.0565 | 12.81 | |
| 0.25 | 0.5780 | 0.0851 | 14.73 | |
| 2 | 1 | 0.3519 | 0.0416 | 11.82 |
| 0.5 | 0.5032 | 0.0669 | 13.30 | |
| 0.25 | 0.6602 | 0.0873 | 13.23 | |
| 3 | 1 | 0.3122 | 0.0396 | 12.70 |
| 0.5 | 0.4710 | 0.0696 | 14.78 | |
| 0.25 | 0.6535 | 0.0967 | 14.80 | |
| Intra-batch | 1 | 0.3119 | 0.0403 | 13.05 |
| 0.5 | 0.4718 | 0.0643 | 13.63 | |
| 0.25 | 0.6305 | 0.0897 | 14.25 |
| Sample | Concentration of SP (ng/mL) | Detection Result | Test Strip Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery Rate (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-chain food packaging bags—tap water rinsing (1 mL) | 0 | Negative | Undetected | Undetected | Undetected |
| 200 | Positive | 166.7 | 83.3 | 2.6 | |
| 400 | Positive | 435.2 | 108.8 | 2.3 | |
| 600 | Positive | 571.7 | 95.2 | 5.8 | |
| 800 | Positive | 752.4 | 94.1 | 6.2 | |
| 900 | Positive | 860.2 | 95.6 | 4.6 | |
| 1000 | Positive | 968.1 | 96.8 | 3.0 |
| Method | Target | Detection Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-AB | S Protein (S1) | 0.001–1000 fg/mL | 1 ag/mL | [48] |
| SPR | S Protein (S1) | 1–100 nM | 0.26 nM | [49] |
| Fluorescence (FL) | S Protein | 10 fg/mL–10 ng/mL | 7.8 fg/mL | [50] |
| PEC | S Protein | 75 fg/mL–150 pg/mL | 1.22 fg/mL | [51] |
| LFA | S Protein (RBD) S Protein (S1) | 62.5–4000 ng/mL 250–4000 ng/mL | 62.5 ng/mL 250 ng/mL | [52] |
| LSPR | S Protein (RBD) | 2.03–9420 pM | 0.83 pM | [53] |
| Name | Speed (s/4 cm) | Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| BSK95 | 100 ± 20 | 12–15 |
| BSK110 | 120 ± 30 | 8–12 |
| BSK140 | 140 ± 30 | 5–8 |
| BSK160 | 160 ± 30 | 4–6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Fang, X.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Z.; Dong, Y. The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging. Molecules 2024, 29, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081776
Li X, Wang J, Yang G, Fang X, Zhao L, Luo Z, Dong Y. The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081776
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaotong, Jiachen Wang, Ge Yang, Xiaona Fang, Lianhui Zhao, Zhaofeng Luo, and Yiyang Dong. 2024. "The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081776
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, J., Yang, G., Fang, X., Zhao, L., Luo, Z., & Dong, Y. (2024). The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging. Molecules, 29(8), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081776