Identification of Leishmania donovani PEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors through Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
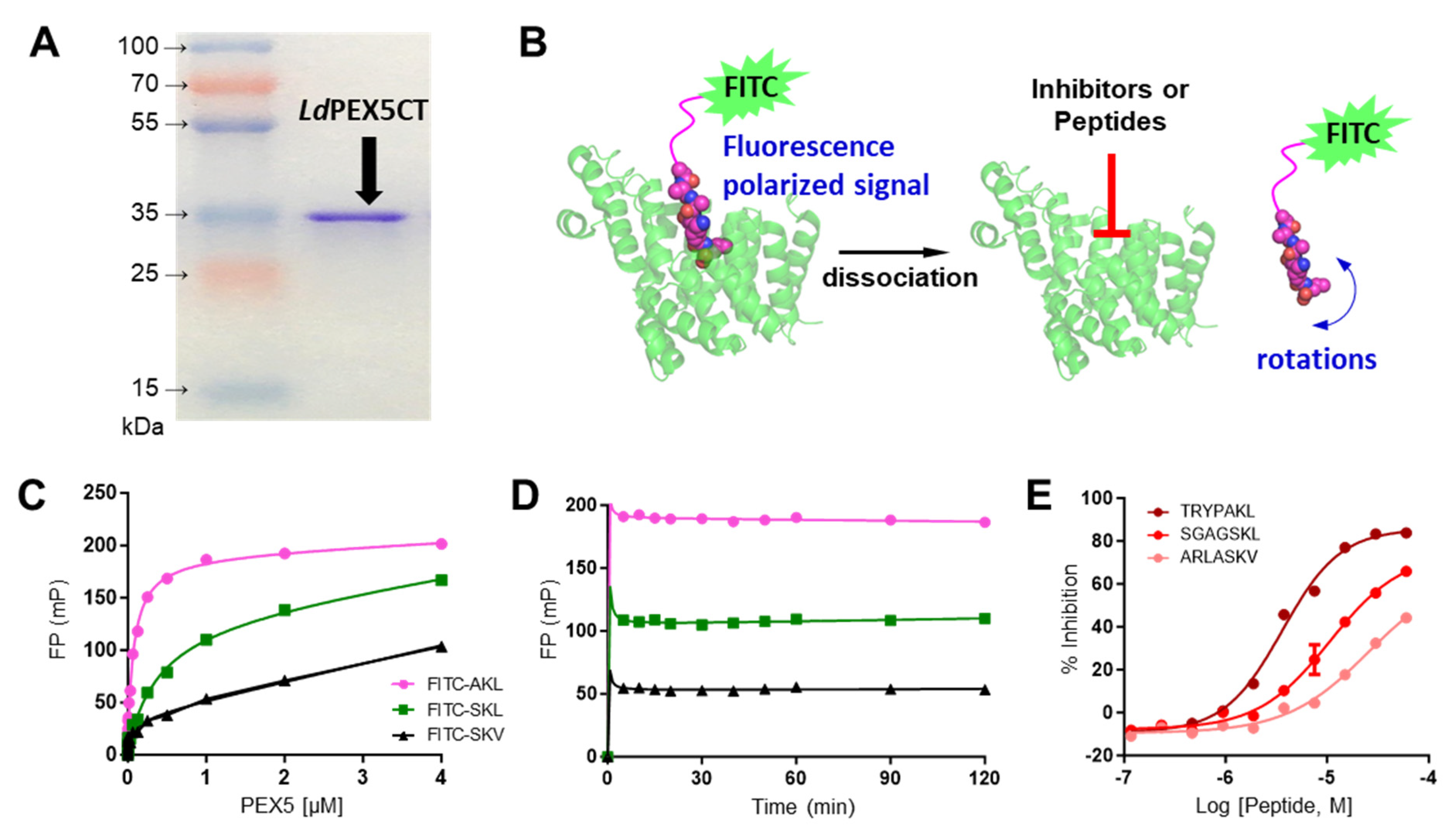
2.1. Characterization of LdPEX5 and PTS1 Interaction and Inhibition with Peptides
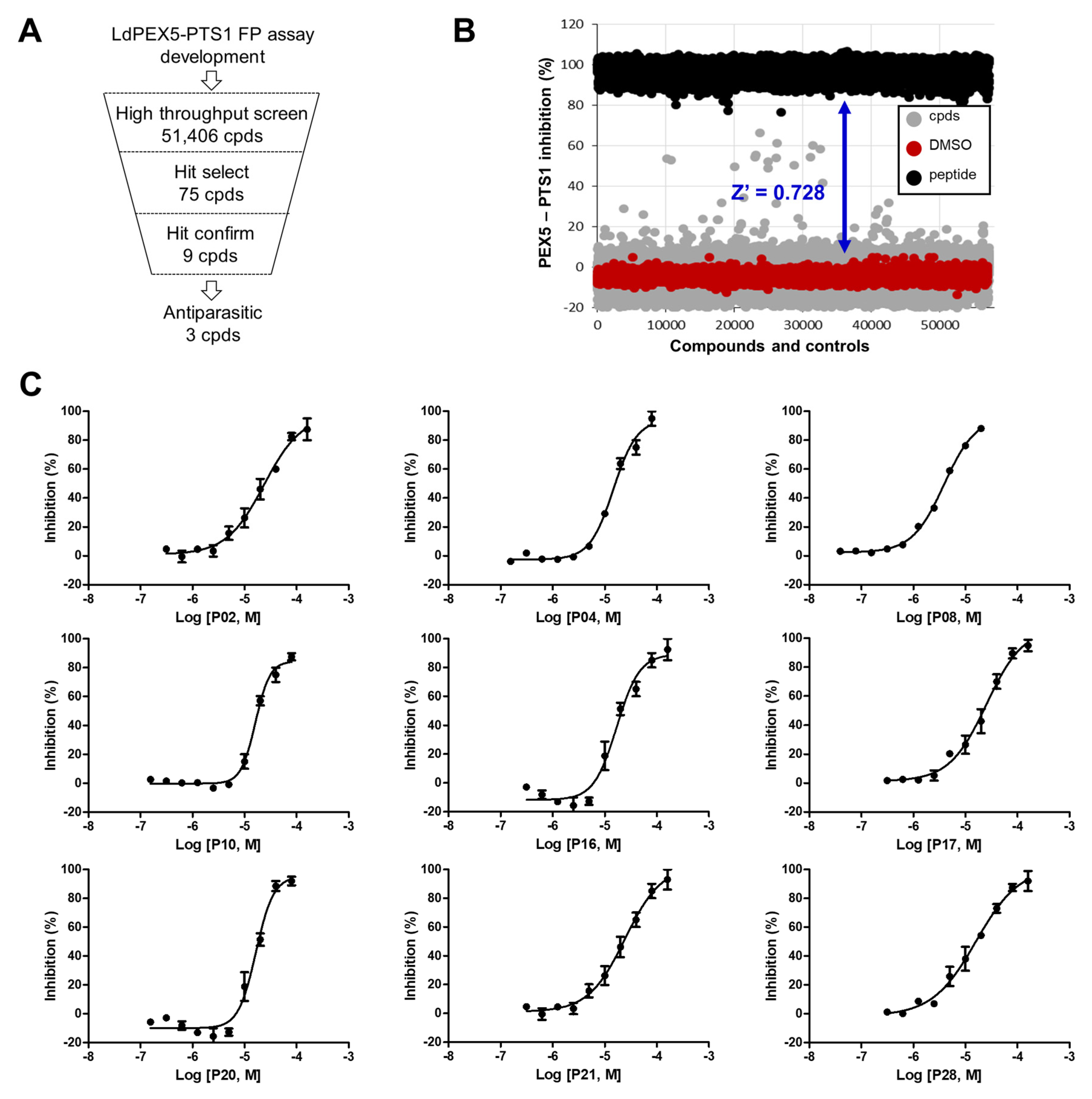
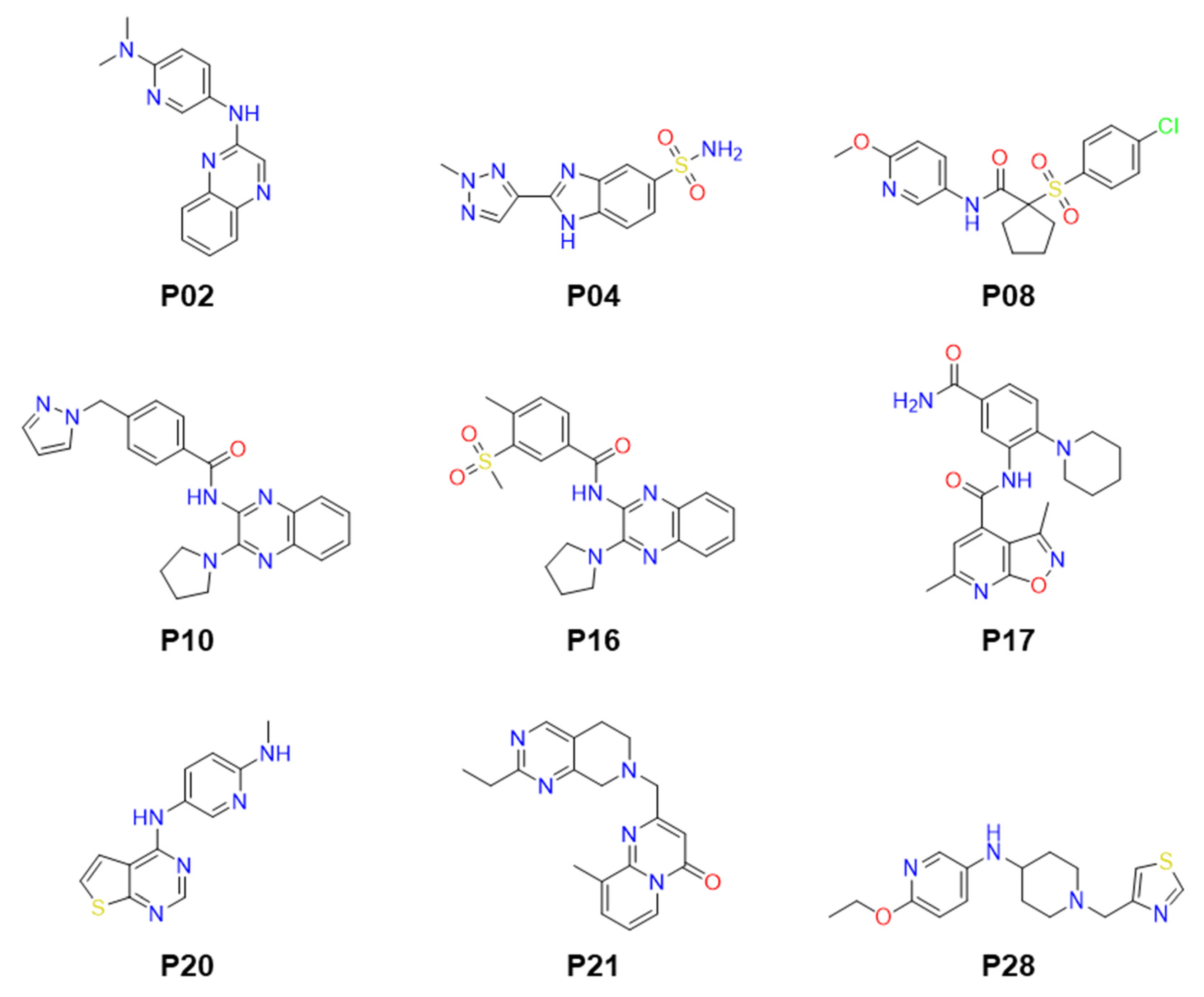
2.2. Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitor through FP-Based HTS
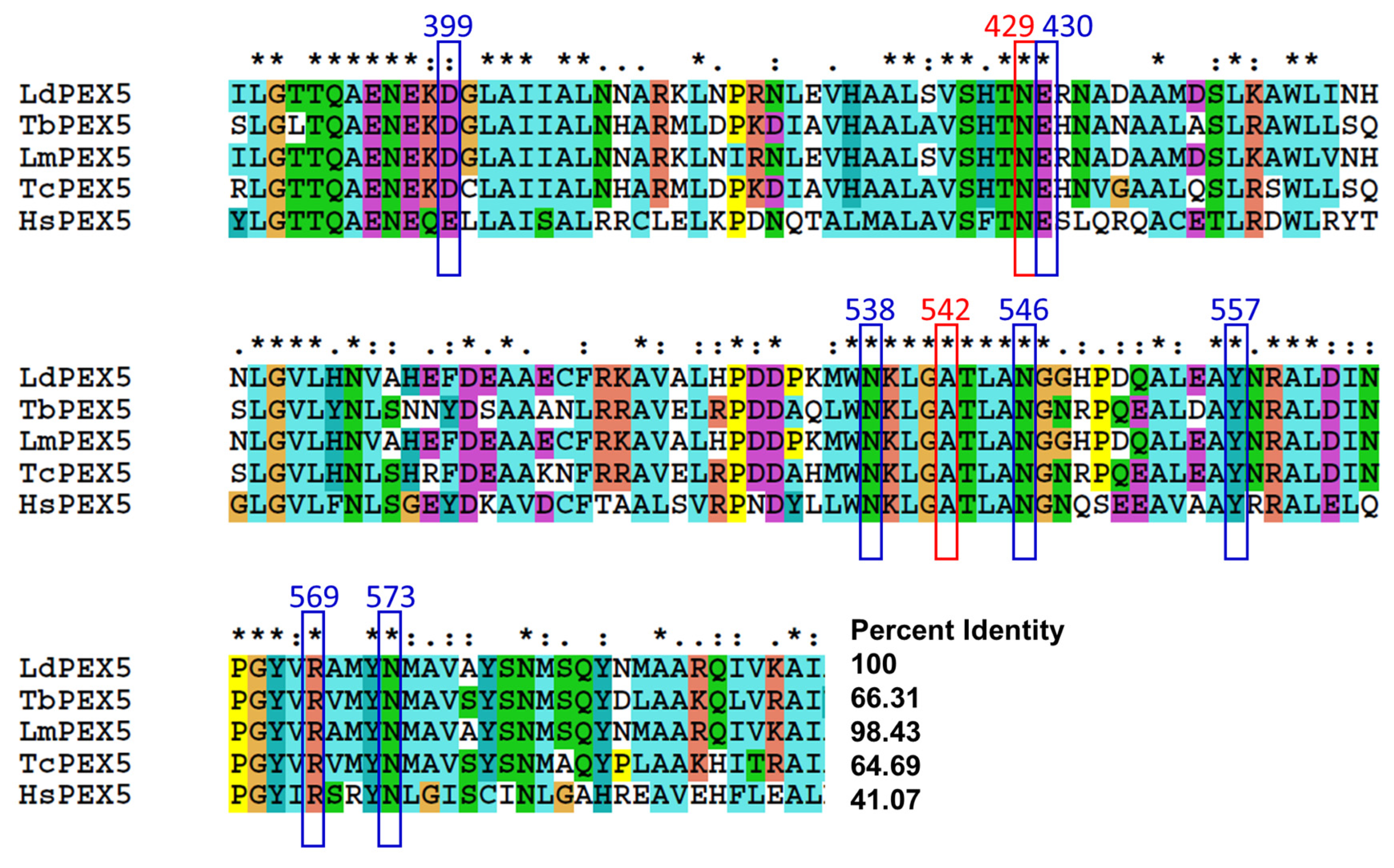
2.3. Molecular Modeling of Inhibitor and LdPEX5 Interaction
2.4. Anti-Parasitic Activity of Identified Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Parasites
4.2. Expression and Purification of His6-LdPEX5CT
4.3. LdPEX5-PTS1 Peptides Interaction Assay
4.4. FP-Based HTS for LdPEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors
4.5. Molecular Modelling Study
4.6. Anti-Parasitic Activity Assessment
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, S.; Frasca, K.; Scherrer, S.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Newman, S.; Ramanan, P.; Suarez, J.A. A Review of Leishmaniasis: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2021, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Leishmaniasis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Pigott, D.M.; Bhatt, S.; Golding, N.; Duda, K.A.; Battle, K.E.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Balard, Y.; Bastien, P.; Pratlong, F.; et al. Global distribution maps of the leishmaniases. eLife 2014, 3, e02851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D. A profile of research on the parasitic trypanosomatids and the diseases they cause. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; Kamhawi, S. Molecular aspects of parasite-vector and vector-host interactions in leishmaniasis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 453–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.H.N.; Chang, K.P.; Costa, D.L.; Cunha, F.V.M. From Infection to Death: An Overview of the Pathogenesis of Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. Drug resistance in leishmaniasis. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, C.P.; Sinha, G.P.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, P.; Hassan, S.M.; Narain, S.; Roy, R.K. Do the diminishing efficacy and increasing toxicity of sodium stibogluconate in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis in Bihar, India, justify its continued use as a first-line drug? An observational study of 80 cases. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1998, 92, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, R.J. Amphotericin B formulations: A comparative review of efficacy and toxicity. Drugs 2013, 73, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, J.H. Visceral leishmaniasis: Revisiting current treatments and approaches for future discoveries. Acta Trop. 2016, 155, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte-Sucre, A.; Gamarro, F.; Dujardin, J.C.; Barrett, M.P.; López-Vélez, R.; García-Hernández, R.; Pountain, A.W.; Mwenechanya, R.; Papadopoulou, B. Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: A 21st century challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, D.T.; Baudhuin, P.; Opperdoes, F.R.; de Duve, C. Biogenesis of the glycosome in Trypanosoma brucei: The synthesis, translocation and turnover of glycosomal polypeptides. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovey, H.F.; Parsons, M.; Wang, C.C. Biogenesis of glycosomes of Trypanosoma brucei: An in vitro model of 3-phosphoglycerate kinase import. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2598–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, P.A. The glycosome of trypanosomes: Properties and biogenesis of a microbody. Exp. Parasitol. 1989, 69, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanstra, J.R.; González-Marcano, E.B.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Michels, P.A. Biogenesis, maintenance and dynamics of glycosomes in trypanosomatid parasites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Paudyal, R. The life of the peroxisome: From birth to death. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, S.J.; Keller, G.A.; Hosken, N.; Wilkinson, J.; Subramani, S. A conserved tripeptide sorts proteins to peroxisomes. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 108, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocard, C.; Hartig, A. Peroxisome targeting signal 1: Is it really a simple tripeptide? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunze, M.; Neuberger, G.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Ma, J.; Eck, T.; Braverman, N.; Schmid, J.A.; Eisenhaber, F.; Berger, J. Structural requirements for interaction of peroxisomal targeting signal 2 and its receptor PEX7. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 45048–45062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperdoes, F.R. The glycosome of Trypanosomes and Leishmania. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1990, 18, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardim, A.; Rager, N.; Liu, W.; Ullman, B. Peroxisomal targeting protein 14 (PEX14) from Leishmania donovani. Molecular, biochemical, and immunocytochemical characterization. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2002, 124, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galland, N.; Demeure, F.; Hannaert, V.; Verplaetse, E.; Vertommen, D.; Van der Smissen, P.; Courtoy, P.J.; Michels, P.A. Characterization of the role of the receptors PEX5 and PEX7 in the import of proteins into glycosomes of Trypanosoma brucei. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, P.S.; Parsons, M. Probing the role of compartmentation of glycolysis in procyclic form Trypanosoma brucei: RNA interference studies of PEX14, hexokinase, and phosphofructokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9030–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, J.M.; Wang, C.C. Targeting proteins to the glycosomes of African trypanosomes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1994, 48, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidowski, M.; Emmanouilidis, L.; Kalel, V.C.; Tripsianes, K.; Schorpp, K.; Hadian, K.; Kaiser, M.; Mäser, P.; Kolonko, M.; Tanghe, S.; et al. Inhibitors of PEX14 disrupt protein import into glycosomes and kill Trypanosoma parasites. Science 2017, 355, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, M.; Mróz, P.; Napolitano, V.; Kalel, V.C.; Fino, R.; Pykacz, E.; Schliebs, W.; Plettenburg, O.; Erdmann, R.; Sattler, M.; et al. Development of novel PEX5-PEX14 protein-protein interaction (PPI) inhibitors based on an oxopiperazine template. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 5, 115587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, V.; Softley, C.A.; Blat, A.; Kalel, V.C.; Schorpp, K.; Siebenmorgen, T.; Hadian, K.; Erdmann, R.; Sattler, M.; Popowicz, G.M.; et al. Small molecule mediated inhibition of protein cargo recognition by peroxisomal transport receptor PEX5 is toxic to Trypanosoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampathkumar, P.; Roach, C.; Michels, P.A.; Hol, W.G. Structural insights into the recognition of peroxisomal targeting signal 1 by Trypanosoma brucei peroxin 5. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukkamala, D.; No, J.H.; Cass, L.M.; Chang, T.K.; Oldfield, E. Bisphosphonate inhibition of a Plasmodium farnesyl diphosphate synthase and a general method for predicting cell-based activity from enzyme data. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 25, 7827–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.N.; Park, K.P.; Benítez, D.; Comini, M.A.; Shum, D.; No, J.H. Discovery of novel Leishmania major trypanothione synthetase inhibitors by high-throughput screening. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 637, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.N.; Baek, K.H.; Lee, N.; Byun, S.Y.; Shum, D.; No, J.H. In vitro and in vivo activity of mTOR kinase and PI3K inhibitors against Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma brucei. Molecules 2020, 25, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
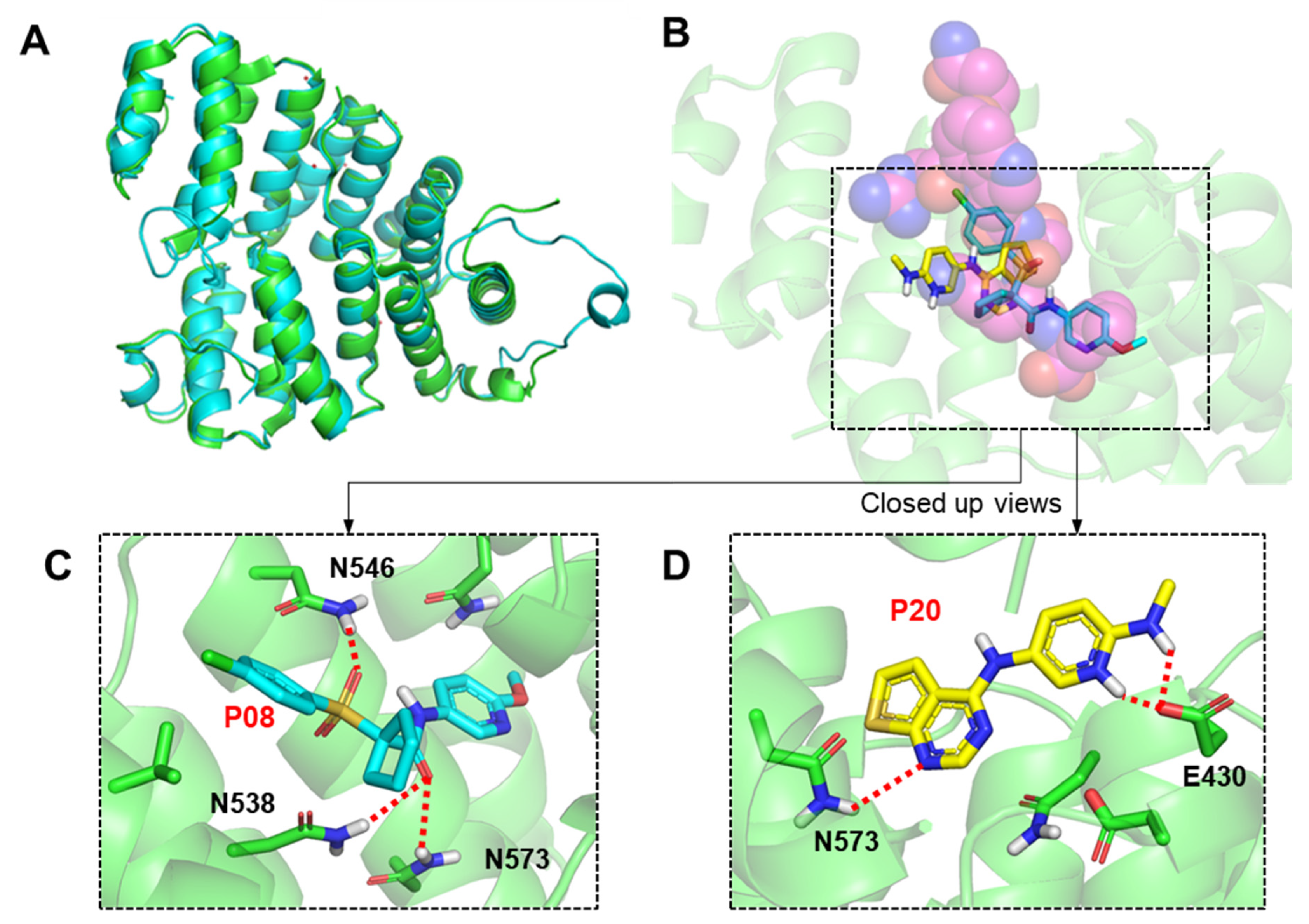
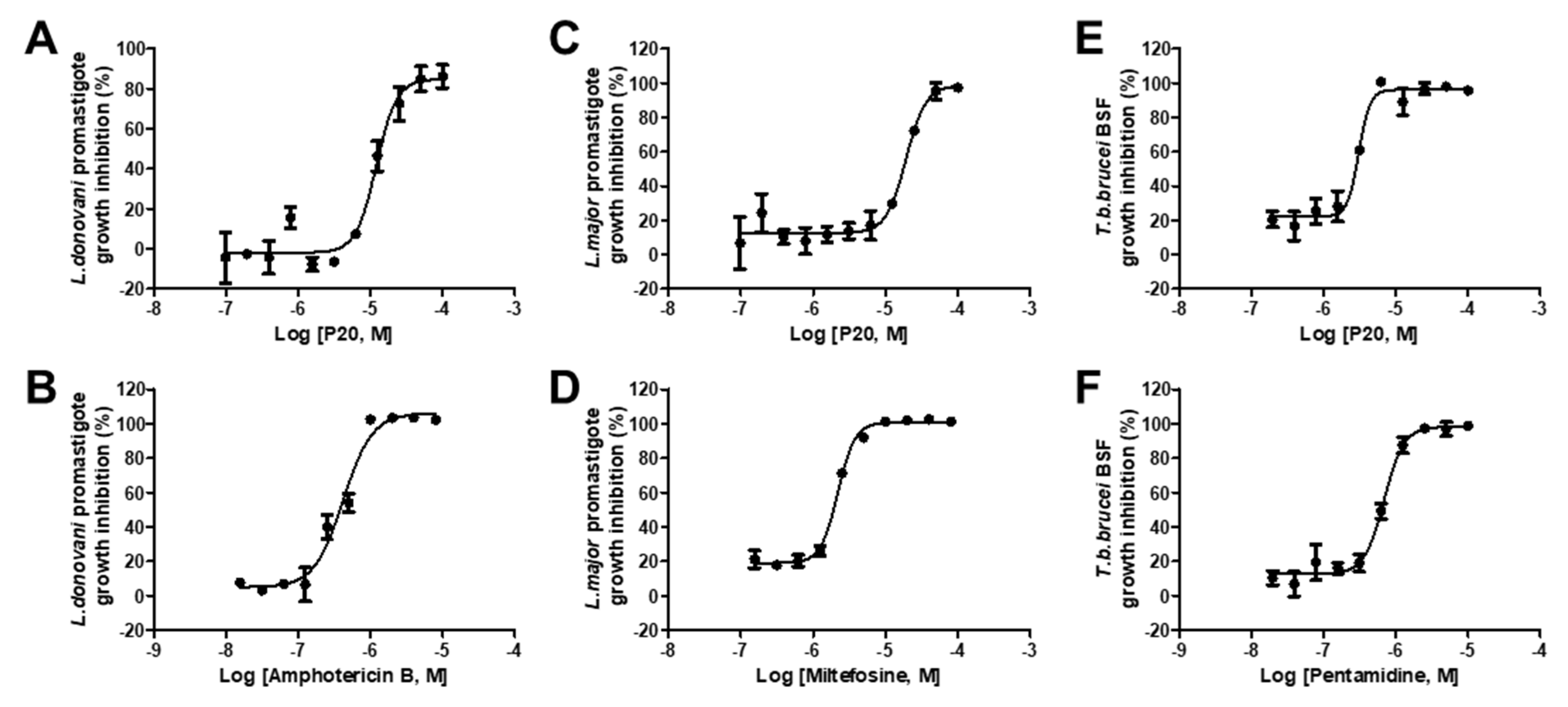
| # | Compounds | LdPEX5-PTS1 Inhibition IC50 ± SD a (µM) | L. donovani IC50 ± SD a (µM) | L. major IC50 ± SD a (µM) | T. brucei IC50 ± SD a (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P02 | 23.64 ± 0.86 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 2 | P04 | 14.61 ± 0.76 | >50 | >50 | 12.05 ± 2.19 |
| 3 | P08 | 3.89 ± 0.15 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 4 | P10 | 16.18 ± 0.92 | 3.3 ± 0.23 | >50 | >50 |
| 5 | P16 | 16.93 ± 1.03 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 6 | P17 | 25.23 ± 0.89 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 7 | P20 | 16.53 ± 0.79 | 12.16 ± 1.36 | 19.21 ± 2.65 | 3.06 ± 0.38 |
| 8 | P21 | 24.50 ± 1.05 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 9 | P28 | 15.98 ± 0.96 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 10 | Amphotericin B | NA | 0.42 ± 0.03 | NA | NA |
| 11 | Miltefosine | NA | NA | 7.37 ± 1.67 | NA |
| 12 | Pentamidine | NA | NA | NA | 0.69 ± 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan, T.-N.; Park, K.-H.P.; Shum, D.; No, J.H. Identification of Leishmania donovani PEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors through Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening. Molecules 2024, 29, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081835
Phan T-N, Park K-HP, Shum D, No JH. Identification of Leishmania donovani PEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors through Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081835
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan, Trong-Nhat, Kyu-Ho Paul Park, David Shum, and Joo Hwan No. 2024. "Identification of Leishmania donovani PEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors through Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081835
APA StylePhan, T.-N., Park, K.-H. P., Shum, D., & No, J. H. (2024). Identification of Leishmania donovani PEX5-PTS1 Interaction Inhibitors through Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening. Molecules, 29(8), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081835






