Biologically Active Peptides from Corn Gluten Meal Improve Microbiota Disorders Caused by Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
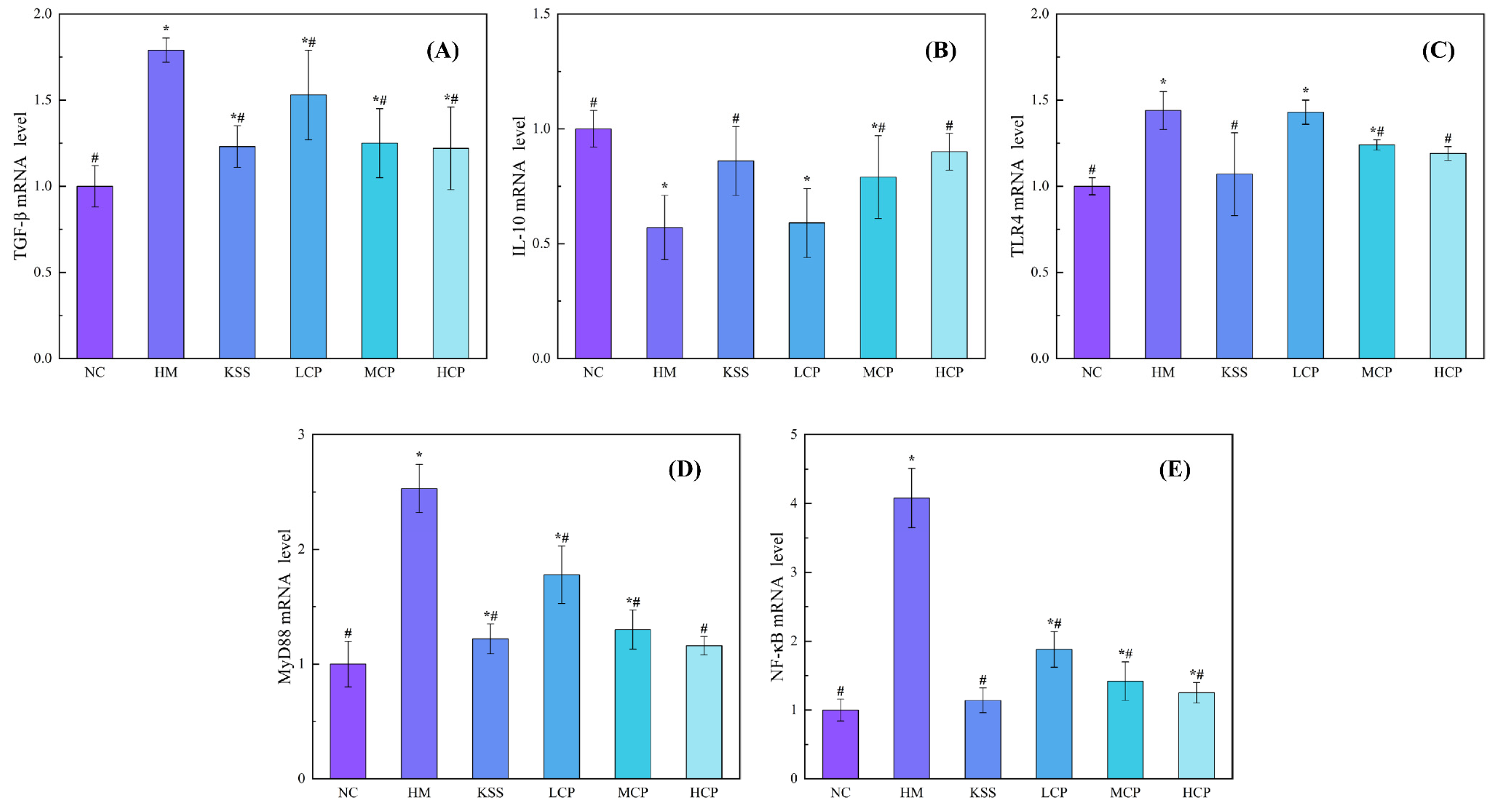
2.1. Effects of CPAP Intervention on mRNA Expression Levels of Inflammatory Factors in Gastric Mucosal
2.2. Regulatory Effect of CPAPs on Gastric Microbiota Disorders by H. pylori Infection
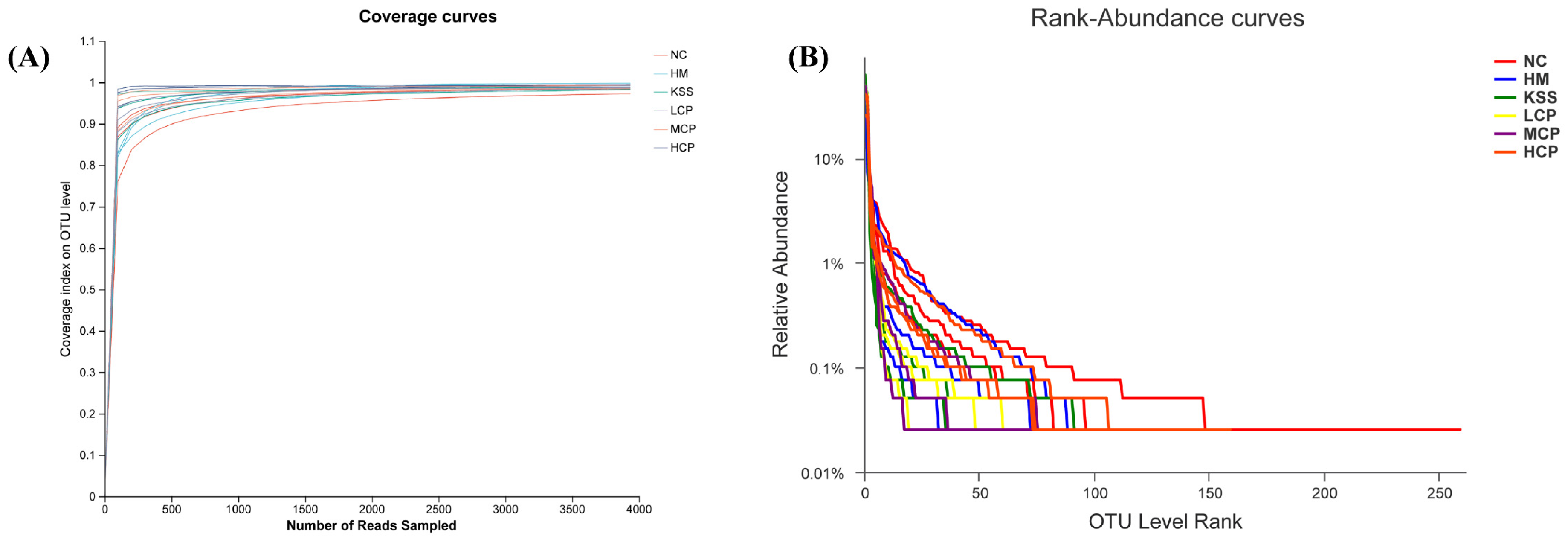
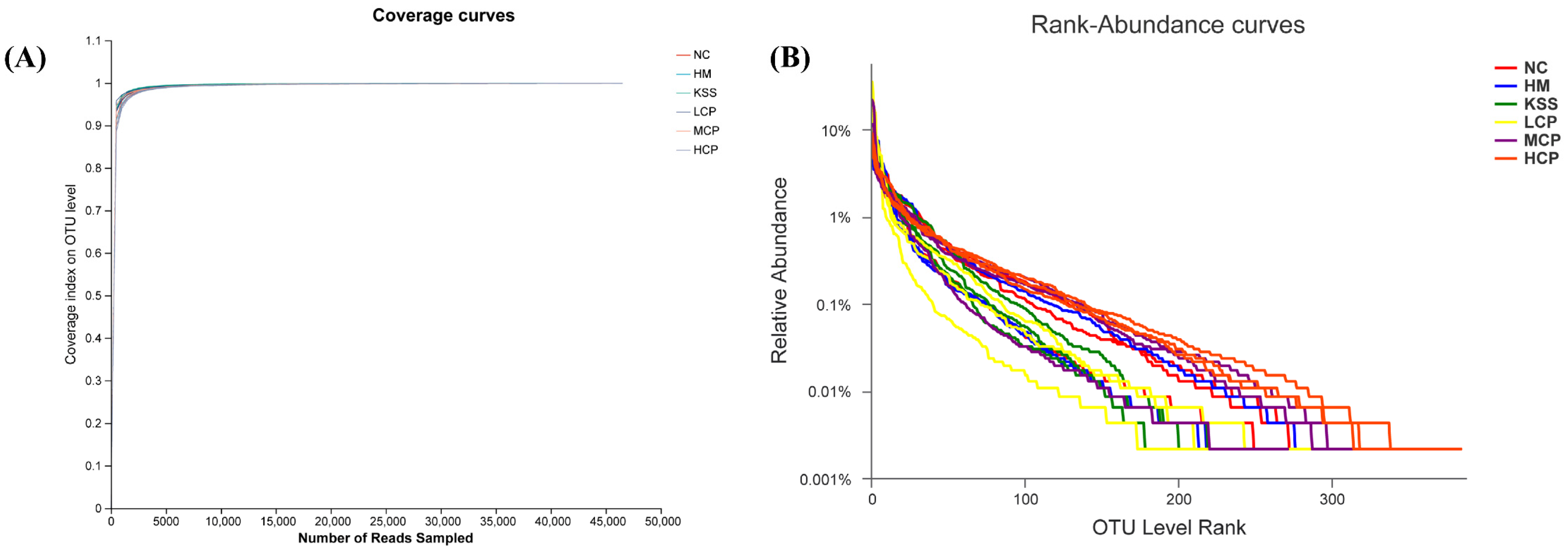
2.2.1. Species Diversity Correlation Curve Analysis of the Gastric Microbiota
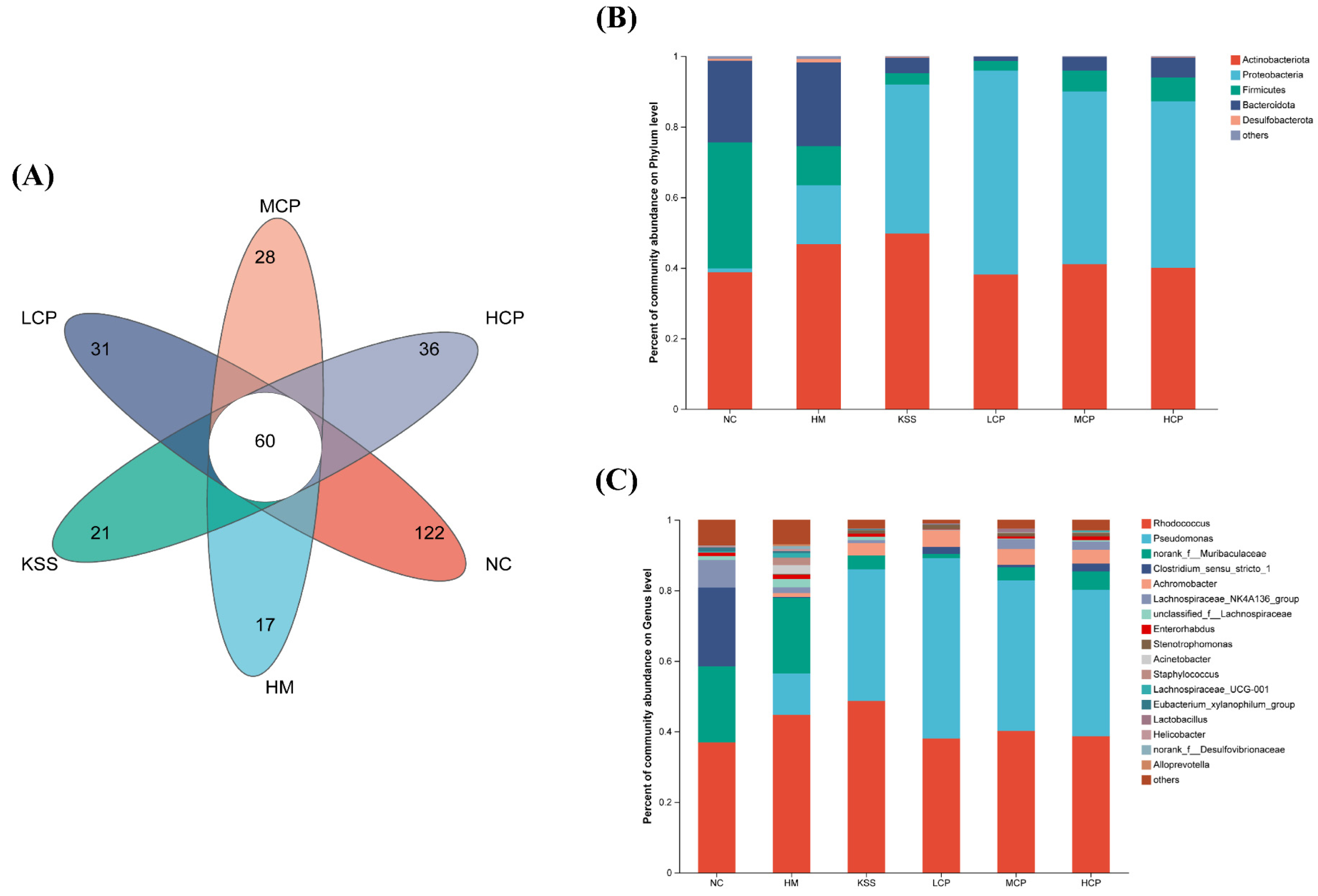
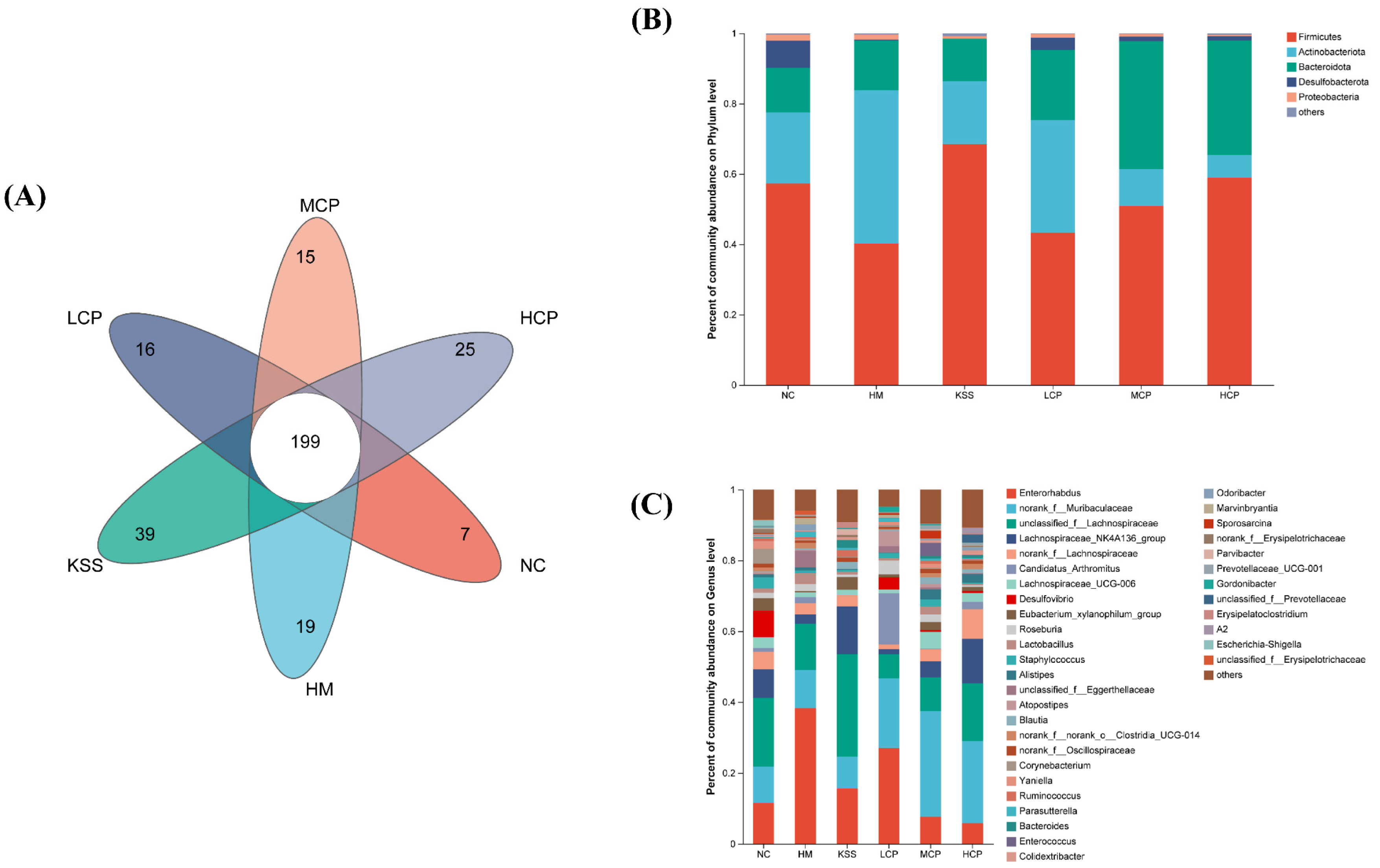
2.2.2. OTUs and Community Composition Analysis of the Gastric Microbiota
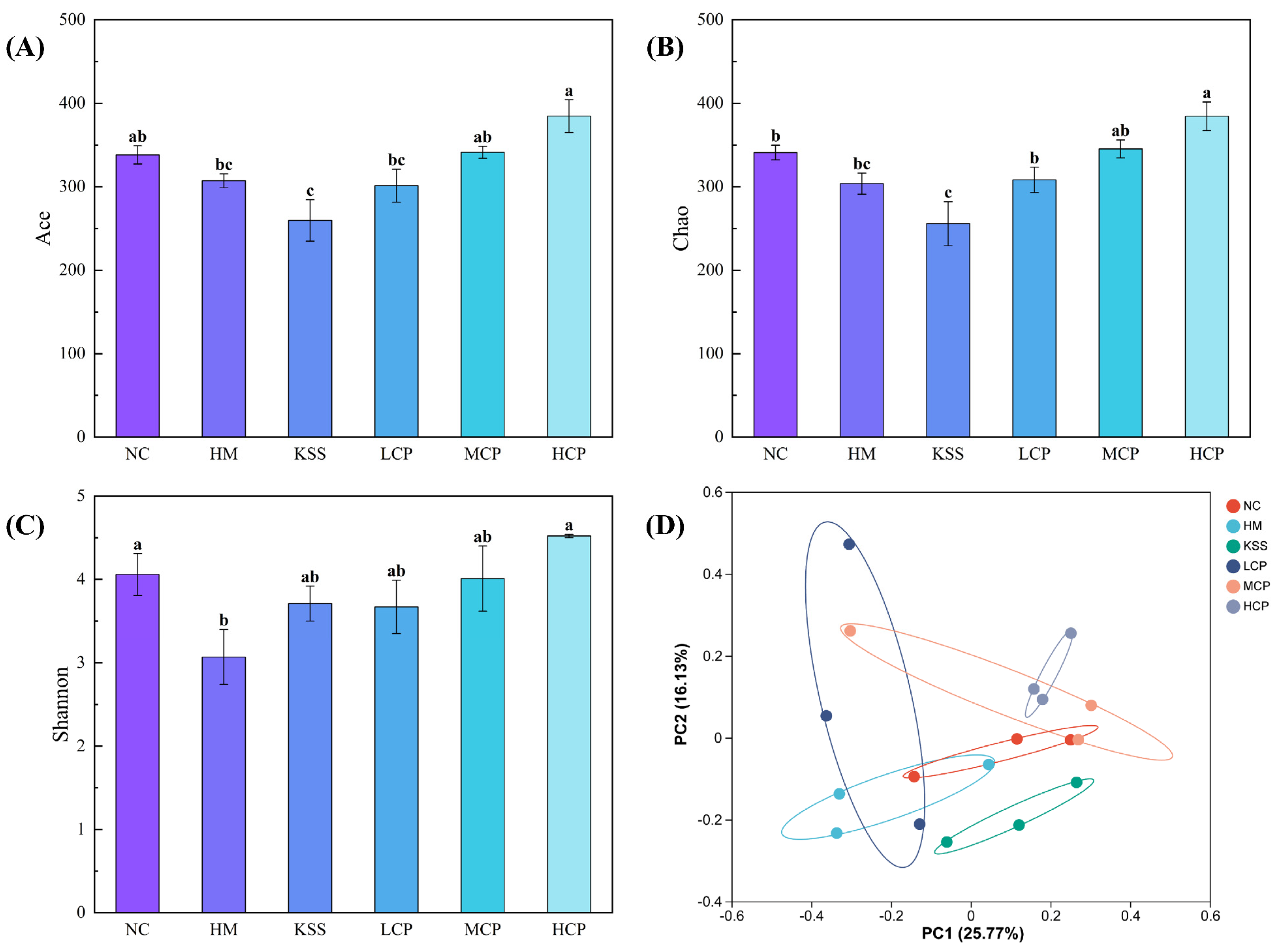
2.2.3. Microbiota Diversity Analysis of the Gastric Microbiota
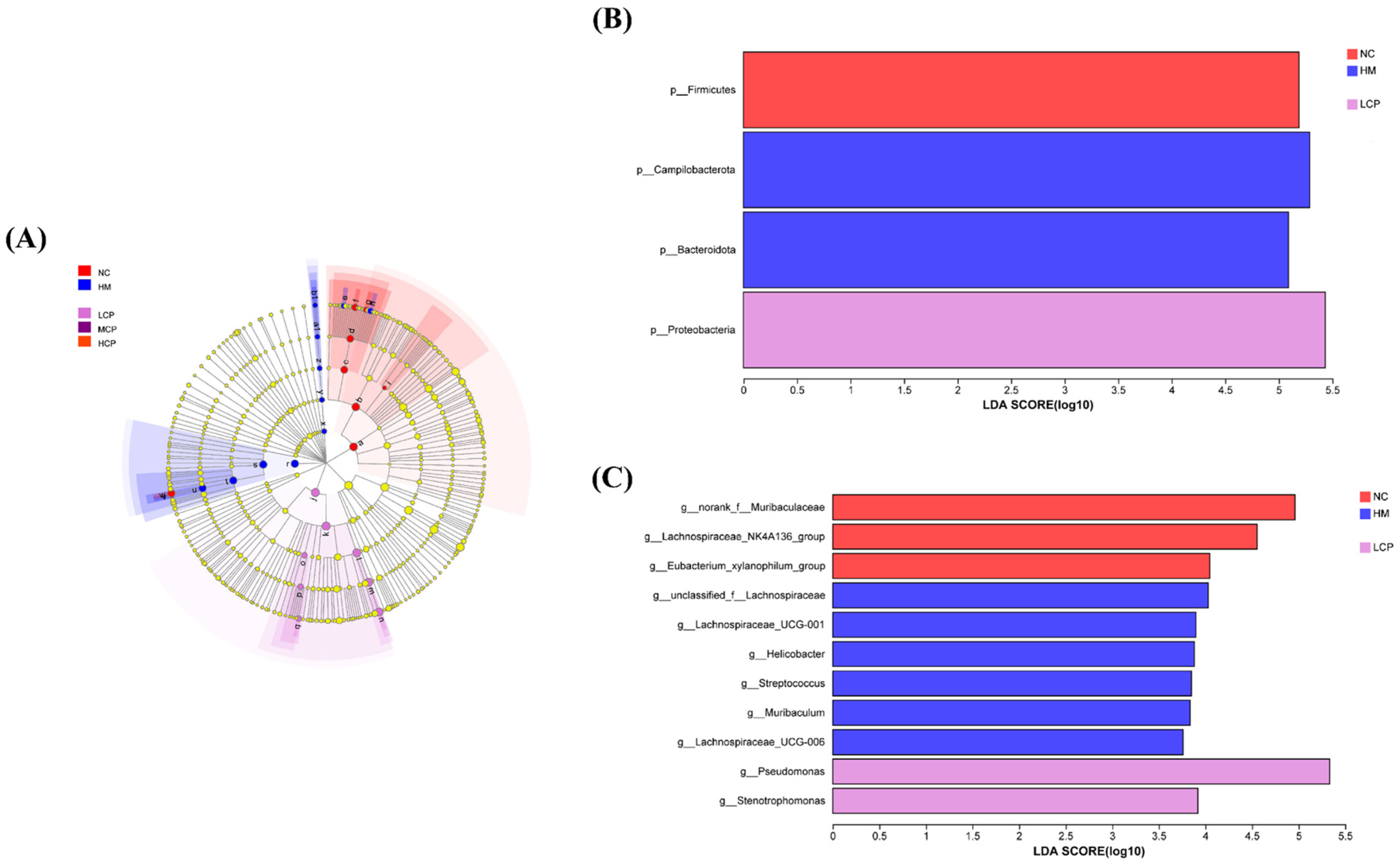
2.2.4. Microbial Community Biomarker Analysis Based on LEfSe
2.3. Regulatory Effect of CPAPs on Intestinal Microbiota Disorders by H. pylori Infection
2.3.1. Species Diversity Correlation Curve Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota
2.3.2. OTUs and Community Composition Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota
2.3.3. Microbiota Divers
2.3.4. Microbial Community Biomarker Analysis Based on LEfSe of the Intestinal Microbiota
2.3.5. Predictive Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota Function
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. CPAP Preparation
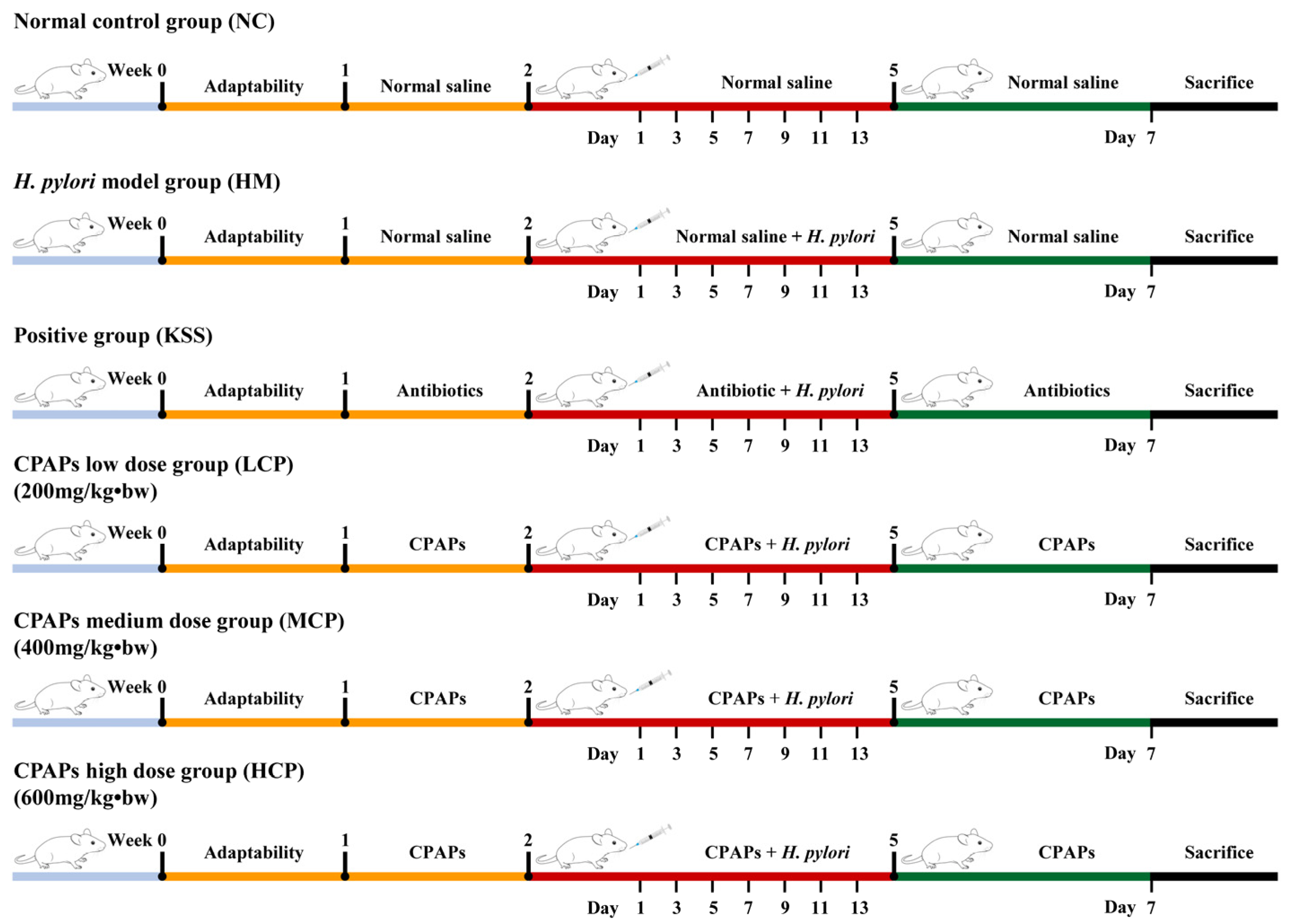
3.3. In Vivo Assay
3.4. qRT-PCR Assay
3.5. Analysis of Gastrointestinal Microbiota by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
3.5.1. DNA Extraction and Concentration Determination
3.5.2. PCR Amplification and Library Construction
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sgamato, C.; Rocco, A.; Compare, D.; Priadko, K.; Romano, M.; Nardone, G. Exploring the Link between Helicobacter pylori, Gastric Microbiota and Gastric Cancer. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Lee, W.H.; Seo, H.; Oh, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Hahm, K.B. Microbiota changes with fermented kimchi contributed to either the amelioration or rejuvenation of Helicobacter pylori-associated chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2021, 69, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Shen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Effects of sodium butyrate supplementation on inflammation, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayed, B.; Jagal, J.; Cagliani, R.; Kedia, R.A.; Elsherbeny, A.; Bayraktutan, H.; Khoder, G.; Haider, M. Co-administration of amoxicillin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and inulin: A novel strategy for mitigating antibiotic resistance and preserving microbiota balance in Helicobacter pylori treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, F. Efficacy of Sucralfate-Combined Quadruple Therapy on Gastric Mucosal Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori and Its Effect on Gastrointestinal Flora. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4936318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sheu, B. Metabolic Interaction of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, O.; Weiss, E.; Sharon, N.; Tabak, M.; Neeman, I.; Ofek, I. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori Adhesion to Human Gastric Mucus by a High-Molecular-Weight Constituent of Cranberry Juice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2002, 42, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Z.; Zheng, X. Anti-adhesive activity peptides against Helicobacter pylori from corn protein: Properties, identification, structural characterization and molecular docking in vitro and in silico. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, J.; Thöle, C.; Niehues, M.; Shevtsova, A.; Glocker, E.; Borén, T.; Hensel, A. Antiadhesive Properties of Abelmoschus esculentus (Okra) Immature Fruit Extract against Helicobacter pylori Adhesion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Zheng, X. Preparation and evaluation of new glycopeptides obtained by proteolysis from corn gluten meal followed by transglutaminase-induced glycosylation with glucosamine. Foods 2020, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S.; Cheng, S. Contribution of specific amino acid and secondary structure to the antioxidant property of corn gluten proteins. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Qu, Y. Preparation of corn glycopeptides and evaluation of their antagonistic effects on alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Ding, Q.; Lin, L.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Yagoub, A. Ultrasonic pretreatment of corn gluten meal proteins and neutrase: Effect on protein conformation and preparation of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory peptides. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, X.; Miao, Z.; Hu, N.; Zheng, X. Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Differences in the gut microbiota composition of rats fed with soybean protein and their derived peptides. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5452–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Qin, H.; Gu, R.; Cai, M. The anti-fatigue activity of corn peptides and their effect on gut bacteria. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 102, 3456–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Soy bioactive peptides an the gut microbiota modulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9009–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J. Two-stage solid-state fermentation to increase the nutrient value of corn processing waste and explore its efficacy as a feed protein source. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced Inflammatory and Oncogenic Responses in Gastric Mucosal Tissues of Mice. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 25, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xue, B.; Gu, R.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 Attenuates Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastritis in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6510–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cui, W.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, Y.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Phenyl lactic acid alleviates Helicobacter pylori infection in C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5032–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, D.; Liu, H.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. Wheat peptide protects against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics cooperate with Helicobacter pylori to promote gastric injury and inflammation in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Qureshi, N.; Xue, B.; Xie, Z.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Preventive and therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus paracasei ZFM54 on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis by ameliorating inflammation and restoring gastric microbiota in mice model. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 972569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, M. Sulfated modification enhances the modulatory effect of yam polysaccharide on gut microbiota in cyclophosphamide-treated mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Wu, S.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Q. Exopolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei alleviates gastritis in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice by regulating gastric microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1426358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Huo, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C. Screening Probiotics for Anti-Helicobacter pylori and Investigating the Effect of Probiotics on Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection. Foods 2024, 13, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, X. Tea polyphenols regulate gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by antibiotic in mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, W.; Guo, X.; et al. Weizmannia coagulans BCF-01: A novel gastrogenic probiotic for Helicobacter pylori infection control. Gut Microbes. 2024, 16, 2313770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Meng, F.; Wang, C.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, X. Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation of Marine Oligosaccharide Coated Microcapsules Containing Probiotics and Their Regulatory Effect on Animal Intestinal Flora. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yan, J.; Zhu, Y.; WeI, Y.; Cai, M.; Gu, R. Regulatory Effect of Whey Protein and Pea Protein on Mice with Intestinal Flora Disorder Caused by Antibiotics. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Mendozzi, L.; Rossi, V.; Mazzali, F.; Piancone, F.; LaRosa, F.; Marventano, I.; Caputo, D.; Felis, G.E.; Clerici, M. Immunological and Clinical Effect of Diet Modulation of the Gut Microbiome in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Pilot Study. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Han, J.; Fang, J. Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication: Exploring their impacts on the gastrointestinal microbiota. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Peng, F.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Guan, Q.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Characterization, mechanism and in vivo validation of Helicobacter pylori antagonism by probiotics screened from infants’ feces and oral cavity. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1170–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Cai, Z.; Chai, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. Egg white peptides ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis symptoms by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulation of gut microbiota composition. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Wan, C.; Xie, Q.; Huang, R.; Tao, X.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Changes in gastric microbiota induced by Helicobacter pylori infection and preventive effects of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY 2013 against such infection. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Chitosan-modified molybdenum selenide mediated efficient killing of Helicobacter pylori and treatment of gastric cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D. Potential effects of mung bean protein and a mung bean protein–polyphenol complex on oxidative stress levels and intestinal microflora in aging mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filaly, H.E.; Outlioua, A.; Medyouf, H.; Guessous, F.; Akarid, K. Targeting IL-1β in Patients with Advanced Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Potential Therapy for Gastric Cancer. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tian, X.; Wei, T.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of a Lactobacillus sp. PW-7 Exopolysaccharide. Foods 2021, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Fu, X. Dendrobium officinale Polysaccharide Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Restoring Gut Microbiota and Repairing Intestinal Barrier via the LPS/TLR4/TRIF/NF-kB Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11929–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Hu, S. Influence of helicobacter pylori on composition and function of gastric microbiota in patients with chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhou, Q. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum ZFM4 in Helicobacter pylori-infected C57BL/6 mice: Prevention is better than cure. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 13, 1320819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, D.; Suazo, F.; Torres, K.; Simón, L. Antitumor Effects of Resveratrol Opposing Mechanisms of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Malhotra, S.; Pothuraju, R.; Shandilya, U.K. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC17 ameliorates type-2 diabetes by improving gut function, oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat-diet fed and streptozotocintreated rats. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, X.; Miao, Z.; Zheng, X. Purification and structural characterization of three novel anti-adhesive peptides against Helicobacter pylori from corn gluten meal. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 112, 105992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| KEGG Pathway | NC | HM | KSS | LCP | MCP | HCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | 76.61 ± 1.02 a | 77.12 ± 0.56 a | 75.30 ± 2.32 a | 76.82 ± 1.00 a | 75.79 ± 0.17 a | 76.07 ± 0.23 a |
| Genetic Information Processing | 7.98 ± 0.07 b | 8.70 ± 0.42 a | 9.33 ± 1.14 ab | 8.23 ± 0.04 b | 8.15 ± 0.08 b | 7.99 ± 0.10 b |
| Environmental Information Processing | 6.68 ± 0.35 ab | 6.11 ± 0.42 b | 6.31 ± 0.32 b | 6.16 ± 0.51 ab | 6.75 ± 0.12 b | 7.10 ± 0.50 a |
| Cellular Processes | 4.16 ± 0.45 ab | 3.62 ± 0.36 ab | 4.27 ± 0.65 b | 4.08 ± 0.42 a | 4.55 ± 0.05 ab | 4.35 ± 0.11 ab |
| Human Diseases | 2.96 ± 0.15 a | 2.91 ± 0.10 a | 3.19 ± 0.47 a | 3.07 ± 0.12 a | 3.11 ± 0.03 a | 2.96 ± 0.06 a |
| Organismal Systems | 1.58 ± 0.03 a | 1.50 ± 0.09 a | 1.59 ± 0.13 a | 1.65 ± 0.06 a | 1.65 ± 0.04 a | 1.53 ± 0.10 a |
| KEGG Pathway | NC | HM | KSS | LCP | MCP | HCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy metabolism | 4.18 ± 0.20 b | 4.96 ± 0.56 a | 4.58 ± 0.55 ab | 4.18 ± 0.28 b | 4.05 ± 0.03 b | 4.15 ± 0.11 b |
| Membrane transport | 4.11 ± 0.34 ab | 3.54 ± 0.47 b | 3.54 ± 0.41 b | 3.65 ± 0.50 b | 4.18 ± 0.11 ab | 4.52 ± 0.43 a |
| Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | 3.96 ± 0.03 a | 3.79 ± 0.02 ab | 3.61 ± 0.26 b | 3.93 ± 0.10 a | 3.87 ± 0.04 a | 3.85 ± 0.07 a |
| Translation | 3.36 ± 0.05 b | 3.73 ± 0.20 ab | 3.99 ± 0.51 a | 3.48 ± 0.02 b | 3.43 ± 0.04 b | 3.34 ± 0.05 b |
| Replication and repair | 2.98 ± 0.06 b | 3.24 ± 0.12 ab | 3.53 ± 0.51 a | 3.08 ± 0.05 b | 3.11 ± 0.04 b | 3.03 ± 0.04 b |
| Nucleotide metabolism | 2.65 ± 0.05 b | 2.76 ± 0.06 a | 2.71 ± 0.03 ab | 2.76 ± 0.05 a | 2.72 ± 0.03 ab | 2.68 ± 0.07 ab |
| Signal transduction | 2.57 ± 0.03 b | 2.57 ± 0.08 b | 2.78 ± 0.12 a | 2.51 ± 0.04 b | 2.56 ± 0.05 b | 2.58 ± 0.07 b |
| Cellular community—prokaryotes | 2.25 ± 0.19 ab | 1.94 ± 0.18 c | 1.97 ± 0.15 c | 2.10 ± 0.11 bc | 2.27 ± 0.04 ab | 2.39 ± 0.14 a |
| Lipid metabolism | 1.84 ± 0.06 ab | 1.72 ± 0.05 b | 1.92 ± 0.21 ab | 1.96 ± 0.15 a | 1.84 ± 0.01 ab | 1.76 ± 0.06 ab |
| Folding, sorting, and degradation | 1.47 ± 0.02 c | 1.57 ± 0.08 ab | 1.59 ± 0.09 a | 1.49 ± 0.04 bc | 1.45 ± 0.01 c | 1.45 ± 0.02 c |
| Metabolism of other amino acids | 1.24 ± 0.08 ab | 1.27 ± 0.05 ab | 1.38 ± 0.12 a | 1.31 ± 0.13 ab | 1.20 ± 0.00 b | 1.18 ± 0.02 b |
| Cell motility | 0.98 ± 0.24 ab | 0.78 ± 0.13 b | 1.34 ± 0.50 a | 0.93 ± 0.32 ab | 1.25 ± 0.08 ab | 1.03 ± 0.09 ab |
| Infectious disease: bacterial | 0.69 ± 0.01 b | 0.73 ± 0.04 ab | 0.91 ± 0.26 a | 0.69 ± 0.03 b | 0.71 ± 0.03 b | 0.64 ± 0.02 b |
| Endocrine system | 0.57 ± 0.02 ab | 0.51 ± 0.07 bc | 0.47 ± 0.06 c | 0.60 ± 0.04 a | 0.59 ± 0.02 ab | 0.56 ± 0.04 ab |
| Aging | 0.28 ± 0.05 ab | 0.25 ± 0.01 ab | 0.30 ± 0.05 a | 0.30 ± 0.04 ab | 0.27 ± 0.01 ab | 0.24 ± 0.00 b |
| Environmental adaptation | 0.21 ± 0.01 ab | 0.20 ± 0.01 ab | 0.26 ± 0.06 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 ab | 0.23 ± 0.01 ab | 0.20 ± 0.02 b |
| Transport and catabolism | 0.19 ± 0.02 ab | 0.17 ± 0.03 b | 0.19 ± 0.06 ab | 0.27 ± 0.05 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 ab | 0.19 ± 0.06 ab |
| Transcription | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.01 ab | 0.21 ± 0.04 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 b |
| Cardiovascular disease | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 ab | 0.15 ± 0.01 ab | 0.16 ± 0.00 ab | 0.16 ± 0.01 ab |
| Neurodegenerative disease | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0.00 ab | 0.13 ± 0.00 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 ab | 0.10 ± 0.01 b |
| Gene | Forward | Reverse | Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | ATCCGGACCCTCCATTGTC | AGCCATGCCAATCTCGTCTT | 11461 |
| TGF-β | ACCTCGACACCGACTACTGCTT | ACTCTTGCGGAAGTCGATGT | 21812 |
| IL-10 | CGGGAGCTGAGGGTGAA | GTGAAGAAGCGGTGACAGC | 16153 |
| TLR4 | GTTCCTGCTGAAATCCCAAA | TATGGATGTGGCACCTTGAA | 21898 |
| MyD88 | TGATGCCTTCATCTGCTACTG | TCCCTCCGACACCTTCTTTCT | 17874 |
| NF-κB | GTGTGAAGAAACGGGAACTG | GGCACGGTTGTCATAGATGG | 18033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X. Biologically Active Peptides from Corn Gluten Meal Improve Microbiota Disorders Caused by Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Molecules 2025, 30, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030705
Li G, Xie Y, Wang Q, Miao Z, Liu X, Zheng X. Biologically Active Peptides from Corn Gluten Meal Improve Microbiota Disorders Caused by Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030705
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanlong, Yongchao Xie, Quanxin Wang, Zhengfei Miao, Xiaolan Liu, and Xiqun Zheng. 2025. "Biologically Active Peptides from Corn Gluten Meal Improve Microbiota Disorders Caused by Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice" Molecules 30, no. 3: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030705
APA StyleLi, G., Xie, Y., Wang, Q., Miao, Z., Liu, X., & Zheng, X. (2025). Biologically Active Peptides from Corn Gluten Meal Improve Microbiota Disorders Caused by Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Molecules, 30(3), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030705






