Oleanolic Acid Slows Down Aging Through IGF-1 Affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
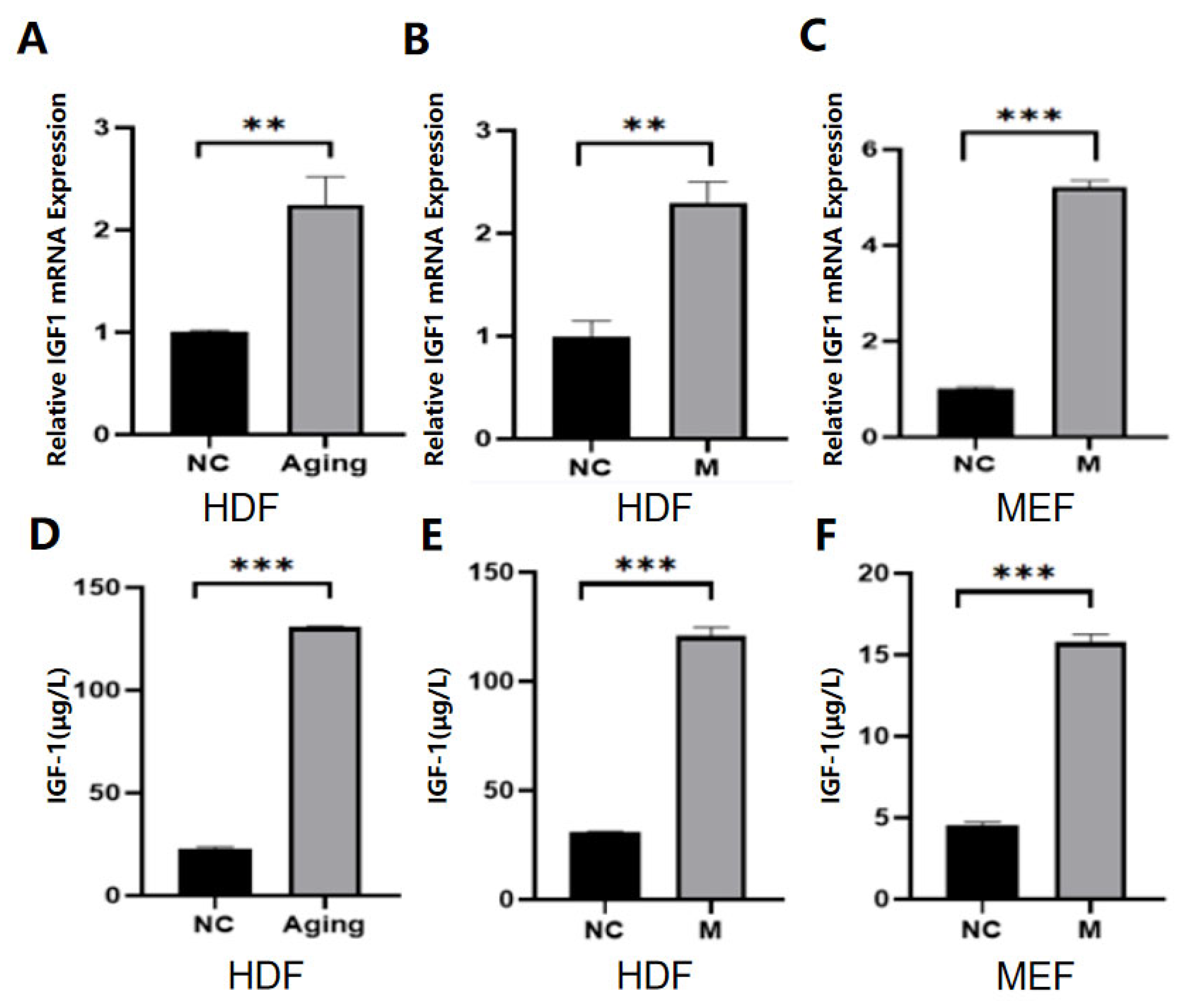
2.1. IGF-1 Was Highly Expressed in Senescent Cells
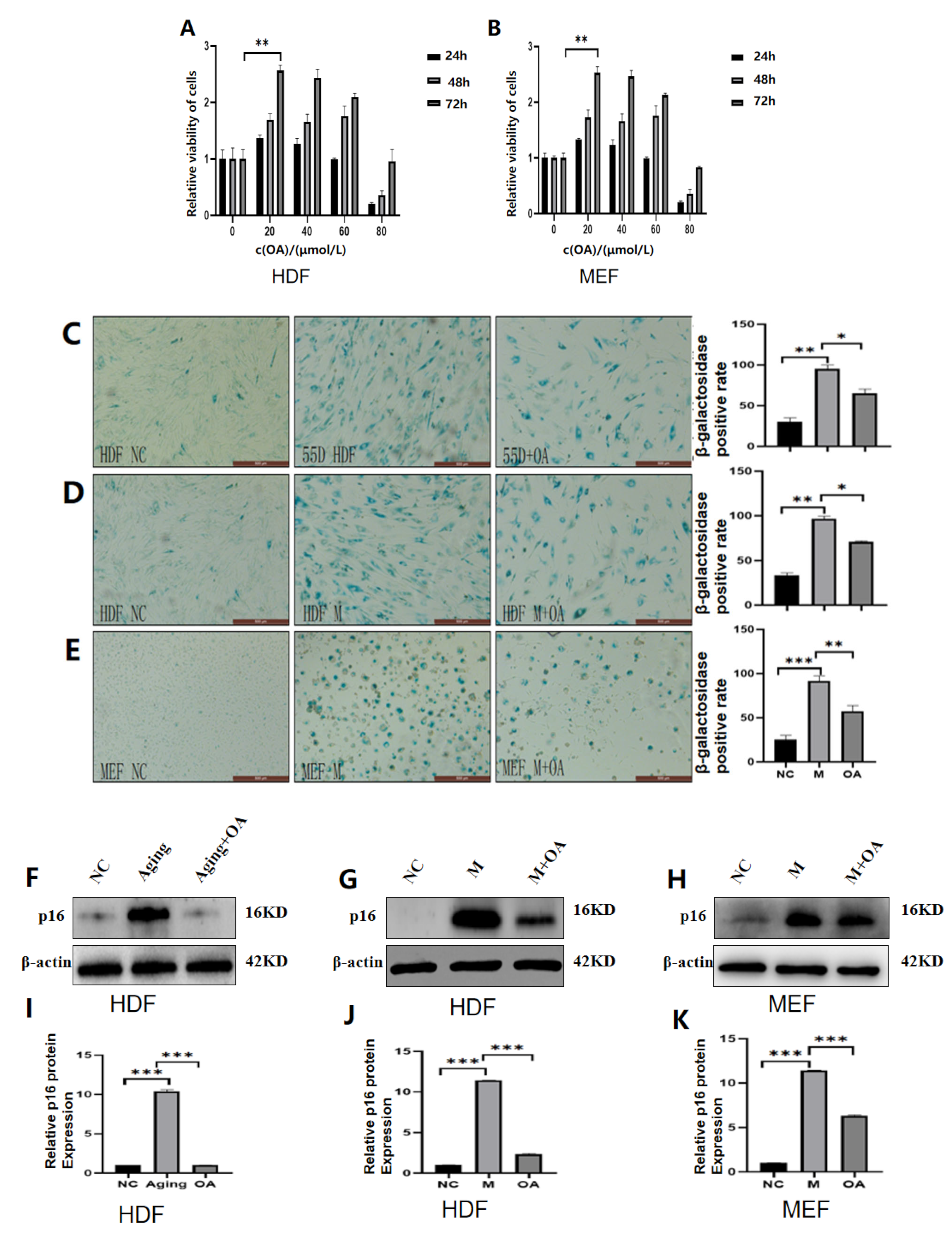
2.2. OA Alleviated Cell Senescence in HDF and MEF Cell Lines
2.3. OA Reduced the Expression of IGF-1 in Senescent Cells
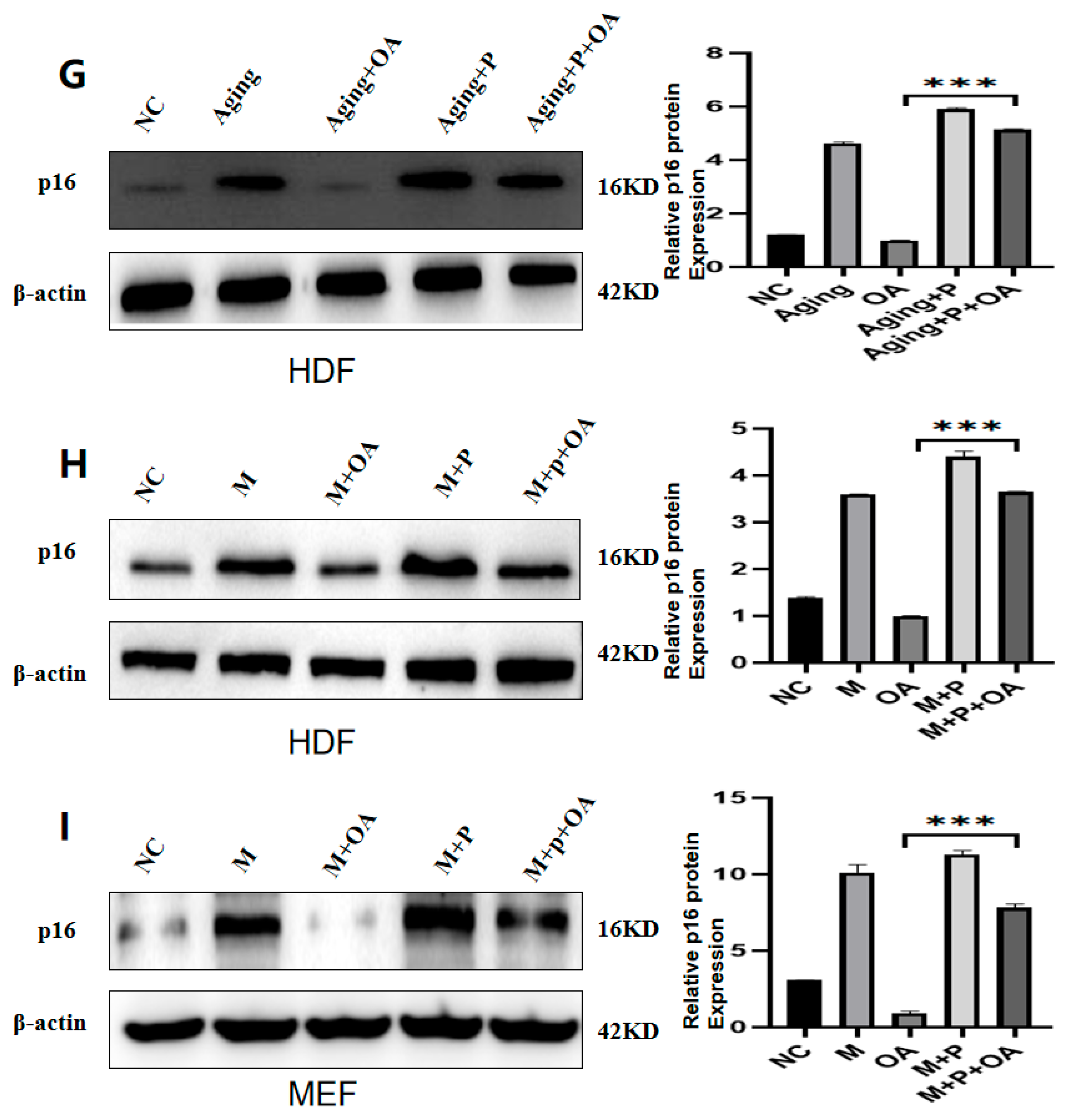
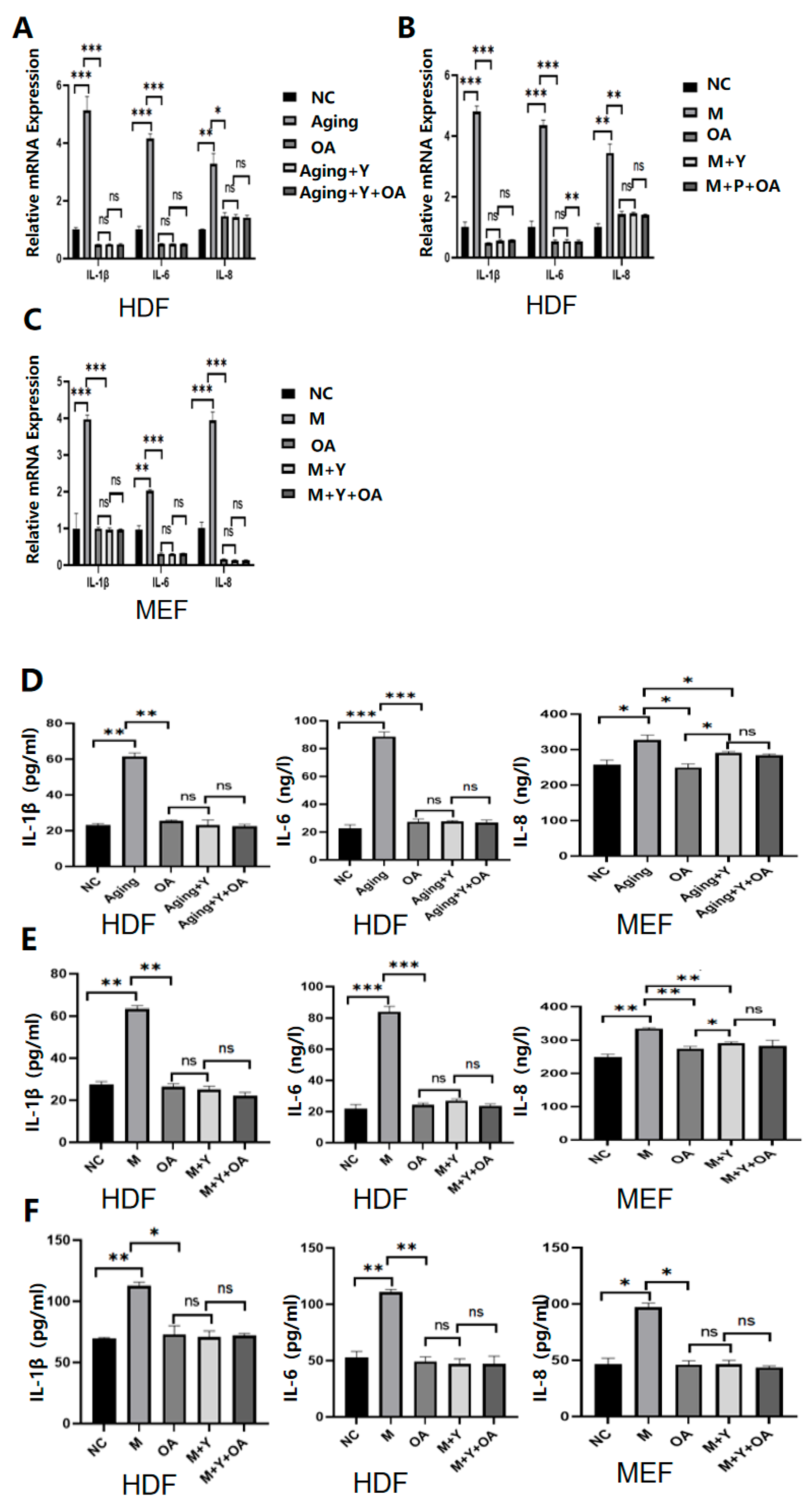
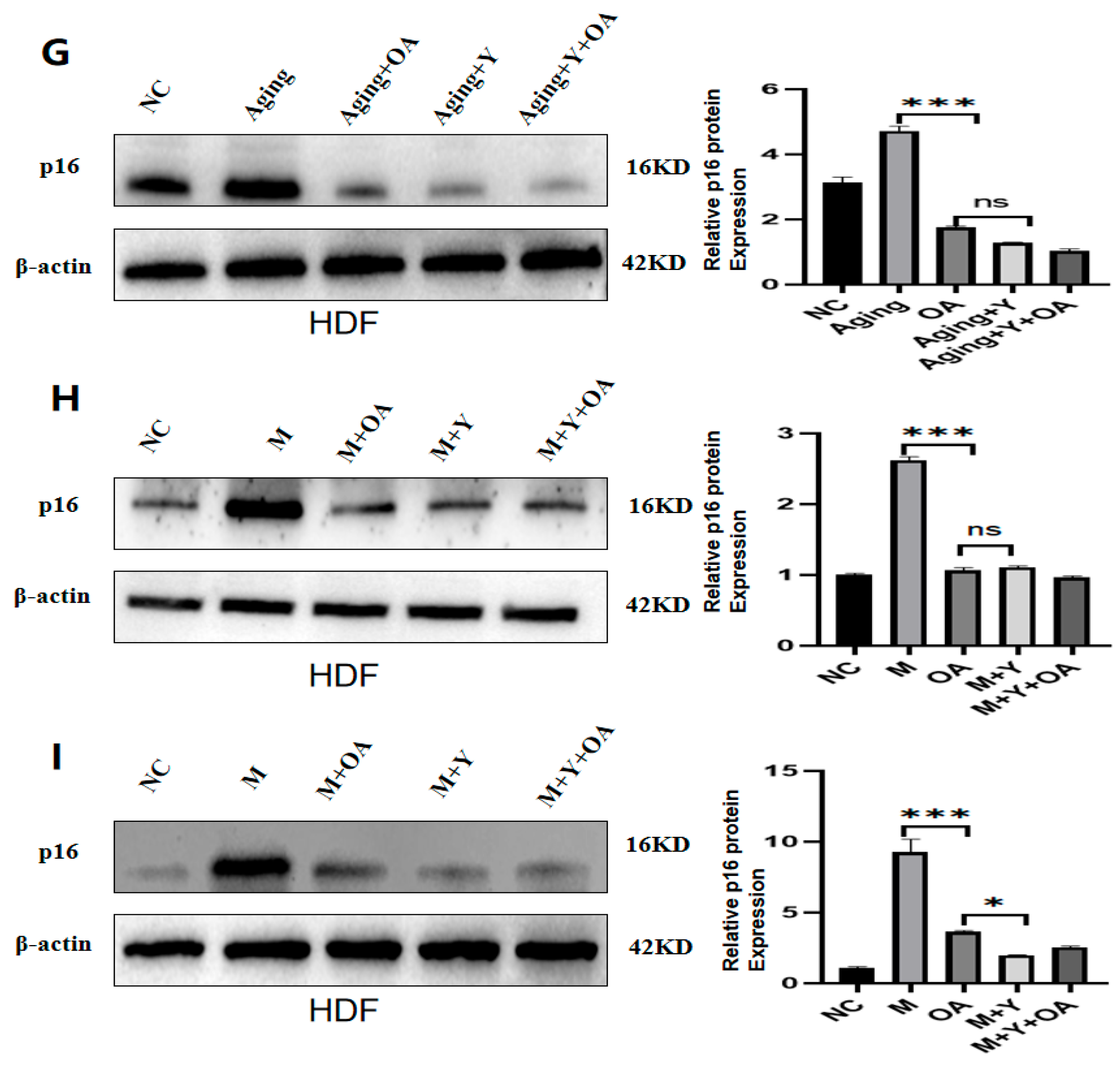
2.4. OA Delays Aging by Targeting the Expression of IGF-1
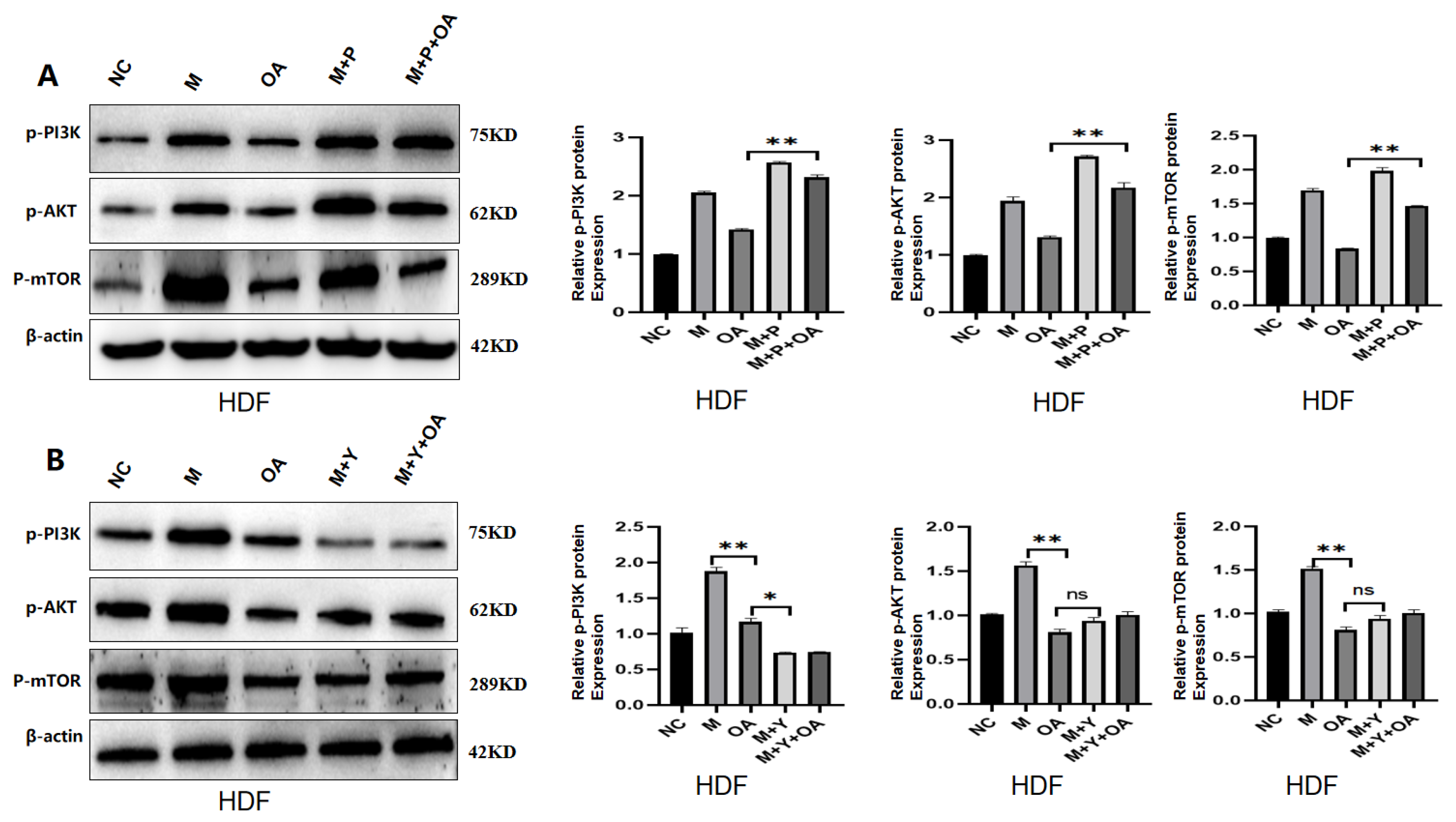
2.5. OA Delayed Aging by Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR via IGF-1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Western Blot
3.2.2. Real-Time-qPCR
3.2.3. Cell Culture
3.2.4. Cell Viability Assessment
3.2.5. Establishment of Cell Senescence Model
3.2.6. SA-β-GAL Staining
3.2.7. ELISA
3.2.8. Analysis of Experimental Data
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antal, B.; McMahon, L.P.; Sultan, S.F.; Lithen, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Dickerson, B.; Ratai, E.M.; Mujica-Parodi, L.R. Type 2 diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline: Complementary findings from UK Biobank and meta-analyses. eLife 2022, 11, e73138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabling, M.G.; Sandhu, V.K.; Downey, C.D.; Torralba, K.D. Cardiovascular disease and bone health in aging female rheumatic disease populations: A review. Womens Health 2023, 19, 17455057231155286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.K.N.; Paradela, R.S.; Grinberg, L.T.; Leite, R.E.; Farias-Itao, D.S.; Paes, V.R.; Braga, M.E.; Naslavsky, M.S.; Zatz, M.; Jacob-Filho, W.; et al. Hypertension may associate with cerebral small vessel disease and infarcts through the pathway of intracranial atherosclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2025, 145, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Liu, T.; Tang, Y.; Liang, W.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Xia, Q.; Xu, F.; Liu, S. Morphological changes in the cerebellum during aging: Evidence from convolutional neural networks and shape analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1359320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montégut, L.; López-Otín, C.; Kroemer, G. Aging and cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2024, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, L.; Falandry, C.; Silvio, M. Senotherapy, cancer, and aging. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2024, 15, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Kasai, S.; Yamazaki, H.; Tatara, Y.; Mimura, J.; Engler, M.J.; Tanji, K.; Nikaido, Y.; Inoue, T.; Suganuma, H.; et al. Sulforaphane Increase Mitochondrial Biogenesis-Related Gene Expression in the Hippocampus and Suppresses Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimon, T.; Chen, P.; Stripp, B.R.; Liang, J.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W.; Parks, W.C.; Yao, C. Senescence of alveolar epithelial progenitor cells: A critical driver of lung fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C483–C495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coryell, P.R.; Diekman, B.O.; Loeser, R.F. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.B.; Ruff, R.R.; He, Z.; Dixit, M.; Yildirim, G.; Jayarathne, H.; Manchanayake, D.H.; Basta-Pljakic, J.; Duran-Ortiz, S.; Schaffler, M.B.; et al. The impact of inactivation of the GH/IGF axis during aging on healthspan. Geroscience 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskusnykh, I.Y.; Zakharova, A.A.; Kryl’skii, E.D.; Popova, T.N. Aging, Neurodegenerative Disorders, and Cerebellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasmari, A.A.; Alhussain, M.H.; Al-Khalifah, A.S.; Alshiban, N.M.; Alharthi, R.; Alyami, N.M.; Alodah, H.S.; Alahmed, M.F.; Aljahdali, B.A.; BaHammam, A.S. Ramadan fasting model modulates biomarkers of longevity and metabolism in male obese and non-obese rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, X.M.; Jing, L.I.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, Y.T.; Fu, J.X.; Feng, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. IGF-1 Accelerates Cell Aging by Inhibiting POLD1 Expression. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, C.L.; Lamming, D.W.; Fontana, L. Molecular mechanisms of dietary restriction promoting health and longevity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, J.A.; Coppotelli, G.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M.; Ross, J.M.; Sinclair, D.A. Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibzadeh, S. Signaling pathways and effectors of aging. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 50–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollier, J.; Goossens, A. Oleanolic acid. Phytochemistry 2012, 77, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Cao, F.; Wang, L.; Pei, Z.; Ren, J. Pentacyclic triterpene oleanolic acid protects against cardiac aging through regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial integrity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Integrative transcriptome and single-cell sequencing technology analysis of the potential therapeutic benefits of oleanolic acid in liver injury and liver cancer. Aging 2023, 15, 15267–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Lai, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, P. Downregulated lncRNA SNHG18 Suppresses the Progression of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Meditates the Antitumor Effect of Oleanolic Acid. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K. Therapeutic potential of oleanolic acid in liver diseases. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 4537–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Tong, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, P.; Lin, S.; Hu, X. Integrating network pharmacology and animal experimental validation to investigate the action mechanism of oleanolic acid in obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.R.; Zhao, B.X.; Zhao, Q.; Ge, Y.C.; Li, M.; Zhao, C.G.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, X.B. Oleanolic acid improves 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal damage and inflammation by alleviating intestinal senescence. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic Acid: Extraction, Characterization and Biological Activity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Zhou, L. Oleanolic acid activates daf-16 to increase lifespan in caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.P.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.T.; Luo, Z.Q. The protective effect of oleanolic acid on NMDA-induced MLE-12 cells apoptosis and lung injury in mice by activating SIRT1 and reducing NF-κB acetylation. J. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.L.; Niu, S.Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.J. Effects of oleanolic acid on the expression of EGF/EGFR in senescent Leydig cells. J. Med. Res. Educ. 2024, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellatif, M.; Trummer-Herbst, V.; Heberle, A.M.; Humnig, A.; Pendl, T.; Durand, S.; Cerrato, G.; Hofer, S.J.; Islam, M.; Voglhuber, J.; et al. Fine-Tuning Cardiac Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Signaling to Promote Health and Longevity. Circulation 2022, 145, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tian, A.L.; Li, B.; Leduc, M.; Forveille, S.; Hamley, P.; Galloway, W.; Xie, W.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; et al. IGF1 receptor inhibition amplifies the effects of cancer drugs by autophagy and immune-dependent mechanisms. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Ortiz, S.; List, E.O.; Ikeno, Y.; Young, J.; Basu, R.; Bell, S.; McHugh, T.; Funk, K.; Mathes, S.; Qian, Y.; et al. Growth hormone receptor gene disruption in mature-adult mice improves male insulin sensitivity and extends female lifespan. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, J.; Montesanto, A.; Giovannucci, E.; Zand, H.; Barati, M.; Kopchick, J.J.; Mirisola, M.G.; Lagani, V.; Bawadi, H.; Vardavas, R.; et al. Association between IGF-1 levels ranges and all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigolon, G.; Araldi, E.; Erni, R.; Wu, J.Y.; Thomas, C.; La Fortezza, M.; Laube, B.; Pöhlmann, D.; Stoffel, M.; Zarse, K.; et al. Grainyhead 1 acts as a drug-inducible conserved transcriptional regulator linked to insulin signaling and lifespan. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadaro, O.; Goldberg, E.L.; Camell, C.D.; Youm, Y.H.; Kopchick, J.J.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Bartke, A.; Sun, L.Y.; Dixit, V.D. Growth Hormone Receptor Deficiency Protects against Age-Related NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Immune Senescence. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, J.D.; Postnikoff, S.D.; Tyler, J.K.; Johnson, J.E. Selenium supplementation inhibits IGF-1 signaling and confers methionine restriction-like healthspan benefits to mice. eLife 2021, 10, e62483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlutsky, A.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Yancey, K.; Podlutskaya, V.; Nagykaldi, E.; Gautam, T.; Miller, R.A.; Sonntag, W.E.; Csiszar, A.; Ungvari, Z. The GH/IGF-1 axis in a critical period early in life determines cellular DNA repair capacity by altering transcriptional regulation of DNA repair-related genes: Implications for the developmental origins of cancer. Geroscience 2017, 39, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Hong, J.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Wei, J. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Exacerbates Pathological Processes of Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Signaling Pathways Mediated by Insulin Receptors. Neurosci. Bull. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato-Basalo, R.; Morente-López, M.; Arntz, O.J.; van de Loo, F.A.; Fafián-Labora, J.; Arufe, M.C. Therapeutic Potential for Regulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Transcription Factor p65 to Prevent Cellular Senescence and Activation of Pro-Inflammatory in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bari, M.A.A.; Xu, P. Molecular regulation of autophagy machinery by mTOR-dependent and -independent pathways. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1467, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, W.; Mao, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, P. Oleanolic Acid Slows Down Aging Through IGF-1 Affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2025, 30, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030740
Xu Y, Wei J, Wang W, Mao Z, Wang D, Zhang T, Zhang P. Oleanolic Acid Slows Down Aging Through IGF-1 Affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030740
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yan, Jianlei Wei, Wang Wang, Zebin Mao, Didi Wang, Tao Zhang, and Pengxia Zhang. 2025. "Oleanolic Acid Slows Down Aging Through IGF-1 Affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway" Molecules 30, no. 3: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030740
APA StyleXu, Y., Wei, J., Wang, W., Mao, Z., Wang, D., Zhang, T., & Zhang, P. (2025). Oleanolic Acid Slows Down Aging Through IGF-1 Affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 30(3), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030740





