Self-Assembled Protein–Polymer Nanoparticles via Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly for Targeted and Enhanced Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
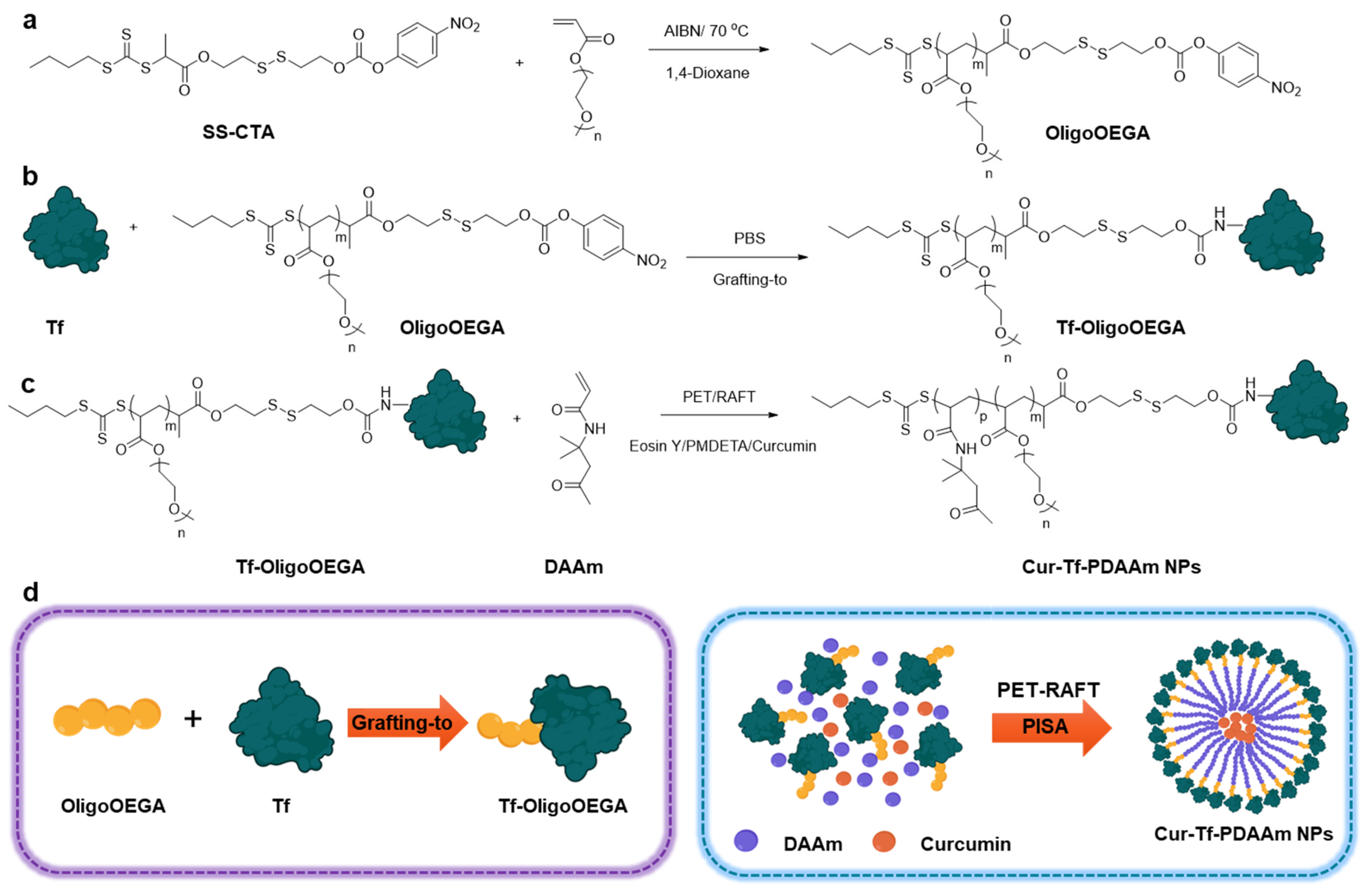
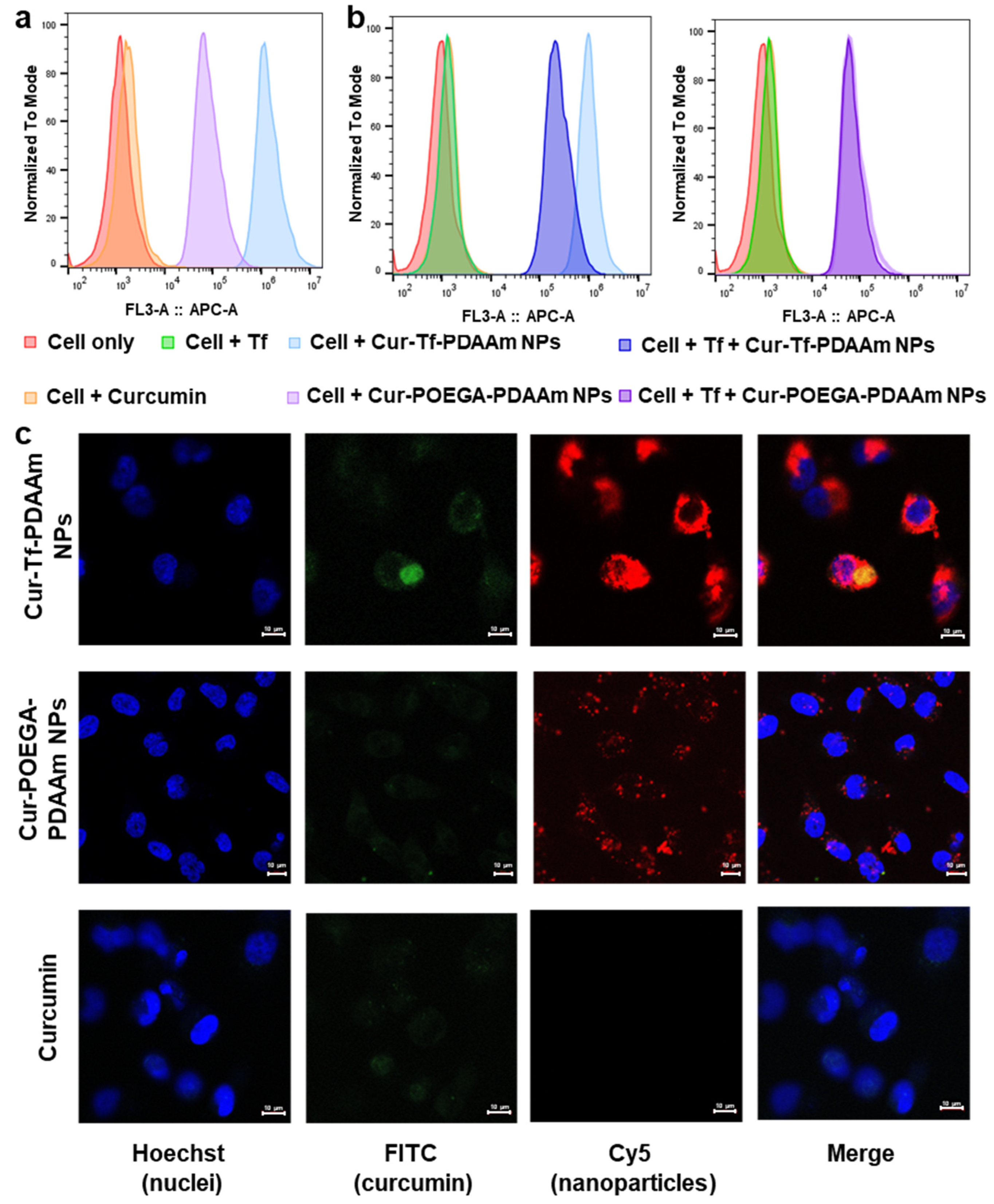
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Ng, D.Y.W.; Weil, T. Polymer bioconjugates: Modern design concepts toward precision hybrid materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 105, 101241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirinichi, F.; Ibrahim, T.; Rodriguez, M.; Sun, H. Assembling the best of two worlds: Biomolecule-polymer nanoparticles via polymerization-induced self-assembly. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C.J.; Zhang, M.; Winterwerber, P.; Wu, Y.; Ng, D.Y.; Weil, T. Functional DNA–polymer conjugates. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11030–11084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, A.S.; Adamiak, L.; Gianneschi, N.C. Biosynthetic Polymers as Functional Materials. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4379–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Tanaka, M.; Ahmad, S.R. Fabrication of polymeric biomaterials: A strategy for tissue engineering and medical devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8224–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskovich, M.; Bettinger, C.J. Biomaterials-based electronics: Polymers and interfaces for biology and medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater 2012, 1, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.A.; Kaur, K.; Klok, H.-A. Self-assembly of protein-polymer conjugates for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, K.L.; Maynard, H.D. Synthesis of protein–polymer conjugates. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, R.P.; Snell, K.; Kunkel, G.; Georgiou, P.; Puente, E.G.; Maynard, H.D. Polymer-mediated Protein/Peptide Therapeutic Stabilization: Current Progress and Future Directions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 156, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, W. Precision conjugation: An emerging tool for generating protein–polymer conjugates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11024–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.S.; Messina, K.M.M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Montgomery, H.R.; Maynard, H.D. Preparation of Biomolecule-Polymer Conjugates by Grafting-From Using ATRP, RAFT, or ROMP. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velonia, K. Protein-polymer amphiphilic chimeras: Recent advances and future challenges. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, L.; Thompson, M.P.; Schara, S.; Cao, W.; Choi, W.; Hu, Z.; Zang, N.; Tan, W.; Gianneschi, N.C. Recent Advances in Amphiphilic Polymer–Oligonucleotide Nanomaterials via Living/Controlled Polymerization Technologies. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.A.; Page, R.C.; Konkolewicz, D. Polymer conjugation of proteins as a synthetic post-translational modification to impact their stability and activity. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 434–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfold, N.J.W.; Yeow, J.; Boyer, C.; Armes, S.P. Emerging Trends in Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 1029–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sun, H.; Yu, M.; Sumerlin, B.S.; Zhang, L. Photo-PISA: Shedding Light on Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Gao, W. Polymerization induced self-assembly of a site-specific interferon α-block copolymer conjugate into micelles with remarkably enhanced pharmacology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, W. In Situ Growth of Self-Assembled Protein-Polymer Nanovesicles for Enhanced Intracellular Protein Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Droumaguet, B.; Velonia, K. In situ ATRP-mediated hierarchical formation of giant amphiphile bionanoreactors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 6263–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueckerath, T.; Strauch, T.; Koynov, K.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Ng, D.Y.; Weil, T. DNA–polymer conjugates by photoinduced RAFT polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2018, 20, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Efficient way to generate protein-based nanoparticles by in-situ photoinitiated polymerization-induced self-assembly. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, B.S.; Coughlin, M.L.; Figg, C.A.; Sumerlin, B.S. Grafting-from proteins using metal-free PET–RAFT polymerizations under mild visible-light irradiation. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xie, J.; Du, Y.; Lu, D.; Hu, Z.; Cai, T. Aqueous protein–polymer bioconjugation via photoinduced RAFT polymerization using high loading heterogeneous catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 44488–44496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jung, K.; Corrigan, N.A.; Boyer, C. Aqueous photoinduced living/controlled polymerization: Tailoring for bioconjugation. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad-Jabali, S.; Mahdinloo, S.; Farshbaf, M.; Sarfraz, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Atyabi, F.; Valizadeh, H. Transferrin receptor-mediated liposomal drug delivery: Recent trends in targeted therapy of cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, W.-E. Advances in redox-responsive drug delivery systems of tumor microenvironment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byard, S.J.; Williams, M.; McKenzie, B.E.; Blanazs, A.; Armes, S.P. Preparation and cross-linking of all-acrylamide diblock copolymer nano-objects via polymerization-induced self-assembly in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Sharma, N.; Manchanda, R.; Gupta, N.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Nimesh, S. PGMD/curcumin nanoparticles for the treatment of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, D.T.; Simpson, J.D.; Fletcher, N.L.; Houston, Z.H.; Fuchs, A.V.; Bell, C.A.; Thurecht, K.J. Oral Delivery of Multicompartment Nanomedicines for Colorectal Cancer Therapeutics: Combining Loco-Regional Delivery with Cell-Target Specificity. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, F.; Garvey, C.J.; Stenzel, M.H. Drug-directed morphology changes in polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA) influence the biological behavior of nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 30221–30233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauraj; Kumar, V.; Kumar, B.; Priyadarshi, R.; Deeba, F.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Kumar, A.; Agrawal, G.; Gopinath, P.; Negi, Y.S. Redox responsive xylan-SS-curcumin prodrug nanoparticles for dual drug delivery in cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M. Glutathione-Responsive Polymeric Micelles Formed by a Biodegradable Amphiphilic Triblock Copolymer for Anticancer Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y. CD44/Folate Dual Targeting Receptor Reductive Response PLGA-Based Micelles for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 829590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Jiang, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B. Hierarchically micro-, meso-, and macro-porous MOF nanosystems for localized cross-scale dual-biomolecule loading and guest-carrier cooperative anticancer therapy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 21911–21924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Chen, H.; Tan, J.; Meng, Q.; Zheng, P.; Ma, P.a.; Lin, J. ZIF-8 nanoparticles evoke pyroptosis for high-efficiency cancer immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, M.; Horibe, T.; Kohno, M.; Kawakami, K. A novel transferrin receptor-targeted hybrid peptide disintegrates cancer cell membrane to induce rapid killing of cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshawwa, S.Z.; Kassem, A.A.; Farid, R.M.; Mostafa, S.K.; Labib, G.S. Nanocarrier drug delivery systems: Characterization, limitations, future perspectives and implementation of artificial intelligence. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araveti, P.B.; Srivastava, A. Curcumin induced oxidative stress causes autophagy and apoptosis in bovine leucocytes transformed by Theileria annulata. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palange, A.L.; Di Mascolo, D.; Carallo, C.; Gnasso, A.; Decuzzi, P. Lipid–polymer nanoparticles encapsulating curcumin for modulating the vascular deposition of breast cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, e991–e1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; McCormick, C.L.; Lowe, A.B. Synthesis and evaluation of new dicarboxylic acid functional trithiocarbonates: RAFT synthesis of telechelic poly(n-butyl acrylate)s. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9518–9525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Xu, J.; Kokotovic, M.; Boyer, C. One-pot synthesis of block copolymers by orthogonal ring-opening polymerization and PET-RAFT polymerization at ambient temperature. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediriweera, G.R.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gong, Y.; Akhter, D.T.; Pang, H.; Han, F.Y.; Chen, C.; Whittaker, A.K.; Fu, C. Stimuli-responsive sulfoxide polymer–protein conjugates with improved pharmacokinetics and tumor delivery. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 7252–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ediriweera, G.R.; Chang, Y.; Yang, W.; Whittaker, A.K.; Fu, C. Self-Assembled Protein–Polymer Nanoparticles via Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly for Targeted and Enhanced Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040856
Ediriweera GR, Chang Y, Yang W, Whittaker AK, Fu C. Self-Assembled Protein–Polymer Nanoparticles via Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly for Targeted and Enhanced Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040856
Chicago/Turabian StyleEdiriweera, Gayathri R., Yixin Chang, Wenting Yang, Andrew K. Whittaker, and Changkui Fu. 2025. "Self-Assembled Protein–Polymer Nanoparticles via Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly for Targeted and Enhanced Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy" Molecules 30, no. 4: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040856
APA StyleEdiriweera, G. R., Chang, Y., Yang, W., Whittaker, A. K., & Fu, C. (2025). Self-Assembled Protein–Polymer Nanoparticles via Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly for Targeted and Enhanced Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Molecules, 30(4), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040856





